Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
CHAPTER 10 ANATOMY
front 1 the scientific study of the structure, function, and diseases of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscular tissues. | back 1 myology |
front 2 the function of these muscles is to move the bones of the skeleton | back 2 skeletal muscles |
front 3 Skeletal muscle tissue is referred to as _________ because alternating light and dark protein bands _________ are visible when the tissue is examined under a microscop | back 3 1. striated 2. striations |
front 4 Skeletal muscle tissue works primarily in a ________ manner; its activity can be __________ controlled | back 4 1. voluntary 2. voluntarily |
front 5 found only in the heart, where it forms most of the heart wall. | back 5 cardiac muscle |
front 6 Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is _______, but its action is _________ | back 6 1. striated 2. involuntary |
front 7 how is cardiac muscle involuntary? | back 7 its alternating contraction and relaxation cannot be consciously controlled. The heart beats because it has a natural pacemaker that initiates each contraction; |
front 8 located in the walls of hollow internal structures, such as blood vessels, airways, and most organs in the abdominopelvic cavity. It is also attached to hair follicles in the skin. | back 8 smooth muscle |
front 9 Smooth muscle tissue gets its name from the fact that, under a microscope, it appears ________ or ________. | back 9 1. nonstriated 2. smooth |
front 10 The action of smooth muscle is usually ___________, and, like cardiac muscle, some smooth muscle tissue has autorhythmicity | back 10 involuntary |
front 11 Both cardiac muscle and smooth muscle are regulated by neurons that are part of the ____________ division of the nervous system (see Chapter 20) and by _________________ | back 11 1. autonomic (involuntary) 2. hormones released by endocrine glands. |
front 12 What are the four functions of smooth muscle? | back 12 1. Contractions move food, bile, and enzymes through the GI tract, gametes through the reproductive system, and urine through the urinary system--> contractions cause various types of organ movement, including propulsion of food through digestive tract, propulsion of urine through the urinary tract, and expulsion of a newborn through the uterus during labor 2. contractions of blood vessels help regulate the rate of blood flow 3. sphincters in hollow organs regulate the outflow of substances through hollow organs 4. contractions are usually involuntary |
front 13 What are the two functions of cardiac muscle? | back 13 1. contractions pump blood through the body's blood vessels/ contractions pump blood to the body 2. contractions are involuntary |
front 14 What are the four functions of skeletal muscle? | back 14 1. Moves skeletal bones --> Contractions in the belly of a muscle produce movement by exerting force on tendons (attached at origins and insertions) which pull on bones, drawing one towards the other 2. Contractions stabalize joints and help maintain posture and body positions 3. contractions produce heat, used to maintain body temperature 4. most contractions are voluntary |
front 15 what are the 4 key functions of muscular tissue? | back 15 1. Producing body movements. 2. Stabilizing body positions 3. Storing and moving substances within the body. 4. Producing heat |
front 16 Total body movements such as walking and running, and localized movements such as grasping a pencil, keyboarding, or raising your hand, rely on the integrated functioning of skeletal muscles, bones, and joints. (a function of muscular tissue) | back 16 Producing body movements. |
front 17 skeletal muscle contractions stabilize joints and help maintain body positions, such as standing or sitting. Postural muscles contract continuously when you are awake; for example, sustained contractions in neck muscles hold your head upright when you are listening intently to an anatomy lecture (a function of muscular tissue) | back 17 Stabilizing body positions |
front 18 Sustained contractions of ringlike bands of smooth muscles called sphincters may prevent outflow of the contents of a hollow organ. Temporary storage of food in the stomach or urine in the urinary bladder is possible because smooth muscle sphincters close off the outlets of these organs. Cardiac muscle contractions pump blood through the body's blood vessels. Contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle in the walls of blood vessels help adjust their diameter and thus regulate the rate of blood flow. Smooth muscle contractions also move food and substances such as bile and enzymes through the gastrointestinal tract, push gametes (sperm and oocytes) through the reproductive systems, and propel urine through the urinary system. Skeletal muscle contractions indirectly promote the flow of lymph throughout the body and aid the return of blood in veins to the heart. (a function of muscular tissue) | back 18 Storing and moving substances within the body |
front 19 As muscular tissue contracts, it also produces heat, a process called thermogenesis (ther′-mō-JEN-e-sis). Much of the heat released by muscle is used to maintain normal body temperature. Involuntary contractions of skeletal muscles, known as shivering, can dramatically increase the rate of heat production (a function of muscular tissue) | back 19 Producing heat |
front 20 Where is smooth tissue found? | back 20 1. within the walls of all hollow or tubular organs of the digestive, respitory, urinary, and reproductive tracts 2. within the walls of blood vessels, the iris, and ciliary muscles of the eye, in the skin of the scrotum and as thin bands called the arrector pilli associated with hair follicles in the skin |
front 21 what are the four properties of muscle tissue? | back 21 1. Extreme excitability 2. contractability 3. Extensibility 4. Elasticity |
front 22 a property of both muscle and nerve cells, is the ability to respond to certain stimuli by producing electrical signals called action potentials (impulses). Action potentials in muscles are referred to as muscle action potentials; those in nerves are called nerve action potentials or nerve impulses. Action potentials can travel along a cell's plasma membrane due to the presence of specific ion channels. Two main types of stimuli trigger action potentials in muscle cells: electrical and chemical. Autorhythmic electrical signals arise in the muscular tissue itself, as in the heart's pacemaker. Chemical stimuli, such as neurotransmitters released by neurons, hormones distributed by the blood, or even local changes in pH, can also trigger action potentials in muscle cells. (one of the properties of muscle tissue) | back 22 Extreme excitability |
front 23 the ability of muscular tissue to contract forcefully when stimulated by an action potential. When a skeletal muscle contracts, it generates tension (force of contraction) while pulling on its attachment points. In some muscle contractions, the muscle develops tension but does not shorten. An example is holding this book in your outstretched hand. In other muscle contractions, the tension generated is greater than resistance, so the muscle shortens and movement occurs. An example is lifting a book off a table (one of the properties of muscle tissue) | back 23 contractability |
front 24 the ability of muscular tissue to stretch, within limits, without being damaged. The connective tissue within the muscle limits the range of extensibility and keeps it within the contractile range of the muscle cells. Normally, smooth muscle is subject to the greatest amount of stretching. For example, each time your stomach fills with food, the muscle in the wall is stretched. Cardiac muscle also is stretched each time the heart fills with blood. (one of the properties of muscle tissue) | back 24 Extensibility |
front 25 the ability of muscular tissue to return to its original length and shape after contraction or extension. (one of the properties of muscle tissue) | back 25 elasticity |
front 26 what are the 3 ways that muscle tissue is categorized? | back 26 1. by its shape 2. the # of nuclei 3. the mechanism of stimulation |
front 27 Where is cardiac tissue found? | back 27 in the wall of the heart in a muscular layer called the myocardium |
front 28 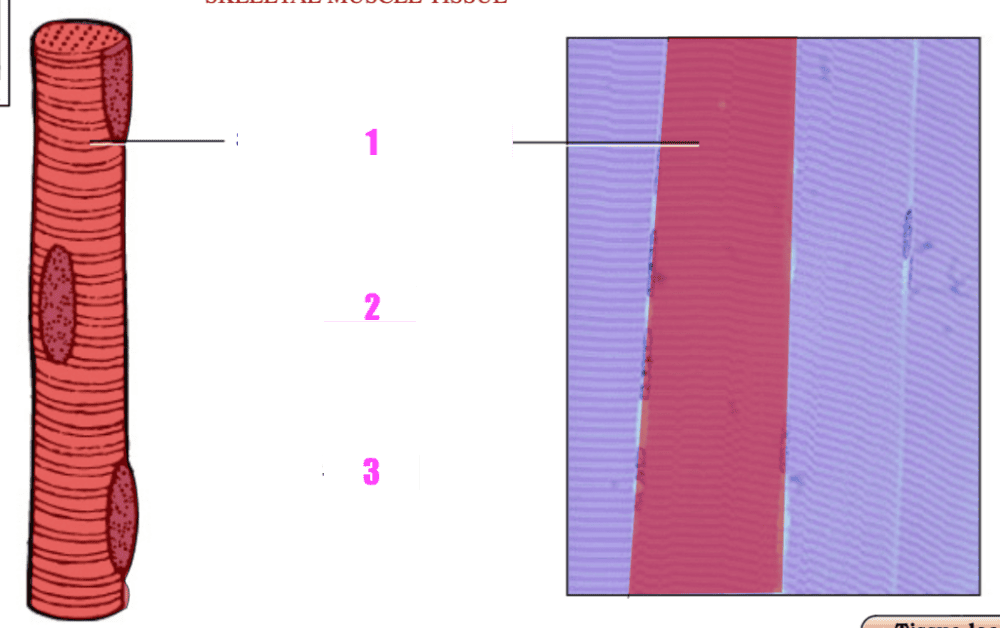 what is #1? | back 28 skeletal muscle fiber (cell) |
front 29 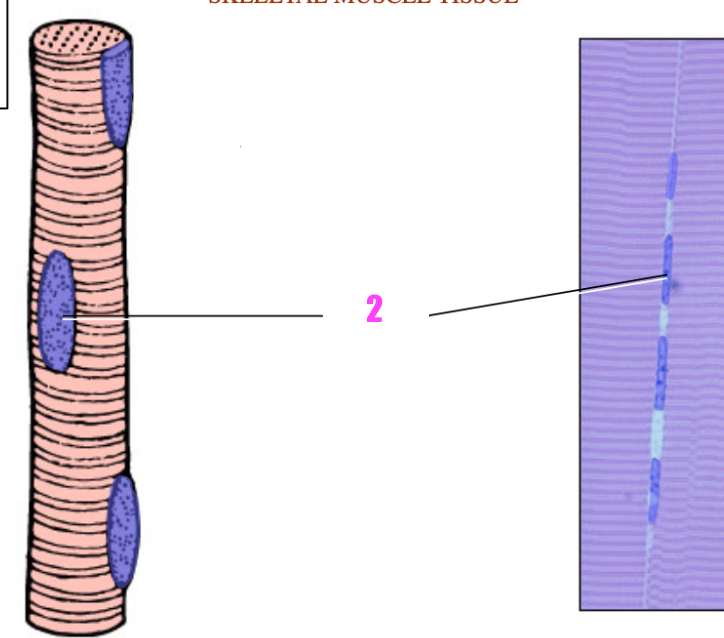 what is #2? | back 29 the nucleus (of skeletal muscle tissues) |
front 30 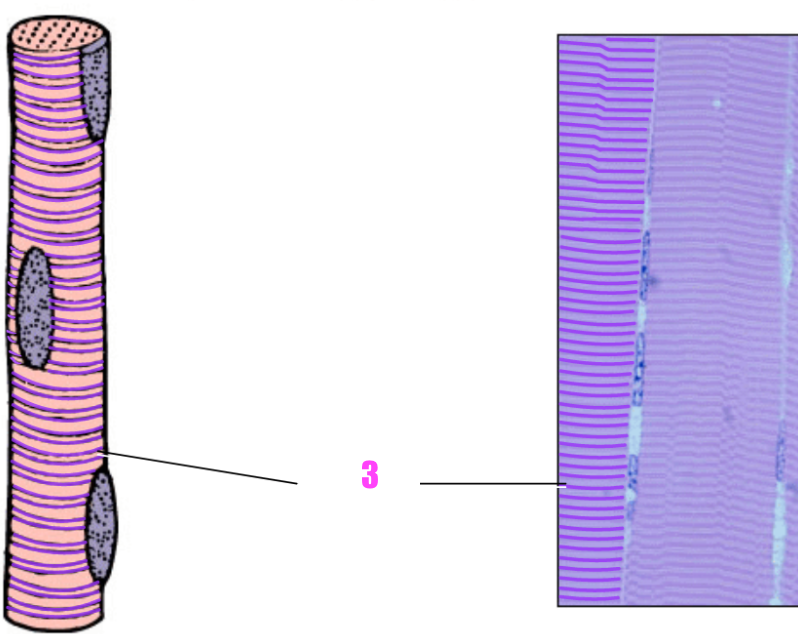 what is #3? | back 30 striations (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 31 where is skeletal muscle tissue located? | back 31 1. it attaches to bones via tendons 2. it is also found in the pharynx & the larynx, the chest, back, & abdominal walls, the face, the tongue, & the diaphragm |
front 32 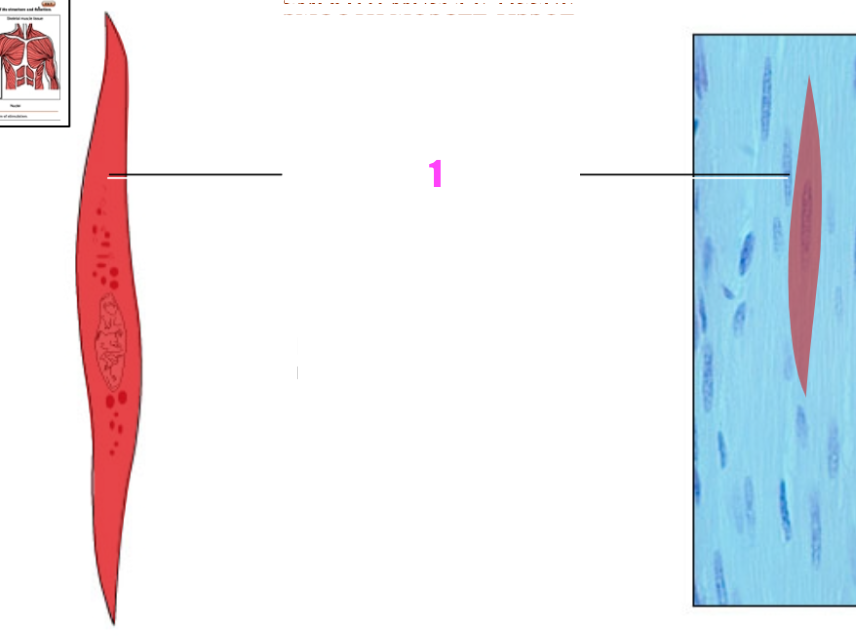 what is #1? | back 32 Smooth muscle fiber (cell) |
front 33 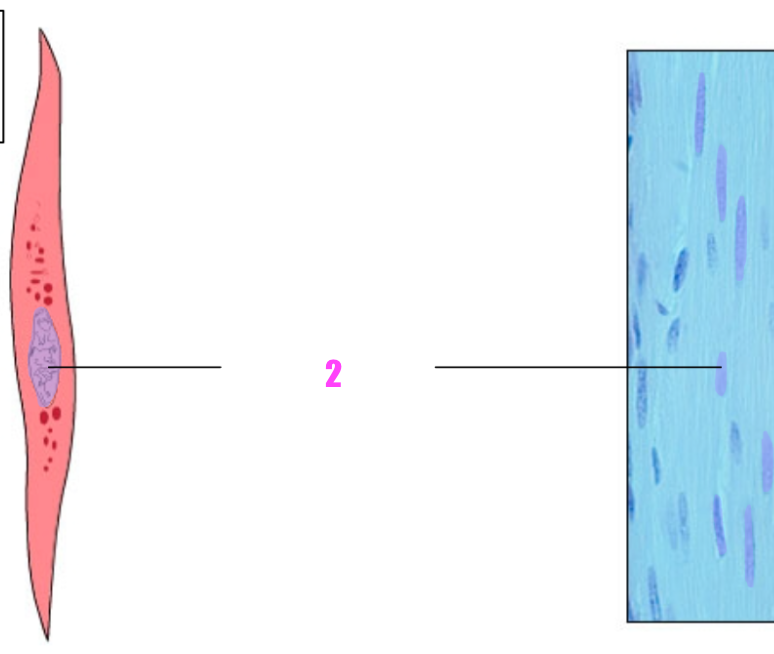 what is #2? | back 33 nucleus of smooth muscle fiber |
front 34 skeletal muscle is a separate organ composed of hundreds to thousands of skeletal muscle cells, also called __________ | back 34 muscle fibers |
front 35 muscle fibers have a ___________ shape | back 35 elongated |
front 36 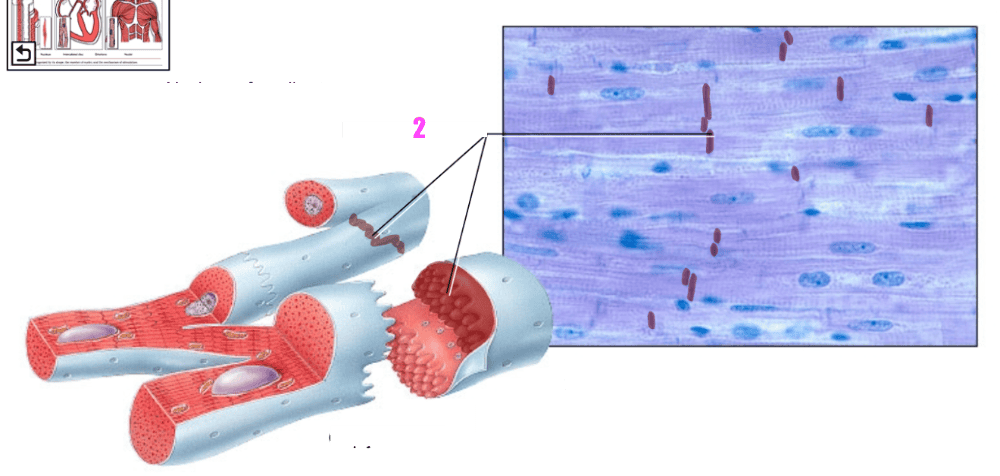 what is #2? | back 36 intercalated discs (of cardiac muscle tissue) |
front 37 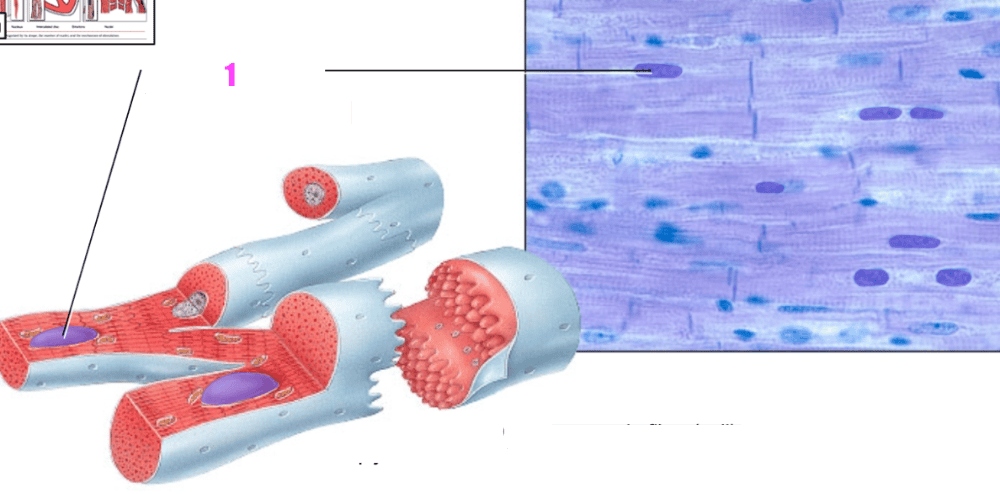 what is # 1? | back 37 the nucleus of cardiac muscle fiber |
front 38 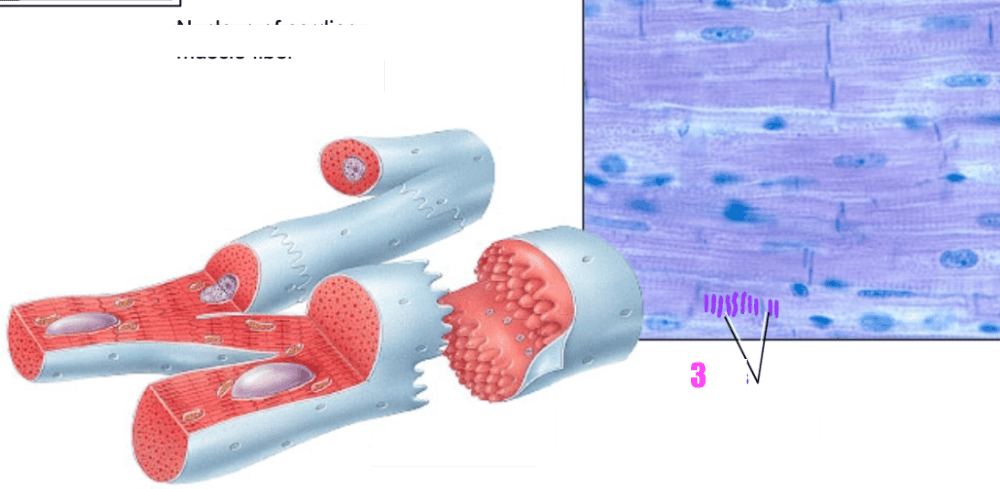 what is #3? | back 38 striations (of cardiac muscle tissue) |
front 39 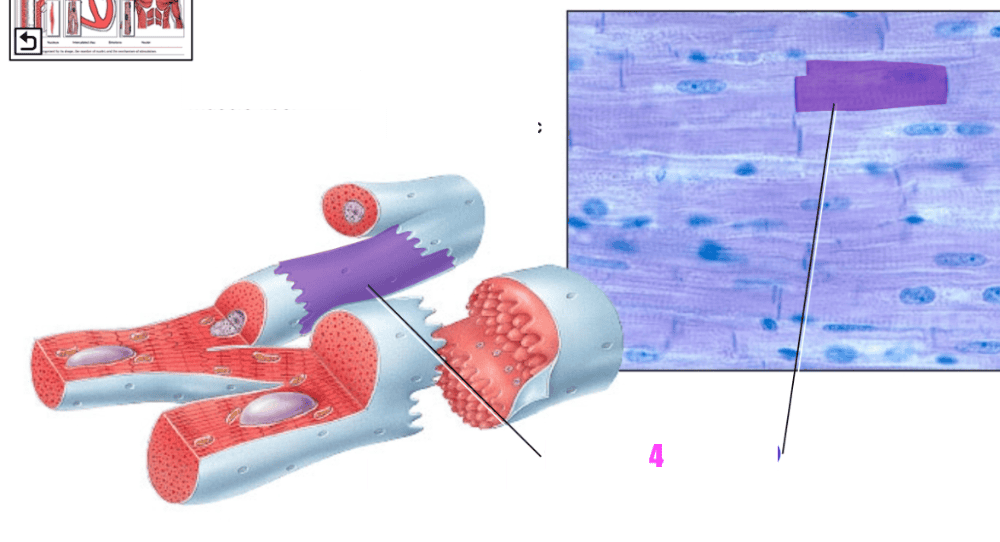 what is #4? | back 39 cardiac muscle fiber (cell) |
front 40 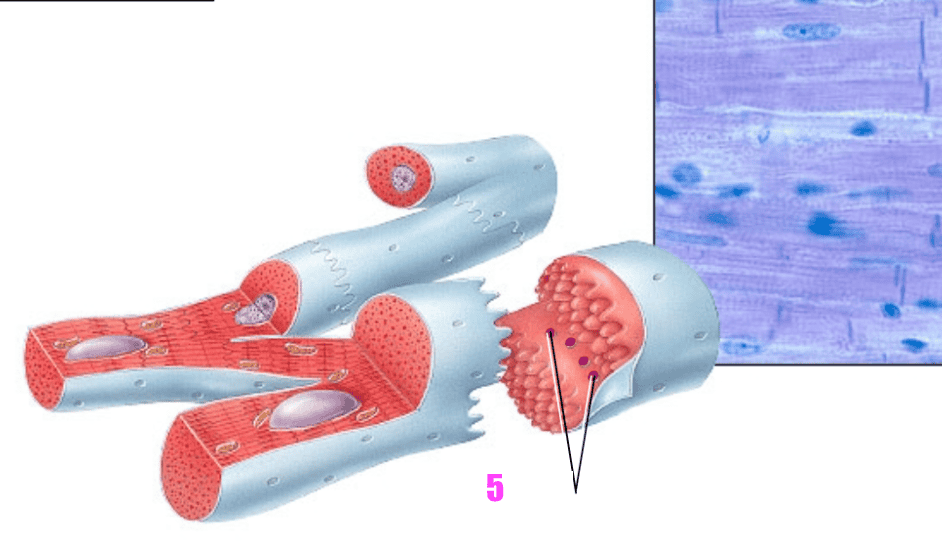 what is #5? | back 40 gap junctions (of cardiac muscle tissue) |
front 41 ______________ surround muscle fibers and whole muscles, and carry the blood vessels and nerves that exert their effects on individual muscle fibers | back 41 Connective tissues |
front 42 A skeletal muscle consists of __________________________________ | back 42 individual muscle fibers (cells) bundled into fascicles and surrounded by three connective tissue layers. |
front 43 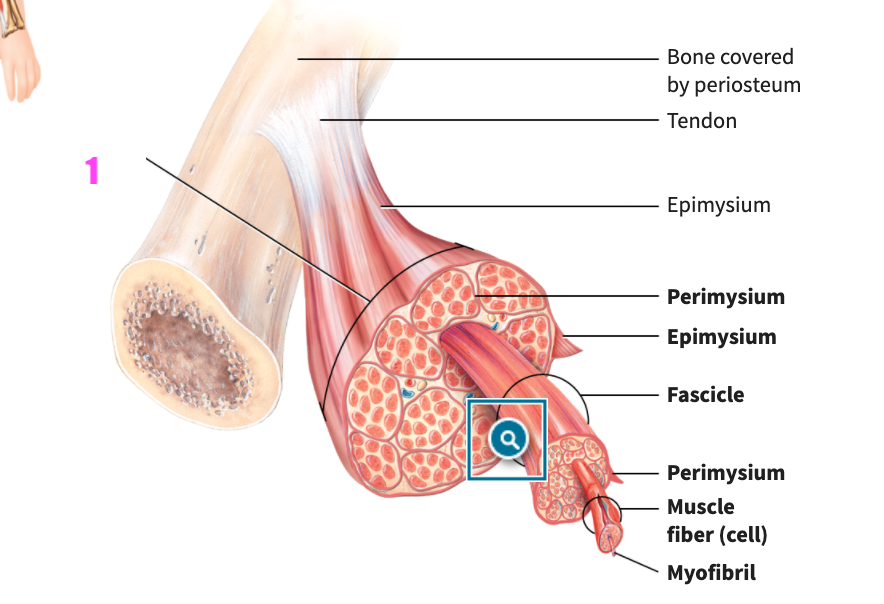 what is #1? | back 43 skeletal muscle (skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 44 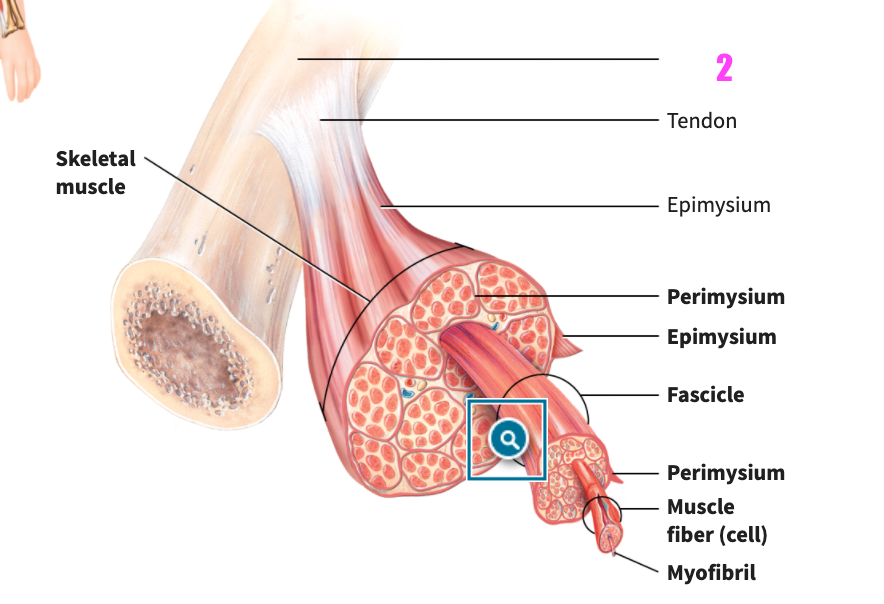 what is #2? | back 44 bone covered by periosteum (skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 45 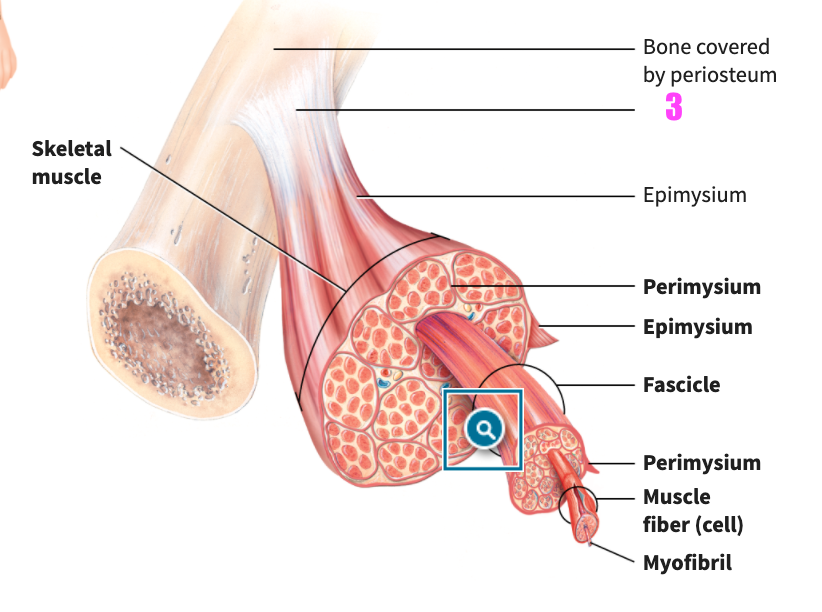 what is #3? | back 45 tendon (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 46 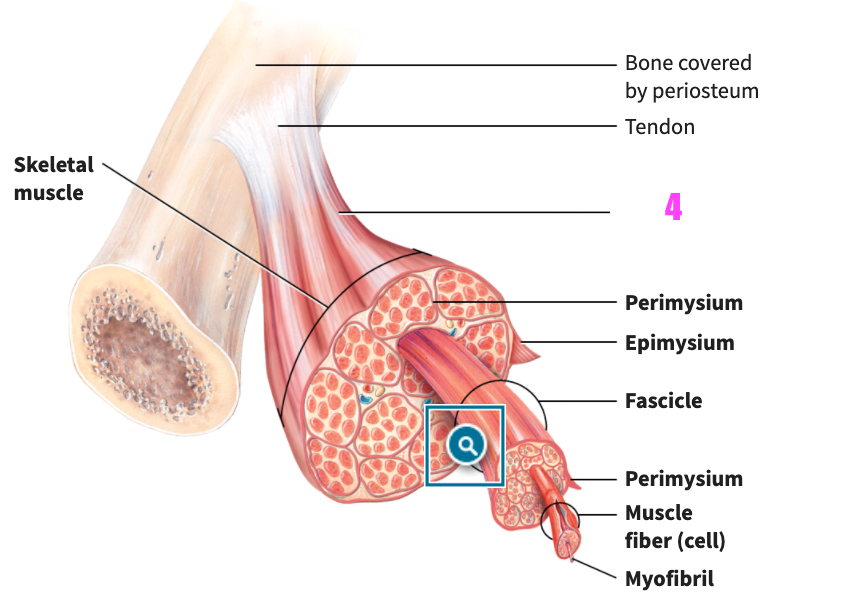 what is #4? | back 46 Epimysium (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 47 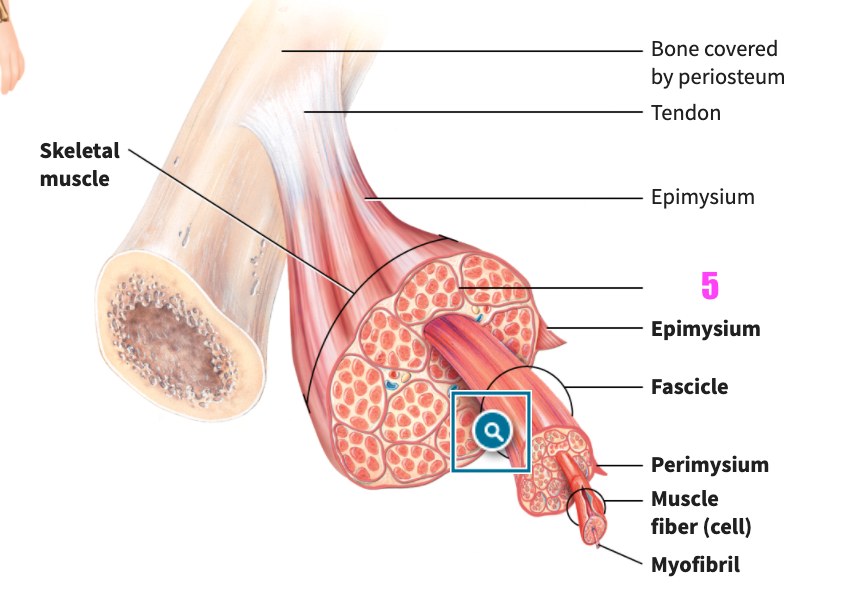 what is #5? | back 47 Perimysium (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 48 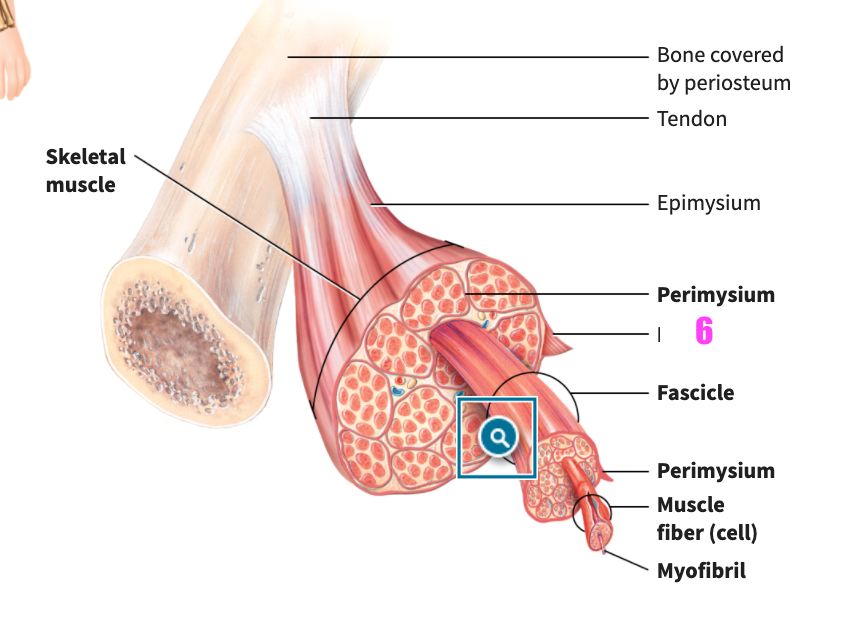 what is #6? | back 48 Epimysium (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 49 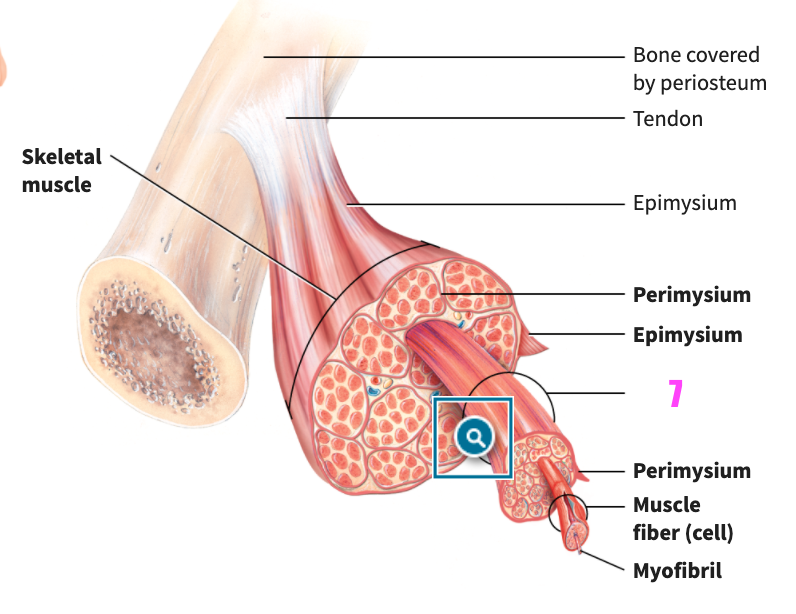 what is #7? | back 49 Fasicle (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 50 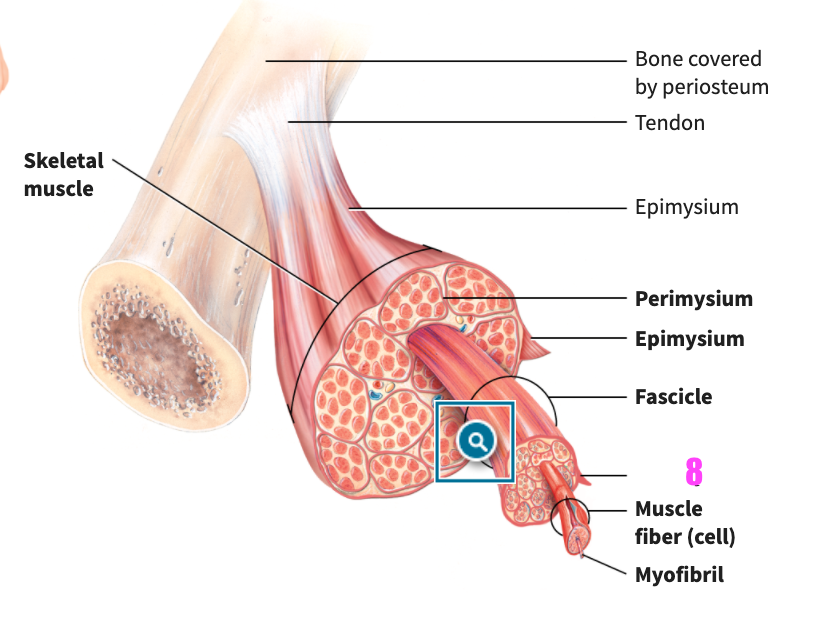 what is #8? | back 50 Perimysium (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 51 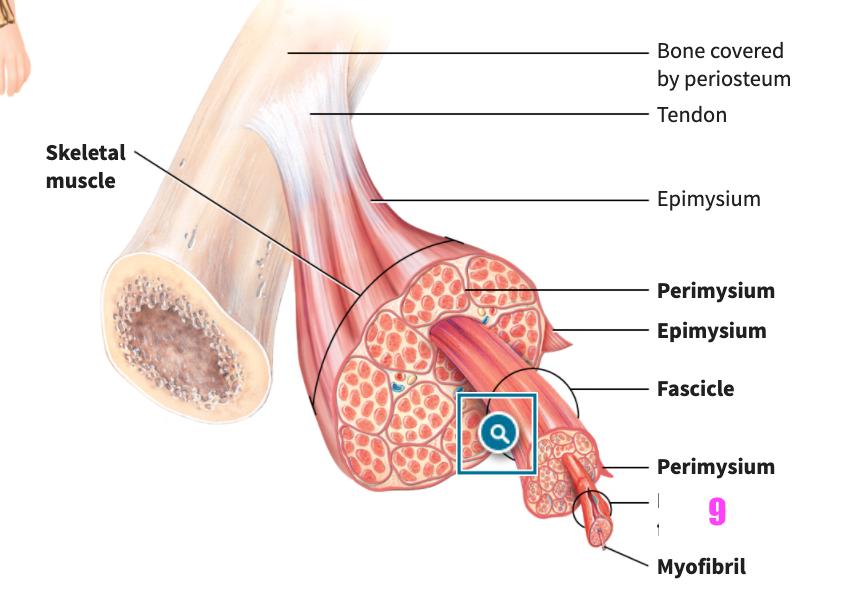 what is #9? | back 51 Muscle fiber (cell) (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 52 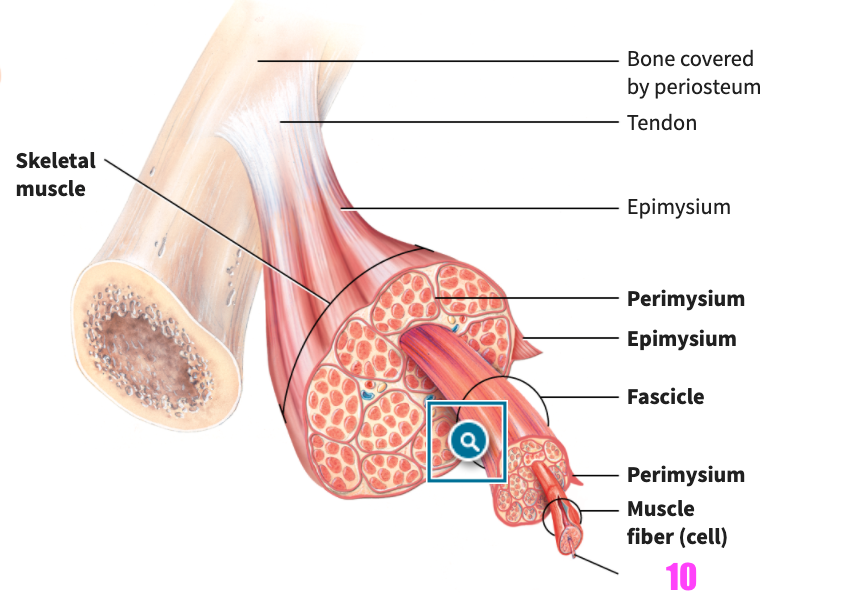 what is #10? | back 52 Myofibril (of skeletal muscle tissue) |
