Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Ch. 16 Quiz Review - Endocrine System
front 1
Chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular
fluids that regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the
body are called ________. | back 1 D) hormones |
front 2 True or False? Direct gene activation involves a second-messenger system. | back 2 FALSE |
front 3 True or False? All peptide hormone synthesis requires gene activation that produces mRNA. | back 3 TRUE |
front 4
Which of the following is not a change that may be caused by
hormonal stimulus? | back 4 B) direct control of the nervous system |
front 5
The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the
presence of a hormone is dependent on ________. | back 5 C) the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ |
front 6
Thyroid hormone (a small iodinated amine) enters target cells
in a manner similar to ________. | back 6 B) steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells |
front 7 What ion is sometimes used as a second messenger of amino acid-based hormones? A) chlorine | back 7 C) calcium |
front 8 True or False? Both "turn on" factors (hormonal, humoral, and neural stimuli) and "turn off" factors (feedback inhibition and others) may be modulated by the activity of the nervous system. | back 8 TRUE |
front 9
Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones
exert their effects through intracellular ________. | back 9 D) second messengers |
front 10 Which of the following is not a type of hormone interaction? A) synergism | back 10 B) feedback |
front 11 Which of the following is not a change typically produced by a hormonal stimulus? A) induces secretory activity | back 11 B) stimulates production of an action potential |
front 12 The second-messenger mechanism of hormone action operates by ________. A) synthesizing more of the hormone than is actually needed | back 12 D) binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP |
front 13 Cells that respond to peptide hormones usually do so through a sequence of biochemical reactions involving receptor and kinase activation. In order for cells to respond, it is necessary for first and second messengers to communicate. This is possible because ________. A) peptide hormones always enter the cell membrane and elicit a
response without | back 13 C) G protein acts as the link between first and second messengers |
front 14
Cellular responses to hormones that initiate second-messenger
systems include ________. | back 14 A) possible activation of several different second-messenger systems |
front 15
In circumstances where the body requires prolonged or
increased levels of a hormone, the DNA of target cells will specify
the synthesis of more receptors on the surface of the cells of the
target organ. This is known as ________. | back 15 C) up-regulation |
front 16 True or False? ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to release corticosteroid hormones. | back 16 TRUE |
front 17 True or False? LH is also referred to as a gonadotropin. | back 17 TRUE |
front 18 True or False? Oxytocin is a strong stimulant of uterine contractions. | back 18 TRUE |
front 19 The hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract ________. A) connects the hypophysis to the pituitary gland | back 19 B) is partly contained within the infundibulum |
front 20 Oxytocin ________. A) release is an example of a positive feedback control
mechanism | back 20 A) release is an example of a positive feedback control mechanism |
front 21 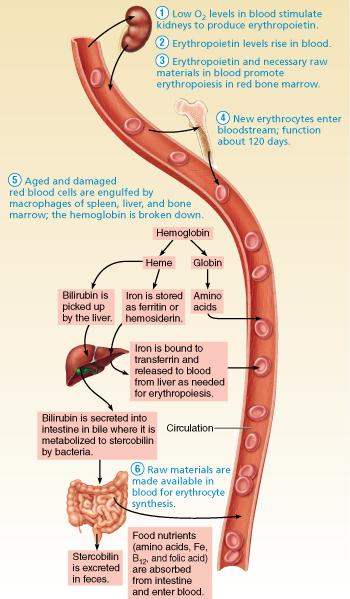 What role do the kidneys play in erythropoiesis? | back 21 The kidneys detect low levels of oxygen in the blood |
front 22  What triggers erythropoietin (EPO) production to make new red blood cells? A) too many platelets | back 22 B) reduced availability of oxygen |
