Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Microbiology Final Exam
front 1 1. Which of the following statements about biofilms is FALSE? A) Compared to free-living bacteria, biofilms are more sensitive to antibiotics. B) Biofilms in pipes can block the flow of water. C) Biofilms in your body protect mucous membranes from harmful microbes. D) Biofilms on medical devices cause infections. E) Biofilms on rocks provide food for animal life. | back 1 Answer: A |
front 2 2. The term used to describe a disease-causing microorganism is A) microbe B) bacterium C) virus D) pathogen E) infection | back 2 Answer: D |
front 3 3. What factors contribute to the rising incidence of antibiotic resistance? A) random mutations, overuse and misuse of specific drugs B) random mutations in bacterial genomes C) overuse of the specific drugs D) misuse of the specific drugs E) overuse and misuse of specific drugs | back 3 Answer: A |
front 4 4. The formal system for classifying and naming organisms was developed by A) Louis Pasteur B) Carolus Linnaeus C) Robert Koch D) Aristotle E) Ignaz Semmelewis | back 4 Answer: B |
front 5 5. A prokaryotic cell may possess each of the following cellular components EXCEPT A) cell wall B) ribosomes C) flagella D) a nucleus E) a cell membrane | back 5 Answer: D |
front 6 6. Microbes that live stably in and on the human body are called the A) human microbiome B) transient microbiota C) opportunistic microbiota D) pathogenic microorganisms E) virulent microorganisms | back 6 Answer: A |
front 7 7. Which of the following is NOT a domain in the three-domain system? A) bacteria B) archaea C) eukarya D) animalia | back 7 Answer: D |
front 8 8. A system of classification grouping organisms into 3 domains based on the cellular organization of organisms was devised by A) Anton van Leewenhoek B) Carolus Linnaeus C) Carl Woese D) Robert Koch E) Louis Pasteur | back 8 Answer: C |
front 9 9. Fungal infections are studied by A) mycologists B) bacteriologists C) herpetologists D) parasitologists E) virologists | back 9 Answer: A |
front 10 10. When our bodies overcome the offensive tactics of a particular microorganism, this is referred to as A) colonization B) disease C) deficiency D) therapy E) resistance | back 10 Answer: E |
front 11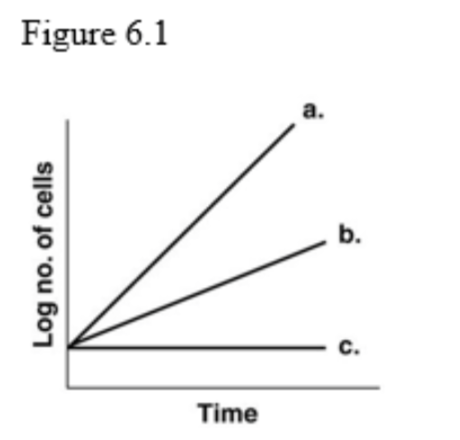  11. In Figure 6.1, which line best depicts an obligate anaerobe in the presence of O2? A) a B) b C) c | back 11 Answer: C |
front 12  12. In Figure 6.1, which line shows the growth of an obligate aerobe incubated anaerobically? A) a B) b C) c | back 12 Answer: C |
front 13  13. In Figure 6.1, which line best illustrates the growth of a facultative anaerobe incubated aerobically? A) a B) b C) c | back 13 Answer: A |
front 14 14. The addition of which of the following to a culture medium will neutralize acids? A) heat B) pH C) sugars D) carbon E) buffers | back 14 Answer: E |
front 15 15. Salts and sugars work to preserve foods by creating a A) lower osmotic pressure B) hypertonic environment C) hypotonic environment D) depletion of nutrients E) lower pH | back 15 Answer: B |
front 16 16. The term aerotolerant anaerobe refers to an organism that A) is killed by oxygen B) tolerates normal atmospheric nitrogen gas levels C) requires less oxygen than is present in air D) requires more oxygen than is present in air E) does not use oxygen but tolerates it | back 16 Answer: E |
front 17 17. Most bacteria reproduce by A) binary fission B) mitosis C) fragmentation D) aerial hyphae E) budding | back 17 Answer: A |
front 18 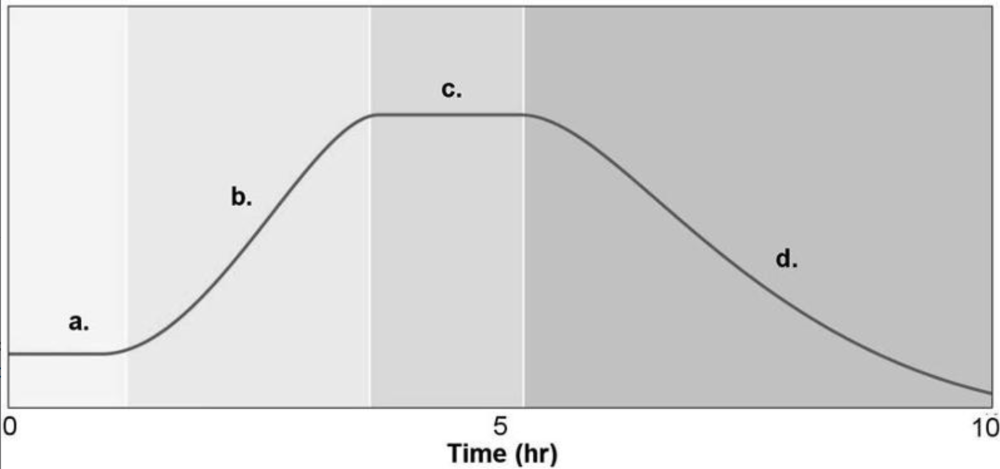 18. Figure 6.2 shows a typical bacterial growth curve with the y-axis indicating the log of the number of bacteria and the x-axis indicating time in culture. In the figure, which section shows a growth phase where the number of cells dying equals the number of cells dividing? A) a B) d C) c D) a and c E) b | back 18 Answer: C |
