Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch 15 pre lec
front 1 In mice, the LD50 for staphylococcal enterotoxin is 1350 ng/kg, and the LD50 for Shiga toxin is 250 ng/kg. Which of the following statements is true? | back 1 Shiga toxin is more lethal than staphylococcal enterotoxin. |
front 2 Which of the following would be an example of an infection initiated via the parenteral route? | back 2 An individual contracts hepatitis B from an accidental stick with a contaminated needle. |
front 3 Which of the following statements about adherence is true? | back 3 Most bacterial adhesins are glycoproteins or lipoproteins.Submit |
front 4 Which type of bacterial enzyme helps spread Streptococcus pyogenes by digesting blood clots? | back 4 fibrinolysin |
front 5 In which of the following cases would the Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) assay be used? | back 5 to ensure that a sterilized medical device is free of endotoxin |
front 6 In January 2010, a devastating earthquake struck Haiti about 15 miles west of the capital city of Port-au-Prince. The earthquake killed over 200,000 people and displaced over 1 million from their homes. Many of these people had nowhere to go other than displacement camps and shantytowns, where the sanitary conditions were less than ideal. It was not only private homes that were destroyed; hospitals, communication networks, land and air transport, and other important infrastructure were damaged.In October 2010, a cholera epidemic was reported in the Artibonite Department (Haitian departments are analogous to states). This was the first cholera epidemic in Haiti in over a century. Within 10 weeks, cholera had spread to all Haitian departments. By the end of the epidemic, more than 470,000 cases had been reported, and more than 6500 people were dead.Both during and after the epidemic, epidemiologists, doctors, and scientists were working to determine the source of the outbreak and its transmission patterns, identify the causative strains, and care for the infected. The ability of Vibrio cholerae to cause disease depends on a number of factors. Which of the following are general requirements for any organism to cause disease within a host? | back 6 adherence to host tissues gaining access to the host via a portal of entry evasion of host defenses |
front 7 Some studies have indicated that the ID50 for Vibrio cholerae can be as high as 108 organisms. Which of the following most likely explains the requirement for this relatively high ID50? | back 7 To establish infection, V. cholerae must survive the host immune response and the acidic environment of the stomach. |
front 8 Which of the following are properties of exotoxins? | back 8 Very small amounts of exotoxin can be lethal. Exotoxins are protein molecules. Exotoxins target specific cellular structures or molecules. |
