front 1 Slides, scalpels, razor blades, cover glasses, and capillary tubes
are all classified as
- electrical hazards
- hazardous chemicals
- infectious agents
| |
front 2 Which of the following would be most appropriate for disposal of
cultures on agar plates?
- normal trash receptacle
- biohazard bag or bin
- sharps container
| |
front 3 The purpose of lab safety rules and protocols is to
- ensure that the lab activities always produce the expected
results
- protect everyone in the lab from injury and
infection
- enable students to complete lab assignments and
activities in less time
- ensure that the lab stays clean and
orderly
| back 3 -
protect everyone in the lab from injury and
infection
|
front 4 Laboratory instruments are sterilized prior to reuse by __________.
- gassing with ethylene oxide
- incineration
- autoclaving
- soaking in disinfectant
| |
front 5 The best source of information regarding the hazards posed by any
chemical and specific handling instructions is the
- lab partner
- GOOGLE
- lab manual
| |
front 6 Which of the following is defined as the ability make an object
appear larger?
- contrast
- media type
- magnification
- resolution
| |
front 7 Which of the following items will you need to make a wet mount?
- transfer pipette
- clean slide
- bunsen
burner
- timer
- tweezers
- cover slip
| back 7 -
transfer pipette
-
clean slide
-
tweezers
-
cover slip
|
front 8 What is enhanced when a stain is used to make a sample, or parts of a
sample, darker than the background in a slide?
- media type
- resolution
- contrast
- magnification
| |
front 9 Which of the following is defined as the ability to distinguish fine detail?
- contrast
- resolution
- media type
- magnification
| |
front 10 Which objective lens provides the highest total magnification?
- scan
- high power
- low power
- oil
immersion
| |
front 11 Which of the following must be visually studied using
electron microscopy?
- fungi
- viruses
- prokaryotes
- eukaryotes
| |
front 12 Which of the image quality factors is usually expressed in a number
such as 40x?
- resolution
- contrast
- magnification
- media type
| |
front 13 Which metric unit is most appropriate for expressing the size of
bacterial cells?
- centimeter
- nanometer
- micrometer
- meter
| |
front 14 Select all of the following that are factors affecting the clarity of
a microscopic image.
- slide material
- resolution
- contrast
- magnification
| back 14 -
resolution
-
contrast
-
magnification
|
front 15 Arrange the following steps of applying immersion oil in the correct sequence.
- Rotate the 100x lens over the microscope slide, and use the
fine focus adjustment knob to sharpen the image.
- Turn the
objectives to half way between the 40x lens and the 100x lens.
- Apply a drop of immersion oil directly onto area of the slide
you were viewing.
- Focus on the specimen using the 40x
objective lens.
| back 15 - Focus on the specimen using the 40x objective lens.
- Turn the objectives to half way between the 40x lens and the
100x lens.
- Apply a drop of immersion oil directly onto area
of the slide you were viewing.
- Rotate the 100x lens over
the microscope slide, and use the fine focus adjustment knob to
sharpen the image.
|
front 16 What does the term motile mean?
- magnification
- solid
- fixed
- movable
| |
front 17 Which of the following must be visually studied using microscopy?
- fungi
- eukaryotes
- prokaryotes
- plants
| |
front 18 Each of the following steps are necessary in preparing and observing
a wet mount. Place the steps in the correct order.
- obtain a clean slide and cover slip
- observe
preparation under 10X objective lens
- using a transfer
pipette, obtain a drop of specimen and place onto the center of the
slide
- observe preparation under the 40X objective lens
- carefully place the cover slip over the drop of specimen
| back 18 - Obtain a clean slide and cover slip.
- Using a transfer
pipette, obtain a drop of specimen and place onto the center of the
slide.
- Carefully place the cover slip over the drop of
specimen.
- Observe preparation under the 10X objective
lens.
- Observe preparation under the 40X objective lens.
|
front 19 The magnification of the ocular lens is
| |
front 20 Select all of the following that can be studied with
brightfield microscopy.
- fungi
- molecules
- viruses
- bacteria
- plants
| |
front 21 If a specimen was being viewed using a 20x objective lens and 10x
ocular lens, what would be the total magnification?
| |
front 22 Which of the following is defined as the ability to distinguish an
object from the background?
- media type
- resolution
- magnification
- contrast
| |
front 23 What is the advantage of using a wet mount?
- The motility of a specimen can be viewed under a
microscope.
- The wet mount is a safer way to view pathogenic
organisms.
- The specimen can be viewed as living cells.
- The contrast of a specimen is enhanced with the addition of
water to the slide.
| back 23 -
The motility of a specimen can be viewed under a
microscope.
-
The specimen can be viewed as living cells.
|
front 24 All three factors affecting image quality can be controlled by
manipulating the microscope.
| |
front 25 Pond water can contain many types of organisms. Which of the
following are you most likely to find in a pond water sample? Please
select all that apply.
- bacteria
- algae
- rotifers
- human
cells
- protozoa
- virus
| back 25 -
bacteria
-
algae
-
rotifers
-
protozoa
|
front 26 A wet mount requires the addition of certain dyes and cell fixatives
approximately 12 hours before viewing the specimen.
| |
front 27 Which objective lens requires oil to be applied?
| |
front 28 Increasing the _____ would allow you to tell if what appears as one
object is really two objects very near each other.
