Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Econ 315 Midterm Review
front 1 If your friend is not looking for a job because she wishes to travel the world, she is _____. | back 1 not in the labor force at all |
front 2 Many retail stores hire sales assistants during the Chrismas season. However, soon thereafter in January, they lay off these people, creating the problem of _______ unemployment. | back 2 seasonal |
front 3 If your friend is unemployed because she has a mismatch of job skills, she is technically classified as a part of ______ unemployment. | back 3 structural |
front 4 The inflation rate for the wholesale industry is measured by _______. | back 4 the Producer Price Index |
front 5 An inflation rate can measured by the change in ____________. | back 5 the consumer price index (CPI), the producer price index (PPI), the GDP deflator |
front 6 If a U.S. company produces and sells $1 million of cars in Europe, it would be included in _______ of the U.S. | back 6 the Gross National Product (GNP) |
front 7 Well-functioning financial markets promote _______ | back 7 growth. |
front 8 Poorly performing financial markets can be the cause of______ | back 8 poverty. |
front 9 Stocks represent the value of ______ whereas bonds represents the value of _____. | back 9 equity; debt |
front 10 If there are a large number of discouraged workers, the official unemployment rate published by the government may ______ the true unemployment rate in the economy. | back 10 under-estimate |
front 11 Which of the following does NOT describes phases of a business cycle? | back 11 unemployment and peak |
front 12 According to Professor Choi, the reason why it is difficult to cure an economic illness such as a cool-down or a recession is because there are time lags. Which of the following describes the time lag that is associated with knowing whether there is an economic problem or not? | back 12 recognition lag |
front 13 Total national output of the U.S. is measured by ______ which is based on the concept of the ______ of production. | back 13 Gross Domestic Product (GDP); location |
front 14 The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is a ________ institute that declares a period of an economic ______, based on the past economic performance data of a nation. | back 14 private and not-for-profit; recession |
front 15 According to Prof. Choi, ______ in an economy is like blood in a human body. | back 15 money |
front 16 Trade deficit exists when exports are _______ imports. | back 16 smaller than |
front 17 When the aggregate or average price level in an economy declines, it is known as ________. | back 17 deflation |
front 18 If your 20-year old friend is "institutionalized," she is _____. | back 18 not in the labor force at all |
front 19 In the past around the 1930s, _______ experienced a severe economic depression but _______ did not. | back 19 the U.S.; Japan |
front 20 If the labor force has 250 million people and 5 million people are unemployed, the unemployment rate is cauclated as _____. | back 20 2% |
front 21 The Gross Domestic Product is based on _______ whereas the Gross National Product (GNP) is based on ______. | back 21 the location of production; the ownership of factors of production |
front 22 Sustained downward movements in the business cycle are referred to as | back 22 recessions. |
front 23 During a recession, output declines result in | back 23 higher unemployment in the economy. |
front 24 Which of the following is most often used in labor union contracts to adjust annual salaries or other compensations? | back 24 the consumer price index (CPI) |
front 25 Trade deficit exists when exports are _______ imports and trade surplus exists when imports are _______ exports. | back 25 smaller than; smaller than |
front 26 If a quarterly inflation rate, as measured by the consumer price index, is 4%, its annualized inflation rate is ______. | back 26 16% |
front 27 The total market value of all final goods and services produced by the factors of production owned by citizens and companies of a given country during a given year, regardless of location of production, is known as _______. | back 27 the Gross National Product (GNP) |
front 28 Strong U.S. dollar against Chinese yuan favors _______ . | back 28 the U.S. importers, the U.S. consumers, the Chinese exporters |
front 29 Weak U.S. dollar against Chinese yuan favors _______ . | back 29 the U.S. exporters, the Chinese importers |
front 30 If the price level increases from 200 in year 1 to 220 in year 2, the rate of inflation from year 1 to year 2 is | back 30 10%. |
front 31 The gross domestic product is the | back 31 the market value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a year. |
front 32 If the aggregate price level at time t is denoted by Pt, the inflation rate from time t - 1 to t is defined as | back 32 πt = (Pt - Pt - 1)/Pt - 1. |
front 33 Professor Choi describes and analyzes the overall health of an economy by identifying such markets as _____? | back 33 The labor market and the product market, The financial market and the foreign market |
