Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 3
front 1 The most frequently used portal of entry for pathogens is the
| back 1 mucous membrane |
front 2 The ability of some microbes such as Trypanosoma or Giardia to alter their surface molecules and evade destruction by the host's antibodies is called
| back 2 antigenic variation |
front 3 Siderophores are bacterial proteins that complete with the host's
| back 3 iron-transport proteins |
front 4 Bacterium - ID50 E.coli O157:H7 - 20 Legionella pneumophilia - 1 Shigella - 10 Treponema pallidum - 57 Which organism in Table 15.2 most easily causes an infection?
| back 4 Legionella pneumophila |
front 5 All of the following are used by bacteria to attach to host cells EXCEPT
| back 5 A-B toxins |
front 6 Bacteria such as E.coli and Salmonella produce invasins that bind host cells, thus causing the cells to
| back 6 engulf the bacteria |
front 7 The best descriptions of direct damage by a pathogen is
| back 7 host cells destroyed when pathogens metabolize and multiply |
front 8 Many pathogens use the same portal for entry and exit from the body
| back 8 True |
front 9 For each of the following statements, select whether the statement BEST applies to exotoxins or endotoxins.
| back 9
|
front 10 All of the following are examples of entry via the parenteral route EXCEPT
| back 10 ingestion |
front 11 Superantigens produce intense immune responses by stimulating lymphocytes to produce
| back 11 cytokines |
front 12 Lysogenic bacteriophages contribute to bacterial virulence because bacteriophages
| back 12 give new gene sequences to the host bacteria |
front 13 Polio is transmitted by ingestion of water contaminated with feces containing the polio virus. What portal of entry does the polio virus use?
| back 13 mucous membranes only |
front 14 Most pathogens that gain access through the skin
| back 14 enter through hair follicles and sweat ducts |
front 15 Antibiotics can lead to septic shock if used to treat
| back 15 gram-negative bacterial infections |
front 16 Which of the following is NOT a cytopathic effect of viruses?
| back 16 toxin production |
front 17  The table shows the ID50 for Staphylococcus aureus in wounds with and without the administration of ampicillin before surgery. Based on the data, the administration of ampicillin before surgery
| back 17 decreases the risk of staohylococcal infection |
front 18 Patients developed inflammation a few hours following eye surgery. Instruments and solutions were sterile, and the Limulus assay was positive. The patients' inflammation was due to
| back 18 endotoxin |
front 19 Match each of the following virulence factor with its effect
| back 19
|
front 20 A commensal bacterium
| back 20 may become an opportunistic pathogen |
front 21 The rise in herd immunity amongst a population can be directly attributed to
| back 21 vaccinations |
front 22 Which one of the following does NOT contribute to the incidence of healthcare-associated infections?
| back 22 gram-negative cell walls |
front 23 Which of the following is NOT a communicable disease?
| back 23 tetanus |
front 24 Which of the following is a fomite?
| back 24 a hypodermic needle |
front 25 Which of the following statements about biological transmission is FALSE?
| back 25 Houseflies are an important vector for biological transmission |
front 26 Symptoms of disease differ from signs of disease in that symptoms
| back 26 are changes felt by the patient |
front 27 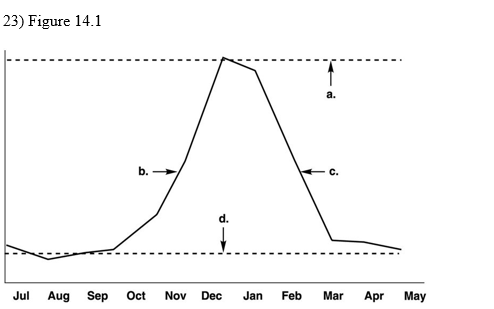 Shows the incidence of influenza during a typical year in the northern hemisphere. Which letter on the graph indicates the endemic level?
| back 27 d |
front 28  Which level indicates the gradual end of the epidemic outbreak?
