Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch. 8
front 1 each strand is used as a template by ___________ to synthesize two new strands of DNA | back 1 DNA Pol |
front 2 the enzyme RNA polymerase synthesizes a strand of RNA from one strand of double-stranded DNA, which serves as a template during what process | back 2 transcription |
front 3 Which of the following about bacteriocins are TRUE | back 3 a) the genes coding for them are on plasmids b) Nisin is a bacteriocin used as food preservative c) they can be used to identify certain bacteria d) bacteriocins kill bacteria |
front 4 When glucose is high, cAMP is _______: CAP ________bind the lac operator, and RNA polymerase _____ bind the lac promoter | back 4 cAMP is low CAP does not RNA polymerase does not |
front 5 Transformation is the transfer fo DNA from a donor to a recipient cell | back 5 as naked DNA in solution |
front 6 Genetic change in bacteria can be brought about by | back 6 a) mutation b) conjugation c) transduction d) transformation |
front 7 Which of the following regarding a bacterium that is R+ is True | back 7 a) It possesses a plasmid b) R+ can be transferred to a cell of the same species c) it is resistant to certain drugs and heavy metal d) R+ can be transferred to a different species |
front 8 Depending on the gene, transcription makes one of three possible kinds of RNA: | back 8 1. messenger RNA (or mRNA) |
front 9 mRNA | back 9 Messenger RNA carries the coded information blueprint (the message)
from the DNA to the ribosome for the making of proteins. |
front 10 rRNA | back 10 Ribosomal RNA forms ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis |
front 11 tRNA | back 11 Transfer RNA bring amino acids (specific amino acids dictated by the
sequence of codons) to the ribosome where they are incorporated into
proteins |
front 12 inducible | back 12 the genes are in the "off" mode until an inducer is present which acts to induce transcription |
front 13 repressible | back 13 the genes are transcribed until they are turned off, or repressed |
front 14 3 ways genetic information is shared between two bacterial cells or between a virus and a bacterial cell | back 14 1. transformation |
front 15 transformation | back 15 so-called naked DNA in solution is taken up by a bacterial cell taking up free floating DNA from environment. |
front 16 conjugation | back 16 requires direct contact between two living cells. A sex pilus connects two cells allowing the transfer of DNA direct contact between two living cells. |
front 17 transduction | back 17 bacterial DNA is transferred from a donor cell to a bacteriophage |
front 18 bacteriophage | back 18 recipient cell inside a virus that infects bacteria |
front 19 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) | back 19 is used to make multiple copies of a desired piece of DNA enzymatically |
front 20 The Ames Test | back 20 Based on observation that most carcinogens are also mutagens |
front 21 vertical gene transfer | back 21 Clonal process of vertical reproduction. When we go from one parent cell to two daughter cells, those two daughter cells are directly identical. No shuffling of genes. No swapping parts. One copy of everything and we are not interacting with another cell in reproduction they divide themselves in half. |
front 22 horizontal gene transfer | back 22 Bacteria can transfer genes between each other as adults. If you could go and swap genes with other people in a room that would be horizontal gene transfer. |
front 23 pili | back 23 establishes a physical bridge in between two cells through which we can transfer genetic information |
front 24 F plasmid transfer | back 24 We start with a cell that makes a pili and one that does not. The one that has the pili and has F plasmid as an F + cell. That is our donor cell and the recipient one is F- cell. Pili forms a physical bridge in between these two cells that penetrates the cell wall. We transfer DNA from along pili from cytoplasm of one cell into the other cytoplasm of other cell. We make copy of F plasmid and transfer copy to other end and at the end of the day when the pili breaks apart we end up with donor cell and recipient cell that now has extra genetic F plasmid info and can make a pili itself so it can go and contact another cell and transfer itself. A copying method |
front 25 Hfr conjugation | back 25 high frequency recombination |
front 26 13) Salts and sugars work to preserve foods by creating a A) depletion of nutrients. B) hypotonic environment. C) lower osmotic pressure. D) hypertonic environment. E) lower pH. | back 26 D |