front 34 An economic recession describes a ______ in the national output and an inflation describes a(n) _______ in an aggregate or average price level. | back 34 decrease; increase |
front 35 The _______ is responsible for formulating and executing the monetary policy via the control of ______. | back 35 Federal Reserve System; money supply |
front 36 Which of the following is most likely to result from a stronger dollar? | back 36 U.S. goods exported abroad will cost more in foreign countries, and so foreigners will buy fewer of them. |
front 37 Everything else constant, a stronger dollar will mean that | back 37 vacationing in England becomes less expensive. |
front 38 Stocks represent ______ and ______ in a company . | back 38 equity; ownership |
front 39 Securities are ________ for the person who buys them, but are ________ for the individual or firm that issues them. | back 39 assets; liabilities |
front 40 The principal lender-savers are | back 40 households. |
front 41 Which of the following can be described as involving indirect finance? | back 41 You make a deposit at a bank. |
front 42 _______ uses the expected inflation rates in two countries to evaluate a forward foreign exchange (FX) rate. | back 42 The purchase power parity |
front 43 The (securitized) bonds issued by government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) are called _________. | back 43 government agency securities |
front 44 The capital market trades ______ financial instruments. | back 44 long-term |
front 45 Which of the following is a contractual savings institution? | back 45 a life insurance company |
front 46 An investment intermediary that lends funds to consumers is | back 46 a finance company. |
front 47 Which of the following are NOT contractual savings institutions? | back 47 credit unions |
front 48 Nonbank financial institutions are also known as _______. | back 48 nonbank banks, shadow banks |
front 49 Indirect financing uses _______________ whereas direct financing uses ________ to connect the lenders to the borrowers. | back 49 financial intermediaries; financial markets |
front 50 If a Japanese company such as Toyota sells a $1000 bond in the United States, the bond is a _____. | back 50 foreign bond. |
front 51 If Microsoft sells a bond in London and it is denominated in US dollars, the bond is a ______. | back 51 Eurodollar bond. |
front 52 If you trade a currency in a 6-month forward foreign exchange (FX) market, you are ______. | back 52 agreeing now on the FX rate that will be used in 6 months from now |
front 53 A trade made via an exchange is guaranteed by _______ whereas that made in an OTC (=over the counter) market is guaranted by __________. | back 53 the exchange; the interested parties |
front 54 The action of buying a certificate of deposit from a bank is a form of ______. | back 54 lending money to the bank |
front 55 The action of buying a sandwich is a form of ______. | back 55 paying money to the merchant |
front 56 When a Japanese merchant quotes the British pound as $2 per British pound, this is known as _______. | back 56 an American quotation or terms |
front 57 If the foreign exchange rate moves from 2 euros per US dollar to 1 euro per US dollar, it means that the euro became _______ and US dollar became _________. | back 57 stronger; weaker |
front 58 The price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency is called the | back 58 exchange rate. |
front 59 The market for initial public offerings (IPOs) of stocks is an example of ________. | back 59 the primary market for stocks |
front 60 The purchasing power parity is often used to determine a _____ forward foreign exchange (FX) rates whereas the interest rate parity is often used to determine a ______ forward FX rates. | back 60 long-term; short-term |
front 61 Bonds issued by state and local governments are called ________ bonds. | back 61 municipal |
front 62 Which of the following instruments are traded in a money market? | back 62 U.S. Treasury bills |
front 63 Equity and debt instruments with maturities greater than one year are called ________ market instruments. | back 63 capital |
front 64 Mortgage-backed securities are similar to ________ but the interest and principal payments are backed by the individual mortgages within the security. | back 64 bonds |
front 65 Which of the following instruments are traded in a capital market? | back 65 corporate bonds |
front 66 A financial market in which only short-term debt instruments are traded is called the ________ market. | back 66 money |
front 67 If the maturity of a debt instrument is less than one year, the debt is called | back 67 short-term. |
front 68 Because these securities are more liquid and generally have smaller price fluctuations, corporations and banks use the ________ securities to earn interest on temporary surplus funds. | back 68 money market |
front 69 The process of indirect finance using financial intermediaries is called | back 69 financial intermediation. |