front 19  19. Figure 6.2 shows a typical bacterial growth curve with the y-axis indicating the log of the number of bacteria and the x-axis indicating time in culture. In the figure, which sections of the graph illustrate a logarithmic change in cell numbers? A) a and c B) b and d C) a and d D) a and b E) c and d | back 19 Answer: B |
front 20  20. In Figure 6.3, which tube shows the expected growth pattern for a microaerophile? A) e B) c C) d D) a E) b | back 20 Answer: A |
front 21 21. Which of the following places the steps of the Gram stain in the correct order? 1-Alcohol-acetone 2-Crystal violet 3-Safranin 4-Iodine A) 4-3-2-1 B) 2-1-4-3 C) 2-4-1-3 D) 1-2-3-4 | back 21 Answer: C |
front 22 22. The purpose of a mordant in the Gram stain is to: A) make the flagella invisible B) prevent the crystal violet from leaving the cells C) remove the simple stain D) make gram-negative cells visible | back 22 Answer: B |
front 23 23. Which of the following places the steps in the correct sequence? 1-Staining 2-Making 3-Fixing A) 1-2-3 B) The order is unimportant C) 2-3-1 D) 1-3-2 | back 23 Answer: C |
front 24 24. Simple staining is often necessary to improve contrast in which microscope? A) electron microscope B) fluorescence microscope C) compound light microscope D) phase-contrast microscope | back 24 Answer: C |
front 25 25. This microscope produces an image of a light cell against a dark background; internal structures are NOT visible. A) electron microscope B) darkfield microscope C) compound light microscope D) fluorescence microscope | back 25 Answer: B |
front 26 26. Which of the following is never useful for observing living cells? A) scanning electron microscope B) darkfield microscope C) brightfield microscope D) scanning acoustic microscope | back 26 Answer: A |
front 27 27. Which microscope is most useful for visualizing a biofilm? A) fluorescence microscope B) compound light microscope C) transmission electron microscope D) scanning acoustic microscope | back 27 Answer: D |
front 28 28. Which step in the Gram stain is the critical step in differentiating gram-positive cells from gram-negative cells? A) safranin B) iodine C) alcohol-acetone D) crystal violet | back 28 Answer: C |
front 29 29. Which microscope is best used for observing the surfaces of intact cells and viruses? A) scanning electron microscope B) phase-contrast microscope C) brightfield microscope D) fluorescence microscope | back 29 Answer: A |
front 30 30. Bacterial smears are fixed before staining to A) make their walls permeable B) accept stain C) affix the cells to the slide D) make the cells visible | back 30 Answer: C |
front 31 31. Which of the following is the best method to sterilize heat-labile solutions? A) pasteurization B) autoclave C) dry heat D) membrane filtration | back 31 Answer: D |
front 32 32. Which of the following best describes the pattern of microbial death? A) Not all of the cells in a culture are killed. B) The pattern varies depending on the antimicrobial agent. C) The cells in a population die at a constant rate. D) All the cells in a culture die at once. E) The pattern varies depending on the species. | back 32 Answer: C |
front 33 33. Which of the following pairs of terms is mismatched? A) sterilant - destroys all living microorganisms B) bacteriostatic - kills vegetative bacterial cells C) germicide - kills microbes D) virucide - inactivates viruses E) fungicide - kills yeasts and molds | back 33 Answer: B |
front 34 34. Which of the following does NOT achieve sterilization? A) ethylene oxide B) supercritical fluids C) autoclave D) pasteurization E) dry heat | back 34 Answer: D |