- resolution
- media type
- magnification
- contrast
| |
front 29 When preparing a wet mount specimen for viewing, the specimen should
be covered with
- another glass slide
- a coverslip
- clean
paper
- transparent tape
| |
front 30 The lenses of a brightfield microscope are responsible for the _____
of the object you are viewing.
- color
- contrast
- media type
- magnification
| |
front 31 What is the correct way to open an agar plate to either remove a
sample or to inoculate?
- Remove the lid completely, holding it in your hand, not
setting it on the bench.
- Open lid slightly on one side, in
a clamshell fashion.
- Remove the lid completely and set it
on the bench in an upright position.
- Remove the lid
completely and set it on the bench upside down.
| back 31 -
Open lid slightly on one side, in a clamshell
fashion.
|
front 32 Which types of culture media are solid? (Select all that apply)
| |
front 33 - Process of adding a microbe to a growth material
- The
material which provides the nutrients for growth
- To
cultivate (verb) or observable growth
- culture
- inoculation
- media
| back 33 - inoculation
- medium
- culture
|
front 34 How is an inoculating loop or needle sterilized prior to use?
- soaking in 95% ethyl alcohol for several minutes and allowing
to air dry
- dipping into a beaker of boiling water
- holding in the hottest part of the Bunsen burner flame until
red-hot
- exposure to UV radiation for 15 seconds
| back 34 -
holding in the hottest part of the Bunsen burner flame until
red-hot
|
front 35 What type of media provides the best option for obtaining a culture
with isolated bacterial colonies?
| |
front 36 A substance used to support the growth of microbial life is referred
to as a
- water
- culture medium
- inoculating loop
- incubator
| |
front 37 Why is 35-37 degrees Celsius a standard incubation temperature range
for many lab exercises involving medically important bacteria?
- This range is energy-efficient.
- This range is close
to human body temperature, a temperature preferred by many of these
organisms.
- This range is cooler than room temperature,
protecting the organisms from death.
- This range denatures
the enzymes that make these organisms pathogenic.
| back 37 -
This range is close to human body temperature, a temperature
preferred by many of these organisms.
|
front 38 Which of the following conditions may increase the level of microbial
contamination in an environment? (Select all that apply)
- warm temperature (25°–40°C)
- moisture
- cold
temperature (0°–10°C)
- contact with humans and/or other
animals
| back 38 -
warm temperature (25°–40°C)
-
moisture
-
contact with humans and/or other
animals/contact
|
front 39 What term is used to describe the cloudiness produced by bacterial
growth in a tube of broth?
- precipitation
- colonies
- particulation
- turbidity
| |
front 40 Put the following steps in order to indicate a correct transfer from
a bacterial culture to a sterile agar slant.
- Heat loop before returning to its receptacle.
- Remove
a small amount of bacteria, heat the mouth of tube, and replace
cap.
- Remove the cap from the sterile slant and heat mouth of
tube.
- Streak the sterile slant surface with the loop.
- Heat mouth of newly inoculated slant tube and replace cap.
- Heat inoculating loop, remove cap of bacterial culture, and heat
mouth of tube.
| back 40 - Heat inoculating loop, remove cap of bacterial culture, and
heat mouth of tube.
- Remove a small amount of bacteria, heat
the mouth of tube, and replace cap.
- Remove the cap from the
sterile slant and heat mouth of tube.
- Streak the sterile
slant surface with the loop.
- Heat mouth of newly inoculated
slant tube and replace cap.
- Heat loop before returning to
its receptacle.
|
front 41 The lab bench is treated with a disinfectant at what points in the
lab exercise?
- before work begins
- after work is finished
- between each separate transfer
- between glove
changes
| back 41 -
before work begins
-
after work is finished
|
front 42 How is air contamination prevented when an inoculating loop is used
to introduce or remove organisms from an agar plate?
- The plate lid is flamed before incubation.
- The plate
lid is kept closed or lifted only slightly when inoculating.
- The plate lid is flamed before insertion of the loop.
- The loop is flamed just before introduction of organisms onto
the plate surface.
| back 42 -
The plate lid is kept closed or lifted only slightly when
inoculating.
|
front 43 Environments with ________ temperatures are likely to show more
bacterial growth on an exposed agar plate.
| |
front 44 The cloudy growth seen in a broth culture is referred to as the
________ of the culture.
- synthetic extract
- precipitate
- nonsynthetic
particles
- turbidity
| |
front 45 Media in slants and Petri dishes is solidified by the addition of
- polypeptides.
- polyacrylamide.
- agar
- gelatin
| |
front 46 What type of medium provides the best opportunity for growing and
observing the morphology of isolated colonies?
| |
front 47 The best time period to observe incubated cultures is between
________ hours.
- 12 and 18
- 4 and 12
- 0 and 4
- 24 and
48
| |
front 48 Gram-negative organisms might incorrectly stain purple.
- You forgot to apply safranin
- You forgot the
decolorization step.
- You forgot the Gram's iodine.
- You applied the decolorizer for too long.
- You forgot
the crystal violet step.