front 70 Which of the following gives an owner a claim to the ownership of a corporation? | back 70 common stock |
front 71 Which of the following is/are the capital market instrument(s)? | back 71 Corporate bonds and Treasury notes, Municipal bonds |
front 72 The financial intermediaries that the average person interacts with most frequently are | back 72 banks. |
front 73 Financial markets promote economic efficiency by | back 73 channeling funds from savers to borrowers, channeling funds from borrowers to savers |
front 74 Financial intermediation conducted by banks and other financial institutions _______. | back 74 can benefit economic performance. |
front 75 Which of the following is a depository institution? | back 75 Commercial banks, Savings and loan associations (S&Ls), Credit unions |
front 76 Lenders are also known as _______. | back 76 bond buyers |
front 77 Borrowers are also known as _______. | back 77 demanders of loanable funds, bond sellers, bond issuers |
front 78 A debt instrument issued by a corporation is called ______ if it has a maturity less than 1 year. | back 78 a commercial paper |
front 79 Corporate checks whose payment terms are guaranteed by an endorsing bank and predominantly, used in international business by importers are ________. | back 79 banker's acceptance |
front 80 Short-term financing arrangements where debt instruments are sold one day and usually repurchased next day (or in a few days) are ________. | back 80 repurchase agreements |
front 81 Which of the following are depository institutions? | back 81 commercial banks, credit unions |
front 82 Which of the following are NOT nonbank financial institutions? | back 82 commercial banks, credit unions |
front 83 The unit of Chinese currency is known as _____. | back 83 yuan |
front 84 The unit of Japanese currency is known as _____. | back 84 yen |
front 85 If an individual moves money from currency to a demand deposit account | back 85 M1 stays the same and M2 stays the same. |
front 86 Recent financial innovation makes the Federal Reserve's job of conducting monetary policy | back 86 more difficult, since the Fed no longer knows what to consider money. |
front 87 Income is based on a ______ concept and money as used in Econ 315 is based on a ______ concept. | back 87 flow; stock |
front 88 The narrowest definition of money used in Econ 315 is ______. | back 88 M1 |
front 89 The Federal Reserve Bank's definition of money or money supply is ______. | back 89 M2 |
front 90 Currency includes | back 90 paper money and coins. |
front 91 Which of the following statements uses the economists' definition of money? | back 91 I hope that I have enough money to buy my lunch today. |
front 92 To an economist, ________ is anything that is generally accepted in payment for goods and services or in the repayment of debt. | back 92 money |
front 93 Money is | back 93 anything that is generally accepted in payment for goods and services or in the repayment of debt. |
front 94 Compared to an economy that uses a medium of exchange, in a barter economy | back 94 transaction costs are higher. |
front 95 Dennis notices that jackets are on sale for $99. In this case money is functioning as a | back 95 unit of account. |
front 96 Whatever a society uses as money, the distinguishing characteristic is that it must | back 96 be generally acceptable as payment for goods and services or in the repayment of debt. |
front 97 Of the following assets, the least liquid is | back 97 a house. |
front 98 If peanuts serve as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value, then peanuts are | back 98 money. |
front 99 When money prices are used to facilitate comparisons of value, money is said to function as a | back 99 unit of account. |
front 100 _________ is a type of e-money that is linked to the bank account for immediate deduction of funds when used. | back 100 A debit card |
front 101 If the price level doubles, the value of money | back 101 falls by 50 percent. |
front 102 During hyperinflations | back 102 money no longer functions as a good store of value and people may resort to barter transactions on a much larger scale. |
front 103 As the payments system evolves from barter to a monetary system, | back 103 commodity money is likely to precede the use of paper currency. |
front 104 Which of the following sequences accurately describes the evolution of the payments system? | back 104 barter, coins made of precious metals, paper currency, checks, electronic funds transfers |
front 105 ________ money could be used for some other purpose other than as a medium of exchange, for example, gold coins could be melted down and turned into gold jewelry. | back 105 Commodity |
front 106 A smart card is the equivalent of | back 106 cash. |
front 107 The gold standard for curency means that currency can be converted into gold at a specified rate. The main issue with the gold standard is: _______. | back 107 When too much gold is supplied, inflation tends to occur. |
front 108 Bitcoin is _______. | back 108 a digital currency |