front 23 What organ in the body regulates erythrocyte production? A) Kidney | back 23 A) Kidney |
front 24 True or False? Peptides called NPY and AgRP are powerful appetite enhancers. | back 24 TRUE |
front 25 True or False? Ghrelin, produced by the stomach, is a powerful appetite stimulant. | back 25 TRUE |
front 26 Many factors influence BMR. What is the most critical factor? A) The ratio of surface area to volume (weight) of the body B) The way skeletal muscles break down glycogen C) The way an individual metabolizes fat D) An individual's body weigh | back 26 A) The ratio of surface area to volume (weight) of the body |
front 27 The amount of ________ produced is probably the most important hormonal factor in determining BMR. A) norepinephrine | back 27 B) thyroxine |
front 28 True or False? When blood glucose levels are low, the body begins to use more noncarbohydrate fuels for energy production. This process is called glucose activation. | back 28 FALSE |
front 29 True or False? The preferred energy fuel for the brain is fat. | back 29 FALSE |
front 30 True or False? The increased use of noncarbohydrate molecules for energy to conserve glucose is called glucose sparing. | back 30 TRUE |
front 31 Glucose can be obtained from ________. A) glycogenolysis | back 31 A) glycogenolysis |
front 32 Which of the choices below is not a source of glucose during the postabsorptive state? A) Absorption of glucose from the GI tract | back 32 A) Absorption of glucose from the GI tract |
front 33 Which hormone directs essentially all the events of the absorptive state? A) growth hormone | back 33 D) insulin |
front 34 Which of the choices below happens during the absorptive state? A) Anabolic processes exceed catabolic ones. | back 34 A) Anabolic processes exceed catabolic ones. |
front 35 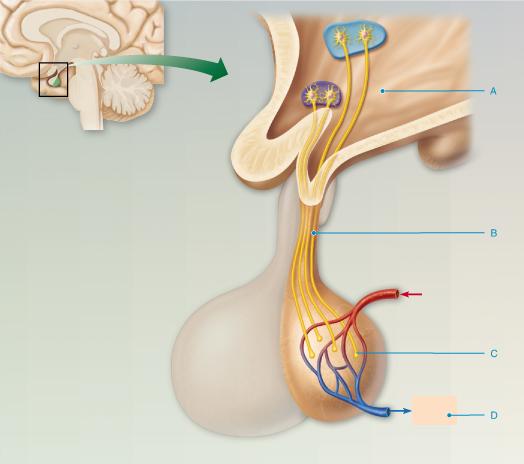 Where are oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) made? Select from letters A-D. | back 35 A |
front 36 Which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus? A) enzyme | back 36 A) enzyme |
front 37 Which of the choices below is not a factor required for target cell activation by hormone receptor interaction? A) blood levels of hormone | back 37 B) type of hormone |
front 38 Which of the following is not a steroid-based hormone? A) estrogen | back 38 C) epinephrine |
front 39 Eicosanoids do not include ________. A) paracrines | back 39 C) hydrocortisones |
front 40 Thyroxine is a peptide hormone, but its mechanism is different from other peptide hormones. Which of the following statements is true concerning this difference? A) It causes positive feedback. | back 40 B) It does not require a second messenger to effect a response. |
front 41 Steroid hormones exert their action by ________. A) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the
expression of a gene | back 41 A) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene |
front 42 Hormones often cause a cell to elicit multiple responses; this is because ________. A) there are thousands of receptors on the cell membrane | back 42 D) during protein kinase activation, enzymes phosphorylate many other enzymes |
front 43 One of the least complicated of the endocrine control systems directly responds to changing blood levels of ions and nutrients. Which of the following describes this mechanism? A) the rapid oxidation of carbohydrates | back 43 D) humoral stimulation |
front 44 ADH ________. A) increases urine production | back 44 D) is inhibited by alcohol |
front 45 Several hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus and transported to the anterior pituitary gland. The mechanism of transportation from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary gland is through the ________. A) hepatic portal system | back 45 C) hypophyseal portal system |
