Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chem 212 Final Review
front 1 The rising of liquids in narrow tubes against the force of gravity is called - capillary action - cohesion - specific elasticity - surface tension - viscosity | back 1 capillary action |
front 2 procaine hydrochloride (M = 272.8g/mol) is used as a local anesthetic. Calculate the molarity of a 2.51 m solution of procaine hydrochloride in water which has a density of 1.057 g/mL - 1.98 M - 1.58 M - 1.87 M - 1.67 M - 1.15 M | back 2  1.58 M |
front 3 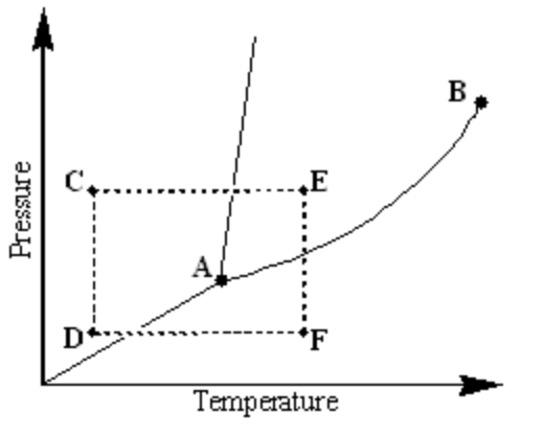 Examine the following phase diagram and identify the phase change occurring as one goes from point D to point F. - deposition caused by increasing the temperature - sublimation caused by increasing the temperature - condensation caused by increasing the temperature - melting caused by increasing the temperature - vaporization caused by increasing the temperature | back 3 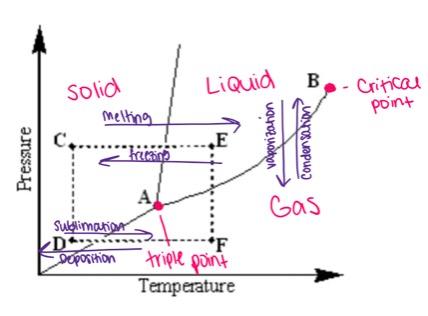 sublimation caused by increasing the temperature |
front 4 the band gap between the valence and conduction bands of semiconductors - is large - is non-existent - decreases with increasing temperature - is relatively small - increases with increasing temperature | back 4 is relatively small |
front 5 which of the following substances will have hydrogen bonds between the molecules? - CH3SH - CH3NH2 - CH3CH2Cl - (CH3)2O - HCl | back 5 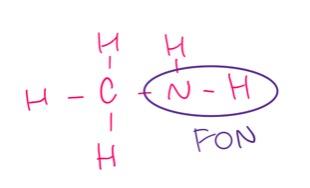 CH3NH2 |
front 6 From the following list of aqueous solutions and water, select the one with the highest boiling point. (Note: Use the ideal values of the van't Hoff factor.) - 0.37 M AlBr3 - 0.74 M SrBr2 - 0.95 M NaBr - 0.57 M Na2S - pure water | back 6  0.74 M SrBr2 |
front 7 The boiling point of the molecular compound A is 55.2°C. How much energy is needed to heat 17.5 g of A from 12.5°C to 91.8°C? Specific heat capacity of A(l ) 3.52 J/(g⋅K) Specific heat capacity of A(g ) 2.11 J/(g⋅K) Heat of vaporization of A 45.7 kJ/mol Molar mass of A 30.4 g/mol - 28.6 kJ - 34.0 kJ - 38.8 kJ - 30.3 kJ - 41.1 kJ | back 7 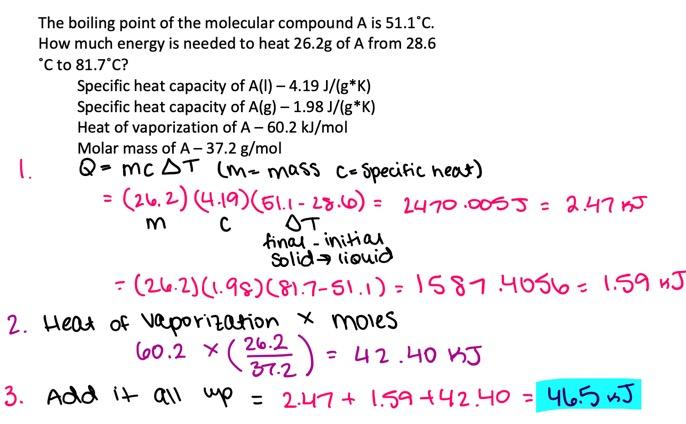 30.3 kJ |
front 8 The Henry's Law constant for carbon monoxide in water at 25°C is 9.71×10-4 mol/L·atm. How many moles of CO will dissolve in 1.00 L of water at this temperature if the partial pressure of CO is 382.1 torr? - 0.00193 mol - 0.000628 mol - 0.000488 mol - 0.000555 mol - 0.371 mol | back 8  0.000488 mol |
front 9 A compound has vapor pressure of 29.5 torr at 41.7°C and 441.0 torr at 141.0°C. Calculate its heat of vaporization. - 29.5 kJ/mol - 25.8 kJ/mol - 31.4 kJ/mol - 36.5 kJ/mol - 40.3 kJ/mol | back 9  29.5 kJ/mol |