- You did not heat fix the smear
correctly.
| back 48 -
You forgot the decolorization step.
|
front 49 Gram-negative organisms might not be visible.
- You forgot to apply safranin
- You forgot the
decolorization step.
- You forgot the Gram's iodine.
- You applied the decolorizer for too long.
- You forgot
the crystal violet step.
- You did not heat fix the smear
correctly.
| back 49 -
You forgot to apply safranin.
|
front 50 Gram-positive organisms might incorrectly stain pink.
- You forgot to apply safranin
- You forgot the
decolorization step.
- You forgot the Gram's iodine.
- You applied the decolorizer for too long.
- You forgot
the crystal violet step.
- You did not heat fix the smear
correctly.
| back 50 -
You forgot the crystal violet step.
-
You forgot the Gram's iodine.
-
You applied the decolorizer for too long.
|
front 51 You may not be able to view any organisms on the slide.
- You forgot to apply safranin
- You forgot the
decolorization step.
- You forgot the Gram's iodine.
- You applied the decolorizer for too long.
- You forgot
the crystal violet step.
- You did not heat fix the smear
correctly.
| back 51 -
You did not heat fix the smear correctly.
|
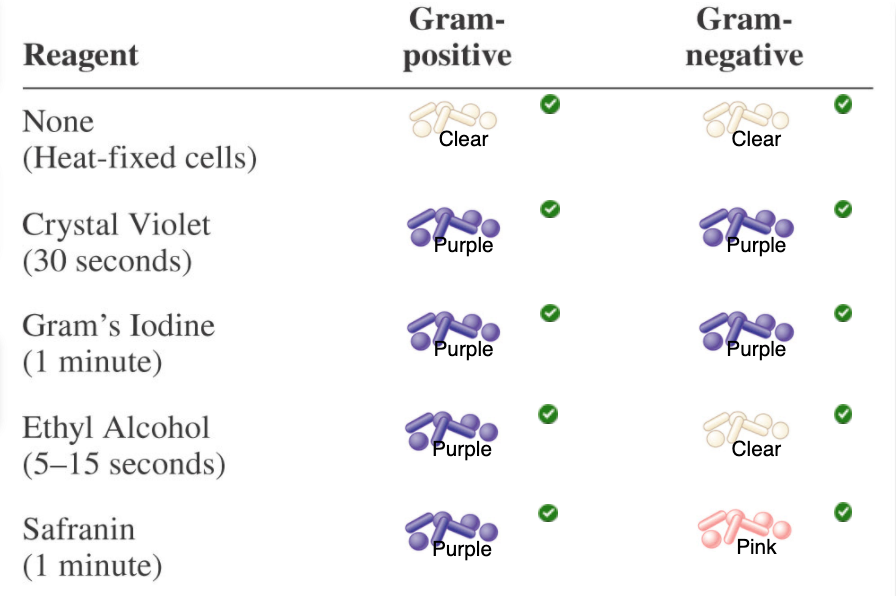
front 52 Reagent
- None (Heat-fixed cells)
- Crystal Violet (30
seconds)
- Gram's Iodine (1 minute)
- Ethyl Alcohol
(5-15 seconds)
- Safranin (1 minute)
| back 52 - None (Heat-fixed cells)
- Crystal Violet (30 seconds)
- Gram's Iodine (1 minute)
- Ethyl Alcohol (5-15
seconds)
- Safranin
(1 minute)
|
| |
| |
front 55 Please order the following choices to reflect the appropriate
sequence of materials used in the Gram staining procedure.
- Gram's Iodine
- Safranin
- Crystal Violet
- Alcohol
| back 55 -
Crystal Violet
-
Gram's iodine
-
Alcohol
-
Safranin
|
front 56 Match the following reagents with their role in the Gram stain procedure.
- Safranin
- Gram's iodine
- Crystal violet
- Alcohol/acetone
- mordant
- primary stain
- counterstain
- decolorizer
| back 56 - Safranin
- Counterstain
- Gram's
iodine
- Mordant
- Crystal violet
- Primary stain
- Alcohol/acetone
- Decolorizer
|
front 57 Before heat fixation, a wet smear of bacterial cells on a slide must
first be
- rinsed briefly with water
- air-dried
- stained
with a basic dye
- blotted dry
| |
front 58 Select the statements that represent goals incorrect smear preparation.
- The cells must be heat fixed to the slide to prevent removal
when stain is washed off the slide.
- It is important to
minimize any artifacts or distortion of the cells for accurate
viewing after staining.
- Smears must be thick in order to
easily take up stains.
- Organisms should be killed on the
inoculating loop before application to the slide.
- Smears
must be thin to allow for observation of single cells.
| back 58 -
The cells must be heat fixed to the slide to prevent removal
when stain is washed off the slide.
-
It is important to minimize any artifacts or distortion of
the cells for accurate viewing after staining.
-
Smears must be thin to allow for observation of single
cells
|
front 59 Order these statements to indicate correct aseptic procedure for
removing organisms from a culture for application to a slide.
- Flame the mouth of the culture tube
- Place organisms
onto the slide in the center of the target circle
- Flame the
loop red-hot before setting aside
- Remove the cap of the
culture tube and flame the mouth of the tube.
