Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Lab 2- Cell
front 1 Small organs that make up a cell are called | back 1 organelle |
front 2 Structural and functional unit of all living things | back 2 Cell |
front 3 Cell gave differences that reflect their specific functions in the body,
| back 3 Growing
|
front 4 External boundary of cell,
| back 4 Cell membrane or Plasma membrane |
front 5 Scattered thoughout the cell; major site of ATP synthesis | back 5 Mitochondria |
front 6 Slender extensions of the plasma membrane that increases its surface area | back 6 Microvilli |
front 7 Stored glycogen granules, crystals, pigments and so on. | back 7 Inclusions |
front 8 Memranous system consisting of flattened sacs and vesicles; packages proteins for export | back 8 Golgi apparatus |
front 9 Control center of the cell; necessary for cell division and cell life | back 9 nucleus |
front 10 Two rod shaped bodies near the nucleus; direct formation of mitotic spindles (made of microtubles) | back 10 Centrioles |
front 11 Dense, darkly stained nuclear body; package site for ribosomes | back 11 Nucleolus |
front 12 Contractile elements of the cytoskeleton | back 12 Microfilaments |
front 13 membranous system; involved in intracellular transport of proteins and synthesis of membrane lipids | back 13 Rough E R |
front 14 Attached to membrane systems or scattered in the cytoplasm; synthesize proteins | back 14 Ribosomes |
front 15 Threadlike structures in the nucleus; contain genetic material, DNA | back 15 Chromatin |
front 16 Site of free radical detoxification | back 16 Peroxisomes |
front 17 Various sized sacs containing digestive enzymes (acid hydrolases) | back 17 Lysosomes |
front 18 A cell's life goes through 2 phases ________ and _____ | back 18 Interphase and Cell division |
front 19 The longest phase of a cell's life
| back 19 Interphase
|
front 20 Cell division consists of a series of events which includes: | back 20 Mitosis and Cytokinesis |
front 21 Mitosis is the division of the | back 21 Nucleus |
front 22 Cytokinesis is the division of the | back 22 Cytoplasm |
front 23 Products of Mitosis | back 23 2 identical DIPLOID daughter cells |
front 24 Phases of Mitosis | back 24 Prophase
|
front 25 Importance of mitotic cell division | back 25 To make a greater amount of cells for repair and growth.
|
front 26 The major structural difference between chromatin and chromasomes is that the latter are ________ | back 26 tightly coiled and condensed |
front 27 Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by undivided structures called _____________ | back 27 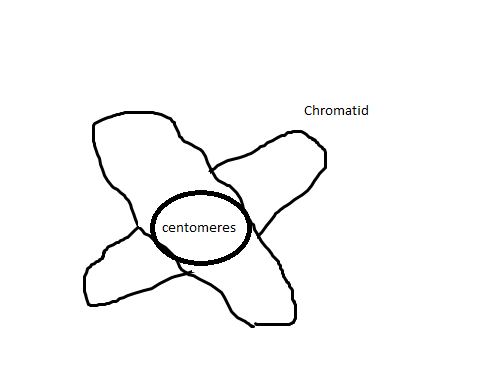 Centromeres |
front 28 If a cell undergoes mitosis but not cytokinesis, the product is ________ | back 28 Binucleated cell |
front 29 The structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachement and movement is called the _____________ | back 29 Mitotic Spindle |
front 30 _____________ is the phase of cell that don't undergo cell division | back 30 Interphase |
front 31 Two cell population in the body that do not under go cell division are _________ and ___________ | back 31 Skeletal and Cardiac |
front 32 The implication of an inability of a cell population to divide is that when some if its members die, they are replaced by __________ | back 32 Scar tissue |
front 33 The mitosis phases where:
| back 33 Prophase |
front 34 The Mitosis phase where:
| back 34 Anaphase |
front 35 The Mitosis phase where:
| back 35 Telophase |
front 36 The Mitosis phase where:
| back 36 Metaphase
|
front 37 The mitosis phase where:
| back 37 Prophase |
front 38 The mitosis phase where:
| back 38 Interphase (S phase ) |
front 39 The mitosis phase where:
| back 39 Prophase |
front 40 The mitosis phase where:
| back 40 Telophase |
front 41 The two mitotic phases where the nuclear envelope is absent | back 41 Metaphase and Anaphase |
front 42 Physical advantage of chromatin coiling and condensing? | back 42 Short, compact bodies easier to manipulate during mitosis.