front 10 Which of the following statements is correct? - Raoult's Law applies exactly to all solutions.- - Raoult's Law relates the vapor pressure of the solvent above the solution to the molarity of the solution. - Raoult's Law relates the vapor pressure of the solvent above the solution to its mole fraction in the solution. - Raoult's Law applies only to non-ideal solutions. - Raoult's Law works best when applied to concentrated solutions. | back 10 Raoult's Law relates the vapor pressure of the solvent above the solution to its mole fraction in the solution. |
front 11 Determine the freezing point of a solution which contains 0.39 mol of sucrose in 93 g of water. (For water K f = 1.86°C/m and K b = 0.512°C/m) - -2.1˚C - -7.8˚C - 0.0˚ C - 2.1˚C - 7.8˚C | back 11  -7.8˚C |
front 12 Which of the following statements is correct? - all of these statements are correct - a solution becomes saturated when no more solute can be dissolved - a solution becomes unsaturated when the solute precipitates in it - none of these statements are correct - supersaturated solutions are quite stable | back 12 a solution becomes saturated when no more solute can be dissolved |
front 13 What is the coordination number for a metal that crystalizes in the face-centered cubic lattice? - 4 - 2 - 8 - 6 - 12 | back 13 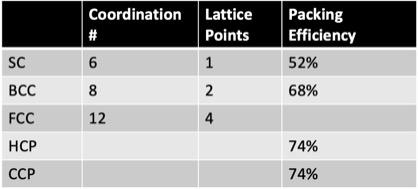 12 |
front 14 Which of the following should have the highest boiling point? - CH3CH3 - CH3SCH3 - CH3TeCH3 - CH3OCH3 - CH3SeCH3 | back 14 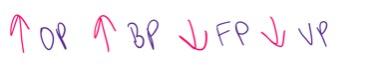 CH3TeCH3 |
front 15 Which of the following pairs of ions is arranged so that the ion with the smaller (i.e. less negative) heat of hydration is listed first? - Al3+, Mg2+ - Ca2+, K+ - None of the above pairs are arranged in this way - Sr2+, Ca2+ - S2–, Se2– | back 15 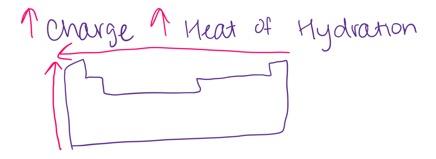 Sr2+, Ca2+ |
front 16 Which of the following statements is correct with regard to the following two solutions? (Note: Use the ideal values of the van't Hoff factor.) (I) 0.52 m RbCl and (II) 0.21 m CaCl2 - Solution (I) has lower osmotic pressure - The two solutions have the same vapor pressure - Solution (I) has lower vapor pressure and lower osmotic pressure - Solution (I) has higher osmotic pressure. - Solution (II) has lower vapor pressure | back 16 Solution (I) has higher osmotic pressure. |
front 17 A metal with a simple cubic lattice will have ________________ atom(s) per unit cell. - 8 - 1 - 4 - 6 - 2 | back 17 1 |
front 18 The heat needed to worm up a liquid depends on - its vapor pressure - its heat capacity - the heat capacity of its vapors - the value of the gas constant, R - its normal boiling point | back 18 its heat capacity |
front 19 An aqueous solution contains 3.77 g of the unknown compound X. The volume of the solution is 895.0 mL and its osmotic pressure is 2.85 atm at 25.0°C. Assuming that X is a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte, what is the molar mass of this compound? - 36.2 g/mol - 30.5 g/mol - 27.9 g/mol - 33.7 g/mol - 50.4 g/mol | back 19  36.2 g/mol |