front 35 35. An agent used to reduce the number of bacteria on a toilet would most accurately be called a(n) A) aseptic B) antiseptic C) virucide D) fungicide E) disinfectant | back 35 Answer: E |
front 36 36. Which of the following methods is used to preserve food by showing the metabolic processes of foodborne microbes? A) freezing B) pasteurization C) nonionizing radiation D) lyophilization E) ionizing radiation | back 36 Answer: A |
front 37 37. All of the following factors contribute to hospital-acquired infections EXCEPT A) some bacteria metabolize disinfectants. B) invasive procedures can provide a portal of entry for bacteria. C) None of the answers is correct; all of these factors may contribute to hospital-acquired infections. D) gram-negative bacteria are often resistant to disinfectants. | back 37 Answer: C |
front 38 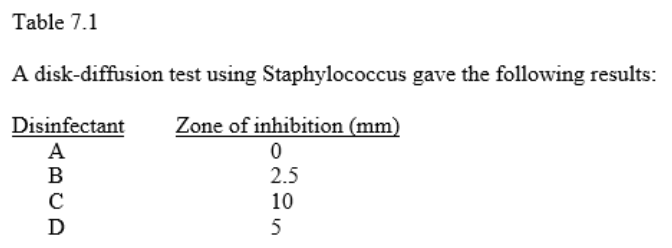 38. In Table 7.1, which compound was the most effective against Staphylococcus? A) D B) A C) C D) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided. E) B | back 38 Answer: C |
front 39 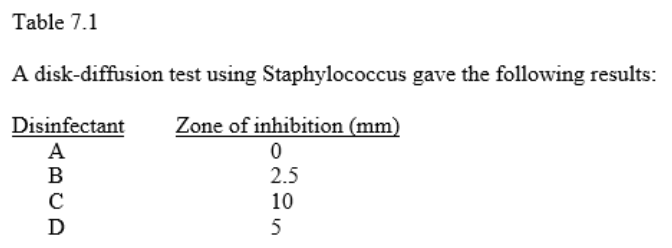 39. In Table 7.1, which compound was the most effective against E. coli? A) C B) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided. C) A D) B E) D | back 39 Answer: B |
front 40  40. In Table 7.2, which preservative is most effective? A) no preservative B) sodium benzoate C) potassium sorbate + sodium benzoate D) potassium sorbate | back 40 Answer: C |
front 41 41. Which of the following organelles most closely resembles a prokaryotic cell? A) mitochrondrion B) cell wall C) vacuole D) nucleus | back 41 Answer: A |
front 42 42. Functions of the glycocalyx include all of the following EXCEPT A) binary fission B) protection against dehydration C) source of nutrition D) biofilm formation | back 42 Answer: A |
front 43 43. Which of the following is NOT found or observed to occur in both mitochondria and prokaryotes? A) cell wall B) 70S ribosomes C) ATP-generating mechanism D) binary fission | back 43 Answer: A |
front 44 44. Which of the following statements is correct about passive diffusion? A) It involves movement of molecules down a concentration gradient and may require a transport protein. B) It may require a transport protein. C) It is a process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration (or up a concentration gradient). D) It requires an expenditure of energy by the cell. | back 44 Answer: A |
front 45 45. The DNA found in most bacterial cells A) is circular in structure B) is linear in structure C) is surrounded by a nuclear membrane D) utilizes histones for chromosomal packaging | back 45 Answer: A |
front 46 46. Cells may frequently find themselves in an environment with very low extracellular concentrations of substances needed in higher amounts inside the cell. To obtain these needed items, such cells would be most likely to engage in A) active transport B) osmosis C) facilitated diffusion D) simple diffusion | back 46 Answer: A |
front 47 47. Where are phospholipids most likely found in a eukaryotic cell? A) the plasma membrane and organelles B) ribosomes C) the plasma membrane D) metachromatic granules | back 47 Answer: A |
front 48 48. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) Endospores allow a cell to survive environmental changes by producing a dormant period with no growth. B) Endospores are easily stained in a Gram stain. C) A cell produces one endospore and keeps growing D) Endospores are for reproduction. | back 48 Answer: A |
front 49 49. Which structure protects bacteria from being phagocytized? A) capsule B) cell membrane C) cell wall D) slime layer | back 49 Answer: A |
front 50 50. The terms "run" and "tumble" are generally associated with: A) taxic movements of the cell in response to attractants or repellents. B) cell wall fluidity. C) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. D) cell membrane synthesis. | back 50 Answer: A |