front 109 Which of the following are the functions of money? | back 109 a store of value a unit of account |
front 110 If you borrow $2000 for two years at an annual interest rate of 5%, you will be paying back _______at the end of the second year. (Assume annual compounding.) | back 110 $2,205 |
front 111 If an interest rate is expected to decrease, you would ______ Treasury bonds now _________ after the interest rate decrease. | back 111 buy; to earn a capital gain |
front 112 If an interest rate is expected to decrease, which debt instrument would give you a larger capital gain if you buy now? | back 112 Treasury bonds |
front 113 If an annual percentage rate (APR) is 10%, its corresponding semi-annual rate is _____ and quarterly rate is ______. | back 113 5%; 2.5% |
front 114 If the current market interest rate is 5% while a consol with a $5 annual coupon payment is being sold at $110, you would ________ the consol because it yields _______ the market interest rate. | back 114 not buy; less than |
front 115 A consol is known as a ______ bond and makes ______ . | back 115 Perpetual; coupon payments forever |
front 116 What is the price of a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of 2 years and a face value of $2,000 when the current market interest rate is 4%? Assume an annual coupon payment. | back 116 $1849.11 |
front 117 What is the price of a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of 3 years and a face value of $3,000 when the current market interest rate is 3%? Assume an annual coupon payment. | back 117 $2745.42 |
front 118 If you buy a 5-year, 5% coupon T-bond with a face value of $1,000 at a price of $1100 and sell it back a year later at a price of $1210, the current yield of this bond is _____ and the total rate of return is _____. | back 118 4.54%; 14.54% |
front 119 If you bought a 10-year, 10% coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 at a price of $950 and sold it back a year later at a price of $990, you would realize a capital gain (or loss) of ______. | back 119 4.21% |
front 120 If you bought a 10-year, 10% coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 at a price of $950 and sold it back a year later at a price of $990, you would realize the total rate of return of ______. | back 120 14.73% |
front 121 If you buy an IBM share at $200 and sell it back a year later at $180, your _____ would be ____. | back 121 capital loss; -10% |
front 122 If you bought an IBM share at $200, received a $25 dividend, and sold it back at $210 a year later, your dividend yield would be _____. | back 122 12.5% |
front 123 If you are quoted of a quarterly interest rate of 0.8%, its annualized interest rate would be _____. | back 123 3.2% |
front 124 Holding all other things constant, when an interest rate (yield) decreases, a bond price ________. | back 124 increases |
front 125 Holding all other things constant, when a bond price decreases, an interest rate (yield) ________. | back 125 increases |
front 126 What is the return on a 5 percent coupon bond that initially sells for $1,000 and sells for $1,200 next year? | back 126 25 percent |
front 127 its semi-annual coupon payment is _______. | back 127 $10 |
front 128 The coupon rate is ____________. | back 128 the interest rate that a bond will pay until its maturity. |
front 129 If there is a 3-year $1,000 bond with a coupon rate of 4%, | back 129 $40 |
front 130 Assume that you are in a 20% tax bracket. If a tax-exempt bond yields 8% and a taxable bond yields 9%, you would prefer to invest in _________. | back 130 the tax-exempt bond of 8% |
front 131 Assume that you are in a 10% tax bracket. If a tax-exempt bond yields 5% and a taxable bond yields 6%, you would prefer to invest in _________. | back 131 the taxable bond of 6% |
front 132 Assuming that the real interest rate is stable, if expected inflation ____, then the nominal interest rate will most likely _____ per the Fisher equation. | back 132 increases; increase decreases; decrease |
front 133 A par bond is found when ______. | back 133 the coupon rate (CR) = the current APR |
front 134 A discount bond is found when ______. | back 134 the current bond price (BP) < the face value (FV) |
front 135 A ________ pays the owner a fixed coupon payment every year until the maturity date, when the ________ value is repaid. | back 135 coupon bond; face |
front 136 Which of the following are TRUE for discount bonds? | back 136 The purchaser receives the face value of the bond at the maturity date. |
front 137 The concept of ________ is based on the common-sense notion that a dollar paid to you in the future is less valuable to you than a dollar today. | back 137 present value |
front 138 If the amount payable in two years is $2420 for a simple loan at 10 percent interest, the loan amount is | back 138 $2000. |
front 139 A discount bond is also called a ________ because the owner does not receive periodic payments. | back 139 zero-coupon bond |
front 140 For a 3-year simple loan of $10,000 at 10 percent, the amount to be repaid is | back 140 $13,310. |