front 20 What is the molality of a solution prepared by dissolving 13.3 g of hexane, C6H14, in 71.0 g of benzene, C6H6? - 2.17 m - 1.57 m - 2.57 m - 2.05 m - 2.74 m | back 20  2.17 m |
front 21 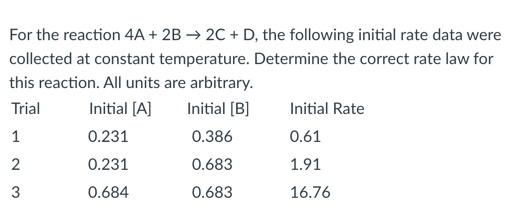 - rate = k - rate = k[A]2 - rate = k[B]2 - rate = k[A]2[B]2 - rate = k[A][B] | back 21  rate = k[A]2[B]2 |
front 22 Which of the following statements about the reaction quotient, Q, and the equilibrium constant, K, is true? - Q can not be affected by the total pressure. - K is affected by the presence of a catalyst but Q is not. - At equilibrium Q reaches a maximum. - Q and K are basically the same thing. - K is related to the rate constants of the forward and reverse reactions. | back 22 K is related to the rate constants of the forward and reverse reactions. |
front 23 At 25oC, the equilibrium constant, for the reaction - 22.6 - 27.4 - 31.4 - 20.9 - 19.4 | back 23  27.4 |
front 24 The equilibrium constant, K c , for the reaction 2A(g) + B(g) ↔ 2C(g) + D(g) is 6.94 at a certain temperature. What is the equilibrium constant
for the following reaction at the same temperature? - 3.47 - 0.0208 - 0.380 - 0.443 - 1.86 | back 24  0.380 |
front 25 Consider the following reaction If [A] is decreasing at the rate of 1.59 mol L-1s-1, at what rate is [D] changing? - 1.77 mol L-1s-1 - 1.42 mol L-1s-1 - 1.99 mol L-1s-1 - 2.98 mol L-1s-1 - 1.14 mol L-1s-1 | back 25  1.99 mol L-1s-1 |
front 26 Consider the following reaction. - low temperature, high pressure - high temperature, low pressure - high temperature, high pressure - low temperature, low pressure - none of the above, unless a catalyst is present | back 26 low temperature, low pressure |
front 27 What is the mass-action expression, Kc , for the following chemical reaction? PbO(s) + CO(g) ↔ Pb(l) + CO2(g) - none of the above expressions is correct - [CO2]/[CO] - [Pb][CO2]/[PbO][CO] - [Pb][CO2]/[CO] - [CO]/[CO2] | back 27 [CO2]/[CO] |
front 28 Compound A decomposes to B and C according to the following equation:
- 0.363 - 0.388 - 0.281 - 0.454 - 0.498 | back 28  0.388 |
front 29 The rate law for the reaction 2A → B + C is rate = k[A]2 with a rate constant k = 0.3765 L mol-1 s-1. If the initial concentration of A is 0.591 mol/L, calculate its concentration 1.69 seconds after the start of the reaction. - 0.420 mol/L - 0.462 mol/L - 0.553 mol/L - 0.593 mol/L - 0.514 mol/L | back 29  0.420 mol/L |
