Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
15
front 1 1) When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result? A) The gene involved is located on the Y chromosome. B) The gene involved is located on the X chromosome. C) The gene involved is located on an autosome, but only in males. D) Other male-specific factors influence eye color in flies. | back 1 B |
front 2 2) Which of the following statements correctly describes the meaning of the chromosome theory of inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century? A) Individuals inherit particular chromosomes attached to genes. B) Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and, in turn, segregate during meiosis. C) No more than a single pair of chromosomes can be found in a healthy normal cell. D) Natural selection acts on certain chromosome combinations rather than on genes. | back 2 C |
front 3 3) Why are males more often affected by sex-linked traits than females? A) Male hormones such as testosterone often alter the effects of mutations on the X chromosome. B) Female hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X chromosome. C) X chromosomes in males generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females. D) Males are hemizygous for the X chromosome. | back 3 D |
front 4 4) The SRY gene is best described as ________. A) a gene present on the X chromosome that triggers female development B) an autosomal gene that is required for the expression of genes on the Y chromosome C) a gene present on the Y chromosome that triggers male development D) an autosomal gene that is required for the expression of genes on the X chromosome | back 4 C |
front 5 5) In cats, black fur color is determined by an X-linked allele; the other allele at this locus determines orange color. The heterozygote is tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you expect from the cross of a black female and an orange male? A) tortoiseshell females; tortoiseshell males B) black females; orange males C) tortoiseshell females; black males D) orange females; black males | back 5 C |
front 6 6) Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son. What are the genotypes of the parents? A) XnXn and XnY B) XNXN and XnY C) XNXN and XNY | back 6 D |
front 7 7) Cinnabar eye color is a sex-linked, recessive characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F1 males will have cinnabar eyes? A) 0% B) 25% C) 50% D) 100% | back 7 D |
front 8 8) Generally, only female cats have the tortoiseshell phenotype for fur color. Which of the following statements explains this phenomenon? A) A male inherits only one allele of the X-linked gene controlling hair color. B) The Y chromosome has a gene blocking orange coloration. C) Only males can have Barr bodies. D) Multiple crossovers on the Y chromosome prevent orange pigment production. | back 8 A |
front 9 9) In birds, sex is determined by a ZW chromosome scheme. Males are ZZ and females are ZW. A recessive lethal allele that causes death of the embryo is sometimes present on the Z chromosome in pigeons. What would be the sex ratio in the offspring of a cross between a male that is heterozygous for the lethal allele and a normal female? A) 2:1 male to female B) 1:2 male to female C) 1:1 male to female D) 3:1 male to female | back 9 A |
front 10 10) Sex determination in mammals is due to the SRY gene found on the Y chromosome. Which of the following situations could allow a person with an XX karyotype to develop a male phenotype? A) the loss of the SRY gene from an autosome B) translocation of SRY to an X chromosome C) the presence of an extra autosomal chromosome D) the presence of one normal and one shortened (deleted) X | back 10 B |
front 11 11) In humans, clear gender differentiation occurs not at fertilization, but after the second month of gestation. Which of the following statements describes the first event of this differentiation? A) formation of testosterone in male embryos B) formation of estrogens in female embryos C) activation of SRY in male embryos and masculinization of the gonads D) activation of SRY in females and feminization of the gonads | back 11 C |
front 12 12) Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a serious condition caused by a recessive allele of a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients have muscles that weaken over time because they have absent or decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein. They rarely live past their 20s. How likely is it for a woman to have this condition? A) Women can never have this condition. B) One-fourth of the daughters of an affected man would have this condition. C) One-half of the daughters of an affected father and a carrier mother could have this condition. D) Only if a woman is XXX could she have this condition. | back 12 C |
