Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
anatomy & physiology
front 1 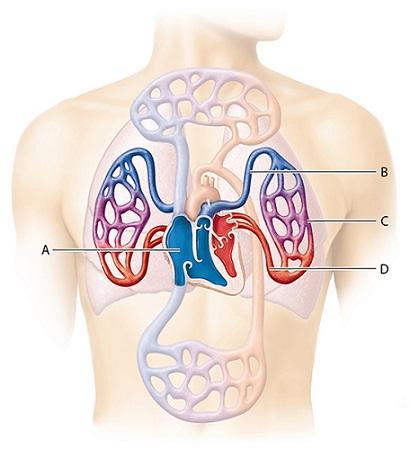 1-The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood into __________. A | back 1 B |
front 2 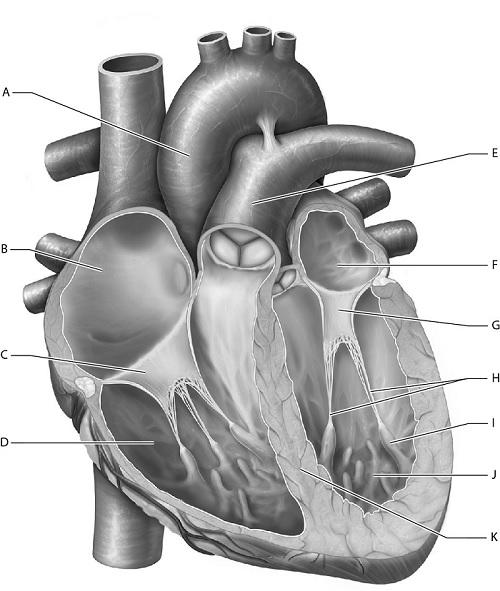 2-Identify the right atrium. E | back 2 B |
front 3  3-Identify the left ventricle. E | back 3 J |
front 4  4- Identify the papillary muscle. K | back 4 I |
front 5  5-Identify the pulmonary trunk. J | back 5 E |
front 6  6-Identify the interventricular septum. K | back 6 K |
front 7  7-Identify the mitral (bicuspid) valve. K | back 7 G |
front 8 8-The apex of the heart is __________. anterior | back 8 inferior |
front 9 9-What surface groove separates the right and left ventricles? interventricular sulcus | back 9 interventricular sulcus |
front 10 10-The pulmonary circuit involves blood flow from the heart to the: lungs. | back 10 lungs. |
front 11 11-The vessels that deliver oxygen to the tissues of the body are part of the __________. pulmonary circuit | back 11 systemic circuit |
front 12 12-Which of the following vessels carries oxygenated blood? superior vena cava | back 12 pulmonary vein |
front 13 13-Blood from the systemic circuit returns to the heart via the __________. pulmonary arteries | back 13 venae cavae |
front 14 14-Which hormone decreases cardiac output by decreasing blood volume and preload? aldosterone | back 14 atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) |
front 15 15-What two values are needed in order to calculate cardiac output (CO) for a ventricle? end-diastolic volume (EDV) and end-systolic volume (ESV)
| back 15 stroke volume (SV) and heart rate (HR) |
front 16 16-What largely determines preload? afterload | back 16 end-diastolic volume (EDV) |
front 17 17-Afterload is described as: the length or degree of stretch of the sarcomeres in the
ventricular cells before they contract. | back 17 the force the ventricles must overcome to eject blood into their respective arteries. |
front 18 18-Which of the following happens immediately after the P wave? The ventricles contract. | back 18 The atria contract. |
front 19 19-The aortic valve closes when __________. the pressure in the left ventricle falls below atrial pressure
| back 19 the pressure in the left ventricle falls below aortic pressure |
front 20 20-During what phase does blood flow from the ventricles into the pulmonary trunk and aorta? ventricular filling | back 20 ventricular ejection phase |
front 21  21-Which of the following events will immediately follow the phase of the cardiac cycle depicted in the figure? the atrioventricular valves open. | back 21 the atrioventricular valves open. |
front 22 22-The P wave on an electrocardiogram (ECG) represents the depolarization of cells in the: atria. | back 22 atria. |
front 23 23-What valve prevents the backflow of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium? tricuspid valve | back 23 tricuspid valve |
front 24 24-What vessel delivers oxygenated blood to systemic capillaries for gas exchange? coronary artery | back 24 aorta |
front 25 25-What vessel(s) deliver oxygenated blood to the left atrium? aorta | back 25 pulmonary veins |
front 26 26-Autorhythmicity in the heart is the responsibility of: skeletal muscle cells. | back 26 cardiac pacemaker cells. |
front 27 27-What characteristic differentiates cardiac muscle cells from skeletal muscle cells? intercalated discs | back 27 intercalated discs |
front 28 28-Unlike skeletal muscle action potentials, cardiac muscle action potentials __________. do not involve repolarization | back 28 involve calcium voltage-gated channel |
front 29 29-What normally serves as the pacemaker of the entire heart? Purkinje fiber system | back 29 sinoatrial (SA) node |