Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam #3 2020
front 1 Which of these descriptions of the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis explains Mendel’s law of segregation? Which of the following statements about the law of segregation is correct? | back 1 The two alleles for each gene separate as homologous chromosomes move apart during anaphase I. It describes the inheritance of different chromosomes relative to one another. |
front 2 When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies, but all the white-eyed flies were male. Which of these best explains Morgan's result? | back 2 The gene involved is located on the X chromosome. |
front 3 In cats, an X-linked locus is responsible for fur color. There are two known alleles at this locus. One results in black fur color; the other results in orange fur color. A heterozygote animal has patches of orange and black fur (tortoiseshell). Which of the following explains the patches of color in female heterozygote cats? | back 3 Random X inactivation affects fur color |
front 4 The SRY gene is best described as ________. | back 4 a gene present on the Y chromosome whose product regulates male development |
front 5 Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) is inherited as an X-linked recessive allele in humans. A woman whose father had G6PD is planning a family with a man who has no history of the disease. What proportion of their sons are expected to have the disease? | back 5 1/2 |
front 6 Which of the following statements regarding gene linkage is correct? | back 6 The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them. |
front 7 The chromosomal alteration that results from a chromosome fragment joined to a nonhomologous chromosome is called a ________. | back 7 translocation |
front 8 Which of the following statements describes the most likely result of a defect in meiosis that results in the failure of spindle microtubules to bind some kinetochores? | back 8 The resulting cells will not receive the correct number of chromosomes in the gametes, a condition known as aneuploidy. |
front 9 Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a serious condition caused by a recessive allele of a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients' muscles weaken over time because they have a lack or decreased levels of dystrophin, a muscle protein. Which of the following correctly predicts the probability of muscular dystrophy in female children? | back 9 One-half of the daughters of an affected man and a carrier woman would have this condition. |
front 10 A recombination frequency of 50% indicates ________. | back 10 the two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes |
front 11 What is an allele? | back 11 an alternative version of a gene |
front 12 Which of the following is true about a plant with the genotype AABbcc? | back 12 it is homozygous at two loci |
front 13 Which of the following statements correctly describes the terms monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross? | back 13 A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters that are being studied, and a monohybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for only one character being studied. |
front 14 Mendel crossed true breeding yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self-pollinate to produce an F2 generation. The results were as follows: 6,022 yellow and 2,001 green (8,023 total). Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship of the allele for green seeds to the allele for yellow seeds? | back 14 The green allele is recessive to the yellow allele. |
front 15 Having polydactyly (extra digits on hands and feet) is a dominant trait. A man has polydactyly. His wife and oldest daughter do not have polydactyly. The couple's second child has polydactyly. What is the probability that their next (third) child will have extra digits? | back 15 1/2 |
front 16 Assuming independent assortment at all loci, what is the probability that a cross between the following parents, AABbCc × AaBbCc, will produce an AaBbCc offspring? | back 16 1/8 |
front 17 Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cacti with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous recessive ss cacti have dull spines. Also, a second gene, N, determines whether or not cacti have spines. Homozygous recessive nn cacti have no spines at all. The relationship between genes S and N is an example of which of the following inheritance patterns? | back 17 epistasis |
front 18 What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? | back 18 All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a heterozygote will differ. |
front 19 When constructing a Punnett square, the symbols on the outside of the boxes represent _______, while those inside the boxes represent _______. | back 19 gametes, progeny |
front 20 True or false? The same phenotype can be produced by more than one genotype. | back 20 True |
front 21 True or false? In diploid organisms, a dominant phenotype will only be expressed if the individual is homozygous dominant for that trait. | back 21 False |
front 22 If an organism with the genotype AaBb produces gametes, what proportion of the gametes would be Bb? | back 22 None |
front 23 Two mice are heterozygous for albinism (Aa) . The dominant allele (A) codes for normal pigmentation, and the recessive allele (a) codes for no pigmentation. What percentage of their offspring would have an albino phenotype? | back 23 25 |
front 24 A tall, purple-flowered pea plant (TtPp) is allowed to self-pollinate. (The recessive alleles code for short plants and white flowers.) The phenotypic ratio of the resulting offspring is 9:3:3:1. What is the genotype of the plant whose phenotype appeared once out of every 16 offspring (the "1" in the 9:3:3:1 ratio)? | back 24 ttpp |
front 25 What fraction of the offspring from a cross between two animals with the genotype AaBbCc are expected to be homozygous recessive for the three traits? | back 25 1/64 |
front 26 In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous (CRCW) offspring of red (CRCR) and white (CW CW) homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1 white? | back 26 roan × roan |
front 27 A man with type A blood marries a woman with type B blood. Their child has type O blood. What is the genotype of the man? What is the genotype of the woman? What is the genotype of the child? What genotypes would you expect in future offspring from this marriage? Select all that apply. In what frequencies would you expect the offspring genotypes? Indicate the frequency of each genotype by dragging the labels to the table. Labels may be used once, more than once, or not at all. | back 27 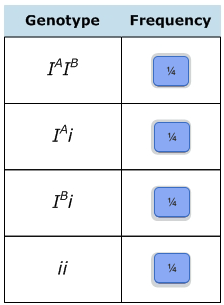 I A i I B i ii ii, I A i, I B i, I A I B |
front 28 Height in humans generally shows a normal (bell-shaped) distribution. What type of inheritance most likely determines height? | back 28 a combination of polygenic inheritance and environmental factors |
front 29 Which of the following inheritance patterns describes the ability of a single allele to have multiple phenotypic effects? | back 29 pleiotropy |
