Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Central Science: Chapter 17
front 1 Which one of the following pairs cannot be mixed together to
form a buffer solution? | back 1 B |
front 2 Which one of the following pairs cannot be mixed together to
form a buffer solution? | back 2 C |
front 3 Which one of the following pairs cannot be mixed together to
form a buffer solution? | back 3 C |
front 4 A solution containing which one of the following pairs of substances
will be a buffer solution? | back 4 D |
front 5 A solution containing which one of the following pairs of substances
will be a buffer solution? | back 5 E |
front 6 What change will be caused by addition of a small amount of HCl to a
solution containing fluoride ions and hydrogen fluoride? | back 6 D |
front 7 The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is ________. | back 7 C |
front 8 In a solution, when the concentrations of a weak acid and its
conjugate base are equal, ________. | back 8 C |
front 9 Which solution has the greatest buffering capacity? | back 9 C |
front 10 Which solution has the greatest buffering capacity? | back 10 C |
front 11 The addition of HF and ________ to water produces a buffer
solution. | back 11 C |
front 12 The addition of HCl and ________ to water produces a buffer
solution. | back 12 A |
front 13 The addition of HCl and ________ to water produces a buffer
solution. | back 13 B |
front 14 The addition of KOH and ________ to water produces a buffer
solution. | back 14 E |
front 15 Which of the following could be added to a solution of sodium acetate
to produce a buffer? | back 15 B |
front 16 Which of the following could be added to a solution of NaF to prepare
a buffer? | back 16 A |
front 17 Which of the following could be added to a solution of HC2H3O2 to
prepare a buffer? | back 17 C |
front 18 Which of the following could be added to a solution of acetic acid to
prepare a buffer? | back 18 B |
front 19 What is the primary buffer system that controls the pH of the
blood? | back 19 C |
front 20 The ________ and ________ are the principal organs that regulate the
pH of the carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system in the
blood. | back 20 C |
front 21 Human blood is considered to be ________. | back 21 C |
front 22 Decreasing the pH of blood will cause hemoglobin to release
________. | back 22 D |
front 23 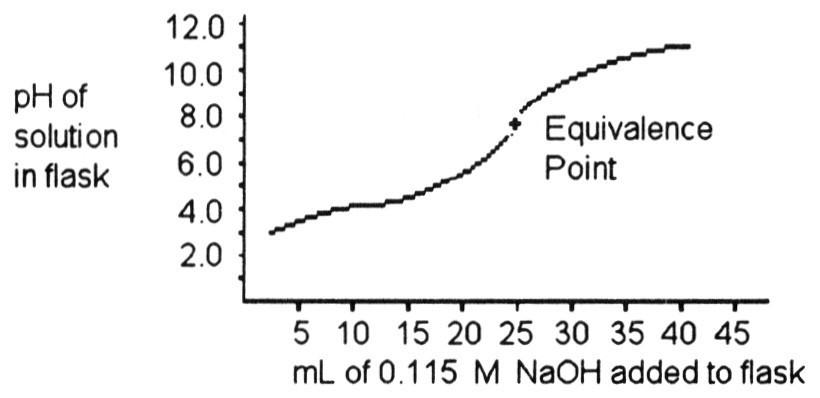 A 25.0 mL sample of a solution of an unknown compound is titrated
with a 0.115 M NaOH solution. The titration curve above was obtained.