front 141 A $1000 face value coupon bond with a $60 coupon payment every year has a coupon rate of | back 141 6 percent. |
front 142 Which of the following bonds would you prefer to be buying? | back 142 a $10,000 face-value security with a 10 percent coupon selling for $9,000 |
front 143 The ________ of a coupon bond and the yield to maturity (=market interest rate) are inversely related. | back 143 price |
front 144 Assume that Bank A offers an APY of 5% and Bank B offers an APR of 5% if you open a 1-year certificate of deposit. Which bank would you deposit your money with if both banks calculate interest monthly? | back 144 Bank B |
front 145 Assume that Bank A offers an APR of 5% and Bank B offers an APY of 5% if you open a 1-year certificate of deposit. Which bank would you deposit your money with if both banks calculate interest monthly? | back 145 Bank A |
front 146 Compared to interest rates on long-term U.S. government bonds, interest rates on three-month Treasury bills change ________ frequently and are ________ on average. | back 146 more; lower |
front 147 The interest rate on a consol equals the | back 147 coupon payment divided by the price. |
front 148 If you borrow $1,000 for two years at an interest rate of 4%, you will be paying back _______ at the end of the second year. (Assume quarterly compounding.) | back 148 $1,082.85 |
front 149 If you bought an IBM share at $200, received a $25 dividend, and sold it back at $210 a year later, your total rate of return would be _____. | back 149 17.5% |
front 150 If you bought an IBM share at $120, received a $3 dividend, and sold it back at $110 a year later, your total rate of return would be _____. | back 150 -5.83% |
front 151 The price paid for the rental of borrowed funds (usually expressed as a percentage of the rental of $100 per year) is commonly referred to as the | back 151 interest rate. |
front 152 High interest rates might cause a corporation to ________ building a new plant that would provide more jobs. | back 152 postpone |
front 153 An increase in interest rates might ________ saving because more can be earned in interest income. | back 153 encourage |
front 154 The _______ frequently compounding occurs, the _______ the ending balance is. | back 154 more; larger |
front 155 An equal decrease in all bond interest rates | back 155 increases the price of a ten-year bond more than the price of a five-year bond. |
front 156 An equal increase in all bond interest rates | back 156 decreases long-term bond returns more than short-term bond returns. |
front 157 What is the price of a 10% coupon bond with a maturity of two years and a face value of $100,000 when the current market interest rate (= APR) is 11%? Assume annual compounding. | back 157 $98,287.47 |
front 158 What is the price of a 10% coupon bond with a maturity of two years and a face value of $100,000 when the current market interest rate (= APR) is 12%? Assume annual compounding. | back 158 $96,619.89 |
front 159 What is the price of a 10% coupon bond with a maturity of two years and a face value of $100,000 when the current market interest rate (= APR) is 5%? Assume annual compounding. | back 159 $109,297.05 |
front 160 Which of the following is the correct expression to calculate Present Value via the Time-Value-of-Money Equation? | back 160 PV = FV/(1+r)^t |
front 161 When there is a monthly compounding of interest, the APR (=annual percentage rate) is _______ the APY (=annual percentage yield). | back 161 less than |
front 162 Which of the following relationship between APR (=annual percentage rate) and APY (=annual percentage yield) is true? | back 162 APR=APY if no compounding |
front 163 If the interest rate increases from 3.01% to 4.25%, the interest rate is increased by ________ basis points. | back 163 124 |
front 164 A decrease in wealth or income is _______ related to the change in the asset demand. | back 164 positively |
front 165 A change in the level of risk is _______ related to the change in the asset demand. | back 165 negatively |
front 166 In the loanable funds framework, borrowers are known as _______ and lenders are known as ______. | back 166 bond issuers; bond demanders bond issuers; investors |
front 167 The loanable fund framework is called the ________ and uses ______ to understand the behavior of interest rates. | back 167 indirect approach; the bond market |
front 168 Holding all else constant, if government deficit increases, the ______ curve of bonds will shift to _______. | back 168 supply; the right |
front 169 Holding all else constant, if government deficit increases, the ______ curve of bonds will shift to _______. | back 169 supply; the right |
front 170 Holding all else constant, if the risk of losing money from bond investment increases, the demand for bonds will ______ and the demand curve for bonds shift to ______. | back 170 decrease; the left |
front 171 When the liquidity effect is _______ the combined force of the income, price level, and expected inflation effects, the interest rate will end up being ______ where it was at. | back 171 smaller than; higher than larger than; lower than |