front 51 51. A clear area against a confluent "lawn" of bacteria is called a A) plaque B) phage C) cell lysis D) rash | back 51 Answer: A |
front 52 52. Which of the following is necessary for replication of a prion? A) PrPSc B) RNA C) DNA polymerase D) DNA | back 52 Answer: A |
front 53 53. A persistent infection is one in which A) the disease process occurs gradually over a long period. B) host cells are gradually lysed. C) host cells are transformed. D) viral replication is unusually slow. | back 53 Answer: A |
front 54 54. An infectious protein is a A) prion B) retrovirus C) viroid D) bacteriophage | back 54 Answer: A |
front 55 55. An example of a latent viral infection is A) cold sores B) influenza C) mumps D) smallpox | back 55 Answer: A |
front 56 56. Which of the following statements about viruses is FALSE? A) Viruses use their own catabolic enzymes. B) Viruses have genes. C) Viruses contain a protein coat. D) Viruses contain DNA or RNA but never both. | back 56 Answer: A |
front 57 57. Some viruses, such as human herpesvirus 1, infect a cell without causing symptoms. These are called A) latent viruses B) lytic viruses C) phages D) slow viruses | back 57 Answer: A |
front 58 58. Oncogenic viruses A) cause tumors to develop B) have no effect on the host cell C) are genetically unstable D) cause acute infections | back 58 Answer: A |
front 59 59. Shingles is an example of A) reactivation of latent virus B) persistent virus C) transformation D) meiosis | back 59 Answer: A |
front 60 60. Why do most scientists agree that viruses are nonliving entities? A) They are not composed of cells. B) They cause diseases in host cells. C) They pass through filters. D) They are composed of relatively simple components. | back 60 Answer: A |
front 61 61. A gene is defined as A) the RNA product of a transcribed section of DNA B) a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a functional product. C) a sequence of nucleotides in RNA that codes for a functional product. D) any random segment of DNA. | back 61 Answer: B |
front 62 62. Which of the following pairs is mismatched? A) DNA polymerase - makes a molecule of DNA from a DNA template. B) DNA ligase - joins segments of DNA. C) DNA gyrase - relaxes supercoiling in DNA ahead of the replication fork. D) RNA polymerase - makes a molecule of RNA from an RNA template. | back 62 Answer: D |
front 63 63. DNA is constructed of A) two strands of nucleotides running in an antiparallel configuration. B) two complementary strands of nucleotides bonded A-C and G-T. C) None of the answers is correct. D) A single strand of nucleotides with internal hydrogen bonding. | back 63 Answer: A |
front 64 64. Which of the following is NOT a product of transcription? A) rRNA B) mRNA C) tRNA D) a new strand of DNA | back 64 Answer: D |
front 65 65. An enzyme produced in response to the presence of a substrate is called a(n) A) inducible enzyme B) promoter C) restriction enzyme D) repressible enzyme | back 65 Answer: A |
front 66 66. Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell A) y sexual reproduction B) as naked DNA in solution C) by crossing over D) by cell-to-cell contact | back 66 Answer: B |
front 67 67. Genetic change in bacteria can be brought about by A) transduction B) conjugation C) All of the answers are correct. D) transformation | back 67 Answer: C |
front 68 68. According to the operon model, for the synthesis of an inducible enzyme to occur, the A) repressor must not be synthesized. B) repressor must bind to the operator. C) end-product must not be in excess. D) substrate must bind to the repressor | back 68 Answer: D |
