Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Test 1
front 1 The Nurse has charted: "Client has an open wound located on the lateral aspect of the leg". This wound would be located on which portion of the leg? | back 1 outer surface or lateral side |
front 2 The serous membrane that covers the intestines is what? | back 2 Visceral Peritoneum |
front 3 A vertical section through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior portions is what? | back 3 Coronal or frontal |
front 4 The anatomical position is used as what? | back 4 A standard reference point for directional terms regardless of the actual position of the body |
front 5 The frontal plane is also called the _______ plane? | back 5 Coronal |
front 6 The dorsal body cavity is the site of what? | back 6 Brain and spinal cord |
front 7 The spleen is located in which quadrant of the body? | back 7 Left upper quadrant |
front 8 Place the following in correct sequence from simplest to most complex
| back 8 Atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ |
front 9 Homeostasis is the condition in which the b.
| back 9 A relatively stable internal environment, within limits |
front 10 The parietal pleura would represent a serous membrane that does what? | back 10 lines the thoracic cavity |
front 11 The anatomical position is characterized by all of the following except_______
| back 11 palms turned posteriorly |
front 12 A negative feedback mechanism works how? | back 12 To prevent sudden severe changes within the body |
front 13 The main, general purpose of negative feedback is? | back 13 to maintain homeostasis |
front 14 True or false
| back 14 True |
front 15 True or False
| back 15 True |
front 16 True or False
| back 16 False |
front 17 True or False
| back 17 False |
front 18 Directly causes mechanical motion | back 18 Muscular |
front 19 Responds to environmental changes by transmitting electrical impulses | back 19 Nervous |
front 20 Provides support and levers for muscle to work on | back 20 Skeletal |
front 21 Protects underlying organs from mechanical damage and synthesizes vitamin D | back 21 Integumentary |
front 22 The other two terms for the horizontal plane are what? | back 22 Transverse and cross section |
front 23 The elbow is _________ to the wrist? | back 23 Proximal |
front 24 The knee is _________ to the hip? | back 24 Distal |
front 25 The knee is ______ to the ankle? | back 25 Proximal |
front 26 True or False
| back 26 True |
front 27 True or False
| back 27 True |
front 28 In anatomic position the great (1st toe) is which of the following?
| back 28 medial |
front 29 A chain of 25 amino acids would be called a what? | back 29 Polypeptide |
front 30 The coiling of the protein chain backbone into an alpha helix is referred to as the what? | back 30 Secondary structure |
front 31 Carbohydrates and proteins are built up from their basic building blocks by the _____? | back 31 Removal of a water molecule between each two units |
front 32 Which statement about enzymes is NOT true?
| back 32 Enzymes raise the activation energy needed to start a reaction |
front 33 What four elements make up about 96% of body matter? | back 33 Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen |
front 34 The structure composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acids is what? | back 34 Tryglycerides |
front 35 The major function of carbohydrates in humans is what? | back 35 Generation of ATP |
front 36 Which of the following is NOT a type of lipid?
| back 36 Glycogen |
front 37 The major functions of proteins in the body are what? | back 37 Structures and enzymes |
front 38 Having a polar and nonpolar portion is called? | back 38 Amphiphatic |
front 39 The plasma membrane on the extracellular side and the cytosolic side are what? | back 39 Not identical in structure |
front 40 The hydrophobic portion of the plasma membrane is made up of what? | back 40 Fatty acid tails |
front 41 The most abundant substance in the plasma membrane is what? | back 41 Phospholipids |
front 42 The cholesterol molecules separate phospholipids, provides an anchoring function in the outer portions of the membrane and what? | back 42 Contributes to fluidity in the inner portion of the membrane |
front 43 Glycolipids and glycoproteins are located at which sites in the plasma membrane? | back 43 Extracellular side |
front 44 Lipid rafts display what characteristic? | back 44 Less fluid than the rest of the membrane |
front 45 The plasma membrane will be disrupted with the removal of what types of proteins? | back 45 Integral proteins |
front 46 Most of the integral proteins are positioned such that they what? | back 46 Face both the cytosolic and extracellular side |
front 47 Peripheral proteins are associated with which portion of the plasma membrane? | back 47 Hydrophilic portion |
front 48 Plasma membrane proteins can move how? | back 48 Laterally in the membrane |
front 49 Integral proteins do not function how? | back 49 Exclusively as transport channels |
front 50 Glycocalyx is associated with what functions? | back 50 Cell recognition, Maintaining the hydration status of the cell, Making the cell slippery |
front 51 The major function of a microvilli is what? | back 51 Increase the surface area of the cell |
front 52 What are the characteristics asoociated with passive movement across a plasma membrane? | back 52 Nonpolar and small molecular size |