- Remove a
loopful of organisms from the culture.
- Return the cap to
the culture tube.
- Heat inoculating loop and wire to
red-hot.
| back 59 - Heat inoculating loop and wire to red-hot.
- Remove the
cap of the culture tube and flame the mouth of the tube.
- Remove a loopful of organisms from the culture.
- Flame
the mouth of the culture tube.
- Return the cap to the
culture tube.
- Place organisms onto the slide in the center
of the target circle.
- Flame the loop red-hot before setting
aside.
|
front 60 How does smear preparation of cells from a liquid medium differ from
preparation of cells from a solid medium?
- Stain is applied to the cells in the culture tube and then
they are applied to the slide.
- Heat fixation is used to
evaporate the liquid medium.
- A needle is used instead of an
inoculating loop.
- Water is applied to the slide before
emulsifying cells from a solid medium.
| back 60 -
Water is applied to the slide before emulsifying cells from
a solid medium.
|
front 61 The Gram stain is an example of a _______ staining procedure, which
takes advantage of the fact that cells or parts of cells react
differently and can be distinguished by the use of two different dyes.
- differential
- synthetic
- negative
- simple
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
front 66 Gram-positive cells
- Cells which contain a thick layer of peptidoglycan and
teichoic acid
- Cells which contain both an inner and outer
membrane as well as a thin layer of peptidoglyan
- Cells
which contain a thick layer of mycolic acid or cord factor
| back 66 -
Cells which contain a thick layer of peptidoglycan and
teichoic acids
|
front 67 Gram-negative cells
- Cells which contain a thick layer of peptidoglycan and
teichoic acid
- Cells which contain both an inner and outer
membrane as well as a thin layer of peptidoglyan
- Cells
which contain a thick layer of mycolic acid or cord factor
| back 67 -
Cells which contain both an inner and outer membrane as well
as a thin layer of peptidoglyan
|
front 68 Acid-fast cells
- Cells which contain a thick layer of peptidoglycan and
teichoic acid
- Cells which contain both an inner and outer
membrane as well as a thin layer of peptidoglyan
- Cells
which contain a thick layer of mycolic acid or cord factor
| back 68 -
Cells which contain a thick layer of mycolic acid or cord
factor
|
| back 69 -
Uses malachite green
-
Distinguishes between active metabolic cells and dormant
structure
|
| back 70 -
Differentiates cells based on thickness of peptidoglycan
layer
-
Does not require heat to be used in staining
process
-
Result is purple and red/pink cells
-
A chemical is used as mordant
|
| back 71 -
Differentiates cells with high lipid content in cell
wall
-
Important diagnostic tool in Mycobacterium
infections
-
Uses carbolfuchsin, acid-alcohol, and methylene
blue
|
front 72 The capsule can be considered a virulence factor and microorganisms
containing one are often pathogenic.
| |
front 73 A _______ stain is one that colors the background surrounding the
cell, leaving the cell itself unstained.
- complex
- differential
- negative
- positive
| |
| back 74 -
Stain with safranin
-
High water content
-
Actively metabolizing
|
| back 75 -
Highly resistant to heat and chemicals
-
Stain with malachite green
-
Require autoclave for destruction
-
Formed when conditions become unfavorable
-
Heat is mordant to facilitate staining of
these
|
front 76 Which of the following is a layer found outside of the bacterial cell
wall and membrane consisting of repeating sugar units and/or proteins
that is resistant to staining.
- glycocalyx and capsule
- capsule
- slime
layer
- glycocalyx
- glycocalyx, capsule, and slime
| back 76 -
glycocalyx, capsule, and slime
|
front 77 Before heat fixation, a wet smear of bacterial cells on a slide must
first be
- air-dried
- stained with a basic dye
- rinsed
briefly with water
- blotted dry
| |
front 78 Order the reagents used in the acid-fast staining procedure.
- Methylene blue
- Acid-alcohol
- Carbolfuchsin
| back 78 - Carbolfuchsin
- Acid-alcohol
- Methylene
blue
|
front 79 You observe this slide under the microscope. It was prepared with a
negative stain used to visualize capsules.
- This bacterium is encapsulated
- This bacterium is not
encapsulated
- The bacterial cells are dark purple
- The
capsules are dark purple
- The background of the slide is
white, indicating that the slide is densely covered with cells
- The capsules are white spaces around dark cells in this
field.
| back 79 -
This bacterium is encapsulated
-
The bacterial cells are dark purple
-
The capsules are white spaces around dark cells in this
field
|
front 80 How does smear preparation of cells from a liquid medium differ from
preparation of cells from a solid medium?
- A needle is used instead of an inoculating loop
- Water
is applied to the slide before emulsifying cells from a solid
medium
- Heat fixation is used to evaporate the liquid
medium
- Stain is applied to the cells in the culture tube and
then they are applied to the slide
| back 80 -
Water is applied to the slide before emulsifying cells from
a solid medium
|
front 81 A ________ is a mound of cells on a solid medium that represents the
progeny from one original bacterial cell.
- streak
- quadrant
- culture
- colony
| |
front 82 The ________ is an appropriate tool to use for inoculating
microorganisms into the butt of an agar slant.