front 53 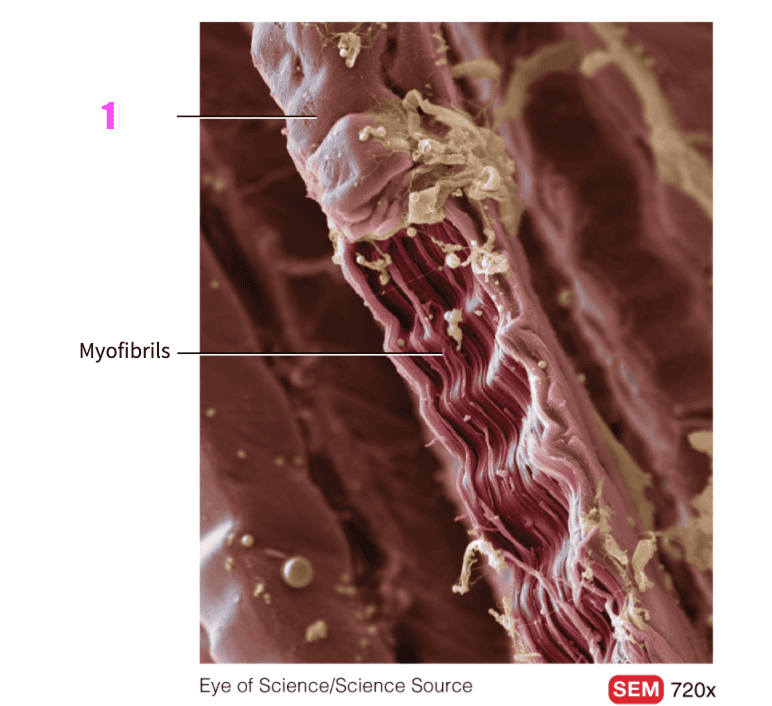 What is #1? | back 53 Muscle fiber (skeletal muscle) |
front 54 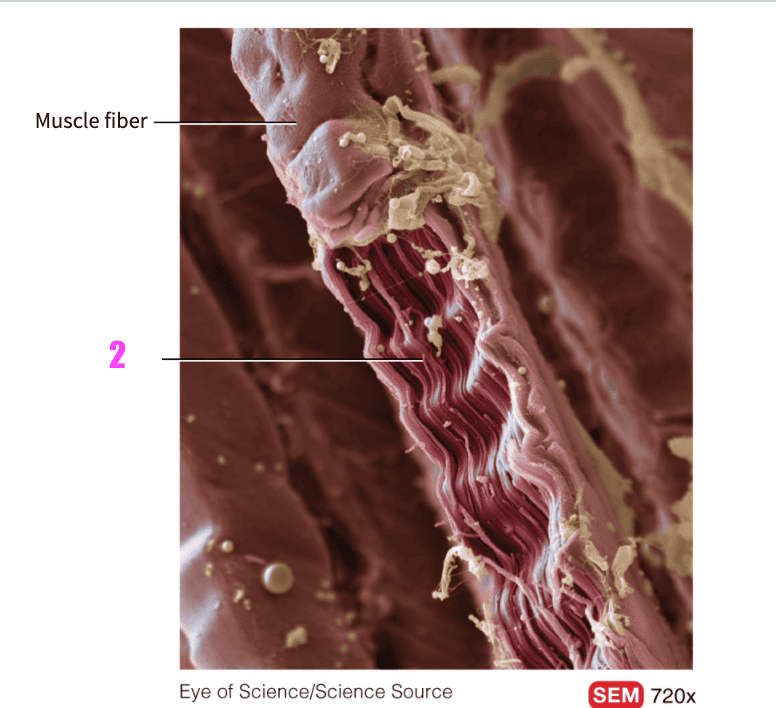 what is #2? | back 54 Myofibrils (skeletal muscle) |
front 55 tough, glistening white dense regular connective tissue structures that attach the muscle belly to the bones, are minimally vascular, lack muscle cells, and consist primarily of parallel arrangements of collagen fibers | back 55 tendons |
front 56 Which connective tissue coat surrounds groups of muscle fibers, separating them into fascicles? | back 56 Perimysium is the connective tissue layer that bundles groups of muscle fibers into fascicles. |
front 57 The contractile elements of muscle fibers are the ___________, which contain overlapping thick and thin filaments. | back 57 myofibrils (skeletal muscle) |
front 58 Which structure shown here releases calcium ions to trigger muscle contraction? | back 58 The sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions to trigger muscle contraction. (skeletal muscle) |
front 59 Among the following, which is smallest: muscle fiber, thick filament, or myofibril? Which is largest? | back 59 Size, from smallest to largest: thick filament, myofibril, muscle fiber (skeletal muscle) |
front 60 Damage to a muscles cell's __________ will directly interfere with the production of the major energy source necessary for body movements. | back 60 mitochondria |
front 61 _____________ is considered the motor protein because it can hydrolyze ATP. | back 61 myosin |
front 62 Put the steps of the skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle contraction
cycle in order: A. 1, 2, 3, 4 B. 4, 2, 1, 3 C. 3, 2, 1, 4 D. 3, 1, 4, 2 | back 62 B. 4, 2, 1, 3 |
front 63 Skeletal muscle contractions will not occur (paralysis) if there is injury or damage of _________ neuron | back 63 somatic motor |
front 64 Injury to an entire motor unit consists of A. all of the sarcomeres that one motor neuron innervates B. all of the myofibrils that one motor neuron innervates C. all of the skeletal muscles that one motor neuron innervates D. all of the muscle fibers that one motor neuron innervates | back 64 D. all of the muscle fibers that one motor neuron innervates |
front 65 ____________ an do work for a moderate length of time such as a 200 meter dash. | back 65 Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers |
front 66 A birth defect that caused developmental anomalies in all three types of muscle tissue most likely originated in the ______________ cells | back 66 mesenchymal cells |
front 67 Connective tissue diseases will effect the _________________ of ______________ muscle | back 67 epimysium of skeletal muscle |
front 68 The neurotransmitter in the neuromuscular junction is ______________ | back 68 acetylcholine |
front 69 To initiate the cross-bridge cycle, _________ must bind to troponin. | back 69 calcium |
front 70 Red muscle fibers __________ than white muscle fibers. A. contain relatively more mitochondria B. have more capillaries C. have more myoglobin D. all of the choices are correct | back 70 D. all of the choices are correct |
front 71 Which fibers tend to be pale or white in color? A. all of the choices are correct B. fast oxidative-glycolytic C. fast glycolytic D. slow oxidative | back 71 C. fast glycolytic |
front 72 Marathon runners would be expected to have higher percentages of _________ compared to short-distance sprinters. | back 72 slow oxidative fibers |
front 73 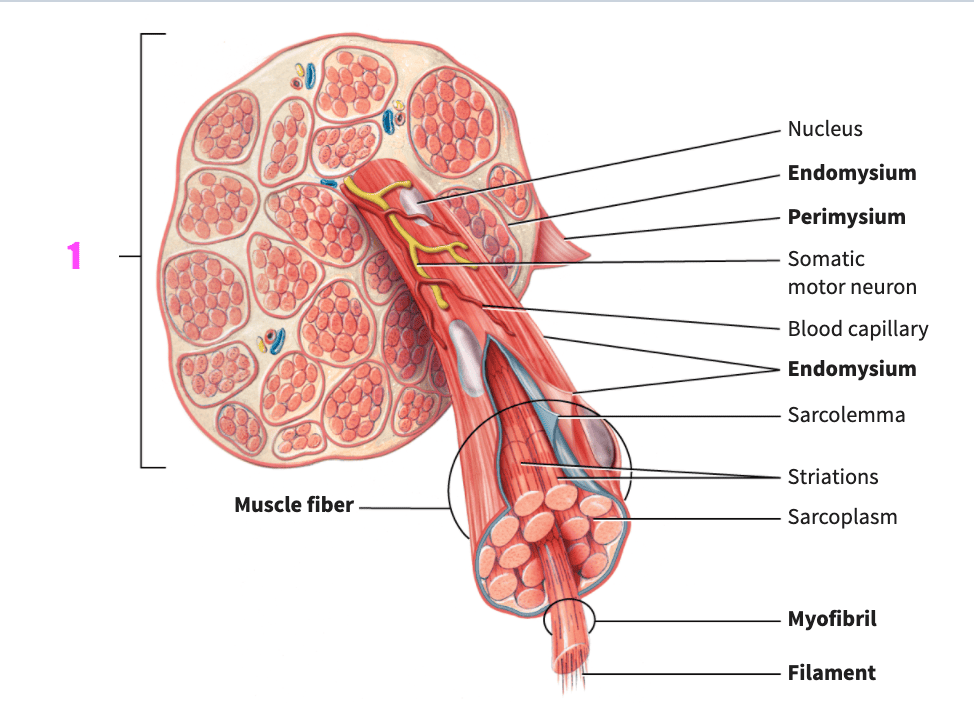 what is #1? | back 73 fascicle (skeletal muscle) |
front 74 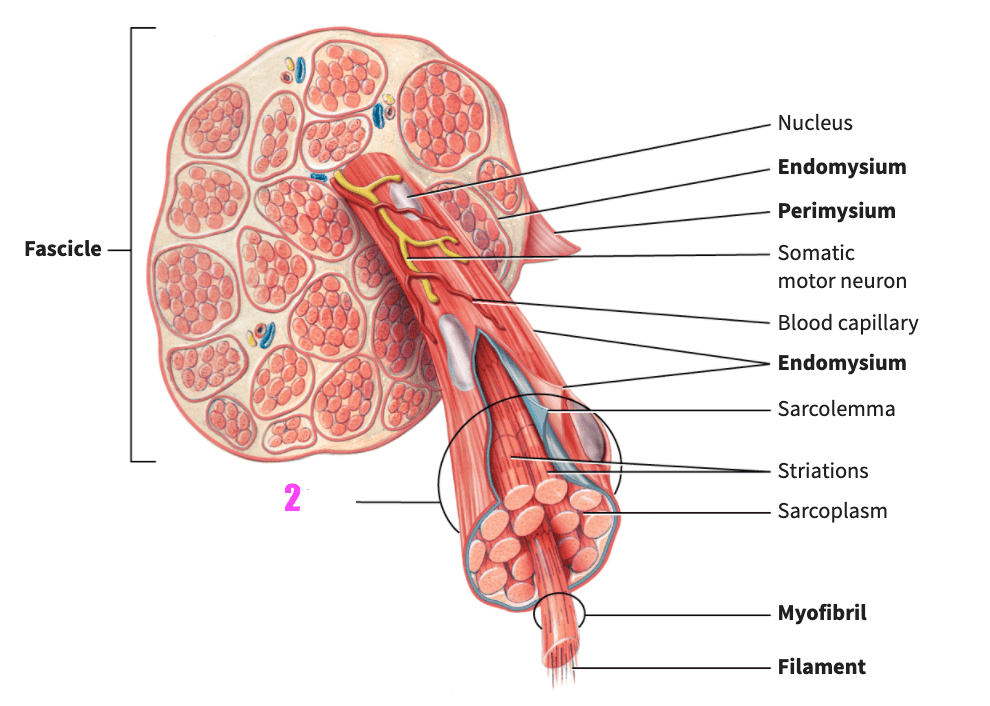 what is #2? | back 74 muscle fiber (skeletal muscle) |
front 75 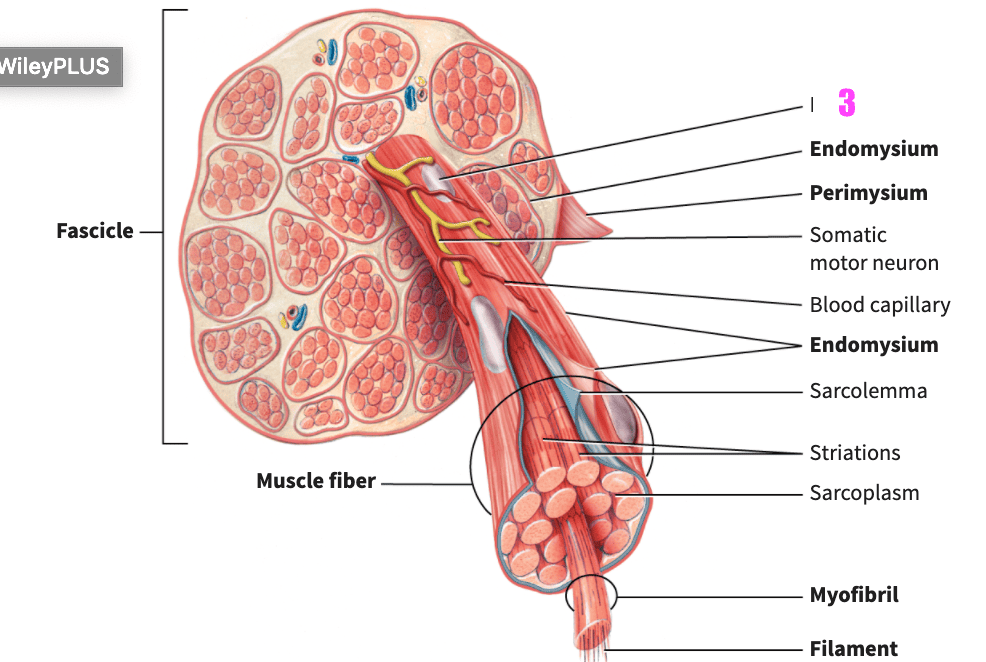 what is #3? | back 75 nucleus (skeletal muscle) |
front 76 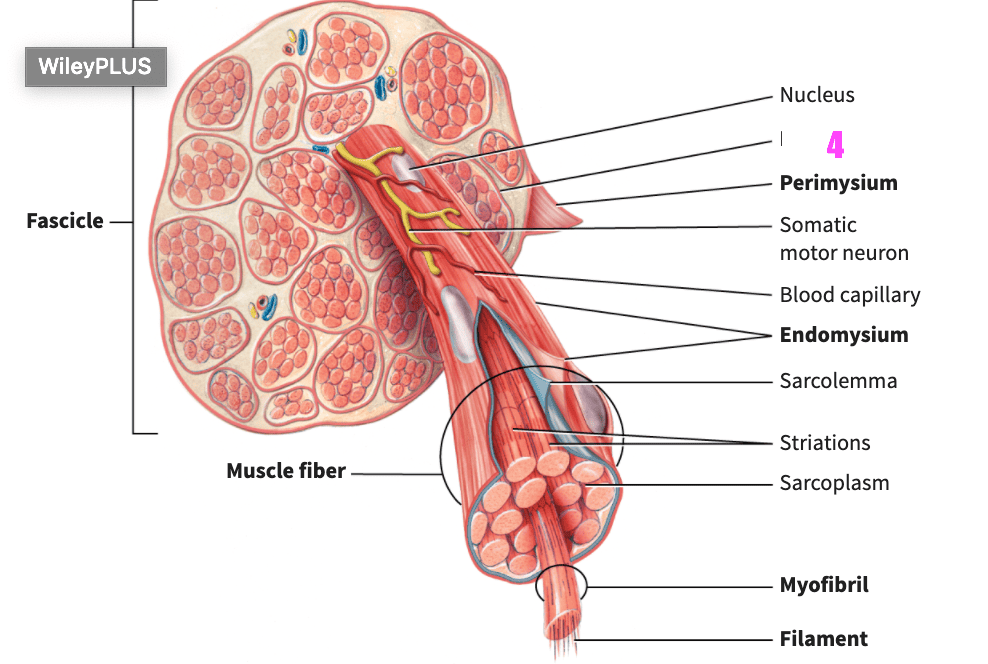 what is #4? | back 76 endomysium (skeletal muscle) |
front 77 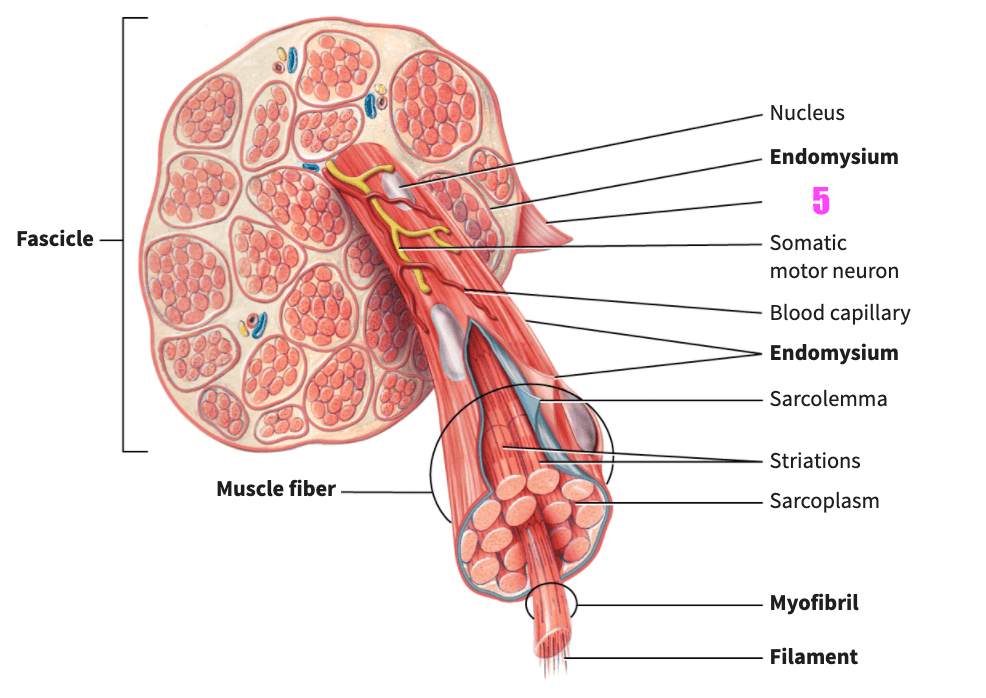 what is #5? | back 77 perimysium (skeletal muscle) |
front 78 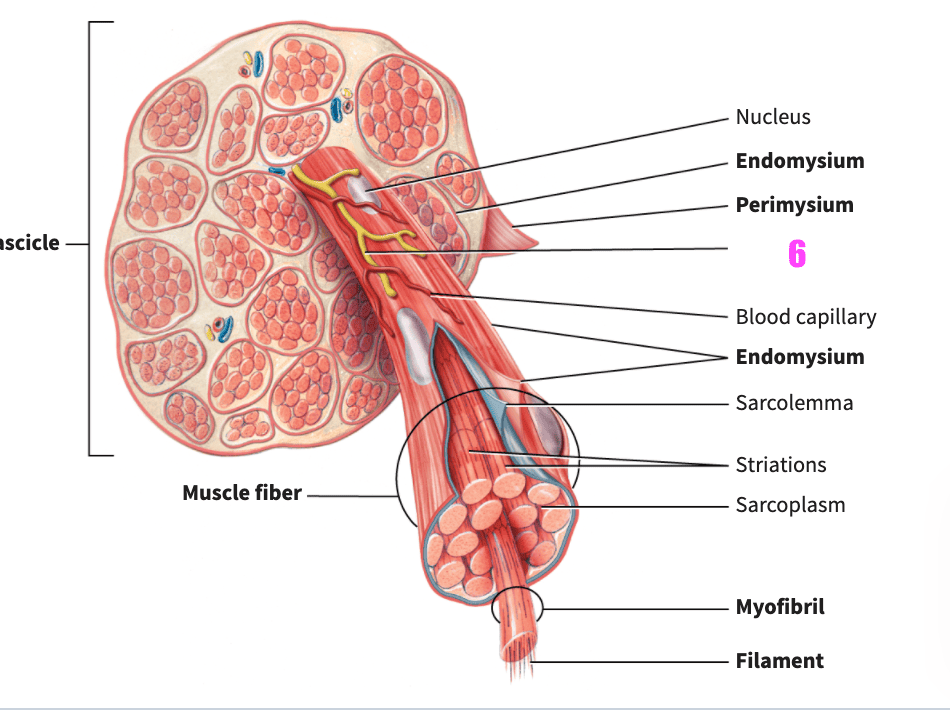 what is #6? | back 78 somatic motor neuron (skeletal muscle) |
front 79 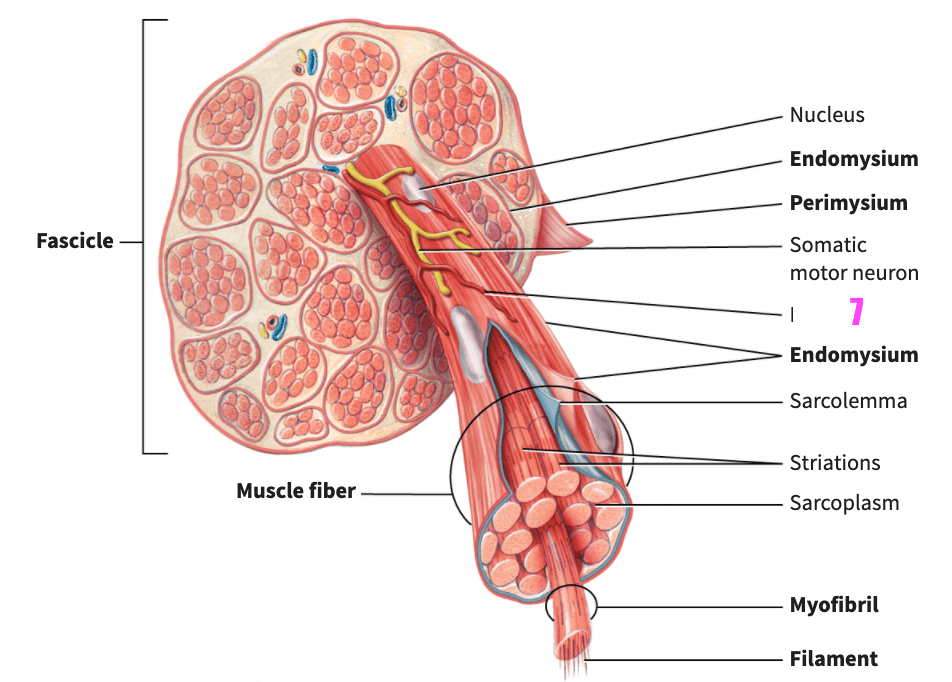 what is #7? | back 79 blood capillary (skeletal muscle) |
front 80 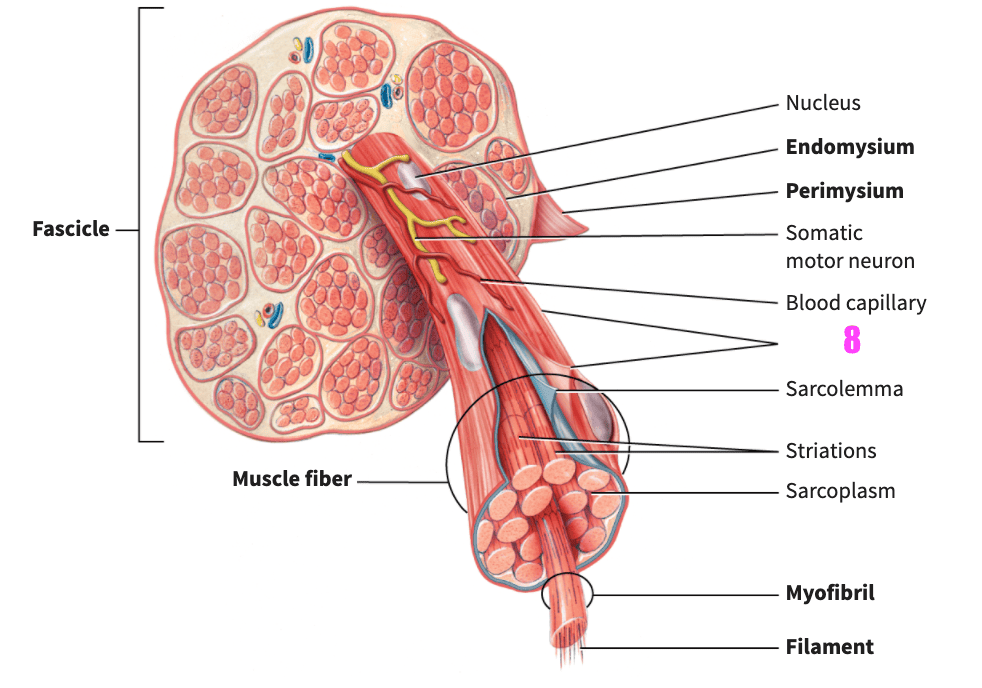 what is #8? | back 80 endomysium (skeletal muscle) |
front 81 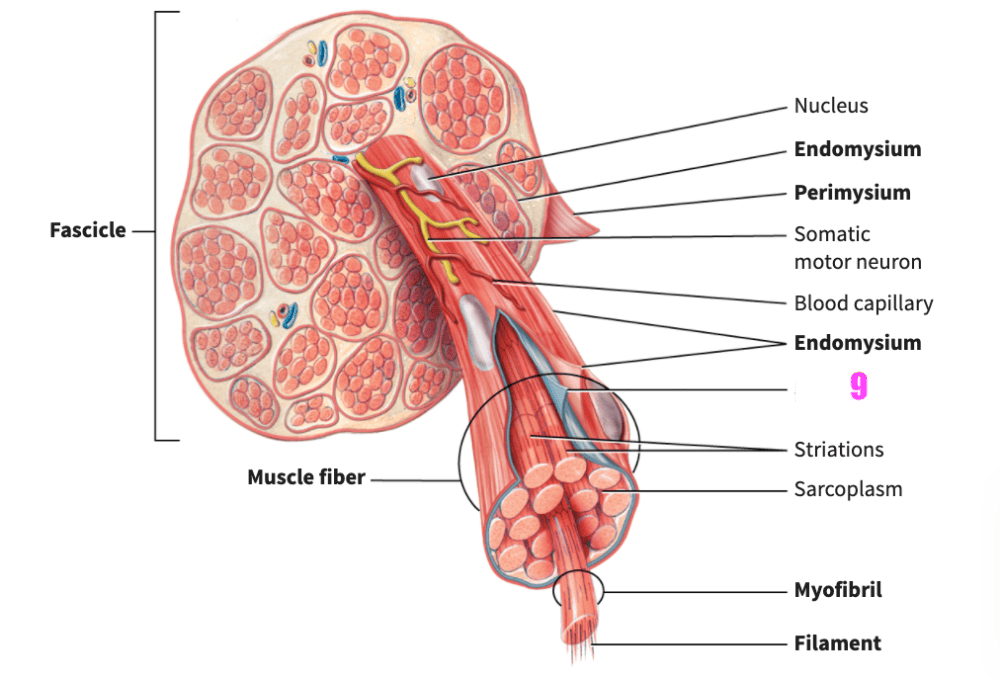 what is #9? | back 81 sarcolemma (skeletal muscle) |
front 82 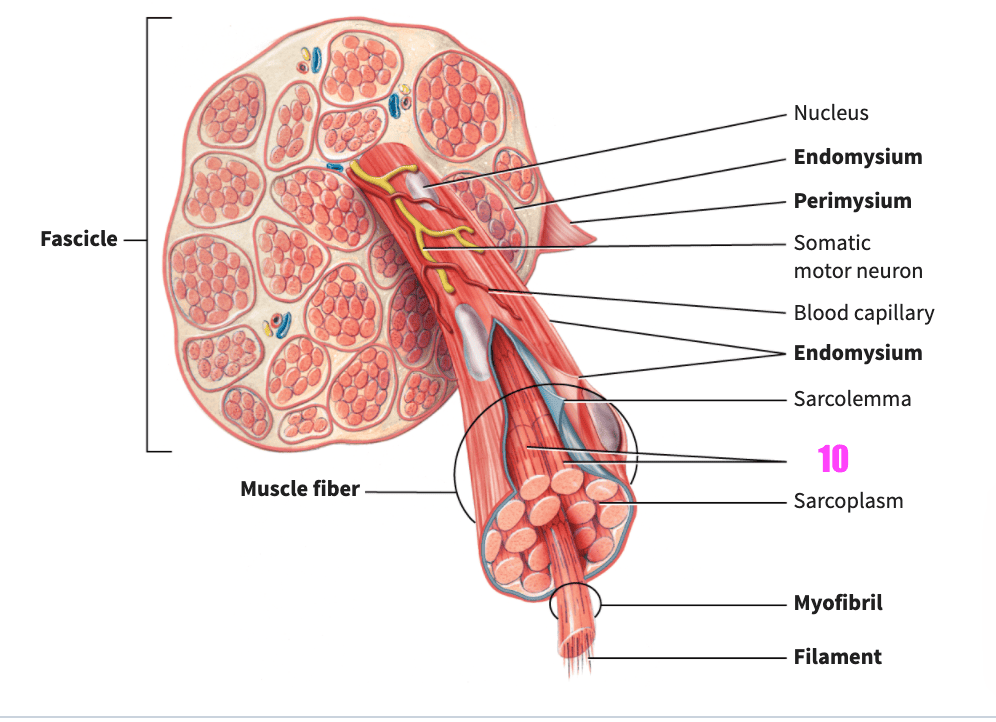 what is #10? | back 82 striations (skeletal muscle) |
front 83 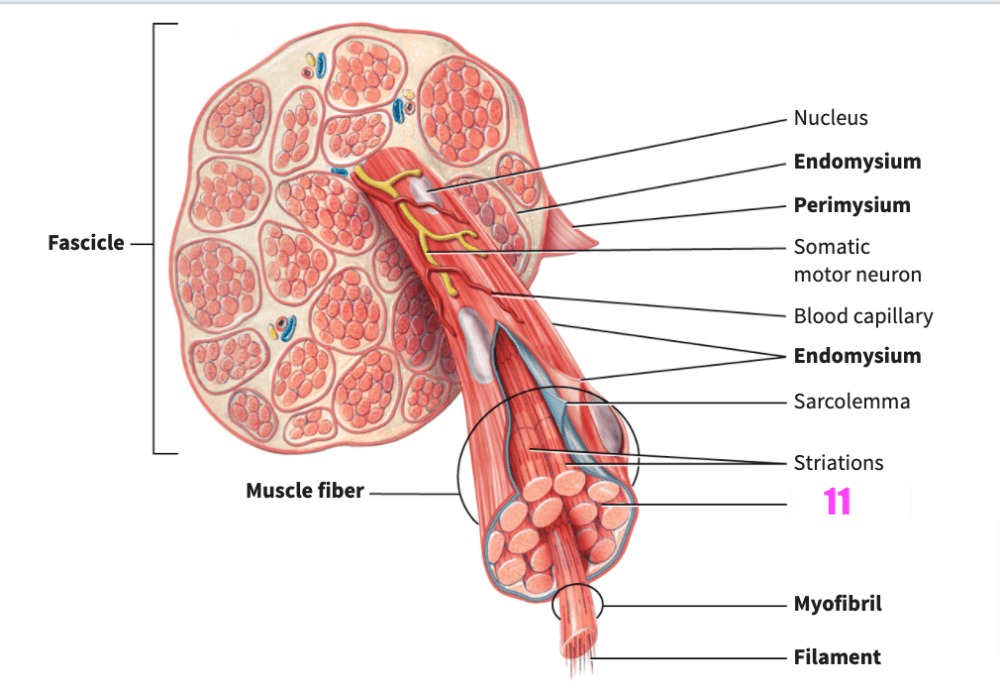 what is #11? | back 83 sarcoplasm (skeletal muscle) |
front 84 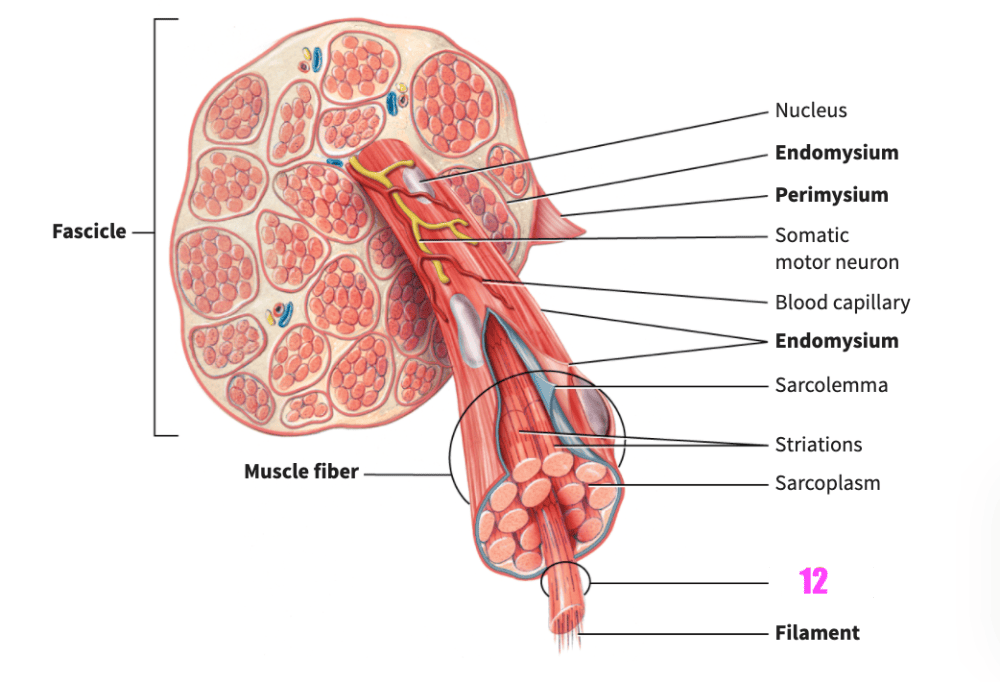 what is #12? | back 84 myofibril (skeletal muscle) |
front 85 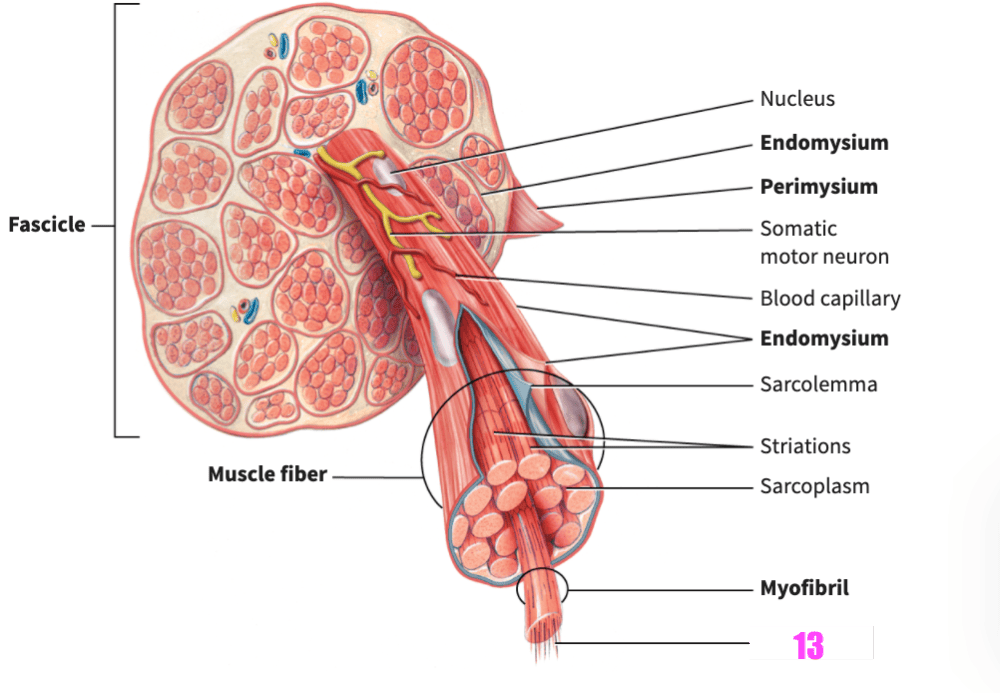 what is #13? | back 85 filament (skeletal muscle) |
front 86 Thin wrapping of mostly reticular fibers. This surrounding connective tissue helps to bind the muscle fibers together, yet it is loose enough to allow them to move freely over one another. In addition, the endomysium carries small blood vessels that supply the fibers with nutrients | back 86 the endomysium |
front 87 groups of muscle fibers form bundles wrapped in a thicker layer of connective tissue. | back 87 a fascicle |
front 88 dense irregular connective tissue covering that surrounds a fasicle | back 88 perimysium |
front 89 a somewhat thicker covering of dense irregular connective tissue which binds all the fascicles together to form the muscle belly | back 89 epimysium |
front 90 explain the continuous network of connective tissue (skeletal muscle tissue) | back 90 So the tendons are a continuous mass of connective tissue that runs through the muscle as the endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium and emerges from the belly of the muscle as the tendons of origin and insertion at either end. This is what makes your muscles so incredibly strong. At its junction with the bone, the surface tissue of the tendon is continuous with the periosteum, while its deeper collagen fibers enter the bone to blend with the collagen of the osseous extracellular matrix. This strong, continuous network of connective tissue is essential to the function of the musculoskeletal system. |
front 91 The various skeletal muscles of the body are further grouped together and protected by large dense irregular connective tissue sheets, called ______________ which wrap around groups of muscles much like a sock encircles your foot. | back 91 fascia ex: For example, underneath the skin and subcutaneous layer in the free lower limbs a thin, tough, glistening sheet of dense irregular connective tissue called the fascia of the free lower limbs surrounds all the muscles. |
front 92
| back 92 muscle fibers/ skeletal muscle fibers |
front 93 During embryonic development, many myoblasts fuse lengthwise to form one ____________________. Once fusion has occurred, a skeletal muscle fiber loses the ability to _____________, but satellite cells retain this ability | back 93 1) skeletal muscle fiber 2) undergo cell division |
front 94 The ____________ of the muscle fiber encloses sarcoplasm and myofibrils, which are striated 1. The multiple nuclei of a skeletal muscle fiber are located just beneath the _________ 2. the plasma membrane of a muscle fiber 3. The cell membrane of a muscle fiber (cell), especially of a skeletal muscle fiber | back 94 sarcolemma |
front 95 Fluid filled _______________ wraps around each myofibril. | back 95 Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) |
front 96 1. The dramatic muscle growth that occurs after birth occurs by enlargement of existing muscle fibers, called ________________ 2. An excessive enlargement or overgrowth of tissue without cell division. 3. due to increased production of myofibrils, mitochondria, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and other organelles. 4. It results from very forceful, repetitive muscular activity, such as strength training. | back 96 hypertrophy |
front 97 1) an increase in the number of fibers. 2) An abnormal increase in the number of normal cells in a tissue or organ, increasing its size. | back 97 hyperplasia |
front 98 1. Small, cylindrical invaginations of the sarcolemma of striated muscle fibers (cells) that conduct muscle action potentials toward the center of the muscle fiber. 2. Thousands of tiny invaginations of the sarcolemma that tunnel in from the surface toward the center of each muscle fiber. Because transverse tubules are open to the outside of the fiber, they are filled with interstitial fluid. | back 98 transverse tubules (t tubules) |
front 99 _____________ propagate along the sarcolemma and through the transverse tubules, quickly spreading throughout the muscle fiber. This arrangement ensures that all the superficial and deep parts of the muscle fiber become excited by an action potential almost simultaneously. | back 99 Muscle action potentials |
front 100 The sarcolemma surrounds the ___________________, the cytoplasm of a muscle fiber | back 100 sarcoplasm |
front 101 explain the sarcoplasms role in providing the muscle with energy | back 101 The sarcoplasm includes a substantial amount of glycogen, a storage molecule that consists of a chain of linked glucose molecules. When the muscle requires energy and has already depleted its available glucose, glucose molecules from glycogen will be released and utilized for the synthesis of ATP. |
front 102
| back 102 myoglobin |
front 103
| back 103 myofibrils |
front 104 1. A fluid-filled system of membranous sacs that encircles each myofibril 2. A network of saccules and tubes surrounding myofibrils of a muscle fiber (cell), comparable to endoplasmic reticulum; functions to reabsorb calcium ions during relaxation and to release them to cause contraction. 3. This elaborate system is similar to smooth endoplasmic reticulum in nonmuscle cells | back 104 sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) |
front 105 In a ____________, the sarcoplasmic reticulum stores calcium ions (Ca2+). When triggered, Ca2+ will be released from the terminal cisterns into the sarcoplasm, which triggers muscle contraction. | back 105 relaxed muscle fiber |
front 106 Within myofibrils are smaller protein structures called _____________ | back 106 filaments |
front 107 thin filaments are mostly composed of the protein __________ | back 107 actin |
front 108 thick filaments are mostly composed of the protein __________ | back 108 myosin |
front 109 Both thin and thick filaments are directly involved in the _____________ | back 109 contractile process |