front 30 When solid magnesium hydroxide is added to water, part of it dissociates into magnesium and hydroxide ions. Mg(OH)2(s) ↔ Mg2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) If the above reaction is at equilibrium at a certain temperature, what would be the effect of adding a small amount of magnesium ions to the solution? - The solution will become supersaturated. - The forward reaction will proceed to establish equilibrium. - The reverse reaction will proceed to establish equilibrium. - None of the above conclusions is justified without additional information. - No effect. | back 30 The reverse reaction will proceed to establish equilibrium. |
front 31 The the units of the rate constant for the reaction A + B → C + D are L2 mol-2 s-1. What is the overall order of the reaction? - first - none of the above - zero - second - third | back 31 third |
front 32 If the activation energy of a certain chemical reaction is 31.3 kJ/mol, by what factor will the rate of this reaction increase when the temperature is increased from 32 oC to 64 oC? (R = 8.314×10-3 kJ/mol⋅K) - 3.48 - 2.35 - 3.23 - 3.81 - 2.49 | back 32 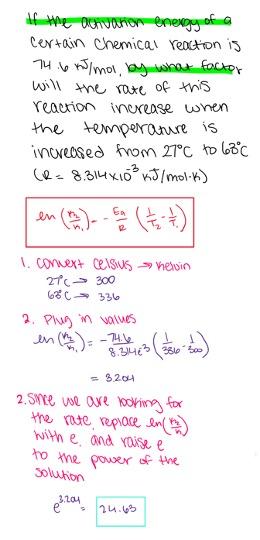 3.23 |
front 33 When the reaction A → B + C is studied, a plot of 1/[A] versus time gives a straight line with a positive slope. What is the the order of the reaction? - first - third - second - more information is needed to determine the order - zero | back 33 second |
front 34 At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant for the
reaction - 0.766 atm - 0.566 atm - 0.473 atm - 0.531 atm - 0.715 atm | back 34  0.566 atm |
front 35 At 25oC, the equilibrium constant for the
reaction - the reverse reaction must proceed to establish equilibrium - the forward reaction must proceed to establish equilibrium - the volume of the container must be known to answer the question - the concentrations of all substances must be known to answer the question - the system is at equilibrium | back 35  the forward reaction must proceed to establish equilibrium |
front 36 Which of the following statements is true? - A catalyst accelerates a reaction by changing the reaction pathway. - A catalyst accelerates a reaction by supplying energy to the reactant molecules. - A catalyst accelerates a reaction by increasing the number of molecular collisions. - A catalyst accelerates a reaction by increasing its activation energy. - A catalyst accelerates a reaction and is consumed in it. | back 36 A catalyst accelerates a reaction by changing the reaction pathway. |
front 37 A particular radioactive isotope undergoes a first order decay with a half-life of 25.1 years. How long would it take for the concentration of this isotope to drop to 53.6 % of its original value? - 30.9 years - 29.3 years - 24.8 years - 26.3 years - 22.6 years | back 37  22.6 years |
front 38 The experimental rate law for the reaction 2A + 2B → D + E is
Rate =
k[A]2 [B]2. Which of
the following statements is correct for the mechanism suggested