|
front 43 Chromosomes connected by a small median body called ______ and an adhesive protein called ______. | back 43 Centromere
|
front 44 Enzyme ______ promotes cleaving of cohesin and the centromere split in Anaphase
| back 44 Separase |
front 45 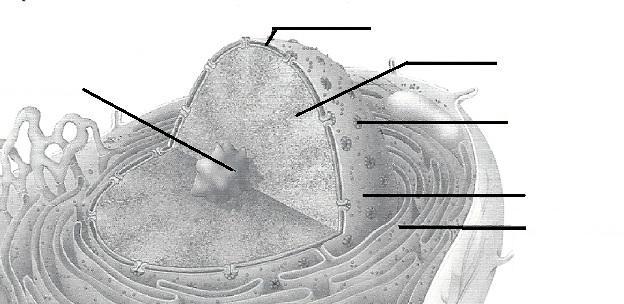 | back 45 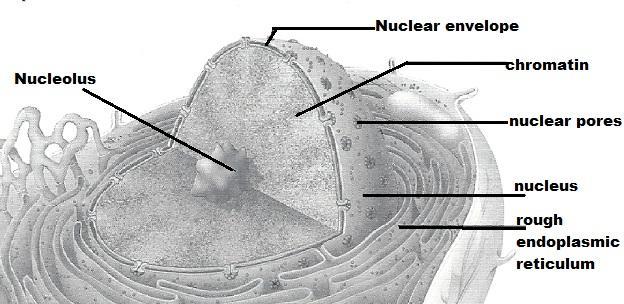 |
front 46 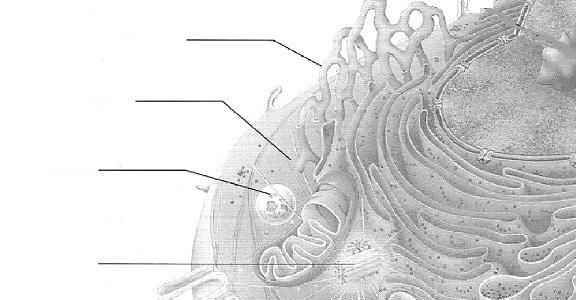 | back 46 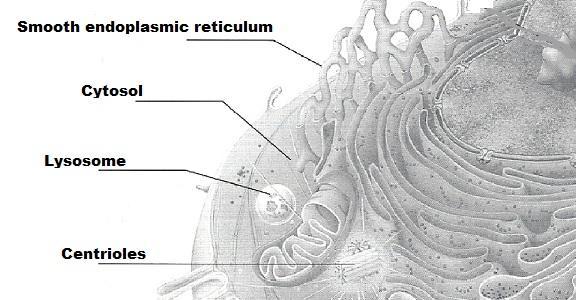 |
front 47 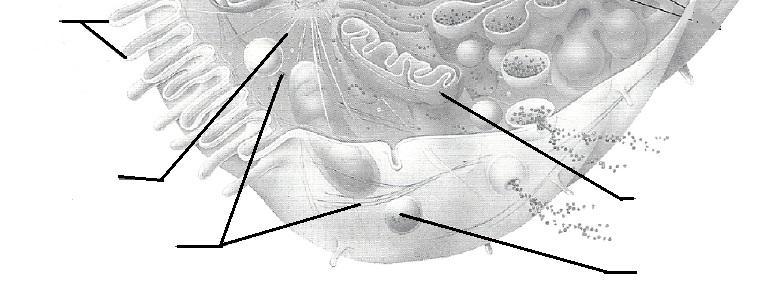 | back 47 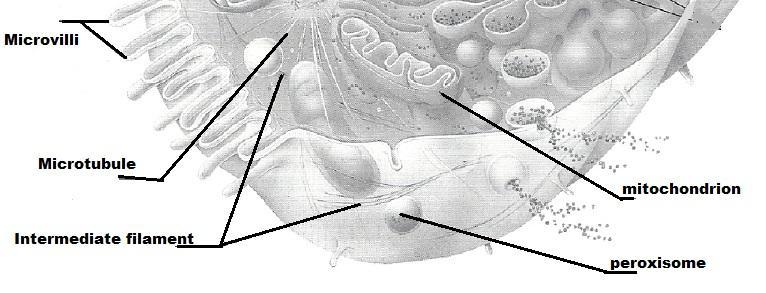 |