front 172 In the loanable funds framework, the ________ curve of bonds is equivalent to the ________ curve of loanable funds. | back 172 demand; supply |
front 173 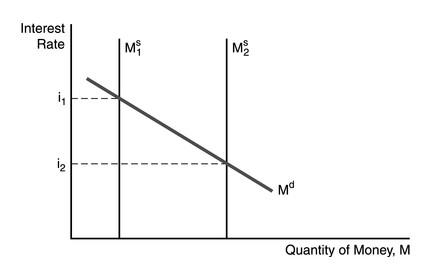 In the figure above, the factor responsible for the decline in the interest rate is | back 173 an increase in the money supply. |
front 174 Using the Liquidity Preference Framework, when the Fed ________ the money stock, the money supply curve shifts to the ________ and the interest rate ________, everything else held constant. | back 174 increases; right; falls |
front 175 Using the Liquidity Preference Framework, when the price level falls, the ________ curve for money ________, and interest rates ________, everything else held constant. | back 175 demand; decreases; fall |
front 176 Assume that stocks and Treasury bills are substitutes in investment. If stock prices are expected to drop dramatically, then, other things equal, the demand for stocks will ________ and that of Treasury bills will ________. | back 176 decrease; increase |
front 177 The demand for silver decreases, other things equal, when | back 177 the gold market is expected to boom. |
front 178 Assume that bonds and gold are substitutes in investment. If prices in the diamond market become less volatile, all else equal, then the demand for diamonds ________ and the demand for gold ________. | back 178 increases; decreases |
front 179 When the price of a bond decreases, all else equal, the bond demand curve | back 179 does not shift. |
front 180 A movement along the bond demand or supply curve occurs when ________ changes. | back 180 bond price |
front 181 Everything else held constant, when the inflation rate is expected to rise, interest rates will ________; this result has been termed the ________. | back 181 rise; Fisher effect |
front 182 During business cycle expansions when income and wealth are rising, the demand for bonds ________ and the demand curve shifts to the ________, everything else held constant. | back 182 rises; right |
front 183 Everything else held constant, an increase in the riskiness of bonds relative to alternative assets causes the demand for bonds to ________ and the demand curve to shift to the ________. | back 183 fall; left |
front 184 Which of the following effects are discussed in the liquidity preference framework? | back 184 Income effect and liquidity effect Price level effect and expected inflation effect |
front 185 It is possible that when the money supply rises, interest rates may ________ if the ________ effect is more than offset by changes in income, the price level, and expected inflation. | back 185 rise; liquidity |
front 186 Of the four effects on interest rates from an increase in the money supply, the one that works in the opposite direction of the other three is the | back 186 liquidity effect. |
front 187 When the growth rate of the money supply is increased, interest rates will fall immediately if the liquidity effect is ________ than the other money supply effects and there is ________ adjustment of expected inflation. | back 187 larger; slow |
front 188 Milton Friedman's analysis of the impact of money supply change on the interest rate is a _______ analysis and that of John Maynard Keynes is a _______ analysis. | back 188 long-term; short-term |
front 189 According to John Maynard Keynes, when government increases _______, the interest rate will tend to ______ in the short run. | back 189 money supply; decrease due to the liquidity effect |
front 190 In the market for money, an interest rate below equilibrium results in an excess ________ money and the interest rate will ________. | back 190 demand for; rise |
front 191 The demand curve for bonds has the usual downward slope, indicating that at ________ prices of the bond, everything else equal, the ________ is higher. | back 191 lower; quantity demanded |
front 192 The supply curve for bonds has the usual upward slope, indicating that as the price ________, ceteris paribus, the ________ increases. | back 192 rises; quantity supplied |
front 193 A situation in which the quantity of bonds supplied exceeds the quantity of bonds demanded is called a condition of excess supply; because people want to sell ________ bonds than others want to buy, the price of bonds will ________. | back 193 more; fall |
front 194 Which of the following is a characteristic of yield curves? | back 194 They tend to swell (move) up and down together. |
front 195 Based on the Expectations Hypothesis, if the short-term interest rate in Year 1 is 5% and the same in Year 2 is expected to be 7%, the interest rate for a 2-year bond would be ______. | back 195 6% |
front 196 Based on the Expectations Hypothesis, if the short-term interest rate in Year 1 is 4% and the same in Year 2 is expected to be 6%, the interest rate for a 2-year bond would be ______. | back 196 5% |
front 197 When yield curves are downward sloping | back 197 short-term interest rates are above long-term interest rates. |