front 13 13) All female mammals have one active X chromosome per cell instead of two. What causes this to happen? A) activation of the XIST gene on the X chromosome that will become the Barr body B) activation of the BARR gene on one X chromosome, which then becomes inactive C) inactivation of the XIST gene on the X chromosome derived from the male parent D) attachment of methyl (-CH3) groups to the X chromosome that will remain active | back 13 A |
front 14 14) A man who is a dwarf with achondroplasia and normal vision marries a color-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was six feet tall, and both the woman's parents were of average height. Dwarfism caused by achondroplasia is autosomal dominant, and red-green color blindness is X-linked recessive. How many of their daughters might be expected to be color-blind with achondroplasia? A) none B) half C) one out of four D) three out of four | back 14 A |
front 15 15) A man who is a dwarf with achondroplasia and normal vision marries a color-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was six feet tall, and both the woman's parents were of average height. Dwarfism caused by achondroplasia is autosomal dominant, and red-green color blindness is X-linked recessive. What proportion of their sons would be color blind and of normal height? A) none B) half C) one out of four D) all | back 15 B |
front 16 16) Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy is a human disorder that causes gradual deterioration of the muscles. Only boys are affected, and they are always born to phenotypically normal parents. Due to the severity of the disease, the boys die in their teens. Is this disorder likely to be caused by a dominant or recessive allele? Is the inheritance of this trait sex-linked or autosomal? A) dominant, sex-linked B) recessive, autosomal C) recessive, sex-linked D) incomplete dominant, sex-linked | back 16 C |
front 17 17) A recessive allele on the X chromosome is responsible for red-green color blindness in humans. A woman with normal vision whose father is color blind marries a color-blind male. What is the probability that this couple's first son will be color blind? A) 1/4 B) 1/2 C) 2/3 D) 3/4 | back 17 B |
front 18 18) Which of the following individuals will inherit an X-linked allele from a man who carries it? A) all of his daughters B) half of his daughters C) all of his sons D) all of his children | back 18 A |
front 19 19) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) is inherited as an X-linked recessive allele in humans. A woman whose father suffered from G6PD marries a normal man. What proportion of their sons is expected to be G6PD? A) 100% B) 1/4 C) 1/2 D) zero | back 19 C |
front 20 20) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) is inherited as an X-linked recessive allele in humans. A woman whose father suffered from G6PD marries a man who has the disease. What proportion of their sons would have the disease? A) 100% B) 1/2 C) 1/4 D) zero | back 20 B |
front 21 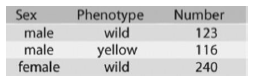 21) Use the following information to answer the question. In a Drosophila experiment, a cross was made between homozygous wild-type females and yellow-bodied males. All of the resulting F1s were phenotypically wild type. However, adult flies of the F2 generation (resulting from matings of the F1s) had the characteristics shown in the figure. How is the mutant allele for yellow body inherited? A) It is recessive. B) It is codominant. C) It is dominant. D) It is incompletely dominant. | back 21 A |
front 22  22) Use the following information to answer the question. In a Drosophila experiment, a cross was made between homozygous wild-type females and yellow-bodied males. All of the resulting F1s were phenotypically wild type. However, adult flies of the F2 generation (resulting from matings of the F1s) had the characteristics shown in the figure. How is the mutant allele for yellow body inherited? A) It is not X-linked. B) It is X-linked. C) It is inherited by X inactivation. D) It is Y-linked. | back 22 B |
front 23 23) Which of the following statements regarding gene linkage is correct? A) The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them. B) The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a maximum value of 100%. C) All of the traits that Mendel studied—seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others—are due to genes linked on the same chromosome. D) Linked genes are found on different chromosomes. | back 23 A |