below? - none of the above is correct - the mechanism should only have a single step - the mechanism is not consistent with the rate law - The mechanism is consistent with the rate law but it is not physically reasonable - The mechanism is consistent with the rate law and it is physically reasonable | back 38 the mechanism is not consistent with the rate law |
front 39 The rate law for the reaction A → B is rate = k[A] with a rate constant of 2.70 s-1. If the initial concentration of A is 0.632 mol/L, what is the half-life of the reaction? - 0.326 s - 0.092 s - 0.586 s - 0.117 s - 0.257 s | back 39  0.257 s |
front 40 At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant for the
reaction - 0.922 M - 0.792 M - 0.531 M - 0.703 M - 0.666 M | back 40  0.666 M |
front 41 Which of the following acids and its conjugate base should be used to
prepare an efficient buffer with a pH = 4.0? - 1 - 3 - 2 - both 2 and 3 would be fine - both 1 and 2 would be fine | back 41  2 |
front 42 What is the pH of a 1.9×10–5 M Ca(OH)2 solution? - 8.96 - 9.28 - 10.77 - 9.58 - 11.36 | back 42  9.58 |
front 43 What is the pK a of the alkylammonium ion R3NH+? (K b = 4.6×10–5 for R3N) - 9.66 - 3.68 - 5.55 - 4.34 - 9.07 | back 43  9.66 |
front 44 The organic acid RCOOH has a pKa = 4.14. What is the pH of a 0.40 M aqueous solution of this acid? - 3.15 - 2.27 - 2.09 - 2.88 - 1.96 | back 44  2.27 |
front 45 Sodium nitrite, NaNO2, is best known as a food additive. What is the pH of a 0.350 M NaNO2 solution in water? (K a of HNO2 is equal to 7.1×10-4) - 7.00 - 5.65 - 8.35 - 5.15 - 8.61 | back 45 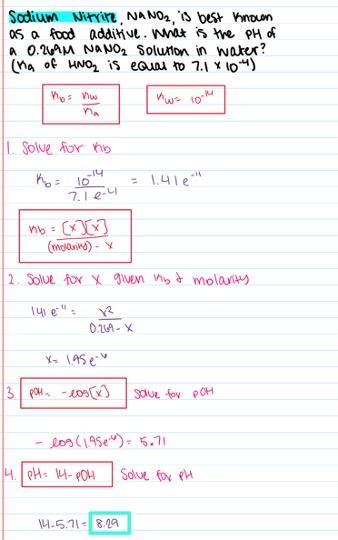 8.35 |
front 46 Calculate the molar solubility of barium sulfate, BaSO4, in 0.34 M BaCl2 solution. (K sp = 1.1×10-10 for BaSO4) - 1.9e-10 M - 6.2e-11 M - 2.4e-9 M - 3.2e-10 M - 9.1e-11 M | back 46  3.2e-10 M |
front 47 Select the pair of substances in which an acid is listed followed by its conjugate base. - NH4 +, NH2 – - H2CO3, CO3 2- - H+, HF - H3PO4, HPO4 2– - HCO3 –, CO3 2- | back 47 HCO3 –, CO3 2- |
front 48 Calculate the molar solubility of Fe(OH)2 in pure water. (K sp = 4.1×10–15) - 1.6e–5 M - 6.4e–8 M - 1.1e–4 M - 5.2e–4 M - 1.0e–5 M | back 48  1.0e–5 M |
front 49 A solution is prepared by adding 0.034 mol of NaCl to 1.00 L of 0.0114 M Pb(NO3)2. Which of the following statements is correct? (K sp = 1.7×10-5 for PbCl2) - The solution is unsaturated and no precipitate forms. - Both sodium nitrate and lead(II) chloride precipitate. - Lead(II) chloride precipitates until the solution is saturated. - Sodium nitrate precipitates until the solution is saturated. - The data is not sufficient to predict precipitation. | back 49  The solution is unsaturated and no precipitate forms. |
front 50 An aqueous solution of NH4Cl would be - either acidic or basic depending on the amount of salt dissolved. - neutral - either acidic or basic depending on the actual values of K a and K b which must be known. - acidic - basic | back 50 acidic |