front 27 The term aerotolerant anaerobe refers to an organism that A) does not use oxygen but tolerates it. B) is killed by oxygen. C) tolerates normal atmospheric nitrogen gas levels. D) requires less oxygen than is present in air. E) requires more oxygen than is present in air. | back 27 A |
front 28 Which of the following is an advantage of the standard plate count? A) can readily count cells that form aggregates B) determines the number of viable cells C) can be performed on very dilute samples, such as lake water D) provides immediate results E) can be used to count heat-sensitive bacteria | back 28 B |
front 29 Bacterial growth refers to an increase in the numbers of cells in a bacterial culture. | back 29 true |
front 30 Pure cultures can easily be obtained on streak plates, even if the desired bacteria are present in very low concentrations in the initial culture broth. | back 30 False |
front 31 Most pathogenic bacteria are thermophiles. | back 31 False |
front 32 Which of the following pairs is mismatched? A) DNA polymerase makes a molecule of DNA from a DNA template B) RNA polymerase makes a molecule of RNA from an RNA template C) DNA ligase joins segments of DNA D) transposase insertion of DNA segments into DNA E) DNA gyrase coils and twists DNA | back 32 B |
front 33 DNA is constructed of A) a single strand of nucleotides with internal hydrogen bonding. B) two complementary strands of nucleotides bonded AC and GT. C) two strands of nucleotides running in an antiparallel configuration. D) two strands of identical nucleotides in a parallel configuration with hydrogen bonds between them. E) None of the answers is correct. | back 33 C |
front 34 Culture 1: F+, leucine+, histidine+ Culture 2: F, leucine, histidine In Table 8.1, what will be the result of conjugation between cultures 1 and 2 (reminder: F+ has a different meaning than Hfr)? A) 1 will remain the same; 2 will become F+, leucine, histidine B) 1 will become F, leu+, his+; 2 will become F+, leu, his C) 1 will become F, leu, his; 2 will remain the same D) 1 will remain the same; 2 will become F+, leu+, his+ E) 1 will remain the same; 2 will become F+ and recombination may occur | back 34 A |
front 35 An enzyme produced in response to the presence of a substrate is called a(n) A) inducible enzyme. B) repressible enzyme. C) restriction enzyme. D) operator. E) promoter. | back 35 A |
front 36 Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell A) by a bacteriophage. B) as naked DNA in solution. C) by cell-to-cell contact. D) by crossing over. E) by sexual reproduction. | back 36 B |
front 37 Genetic change in bacteria can be brought about by A) mutation. B) conjugation. C) transduction. D) transformation. E) All of the answers are correct. | back 37 E |
front 38 Which of the following statements regarding a bacterium that is R+ is FALSE? A) It possesses a plasmid. B) R+ can be transferred to a cell of the same species. C) It is resistant to certain drugs and heavy metals. D) It is F+. E) R+ can be transferred to a different species. | back 38 D |
front 39 The initial effect of ionizing radiation on a cell is that it causes A) DNA to break. B) bonding between adjacent thymines. C) base substitutions. D) the formation of highly reactive ions. E) the cells to get hot. | back 39 D |
front 40 According to the operon model, for the synthesis of an inducible enzyme to occur, the A) end-product must not be in excess. B) substrate must bind to the enzyme. C) substrate must bind to the repressor. D) repressor must bind to the operator. E) repressor must not be synthesized | back 40 C |
front 41 Synthesis of a repressible enzyme is stopped by the A) allosteric transition. B) substrate binding to the repressor. C) corepressor binding to the operator. D) corepressor-repressor complex binding to the operator. E) end product binding to the promoter. | back 41 D |
front 42 In Figure 8.3, if compound C reacts with the allosteric site of enzyme A, this would exemplify A) a mutation. B) repression. C) feedback inhibition. D) competitive inhibition. E) transcription. | back 42 C |
front 43 In Figure 8.3, if enzyme A is an inducible enzyme, A) compound C would bind to the repressor for Gene a. B) compound A would bind to the repressor for Gene a. C) compound B would bind to enzyme A directly. D) compound A would react with enzyme B directly. E) compound C would react with gene a directly. | back 43 B |