front 9 The physical symptoms of cholera present only after a specific series of events has taken place. What is the most likely sequence of events in the pathogenesis of V. cholerae? | back 9 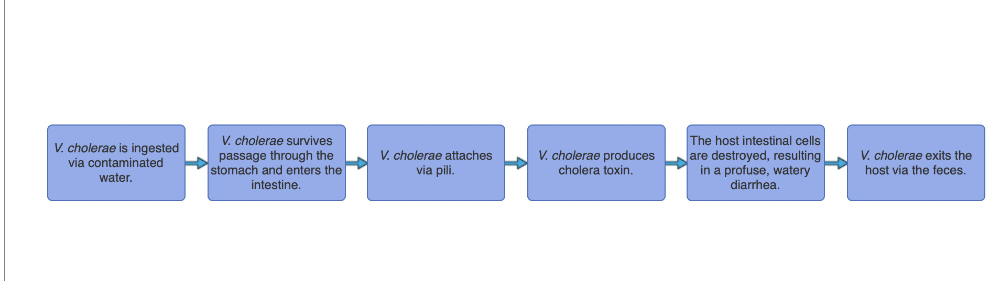 |
front 10 Although cholera can be treated with antibiotics, data suggest that antibiotic treatment alone is NOT the most effective therapy. Which of the following statements describes the most likely reason for supplementing antibiotic therapy? | back 10 Antibiotic therapy addresses only the growth of V. cholerae; it doesn’t address the extreme dehydration suffered by a person infected with V. cholerae. |
front 11 Disease research and epidemiology bring together many different facets to help us better understand disease pathology and spread. Which of the following statements are true? | back 11 Some pathogens are able to cause disease within a host without penetrating the body. The interactions that occur between a microbe and host influence the evolution of both. |
front 12 Exotoxins and endotoxins are two fundamentally different types of bacterial toxins. In this activity, you will determine whether each of the following statements applies to exotoxins or endotoxins. Some statements may apply to both types of toxins. | back 12 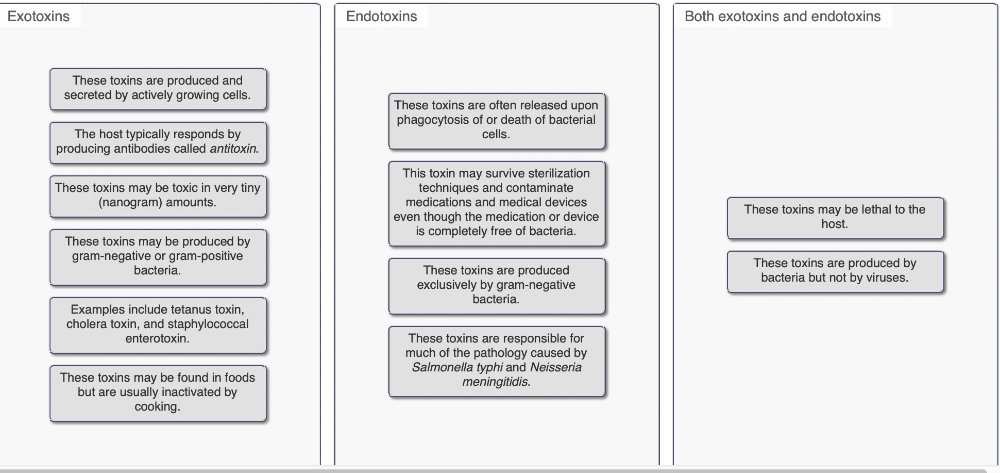 |
front 13 The majority of exotoxins are A-B toxins, which are composed of two polypeptide subunits referred to as A and B. The B component functions to bind or attach to the host cell, whereas the A component exerts its toxic effects on the cell. This activity asks you to place the images in the correct order as they occur when an A-B toxin interacts with the host cell. | back 13 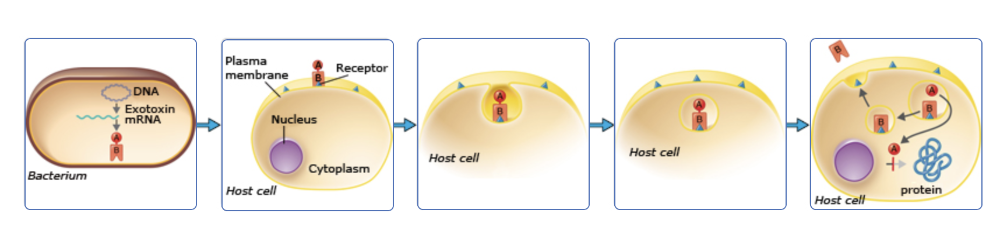 |
front 14 Which of the following strategies might be used to block the activity of an A-B toxin? | back 14 blocking host cell receptors to which A-B toxins bind blocking receptor-mediated endocytosis in cells targeted by the A-B toxin blocking the binding sites on the B portion of an A-B toxin |
front 15 Considering the pathology of a cytokine storm, select possible strategies that would be likely to diminish the harmful effects of superantigen toxins. | back 15 blocking secretion of proteins by bacterial cells blocking the release of cytokines from T cells blocking molecular determinants on superantigens that interacts with T cells neutralizing circulating cytokines |
front 16 Consider the structure of a plasma membrane. Select the mechanisms through which a toxin is likely to disrupt the plasma membrane of a host cell. | back 16 disruption of phospholipid bilayer insertion of a protein channel in the host cell plasma membraneSubmit |