- spreader
- inoculating loop
- pipette
- inoculating needle
| |
front 83 Which of the following may indicate that you have correctly
subcultured an organism from a plate to a slant? (Check all that apply.)
- After Gram staining a smear prepared from the slant, all of
the cells have similar color and morphology under the
microscope.
- The slant shows colonies in three different
colors
- The slant shows only one color of growth
- The
slant appear turbid
| back 83 -
After Gram staining a smear prepared from the slant, all of
the cells have similar color and morphology under the
microscope
-
The slant shows only one color of growth
|
front 84 When completing a quadrant streak, when do you flame the loop? (Check
all that apply.)
- before you pick up a loopful of organisms from the original
culture
- before you streak quadrant one
- before you
streak quadrants two, three, and four
- before you return the
loop to the receptacle
| back 84 -
before you pick up a loopful of organisms from the original
culture
-
before you streak quadrants two, three, and
four
-
before you return the loop to the receptacle
|
front 85 When completing a quadrant streak, when do you flame the loop? (Check
all that apply.)
- It requires fewer materials
- It requires less
skill
- It is a very quick process
- It does not require
the use of heat
| back 85 -
it requires fewer materials
-
it is a very quick process
|
front 86 Please select all of the statements which are true regarding
isolated colonies.
- The colony results from a single cell or a cluster of cells
multiplying into a visible mass.
- The cells within the
colony are all the same species.
- Isolated colonies form on
solid nutrient media.
- Isolated colonies form in liquid
nutrient media.
- Isolated colonies can only be obtained via
the streak plate method
| back 86 -
The colony results from a single cell or a cluster of cells
multiplying into a visible mass.
-
The cells within the colony are all the same
species.
-
Isolated colonies form on solid nutrient
media.
|
front 87 You have a nutrient broth, an agar slant, and an agar plate with
bacterial growth in or on each. If you wanted to evaluate the
macroscopic appearance of the bacteria growing in or on the medium,
which of the cultures would be the best choice?
- agar plate
- agar slant
- broth
| |
front 88 Which of the following is a possible mistake when performing a
quadrant streak that could lead to no growth beyond the first
quadrant? Select all that apply.
- beginning the second quadrant streak while the loop is still
hot
- forgetting to sample from the original culture before
beginning the second quadrant streak
- forgetting to flame
the loop before beginning the second quadrant streak
- touching the loop to your bench before beginning the second
quadrant streak
| back 88 -
beginning the second quadrant streak while the loop is still
hot
|
front 89 Which of the following methods can be used to generate isolated
colonies? Select all that apply.
- quadrant streak plate method
- pour plate method
- dilution series plating
- optical density reading
- butt inoculation of an agar slant
| back 89 -
quadrant streak plate method
-
pour plate method
-
dilution series plating
|
front 90 Which of the following may indicate that you have correctly
subcultured an organism from a plate to a slant? (Check all that apply.)
- After Gram staining a smear prepared from the slant, all of
the cells have similar color and morphology under the
microscope.
- The slant shows colonies in three different
colors
- The slants shows only one color of growth
- The
slant appear turbid
| back 90 -
After Gram staining a smear prepared from the slant, all of
the cells have similar color and morphology under the
microscope.
-
The slant shows only one color of growth
|
front 91 What advantage does the pour plate method have over the quadrant
streak plate method?
- It requires fewer materials
- It requires less
skill
- It only requires an inoculating tool and one plate
- It provides isolated colonies
| |
front 92 When preparing pure cultures, dilution is necessary for
- providing a hypotonic environment to enhance bacterial
growth.
- ensuring that the bacteria receive adequate nutrition
during incubation.
- preparing the melted agar for pour
plating.
- reducing the number of inoculated organisms so that
isolated colonies can develop.
| back 92 -
reducing the number of inoculated organisms so that isolated
colonies can develop.
|
front 93 The type of culture most frequently used in the laboratory which
contains only a single species of microbe.
- Pure culture
- Subculture
- Mixed culture
- Contaminated culture
| |
front 94 A second-level culture where an isolated colony from one culture is
taken and transferred into a new medium.
- Pure culture
- Subculture
- Mixed culture
- Contaminated culture
| |
front 95 A culture which contains two or more species which can be easily differentiated.
- Pure culture
- Subculture
- Mixed culture
- Contaminated culture
| |
front 96 A culture which contains one or more unwanted and often unidentified microbes.
- Pure culture
- Subculture
- Mixed culture
- Contaminated culture
| |
front 97 A ________ is a mound of cells on a solid medium that represents the
progeny from one original bacterial cell.
- streak
- culture
- colony
- quadrant
| |
front 98 Place the following steps in order to demonstrate your understanding
of the pour plate method.
- Remove loopful of organisms from culture using aseptic
technique.
- Incubate for 24–48 hours.
- Liquefy
nutrient agar tubes and maintain at 50 degrees Celsius.
- Transfer one loopful from one agar tube into another agar tube,
and repeat this again with a third agar tube.
- Add loopful
of organisms to an agar tube.
- Pour liquefied agar tubes
into empty plates.
| back 98 -
Liquefy nutrient agar tubes and maintain at 50 degrees
Celsius.