front 110
| back 110 sarcomeres |
front 111 Narrow, plate-shaped regions of dense protein material called ___________ separate one sarcomere from the next. Thus, a sarcomere extends from __________ to the _________. | back 111
|
front 112 The dark, middle part of the sarcomere that extends the entire length of the thick filaments and also includes those parts of the thin filaments that overlap with the thick filaments | back 112 A band |
front 113
| back 113 I band |
front 114 A narrow region in the center of each A band that contains thick filaments but no thin filaments | back 114 H zone |
front 115 A region in the center of the H zone that contains proteins that hold the thick filaments together at the center of the sarcomere | back 115 M line |
front 116 Myofibrils are built from 3 kinds of proteins: (list them) | back 116
|
front 117 what are the 2 contractile proteins? How can we identify them? | back 117
|
front 118 Contractile proteins (myosin and actin) _______________, and regulatory proteins (troponin and tropomyosin) _________________. | back 118 1. generate force during contraction 2. help switch contraction on and off |
front 119 Which proteins connect to the Z disc? Which proteins are present in the A band? In the I band? | back 119 Actin and titin anchor into the Z disc. A bands contain myosin, actin, troponin, tropomysin, and titin; I bands contain actin, troponin, tropomysin, and titin. |
front 120 what are the 2 regulatory proteins? | back 120
|
front 121 give some info about tropomyosin and troponin (2 regulatory proteins) | back 121 1. are thin filaments 2. In relaxed muscle, myosin is blocked from binding to actin because strands of tropomyosin cover the myosin-binding site on actin. The tropomyosin strand, in turn, is held in place by troponin molecules. You will soon learn that when calcium ions (Ca2+) bind to troponin, it undergoes a change in shape; this change moves tropomyosin away from myosin-binding sites on actin, allowing myosin to bind to actin and muscle contraction to begin. |
front 122 what are the 4 key structural proteins? | back 122
|
front 123 A regulatory protein that is a component of the thin filament. When a skeletal muscle fiber is relaxed, tropomyosin covers the myosin-binding sites on actin molecules, thereby preventing myosin from binding to actin. | back 123 tropomyosin |
front 124 regulatory protein that is a component of the thin filament. When calcium ions (Ca2+) bind to troponin, it undergoes a change in shape; this conformational change moves tropomyosin away from myosin-binding sites on actin molecules, and muscle contraction subsequently begins as myosin binds to actin. | back 124 troponin |
front 125 Proteins that generate force during muscle contractions. | back 125 contractile proteins |
front 126 A contractile protein that makes up the thick filament. A myosin molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin-binding sites on actin molecules of a thin filament during muscle contraction. | back 126 myosin |
front 127 A contractile protein that is the main component of the thin filament. On each actin molecule is a myosin-binding site where a myosin head of a thick filament binds during muscle contraction. | back 127 actin |
front 128 Proteins that help switch the muscle contraction process on and off. | back 128 regulatory proteins |
front 129 Proteins that keep the thick and thin filaments of the myofibrils in proper alignment, give the myofibrils elasticity and extensibility, and link the myofibrils to the sarcolemma and extracellular matrix. | back 129 structural proteins |
front 130 an organ made up of fascicles that contain muscle fibers (cells), blood vessels, and nerves. The skeletal muscle is wrapped in epimysium. | back 130 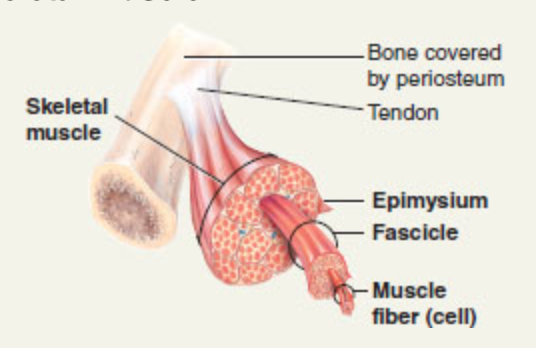 skeletal muscle |
front 131 a bundle of muscle fibers wrapped in perimysium. | back 131 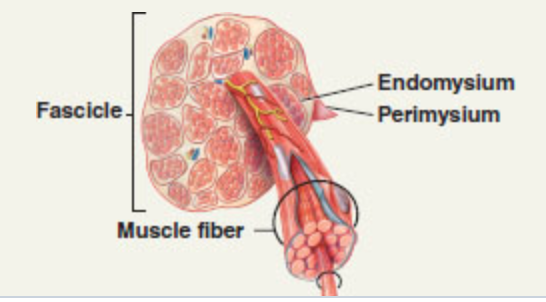 fascicle |
front 132 Long cylindrical cell covered by a vascular endomysium. The cell membrane, the sarcolemma, surrounds the sarcoplasm with its myofibrils, many peripherally located nuclei, mitochondria, transverse tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and terminal cisterns. The fiber has a striated appearance. | back 132 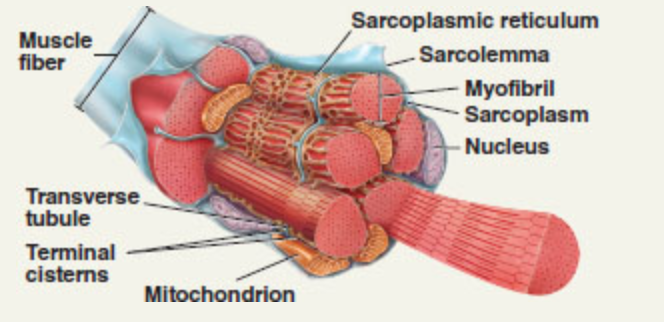 muscle fiber (cell) |
front 133 Threadlike contractile elements within the sarcoplasm of a muscle fiber that extend the entire length of the fiber; composed of filaments. | back 133 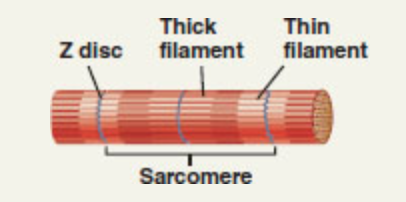 myofibril |
front 134 Contractile proteins within myofibrils that are of two types: thick filaments composed of myosin and thin filaments composed of actin, tropomyosin, and troponin; the sliding of the thin filaments past the thick filaments produces muscle shortening. | back 134 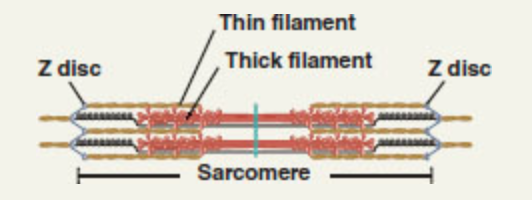 filaments (myofilaments) |
front 135 What part of the sarcolemma contains acetylcholine receptors? | back 135 The part of the sarcolemma that contains acetylcholine receptors is the motor end plate. |
front 136
| back 136 muscle tone |
front 137 Muscle contraction may either be ___________ or _____________ | back 137 isotonic or isometric |
front 138 1. the muscle remains almost constant while the muscle changes its length 2. these are used to produce body movements and for moving objects 3. two types are: concentric & eccentric | back 138 isontonic contraction |
front 139 what are the 2 types of isotonic contractions? | back 139 1. concentric isotonic contraction 2. eccentric isotonic contraction |
front 140
| back 140 Concentric isotonic contraction(s) |
front 141
| back 141 Eccentric isotonic contraction(s) |
front 142
| back 142 isometric contractions ⤻ |
front 143 Most activities include both _________ and ________ contractions. | back 143
|
front 144 Skeletal muscle fibers vary in their content of ____________, the red protein that binds oxygen in muscle fibers | back 144 myoglobin |
front 145 Those with a high myoglobin content are called _____________, while those that have a low myoglobin content are called __________________ | back 145
|
front 146 Red muscle fibers also contain more ________________ and are supplied by more ______________ than white muscle fibers. | back 146 1. mitochondria 2. blood capillaries |
front 147 Skeletal muscle fibers are classified as one of 3 types: (list the 3 types) | back 147
|
front 148
| back 148 slow oxidative (SO) fibers |
front 149 type IIa fibers are typically the largest fibers. Like slow oxidative fibers, they contain large amounts of myoglobin and many blood capillaries, giving them a dark red appearance. 2. these fibers can generate considerable ATP by aerobic cellular respiration, which gives them a moderately high resistance to fatigue. 3. Because their intracellular glycogen level is high, they also generate ATP by anaerobic (oxygen-free) glycolysis. 4. fibers are “fast” because they use ATP at a fast rate, which makes their speed of contraction faster than SO fibers. 5. These fibers contribute to activities such as walking and sprinting. | back 149 Fast oxidative-glycolytic (FOG) fibers |
front 150 1) type IIb fibers have low myoglobin content, relatively few blood capillaries and few mitochondria, and appear white in color. T 2) they contain large amounts of glycogen and generate ATP mainly by anaerobic (nonoxygen-requiring) cellular respiration (glycolysis). 3) Due to their ability to use ATP at a fast rate, __________ fibers contract strongly and quickly. These fast-twitch fibers are adapted for intense anaerobic movements of short duration, such as weight lifting or throwing a ball, but they fatigue quickly. Strength training programs that engage a person in activities requiring great strength for short times produce increases in the size, strength, and glycogen content of fast glycolytic fibers. The __________ fibers of a weight lifter may be 50 percent larger than those of a sedentary person or an endurance athlete because of increased synthesis of muscle proteins. The overall result is muscle enlargement due to hypertrophy of the __________ fibers. | back 150 Fast Glycolytic (FG) Fibers |
front 151 Most skeletal muscles are a __________ of all three types of skeletal muscle fibers. The proportions vary somewhat, depending on the action of the muscle, the person's training regimen, and genetic factors. | back 151 mixture |
front 152 1. The principal tissue in the heart wall 2. cannot be controlled voluntarily 3. display autorhythmicity--> the ability to repeatedly generate spontaneous action potentials. 4. these action potentials cause alternating contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle fibers 5. are shorter in length and less circular in transverse section 6. exhibit branching, which gives individual ______________ a “stair-step” appearance. 7. Usually one centrally located nucleus is present, although an occasional cell may have two nuclei | back 152 1. (overall) cardiac muscle tissue 2. (blank) cardiac muscle fibers |
front 153
| back 153 intercalated discs |
front 154
| back 154 gap junctions |
front 155 The intercalated discs contain ______________, which hold the cardiac muscle fibers together | back 155 desmosomes |
front 156 Cardiac muscle tissue has an endomysium, but lacks a ___________ and ____________. | back 156
|
front 157 Cardiac muscle fibers display ______________, the ability to repeatedly generate spontaneous action potentials. | back 157 autorhythmicity |
front 158 _____________ are larger and more numerous in cardiac muscle fibers than in skeletal muscle fibers. | back 158 Mitochondria |
front 159 ___________ muscle fibers have the same arrangement of actin and myosin, and the same bands, zones, and discs, as skeletal muscle fibers | back 159 Cardiac |
front 160 The transverse (T) tubules of cardiac muscle are _________________ than those of skeletal muscle; there is one T tubule per sarcomere, located at the Z disc. | back 160 wider but less abundant |
front 161 The _______________ of cardiac muscle fibers is somewhat smaller than the _____ of skeletal muscle fibers. | back 161 sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 162 Cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that cardiac muscle only has A. transverse tubules B. intercalated discs C. nuclei D. striations | back 162 B. intercalated discs |
front 163 Which is likely to occur with someone who has an overworked heart? A. mitochondria decrease in number B. the lungs enlarge C. the heart enlarges D. the capillary network around the heart decreases | back 163 C. the heart enlarges |
front 164 Which muscle tissue has the least amount of sarcoplasmic reticulum? | back 164 Smooth muscle tissue |
front 165 Compared to other muscle tissues, smooth muscle differs in that it lacks ___________________ | back 165 transverse tubules |
front 166 Which gives rise to skeletal muscle A. ectome B. myotome C. dermatome D. sclerotome | back 166 B. myotome |