front 17 Select the statements that correctly describe endotoxins. | back 17 Sterilized items may contain endotoxins and cause a reaction in a patient. Symptoms caused by endotoxins may actually worsen after treatment of an infection caused by gram-negative bacteria. Endotoxins can cause fever, chills, weakness, and fatigue. Endotoxins may cause a life-threatening drop in blood pressure known as endotoxic shock.Submit |
front 18 Endotoxin is well known for its ability to produce a pyrogenic response (fever). Place in the correct order the steps by which gram-negative bacteria may bring about fever response. | back 18 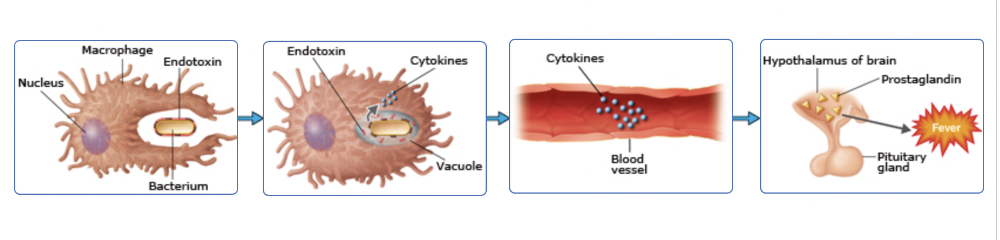 |
front 19 In this activity, you will identify portals of entry and exit found in a human host. | back 19
|
front 20 In this activity, you will view scenarios for the initiation of an infection and determine whether they relate to the number of invading microbes or adherence to the host tissue. | back 20  |
front 21 Bacillus anthracis can cause infection via three different portals of entry. The ID50 of cutaneous anthrax is 10 to 50 endospores, whereas inhalation anthrax requires 10,000 to 20,000 endospores, and gastrointestinal anthrax requires 250,000 to 1,000,000 endospores. Which statement best describes a conclusion that can be drawn based on this information? | back 21 It is significantly easier to be infected with cutaneous anthrax as compared to other forms of anthrax.Submit |
front 22 In this activity, you will match each factor that influences a pathogen’s ability to penetrate or evade host defenses with its best description. | back 22 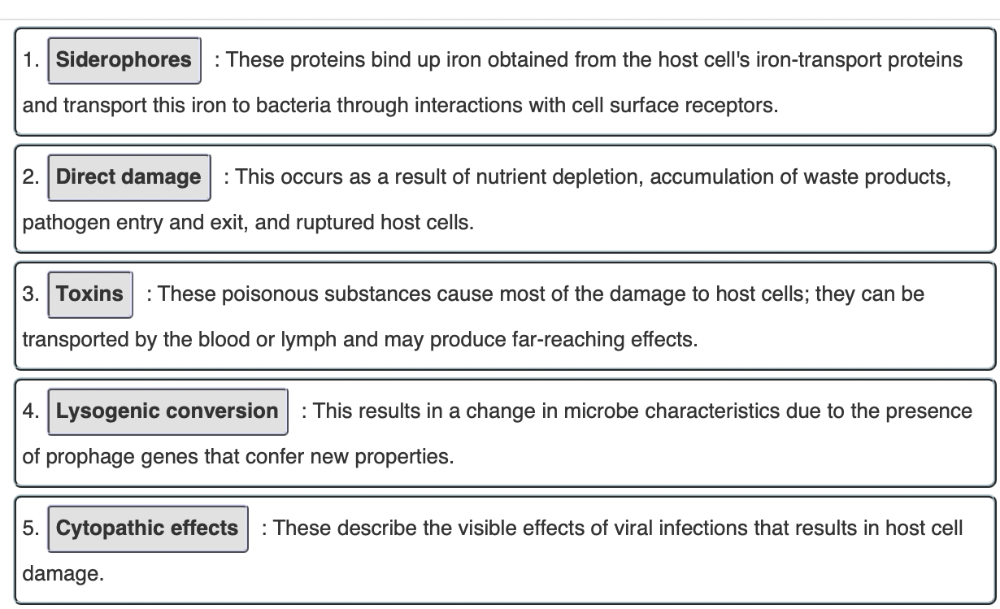 |
front 23 In this activity, you will consider several scenarios and determine whether infection is likely or unlikely to occur.Reviewing the overall microbial mechanisms of pathogenicity (Figure 15.9), predict the ability of the pathogen to cause infection in each of the following scenarios. | back 23  |
front 24 Endotoxins are also known as | back 24 Lipid A. |
front 25 When would endotoxins be released from a bacterial cell? | back 25 When the cell dies |
front 26 Which of the following would be the first sign of an infection that resulted in the release of endotoxin? | back 26 Fever |
front 27 Why is a release of endotoxin into the bloodstream potentially deadly? | back 27 It can lower blood pressure and cause the patient to go into shock. |
front 28 Which of the following features of Salmonellaprevent it from being phagocytosed? | back 28 FlagellaSubmit |
front 29 Where do Salmonellapathogens grow and replicate in the infected host? | back 29 Inside |
front 30 Where is the site of Shigellaattachment in the host? | back 30 M cells |
front 31 How do Shigellacells move between host cells? | back 31 They can polymerize actin molecules from the epithelial cells into tail-like structures that propel them from one cell to another. |
