Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Midterm Review - Quiz 5
front 1
Immediately following the arrival of the stimulus at a
skeletal muscle cell there is a short period called the ________
period during which the neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis,
diffuses across the synaptic cleft, and binds to its
receptors. | back 1 D) latent |
front 2 True or False? Muscle tone is the small amount of tautness or tension in the muscle due to weak, involuntary contractions of its motor units. | back 2 TRUE |
front 3
Which ion channel opens in response to a change in membrane
potential and participates in the generation and conduction of
action potentials? | back 3 D) voltage-gated channel |
front 4 Schwann cells are functionally similar to _______? A) neurons B) muscle cells C) oligodendrocytes D) red blood cells | back 4 C) oligodendrocytes |
front 5
What structure in skeletal muscle cells functions in calcium
storage? | back 5 D) sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 6 Which of the choices below describes the ANS? A) motor fibers that conduct nerve impulses from the CNS to smooth
muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands | back 6 A) motor fibers that conduct nerve impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands |
front 7 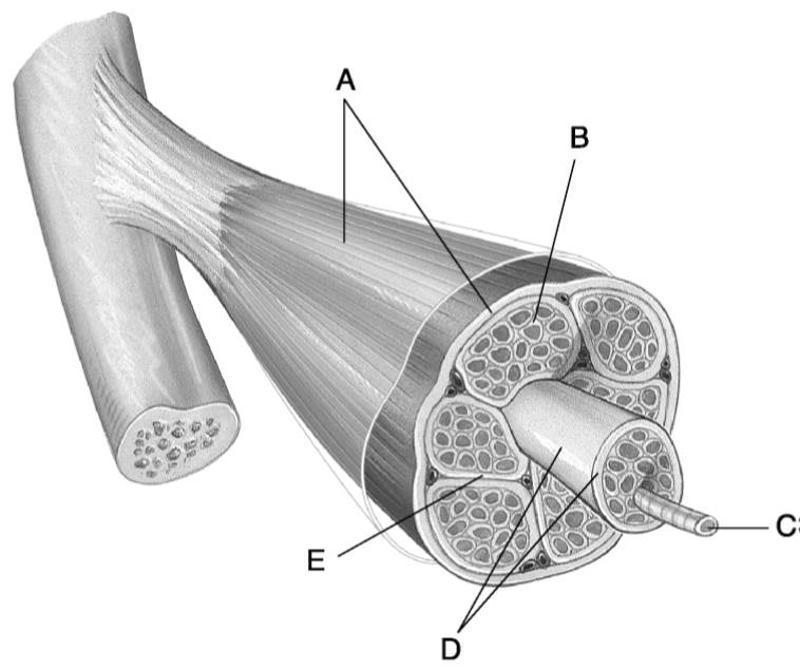
Using Figure 9.1, match the following: | back 7 1) B |
front 8 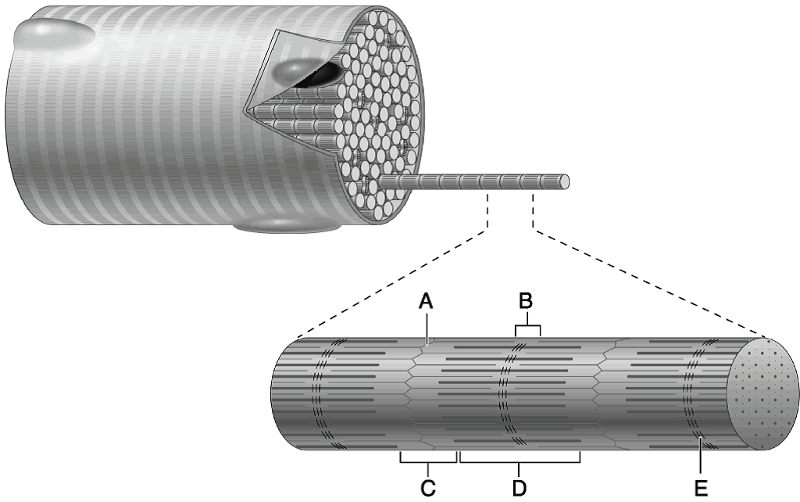
Using Figure 9.2, match the following: | back 8 1) C 2) B 3) D 4) A 5) E |
front 9 Which of the following surrounds the individual muscle cell? A) epimysium | back 9 B) endomysium |
front 10 True or False? In myelinated axons the voltage-regulated sodium channels are concentrated at the nodes of Ranvier. | back 10 TRUE |
front 11
What does the central nervous system use to determine the
strength of a stimulus? | back 11 A) frequency of action potentials |
front 12 Collections of nerve cell bodies outside the central nervous system are called ________. A) motor endplates | back 12 D) ganglia |
front 13
Which of the following would be recruited later in muscle
stimulation when contractile strength increases? | back 13 C) motor units with larger, less excitable neurons |
front 14
Which of the following describes the nervous system
integrative function? | back 14 B) analyzes sensory information, stores information, makes decisions |
front 15 True or False? The peripheral nervous system is divided into afferent and efferent divisions | back 15 TRUE |
front 16 True or False? An increase in the calcium ion level in the sarcoplasm starts the sliding of the thin filaments. When the level of calcium ions declines, sliding stops. | back 16 TRUE |
front 17 True or False? During depolarization, the inside of the neuron's membrane becomes less negative. | back 17 TRUE |
front 18 True or False? Axon diameter and degree of myelination determine nerve impulse conduction velocity. | back 18 TRUE |
front 19
The sliding filament model of contraction involves
________. | back 19 B) actin and myosin sliding past each other and partially overlapping |
front 20 These cells in the CNS have cilia that move in order to circulate cerebrospinal fluid ______. A) ependymal cells B) astrocytes C) oligodendrocytes D) Schwan cells | back 20 A) ependymal cells |
front 21
During muscle contraction, myosin cross bridges attach to
which active sites? | back 21 C) actin filaments |
front 22
What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscles?