front 44 Conjugation differs from reproduction because conjugation A) replicates DNA. B) transfers DNA vertically, to new cells. C) transfers DNA horizontally, to nearby cells without those cells undergoing replication. D) transcribes DNA to RNA. E) copies RNA to make DNA. | back 44 C |
front 45 The necessary ingredients for DNA synthesis can be mixed together in a test tube. The DNA polymerase is from Thermus aquaticus, and the template is from a human cell. The DNA synthesized would be most similar to A) human DNA. B) T. aquaticus DNA. C) a mixture of human and T. aquaticus DNA. D) human RNA. E) T. aquaticus RNA. | back 45 A |
front 46 In Figure 8.4, the antibiotic chloramphenicol binds the 50S large subunit of a ribosome as shown (the light gray area is the large subunit, while the black shape is the drug). From this information you can conclude that chloramphenicol A) prevents transcription in eukaryotes. B) prevents translation in eukaryotes. C) prevents transcription in prokaryotes. D) prevents translation in prokaryotes. E) prevents mRNA-ribosome binding. | back 46 D |
front 47 The mechanism by which the presence of glucose inhibits the lac operon is A) catabolite repression. B) translation. C) DNA polymerase. D) repression. E) induction. | back 47 A |
front 48 If you knew the sequence of nucleotides within a gene, which one of the following could you determine with the most accuracy? A) the primary structure of the protein B) the secondary structure of the protein C) the tertiary structure of the protein D) the quaternary structure of the protein E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided. | back 48 A |
front 49 An enzyme that makes covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate groups in another nucleotide in DNA is | back 49 DNA ligase |
front 50 An enzyme that copies DNA to make a molecule of RNA is A) RNA polymerase. B) DNA ligase. C) DNA helicase. D) transposase. E) DNA polymerase. | back 50 A |
front 51 An enzyme that catalyzes the cutting and resealing of DNA, and is translated from insertion sequences, is A) RNA polymerase. B) DNA ligase. C) DNA helicase. D) transposase. E) DNA polymerase. | back 51 D |
front 52 Repair of damaged DNA, in some instances and mechanisms, might be viewed as a race between an endonuclease and A) DNA ligase. B) DNA polymerase. C) helicase. D) methylase. E) primase. | back 52 D |
front 53 The cancer gene ras produces mRNA containing an extra exon that includes a number of UAA codons. Cancer cells produce ras mRNA missing this exon. This mistake most likely is due to a mistake by A) a chemical mutagen. B) DNA polymerase. C) photolyases. D) snRNPs. E) UV radiation. | back 53 snRNPs |
front 54 The miRNAs in a cell A) are found in prokaryotic cells. B) are a part of the prokaryotic ribosome. C) are a part of the eukaryotic ribosome. D) allow different cells to produce different proteins. E) are responsible for inducing operons. | back 54 D |
front 55 Assume the two E.coli strains shown below are allowed to conjugate. Hfr: pro+, arg+, his+, lys+, met+, ampicillin-sensitive F-: pro, arg, his, lys, met, ampicillin-resistant What supplements would you add to glucose minimal salts agar to select for a recombinant cell that is lys+, arg+, amp-resistant? A) ampicillin, lysine, arginine B) lysine, arginine C) ampicillin, proline, histidine, methionine D) proline, histidine, methionine E) ampicillin, proline, histidine, lysine | back 55 C |
front 56 Recombination will always alter a cells genotype. | back 56 true |
front 57 Open-reading frames are segments of DNA in which both start and stop codons are found. | back 57 true |
front 58 Bacteria typically contain multiple chromosomes. | back 58 false |
front 59 Mutations that are harmful to cells occur more frequently than those that benefit cells. | back 59 true |
front 60 The miRNAs in a cell inhibit protein synthesis by forming complementary bonds with rRNA. | back 60 false |
front 61 Some cells may contain multiple genomes. | back 61 false |
front 62 Both base substitution and frameshift mutations can result in the formation of premature stop codons | back 62 true |
front 63 In the Ames test, any colonies that form on the control should be the result of spontaneous mutations. | back 63 true |
front 64 Transposition (insertion of a transposon into a DNA sequence) results in the formation of base substitution mutations in a cells DNA. | back 64 false |
front 65 Cell-to-cell contact is required for transduction to occur | back 65 false |
front 66 A red pigment produced by a bacterial species is an example of a(n)?