front 32 What is the etiologic agent of typhoid? | back 32 Salmonella |
front 33 An exotoxin that has the ability to kill or damage host cells is referred to as a(n) | back 33 cytotoxin |
front 34 Which domain of the A-B toxin binds to cell surface receptors on the host cell? | back 34 B domainSubmit |
front 35 How are superantigens different from other types of exotoxins? | back 35 Superantigens cause an overstimulation of the host immune system.Submit |
front 36 A person who attended a picnic early in the day develops a very high fever and is unresponsive by the evening. This person most likely has been exposed to a(n) | back 36 superantigen |
front 37 A patient who has been hospitalized with uncontrolled muscle spasms has probably been infected with bacteria that secrete a(n) | back 37 neurotoxin |
front 38 How are immune cells able to detect foreign pathogens? | back 38 They are able to detect structures on the surfaces of foreign cells that are not found in the host. |
front 39 How does a capsule help certain bacteria evade detection by the immune system? | back 39 The capsule is composed of polysaccharides that are similar to those found in the host; thus, the immune system does not recognize it as foreign.Submit |
front 40 Which of the following microorganisms actually grows inside the macrophage? | back 40 Tuberculosis |
front 41 How does the protozoan Trypanosomaevade detection by the immune system? | back 41 It can change the surface antigens frequently, preventing the immune system from tracking it.Submit |
front 42 What are leukocidins? | back 42 Molecules that are capable of destroying phagocytesSubmit |
front 43 Measles viruses are capable of inactivating host defenses by | back 43 suppressing |
front 44 Meningitis and gonorrhea are caused by | back 44 Neisseria species. |
front 45 How do superantigens enable pathogens to hide from the immune system if they actually stimulatethe immune system? | back 45 They cause the immune system to produce an exaggerated response, distracting it from the actual pathogen.Submit |
front 46 How can capsules enable bacteria to evade the immune system? | back 46 Capsules block the complement biding sites on the surface of the pathogen. |
front 47 Certain traits that allow pathogens to create infection and cause disease are termed | back 47 virulence factors. |
front 48 Which of the following enzymes breaks down the "glue" that holds cells together? | back 48 Hyaluronidase |
front 49 Which of the following virulence factors would be found in Staphylococcus aureus? | back 49 Staphylokinase |
front 50 How do fibrinolysins enhance a pathogen's virulence? | back 50 They break down fibrin proteins that are involved in clot formation, allowing the cells to penetrate deep into damaged skin.Submit |