front 46 The neurohypophysis or posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is not a true endocrine gland because ________. A) it is strictly a part of the neural system and has little or
nothing to do with hormonal release | back 46 D) it is only a hormone storage area that receives hormones from the hypothalamus for release |
front 47 The major targets of growth hormone are ________. A) the blood vessels | back 47 D) bones and skeletal muscles |
front 48 Regulating hormones from the hypothalamus ________. A) enter venous circulation and travel to the heart, which pumps the
hormone-containing | back 48 D) first enter into the hypophyseal portal system |
front 49 Why does antidiuretic hormone help regulate an abnormal increase in solute concentration in the extracellular fluid? A) It causes secretion of solutes by the kidney, resulting in a
decreased solute concentration. | back 49 E) It causes reabsorption of water by the kidney, resulting in increased blood water volume and a decreased solute concentration. |
front 50 True or False? Oxytocin and ADH are produced in the posterior pituitary. | back 50 FALSE |
front 51 True or False? Growth hormone solely exerts its influence by targeting other endocrine glands to produce hormones. | back 51 FALSE |
front 52 True or False? Iodine is an essential element required for the synthesis of thyroxine. | back 52 TRUE |
front 53 True or False? The endocrine gland that is probably malfunctioning if a person has a high metabolic rate is the parathyroid. | back 53 FALSE |
front 54 True or False? Thyroid hormone production requires the presence of iodine and calcium. | back 54 FALSE |
front 55 ACTH ________. A) is secreted by the posterior pituitary | back 55 B) secretion is regulated by a hypothalamic secretion |
front 56 A man has been told that he is not synthesizing enough follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and for this reason he may be unable to father a child. Choose the correct statement to explain this problem. A) FSH stimulates estrogen secretion by ovarian cells; therefore it
is not synthesized by males. | back 56 C) FSH stimulates sperm production in the testes. |
front 57 Which of the following is not a parathyroid gland mechanism to maintain adequate levels of blood calcium? A) activation of osteoclasts | back 57 D) inhibition of calcitonin synthesis |
front 58 The single most important regulator of calcium levels in the blood is ________. A) parathyroid hormone | back 58 A) parathyroid hormone |
front 59 True or False? The prime metabolic effect of cortisol is gluconeogenesis. | back 59 TRUE |
front 60 True or False? Atrial natriuretic peptide is a hormone that controls blood pressure in part by increasing the urinary excretion of sodium. | back 60 TRUE |
front 61 True or False? Glucocorticoids are steroid hormones that usually enhance the immune responses when an individual is suffering from severe stress. | back 61 FALSE |
front 62 Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver due to the action of ________. A) Cortisol | back 62 A) Cortisol |
front 63 When it becomes necessary to enlist the fight-or-flight response, a hormone that is released during the alarm phase of the general adaptation syndrome is ________. A) estrogen | back 63 B) epinephrine |
front 64 Mineralocorticoid is to aldosterone as glucocorticoid is to ________. A) testosterone | back 64 C) cortisol |
front 65 The most important regulator of electrolyte concentrations in extracellular fluids is ________. A) insulin | back 65 B) aldosterone |
front 66 Aldosterone ________. A) is secreted by the neurohypophysis | back 66 B) functions to increase sodium reabsorption |
front 67 True or False? Addison's disease is due to a insufficient output of glucocorticoids only. | back 67 FALSE |
front 68 True or False? Hypersecretion of catecholamines can result in hypertension. | back 68 TRUE |