| back 66 phenotype |
front 67 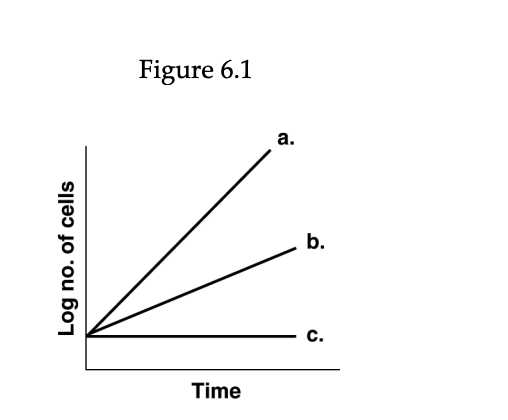 In Figure 6.1, which line best depicts a facultative anaerobe in the absence of O2? A) a B) b C) c | back 67 B |
front 68 In Figure 6.1, which line best illustrates a mesophile at 5°C above its optimum temperature? A) a B) b C) c | back 68 B |
front 69 In Figure 6.1, which line best depicts a mesophile with an optimum temperature of 35°C incubated at 40°C? A) a B) b C) c | back 69 B |
front 70 In Figure 6.1, which line shows the growth of an obligate aerobe incubated anaerobically? A) a B) b C) c | back 70 C |
front 71 In Figure 6.1, which line best illustrates the growth of a facultative anaerobe incubated aerobically? A) a B) b C) c | back 71 A |
front 72 ) Micrococci are facultative halophiles. In Figure 6.1, which line best depicts the growth of Micrococcus luteus in a nutrient medium containing 7.5% NaCl? A) a B) b C) c | back 72 B |
front 73 In Figure 6.1, which line best depicts a psychrophile incubated at room temperature? A) a B) b C) c | back 73 C |
front 74 In Figure 6.1, which line best depicts Neisseria gonorrhoeae when growing inside the human body? A) a B) b C) c | back 74 A |
front 75 The term facultative anaerobe refers to an organism that A) Doesn't use oxygen but tolerates it. B) Is killed by oxygen. C) Uses oxygen or grows without oxygen. D) Requires less oxygen than is present in air. E) Prefers to grow without oxygen. | back 75 C |
front 76 Figure 6.3 shows three containers of water connected by tubes. A selectively permeable membrane divides each tube. Solutes are added to each container to give final concentrations of 5% NaCl in (a); 10% NaCl in (b); and 5% sucrose in c). When the experiment is first set up, the initial movement of water will be A) a to b; b to c; c to a. B) a to b; c to b; c to a. C) a to c; b to c; c to a. D) a to c; c to b; c to a. E) b to a; b to c; c to a. | back 76 B |
front 77 A culture medium on which only gram-positive organisms grow and a yellow halo surrounds Staphylococcus aureus colonies is called a(n) A) Selective medium. B) Differential medium. C) Enrichment culture. D) A and B E) B and C | back 77 d |
front 78 Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction: O2- + O2- + 2H+ → H2O2 + O2? A) Catalase B) Oxidase C) Peroxidase D) Superoxide dismutase | back 78 D |
front 79 Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction: 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2? A) Catalase B) Oxidase C) Peroxidase D) Superoxide dismutase | back 79 A |
front 80 Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction: H2O2 + 2H+ → 2H2O? A) Catalase B) Oxidase C) Peroxidase D) Superoxide dismutase | back 80 C |
front 81 Which of the following is the best method to sterilize heat-labile solutions? A) Dry heat B) Autoclave C) Membrane filtration D) Pasteurization E) Freezing | back 81 C |
front 82 Which of the following best describes the pattern of microbial death? A) The cells in a population die at a constant rate. B) All the cells in a culture die at once. C) Not all of the cells in a culture are killed. D) The pattern varies depending on the antimicrobial agent. E) The pattern varies depending on the species. | back 82 A |
front 83 Which of the following substances is used for surgical hand scrubs? A) Phenol B) Chlorine bleach C) Chlorhexidine D) Soap E) Glutaraldehyde | back 83 C |
front 84 Which of the following substances can sterilize? A) Alcohol B) Phenolics C) Ethylene oxide D) Chlorine E) Soap | back 84 C |
front 85 Place the following surfactants in order from the most effective to the least effective antimicrobial activity: 1-Soap; 2-Acid-anionic detergent; 3-Quats. A) 1, 2, 3 B) 1, 3, 2 C) 2, 1, 3 D) 3, 2, 1 E) 3, 1, 2 | back 85 D |