front 69 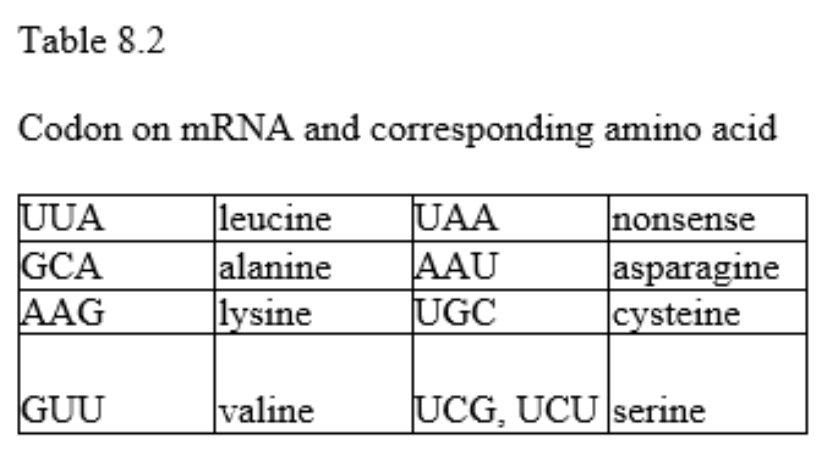 69. Refer to Table 8.2, the anticodon for valine is A) CUU B) CAA C) GTA D) CTT | back 69 Answer: B |
front 70 70. Refer to 8.2. If an indeterminate frameshift mutation occurred (that is, one at a random location) in the sequence of bases shown below, what would be the sequence of amino acids coded for? 3' ATTACGCTTTGC 5' A) leucine-arginine-lysine-alanine B) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided. C) asparagine-cytesine-valine-serine D) asparagine-arginine-lysine-alanine | back 70 Answer: B |
front 71 71. Conjugation differs from reproduction because conjugation A) transcribes DNA to RNA. B) replicates DNA. C) transfers DNA horizontally, to nearby cells without those cells undergoing replication. D) copies RNA to make DNA. | back 71 Answer: C |
front 72 72. The necessary ingredients for DNA synthesis can be mixed together in a test tube. The DNA polymerase is from Thermus aquaticus, and the template is from a human cell. The DNA synthesized would be most similar to A)aquaticus DNA B) a mixture of human and aquaticus DNA C) human DNA D) human RNA | back 72 Answer: C |
front 73 73. If you knew the sequence of nucleotides within a gene, which one of the following could you determine with the most accuracy? A) the tertiary structure of the protein B) the secondary structure of the protein C) the quarternary structure of the protein D) the primary structure of the protein | back 73 Answer: D |
front 74 74. An enzyme that copies DNA to make a molecule of RNA is A) DNA ligase B) RNA polymerase C) DNA helicase D) DNA polymerase | back 74 Answer: B |
front 75 75. When two genes from two different people are sequenced and aligned, it is discovered that there are multiple sequence differences in the coding segment DNA level. However, when the proteins formed by genes have their amino acids sequenced, there is no difference observed between the two. What is the most likely explanation for this observation? A) Mutations at the DNA level are not reflected in proteins produced. B) The mutations are repaired at the mRNA level after transcription has occurred, but before translation. C) The mutations lie at locations where they don't affect protein sequence due to degeneracy of the genetic code. D) RNA processing removes the different segments from the mRNA molecules of each person prior to translation. | back 75 Answer: C |
front 76 76. Open-reading frames are segments of DNA in which both start and stop codons are found. A) True B) False | back 76 Answer: A |
front 77 77. Bacteria usually contain multiple chromosomes. A) True B) False | back 77 Answer: B |
front 78 78. Both base substitution and frameshift mutations can result in the formation of premature stop codons. A) True B) False | back 78 Answer: A |
front 79 79. In the Ames test, any colonies that form on the control plates, in the absence of chemical being tested, should be the result of spontaneous mutations. A) True B) False | back 79 Answer: A |
front 80 80. Cell-to-cell contact is required for transduction to occur. A) True B) False | back 80 Answer: B |
front 81 81. Most of the available antimicrobial agents are effective against A) bacteria B) protozoa C) viruses D) fungi | back 81 Answer: A |
front 82 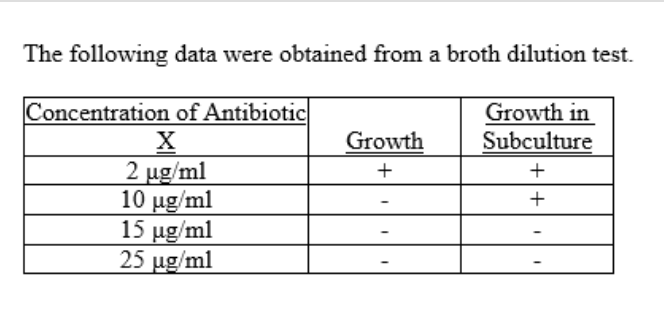 82. In Table 20.1, as illustrated by the data shown, the minimal bactericidal concentration of antibiotic X is: (note: subculture means they grow again from the growth column in this case) A) 25 ug/mL B) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided. C) 15 ug/mL D) 10 ug/mL | back 82 Answer: C |
front 83  83. In Table 20.1, the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibiotic X is A) 15 ug/mL B) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided. C) 25 ug/mL D) 10 ug/mL | back 83 Answer: D |