The unknown compound is ________. | back 23 C |
front 24  A 50.0 mL sample of a solution of a monoprotic acid is titrated with
a 0.115 M NaOH solution. The titration curve above was obtained. The
concentration of the monoprotic acid is about ________ mol/L. | back 24 D |
front 25 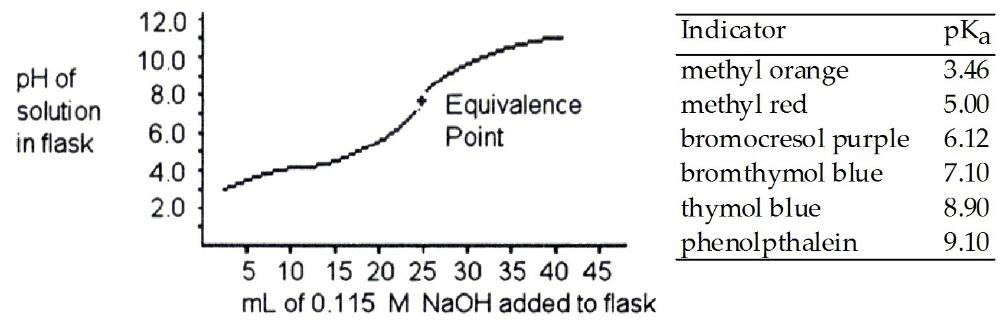 A 25.0 mL sample of a solution of a monoprotic acid is titrated with
a 0.115 M NaOH solution. The titration curve above was obtained. Which
of the following indicators would be best for this titration? | back 25 B |
front 26  Which compound listed below has the greatest molar solubility in
water? | back 26 D |
front 27  Which compound listed below has the smallest molar solubility in
water? | back 27 D |
front 28 The molar solubility of ________ is not affected by the pH of the
solution. | back 28 C |
front 29 In which one of the following solutions is silver chloride the most
soluble? | back 29 C |
front 30 Which one of the following is not amphoteric? | back 30 B |
front 31 For which salt should the aqueous solubility be most sensitive to
pH? | back 31 C |
front 32 Which one of the following is amphoteric? | back 32 D |
front 33 Why does fluoride treatment render teeth more resistant to
decay? | back 33 D |
front 34 A result of the common-ion effect is ________. | back 34 C |
front 35 The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.30 × 10-5. The pH of a buffer
prepared by combining 50.0 mL of potassium benzoate and 50.0 mL of
1.00 M benzoic acid is ________. | back 35 D |
front 36 Calculate the pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.150 mol of
benzoic acid and 0.300 mol of sodium benzoate in water sufficient to
yield 1.00 L of solution. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.30 X 10-5
| back 36 C |
front 37 Calculate the pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.150 mol of
acetic acid and 0.300 mol of sodium acetate in water sufficient to
yield 1.00 L of solution. The Ka of acetic acid is 1.76 X 10-5
| back 37 E |
front 38 The pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.550 mol of solid
methylamine hydrochloride (CH3NH3Cl) in 1.00 L of 1.35 M methylamine
(CH3NH2) is ________. The Kb for methylamine is 4.40 X 10-4
(Assume the final volume is 1.00 L.) | back 38 A |
front 39 The pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.350 mol of acid in 1.00
L of 1.10 M of conjugate base is ________. The Kb for the conjugate
base is 5.40 X 10-4 (Assume the final volume is 1.00
L.) | back 39 A |
front 40 A 25.0 mL sample of 0.723 M HClO4 is titrated with a 0.27 M KOH
solution. The H3O+ concentration after the addition of of KOH is
________ M. | back 40 D |
front 41 The pH of a solution prepared by mixing 50.0 mL of 0.125 M KOH and
50.0 mL of 0.125 M HCl is ________. | back 41 B |
front 42 The pH of a solution prepared by mixing 40.0 mL of 0.125 M Mg(OH)2
and 150.0 mL of 0.125 M HCl is ________. | back 42 E |
front 43 The pH of a solution prepared by mixing 50.0 mL of 0.125 M NaOH and
40.0 mL of 0.125 M HNO3 is ________. | back 43 E |
front 44 A 50.0 mL sample of an aqueous H2SO4 solution is titrated with a
0.375 M NaOH solution. The equivalence point is reached with 62.5 mL
of the base. The concentration of H2SO4 is ________ M. | back 44 A |
front 45 The concentration of iodide ions in a saturated solution of lead (II)
iodide is ________ M. The solubility product constant of PbI2 is 1.4 x 10-8
| back 45 B |
front 46 The concentration of fluoride ions in a saturated solution of barium
fluoride is ________ M. The solubility product constant of BaF2 is 1.7
x 10-6
| back 46 C |
front 47 The concentration of iodide ions in a saturated solution of silver
iodide is ________ M. The solubility product constant of AgI is 8.3 x 10-17
| back 47 C |
front 48 The solubility of lead (II) chloride (PbCl2) is 1.6 x 10-2
M. What is the Ksp of PbCl2? | back 48 D |
front 49 The solubility of manganese (II) hydroxide (Mn(OH)2) is 2.2 x
10-5 M. What is the Ksp of Mn(OH)2? | back 49 B |
front 50 Determine the Ksp for magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) where the
solubility of Mg(OH)2 is 1.4 x 10-4 M | back 50 B |
front 51 Calculate the maximum concentration (in M) of silver ions (Ag+) in a
solution that contains 0.025 M of CO32-. The Ksp of Ag2CO3 is 8.1 x 10-12
| back 51 A |
front 52 Calculate the maximum concentration (in M) of calcium ions (Ca2+) in
a solution that contains 0.055 M of CO32-. The Ksp of CaCO3 is 3.4 x 10-9
| back 52 D |
front 53 What is the solubility (in M) of PbCl2 in a 0.15 M solution of HCl?