front 86 The initial effect of ionizing radiation on a cell is that it causes A) DNA to break. B) Bonding between adjacent thymines. C) Base substitutions. D) The formation of highly reactive ions. E) The cells to get hot. | back 86 D |
front 87 According to the operon model, for the synthesis of an inducible enzyme to occur, the A) End-product must not be in excess. B) Substrate must bind to the enzyme. C) Substrate must bind to the repressor. D) Repressor must bind to the operator. E) Repressor must not be synthesized. | back 87 C |
front 88 The mechanism by which the presence of arabinose controls the arabinose operon is A) Catabolite repression. B) Translation. C) DNA polymerase. D) Repression. E) Induction. | back 88 E |
front 89 In transcription, A) DNA is changed to RNA. B) DNA is copied to RNA. C) DNA is replicated. D) RNA is copied to DNA. E) Proteins are made. | back 89 B |
front 90 In a DNA double-helix, nucleotides on complementary strands are held together by
| back 90 hydrogen bonds |
front 91 Which of the following is found at the 5 end of a DNA strand? A) a phosphate group B) a hydrogen bond C) a hydroxyl group D) histones E) a methyl group | back 91 A |
front 92 The bacterial chromosome is A) usually circular. B) found in a nucleoid. C) found in a nucleus. D) both circular and found in a nucleoid. E) both circular and found in a nucleus. | back 92 D |
front 93 ) Which of the following types of plasmids allows a bacterial cell to kill its competitors? A) virulence factors B) fertility factors C) bacteriocin factors D) resistance factors E) cryptic plasmids | back 93 C |
front 94 Which of the following statements is true of bacterial plasmids? A) They are found in the nucleoid. B) They can replicate autonomously. C) They carry genes for essential metabolic functions. D) They are small circular DNA molecules. E) They are small circular DNA molecules that can replicate autonomously. | back 94 E |
front 95 Which of the following statements concerning transcription in bacteria is FALSE? A) It occurs in the nucleoid region. B) Sigma factors are parts of RNA polymerase that recognize promoter regions. C) The same RNA polymerase transcribes primer RNA, mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. D) Termination is either self-induced or due to the presence of Rho protein. E) There are a variety of sigma factors that affect transcription. | back 95 C |
front 96 A charged tRNA first enters the ribosomal ________ site and then moves into the ________ site. A) A, E B) P, A C) P, E D) A, P E) E, A | back 96 D |
front 97 Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand. B) nucleotides are constantly being recycled as cells make DNA. C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only part of the time. D) the sequence of a DNA molecule is preserved as it is being replicated. E) each strand of a double-stranded DNA molecule is replicated differently. | back 97 A |
front 98 Inducible operons A) are active in the presence of a repressor. B) are generally anabolic pathways. C) are normally active. D) usually require an activator to be transcribed. E) usually require a repressor to be transcribed. | back 98 B |
front 99 If the codon AAA is changed to AAG, it still codes for the amino acid lysine; this is an example of a A) silent mutation. B) nonsense mutation. C) frameshift mutation. D) gross mutation. E) missense mutation. | back 99 A |
front 100 The Ames test proves that a chemical is A) carcinogenic. B) carcinogenic in Salmonella. C) mutagenic in Salmonella. D) carcinogenic in humans. E) mutagenic in humans. | back 100 C |
front 101 The horizontal transfer process known as transduction A) involves a virus. B) requires a pilus. C) requires a cell to be "competent." D) requires a plasmid. E) involves a mutagen. | back 101 A |