front 48 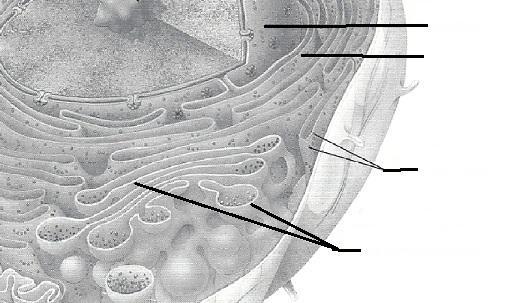 | back 48 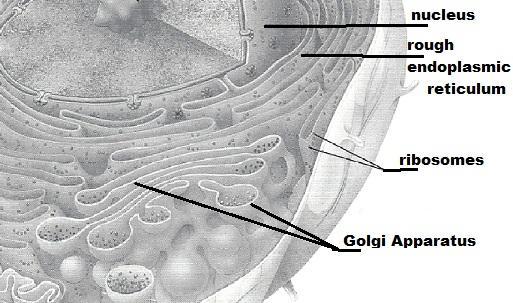 |
front 49 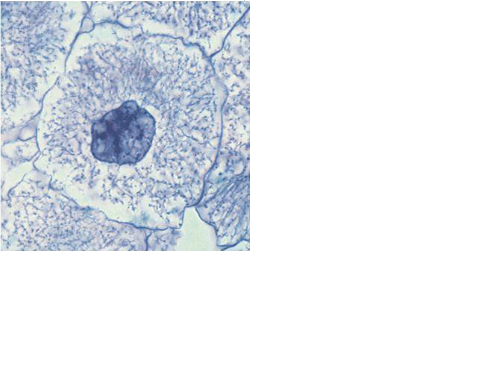 | back 49 Interphase |
front 50 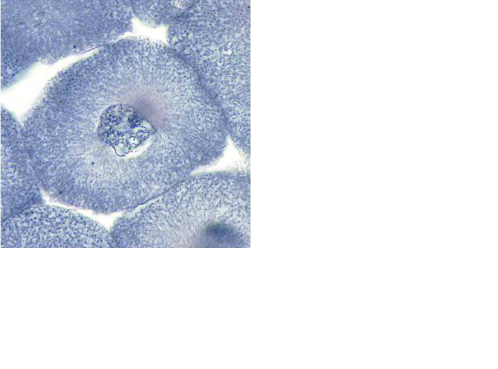 | back 50 Early Prophase |
front 51 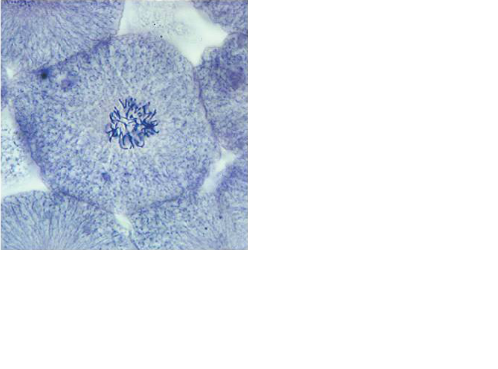 | back 51 Late Prophase |
front 52 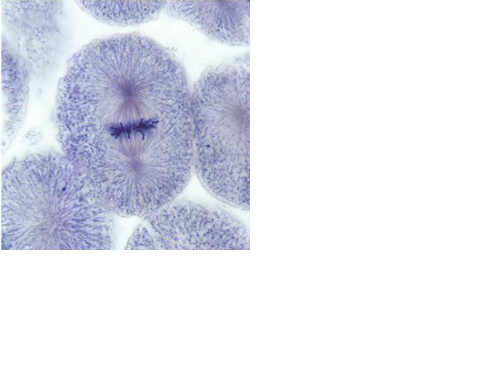 | back 52 Metaphase |
front 53 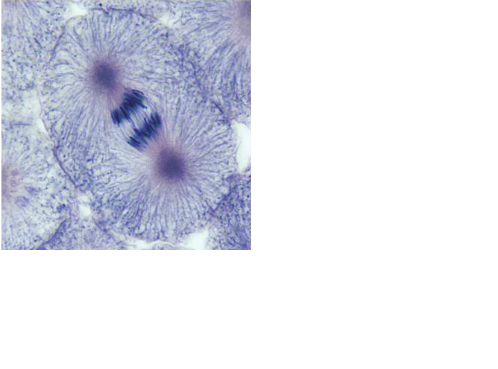 | back 53 Metaphase |
front 54  | back 54 Telophase and Cytokinesis |