front 69 True or False? The pineal gland is used as a brain orientation landmark for brain X rays. | back 69 TRUE |
front 70 True or False? The hormone that raises blood sugar levels is insulin. | back 70 FALSE |
front 71 True or False? Type 2 diabetics may reflect declining receptor sensitivity to insulin rather than decreased insulin production. | back 71 TRUE |
front 72 True or False? Many hormones synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract are chemically identical to brain neurotransmitters. | back 72 TRUE |
front 73 Glucocorticoids enable the body to deal appropriately with stress. They accomplish this by ________. A) increasing blood glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid levels and
enhancing blood pressure | back 73 A) increasing blood glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid levels and enhancing blood pressure |
front 74 Which organ is responsible for synthesizing ANP? A) the heart | back 74 A) the heart |
front 75 Leptin is secreted by ________. A) lymphocytes | back 75 B) adipocytes |
front 76 True or False? Enteroendocrine cells of the GI tract produce some hormones that are chemically identical to neurotransmitters. | back 76 TRUE |
front 77 True or False? The beta cells in the pancreatic islets produce insulin. | back 77 TRUE |
front 78 True or False? In aged individuals, chronic stress may increase blood levels of cortisol and possibly contribute to memory deterioration. | back 78 TRUE |
front 79 True or False? Most type 2 diabetics do not produce insulin. | back 79 FALSE |
front 80 Which of the following is not a cardinal sign of diabetes mellitus? A) polyuria | back 80 C) polyphagia |
front 81 Which of the following hormones suppresses appetite and increases energy expenditure? A) gastrin | back 81 C) leptin |
front 82 Normal development of the immune response is due in part to hormones produced by the ________. A) adrenal medulla | back 82 D) thymus gland |
front 83 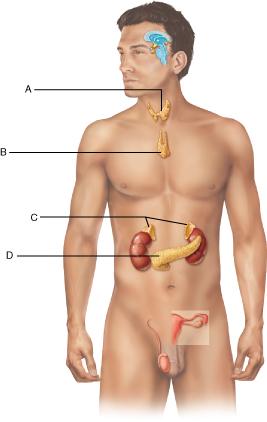 Identify the thyroid gland. Select from letters A-D. | back 83 A |
front 84 What is the primary function of hormones? A) Cause allergic reactions | back 84 B) Alter cell activity |
front 85 Which of the following mechanisms of hormone action is used by neurotransmitters and olfactory receptors? A) ATP | back 85 C) cAMP |
front 86 __________ is the situation when one hormone cannot exert its full effects without another hormone being present. A) Antagonism B) Permissiveness C) Activism D) Synergism | back 86 B) Permissiveness |
front 87 The stimuli causing endocrine glands to secrete their hormones in direct response to changing blood levels of certain critical ions and nutrients are called __________. A) Neural stimuli B) Humoral stimuli C) Hormonal stimuli D) Endocrinal stimuli | back 87 B) Humoral stimuli |
front 88 True or False? Up-regulation involves the loss of receptors and prevents the target cells from overreacting to persistently high hormone levels. | back 88 FALSE |
front 89 True or False? The hypothalamus is known to control the activity of the anterior pituitary, which has traditionally been called the "master endocrine gland." | back 89 TRUE |
front 90 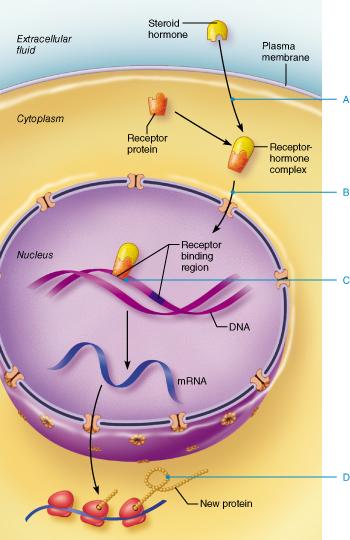 At which point does the hormone bind to its intracellular receptor? Determine the receptor-hormone complex. Select from letters A-D. | back 90 A |
front 91  What amino acid-based hormone uses the direct gene activation method illustrated in this image? | back 91 thyroxine |
front 92 Hyperprolactinemia may be caused by? A) Hypersecretion of dopamine | back 92 A) Hypersecretion of dopamine |
front 93 What is required for the production of anterior pituitary gland hormones? A) Humoral stimuli | back 93 A) Humoral stimuli |
front 94 Hormones that regulate the secretory action of other endocrine glands are called __________. A) Somatotropin B) Somatostatins C) Tropins D) GHIH | back 94 C) Tropins |