front 51 The species NH3 is classified as a(n) - none of the above - Lewis acid - Arrhenius base - Arrhenius acid - Lewis base | back 51 Lewis base |
front 52 A 0.41 M solution of a given weak acid, HA, has a pH of 4.81. What is the pKa of the acid? - 12.66 - 8.67 - 7.97 - 11.55 - 9.23 | back 52  9.23 |
front 53 What is the pH of a buffer that consists of 0.32 M HClO and 0.67 M NaClO? (K a(HClO) = 2.9×10–8) - 7.17 - 10.98 - 10.13 - 9.16 - 7.86 | back 53  7.86 |
front 54 The acid ionization constant of H2SO3 is
K a = 1.4×10–2 and that of HClO is
K a = 2.9×10–8. Which statement about
the equilibrium below is correct? - The initial concentrations of the reactants must be known before any prediction can be made. - The reactants will be favored at equilibrium. - Neither reactants nor products will be favored because all of the species are weak acids or bases. - The products will be favored at equilibrium. - Neither reactants nor products will be favored because the reaction is impossible. | back 54 The products will be favored at equilibrium. |
front 55 When a strong base is titrated with a strong acid, the pH at the equivalence point is - strongly acidic - neutral - slightly acidic - slightly basic - strongly basic | back 55 neutral |
front 56 Which of the following arrangements has the strongest acid listed first and the weakest acid listed last? - H3N > HF > H2O - HF > H2O > H3N - H2O > HF > H3N - HF > H3N > H2O - H2O > H3N > HF | back 56 HF > H2O > H3N |
front 57 A particular acid-base indicator has an acid ionization constant, K In = 6.4×10–9. What would be the approximate pH range over which it changes color? - 7.2-92 - 8.2-10.2 - 5.2-7.2 - 4.2-6.2 - 6.2-8.2 | back 57  7.2-9.2 |
front 58 A solution is prepared by adding 2.6 mol of KCN to 1.00 L of 0.30 M Zn(NO3)2. What is the equilibrium concentration of Zn2+ ions? (K f = 4.2×1019 for Zn(CN)4 2-) - 2.0e-22 M - 1.4e–20 M - 1.9e–21 M - 6.2e–21 M - 1.1e–20 M | back 58  1.9e–21 M |
front 59 Calculate the pH during the titration of 34.0 mL 0.103 M formic acid (pKa = 3.74) with 0.110 M NaOH after the addition of 17.0 mL of the titrant. - 3.52 - 3.28 - 3.80 - 4.21 - 3.94 | back 59  3.80 |
front 60 Which, if any, of the following aqueous mixtures would be buffer systems? (1) HNO2 , KH2PO4 (2) H2SO3 , NaHSO3 - 1 is a buffer but 2 is not - neither 1 nor 2 are buffers - none of above - 2 is a buffer but 1 is not - both 1 and 2 are buffers | back 60 2 is a buffer but 1 is not |
front 61 How long would it take to deposit 8.43 g of copper (molar mass 63.55 g/mol) at the cathode of an electrolytic cell, if a current of 14.7 A is passed through an aqueous solution of CuSO4? - 38.7 min - 44.8 min - 29.0 min - 24.0 min - 25.5 min | back 61  29.0 min |