front 24 24) Which of the following statements would explain a testcross involving F1 dihybrid flies in which more parental-type offspring than recombinant-type offspring are produced? A) The two genes are closely linked on the same chromosome. B) The two genes are linked but on different chromosomes. C) Recombination did not occur in the cell during meiosis. D) Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene. | back 24 A |
front 25 25) What does a recombination frequency of 50% indicate? A) The two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes. B) All of the offspring have combinations of traits that match one of the two parents. C) The genes are located on sex chromosomes. D) Abnormal meiosis has occurred. | back 25 A |
front 26 26) Which of the following phrases correctly defines what one map unit is? A) the physical distance between two linked genes B) a 1% frequency of recombination between two genes C) 1 nanometer of distance between two genes D) the recombination frequency between two genes assorting independently | back 26 B |
front 27 27) Which of the following occurrences describes how recombination between linked genes comes about? A) Nonrecombinant chromosomes break and then rejoin with one another. B) Independent assortment sometimes fails. C) Linked genes travel together at anaphase. D) Crossovers between these genes result in chromosomal exchange. | back 27 D |
front 28 28) What is an adaptive advantage of recombination between linked genes? A) Recombination is required for independent assortment. B) Recombination must occur or genes will not assort independently. C) New allele combinations are acted upon by natural selection. D) The forces on the cell during meiosis II result in recombination. | back 28 C |
front 29 29) Map units on a linkage map cannot be relied upon to calculate physical distances on a chromosome for which of the following reasons? A) The frequency of crossing over varies along the length of the chromosome. B) The relationship between recombination frequency and map units is different in every individual. C) Physical distances between genes change during the course of the cell cycle. D) The gene order on the chromosomes is slightly different in every individual. | back 29 A |
front 30 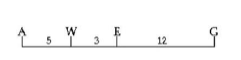 30) Use the following map of four genes on a chromosome to answer the question. Between which two genes would you expect the highest frequency of recombination? A) A and W B) E and G C) A and E D) A and G | back 30 D |
front 31 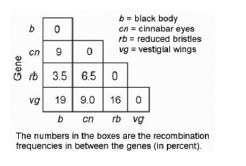 31) Use the following information to answer the question. In a series of mapping experiments, the recombination frequencies for four different linked genes of Drosophila were determined as shown in the figure. Based on this information, what is the order of these genes on a chromosome map? A) rb-cn-vg-b B) cn-rb-b-vg C) b-rb-cn-vg D) vg-cn-b-rb | back 31 C |
front 32 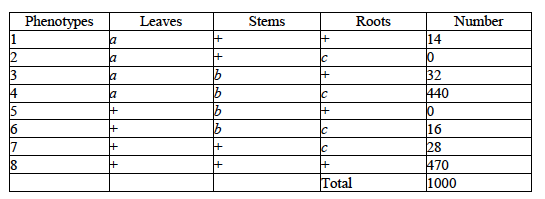 32) Use the following information to answer the question. A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type): Which of the following are the phenotypes of the parents in this cross? A) 2 and 5 B) 1 and 6 C) 4 and 8 D) 3 and 7 | back 32 C |
front 33  33) Use the following information to answer the question. A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type): Which of the progeny phenotypes will require recombination between genes A and B? A) 1, 2, 5, and 6 B) 1, 3, 6, and 7 C) 2, 4, 5, and 8 D) 2, 3, 5, and 7 | back 33 A |
front 34  34) Use the following information to answer the question. A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type): If recombination frequency is equal to distance in map units, what is the approximate distance between genes A and B? A) 3 map units B) 6 map units C) 15 map units D) 30 map units | back 34 A |
front 35  35) Use the following information to answer the question. A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type): What is the greatest benefit of having used a testcross for this experiment? A) The homozygous recessive parents are obvious to the naked eye. B) The homozygous parents are the only ones whose crossovers make a difference. C) The phenotypes of the progeny reveal the allelic content of the gamete from the heterozygous parent. D) All of the progeny will be heterozygous. | back 35 C |
front 36  36) Use the following information to answer the question. A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type): The greatest distance among the three genes is between a and c. What does this mean? A) Gene c is between a and b. B) Genes are in the order: a-b-c. C) Gene a is not recombining with c. D) Gene a is between b and c. | back 36 B |