| back 28 c |
front 29 A healthcare-associated infection (traditionally known as a nosocomial infection) is
| back 29 acquired during the course of hospitalization |
front 30 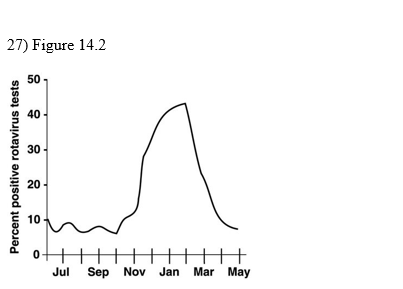 When is the prevalence the highest?
| back 30 February |
front 31 A disease in which the causative agent remains inactive for a time before producing symptoms is referred to as
| back 31 latent |
front 32 In which of the following diseases can gender be considered a viable predisposing factor?
| back 32 urinary tract infections |
front 33 The major significance of Robert Koch's work is that
| back 33 microorganisms cause disease |
front 34 The yeast Candida albicans does NOT normally cause disease because of
| back 34 mutualistic bacteria |
front 35 If a prodromal period exists for a certain disease , it should occur prior to
| back 35 illness |
front 36 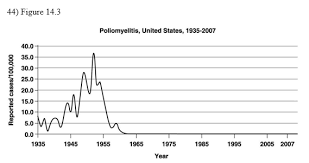 The graph shows the incidence of polio in the United States. The period 1945 and 1955 indicates a(n)
| back 36 epidemic level |
front 37  Interpreting this graph, can we conclude that polio has been eradicated globally? Why or why not?
| back 37 No, because the graph only depicts incidence of polio in the United States |
front 38 Which of the following diseases is NOT spread by droplet infection?
| back 38 HIV |
front 39 Biological transmission differs from mechanical transmission in that biological transmission
| back 39 involves reproduction of a pathogen in an arthropod vector prior to transmission |
front 40 Focal infections initially start out as
| back 40 local infections |
front 41 Which of the following statements about the human microbiome is false?
| back 41 The relationship between a person and their normal microbiota can be categorized as parasitism |
front 42 The etiologic agent of COVID-19 is bacterium
| back 42 False |
front 43 Match the following terms with the correct definition
| back 43
|
front 44 Match the following terms with the BEST example
| back 44
|
front 45 Which of the following might violate (go against) Koch's postulates?
| back 45 Some cattle that died of anthrax had the pathogen Bacillus anthracis while others did not. |
front 46 Innate immunity
| back 46 is nonspecific and present at birth |
front 47 Innate immunity includes all of the following except
| back 47 production of antibody |
front 48 All of the following protect the skin and mucous membranes from infection except
| back 48 hydrochloric acid |
front 49 All of the following increase blood vessels permeability except
| back 49 lysozymes |
front 50 A child falls and suffers a deep cut on her leg. The cut went through her skinn and she is bleeding. Which of the following defense mechanisms will participate in eliminating contaminating microbes?
| back 50 phagocytosis in the inflammatory response |
front 51 Which of the following is mismatched?
| back 51 chemotaxis - chemical degradation inside a phagolysosome |
front 52 A chill is a sign that
| back 52 body temperature is rising |
front 53 Normal microbiota provide protection from infection in each of the following ways except
| back 53 they produce lysozyme |
front 54 Each of the following is an effect of complement activation except
| back 54 interference with viral replication |
front 55 Which of the following is involved in resistance to parasitic helminths?
| back 55 eosinophils |
front 56 Which non-specific defense mechanism is mismatched with its associated body structure or body fluid?