front 62 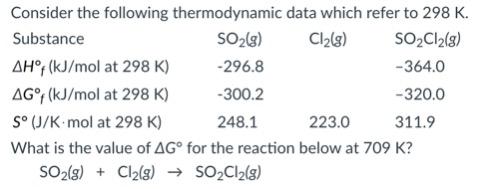 - 19.8 kJ - 45.7 kJ - -67.2 kJ - -45.7 kJ - 19.8 kJ | back 62  45.7 kJ |
front 63 Predict the sign of ΔSo for the following reaction. C2H5OH (l) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l) - ∆S˚ > 0 - ∆S˚ ≈ 0 - More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction. - ΔSo < 0 - ΔSo could be positive or negative depending on the sign of ΔH°. | back 63  ΔSo < 0 |
front 64 Consider the following redox equation - 3 - 4 - 1 - 2 - 5 | back 64 2 |
front 65 If Eo cell = 0.30 V for the reaction below at 25oC, what is the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature. Sn2+ (aq) + Fe(s) ↔ Fe2+ (aq) + Sn(s) - 2.2e0 - 7.3e-11 - 1.0e0 - 1.4e10 - 1.2e5 | back 65  1.4e10 |
front 66 Use the table of standard reduction potentials attached to your test to calculate Eo cell for the following reaction and determine if it is spontaneous at standard conditions. Ca2+ (aq) + Cd(s) → Cd2+ (aq) + Ca(s) - Eo cell = –2.47 V, spontaneous - Eo cell = 2.47 V, spontaneous - Eo cell = –3.27 V, non-spontaneous - Eo cell = 2.47 V, non-spontaneous - Eo cell = –2.47 V, non-spontaneous | back 66  Eo cell = –2.47 V, non-spontaneous |
front 67 Which, if any, of the following two elements can be isolated by
electrolysis of the the aqueous salt shown? - Neither (1) nor (2) can be isolated. - Both (1) and (2) can be isolated. - (1) can not be isolated but (2) can be isolated - (1) can be isolated but (2) can not be isolated. | back 67  Both (1) and (2) can be isolated. |
front 68 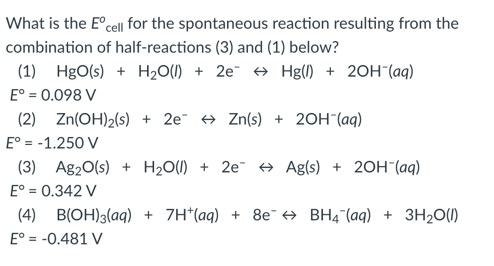 - 0.244 V - -0.244 V - 0.220 V - -0.440 V - 0.440 V | back 68 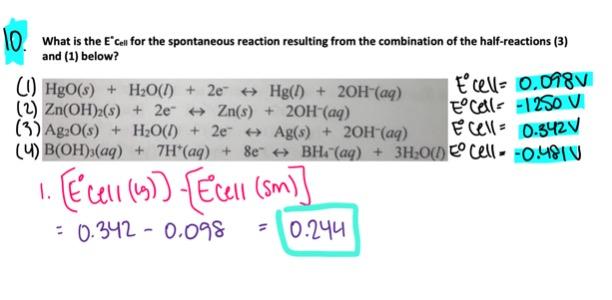 0.244 V |
front 69 For a given chemical reaction, ΔΗ > 0 and ΔS < 0. Therefore, - The reaction is spontaneous only at high temperatures. - The reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures. - The reaction is spontaneous only at low temperatures. - The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures. | back 69  The reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures. |
front 70 For the reaction below, ΔGo = 24.0 kJ/mol at 989
K. If at 989 K, an excess of the solid A(s) is added to the
gases B(g) and C(g) both having partial pressures of
0.76 atm, which statement is true? - The reverse reaction will proceed spontaneously. - The reaction will be at equilibrium. - The reaction quotient will become negative. - The equilibrium constant will increase. - The forward reaction will proceed spontaneously. | back 70  The reverse reaction will proceed spontaneously. |