front 102 Frederick Griffith discovered A) transformation. B) transposons. C) the lac operon. D) DNA. E) conjugation. | back 102 A |
front 103 In conjugation, F+ cells A) serve as recipient cells. B) contain an F plasmid. C) do not have conjugation pili. D) can transfer DNA only to other F+ cells. E) contain "jumping genes." | back 103 B |
front 104 The energy required for DNA replication comes from A) DNA polymerase. B) triphosphate deoxyribonucleotides. C) DNA ligase. D) RNA primer. E) the leading strand. | back 104 B |
front 105 Prokaryotic cells are diploid. | back 105 False |
front 106 The most common type of mutation is a point mutation. | back 106 true |
front 107 Bidirectional replication means that each strand of a DNA molecule is replicated in the opposite direction from the other. | back 107 false |
front 108 t/f the repressor for the lac operon is active when lactose is present | back 108 false |
front 109
| back 109 D |
front 110 Table 8.2 UUA leucine GCA alanine AAG lysine GUU valine UAA nonsense AAU sparagine UGC cysteine UCG, UCU serine
| back 110 B |
front 111 Table 8.2 UUA leucine GCA alanine AAG lysine GUU valine UAA nonsense AAU sparagine UGC cysteine UCG, UCU serine
A) 5′ ACAGTTTCAAT C) 3′ UGUGCAAAGUUA D) 3′ UCUCGAAAGUUA E) 3′ TCACGUUUCAAU | back 111 B |
front 112 Table 8.2 UUA leucine GCA alanine AAG lysine GUU valine UAA nonsense AAU sparagine UGC cysteine UCG, UCU serine What is the sequence of amino acids encoded by the following sequence of bases in a strand of DNA? 3′ ATTACGCTTTGC A) Leucine-arginine-lysine-alanine D) Transcription would stop at the first codon E) Can't tell | back 112 D |
front 113 Table 8.2 UUA leucine GCA alanine AAG lysine GUU valine UAA nonsense AAU sparagine UGC cysteine UCG, UCU serine
| back 113 E |
front 114
E) Bind to gene a. | back 114 C |
front 115 In Figure 8.3, if enzyme A is an inducible enzyme, A) Compound C would bind to the repressor. B) Compound A would bind to the repressor. C) Compound B would bind to enzyme A. D) Compound A would react with enzyme B. E) Compound C would react with gene a. | back 115 B |
front 116 An enzyme that cuts double-stranded DNA at specific nucleotide sequences. A) RNA polymerase B) DNA ligase D) Transposase | back 116 D |
front 117 Which mutation would most severely affect the protein coded for by a gene? | back 117 A frameshift deletion at the beginning of the gene |
front 118 True or False? When treating an organism with a mutagen, although it is possible that homozygous mutations will occur, it is more likely that most new mutations will be heterozygous or hemizygous. | back 118 true |
front 119 True or False? A missense mutation causes premature chain (protein) termination. | back 119 false |
front 120 True or false? All compounds that have been found to be mutagenic in the Ames test are also carcinogenic | back 120 false |
front 121 Which bacteria grow on the Agar plate if the Ames test is positive? | back 121 his+ prototroughs |
front 122 Genetic change in bacteria can be brought about by? | back 122 E |
front 123 In E. coli, the lactose operon is? | back 123 D |
front 124 In E. coli, the tryptophan operon is? | back 124 B |
front 125 The region of DNA at which RNA polymerase binds to start
transcription is the? | back 125 A |
front 126 Which of the following is not true of RNA molecules? | back 126 C |
front 127 Conjugation differs from reproduction because conjugation? | back 127 A |
front 128 The purpose of the Southern blotting techniques is to? | back 128 E |
front 129 A small molecule that combines with a specific allosteric protein so
that both prevent RNA | back 129 C |
front 130 Hfr strains of bacteria: | back 130 C |