front 167 Myotome gives rise to A. arrector pili muscle B. biceps brachii muscle C. skin D. vertebrae | back 167 B. biceps brachii muscle |
front 168 With aging, skeletal muscle is replaced by ______________ | back 168 fibrous connective tissue |
front 169 Which muscle should decline in mass first as we age? A. deltoid of shoulder B. palmaris longus of forearm C. biceps brachii of arm D. rectus femoris of thigh | back 169 D. rectus femoris of thigh |
front 170 In addition to muscle tissue, can you speculate as to what other tissue of the body is capable of responding to certain stimuli by producing action potentials? A. epithelium B. cartilage C. bone D. nervous | back 170 D. nervous |
front 171 Once you begin to exercise, you notice your desire to turn on the air conditioning. This desire is the result of which property of muscle tissue? | back 171 thermogenesis |
front 172 The process of exercising with progressively heavier resistance to strengthen the musculoskeletal system is known as | back 172 strength training |
front 173 A genetic mutation that results in malformation of the actin protein will directly effect the function of which type(s) of muscle tissue? Select all that apply. A. skeletal B. smooth C. cardiac | back 173 A. skeletal B. smooth C. cardiac |
front 174 Human normally undergo a slow progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass after the age of 30. A. True B. False | back 174 A. True |
front 175 Acetylcholine receptors are found along the ______________ | back 175 motor end plate |
front 176 During a contraction, the _________ band remain(s) unchanged in size. | back 176 A band |
front 177 Muscle cells are innervated by somatic motor neurons in ______________ | back 177 skeletal muscle |
front 178 Skeletal muscle tissue formation begins during the fourth week of embryonic development as specialized mesodermal cells, called _____________, fuse together. | back 178 myoblasts |
front 179 Strength training results in muscle cells that undergo _____________ | back 179 hypertrophy |
front 180 A genetic mutation that results in malformation of the myosin protein will directly effect the function of which type(s) of muscle tissue? Select all that apply. A. skeletal B. smooth C. cardiac | back 180 A. skeletal B. smooth C. cardiac |
front 181 The sliding filament theory describes the sliding of actin and ________________ | back 181 myosin filaments |
front 182 When acetylcholine binds to receptors on the motor end plate, ________ enters the sarcoplasm | back 182 sodium |
front 183 Which muscle(s) is/are controlled by the somatic nervous system? | back 183 skeletal |
front 184 The small amount of tautness or tension in the muscle due to weak, involuntary contractions of its motor units is known as muscle _____________ | back 184 muscle tone |
front 185 As muscles age, many changes can take place. Select all that apply. A. decrease in strength B. loss of muscle mass C. decrease in flexibility D. muscle hypertrophy E. increase of reflex speed | back 185 A. decrease in strength B. loss of muscle mass C. decrease in flexibility |
front 186 Diminished levels of oxygen found in skeletal muscle fibers can be a direct consequence of __________ protein defect. | back 186 myoglobin |
front 187 Desmosomes and gap junctions form _________ in cardiac tissue. | back 187 intercalated discs |
front 188 This fiber is smallest in diameter and the least powerful; it contracts slowly and is very resistant to fatigue. | back 188 slow oxidative |
front 189 When muscle cells produce new thick and thin filaments, they get larger in size for example from weight training exercises. This process is referred to as ______________ | back 189 hypertrophy |
front 190 Striated muscle tissues develop from the embryonic ___________________ | back 190 mesoderm |
front 191 In terms of autorhythmicity, single-unit smooth muscle tissue is most like a. cardiac muscle tissue b. skeletal muscle tissue | back 191 a. cardiac muscle tissue |
front 192 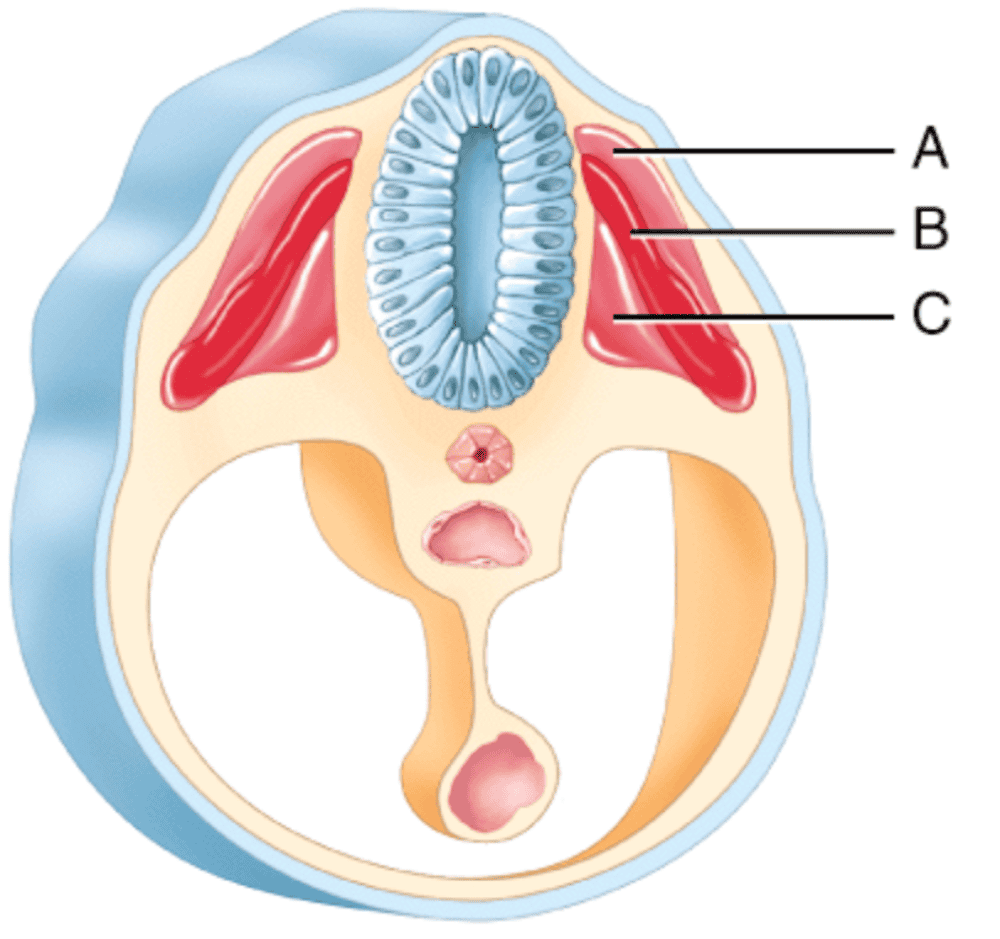 Which somatic region will develop into the vertebrae? A. C B. A C. B | back 192 A. C |
front 193 Neuromuscular junctions function when __________ are released into the synaptic cleft. | back 193 neurotransmitters |
front 194 Over time, how is it possible for a weight lifter to become a marathon runner? A. decrease the percentage of SO fibers B. increase the percentage of SO fibers C. decrease FOG fibers and increase FG fibers D. increase the proportion of FG fibers | back 194 B. increase the percentage of SO fibers |
front 195 Which muscle(s) is/are non-striated and involuntary? | back 195 smooth muscles |
front 196 During a skeletal muscle contraction, which of the following structures shorten? Select all that apply. A. sarcomere B. myofibril C. myosin D. actin E. muscle cell F. fascicle G. skeletal muscle | back 196 A. sarcomere B. myofibril E. muscle cell F. fascicle G. skeletal muscle |
front 197 As one ages, the presence of slow oxidative fibers A. slightly decreases B. stays the same C. decreases D. increases | back 197 D. increases |
front 198 Which benefits result from strength training? Select all that apply. A. increase in muscle mass and strength B. decrease in the amount of energy spent at rest C. decrease in resting metabolic rate D. increase mineral deposition into bone | back 198 A. increase in muscle mass and strength D. increase mineral deposition into bone |
front 199 When an action potential arrives are the synaptic end bulb, ________-gated calcium channels allow calcium to move ________. | back 199
|
front 200 When the doctor uses a reflex hammer and taps on the patellar tendon you respond by automatically "kicking out" i.e. extending your leg. As you age this patellar tendon reflex __________________ | back 200 slows (hyporflexia) |
front 201 In terms of mitochondria, cardiac muscle cells resemble A. slow oxidative skeletal muscle cells B. fast oxidative-glycolytic skeletal muscle cells C. fast glycolytic skeletal muscle cells | back 201 A. slow oxidative skeletal muscle cells |
front 202 Elderly persons often lose overall flexibility due to the conversion of fast glycolytic skeletal muscle fibers into fast oxidative glycolytic skeletal muscle fibers. A. True B. False | back 202 B. False |
front 203 A state of decreased levels of calcium circulating in the blood (hypcalcemia) will not effect smooth muscle contractions. A. True B. False | back 203 B. False |
front 204 A virus that invades the body and initiates muscle protein destruction leaves ________ muscle fibers most vulnerable to the virus. | back 204 red muscle fibers |
front 205  Which somatic region is the dermatome? Options:
| back 205 1. A |
front 206 The advantage of engaging in regular strength training at the gym versus taking anabolic steroids to build muscle mass include the following. Select all that apply. A. Regular strength training increases basal metabolic rate and therefore better weight control. B. Regular injections of anabolic steroids increases the chances of causing liver and kidney damage. C. Regular injections of anabolic steroids increases the risk of heart disease. D. Regular strength training increases bone deposition and therefore bone strength. | back 206 A. Regular strength training increases basal metabolic rate and therefore better weight control. B. Regular injections of anabolic steroids increases the chances of causing liver and kidney damage. C. Regular injections of anabolic steroids increases the risk of heart disease. D. Regular strength training increases bone deposition and therefore bone strength. |
front 207 As persons age, ATP will be expended more ____________ in skeletal muscle tissue. | back 207 slowly |
front 208 _____________ can be caused by either electrical or chemical stimuli in muscles. | back 208 electrical excitability |
front 209 As persons age there becomes a greater proportion of fast ___________ skeletal muscle fibers. | back 209 slow oxidative skeletal muscle fibers |
front 210 As persons age more or less aerobic cellular respiration will be used to generate ATP in skeletal muscle tissue | back 210 more |
front 211 When myosin heads pivot, they pull the thin filaments towards the ______________ | back 211 M line |
front 212 During contraction of a cardiac muscle cell A. both the I and A bands lengthen B. neither the H band nor the I band shortens C. both the H and I bands shorten D. the H band shortens while the A band lengthens | back 212 C. both the H and I bands shorten |
front 213 Drugs that block the acetylecholine receptors located on muscle tissue sarcolemma would cause complete cessation of ______________ muscle contractions | back 213 skeletal |
front 214 When muscle action potentials enter transverse tubules, ___________ __________(chemical symbol __________ ) is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. | back 214
|
front 215 Muscle action potentials arise at the _______________ junction when acetylcholine stimulates the sarcolemma. | back 215 neuromuscular |
front 216 Lifting a cell phone off of a counter to your ear is an example of a/an __________________ | back 216 concentric isotonic contraction |
front 217 The _____________ filament mechanism is the process in which the myosin heads attach to a “walk” along the thin filaments. | back 217 sliding filament mechnism |
front 218 The enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft is _______________ | back 218 acetylcholinesterase |
front 219 The tension generated is not enough to exceed the resistance of the object to be moved and the muscle does not change its length in a/an ______________ contraction | back 219 isometric |
front 220 When a skeletal muscle is not stimulated and not contracting, calcium ions are stored in the __________________ | back 220 sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 221 When a sarcomere contracts, which bands/zones shorten? | back 221 H bands & I bands |
front 222 Strength and endurance training can provide many health benefits. Select all that apply. A. lengthened bones B. injury prevention C. improved physical form D. increased fatigue and stress E. stronger bones F. increased flexibility | back 222 B. injury prevention C. improved physical form E. stronger bones F. increased flexibility |
front 223 For hypertrophy to occur in skeletal muscle fibers, which subcellular changes must be seen in a muscle cell? Select all that apply. A. Myosin and actin will increase in numbers. B. Muscle cells will increase in numbers. C. The amount of sarcoplasm will increase. D. The muscle cell will split and grow. | back 223 A. Myosin and actin will increase in numbers. C. The amount of sarcoplasm will increase. |
front 224 Which skeletal muscle fiber type will generate the most force during contraction? | back 224 fast glycotic fiber |
front 225 Smooth muscle is so-named because of the absence of striations noted in its muscle cells. The absence of striations indicates that thin and thick filaments are consequently absent. A. True B. False | back 225 B. False |
front 226  Which somatic region is the myotome?