front 95  What hormone released into the blood (shown by letter D) by the posterior pituitary inhibits or prevents urine formation? A) Norepinephrine | back 95 D) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) |
front 96 Hypersecretion of what hormone can produce the effects of gigantism? A) thyroid hormones (TH) | back 96 C) growth hormone (GH) |
front 97 What gland secretes growth hormone? A) anterior pituitary (lobe) | back 97 A) anterior pituitary (lobe) |
front 98 You would predict that iodized salt would have no effect on any cases of ____________. A) cretinism | back 98 B) Graves' disease |
front 99 Which hormone is the body's major metabolic hormone? A) thyroid hormone | back 99 A) thyroid hormone |
front 100 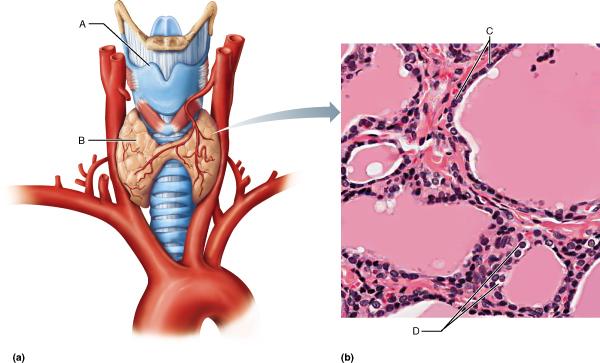 What type of cell is shown at letter C? | back 100 Follicular cells |
front 101  What hormone is released by the cells pictured in letter D? | back 101 Calcitonin |
front 102 True or False? Osteitis fibrosa is a rare complication of hyperparathyroidism where the bones soften and deform. | back 102 TRUE |
front 103 Aldosteronism will cause ______. A) Decreased secretion of renin | back 103 A) Decreased secretion of renin |
front 104 Cushing's syndrome and aldosteronism have the same effects on ______. A) blood pressure | back 104 A) blood pressure |
front 105 Which hormone(s) is/are essential to our ability to deal with stress? A) insulin | back 105 C) glucocorticoids |
front 106 Which of the following adrenal gland homeostatic imbalances is characterized by persistent elevated blood glucose levels, dramatic losses in muscle and bone protein, and water and salt retention, leading to hypertension and edema? A) cretinism | back 106 D) Cushing's syndrome |
front 107 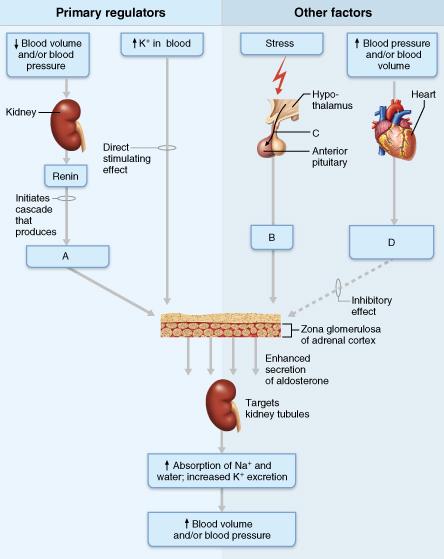 What hormone, notated by letter B, is released by the anterior pituitary to target the adrenal cortex when we are under stress? A) parathyroid hormone | back 107 adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) |
front 108 One can predict that a person suffering from diabetes mellitus would probably have ______. A) increased secretion of ANP (atrial natiuretic peptide) | back 108 B) increased secretion of ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) |
front 109 Which of the following is NOT a property of endocrine glands? A) They have ducts B) They drain vascularly C) They drain lymphatically D) They produce hormones. | back 109 A) They have ducts |
front 110 Which of the following is not an endocrine gland? A) Pituitary gland | back 110 D) Adenoid gland |
front 111  Which letter represents the adrenal glands? Select from letters A-D. | back 111 C |
front 112  Identify the pancreas. Select from letters A-D. | back 112 D |
front 113 Which of the following is NOT a major type of stimulus that triggers endocrine glands to manufacture and release hormones? A) enzymatic B) hormonal C) neural D) humoral | back 113 A) enzymatic |
front 114 Which of the following occurs in situations where more than one hormone produces the same effects at the target cell and their combined effects are amplified? A) antagonism B) synergism C) permissiveness D) summation | back 114 B) synergism |
front 115  At what point does the receptor-hormone complex bind to DNA? Select from letters A-D. | back 115 C |
front 116 A blow to the head may cause diabetes insipidus by ______. A) triggering the hypersecretion of hypothalamic-inhibiting
hormones | back 116 C) interfering with the normal transmission of ADH to the posterior pituitary via the axons of hypothalamic neurons |
front 117 Acromegaly may be caused by all EXCEPT which of the following? A) hypersecretion of GHRH (growth hormone-releasing hormone) B) pancreatic tumor C) lack of negative feedback by insulin-like growth factors D) positive feedback by GH (growth hormone) on the anterior pituitary | back 117 D) positive feedback by GH (growth hormone) on the anterior pituitary |