front 37 37) Which of the following statements correctly describes the reason that closely linked genes are typically inherited together? A) They are located close together on the same chromosome. B) The number of genes in a cell is greater than the number of chromosomes. C) Alleles are paired together during meiosis. D) Genes align that way during metaphase I of meiosis. | back 37 A |
front 38 38) A homozygous tomato plant with red fruit and yellow flowers was crossed with a homozygous tomato plant with golden fruit and white flowers. The F1 all had red fruit and yellow flowers. The F1 were testcrossed by crossing them to homozygous recessive individuals, and the following offspring were obtained: Red fruit and yellow flowers—41 Red fruit and white flowers—7 Golden fruit and yellow flowers—8 Golden fruit and white flowers—44 How many map units separate these genes? A) 17.6 B) 15 C) 17.1 D) 18.1 | back 38 B |
front 39 39) In Drosophila melanogaster, vestigial wings are determined by a recessive allele of a gene that is linked to a gene with a recessive allele that determines black body color. T. H. Morgan crossed black-bodied, normal-winged females and gray-bodied, vestigial-winged males. The F1 were all gray bodied, normal winged. The F1 females were crossed to homozygous recessive males to produce testcross progeny. Morgan calculated the map distance to be 17 map units. Which of the following information is correct about the testcross progeny? A) black-bodied, normal-winged flies = 17% of the total B) black-bodied, normal-winged flies plus gray-bodied, vestigial-winged flies = 17% of the total C) gray-bodied, normal-winged flies plus black-bodied, vestigial-winged flies = 17% of the total D) black-bodied, vestigial-winged flies = 17% of the total | back 39 C |
front 40 40) If cell X enters meiosis, and nondisjunction of one chromosome occurs in one of its daughter cells during meiosis II, how will this affect the gametes at the completion of meiosis? A) All the gametes descended from cell X will be diploid. B) Half of the gametes descended from cell X will be n + 1, and half will be n - 1. C) One-quarter of the gametes descended from cell X will be n + 1, one-quarter will be n - 1, and half will be n. D) Two of the four gametes descended from cell X will be haploid, and two will be diploid. | back 40 C |
front 41 41) One possible result of chromosomal breakage is for a fragment to join a nonhomologous chromosome. What is this type of chromosomal alteration called? A) deletion B) inversion C) translocation D) duplication | back 41 C |
front 42 42) Which of the following statements correctly describes what happens to a chromosome after a nonreciprocal translocation occurs? A) A deletion of part of the chromosome occurs. B) A duplication of part of the chromosome occurs. C) Nondisjunction of pairs of homologous occurs. D) A chromosome transfers a fragment but receives none in return. | back 42 D |
front 43 43) Of the following human aneuploidies, which is the one that generally has the most severe impact on the health of the individual? A) 47, trisomy 21 B) 47, XXY C) 47, XXX D) 45, X | back 43 A |
front 44 44) A phenotypically normal prospective couple seeks genetic counseling because the man knows that he has a translocation of a portion of his chromosome 4, which has been exchanged with a portion of his chromosome 12. Although his translocation is balanced, he and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm will be abnormal. What is your prognosis regarding his sperm? A) One-quarter will carry the two normal chromosomes, 4 and 12, one-quarter will have only the two translocation chromosomes and no normal chromosomes 4 and 12, and half will have one normal and one translocated chromosome. B) All will carry the same translocation as the father. C) None will carry the translocation. D) Half will be normal, and the rest will have the father's translocation. | back 44 A |
front 45 45) Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions. Which of the following events might then occur to make the cancer worse? A) an increase in nondisjunction B) expression of inappropriate gene products C) a decrease in mitotic frequency D) failure of the cancer cells to multiply | back 45 B |
front 46 46) A couple has a child with Down syndrome. The mother is 39 years old at the time of delivery. Which of the following is the most probable cause of the child's condition? A) The woman inherited this tendency from her parents. B) The mother had a chromosomal duplication. C) One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in somatic cell production. D) One of the gametes in the mother most likely underwent nondisjunction during meiosis. | back 46 D |