| back 226 3. B |
front 227 Blood vessel diameter fluctuates between being constricted and being dilated. This is the primary contributor to blood pressure. In order for blood vessels (arterioles) to maintain a steady pressure, there must be a prolonged presence of what ion in the smooth muscle cell's cytosol? | back 227 calcium (Ca) |
front 228 A tight ligature wrapped around the forearm can destroy muscle fibers which get replaced by fibrous connective tissue and leads to a permanent shortening (contracture) of the forearm muscles. Which feature of muscle tissue will be compromised by the presence of this scar tissue? | back 228 extensibility |
front 229 As persons age, muscle tissue gets replaced by (select all that apply) A. fat B. fibrous connective tissue C. bone tissue D. lymph E. adipose tissue | back 229 A. fat B. fibrous connective tissue E. adipose tissue |
front 230 Pushing against an immovable object is an example of which strength-training exercise A. isotonic B. concentric C. eccentric D. isometric | back 230 D. isometric |
front 231 The heart's autorhymicity is eliminated when a person exercises.
| back 231 false |
front 232 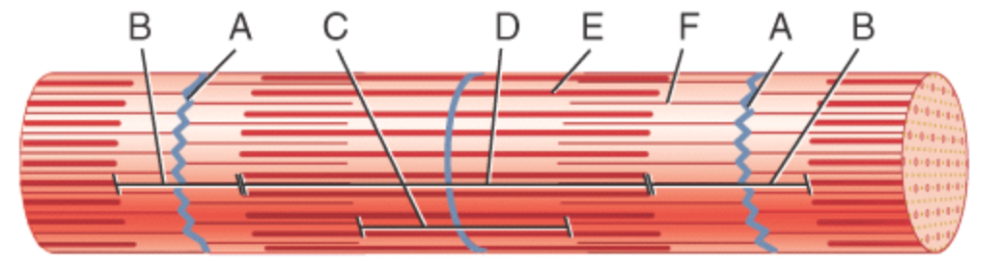 Which of the following anchors A in the figure to myomesin? | back 232 titin |
front 233 After a contraction, calcium in the sarcoplasm must be removed in order for sarcomere relaxation. Where does the calcium get transported to and how? | back 233 where: it gets transported into sarcoplasmic reticulum; how: it gets actively transported |
front 234 Which of the following could help explain the decrease in muscle strength as your parents age from their twenties to their sixties? Select all that apply. A. skeletal muscle is replaced by fibrous connective tissue B. up to fifty percent loss of overall muscle mass C. atrophy caused by loss of all skeletal muscle fiber types D. regular aerobic work-outs at the gym E. smooth muscle is replaced by adipose tissue | back 234 A. skeletal muscle is replaced by fibrous connective tissue B. up to fifty percent loss of overall muscle mass |
front 235 When individuals discuss white meat and dark meat, which fibers would be classified as dark meat? Select all that apply. A. slow oxidative fibers B. fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers C. fast glycolytic fibers | back 235 A. slow oxidative fibers B. fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers |
front 236 By the end of the fifth week, approximately 30 days, ____________ somites are formed. | back 236 42-44 pairs of somites are formed |
front 237 It is conceivable that 50% of your muscle mass could be lost up to ten years prior to your notice of loss in muscle strength.
| back 237 true |
front 238 Muscles of the upper limb develop from the embryonic ___________ while muscles of the lower limb develop from the embryonic _____________. | back 238
|
front 239 Which statement best describes smooth muscle? A. No transverse tubules are present in smooth muscle. B. Smooth muscle cells have well-developed sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Smooth muscle contains the same proteins as cardiac and skeletal muscle. D. Smooth muscle consists of desmosomes in the form of intercalated discs. | back 239 A. No transverse tubules are present in smooth muscle. |
front 240 ______________ steroids are testosterone-like and can be abused by individuals to increase muscle size. | back 240 Anabolic steroids |
front 241 Disruption of embryonic paraxial mesoderm formation will ultimately interfere with the further development of ________________ | back 241 skeletal muscle |
front 242 Calcium in cardiac muscle is stored in _________________ | back 242 sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) |
front 243 Anabolic steroids, also known as androgenic steroids, promote growth and develop masculine characteristics. What type of actions do anabolic steroids have on skeletal muscles? Select all that apply. A. have the same effect on the body as human growth hormone B. inhibit breakdown of muscle tissue C. increase protein synthesis D. improve protein consumption | back 243 B. inhibit breakdown of muscle tissue C. increase protein synthesis |
front 244 A bands, I bands, H bands and sarcomeres are present in (select all that apply) A. smooth muscle tissue B. cardiac muscle tissue C. skeletal muscle tissue | back 244 B. cardiac muscle tissue C. skeletal muscle tissue |
front 245 ____________ allow you to respond super-quickly with short bursts of energy. | back 245 Fast glycotic fibers |
front 246 Smooth muscle is so-named because of the absence of striations noted in its muscle cells. The absence of striations indicates that the actin and myosin proteins are consequently absent.
| back 246 2. false |
front 247 Dense bodies are connected to each other by ________________ | back 247 intermediate filaments |
front 248 ___________ muscle stabalizes body positions | back 248 skeletal |
front 249 Which muscle(s) is/are striated and voluntary? | back 249 skeletal |
front 250 In smooth muscle, instead of pulling against Z discs, myofilaments pull against ___________ bodies. | back 250 dense bodies |
front 251 Once calcium flows into a muscle fiber, the events of contraction are set into motion. Why does it take longer for calcium ions to reach the myofilaments in a smooth muscle fiber than it does in a skeletal muscle fiber? | back 251 because skeletal muscle fibers have transverse tubules to facilitate the flow of calciuum |
front 252 Multiunit smooth muscle fibers that contract like skeletal muscle fibers, i.e. individually, do so because _______________ | back 252 there are no gap junctions |
front 253 A virus that invades the epimysium of skeletal muscle tissue will also be found within the epimysium of cardiac muscle tissue.
| back 253 false |
front 254 After death, rigor mortis occurs (muscles cannot contract or stretch) because cellular membranes become leaky and the calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum enters the sarcoplasm of the muscle. After 24 hours, however, the muscles relax again. In order for that to occur, what must be broken down? | back 254 cross-bridges |
front 255 Smooth muscle tone is possible due to _________________ | back 255 prolonged calcium presence in the sarcoplasm |
front 256 ____________ muscle is the only muscular tissue with good regeneration capability. | back 256 Smooth muscle |
front 257 In terms of function, cardiac muscle contractions resemble ___________ smooth muscle contractions. A. Single-unit B. Multi-unit | back 257 A. Single-unit |
front 258 When do muscle tissues stretch best? A. The muscle cell temperature is warm. B. The muscle cell temperature is cold. C. The temperatures are the same as the external environment. D. The temperature does not affect muscles' ability to stretch. | back 258 A. The muscle cell temperature is warm. |
front 259 During senescence (aging) as more of the skeletal muscle fibers convert to slow oxidative skeletal muscle fibers, aerobic and strength training exercises are not recommended.
| back 259 2. false |
front 260 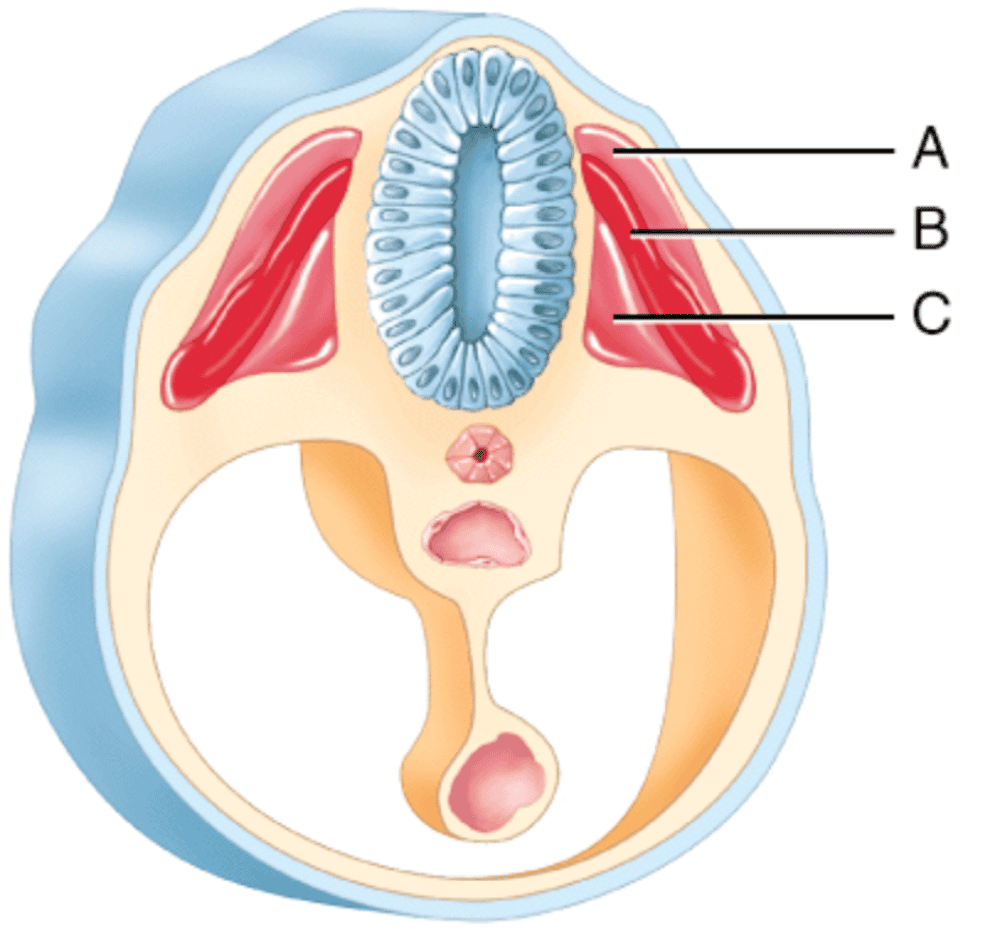 Which somatic region will develop into skeletal muscles? 1. C 2. A 3. B | back 260 3. B |
front 261 Which of the following would you most likely expect to observe in a seventy-year old male patient? Assume no great fluctuations in weight or health. A. a complete inability to perform any aerobic or strength training exercises B. greater proportion of fibrous connective tissue compared to when he was thirty five years old C. lesser proportion of adipose tissue as compared to when he was thirty-five years old D. overall number of skeletal muscle fibers have been converted to cardiac and smooth muscle fibers | back 261 B. greater proportion of fibrous connective tissue compared to when he was thirty five years old |
front 262 Which contributes to the loss of muscle mass with aging? A. decreased strength B. increased aerobic exercise C. increased number of SO fibers D. decreased physical activity | back 262 D. decreased physical activity |
front 263 Age-related muscle mass loss can be reversed by chronic bed-rest.
| back 263 false |
front 264 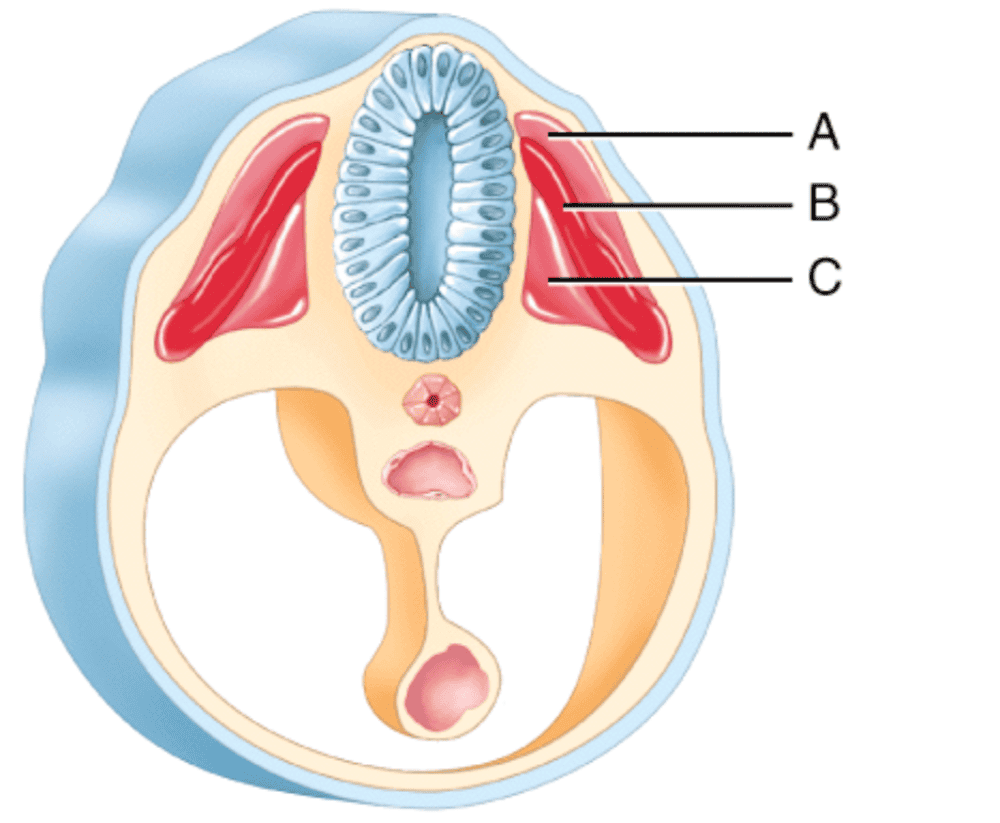 Which somatic region becomes part of the integumentary region composed of dense irregular connective tissue?
| back 264 1. A |
front 265 Failure of the paraxial mesoderm to segment during embryonic development will affect further development of (select all that apply) A. muscles of the back B. muscles of the lower limb C. the brain D. dermis of the skin E. chewing muscles | back 265 A. muscles of the back B. muscles of the lower limb D. dermis of the skin E. chewing muscles |
front 266 three athletes' muscle fibers were analyzed in their leg muscles.
Which athlete is probably a sprinter? A. Athlete 1 B. Athlete 2 C. Athlete 3 | back 266 C. Athlete 3 |
front 267 Three athletes' muscle fibers were analyzed in their leg muscles.
Which athlete is probably a distance runner? A. Athlete 1 B. Athlete 2 C. Athlete 3 | back 267 A. Athlete 1 |
front 268 Muscles that tire quickly and rely on anaerobic respiration will have contractions that are A. moderate B. fast C. slow | back 268 B. fast |
front 269 Fast glycolytic fibers produce more tension because they have more __________________ | back 269 have more myosin and actin cross-bridges |
front 270 ___________ filaments of your postural muscles are composed of actin, nebulin, troponin and tropomyosin. | back 270 thin |
front 271 The ability to store urine in the bladder or feces in the rectum prior to voiding is dependent upon _______________ muscle sphincters. Select all that apply. A. nonstriated B. striated C. skeletal D. smooth | back 271 A. nonstriated B. striated C. skeletal D. smooth |
front 272 In smooth muscle most of the calcium comes from __________________ | back 272 interstitial fluid |
front 273 ______________ smooth muscle cells contract independently of each other and rarely contain gap junctions. | back 273 Multi-unit |
front 274 A virus that invades the connective tissue of visceral smooth muscle will be discovered in the ________________ | back 274 endomysium |
front 275 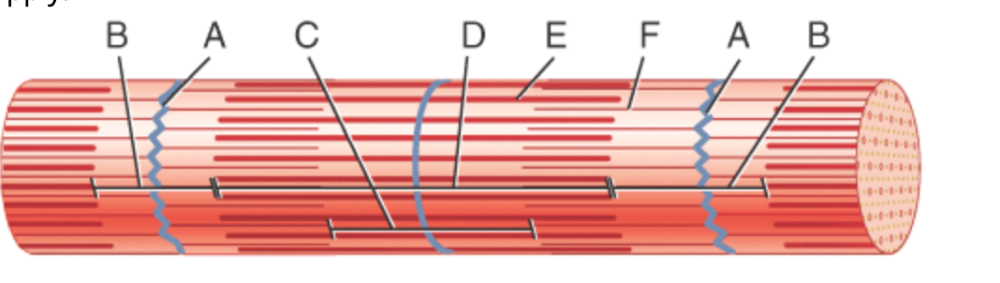 In a maximally contracted muscle, which of the following disappears entirely? Select all that apply.
| back 275 3. C 4. B |
front 276 ____________ has an intracellular cytoskeleton composed of intermediate filaments. | back 276 Smooth muscle |
front 277 Goosebumps are caused by _______________ | back 277 multi-unit smooth muscle |
front 278 A drug that selectively binds the desmin protein will interfere with ___________________. | back 278 the contraction of smooth muscle cells |
front 279 Increasing extracellular levels of calcium will have the least affect on __________________ muscle tissue when considering making the calcium available intracellularly for contraction. | back 279 smooth |
front 280 Individuals who change their training regimen from sprinting to long-distance running will experience changes in muscle cell types from: A. fast glycolytic into slow oxidative B. fast glycolytic into fast oxidative-glycolytic C. fast oxidative-glycolytic into fast glycolytic D. slow oxidative into fast glycolytic | back 280 B. fast glycolytic into fast oxidative-glycolytic |
front 281 Cardiac muscle contraction is initiated by an impulse received from somatic motor neurons.
| back 281 false |
front 282 Which property do cardiac and smooth muscle share? A. gap junctions B. sarcomeres C. dense bodies D. intercalated discs | back 282 A. gap junctions |
front 283 Decreased levels of calcium (hypocalcemia) will have the most profound effect on ________________ muscle contraction. | back 283 smooth muscle contraction |
front 284 Which part of the somite develops into the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccyx bones? | back 284 sclerotome |
front 285 Damage to embryonic somites will inhibit the formation of the muscles responsible for chewing.
| back 285
|
front 286 Electrical signaling between cardiac cells is due to _____________-- | back 286 gap junctions |
front 287  Which somatic region will develop into the dermis?
| back 287 1. A |
front 288 Which of the following unique features of cardiac muscle cells accounts for synchronous contractions? A. they are striated B. they are involuntary C. they have intercalated discs D. they are nonstriated | back 288 C. they have intercalated discs |
front 289 Disruption of the ________ of cardiac muscle tissue would interfere with the heart's ability to beat in synchronous fashion | back 289 gap junctions |
front 290 The stomach, urinary bladder and small intestines will have A. cardiac muscle B. single-unit smooth muscle C. skeletal muscle D. multi-unit smooth muscle | back 290 B. single-unit smooth muscle |
front 291 _________________ smooth muscle cells contract independently of each other. | back 291 Visceral, Single-unit |
front 292 The inability to internalize signals from the outside of a cardiac muscle cell to the interior reflects a dysfunction of the cell's _____________. | back 292 transverse tubules |
front 293 An Olympic athlete who trains for eight hours a day most likely develops a ___________ enlarged heart. | back 293 physiological |
front 294 Examination of tissue obtained from a muscle biopsy reveals alternating light and dark protein bands. Deduce from where this biopsy was taken? Select all that apply. A. the heart B. the stomach C. the bronchioles (airway) D. a blood vessel E. the gastrocnemius (calf muscle | back 294 A. the heart E. the gastrocnemius (calf muscle |
front 295 During fibrillation the chambers of the heart are unable to adequately relax and fill with blood. Which of the following describes how the healthy heart achieves optimal filling of its chambers? A. by increasing the number of gap junctions used for each cardiac muscle contraction B. by eliminating all of the calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of cardiac muscle fibers C. by allowing sustained contractions of cardiac muscle tissue (tetanus) D. by maintaining cardiac muscle contractions longer than skeletal muscle contractions | back 295 D. by maintaining cardiac muscle contractions longer than skeletal muscle contractions |
front 296 Action potentials in cardiac muscle tissue are generated by neurotransmitters (chemical messengers).
| back 296 false |
front 297 The actin and myosin myofilaments are arranged into sarcomeres in cardiac muscle tissue.