front 30 Marfan syndrome in humans is caused by an abnormality of the connective tissue protein fibrillin. Patients are usually very tall and thin, with long spindly fingers, curvature of the spine, sometimes weakened arterial walls, and sometimes eye problems, such as lens dislocation. Which of the following would you conclude about Marfan syndrome from this information? | back 30 It is pleiotropic. |
front 31 When a dominant allele coexists with a recessive allele in a heterozygote individual, how do they interact with each other? | back 31 They do not interact at all. |
front 32 Quaking aspen trees usually reproduce by extending underground stems that then push aboveground and grow into trees. Sexual reproduction is not as common, but when it does happen, the haploid gametes have 19 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are in the cells of the underground stems? | back 32 38 |
front 33 Which of the following statements best describes homologous chromosomes? | back 33 They carry information for the same traits. |
front 34 In a typical animal, mitosis produces _________, while meiosis produces____________. | back 34 two diploid daughter cells, four haploid daughter cells |
front 35 Which of the following answers describes the phenomenon of crossing over in meiosis? | back 35 the exchange of homologous portions of nonsister chromatids |
front 36 The two homologs of a pair move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during | back 36 meiosis I |
front 37 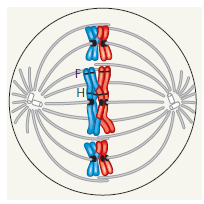 How can you tell that the cell in the figure below is undergoing meiosis, not mitosis? | back 37  |
front 38 During which of the following phases of meiosis do centromeres split and sister chromatids migrate to opposite poles of the cell? | back 38 anaphase II |
front 39 Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of which of the following processes? | back 39 the random way each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I |
front 40 Two different species of protists living in a tide pool. Species A reproduces both sexually and asexually, and Species B reproduce only asexually. The pool gradually becomes infested with disease-causing viruses. Which species are more likely to survive in the changing environment? | back 40 Species A only |
front 41 Two sister chromatids are joined at the centromere prior to meiosis. Which statement is correct? | back 41 Barring mutation, the two sister chromatids must be identical |
front 42 In alternation of generations, what is the diploid stage of a plant that follows fertilization called? | back 42 sporophyte |
front 43 What number and types of chromosomes are found in a human somatic cell? | back 43 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes |
front 44 Which of the following statements best describes homologous chromosomes? | back 44 They carry information for the same traits. |
front 45 Which of the following statements correctly describes how sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes differ from each other? | back 45 Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication. |
front 46 In a typical animal, mitosis produces _________, while meiosis produces____________. | back 46 two diploid daughter cells, four haploid daughter cells |
front 47 Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that | back 47 sister chromatids separate during anaphase |
front 48 Which of the following processes has just occurred when chiasmata can first be viewed under a microscope? | back 48 prophase I |
front 49 How do cells at the completion of meiosis compare with cells that are in prophase of meiosis I? | back 49 The cells have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA. |
front 50 For the following question, match the key event of meiosis with the
stages listed below. | back 50 II |
front 51 For a species with a haploid number of 23 chromosomes, how many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible for the gametes based on the independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis? | back 51 about 8 million |
front 52 Which of the following conditions is required for a target organ to respond to a particular hormone? | back 52 The target organ must have receptors that recognize and bind the hormone molecule |
front 53 When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway? | back 53 signal molecule |
front 54 When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway? | back 54 signal molecule |
front 55 Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane? | back 55 ligand-gated ion channel |
front 56 Which of the following are among the most common second messengers? | back 56 calcium ions and cAMP |
front 57 Which of the following statements best describes why phosphorylation cascades are useful in cellular signal transduction? | back 57 they amplify the original signal many times |
front 58 Part completeWhat is the name of the region on duplicated chromosomes where the sister chromatids are most closely attached to each other? | back 58 the centromere |
front 59 Which of the following occurs during S phase? | back 59 replication of the DNA |
front 60 Which of the following statements describes a characteristic feature of metaphase? | back 60 alignment of chromosomes on the equator of the cell |
front 61 Besides the ability of some cancer cells to over proliferate, which of the following situations is most likely to result in a tumor? | back 61 lack of appropriate cell death |
front 62 Which of the following statements best describes a cleavage furrow? | back 62 a groove in the plasma membrane between daughter nuclei |
front 63 A type of localized signaling in which a cell secretes a signal molecule that affects neighboring cells is best described as which of the following? | back 63 paracrine signaling |
front 64 Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as aldosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because | back 64 intracellular receptors are present only in target cells |
front 65 Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane? | back 65 ligand-gated ion channel |
front 66 Which of the sequences below best describes the sequential steps
(numbered 1-5) in a signal transduction pathway that utilizes a G
protein-coupled receptor? | back 66 3, 1, 5, 2, 4 |
front 67 What is apoptosis? | back 67 controlled cell suicide |
front 68 Eukaryotic chromatin is composed of which of the following macromolecules? | back 68 DNA and proteins |
front 69 Which of the following correctly matches a phase of the cell cycle with its description? | back 69 G1, follows cell division |
front 70 Cell A has half as much DNA as cells B, C, and D in a mitotically active tissue. Cell A is most likely in | back 70 G1 |
front 71 Which of the following statements best describes how cytokinesis differs between plant and animal cells? | back 71 Plant cells deposit vesicles containing cell wall building blocks on the metaphase plate; animal cells form a cleavage furrow. |
front 72 Which of the following statements describes a characteristic feature of metaphase? | back 72 alignment of chromosomes on the equator of the cell |