front 47 47) What is a syndrome? A) a characteristic facial appearance B) a trait that leads to cancer at some stage in life C) a group of traits typically found in conjunction with a particular chromosomal aberration or gene mutation D) a specific characteristic that appears in conjunction with one specific aneuploidy | back 47 C |
front 48 48) Which of the following correctly describes a Philadelphia chromosome? A) a human chromosome 22 that has had a specific translocation B) a human chromosome 9 that is found only in one type of cancer C) an animal chromosome found primarily in the mid-Atlantic area of the United States D) a chromosome found only in mitochondria | back 48 A |
front 49 49) Which of the following statements is generally true of aneuploidies in newborns? A) A monosomy is more frequent than a trisomy. B) Monosomy X is the only viable monosomy known to occur in humans. C) Human aneuploidy usually conveys an adaptive advantage in humans. D) An aneuploidy resulting in the deletion of a chromosome segment is less serious than a duplication. | back 49 B |
front 50 50) A woman is found to have 47 chromosomes, including three X chromosomes. Which of the following statements describes her expected phenotype? A) a female with masculine characteristics such as facial hair B) an apparent male who is sterile C) healthy female of slightly above-average height D) a sterile female | back 50 C |
front 51 51) Which of the following is an example of monosomy in humans? A) Turner syndrome B) Klinefelter syndrome C) Down syndrome D) trisomy X | back 51 A |
front 52 52) Genomic imprinting is generally due to the addition of methyl (-CH3) groups to C nucleotides and chemical histone changes to silence a given gene. If this depends on the sex of the parent who transmits the gene, which of the following statements must be true? A) Genes required for early development stages must not be imprinted. B) Methylation of this kind must occur more in males than in females. C) Methylation must be reversible in ovarian and testicular cells. D) The imprints are transmitted only to gamete-producing cells. | back 52 C |
front 53 53) German scientist Carl Correns found that the inheritance of variegated color on the leaves of certain plants was determined only by the maternal parent. What phenomenon explains this pattern of inheritance? A) ribosome structure B) inheritance of plastid genes C) genomic imprinting D) sex linkage | back 53 B |
front 54 54) Mitochondrial DNA is primarily involved in coding for proteins needed for protein complexes of the electron transport chain and ATP synthase. Therefore, mutations in mitochondrial genes would most affect which of the following processes? A) DNA synthesis in cells of the immune system B) the movement of oxygen into erythrocytes C) generation of ATP in muscle cells D) the storage of urine in the urinary bladder | back 54 C |
front 55 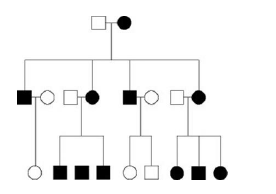 55) Use the following figure to answer the question. The pedigree in the figure shows the transmission of a trait in a particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is most likely ________. A) mitochondrial B) sex-linked dominant C) sex-linked recessive D) autosomal dominant | back 55 A |
front 56 56) A certain kind of snail can have a right-handed direction of shell coiling (DD or Dd) or left-handed coiling (dd). However, if direction of coiling is due to a protein deposited by the mother in the egg cytoplasm, then a Dd egg-producing snail and a dd sperm-producing snail will have offspring of which genotype(s) and phenotype(s)? A) 1/2 Dd:1/2 dd; all right-coiling B) all Dd; all right-coiling C) 1/2 Dd: 1/2 dd; half right-coiling and half left-coiling D) all Dd; half right-coiling and half left-coiling | back 56 A |
front 57 57) During meiosis, a defect occurs in a cell that results in the failure of spindle microtubules binding at the kinetochores. Which of the following statements describes the most likely result of such a defect? A) New microtubules with more effective binding capabilities to kinetochores will be synthesized to compensate for the defect. B) Excessive cell divisions will occur resulting in cancerous tumors and an increase in the chromosome numbers known as polyploidy. C) The defect will be bypassed in order to ensure normal chromosome distribution in the new cells. D) The resulting cells will not receive the correct number of chromosomes in the gametes, a condition known as aneuploidy. | back 57 D |
front 58 58) Inheritance patterns cannot always be explained by Mendel's models of inheritance. If a pair of homologous chromosomes fails to separate during meiosis I, select the choice that shows the chromosome number of the four resulting gametes with respect to the normal haploid number (n)? A) n + 1; n + 1; n - 1; n - 1 B) n + 1; n - 1; n; n C) n + 1; n - 1; n - 1; n - 1 D) n + 1; n + 1; n; n | back 58 A |