-
Remove loopful of organisms from culture using aseptic
technique.
-
Add loopful of organisms to an agar tube.
-
Transfer one loopful from one agar tube into another agar
tube, and repeat this again with a third agar tube.
-
Pour liquefied agar tubes into empty plates.
-
Incubate for 24–48 hours.
|
front 99 When performing a Standard Plate Count (SPC), plates that contain
________ colonies are selected for counting with a colony counter.
- 30-300 colonies
- 50-100 colonies
- 100-500
colonies
- 10-100 colonies
| |
front 100 Which gas is produced by cell respiration?
- hydrogen
- oxygen
- carbon dioxide
- nitrogen
| |
front 101 Starch is a(n)
- oligosaccharide
- monosaccharide
- disaccharide
- polysaccharide
| |
front 102 The main products of yeast fermentation are (Check all that apply)
- alcohol
- FADH
- CO
- CO2
- latic
acid
- NAD+
- NADH
- pyruvate
| |
front 103 Polysaccharides are polymers composed of
- fatty acids
- nucleotides
- amino acids
- nucleic acids
- sugars
| |
front 104 All of the following are the end products of glycolysis except
- energy
- pyruvate
- ATP
- NAD+
- NADH
| |
front 105 When testing for starch within the potato and onion, the test tube
containing potato turned purple while the test tube containing onion
turned orange. What can you conclude about the amount of starch in
these two vegetables?
- The potato contained a higher concentration of starch than the
onion.
- The potato contained starch, but the onion did
not.
- The potato contained no starch, but the onion did.
- The potato contained lower concentration of starch than the
onion did.
- Neither the potato nor the onion contained
starch.
| back 105 -
The potato contained a higher concentration of starch than
the onion.
|
front 106 Which of the following does NOT occur during yeast fermentation?
- NADH is oxidized to NAD+
- Lactate is produced
- Glucose is oxidized to make Pyruvate
- Pyruvate is
oxidized forming CO2 and ethanol
- NAD+ is reduced to
NADH
| |
front 107 Select all of the following that are products of lactic acid fermentation.
- glucose
- water
- oxygen
- lactic
acid
- carbon dioxide
- ATP
| back 107 -
Lactic acid
-
Cardon dioxide
-
ATP
|
front 108 Yeast cells under anaerobic conditions
- die
- switch to oxidative respiration
- push the
glycolytic pathway backward
- produce oxygen
- produce
ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
| back 108 -
produce ethyl alcohol (ethanol).
|
front 109 Select all of the following that are true statements about fermentation.
- lactate may be produced
- a large amount of ATP is
produced
- ethanol may be produced
- the reactions
happen in the cytoplasm
- NADH is produced
- the
reactions happen in the mitochondria
- CO2 may be
produced
| back 109 -
lactate may be produced
-
ethanol may be produced
-
the reactions happen in the cytoplasm
-
CO2 may be produced
|
front 110 Starch is classified as a
- nucleic acid
- protein
- lipid
- carbohydrate
| |
front 111 Which of the following is absolutely required for the production of ATP?
- Pi
- production of water
- glucose
- ADP
and Pi
- ADP only
| |
front 112 The positive control for the Iodine test was the
- olive oil
- glucose solution
- starch
solution
- distilled water
- albumin solution
| |
front 113 What must occur before sucrose is used in cellular respiration?
- Glucose and fructose must be bonded together
- Oxygen
levels must be low from increased metabolism
- Sucrase enzyme
breaks it down to glucose and fructose
- Sucrose must first
be converted into a disaccharide
| back 113 -
Sucrase enzyme breaks it down to glucose and
fructose
|
front 114 What is produced when beer is made?
- oxygen and ethanol
- lactate and ethanol
- ethyl
alcohol and water
- water, hydrogen gas, and ethanol
- CO2 and ethanol
| |
front 115 Under what environmental conditions do yeast carry out fermentation?
- All of the choices are correct
- absence of oxygen
- high osmotic pressure
- high temperature
- low
pH
| |
front 116 What anaerobic pathway in cellular respiration generates ATP from the
breakdown of glucose?
- the light reactions
- Calvin cycle
- electron
transport chain
- citric acid cycle
- glycolysis
| |
front 117 Which of the following is the purpose of cellular respiration?
- splitting water
- production of glucose
- production of ATP
- production of water
| |
front 118 What would you predict would happen to the fermentation rate if you
used yeast suspension that had not been swirled/mixed each time before
it was dispensed into test tubes?
- The reaction rate would be uniform, since the yeast would be
undisturbed
- The reaction rate would be very low
- The
reaction rate would be unaffected
- The reaction rate would
be very high at first, but would steadily decrease over time
- The reaction rate would be very high
| back 118 -
The reaction rate would be very low
|
front 119 Bacteria that are able to hydrolyze urea will change the color of the
urease test medium from yellow to
| |
front 120 The phenol red indicator used in the urease test turns pink when the
test medium
- is basic
- has a pH less than 7
- liquifies
- is acidic
| |
front 121 An amino acid consists of
- a carboxyl group
- an amino group
- a ribose
group
- a side group
- a hydroxyl group
| back 121 -
a carboxyl group
-
an amino group
-
a side group
|
front 122 The color change in a positive citrate test is due to a/an
_____________ in pH.
| |
front 123 What is the color change that indicates a positive citrate test?