| back 297 true |
front 298 Intermediate filaments have a role in smooth muscle tissue analogous to the role of ________ in skeletal muscle tissue. | back 298 dystrophin |
front 299 Smooth muscle contractions within a blood vessel serve to decrease the size of the vessel's opening (vasoconstriction). In this particular instance these smooth muscle contractions result in _____________ blood pressure within the blood vessel | back 299 higher |
front 300 What can you do to slow down the typical progressive muscle mass declines associated with aging? Select all that apply. A. lift weights B. increase lipid intake C. exercise aerobically D .reduce protein intake | back 300 A. lift weights C. exercise aerobically |
front 301 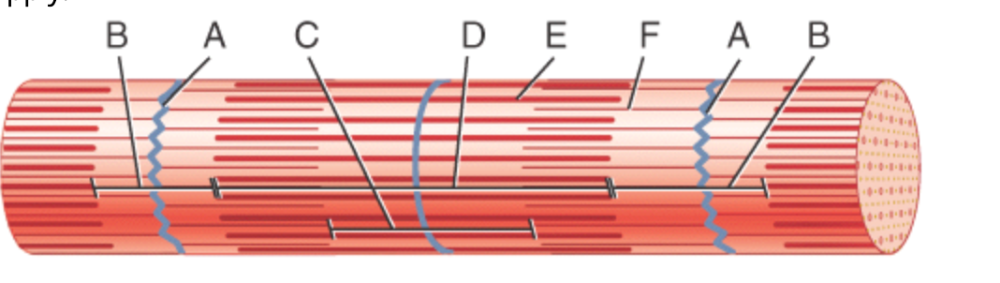 Sarcomeres that display only D with no B and no C would be true of a muscle that is __________________ | back 301 maximally contracted |
front 302 _______________ is a structural protein that allows for a lot of the elasticity and extensibility exhibited in myofibrils. | back 302 titin |
front 303 Which is a function of muscle? Select all that apply. A. protection of underlying tissues B. pushing eggs and sperm C. storage of material in intestines D. shivering E. lubrication F. maintaining postures | back 303 B. pushing eggs and sperm C. storage of material in intestines D. shivering F. maintaining postures |
front 304 Calcium plays an important role in successful skeletal muscle contractions. Identify all of the places where voltage-gated calcium channels occur that are relevant to skeletal muscle contractions. Select all that apply. A. synaptic end bulbs B. thin filaments C. motor end plate D. transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum interface | back 304 A. synaptic end bulbs D. transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum interface |
front 305 ____________ is a structural protein that helps regulate the length and tension of thin filaments. | back 305 Nebulin |
front 306 The contractile proteins in all three types of muscle tissue are ___________ and __________ | back 306 actin & myosin |
front 307 Which myofibril proteins of the slow oxidative skeletal muscle fibers generate force during a contraction? | back 307 contractile proteins |
front 308 This fiber is intermediate in diameter, has lots of myoglobin, can contract quickly and has moderate resistance to fatigue. | back 308 fast oxidative-glycolytic |
front 309 When you become a grandparent around age sixty-five, which of the following will be the first activity that noticeably becomes more difficult to do? A. kissing your granddaughter goodnight B. racing your grandson on bicycles C. hugging your grandson D. throwing a ball to your granddaughter | back 309 b. racing your grandson on bicycles |
front 310 Much of the heat in the body is produced by __________ muscle | back 310 skeletal muscle |
front 311 In an oxygen-depleted environment, which skeletal muscle fiber(s) will be least acutely effected? | back 311 fast glycotic |
front 312 Myoglobin is most abundant in which skeletal muscle fiber type? | back 312 slow oxidative fiber |
front 313 At what age would you most likely be if your muscle mass dropped from 60 pounds (27 kg) to 54 pounds (24.5 kg)?
| back 313 2. 70 yrs |
front 314 Frank wants to enter his triathlon but is unsure he is physically ready. He consults his A&P teacher about what type of muscle fibers he can develop. What explanation do you expect his teacher to give? A. Repeated stimulation of endurance training activities will just cause hypertrophy in the fibers that are preexisting. B. All fibers are genetically predetermined and cannot be changed. C. Repeated stimulation of endurance training activities will help fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers develop from fast oxidative fibers. D. Over time, with appropriate endurance training, all fibers can be changed in slow oxidative and fast oxidative-glycolytic | back 314 C. Repeated stimulation of endurance training activities will help fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers develop from fast oxidative fibers. |
front 315 Assisted-living facilities (nursing homes) for the elderly should not provide a work-out room for their clients since exercise is not effective in older people.
| back 315 false |
front 316 When a skeletal muscle is stretched, the A. A band will decrease B. I band will increase C. I band will decrease D. A band will increase | back 316 B. I band will increase |
front 317 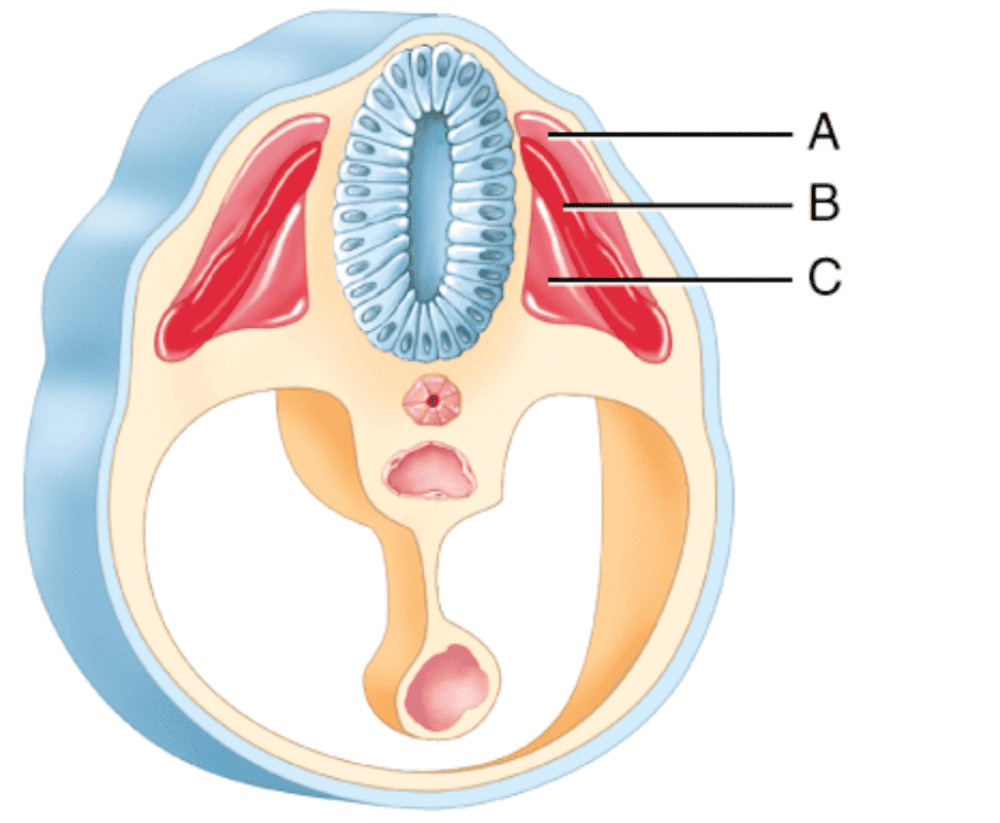 Which somatic region develops to protect the spinal cord?
| back 317
|
front 318 What do intercalated discs and the ligand gates on motor end plates have in common? | back 318 Both are involved in depolarization of the cellular membrane |
front 319 What is the relationship between cardiac and skeletal muscle? Select all that apply. A. Cardiac and skeletal muscle have different regulatory proteins used in muscle contraction. B. In cardiac and skeletal muscle, myosin will hydrolyze ATP before crossbridges will form. C. The method by which calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum is the same in cardiac and skeletal muscle. D. In cardiac and skeletal muscle, crossbridges will not detach unless myosin binds to an ATP molecule. | back 319 B. In cardiac and skeletal muscle, myosin will hydrolyze ATP before crossbridges will form. D. In cardiac and skeletal muscle, crossbridges will not detach unless myosin binds to an ATP molecule. |
front 320 Harvey was recently diagnosed with myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disease that causes the number of functional acetylcholine receptors in the motor end plate to decrease. Various drugs can be used to treat this condition. Which of the following mechanisms of such drugs would help relieve the symptoms? A. calcium inhibitors B. acetylcholine inhibitors C. acetylcholinesterase inhibitors D. sodium channel inhibitors | back 320 C. acetylcholinesterase inhibitors |
front 321 Multiunit smooth muscle tissue contracts similarly to skeletal muscle fibers of ____________ motor units. | back 321 small |
front 322 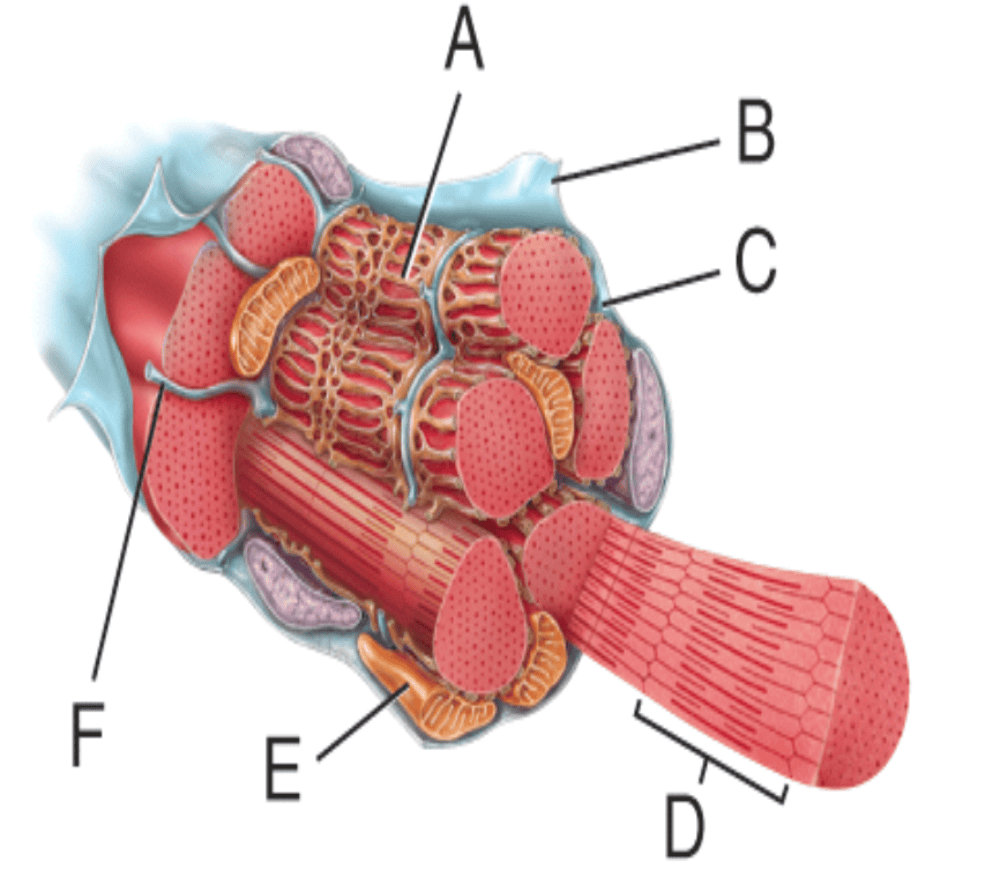 identify letter C | back 322 sarcoplasm |
front 323 ___ (#) terminal cisternae and the T-tubule compose a triad | back 323 2 |
front 324 Myosin attaches to thin filaments and slides them using _______________ as an energy source | back 324 ATP, adenosine triphosphate |
front 325 ____ (#) thin filaments are associated with every thick filament, i.e indicate how many. | back 325 2 |
front 326 An action potential propagating down the transverse tubule causes the terminal cisterns to release _________________ | back 326 calcium |
front 327 Three hearts are dissected from individuals with unknown histories. Two of the three hearts are enlarged. Select all of the possible reasons the two hearts may be enlarged. A. They are from individuals who had low blood pressure histories. B. They are from well-trained professional athletes. C. They are from individuals with a history of heart disease. D. They are from individuals who had arthritis issues. | back 327 B. They are from well-trained professional athletes. C. They are from individuals with a history of heart disease. |
front 328 Muscles that resist fatigue and rely on aerobic oxygen will have contractions that are A. fast B. quick C. slow | back 328 C. slow |
front 329 During the "World's Strongest Man" competition much attention was given to the winner of the giant log lift for setting a record of 212.5 kg (467.5 lbs). You speculate that this athlete has a greater proportion of _________ skeletal muscle fibers than any of the other fiber types. | back 329 fast glycotic |
front 330 A man who has fallen from a ladder is now paraplegic (paralyzed from the waist down). Which type(s) of muscle fibers will be lost as a result? Select all that apply. A. type IIb B. slow oxidative C. fast glycolytic D. type IIa E. type I | back 330 B. slow oxidative D. type IIa |
front 331 A cardiac event that has damaged the heart's pacemaker will have a direct effect on which of the following? A. ability of the cardiac muscle to stretch B. ability of the cardiac muscle to generate nerve impulses C. autorhythmicity D. chemical stimulation of the cardiac muscle | back 331 C. autorhythmicity |
front 332 At twenty-five years of age, John weighed 180 pounds (81 kg) and had a total muscle mass of 76 pounds (34 kg). Approximately how old will John be when his total muscle mass measures 38 pounds (17 kg) given that his total weight has remained fairly constant through time? A. eighty-five years old B. sixty years old C. forty-five years old D. thirty years old | back 332 B. sixty years old |