front 71 Which one of the following statements about electrochemical cells is correct? - The free energy change is negative for an electrolytic cell. - The cathode is labeled as negative (-) in a voltaic cell but positive (+) in an electrolytic cell. - Reduction occurs at the cathode of both galvanic and electrolytic cells. - In the salt bridge cations travel toward the anode and anions toward the cathode. - None of the above statements is correct. | back 71 Reduction occurs at the cathode of both galvanic and electrolytic cells. |
front 72 A galvanic cell consists of an Au/Au3+ electrode (Eo = +1.50 V) and a Ag/Ag+ electrode (Eo = +0.80 V). Calculate the cell potential, E cell, at 25oC if [Au3+] = 6.9×10–7 M and [Ag+] = 3.6×10–4 M. - 0.73 V - 0.81 V - 0.70 V - 0.78 V - 0.89 V | back 72  0.78 V |
front 73  - 657.3 J/K - 46.1 J/K - -277.6 J/K - 277.6 J/K - -46.1 J/K | back 73  - 277.6 J/K |
front 74 Which of the following relationships best describes ΔSo for the following reaction. HCl (g) → H+(aq) + Cl- (aq) - ΔSo ≈ 0 - ΔSo > 0 - More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction. - ΔSo = TΔH° - ΔSo < 0 | back 74 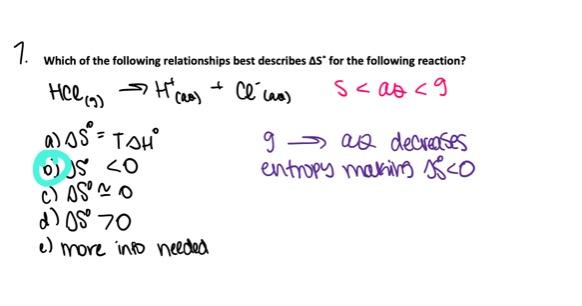 ΔSo < 0 |
front 75 Examine the table of standard reduction potentials attached to your test and determine which of the following species is the strongest oxidizing agent? - Sn2+ (aq) - Sn(s) - Sn4+ (aq) - Au3+ (aq) - NO3 – (aq) | back 75  Au3+ (aq) |
front 76  - 521.4 K - 718.9 K - 454.6 K - 591.1 K - 269.9 K | back 76 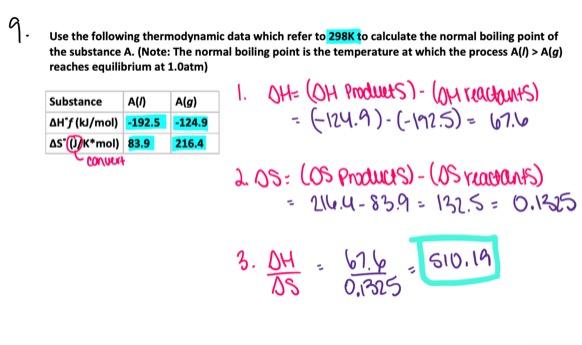 591.1 K |
front 77 Which of the following should have the greatest molar entropy at 298 K? - Cl2 (aq) - F2 (g) - Cl2 (g) - all should have the same molar entropy since the temperature is constant - F2 (aq) | back 77  Cl2 (g) |
front 78 For the reaction below, ΔHr
o = 178.5 kJ/mol and
ΔSr o = 159.0
J/mol⋅K at 298 K. What is the equilibrium constant of this reaction
at 572.0 K? - 1.9e-8 - 7.0e-9 - 1.0e-8 - 8.4e-9 - 6.2e-9 | back 78  1.0e-8 |
front 79 A galvanic cell has the following notation: Sn(s) | Sn2+(aq) || Fe3+(aq), Fe2+(aq) | Pt(s) Which of the following equations correctly represents the overall cell reaction? - Sn(s) + Fe2+(aq) → Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) - Sn2+(aq) + Fe2+(aq) → Sn(s) + Fe3+(aq) - Sn(s) + 2Fe3+(aq) → Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq) - Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) → Sn(s) + 2Fe2+(aq) - Sn(s) + Fe3+(aq) → Sn2+(aq) + Fe2+(aq) | back 79 Sn(s) + 2Fe3+(aq) → Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq) |
front 80 Which, if any, of the following three metals could be used as
sacrificial anodes for protection of a metal with E° = 0.93
V? (All E° values refer to the M3+/M half-cell
reactions.) - none of them could be used - only (3) could be used - all three of them could be used - only (1) and (2) can be used - only (2) and (3) could be used | back 80  only (2) and (3) could be used |