- Green to blue
- Yellow to pink
- Blue to
green
- Pink to yellow
| |
front 124 Amino acids are joined by
- ionic bonds
- glycosidic bonds
- peptide
bonds
- ester bonds
| |
front 125 What is the product of urea hydrolysis?
- ammonia and carbon dioxide
- ammonia
- carbon
dioxide
- organic acids
| back 125 -
ammonia and carbon dioxide
|
front 126 After inoculating and incubating a gelatin deep with an unknown
bacterium, you observe that the gelatin deep has liquified. What is
the next step in the experiment?
- Test the components of the liquid gelatin
- Conclude
that the unknown bacterium is able to hydrolyze gelatin
- Place the gelatin deep on ice
- Incubate the gelatin deep
for an additional 48 hours
| back 126 -
Place the gelatin deep on ice.
|
front 127 Proteins are made up of _______________ subunits. | |
front 128 Helicobacter pylori gastric infections can be diagnosed by a
breath test. Patients are instructed to exhale into a balloon-like bag
30 minutes after drinking a urea solution. What gas is being measured
when a patient exhales into the bag?
- nitrous oxide
- oxygen
- carbon dioxide
- nitrogen
| |
front 129 Which of the following can occur during protein catabolism?
- desulfhydrase reaction
- decarboxylation
- deamination
- All of the above
| |
front 130 What is the smallest unit of a protein?
- an amino acid
- a polypeptide
- a
monosaccharide
- a nucleic acid
| |
front 131 After 2 days you observe a black precipitate in your Peptone Iron
deep containing the amino acid cysteine, after it was inoculated with
Proteus vulgaris. What could you conclude?
- Cysteine has been decarboxylated, and its COOH removed
- Cysteine has been converted into smaller amino acids
- The bacteria has released cysteine from the polypeptide
chains
- The bacteria has released Hydrogen Sulfide from
cysteine
| back 131 -
The bacteria has released Hydrogen Sulfide from
cysteine
|
front 132 Why would we look for the production of ferrous sulfide (black
precipitate) closer to the
bottom of the stab in the Peptone Iron Deeps in
order to determine if Hydrogen Sulfide was produced?
- Because Hydrogen Sulfide is produced by anaerobic
organisms
- Because the cells are motile and have travelled to
the bottom of the stab
- Because there is more bacterial
growth at the bottom of the stab
- Because Hydrogen Sulfide
gas is released into the air closer to the media surface and
therefore wouldn't produce the ferrous sulfide black
precipitate.
| back 132 -
Because Hydrogen Sulfide gas is released into the air closer
to the media surface and therefore wouldn't produce the ferrous
sulfide black precipitate.
|
front 133 What would the Litmus Milk test look like if the inoculated bacteria
was able to ferment lactose?
- The media would clear
- The media would change to
purple
- There would be white precipitates in the media
- The media would change to pink
| back 133 -
The media would change to pink
|
front 134 What change in litmus milk would occur if amino acids were catabolized?
- Coagulation of media would occur
- Media would turn
pink
- Media would turn purple
- Media would turn
clear
| |
front 135 What change in litmus milk would occur if there were very high levels
of acid produced following lactose fermentation?
- Coagulation of media would occur
- Media would turn
purple
- Media would turn clear
- Media would turn
pink
| back 135 -
Coagulation of media would occur
|
front 136 Which of the following is NOT found in Litmus Milk media?
- lactose sugar
- Bromthymol blue
- milk casein
protein
- litmus
| |
front 137 Which of the following is NOT present in Triple Sugar Iron Agar media?
- All of the above are included
- phenol red
indicator
- 0.1% glucose
- 1% lactose
- 1%
sucrose
| back 137 -
All of the above are included
|
front 138 Which one of the following can be determined through the results of a
Triple Sugar Iron Agar Test?
- All of the above
- Fermentation of glucose
- Fermentation of lactose and sucrose
- Production of
hydrogen sulfide
| |
front 139 What is the final step in aerobic cellular respiration?
- Lactic Acid Fermentation
- Electron Transport
Chain
- Kreb's Cycle
- Glycolysis
| |
front 140 What is the final step in aerobic cellular respiration?
- Lactic Acid Fermentation
- Electron Transport
Chain
- Kreb's Cycle
- Glycolysis
| |
front 141 Coagulase Test: Place the following steps in the correct order.
- look for clotting
- Using sterile loop, obtain bacteria
colony and mix with coagulase plasma
- Place loopful of
coagulase plasma on clean slide using sterile loop.
| back 141 - Place loopful of coagulase plasma on clean slide using sterile
loop.
- Using sterile loop, obtain bacteria colony and mix with
coagulase plasma
- Look for clotting
|
front 142 If no color change has occurred in the nitrate reductase test after
adding Nitrate I and Nitrate II to your culture, what do you add to
your culture to determine if you have a positive or negative result?
- Potassium
- Zinc
- Carbon
- Magnesium
| |
front 143 This test is used to differentiate between Staphylococcus
(catalase-positive) and Streptococcus (catalase-negative), as both are
Gram-positive cocci.