front 84  84. From the data in Table 20.1, you can predict that the effect of the drug on a different microbe A) will be the same. B) can't be predicted from the information provided. C) will be weaker. D) will be stronger. | back 84 Answer: B |
front 85 85. More than half of our antibiotics are A) synthesized in laboratories. B) produced by eukaryotic organisms. C) produced by bacteria. D) produced by Fleming. | back 85 Answer: C |
front 86 86. Which of the following statements about drug resistance is FALSE? A) It may be carried on a plasmid B) It may be due to enzymes that degrade some antibiotics C) It may be due to decreased uptake of a drug D) It is found only in gram-negative bacteria | back 86 Answer: D |
front 87 87. Drug resistance occurs A) because bacteria are normal microbiota B) when antibiotics are used indiscriminately C) when antibiotics are taken after the symptoms disappear D) against antibiotics and not against synthetic chemotherapeutic agents | back 87 Answer: B |
front 88 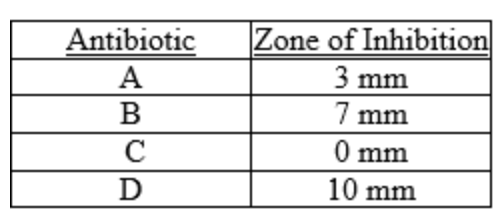 88. In Table 20.2, the most effective antibiotic tested was A) A B) B C) C D) D E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided. | back 88 Answer: D |
front 89 89. Use of antibiotics in animal feed leads to antibiotic-resistant bacteria because A) the antibiotics persist in soil and water B) the antibiotics cause new mutations to occur in the surviving bacteria, which results in resistance to antibiotics. C) the antibiotics kill susceptible bacteria, but the few that are naturally resistant live and reproduce, and their progeny repopulate the host animal. D) bacteria from other animals replace those killed by the antibiotics | back 89 Answer: C |
front 90 90. Community acquired MRSA is typically less virulent than healthcare-associated MRSA. A) True B) False | back 90 Answer: B |
front 91 91. A population of cells carrying a desired plasmid is called a A) clone B) vector C) Southern blot D) PCR | back 91 Answer: A |
front 92 92. Which enzyme would cut this strand of DNA? GCATGGATCCCAATGC A) A-BamHI B) B-EcoRI C) No answer text provided. D) C-HaeIII | back 92 Answer: A |
front 93 93. Which of the following places the steps in the PCR procedure in the correct order? 1. Incubate at 94C to denature DNA strands 2. Incubate at 72C for DNA synthesis 3. Incubate at 60C for primer hybridization A) 1, 3, 2 B) 2, 1, 3 C) 1, 2, 3 D) 3, 1, 2 | back 93 Answer: A |
front 94 94. A source of heat-stable DNA polymerase is A) Thermus aquaticus B) Saccharomyes cerevisiae C) Bacillus thuringiensis D) human | back 94 Answer: A |
front 95 95. Biotechnology involves the A) use of microorganisms to make desired products, the use of animal cells to make vaccines, and the development of disease-resistant crop plants B) use of microorganisms to make desired products and the use of animal cells to make vaccines C) development of disease-resistant crop plants D) use of animal cells to make vaccines | back 95 Answer: A |
front 96 96. Which of the following is NOT a desired characteristic of DNA vectors used in gene cloning procedures? A) large size B) has a selectable marker C) self-replication D) may replicate in several species | back 96 Answer: A |
front 97 97. The use of an antibiotic-resistance gene on a plasmid used in genetic engineering makes A) direct selection possible B) the recombinant cell dangerous C) the recombinant cell unable to survive D) All of the answers are correct | back 97 Answer: A |
front 98 98. Choose the best pair to complete the following sentence. While _____ is/are responsible for the diversity of life, ______ is/are responsible for shaping a population with organisms possessing characteristics that enhance survival A) mutations; selection B) selection; mutations C) properties; vectors D) microbes; DNA | back 98 Answer: A |