| back 22 B) Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules. |
front 23 True or False? Although there are no sarcomeres, smooth muscle still possesses thick and thin filaments. | back 23 TRUE |
front 24
What part of the sarcolemma contains acetylcholine
receptors? | back 24 A) motor end plate |
front 25 True or False? excitability is the ability of a cell to receive and respond to stimulus by changing its membrane potential | back 25 TRUE |
front 26 Which of the following is not a function of the autonomic nervous system? A) innervation of skeletal muscle B) regulate heart rate C) regulate digestion D) regulate blood pressure | back 26 A) innervation of skeletal muscle |
front 27 True or False? A contraction in which the muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called isometric contraction. | back 27 TRUE |
front 28
The effect of acetylcholine can be stimulating or inhibiting.
Which of the following gives the best explanation for why this is
so? | back 28 D) Different post synaptic cells will have different receptors. |
front 29 True or False? The thin filaments (actin) contain a polypeptide subunit G actin that bears active sites for myosin attachment. | back 29 TRUE |
front 30
When a neurotransmitter like acetylcholine is acting in an
excitatory manner which of the following is likely a result of the
acetylcholine acting on the post synaptic cell? | back 30 C) Chemically gated sodium channels will open. |
front 31
The period after an initial stimulus when a neuron is not
sensitive to another stimulus is the ________. | back 31 B) absolute refractory period |
front 32
The term central nervous system refers to the
________. | back 32 A) brain and spinal cord |
front 33 Sarcomeres are the functional units of _____ muscle. A) smooth | back 33 D) cardiac and skeletal only |
front 34
The contractile units of skeletal muscles are
________. | back 34 B) myofibrils |
front 35 True or False? One of the important functions of skeletal muscle contraction is production of heat. | back 35 TRUE |
front 36 Which of the following is NOT a function of dendrites? A) provide enormous surface area for receiving signals from other neurons B) generate nerve impulses and transmit them away from the cell body C) convey incoming messages toward the cell body D) produce short-distance signals called graded potentials | back 36 B) generate nerve impulses and transmit them away from the cell body |
front 37
The strongest muscle contractions are normally achieved by
________. | back 37 C) increasing the stimulation up to the maximal stimulus |
front 38
After nervous stimulation stops, what prevents ACh in the
synaptic cleft from continuing to stimulate contraction?
| back 38 B) acetylcholinesterase destroying the ACh |
front 39
When a muscle is unable to respond to stimuli temporarily, it
is in which of the following periods? | back 39 C) refractory period |
front 40 Of the following muscle types, which has the longest muscle cells and has obvious stripes called striations? A) multiunit smooth muscle B) skeletal muscle C) cardiac muscle D) visceral smooth muscle | back 40 B) skeletal muscle |
front 41
An excitatory neurotransmitter secreted by motor neurons
innervating skeletal muscle is ________. | back 41 C) acetylcholine |
front 42
Muscle tone is ________. | back 42 C) a state of sustained partial contraction |
front 43
The concentration of ions in the chemical environment
surrounding the neurons must be tightly regulated for neurons to
function properly. Which of the following cells is most responsible
for this? | back 43 B) astrocytes |
front 44
Bipolar neurons are commonly ________. | back 44 C) found in the retina of the eye |
front 45
Saltatory conduction is made possible by ________.
| back 45 D) the myelin sheath |