Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology 1406 Ch. 20 Viruses, Bacteria, Archaea
front 1 Which of these is the best description of a virus? | back 1
|
front 2 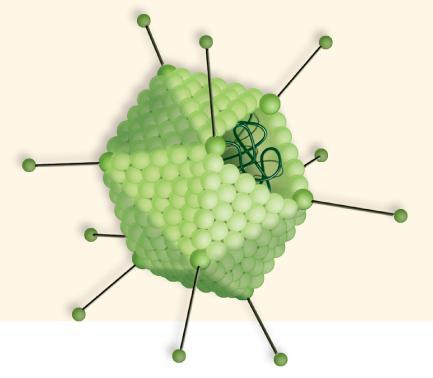 | back 2 1. Capsid (left) 2.fiber protein 3.fiber 4. RNA or DNA 5. Protein Unit |
front 3 All of the following are diseases caused by viruses except | back 3 strep throat |
front 4 Select the components present in all viruses. (Select all that apply). | back 4
|
front 5 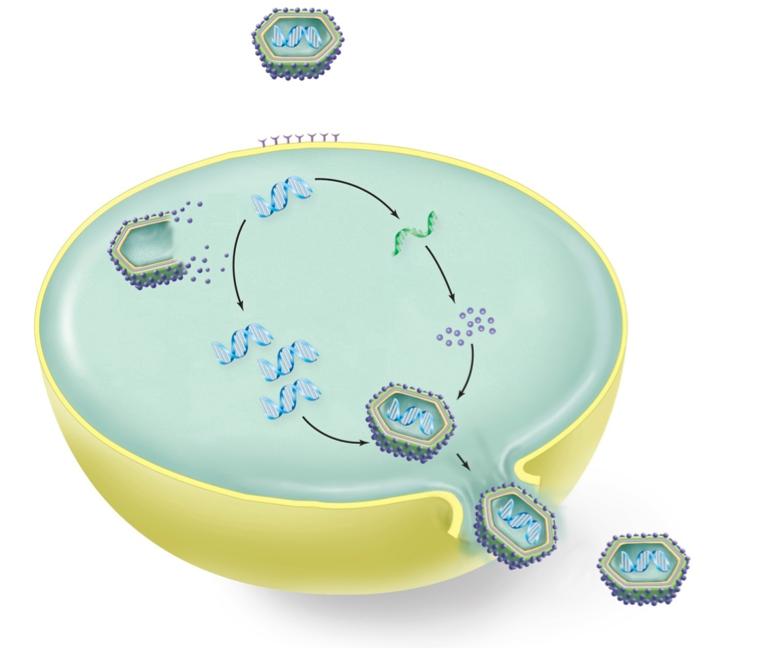 | back 5 no data |
front 6 Arrange the steps in the order that they occur during viral infection and replication. | back 6 1. Attachment of virus to host cells. 2. Penetration of entire virus into host cell or injection of viral genome. 3.Synthesis of viral nucleic acid and proteins 4.Assembly of new viruses 5.Release of viruses from the host cell |
front 7 Viruses reproduce by | back 7
|
front 8 Phages are viruses that can infect | back 8
|
front 9 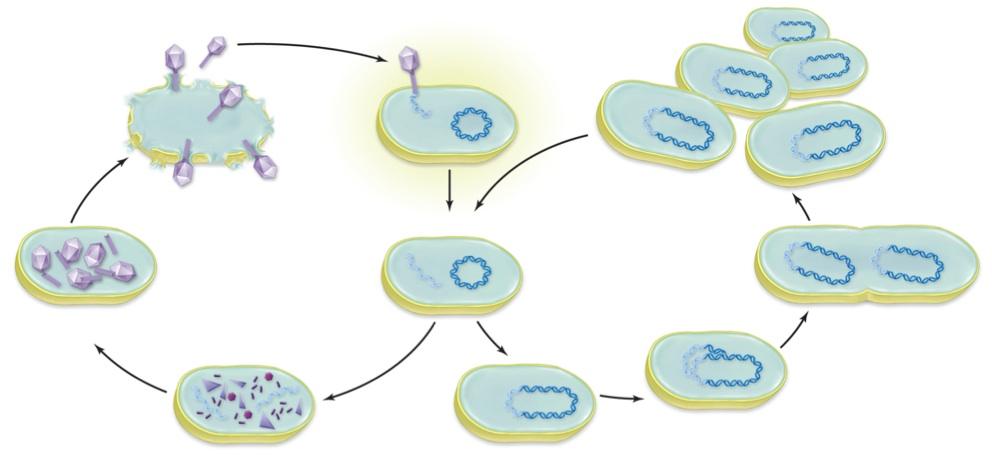 | back 9 no data |
front 10 What is similar between the lysogenic cycle of a bacterial virus and the HIV infection cycle? | back 10
|
front 11 Complete the following sentences to describe the stages of the lytic cycle of viruses. Then, place the stages in chronological order for full credit. | back 11 1.During the attachment stage, the capsid of a virus combines with receptors on the host cell's plasma membrane. 2.During the biosynthesis stage, enzymes digest cell wall and membrane material so that viral nucleic acids can enter into the host cell. 3.During the penetration stage, viral nucleic acids and capsid components are produced. 4.During the maturation stage, viral nucleic acids and capsid components are assembled to produce viral particles. 5.During the release stage, lysozyme enzyme is produced, rupturing the cell membrane and releasing viral particles. |
front 12 Infection with HIV viruses causes the death of immune system cells called ______, and over many years, HIV can lead to a disease called ______ in which the immune system is deficient. | back 12