front 118 Which of the following is a hormone produced by the posterior pituitary? A) ADH | back 118 D) none of these |
front 119 Which of the following hormones stimulates the adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids that help the body to resist stressors? A) adrenocorticotropic hormone | back 119 A) adrenocorticotropic hormone |
front 120 Which of the following hormones mainly serves to stimulate milk production by the breasts? A) thyroid-stimulating hormone | back 120 C) prolactin |
front 121 True or False? Major hormones circulate to virtually all tissues. | back 121 TRUE |
front 122 True or False? The anatomical effects of acromegaly can usually be reversed by surgically removing the tumor from the anterior pituitary. | back 122 FALSE |
front 123  Where are the hormones oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) stored? Select from letters A-D. | back 123 C |
front 124 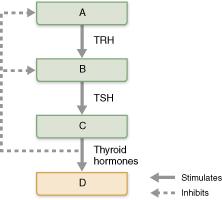 What is the target organ of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)? Select from letters A-D. | back 124 C |
front 125  What is the target organ of thyroid-releasing hormone (TRH)? Select from letters A-D. | back 125 B |
front 126 Which of the following is NOT a homeostatic imbalance related to underactivity of the thyroid gland? A) endemic goiter | back 126 B) Graves' disease |
front 127  Name two hormones produced by the gland identified by letter B | back 127 thyroid hormones and calcitonin |
front 128 Hypocalcemia could be caused by the ______. A) apoptosis of parathyroid cells | back 128 D) All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 129 Which of the following hormones regulates blood calcium ion levels? A) luteinizing hormone B) thyroid hormone C) parathyroid hormone D) follicle-stimulating hormone E) insulin | back 129 C) parathyroid hormone |
front 130 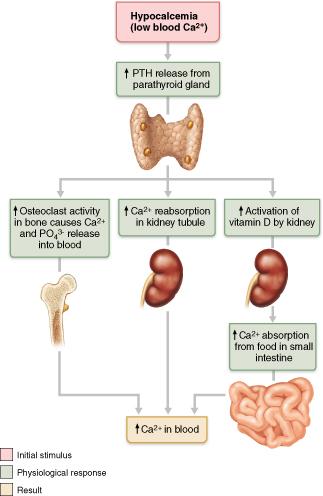 What type of stimulation controls parathyroid release? | back 130 humoral |
front 131  What cells release parathyroid hormone? | back 131 parathyroid cells |
front 132 Which of the following glands is found atop the kidneys? A) adrenal | back 132 A) adrenal |
front 133  What factor inhibits aldosterone release? Select from letters A-D. | back 133 D |
front 134  Which letter represents the hormone that promotes a decrease in blood pressure and a loss of sodium and water in urine? Select from letters A-D. | back 134 D |
front 135 Which pancreatic hormone functions to lower blood glucose levels? A) somatostatin B) glucagon C) gastrin D) insulin | back 135 D) insulin |
front 136 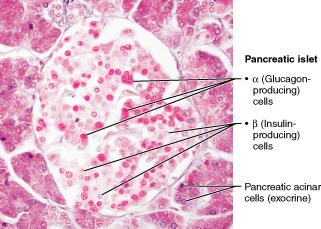 Which of the following best describes the main effects of insulin? | back 136 lower blood glucose levels |
front 137  Which of the following is a hypoglycemic hormone? | back 137 Insulin |
front 138  Which hormone is involved in diabetes mellitus (DM)? | back 138 Insulin |
front 139 True or False? Hormones are long-distance chemical signals that travel in blood or lymph throughout the body. | back 139 True |
front 140 True or False? Nitric oxide is known to be the first gas to act as a biological messenger. | back 140 True |
front 141
Which hormone directs essentially all the events of the
absorptive state? | back 141 D) Insulin |
front 142 True or False? Most ATP in cellular respiration is generated in glycolysis. | back 142 FALSE |
front 143 True or False? The body is able to form glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. | back 143 TRUE |
front 144 Sometimes prolonged exessive exposure to high hormone concentrations causes a phenomenon known as? A) Metabolism of protein kinases | back 144 C) Down regulation |
front 145
Insulin promotes all the following EXCEPT? | back 145 B) Protein synthesis |