- Catalase Test
- Coagulase Test
- Nitrate
Reductase Test
- Gram Staining Test
- Oxidase
Test
| |
front 144 Coagulase Test: A positive test is indicated by ____? | |
front 145 Which of the following is not found in a Mannitol Salt Agar Plate?
- peptone
- salt
- mannitol
- alcohol
| |
front 146 This media differentiates between lactose fermentors.
- none of these options are correct
- Mannitol Salt
Agar
- Eosin Methylene Blue
- Blood Agar
| |
front 147 Which of the following is not a correct description of selective media?
- contains one or more specific compounds that can prevent the
growth of certain bacterial species
- inhibitors in the media
may adversely effect DNA synthesis, gene expression, enzymatic
activity or membrane permeability all of which can destroy or
inhibit the growth of certain bacterial species
- allows the
growth of some bacterial species while inhibiting the growth of
other bacterial species
- contains one or more specific
compounds that can distinguish between bacterial species
- can be used to identify bacteriacan
| back 147 -
contains one or more specific compounds that can distinguish
between bacterial species
|
front 148 A clinical sample may contain many different types of bacteria that
do not have to be identified. You wouldn't want to waste time
culturing all bacteria if, for example, you suspect a gram-negative
bacteria is what is causing the infection. What plate can you use to
select for only gram-negative bacteria?
- Eosin Methylene Blue
- Nutrient Agar
- Mannitol
Salt Agar
- Blood Agar
| |
front 149 This test is used to identify bacteria who have similar Electron
Transport Chains to those found in Eukaryotes, which contain the
Enzyme Complex IV (Cytochrome C Oxidase).
- Catalase Test
- Oxidase Test
- Cytochrome C
test
- Coagulase Test
- Nitrate Reductase Test
| |
front 150 Which of the following is true?
- The nitrate reductase test is important in the identification
of both gram-positive and gram-negative species.
- In the
nitrate reductase test, there are two ways to read a positive result
but only one way to be negative.
- The oxidase test is
basically a test to see if an organism is an aerobe.
- In the
electron transport chain, O2 is typically the final
electron acceptor.
| back 150 -
The nitrate reductase test is important in the
identification of both gram-positive and gram-negative
species.
-
In the nitrate reductase test, there are two ways to read a
positive result but only one way to be negative.
-
In the electron transport chain, O2 is typically
the final electron acceptor.
|
front 151 Which of the following is false?
- Staphylococcus aureus would yield a negative result in a
coagulase test.
- Staphylococcus epidermis would yield a
positive result in a coagulase test.
- Staphylococcus aureus
ferments mannitol, causing the phenol red to turn yellow.
- Staphylococcus epidermis tolerates high salt concentration and
grows on Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA).
- Staphylococcus epidermis
is gram-positive cocci and coagulase-positive.
- Staphylococcus aureus is gram-negative cocci and
coagulase-negative.
| back 151 -
Staphylococcus aureus would yield a
negative result in a coagulase test.
-
Staphylococcus epidermis would yield a positive result in a
coagulase test.
-
Staphylococcus epidermis is gram-positive cocci and
coagulase-positive.
- Staphylococcus aureus is
gram-negative cocci and coagulase-negative.
|
front 152 Take a look at the results of a Nitrate Reductase test below.
Which of the following (if any) is considered a negative result?
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- None of the bacteria tested
yielded a negative result.
- Escherichia coli
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
| |
front 153 Which of the following is produced by the human immune system and is
a common byproduct of metabolic reactions that take place in the
presence of water and oxygen?
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Nitrite
- Dihydrogen
Monoxide
- Oxygen
- Nitrate
| |
front 154 Which of the following is not considered a positive result?
- If no color change occurs upon addition of zinc then this
means that the NO3- was converted to NO2- and
then was converted to some other undetectable form of nitrogen.
- If no red color forms upon addition of nitrate I and II, this
indicates that NO3- was converted to NO2- and
then immediately reduced to some other, undetectable form of
nitrogen.
- If nitrite is present in the media, then it will
react with nitrate I and nitrate II to form a red compound.
- Zinc will convert any remaining NO3- to
NO2- thus allowing nitrate I and nitrate II to react with
the NO2- and form the red pigment.
| back 154 -
Zinc will convert any remaining NO3- to
NO2- thus allowing nitrate I and nitrate II to react
with the NO2- and form the red pigment.
|
front 155 Match the following descriptions to their respective plates.
- Can be used as a positive control for selective and
differential media
- selects for gram-positive cells
- Clear ring around colony distinguishes certain bacteria
- medium fermenters result in purple colonies
- Eosin Methylene Blue Agar
- Blood Agar
- Mannitol Salt Agar
- Nutrient Agar
| back 155 - Can be used as a positive control for selective and
differential media
- Nutrient Agar
- selects for gram-positive cells
- Mannitol Salt Agar
- Clear ring around colony distinguishes certain bacteria
- Blood Agar
- medium fermenters result
in purple colonies
- Eosin Methylene Blue Agar
|
front 156 Which of the following is not found in an Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Plate?
- polypeptides
- eosin
- methylene blue
- lactose
- galactose
| |