|
front 13 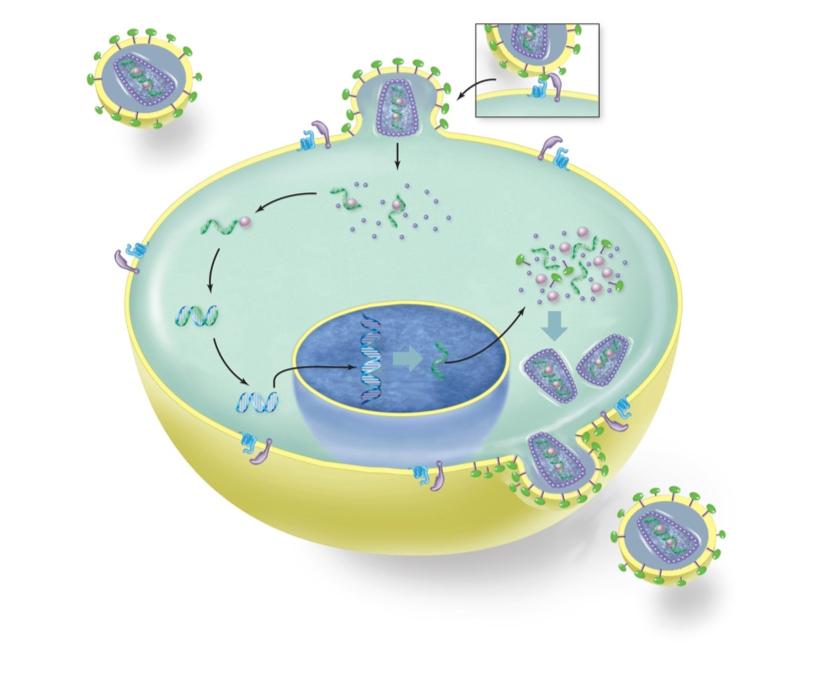 | back 13 no data |
front 14 Arrange the steps in the order that they occur during HIV infection and replication. | back 14 no data |
front 15 Which statement is NOT true about retroviruses? | back 15
|
front 16 What are zoonotic diseases? | back 16
|
front 17 Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) presently infects about 40 million people worldwide. In what organisms did HIV originate? | back 17
|
front 18 Which of the following would be classified as a zoonotic disease? | back 18
|
front 19 What are the two prokaryotic domains? | back 19
|
front 20 Complete the following paragraph to describe the components of bacterial cells. | back 20 Prokaryotes are surrounded by a cell envelope that contains the plasma membrane to regulate the entry and exit of materials through the cell, the cell wall to help maintain cell shape and structure, and the glycocalyx (when present) to aid in attachment and evasion. The DNA of a prokaryote is arranged in a single coiled chromosome located in the nucleoid. Some prokaryotes carry genes on extrachromosomal pieces of circular DNA called plasmids. Embedded within the cytoplasm are small particles called ribosomes that function in protein synthesis. Some prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria are photosynthetic and contain thylokoids to aid in photosynthesis. |
front 21 Binary fission is a form of sexual reproduction in which the daughter cells have a different genetic combination than the parent cell. | back 21 True False |
front 22 Bacteriophages carry portions of bacterial DNA from one cell to another in a process called | back 22
|
front 23 Bacterial cells pick up free pieces of DNA that were secreted by live bacteria or released from dead bacteria in their environment. This process is called | back 23
|
front 24 When conditions are unfavorable, some bacteria form | back 24
|
front 25 Which of the following is a mismatch for the environment in which Archaean lives? | back 25
|