front 99 99. In recombinant DNA technology, a vector is a self-replicating segment of DNA, such as a plasmid or viral genome. A) True B) False | back 99 Answer: A |
front 100 100. What percentage of patients with whooping cough die? A) 1% B) 10% C) 4% D) 3% | back 100 Answer: A |
front 101 101. What doctor demonstrated that cowpox infection prevented smallpox? | back 101 Edward Jenner |
front 102 102. What stopped the measles virus from spreading throughout New York? A) antibiotics B) doctor interventions C) hand sanitizer D) herd immunity | back 102 Answer: D |
front 103 103. Autism is most likely caused by ______. A) genetic B) vaccine C) vitamins D) food | back 103 Answer: A |
front 104 104. The HPV vaccine can prevent A) whooping cough B) mumps C) cancer D) measles | back 104 Answer: C |
front 105 105. All of the following diseases that were largely eradicated in the US a generation ago are returning EXCEPT: A) diptheria B) mumps C) pertussis D) measles | back 105 Answer: A |
front 106 106. What percent of parents in the US vaccinate their children? A) 90% B) 50% C) 10% D) 60% | back 106 Answer: A |
front 107 107. How many people without immunity of the disease will get the measles if exposed to it? A) 10% B) 70% C) 65% D) 90% | back 107 Answer: D |
front 108 108. Once infected with measles, it is likely you will be infected again. A) True B) False | back 108 Answer: B |
front 109 109. Briefly, would you say that vaccination is different from other types of personal health decisions? If so, how? | back 109 I think it's no different from other types of personal health decisions. People have the option to say "yes" or "no" if they want to take the vaccine. Just like any other personal health decision, there are pros and cons that people weigh when they make a decision if they want the vaccination or not. |
front 110 110. You can catch ebola from sitting near someone on a plane. A) True B) False | back 110 Answer: B |
front 111 111. _____ are most likely the natural reservoir for Ebola virus. | back 111 Bats |
front 112 112. What is the biggest risk factor for infection with Ebola? A) Nursing a patient at home B) Working in a category IV laboratory C) Going grocery shopping D) Attending football matches or large gatherings | back 112 Answer: A |
front 113 113. An animal disease transmissible to humans is called A) zoonosis B) spillover C) amplifier D) pandemic | back 113 Answer: A |
front 114 114. An organism that carries the pathogen while suffering little to no illness is called A) reservoir host B) carrier C) fomite D) all of the aboce | back 114 Answer: A |
front 115 115. What is the treatment for Zika fever? A) There is no specific treatment. B) use of antiviral C) antibiotics D) blood transfusion | back 115 Answer: A |
front 116 116. How is Zika transmitted? | back 116 It is transmitted to people primarily through the bite of mosquitos. (but can spread through sex and from a pregnant woman to her fetus) |
front 117 117. What is a spillover event? | back 117 Occurs when a reservoir population with a high pathogen prevalence comes into contact with a novel host population |
front 118 118. Which of the following statements about healthcare associated infections is FALSE? A) They may be caused by opportunists. B) They may be caused by drug resistant bacteria. C) They occur in compromised patients. D) The patient was infected before hospitalization. | back 118 Answer: D |
front 119 119. A healthcare-associated infection (traditionally known as a nosocomial infection) is A) always caused by pathogenic bacteria B) acquired during the course of hospitalization C) always caused by medical personnel D) only a result of surgery | back 119 Answer: B |