| back 56 mucocillary escalator - intestines |
front 57 Lysozyme and the antibiotic penicillin have similar mechanisms of action in that they both cause damge to the bacterial
| back 57 cell wall |
front 58 All of the following are iron-binding proteins found in humans except
| back 58 siderophorin |
front 59 Please match the following terms with the correct description
| back 59
|
front 60 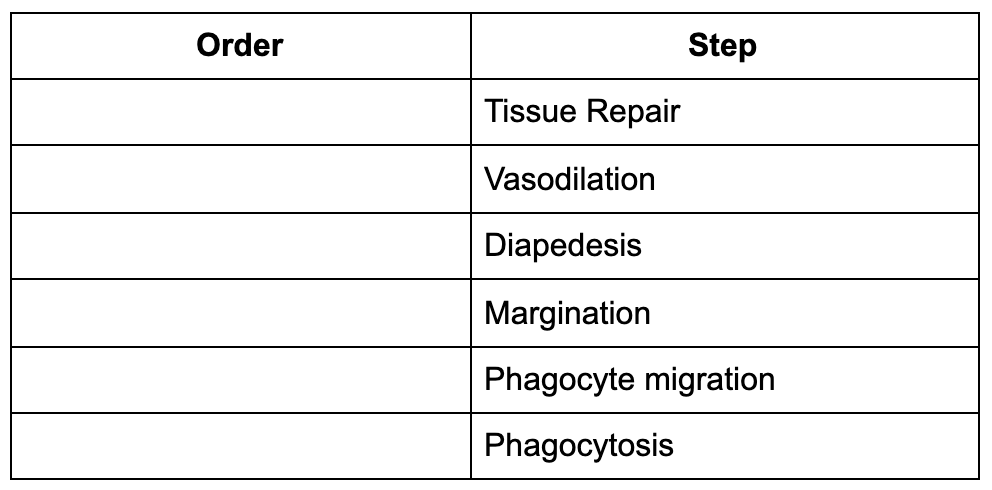 Place the steps in the right order. Fill in the blanks with numbers 1-6. | back 60 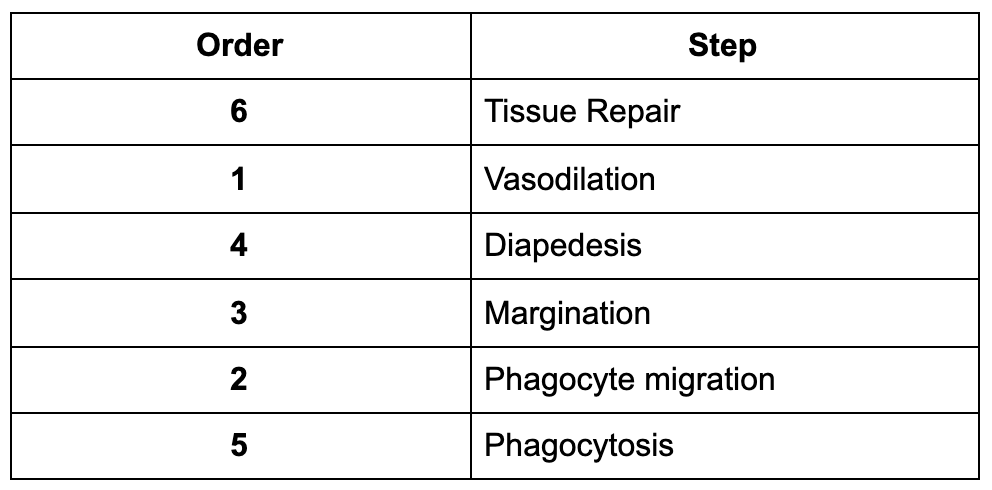 |
front 61 An abnormally high body temperature is called a ________.
| back 61 fever |
front 62 Which of the following is an effect of opsonization?
| back 62 increased adherence of phagocyres to microorganisms |
front 63 All of the following protect the skin and mucous membranes from infection except
| back 63 HCI |
front 64 All of the following are effects of kinins except
| back 64 production of antibodies |
front 65 Which non-specific defense mechanism is mismatched with its associated body structure or body fluid?