The Ksp of PbCl2 is 1.6x 10-5
| back 53 D |
front 54 The Ksp for Cu(OH)2 is 4.8 × 10-20. Determine the molar
solubility of Cu(OH)2 in a buffer solution with a pH of 10.1. | back 54 C |
front 55 Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.278 M in sodium formate
(NaHCO2) and 0.222 M in formic acid (HCO2H). The Ka of formic acid is
1.77 × 10-4. | back 55 A |
front 56 Calculate the percent ionization of formic acid (HCO2H) in a solution
that is 0.322 M in formic acid and 0.178 M in sodium formate (NaHCO2).
The Ka of formic acid is 1.77 × 10-4. | back 56 B |
front 57 Calculate the percent ionization of formic acid (HCO2H) in a solution
that is 0.152 M in formic acid. The Ka of formic acid is 1.77 ×
10-4. | back 57 C |
front 58 Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.322 M in nitrous acid (HNO2)
and 0.178 M in potassium nitrite (KNO2). The acid dissociation
constant of nitrous acid is 4.50 × 10-4
| back 58 A |
front 59 What is the percent ionization of nitrous acid in a solution that is
0.222 M in nitrous acid (HNO2) and 0.278 M in potassium nitrite
(KNO2)? The acid dissociation constant of nitrous acid is 4.50 x 10-4
| back 59 E |
front 60 What is the percent ionization of nitrous acid in a solution that is
0.189 M in nitrous acid? The acid dissociation constant of nitrous
acid is 4.50 x 10-4
| back 60 E |
front 61 Which solution would have the greatest buffering capacity? | back 61 D |
front 62 The addition of hydrofluoric acid and ________ to water produces a
buffer solution. | back 62 A |
front 63 What is the pH of a buffer solution that is 0.266 M in lactic acid
and 0.111 M in sodium lactate? The Ka of lactic acid is 1.4 × 10-4
| back 63 D |
front 64 What is the pH of a buffer solution that is 0.172 M in hypochlorous
acid (HClO) and 0.131 M in sodium hypochlorite? The Ka of hypochlorous
acid is 3.8 × 10-8
| back 64 E |
front 65 A solution is prepared by dissolving 0.23 mol of hypochlorous acid
and 0.27 mol of sodium hypochlorite in water sufficient to yield 1.00
L of solution. The addition of 0.05 mol of HCl to this buffer solution
causes the pH to drop slightly. The pH does not decrease drastically
because the HCl reacts with the ________ present in the buffer
solution. The Ka of hypochlorous acid is 1.36 ×
10-3. | back 65 C |
front 66 A solution is prepared by dissolving 0.23 mol of benzoic acid and
0.27 mol of sodium benzoate in water sufficient to yield 1.00 L of
solution.The addition of 0.05 mol of NaOH to this buffer solution
causes the pH to increase slightly. The pH does not increase
drastically because the NaOH reacts with the ________ present in the
buffer solution. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.3 ×
10-5. | back 66 D |
front 67 What is the pH of a solution that contains 0.800 M weak acid (Ka =
1.76 × 10-5) and 0.172 M of its conjugate base? | back 67 D |
front 68 Consider a solution containing 0.100 M fluoride ions and 0.126 M
hydrogen fluoride. The concentration of fluoride ions after the
addition of 9.00 mL of 0.0100 M HCl to 25.0 mL of this solution is
________ M. | back 68 D |
front 69 A buffer solution contains 0.100 M fluoride ions and 0.126 M hydrogen
fluoride. What is the concentration (M) of hydrogen fluoride after
addition of 9.00 mL of 0.0100 M HCl to 25.0 mL of this
solution? | back 69 D |
front 70 The Ka of some weak acid HA is 1.76 × 10-5. The pH of a
buffer prepared by combining 15.0 mL of 1.00 M A- and 50.0 mL of 1.00
M HA is ________. | back 70 B |
front 71 The Kb of ammonia is 1.76 × 10-5. What is the pH of a