front 120 120. The major significance of Robert Koch's work is that? A) diseases can be transmitted from one animal to another B) microorganisms are the result of disease C) microorganisms cause disease D) microorganisms are present in a diseased animal. | back 120 Answer: C |
front 121 121. Biological transmission differs from mechanical transmission in the biological transmission? A) involves fomites B) involves the reproduction of a pathogen in an arthropod vector prior to transmission C) works only with noncommunicable diseases D) requires direct contact | back 121 Answer: B |
front 122 122. Which of the following definitions is INCORRECT? A) sporadic: a disease that affects a population occasionally B) pandemic: a disease that affects a large number of people in the world in a short time C) incidence: number of new cases of a disease D) epidemic: a disease that is constantly present across the world | back 122 Answer: D |
front 123 123. The rise in herd immunity amongst a population can be directly attributed to A) vaccinations B) antibiotic-resistant microorganisms C) improved handwashing D) None of the answers is correct. | back 123 Answer: A |
front 124 124. Transient microbiota differ from normal microbiota in that transient microbiota A) never cause disease B) are found in a certain location on the host C) are always acquired by direct contact D) are present for a relatively short time | back 124 Answer: D |
front 125 125. Which of the following is NOT a communicable disease? A) malaria B) AIDS C) Covid-19 D) tetanus | back 125 Answer: D |
front 126 126. Which of the following is NOT a reservoir of infection? A) none of the answers is correct; all of these can be reservoirs of infection B) a sick animal C) a hospital D) a healthy person | back 126 Answer: A |
front 127 127. Which of the following is a fomite? A) insects B) droplets from a sneeze C) water D) a hypodermic needle | back 127 Answer: D |
front 128 128. The entry, establishment, and multiplication of a pathogen in a host is called A) exposure B) infection C) inflammation D) disease | back 128 Answer: B |
front 129 129. Which one of the following is an example of an indirect method of disease transmission? A) eating contaminated food B) sneezing C) coughing D) shaking hands | back 129 Answer: A |
front 130 130. True or False? Direct methods for the transmission of disease include hand contact and contact with animals? A) true B) false | back 130 Answer: A |
front 131 131. Endotoxins are released when: A) the host is injured during an infection B) bacterial pathogens leave through a portal of exit C) ram-negative bacterial cells disintegrate D) an infection occurs in the body | back 131 Answer: C |
front 132 132. Which of the following microbes would be considered avirulent? A) Neisseria meningitidis B) Vibrio cholerae C) Lactobacillus lactis D) Mycobacterium tuberculosis | back 132 Answer: C |
front 133 133. An outbreak is considered to be a more contained: A) pandemic disease B) epidemic disease C) local disease D) endemic disease | back 133 Answer: B |
front 134 134. True or False? Phagocytosis is a form of adaptive immunity in the body. A) True B) False | back 134 Answer: B |
front 135 135. All the following statements apply to antigens, except: A) antigens trigger the production of antibodies B) antigens are unique chemical groups that are not normally present in the body C) antigens contain recognizable epitopes D) antigens are part of the innate immune response | back 135 Answer: D |
front 136 136. Where are B cells and T cells "born"? A) in the blood B) in the thyroid C) in the bone marrow D) in the thymus | back 136 Answer: C |
front 137 137. On average, how long does it take the adaptive immunity response to become fully active to an infecting pathogen? A) 10 to 14 days B) 2 to 3 days C) 18 to 24 days D) 28 to 30 days | back 137 Answer: A |