| back 65 cilary escalator - intestines |
front 66 TLRs attach to all of the following except
| back 66 antimicrobial peptides |
front 67 Match the following leukocytes with the correct description
| back 67
|
front 68 The body has two circulatory systems, the lymphatic system and the blood circulatory system
| back 68 True |
front 69 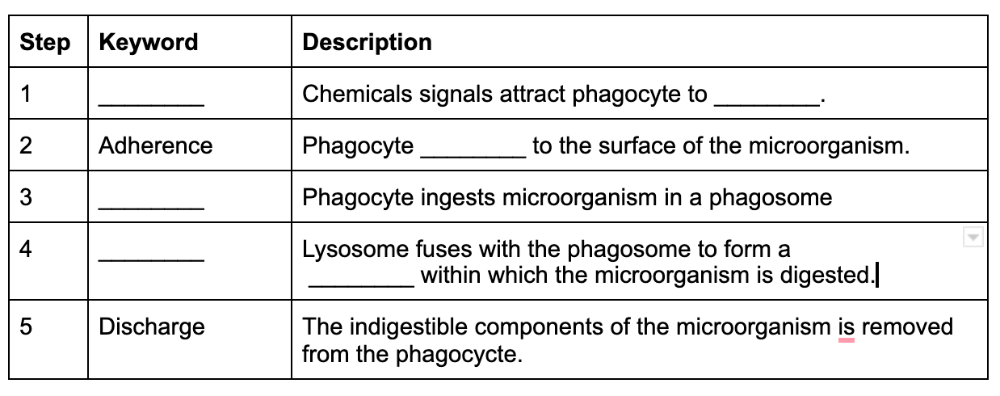 Fill in the following table with the information about phagocytosis | back 69 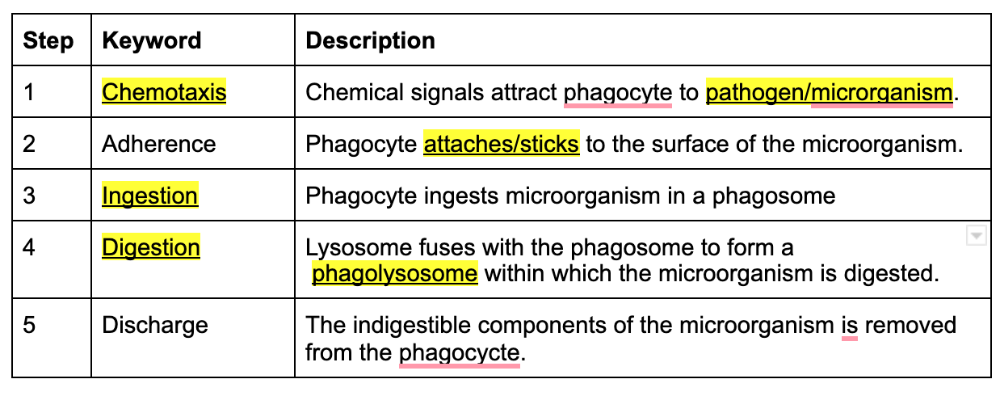 |
front 70 Which of the following is the best definition of epitope?
| back 70 specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies |
front 71 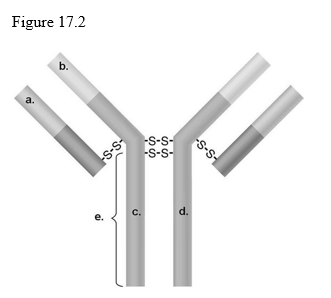 Which areas are different for all IgM antibodies?
| back 71 a and b |
front 72 Which of the follwoing is the best defintion of antigen?
| back 72 a chemical that elicts an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies |
front 73 Which of the following statements is NOT a possible outcome of antigen-antibody reaction?
| back 73 clonal deletion |
front 74 When an antibody binds to a toxin, the resulting action is referred to as
| back 74 neutralization |
front 75 Which of the following recognizes antigens displayed on host cells with MHC II?
| back 75 TH cell |
front 76 Which of the following destroys virus-infected cells?
| back 76 CTL |
front 77 The specificity of an antibody is due to
| back 77 the variable portions of the H and L chains |
front 78 Which one of the following causes transmembrane channels in target cells?
| back 78 perforin |
front 79 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of B cells?
| back 79 They recognize antigens associated with MHC I. |
front 80 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cellular immunity?
| back 80 B cells make antibodies |
front 81  Which areas are similar for all IgG antibodies?