front 333 A genetic mutation that results in malformation of the actin protein will directly effect the function of which type(s) of muscle tissue? Select all that apply. A. cardiac B. smooth C. skeletal | back 333 A. cardiac B. smooth C. skeletal |
front 334 A genetic mutation that results in malformation of the myosin protein will directly effect the function of which type(s) of muscle tissue? Select all that apply. A. cardiac B. smooth C. skeletal | back 334 A. cardiac B. smooth C. skeletal |
front 335 A virus that destroyed somites would cease further development of the (select all that apply) A. pharyngeal pouches B. intermediate mesoderm C. somitomeres D. vertebrae E. muscles that move the back | back 335 D. vertebrae E. muscles that move the back |
front 336 Failure of mesodermal cells to migrate during the embryonic period will not effect further development of muscle of the A. bladder B. stomach C. heart D. limbs | back 336 D. limbs |
front 337 When muscles undergo resistance training there is trauma to the muscle cells. Which cells are present on the periphery to help repair the damaged area? | back 337 satellite cells |
front 338 Which would have the lowest number of motor units? A. postural muscles in the back B. muscles of the upper arm C. facial muscles D. muscles in the toes E. muscles moving the eyeball | back 338 A. postural muscles in the back |
front 339 These fibers have a high amount of myoglobin, which gives them a reddish or pinkish coloration. Select all that apply. A. slow oxidative fibers B. fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers C. fast glycolytic fibers | back 339 A. slow oxidative fibers B. fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers |
front 340 Aerobic exercises such as running and swimming will have which effect on skeletal muscle? A. increase the number of mitochondria per cell B. increase the number of fascicles C. increase the number of motor units D. increase the number of muscle cells | back 340 A. increase the number of mitochondria per cell |
front 341 Perform these movements: blink your eye, squeeze your calf (soleus muscle), and squeeze your anal sphincter. Which contains fast twitch fibers? A. anal sphincter muscles B. calf muscles (soleus) C. eye muscles | back 341 C. eye muscles |
front 342 Long-distance running and biking will have what effect on skeletal muscle tissue? A. Increase number of muscle cells per muscle cell B. Increase number of mitochondria and myoglobin per muscle cell C. Increase number of motor units D. Increase number of fast glycolytic fibers | back 342 B. Increase number of mitochondria and myoglobin per muscle cell |
front 343 An individual is often fatigued from strength training when she used to be able to withstand high-energy activities. The doctor orders biopsies from her muscles to test for mitochondrial myopathy. Which type of fiber should the doctor not biopsy? A. fast oxidative B. slow oxidative C. fast oxidative-glycolytic | back 343 C. fast oxidative-glycolytic |
front 344 Connective tissues in skeletal muscles function in A. storing creatine phosphate B. regulating frequency of muscle contractions C. depolarizing the membrane D. aligning the myofibrils with the muscle cell membrane E. transmitting mechanical force | back 344 E. transmitting mechanical force |
front 345 Stretching your muscles prior to strength training can be accomplished in less time during the __________ months. | back 345 summer |
front 346 The muscles of athletes from various sports were analyzed during a physiology lab and only one had a high proportion of fast glycolytic fibers relative to slow oxidative fibers. Which type of sport does this athlete most likely participate in? A. two of the choices are correct B. long-distance swimmer C. marathon runner D. sprinter | back 346 D. sprinter |
front 347 Muscle enlargement seen in body builders, for example, is a consequence of muscle _________________ | back 347 hypertrophy |
front 348 A single motor unit will innervate A. a mixture of fiber types B. FOG fibers only C. one fiber type D. FG fibers only | back 348 C. one fiber type |
front 349 Which skeletal muscle fiber type would contain the most thick and thin filaments? A. fast oxidative-glycolytic fiber B. slow oxidative fiber C. fast glycolytic fiber | back 349 C. fast glycolytic fiber |
front 350 Which skeletal muscle fiber type can perform aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration A. slow oxidative fiber B. fast glycolytic fiber C. fast oxidative-glycolytic fiber | back 350 C. fast oxidative-glycolytic fiber |
front 351 __________ will be most abundant in a marathon runner. A. Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers B. FOG fibers C. Fast glycolytic fibers D. Slow oxidative fibers | back 351 D. Slow oxidative fibers |
front 352 Low-intensity activity, such as standing, will recruit A. None of the choices is correct. B. slow oxidative fibers C. fast glycolytic fibers D. fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers | back 352 B. slow oxidative fibers |
front 353 Which skeletal muscle fiber type is the first to be recruited for contractions? | back 353 slow oxidative fiber |
front 354 _______________ allows the heart to stretch without tearing. | back 354 extensibility |
front 355 ___________, ____________, or _______________ muscle initiates its own contractions all throughout one's lifetime. | back 355 Cardiac, visceral, or smooth |
front 356 Picking up a twenty ounce bottle of soda would primarily require the recruitment and activation of ______________ motor units. | back 356 slow oxidative |
front 357 Which of the following words would best indicate the notion that energy for a skeletal muscle fiber is generated anaerobically? A. fast B. slow C. oxidative D. glycolytic | back 357 D. glycolytic |
front 358 _____________ are better suited for a 400-800 meter run. A. Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers B. Slow oxidative fibers C. Slow oxidative fibers and fast glycolytic fibers D. Fast glycolytic fibers | back 358 A. Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers |
front 359 Most body muscles contain _____________ that allow(s) them to exhibit a range of contractile speeds and fatigue resistance. A. one fiber type B. only SO and FOG fiber types C. only FG and SO fiber types D. a mixture of fiber types | back 359 D. a mixture of fiber types |
front 360 Which location would be described if fast glycolytic was the most abundant skeletal muscle fiber type? A. gastrocnemius B. quadriceps femoris group C. biceps brachii and triceps brachii D. trapezius | back 360 C. biceps brachii and triceps brachii |
front 361 The principal tissue in the heart wall is ________________ | back 361 cardiac muscle tissue |
front 362 How is cardiac muscle similar and different from skeletal muscle tissue? (list 1 way it is similar & 1 way it is different) | back 362
|
front 363
| back 363 autorhythmicity |
front 364 What is the effect that autorhythmicity has on the heart? | back 364 it generates these action potentials that cause alternating contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle fibers |
front 365 what are 3 aspects of the structure of cardiac muscle fibers? | back 365
|
front 366 Are nuclei present in cardiac muscle fibers? | back 366 Usually one centrally located nucleus is present, although an occasional cell may have two nuclei |
front 367
| back 367 intercalated discs |
front 368 1. hold cardiac fibers together 2. embedded in intercalated discs | back 368 desmosomes |
front 369 What 2 things are apart of the intercalated discs? | back 369 1. desmosomes 2. gap junctions |
front 370 1. Cell junctions that allow muscle action potentials to spread from one cardiac muscle fiber to its neighbors. 2. allow muscle action potentials to spread from one muscle fiber to its neighbors 3. embedded in intercalated discs | back 370 gap junctions |
front 371 does cardiac muscle tissue have/ is it made up of all 3 types of connective tissue? (the -mysiums) | back 371 no, cardiac muscle tissue has an endomysium, but lacks a perimysium and epimysium |
front 372 Cardiac muscle fibers display autorhythmicity, the ability to ___________________________________ | back 372 repeatedly generate spontaneous action potentials |
front 373 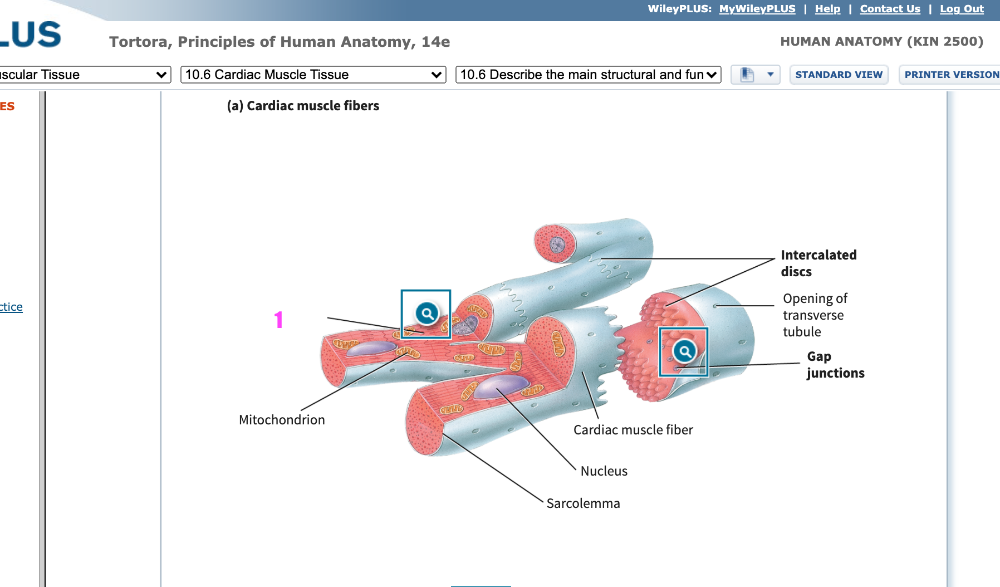 what is #1? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 373 desmosomes |
front 374 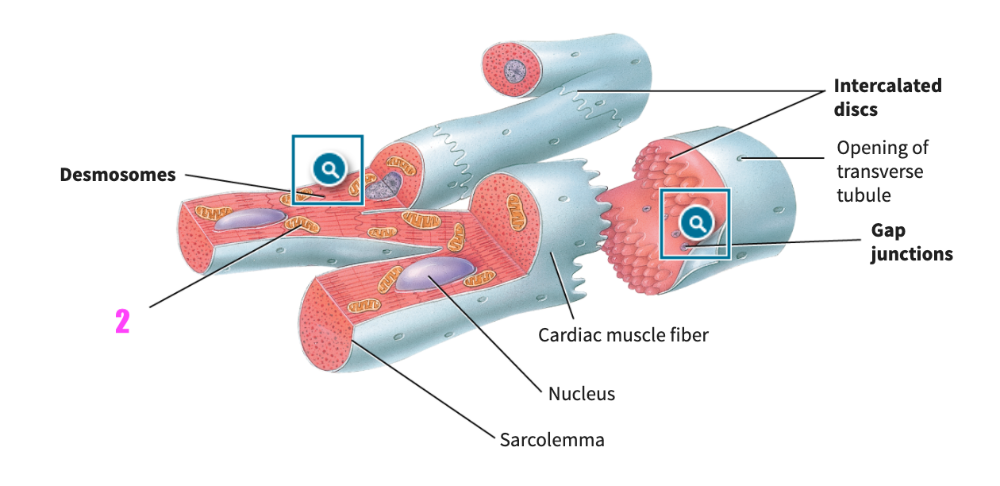 what is #2? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 374 Mitochondrian |
front 375 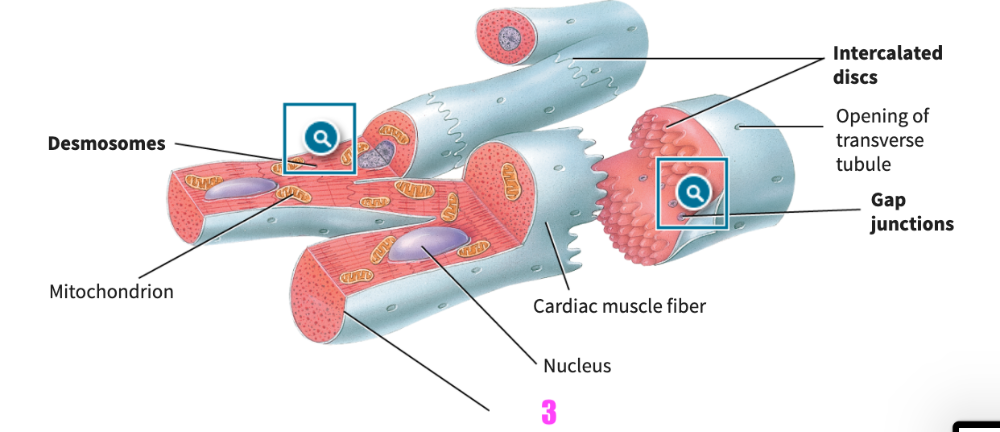 what is #3? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 375 sarcolemma |
front 376 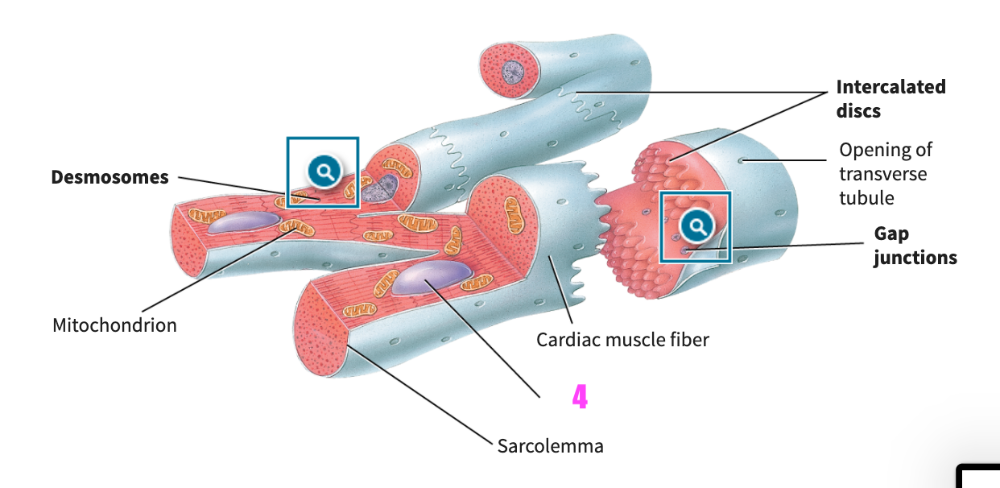 what is #4? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 376 nucleus |