buffer which is prepared by combining 50.0 mL of 1.00 M ammonia and
45.0 mL of 1.00 M ammonium nitrate? | back 71 D |
front 72 Calculate the pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.270 mol of
weak acid HA and 0.260 mol of its conjugate base in water sufficient
to yield 1.00 L of solution. The Ka of HA is 1.77 x 10-4
| back 72 B |
front 73 What is the pH of a solution which is prepared by dissolving 0.850
mol of NH3 and 0.300 mol of NH4Cl in water sufficient to yield 1.00 L
of solution? The Kb of ammonia is 1.77 x 10-5
| back 73 A |
front 74 Calculate the pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.250 mol of
benzoic acid (C7H5O2H) and 0.150 mol of sodium benzoate (NaC7H5O2) in
water sufficient to yield 1.00 L of solution. The Ka of benzoic acid
is 1.8 x 10-5
| back 74 B |
front 75 A buffer solution with a pH of 4.31 is prepared with 1.0 M HC2H3O2
and ________ M NaC2H3O2. The Ka of HC2H3O2 is 1.8 x 10-5
| back 75 A |
front 76 A buffer solution with a pH of 4.63 is prepared with 0.14 M formic
acid and ________ M sodium formate. The Ka of formic acid is 1.8 x 10-4
| back 76 A |
front 77 0.78 M NaC2H3O2 and ________ M HC2H3O2 are required to prepare a
buffer solution with a pH of 4.40 . The Ka of HC2H3O2 is 1.8 x 10-5
| back 77 C |
front 78 ________ M formic acid and 0.90 M sodium formate are required to
prepare a buffer solution with a pH of 4.78 . The Ka of formic acid is
1.8 x 10-4
| back 78 B |
front 79 How many milliliters of 0.0839 M NaOH are required to titrate 25.0 mL
of 0.0990 M HBr to the equivalence point? | back 79 A |
front 80 A 25.0 mL sample of 0.150 M acetic acid is titrated with a 0.150 M
NaOH solution. What is the pH at the equivalence point? The Ka of
acetic acid is 4.50 × 10-4. | back 80 E |
front 81 A 25.0-mL sample of 0.150 M hydrocyanic acid is titrated with a 0.150
M NaOH solution. What is the pH before any base is added? The Ka of
hydrocyanic acid is 4.9 × 10-10. | back 81 A |
front 82 A 25.0 mL sample of 0.150 M hydrazoic acid is titrated with a 0.150 M
NaOH solution. What is the pH after 26.0 mL of base is added? The Ka
of hydrazoic acid is 1.9 × 10-5. | back 82 B |
front 83 How many milliliters of 0.120 M NaOH are required to titrate 50.0 mL
of 0.0998 M hypochlorous acid to the equivalence point? The Ka of
hypochlorous acid is 3.0 × 10-8. | back 83 C |
front 84 Which is the correct Ksp expression for PbCl2 (s) dissolving in
water? | back 84 A |
front 85 A 25.0-mL sample of 0.150 M hypochlorous acid is titrated with a
0.150 M NaOH solution. What is the pH after 13.3 mL of base is added?
The Ka of hypochlorous acid is 3.0 × 10-8. | back 85 D |
front 86 A 25.0 mL sample of 0.723 M HCl is titrated with a 0.273 M KOH
solution. The H3O+ concentration after the addition of 0.00 mL of KOH
is ________ M. | back 86 C |
front 87 A 25.0 mL sample of an acetic acid solution is titrated with a 0.175
M NaOH solution. The equivalence point is reached when 10.2 mL of the
base is added. The concentration of acetic acid in the sample was
________ M. | back 87 D |
front 88 A 25.0 mL sample of an HCl solution is titrated with a 0.139 M NaOH
solution. The equivalence point is reached with 15.4 mL of base. The
concentration of HCl is ________ M. | back 88 C |
front 89 The pH of a solution prepared by mixing 45.0 mL of 0.183 M KOH and
35.0 mL of 0.145 M HCl is ________. | back 89 D |
front 90 What is the pH of a solution which is prepared by mixing 55.0 mL of
0.183 M KOH and 10.0 mL of 0.145 M HC2H3O2? | back 90 A |
front 91 What is the molar solubility of calcium carbonate ( CaCO3 ) in water?