| back 81 c and d |
front 82 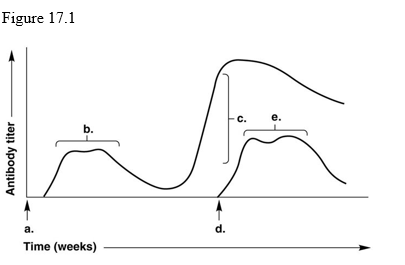 Which letter on the graph indicates the patient's secondary response to a repeated exposure with the identical antigen?
| back 82 c |
front 83 Which of the following is not a professional antigen-presenting cell?
| back 83 T cells |
front 84 Which of the following recognizes antigens displayed on host cells with MHC II?
| back 84 Helper T cell |
front 85 ADCC is a process that is most effective in destroying
| back 85 eukaryotic pathogens |
front 86 Which of the following WBCs are not lymphocytes?
| back 86 macrophages |
front 87 Which of the following is involved in ensuring that a mother's antibodies do not react against her fetus?
| back 87 Treg cells |
front 88 Which of the following is the best definition of antigen?
| back 88 a molecule that can bind to antibodies to be produced |
front 89 Please match the type of immunity with correct example
| back 89
|
front 90 PLease match each of the following descriptions to the right class of antibodies
| back 90
|
front 91 The secondary immune response takes longer to be activated compared to primary immune response.
| back 91 False |
front 92 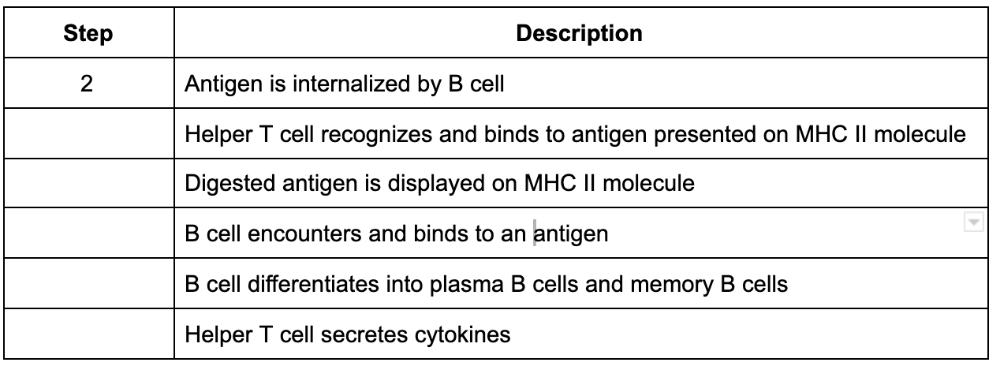 Arrange the following steps of B cell activation in the right order. | back 92 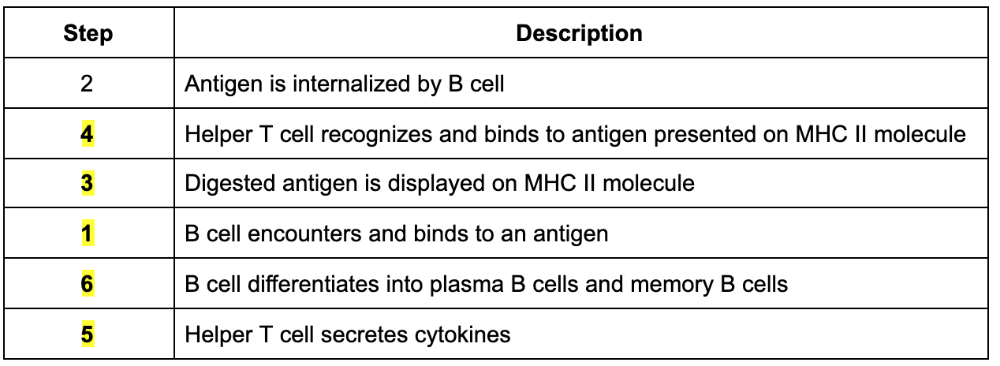 |