front 377 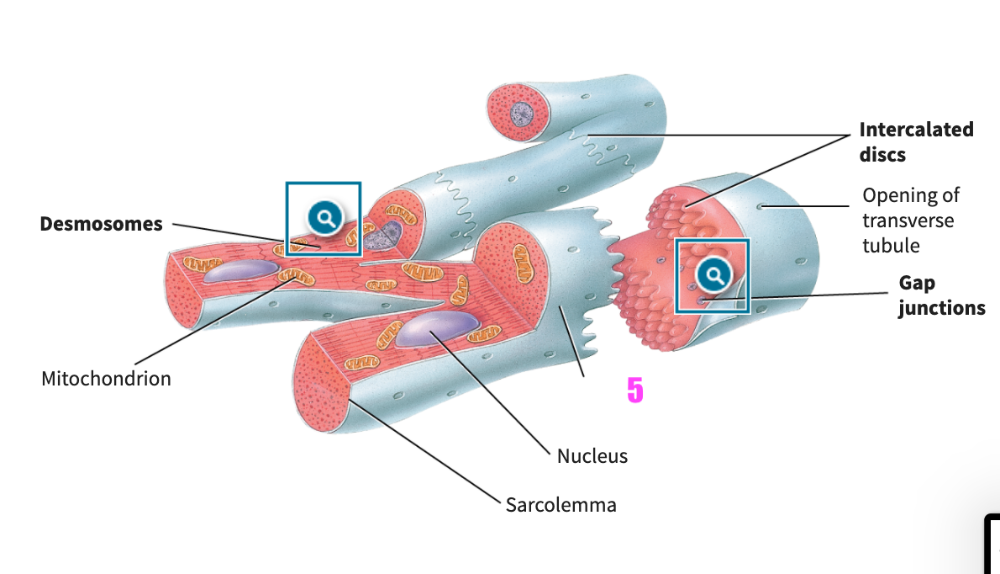 what is #5? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 377 cardiac muscle fiber |
front 378 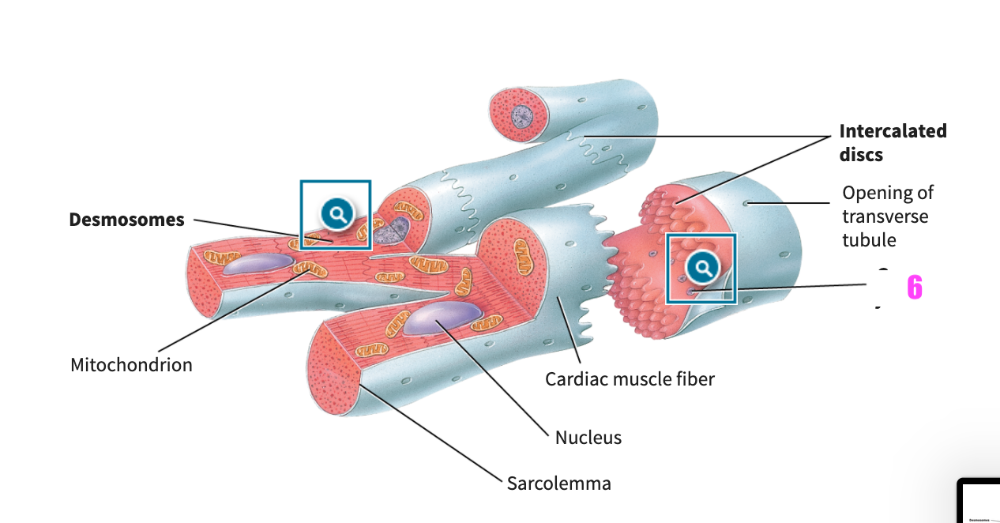 what is #6? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 378 gap junctions |
front 379 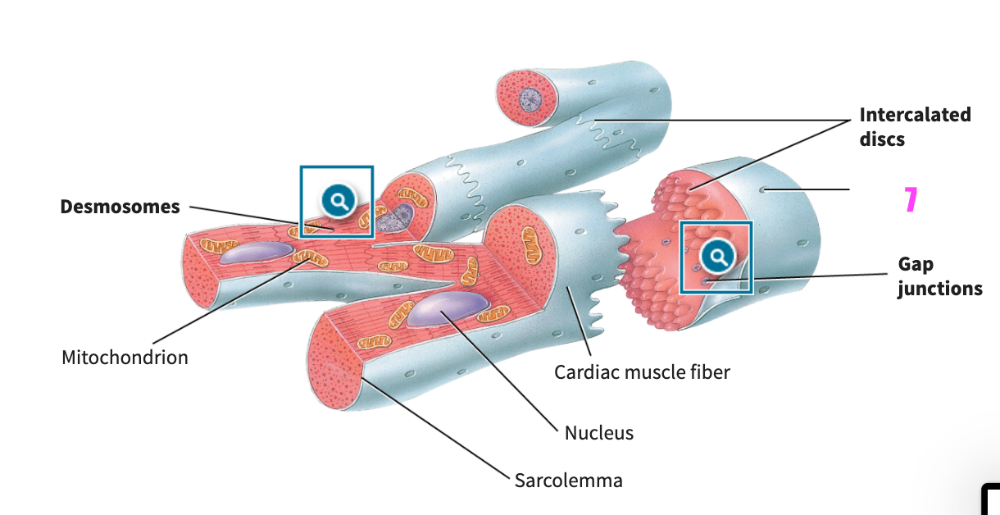 what is #7? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 379 opening of transverse tubule |
front 380 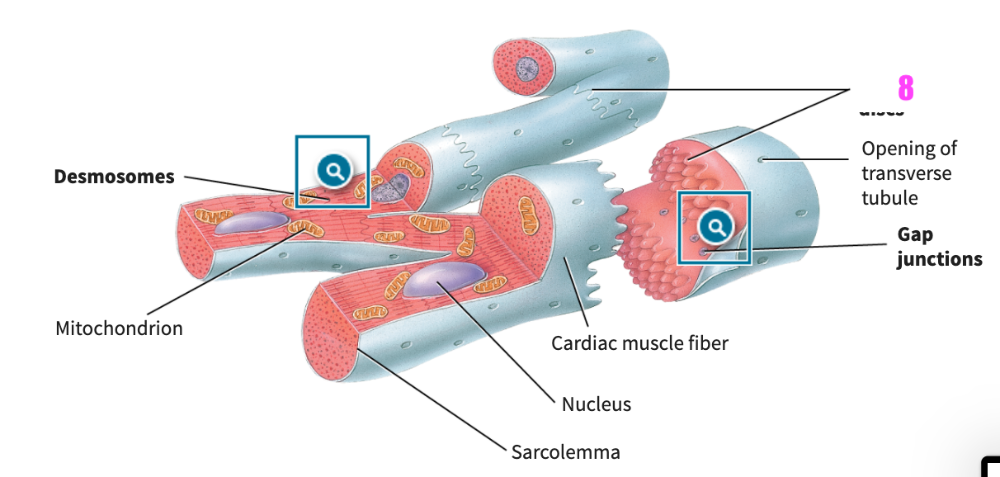 what is #8? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 380 gap junctions |
front 381 What are the functions of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle fibers? | back 381 The intercalated discs contain desmosomes that hold the cardiac muscle fibers together and gap junctions that enable action potentials to be spread from one muscle fiber to another. |
front 382 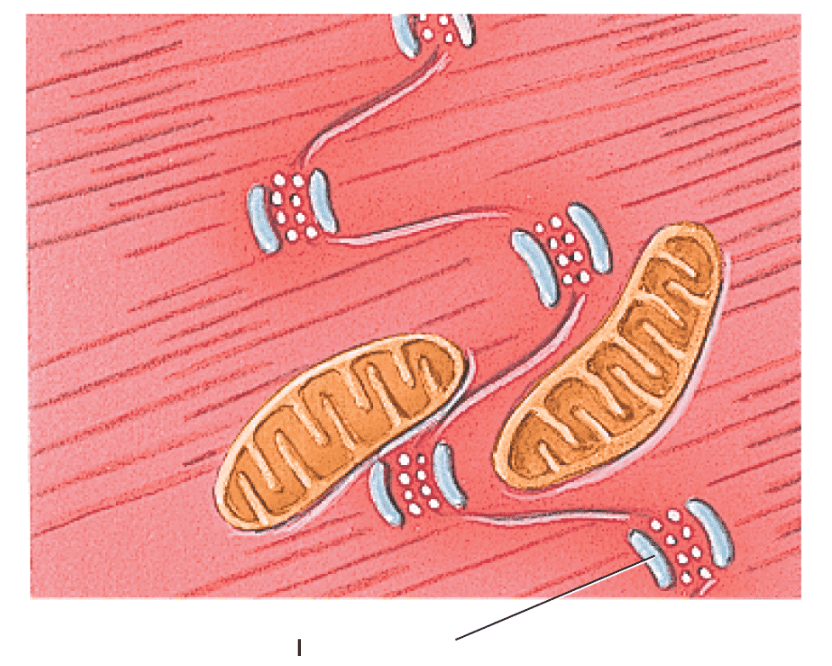 what is this structure? | back 382 desmosomes |
front 383 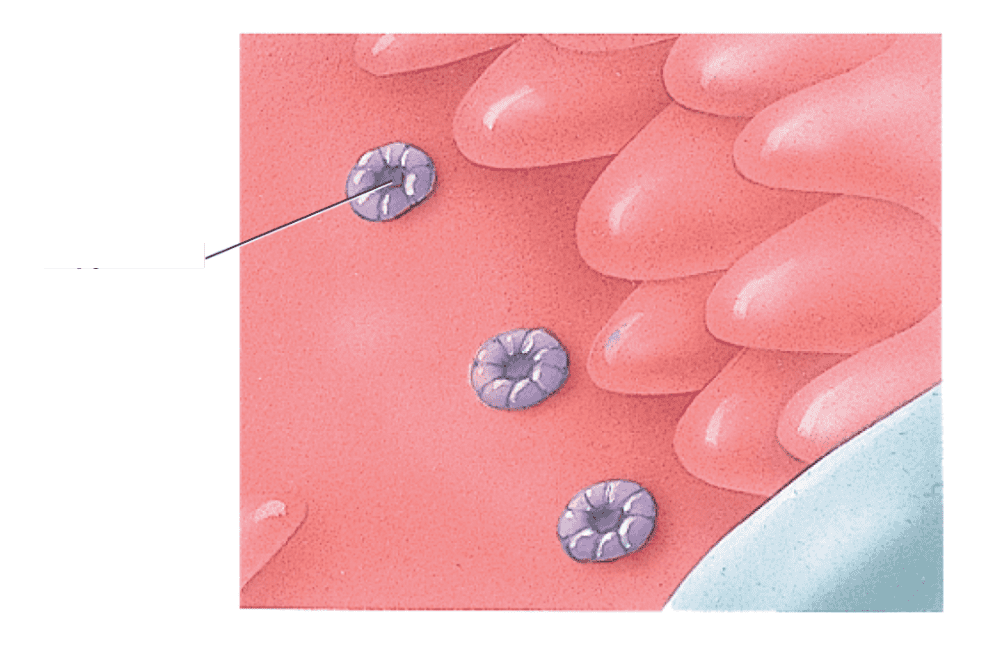 what is this structure? | back 383 gap junctions |
front 384 __________ are larger and more numerous in cardiac muscle fibers than in skeletal muscle fibers. | back 384 Mitochondria |
front 385 Cardiac muscle fibers have the same arrangement of __________ and __________, and the same _________, ___________, and _________, as skeletal muscle fibers | back 385
|
front 386 The ________________ of cardiac muscle are wider but less abundant than those of skeletal muscle; | back 386 transverse (T) tubules |
front 387 In cardiac muscle fibers, there is one T tubule per _________, located at the _______ | back 387
|
front 388 The sarcoplasmic reticulum of cardiac muscle fibers is ______________ than the SR of skeletal muscle fibers. | back 388 somewhat smaller |
front 389 What is the major functional difference b/t cardial & skeletal muscle tissue? | back 389 Under normal resting conditions, cardiac muscle tissue contracts and relaxes about 75 times per minute ⭆This continuous, rhythmic activity is a major functional difference between cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue. |
front 390 two main differences between skeletal & cardiac muscle? 1. 2. | back 390
|
front 391 When can skeletal muscle tissue contract? | back 391 only when stimulated by acetylcholine released by an action potential in a somatic motor neuron |
front 392 when can cardiac muscle contract? | back 392 cardiac muscle tissue can contract without extrinsic (outside) nervous or hormonal stimulation |
front 393 what is cardiac muscle tissue's source of stimulation? | back 393 1. a conducting network of specialized cardiac muscle fibers within the heart [Stimulation from the body's nervous system or endocrine system merely causes the conducting fibers to increase or decrease their rate of discharge] |
front 394 Cardiac muscle tissue remains contracted _________________ than skeletal muscle tissue, allowing time for the chambers of the heart to relax and fill with blood between beat | back 394 10 to 15 times longer |
front 395 cardiac muscle tissues contraction pattern permits the heart rate to increase significantly while preventing _________ | back 395 tetanus |
front 396
| back 396 tetanus |
front 397 Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle fibers can undergo ___________ in response to an increased workload | back 397 hypertrophy |
front 398
| back 398 hypertrophy |
front 399 By contrast, a ________________ is related to significant heart disease | back 399 pathological enlarged heart |
front 400 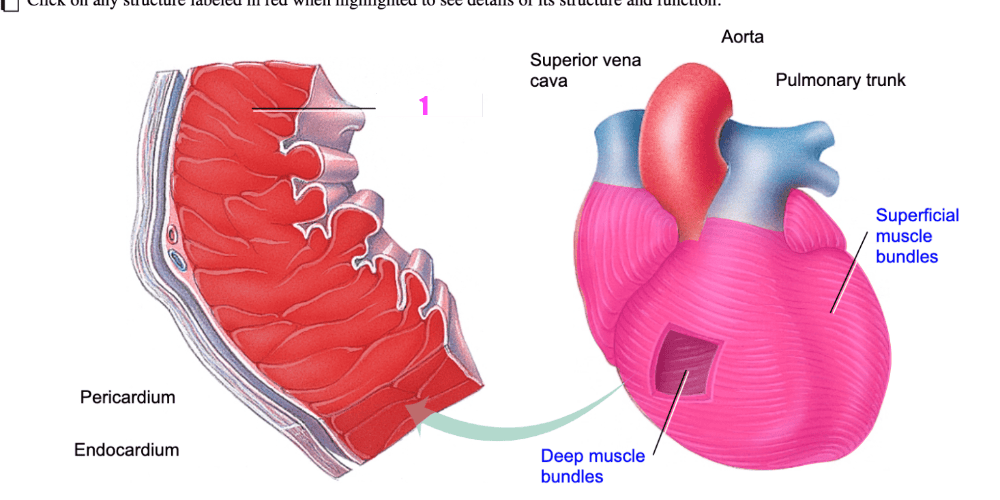 what is #1? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 400 myocardium |
front 401 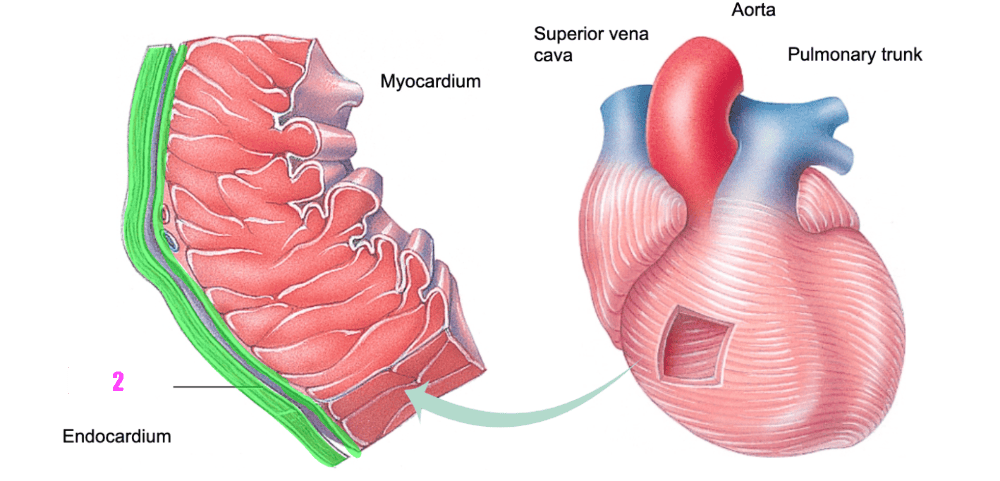 what is #2? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 401 pericardium |
front 402 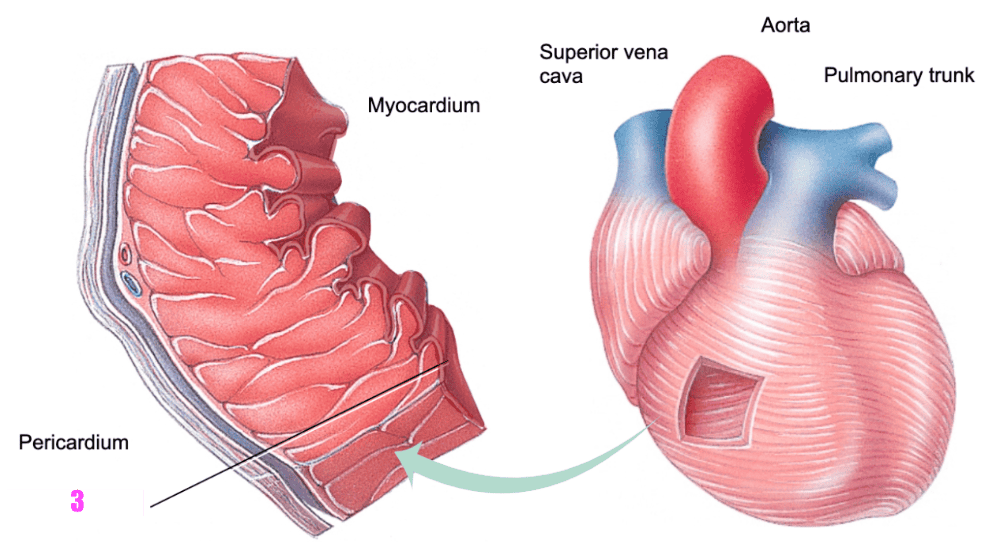 what is #3? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 402 endocardium |
front 403 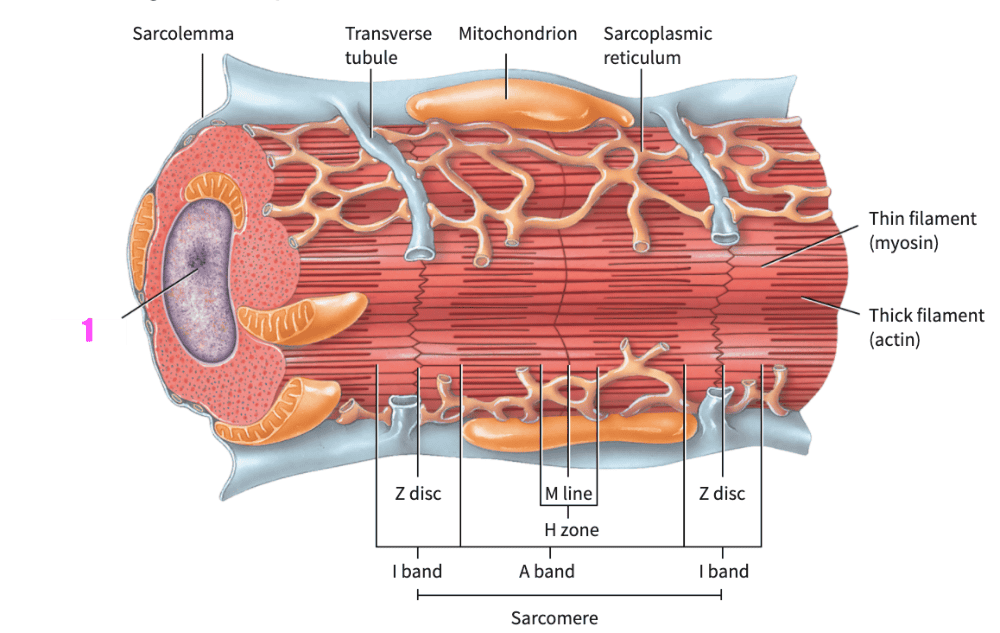 what is #1? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 403 nucleus |
front 404 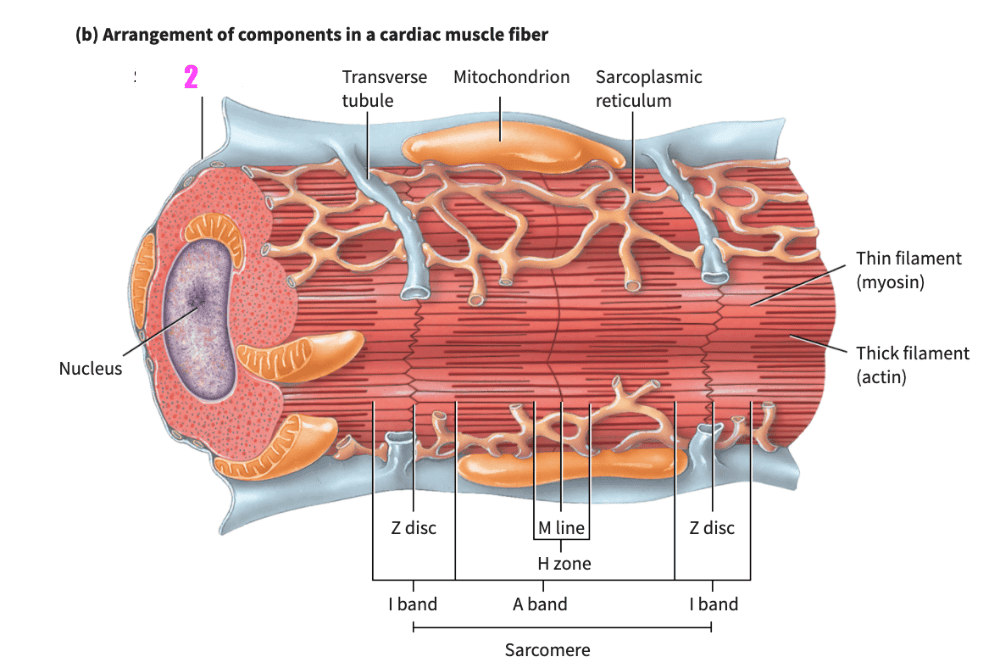 what is #2? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 404 sarcolemma |
front 405 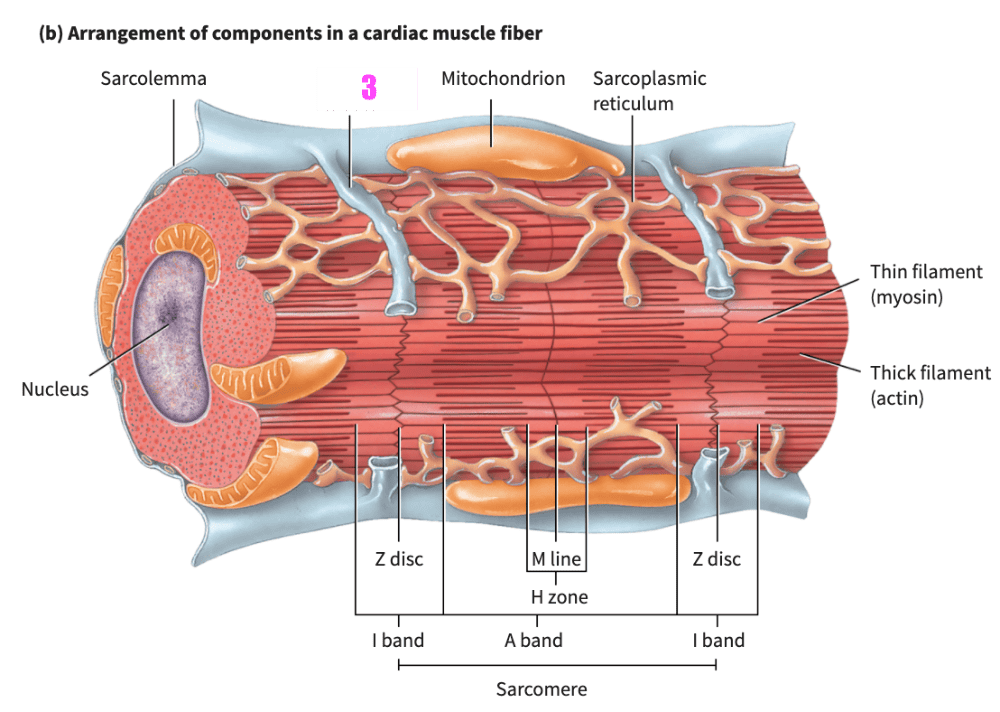 what is #3? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 405 transverse tubule |
front 406 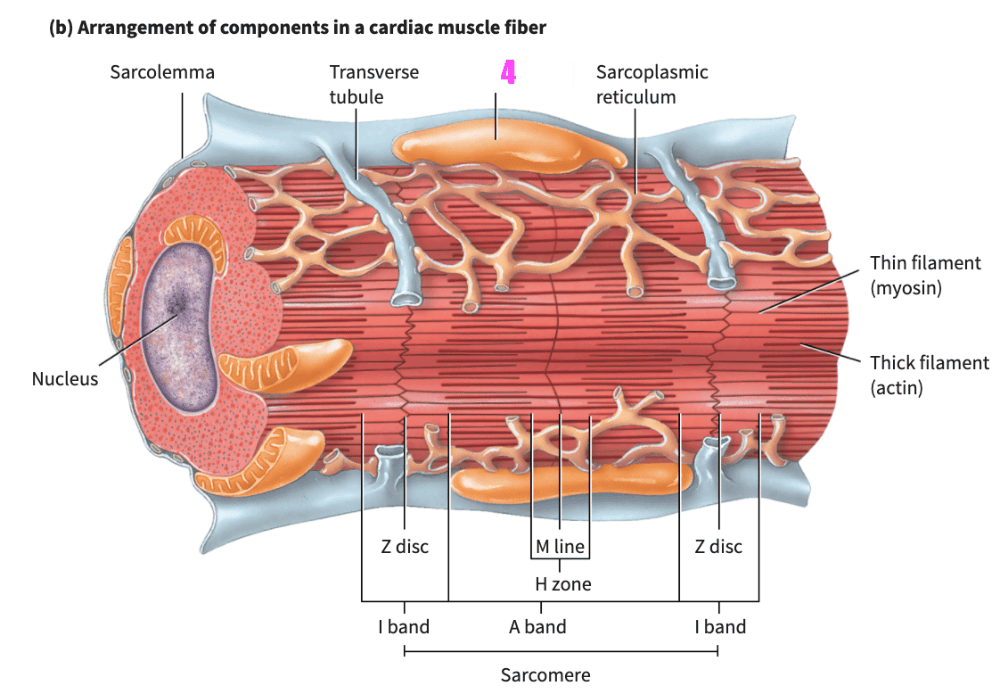 what is #4? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 406 mitochondrian |
front 407 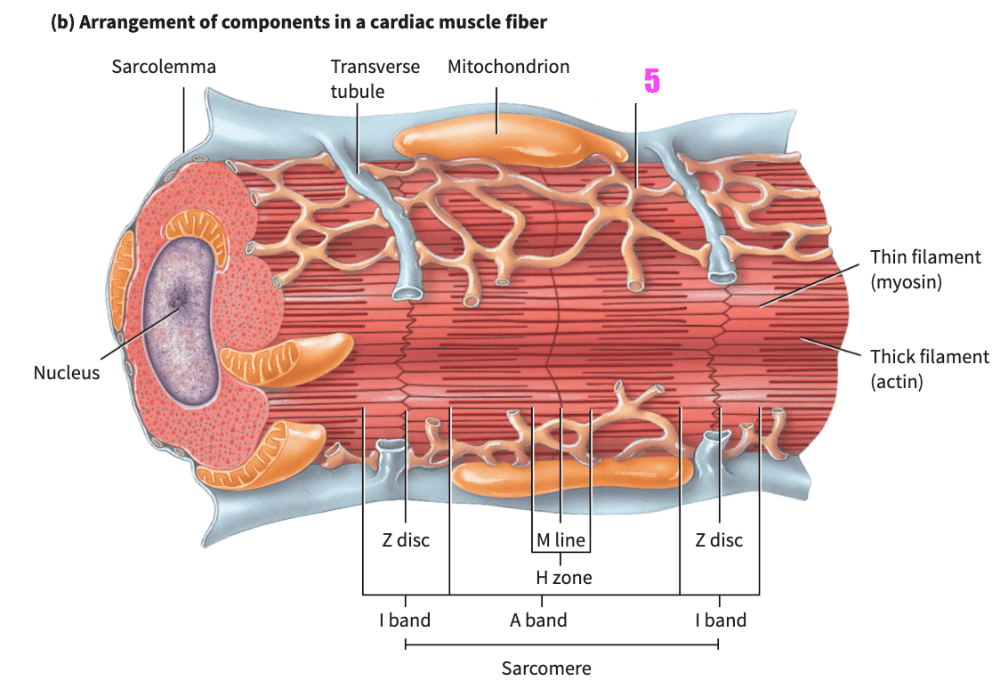 what is #5? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 407 sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 408 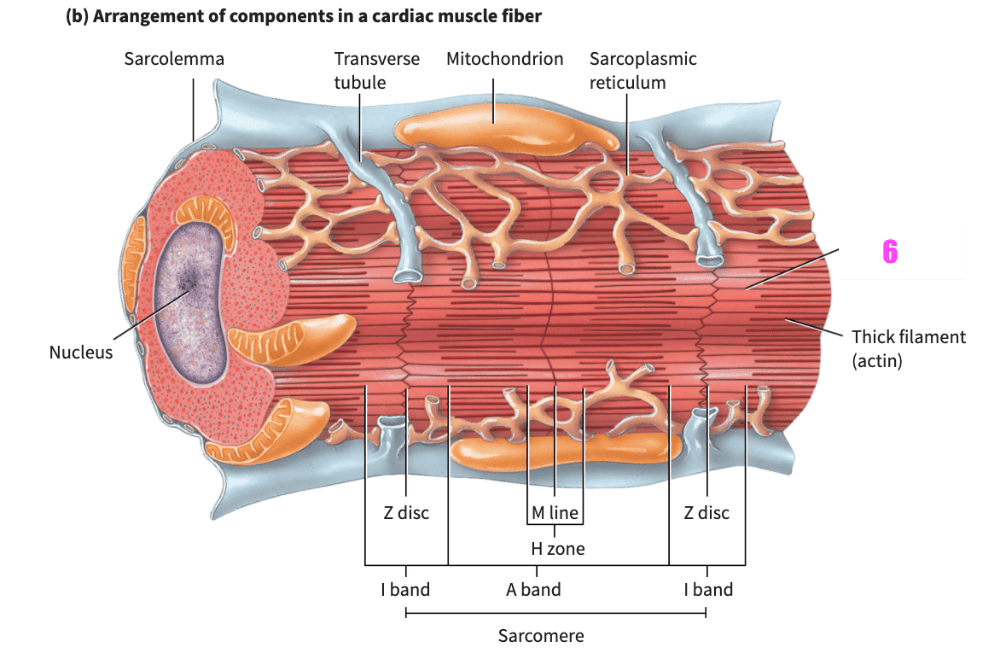 what is #6? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 408 thin filament (myosin) |
front 409 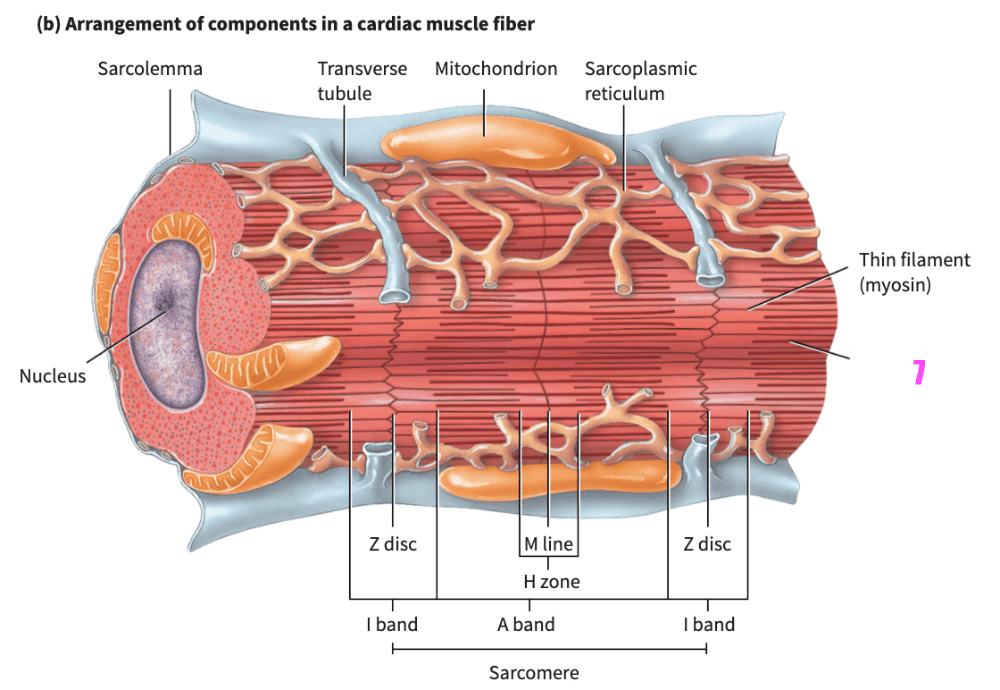 what is #7? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 409 thick filament (actin) |
front 410 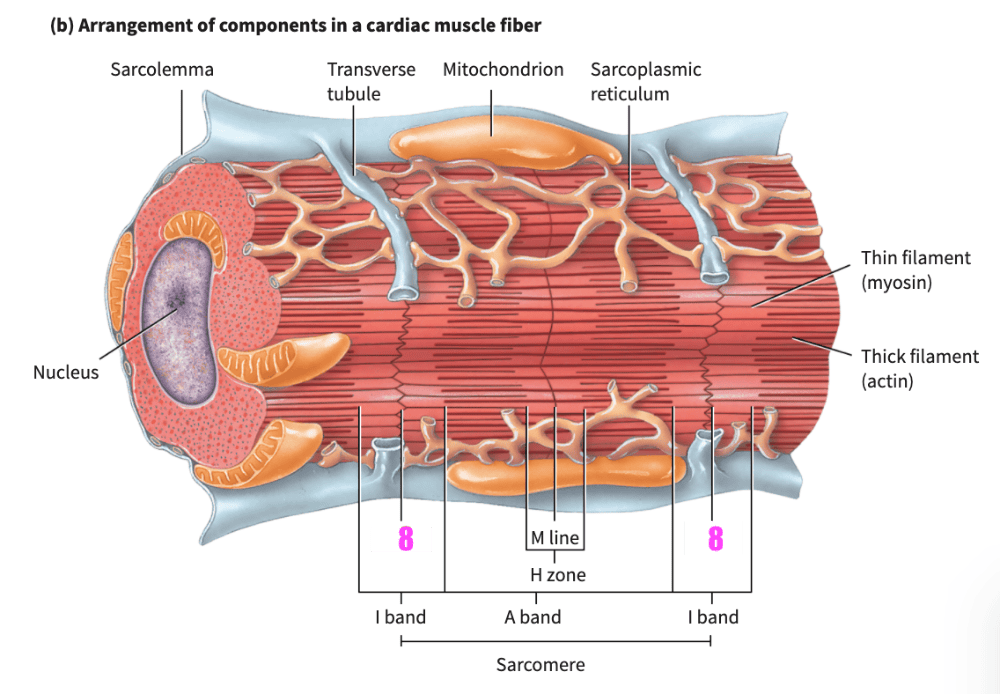 what is #8? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 410 Z Discs |
front 411 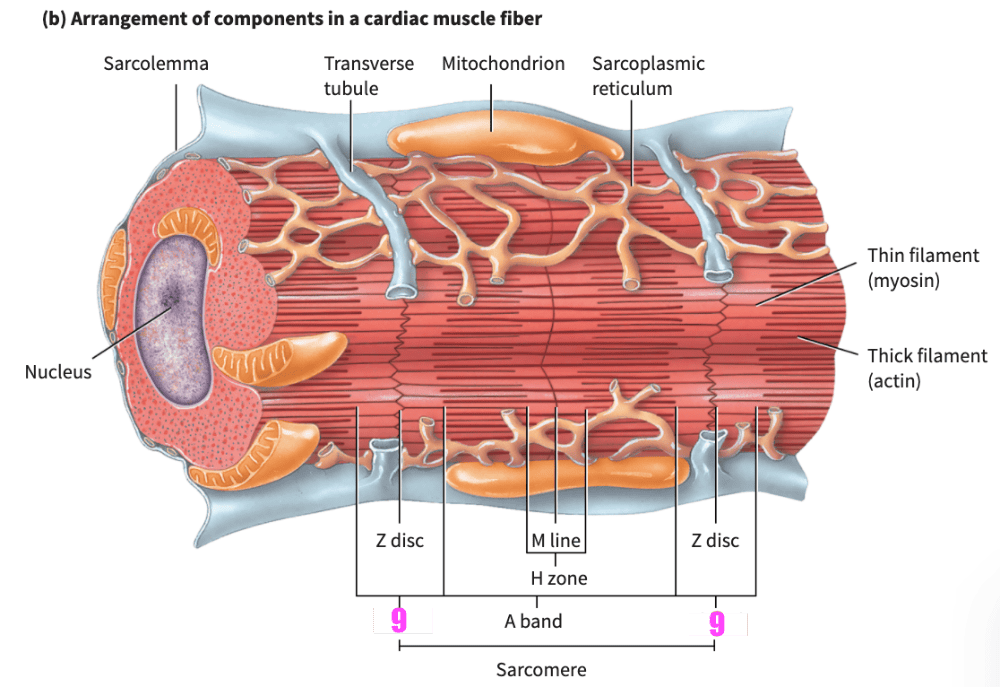 what is #9? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 411 I Band |
front 412 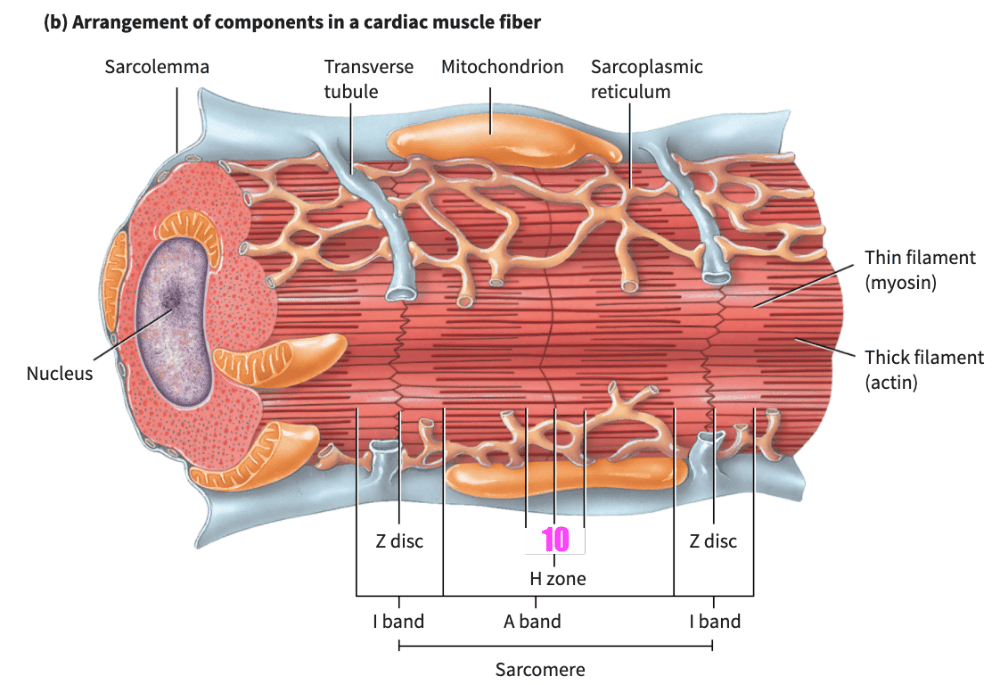 what is #10? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 412 M line |
front 413 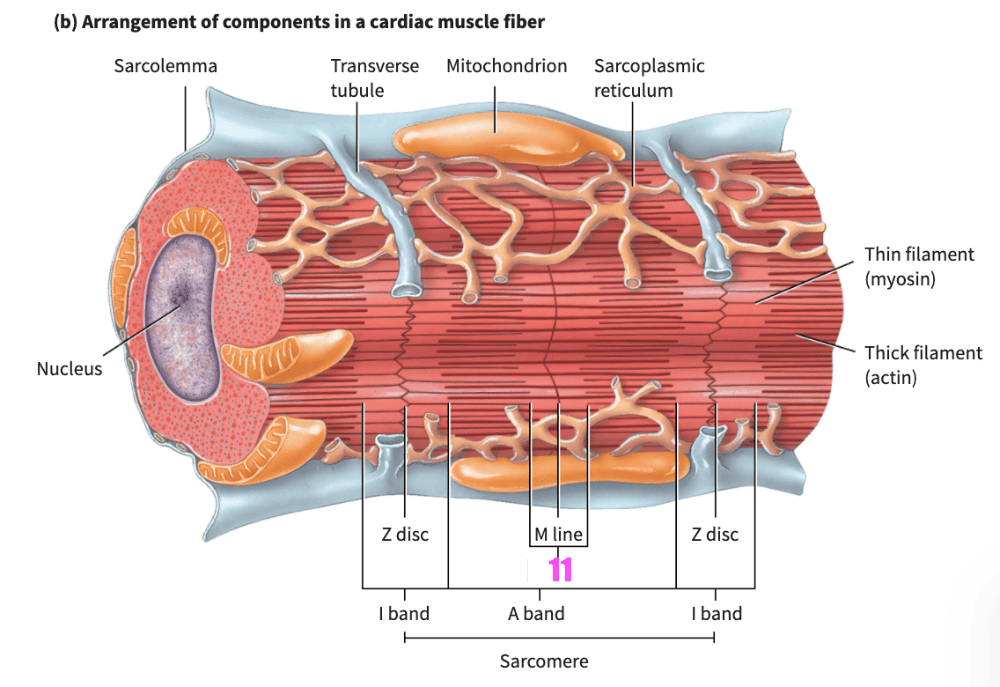 what is #11? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 413 H zone |
front 414 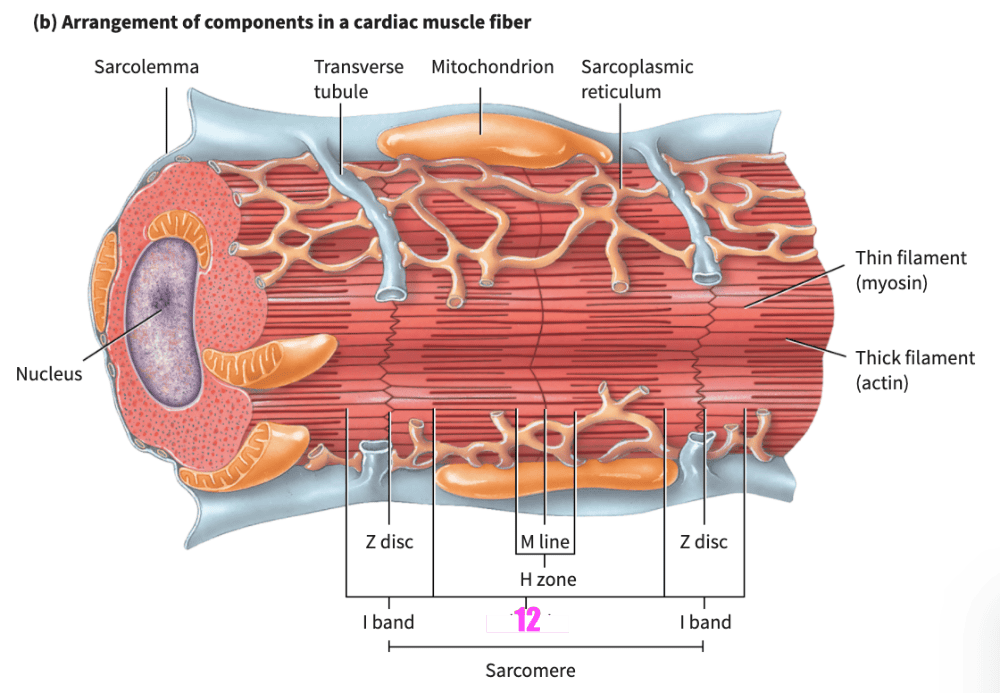 what is #12? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 414 A band |
front 415 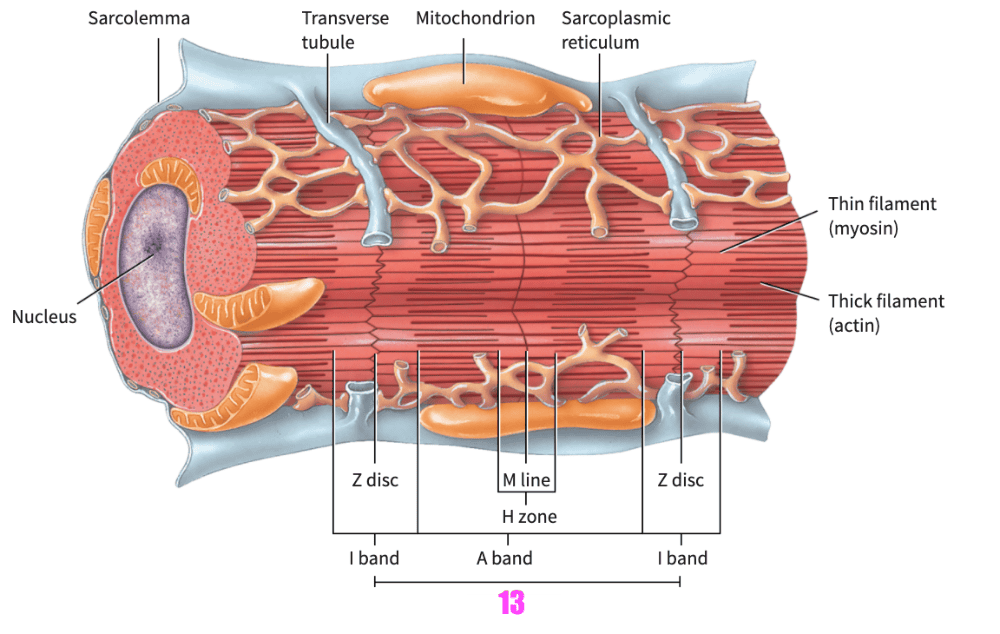 what is #13? (cardiac muscle tissue) | back 415 sarcomere |
front 416 how is smooth muscle tissue similar to cardiac muscle tissue? | back 416 it is activated involuntarily |
front 417 what are the 2 types of smooth muscle tissue? | back 417 1. visceral smooth muscle tissue 2. multi-unit smooth muscle tissue |
front 418
| back 418 visceral smooth muscle tissue |
front 419 (a), one autonomic motor neuron synapses with several visceral smooth muscle fibers, and action potentials spread to neighboring fibers through gap junctions. (b), three autonomic motor neurons synapse with individual multi-unit smooth muscle fibers. Stimulation of one multi-unit fiber causes contraction of that fiber only. (c) Comparison between a relaxed and contracted smooth muscle fiber | back 419 histology of smooth muscle tissue |
front 420 Smooth muscle fibers have thick and thin filaments but no ______________ and little ______________ | back 420
|
front 421 Which type of smooth muscle is more like cardiac muscle than skeletal muscle, with respect to both its structure and function? | back 421 Visceral smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are similar in that both contain gap junctions, which allow action potentials to spread from one cell to its neighbors. |
front 422
| back 422 multi-unit smooth muscle tissue |
front 423 As you just learned, stimulation of one visceral muscle fiber causes contraction of many adjacent fibers; in contrast, stimulation of one multi-unit smooth muscle fiber causes ____________________ | back 423 contraction of that fiber only |
front 424 What are 5 examples of parts of the body that contain multi-unit smooth muscle tissue? | back 424
|
front 425 Smooth muscle fibers are ______________ than skeletal muscle fibers | back 425 considerably smaller |
front 426 A single relaxed smooth muscle fiber is ___________ long, _________ in the middle (3–8 μm), and _________ at each end | back 426
|
front 427 Within each smooth muscle fiber is a single, ________, ___________________. | back 427 oval, centrally located nucleus |
front 428 The ___________ of smooth muscle fibers contains both thick filaments and thin filaments, in ratios between about 1:10 and 1:15 respectively, but they are not arranged in orderly sarcomeres as in striated muscle. | back 428 sarcoplasm |
front 429 1. filaments that contain the protein desmin and appear to have a structural rather than contractile role 2. Protein filament, ranging from 8 to 12 nm in diameter, that may provide structural reinforcement, hold organelles in place, and give shape to a cell. | back 429 intermediate filaments |
front 430 Because the various intermediate filaments have no regular pattern of overlap, smooth muscle fibers _______________—thus the name smooth | back 430 do not exhibit striations |
front 431 Smooth muscle fibers also lack _____________ and have little sarcoplasmic reticulum for storage of _____. | back 431 1. transverse tubules 2. sarcoplasmic reticulum 3. Ca2+ |
front 432 Smooth muscle tissue has an endomysium, but lacks a ___________ and ____________. | back 432 1. perimysium 2. epimysium |