The solubility-product constant for CaCO3 is 4.5 × 10-9 at
25 °C. | back 91 E |
front 92 What is the molar solubility of silver carbonate ( Ag2CO3 ) in water?
The Ksp for Ag2CO3 is 8.1 × 10-12 at 25 °C | back 92 A |
front 93 In which aqueous system is CaF2 least soluble? | back 93 E |
front 94 AgBr would have the lowest solubility in ________. | back 94 A |
front 95 In which of the following aqueous solutions would you expect AgI to
have the highest solubility? | back 95 A |
front 96 In which of the following aqueous solutions would you expect AgF to
have the lowest solubility? | back 96 A |
front 97 ) In which of the following aqueous solutions would you expect AgF to
have the highest solubility? | back 97 A |
front 98 In which of the following aqueous solutions would you expect CuBr to
have the highest solubility? | back 98 A |
front 99 In which of the following aqueous solutions would you expect PbCl2 to
have the lowest solubility? | back 99 A |
front 100 Of the substances below, ________ will decrease the solubility of
Pb(CN)2 in a saturated solution. | back 100 A |
front 101 A solution of NaF is added dropwise to a solution that is 0.0122 M in
Ba2+. When the concentration of F- exceeds
________ M, BaF2 will precipitate. Neglect volume changes. For BaF2,
Ksp = 1.7 x 10-6
| back 101 B |
front 102 Calculate the pH of a buffer that contains 0.270 M hydrofluoric acid (HF) and 0.180 M cesium fluoride (CsF). The Ka of hydrofluoric acid is 6.80 × 10-4. | back 102 2.99 |
front 103 Calculate the pH of a buffer solution that contains 0.010 moles of A- and 0.010 moles of HA in 100 ml of water. The Ka of HA is 1.77 × 10-5. | back 103 4.75 |
front 104 Suppose you have just added 50.0 ml of a solution containing 0.0400 moles of weak acid HA to 500.0 ml of 0.6000 M NaOH. What is the final pH? The Ka of HA is 1.77 × 10-5. | back 104 13.67 |
front 105 Suppose you have just added 500.0 ml of a solution containing 0.2000 moles of acetic acid per liter to 200.0 ml of 0.250 M NaOH. What is the final pH? The Ka of acetic acid is 1.77 × 10-5. | back 105 4.75 |
front 106 Suppose you have just added 100.0 ml of a solution containing 1.00 mole of acetic acid per liter to 500.0 ml of 0.100 M KOH. What is the final pH? The Ka of acetic acid is 1.77 × 10-5. | back 106 4.75 |
front 107 In general, the solubility of a slightly soluble salt is decreased by the presence of a second solute that furnishes a ________. | back 107 common ion |
front 108 CaCO3 is very soluble in the presence of ________. | back 108 acid |
front 109 A complex ion is when a metal ion binds to a ________. | back 109 Lewis base |
front 110 Metal oxides and hydroxides that are relatively insoluble in neutral water, but are soluble in both strongly acidic and strongly basic solutions are said to be ________. | back 110 amphoteric |
front 111 ________ analysis determines how much of a given substance is present. | back 111 Quantitative |
front 112 The extent of ionization of a weak electrolyte is increased by adding to the solution a strong electrolyte that has an ion in common with the weak electrolyte. | back 112 false |
front 113 For any buffer system, the buffer capacity depends on the amount of acid and base from which the buffer is made. | back 113 true |
front 114 The solubility product of a compound is numerically equal to the product of the concentration of the ions involved in the equilibrium, each raised by its coefficient in the equilibrium reaction. | back 114 true |
front 115 The solubility of a slightly soluble salt is increased by the presence of a second solute that provides a common ion to the system. | back 115 false |
front 116 The solubility of slightly soluble salts containing basic anions is directly proportional to the pH of the solution. | back 116 false |