front 198 When yield curves are steeply upward sloping | back 198 long-term interest rates are above short-term interest rates. |
front 199 The typical shape for a yield curve is | back 199 gently upward sloping. |
front 200 If 1-year interest rates for the next five years are expected to be 4, 2, 5, 4, and 5 percent, and the 5-year term premium is 1 percent, then the 5-year bond rate will be | back 200 5 percent. |
front 201 If the expected path of 1-year interest rates over the next five years is 1 percent, 2 percent, 3 percent, 4 percent, and 5 percent, the expectations theory predicts that the bond with the highest interest rate today is the one with a maturity of | back 201 five years. |
front 202 If investors expect interest rates to fall significantly in the future, the yield curve will be inverted. This means that the yield curve has a ________ slope. | back 202 downward |
front 203 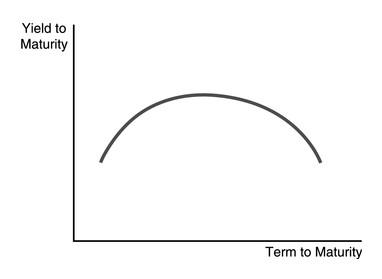 The mound-shaped yield curve in the figure above indicates that the inflation rate is expected to | back 203 rise moderately in the near-term and fall later on. |
front 204 The additional incentive that the purchaser of a Treasury security requires to buy a long-term security rather than a short-term security is called the | back 204 term premium. |
front 205 Given a yield curve, when the short-term interest rate is _____, the yield curve will tend to show a ______ slope. | back 205 low; positive high; negative |
front 206 TransUnion is a credit-rating company for ____. | back 206 Individuals |
front 207 If you are to borrow money (=U.S. dollars) outside the U.S. such as London, which of the following interest rate would be most directly relevant to you? | back 207 The LIBOR |
front 208 Which of the following long-term bonds has the highest interest rate? | back 208 corporate Baa bonds |
front 209 Bonds with relatively low risk of default are called ________ securities and have a rating of Baa (or BBB) and above; bonds with ratings below Baa (or BBB) have a higher default risk and are called ________. | back 209 investment grade; junk bonds |
front 210 If the risk-free rate is 2% and the interest rate on a risky asset is 3%, the risk premium is ____. | back 210 1% |
front 211 ________ states that yield curves reflect the term-to-maturity premium such that a longer-term bond has a higher term premium. | back 211 The liquidity premium hypothesis |
front 212 Municipal bonds have default risk, yet their interest rates are lower than the rates on default-free Treasury bonds. This suggests that | back 212 the benefit from the tax-exempt status of municipal bonds exceeds their default risk. |
front 213 The spread between the interest rates on bonds with default risk and default-free bonds is called the | back 213 risk premium. |
front 214 If the probability of a bond default increases because corporations begin to suffer large losses, then the default risk on corporate bonds will ________ and the expected return on these bonds will ________, everything else held constant. | back 214 increase; decrease |
front 215 Assume that corporate bonds and Treasury bonds are substitutes in investment. An increase in the riskiness of corporate bonds will ________ the price of corporate bonds and ________ the price of Treasury bonds, everything else held constant. | back 215 reduce; increase |
front 216 If the possibility of a default increases because corporations begin to suffer losses, then the default risk on corporate bonds will ________, and the bonds' returns will become ________ uncertain, meaning that the expected return on these bonds will decrease, everything else held constant. | back 216 increase; more |
front 217 As default risk increases, the expected return on corporate bonds ________, and the return becomes ________ uncertain, everything else held constant. | back 217 decreases; more |
front 218 Assume that corporate bonds and Treasury bonds are substitutes in investment. An increase in the riskiness of corporate bonds will ________ the yield on corporate bonds and ________ the yield on Treasury bonds, everything else held constant. | back 218 increase; reduce |
front 219 A bond with default risk will always have a ________ risk premium and an increase in its default risk will ________ the risk premium. | back 219 positive; raise |
front 220 Which of the following statements is TRUE? | back 220 A liquid asset is one that can be quickly and cheaply converted into cash. |
front 221 Bonds with no default risk are called | back 221 default-free or risk-free bonds. |
front 222 Assume that currently, the prime rate is 3% and the LIBOR is 2.9%. If Bank A charges you a prime rate + a risk premium of 2% and Bank B charges you a LIBOR + a risk premium of 2.2%, which bank would you borrow money from? | back 222 Bank A |
front 223 The interest rate on Baa corporate bonds is ________, on average, than interest rates on Treasuries, and the spread between these rates became ________ in the 1970s. | back 223 higher; larger |