Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exercise 45: Principles of Heredity
front 1 Actual genetic makeup | back 1 Genotype |
front 2 Chromosomes determining malesness/femaleness | back 2 Sex Chromosomes |
front 3 situation in which an individual has identical alleles for a particular trait | back 3 Homozygons |
front 4 genes not expressed unless they are present in homozygous condition | back 4 recessive |
front 5 Expression of a genetic trait | back 5 phenotype |
front 6 Situation in which an individual has different alleles making up his genotype for a particular trait | back 6 heterozygous |
front 7 genes for the same trait that may have different expressions | back 7 alleles |
front 8 chromosomes regulating most body characteristics | back 8 autosomes |
front 9 The more potent gene allele: masks the expression fo the less potent allele | back 9 dominant |
front 10 In humans, farsightedness is inherited by possession of a dominant allele (A). If a man who is homozygous for normal vision (aa) marries a woman who is heterozygous for farsightedness (Aa), what proportion of their children would be expected to be Farsighted? _____% | back 10 If the man is aa he can donate a or a to his child. The woman can donate A or a. So the possibilities are: Aa, Aa, aa, aa
|
front 11 A metabolic disorder call phenylketonuria (PKU) is due to an adnormal recessive gene (p). Only homozygous recessive individuals exhibit this disorder. What percentage of the offspring will be anticipated to have PKU if the parents are Pp and pp? _____% | back 11 The possibilities are: Pp, Pp, pp, pp so the answer is: 50% |
front 12 A man obtained 32 spotted and 10 solid color rabbits from a mating of two spotted rabbits. Which trait is dominant? Recessive? what is the probable genotype of the rabbit parents? _____x_____ | back 12 Spotted is dominant (there are more of them occuring in the same mating pair)
|
front 13 Assume that that allele controlling brown eyes (B) is dominant over that controlling blue eyes (b) in humans. A blue eyed man marries a brown eyes woman and they have six children, all brown eyed. What is that most likely genotype of the father? of the Mother? If the seventh child had blue eyes what could you conclude about the parents genotype? | back 13 Father: bb
|
front 14 Tail length on a bobcat is controlled by incomplete dominance. The alleles are (T) for normal tail length and (t) for tail-less
| back 14 For this one since TT is a normal tail and tt is tail-less, Tt would produce a short tail since its inbetween the two.
|
front 15 If curly-haird individuals are genotypically CC, strait-haired are cc, and wavy haired individuals are heterozygotes (Cc), what percentage of various phenotypes would be anticipated from a cross between a CC woman and a cc man?
| back 15 Curly: 0%
|
front 16 What does it mean when someone says a particular characteristic is sex-linked? | back 16 It is carried on the F(X) sex chromosome |
front 17 You are a male and you have been told that hemophilia "runs in your genes" whose ancestors, your mother's or your father's should you investigate? Why? | back 17 Moms because males can only receive the X chromosome from their mothers, the fathers contribution is always Y |
front 18 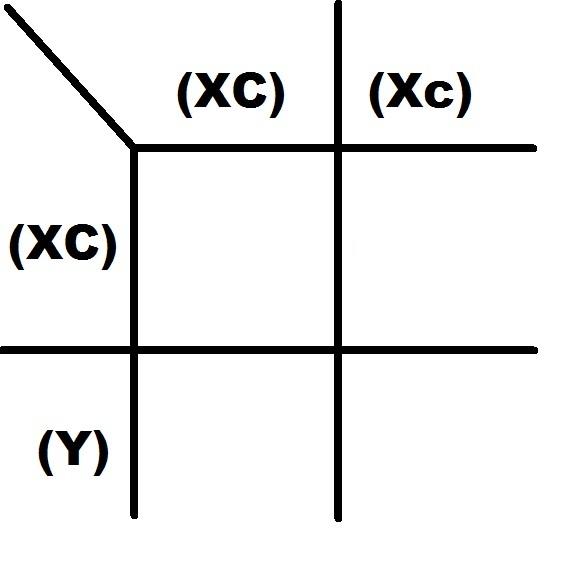 An (XC)(Xc) female marries and (Xc)(Y) man:
| back 18 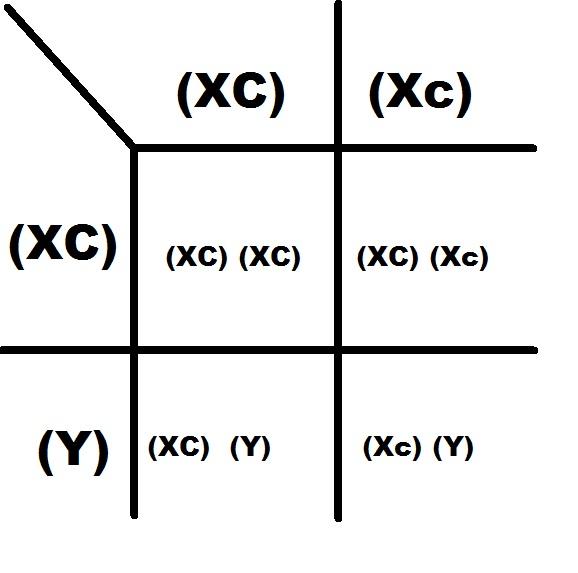 Well the key to this problem is that color blind is recessive, so little c. The mother is a carrier.
|
front 19 Why are marriages between blood relatives prohibited in most cultures? | back 19 Because blook relatives have similar gene pools thus the likelihood of receiving a double-dose of recessive genes is increased. |
front 20 What is the probability of having three daughters in a row? | back 20 The empirical probability is approximately 12.5%.
|