Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology Module 6: Mendelian Genetics
front 1 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 1 3/16 |
front 2 Which of the following provides an example of epistasis? | back 2 In rabbits and many other mammals, one genotype (cc) prevents any fur color from developing. |
front 3 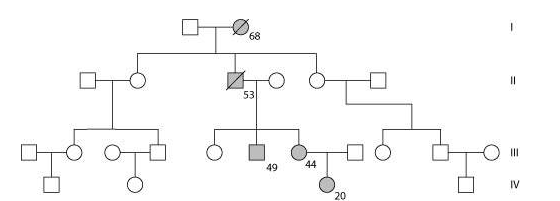 Use the following pedigree (Figure 14.3) for a family in which
dark-shaded symbols represent individuals with one of the two major
types of colon cancer. Numbers under the symbols are the individual's
age at the time of diagnosis.
| back 3 heterozygous for a gene for colon cancer |
front 4 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 4 6:3:3:2:1:1 |
front 5 Use the information given here to answer the following questions.
| back 5 green and yellow offspring |
front 6 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 6 Each parent is either M or MN. |
front 7 Two plants are crossed, resulting in offspring with a 3:1 ratio for a particular trait. What does this suggest? | back 7 that the parents were both heterozygous for a single trait |
front 8 Use the information given here to answer the following questions.
| back 8 yyBb and yyBb |
front 9 Which of the following describes the ability of a single gene to have multiple phenotypic effects? | back 9 pleiotropy |
front 10 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 10 IAi |
front 11 Use the following information to answer the questions below. | back 11 incomplete dominance |
front 12 What do we mean when we use the terms monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross? | back 12 A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one. |
front 13 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 13 B positive |
front 14 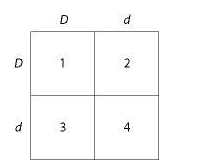 Use Figure 14.1 and the following description to answer the questions below.
| back 14 1 and 4 only |
front 15 A sexually reproducing animal has two unlinked genes, one for head shape (H) and one for tail length (T). Its genotype is HhTt. Which of the following genotypes is possible in a gamete from this organism? | back 15
HT
|
front 16 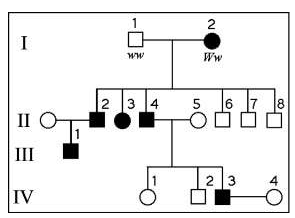 The following questions refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2
for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait,
W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
| back 16 ww |
front 17 Given the parents AABBCc x AabbCc, assume simple
dominance for each trait and independent assortment. What proportion
of the progeny will be expected to phenotypically resemble the first parent? | back 17 3/4 |
front 18 Mendel accounted for the observation that traits which had disappeared in the F1 generation reappeared in the F2 generation by proposing that | back 18 traits can be dominant or recessive, and the recessive traits were
obscured by the dominant ones in the F1. |
front 19 Mendel's observation of the segregation of alleles in gamete formation has its basis in which of the following phases of cell division? | back 19 anaphase I of meiosis |
front 20 Mendel's second law of independent assortment has its basis in which of the following events of meiosis I? | back 20 alignment of tetrads at the equator |
front 21 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 21 purple and long |
front 22 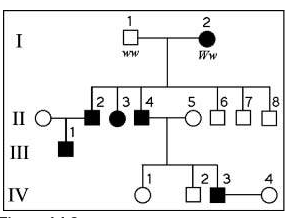 The following questions refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2
for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait,
W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
| back 22 1 |
front 23 Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b).
Short tails (T) are dominant to long tails (t). What
fraction of the progeny of crosses BbTt x BBtt
| back 23 1/2 |
front 24 Hydrangea plants of the same genotype are planted in a large flower garden. Some of the plants produce blue flowers and others pink flowers. This can be best explained by which of the following? | back 24 environmental factors such as soil pH |
front 25 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 25 6:3:3:2:1:1 |
front 26 Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, the pancreas, the digestive system, and other organs, resulting in symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to recurrent infections. Which of the following terms best describes this? | back 26 pleiotropy |
front 27 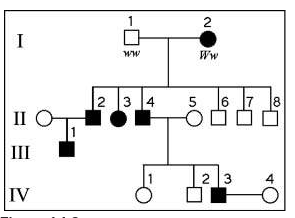 The following questions refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2
for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait,
W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
| back 27 50% |
front 28 When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a single trait with a heterozygote, what is the chance of producing an offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype? | back 28 50% |
front 29 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 29 TtRr-tall and pink |
front 30 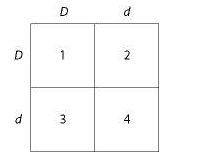 Use Figure 14.1 and the following description to answer the questions below.
| back 30 2 and 3 |
front 31 In the cross AaBbCc x AaBbCc, what is the probability of producing the genotype AABBCC? | back 31 1/64 |
front 32 Which of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance? | back 32 skin pigmentation in humans |
front 33 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 33 all +bt +vg heterozygotes |
front 34 Marfan syndrome in humans is caused by an abnormality of the connective tissue protein fibrillin. Patients are usually very tall and thin, with long spindly fingers, curvature of the spine, sometimes weakened arterial walls, and sometimes ocular problems, such as lens dislocation. Which of the following would you conclude about Marfan syndrome from this information? | back 34 It is pleiotropic. |
front 35 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 35 IBi |
front 36 In certain plants, tall is dominant to short. If a heterozygous plant is crossed with a homozygous tall plant, what is the probability that the offspring will be short? | back 36 0 |
front 37 In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous (Rr) offspring of red (RR) and white (rr) homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1 white? | back 37 roan x roan |
front 38 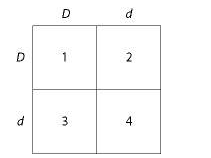 Use Figure 14.1 and the following description to answer the questions below.
| back 38 1, 2, and 3 |
front 39 Use the following information to answer the questions below.
| back 39 3/16 |