front 53 Give examples of classified passive processes? | back 53 Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion, Diffusion through channels |
front 54 What is one example that is not a classified passive process? | back 54 Vesicular transport |
front 55 What are examples of passive process simple diffusion? | back 55 Oxygen, alcohol |
front 56 What are examples of passive process Facilitated diffusion? | back 56 Glucose, Galactose |
front 57 What are examples of passive process Osmosis? | back 57 Water |
front 58 Osmosis is the movement of water from? | back 58 An area of low to high solute concentration |
front 59 The generation of the resting membrane potential is most associated with what channel? | back 59 Leakage channel |
front 60 There are not more leakage channels for sodium in the plasma membrane than for what? | back 60 Potassium |
front 61 Gated channels can be opened by what mechanism? | back 61 Ligands, Voltage change, Mechanical stimulation of the plasma membrane |
front 62 A cell that is surrounded by a hypertonic extracellular fluid will do what? | back 62 shrink |
front 63 A substance that binds to a plasma membrane receptor to trigger a cellular response is what? | back 63 Ligand |
front 64 What are some examples of ligands? | back 64 Neurostansmitter, hormones and drugs |
front 65 What does the sodium-potassium ATPase pump do? | back 65 3 sodium ions are pumped from the intracellular to the extracellular space |
front 66 Active transport does what? | back 66 Release of acetylcholine from a secretory vesicel via exocytosis |
front 67 Phagocytosis is best described by what? | back 67 An active process in which lysosomes fuse with the enveloped vesicle |
front 68 Membrane-enclosed vesicles formed in the golgi complex that contains strong hydrolytic and digestive enzymes | back 68 Lysosomes |
front 69 Network of protein filaments that extend throughout the cytoplasm, providing cellular shape, organization and movement | back 69 Cytoskeleton |
front 70 Sites of protein synthesis | back 70 Ribosomes and Rough ER |
front 71 Contains enzymes that break apart unneeded, damaged or faulty proteins into smaller peptides | back 71 proteosomes |
front 72 Site where secretory proteins and membrane molecules are synthesized | back 72 Rough ER |
front 73 Membrane-enclosed vesicle that contains enzymes that oxidize various organic substances | back 73 Peroxisomes |
front 74 Short microtubular structures extending from the plasma membrane and involved in movement of materials along the cell's surface | back 74 Cilia |
front 75 Modifies, sorts, packages, and transports molecules synthesized in the rough ER | back 75 Golgi complex |
front 76 An organizing center for growth of the mitotic spindle | back 76 Centrosome |
front 77 Functions in ATP generation | back 77 Mitochondria |
front 78 Functions in synthesizing fatty acids and steroids, helping liver cells release glucose into the bloodstream, and detoxification | back 78 Smooth ER |
front 79 Membrane-bound sacs that transport, transfer or secrete proteins | back 79 Vesicles |
front 80 Long microtubular structures extending from the plasma membrane and involved in the movement of a cell | back 80 Flagellum |
front 81 Cristae | back 81 Mitochondria |
front 82 Cis and trans face | back 82 Golgi apparatus |
front 83 Cisternal system that is located immediately adjacent to the nucleus and is involved in protein synthesis | back 83 Rough ER |
front 84 movement of sperm | back 84 Flagellum |
front 85 Vesicles that contain oxidases and catalases | back 85 Peroxisome |
front 86 Smallest of the cytoskeletal elements; example is actin | back 86 Microfilaments |
front 87 Site of attachment of tRNA | back 87 Ribosome |
front 88 Exhibits a beating motion for movement of particles in the respiratory and female reproductive tract | back 88 Cilia |
front 89 Site of assembly of ribosomes | back 89 Nucleolus |
front 90 Associated with the proteins kinesins and dyneins for movement | back 90 Microtubules |
front 91 Degradation of damaged or old proteins; peptide chains broken down into amino acids | back 91 Proteosome |
front 92 Electron transport chain | back 92 Mitochondria |
front 93 Cisternal system that has vesicles budding from its surface | back 93 Golgi apparatus |
front 94 Sarcoplasmic reticulum | back 94 Smooth ER |
front 95 Mitotic spindle | back 95 centriole |
front 96 Vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes | back 96 Lysosome |
front 97 Conversion of hydrogen peroxide to a non-harmful substance | back 97 Perioxisome |
front 98 Transport of substances that have entered the cell via endocytosis to various organelles | back 98 Endosomes |
front 99 Opening in double layered membrane by which mRNA exits in route to the cytosol | back 99 Nuclear pore |
front 100 Synthesis of fatty acids and steroids and detoxification of some substances (ex: alcohol) | back 100 Smooth ER |
front 101 Cytoskeletal element associated with red blood cell structural integrity | back 101 Intermediate filament |
front 102 What processes occur in the cell's nucleus? | back 102 Replication and trancription |
front 103 How many nucleus' do all cell's contain? | back 103 1 or more |
front 104 Double layered and selectively permeable | back 104 Nuclear membrane |
front 105 A nucleosome contains how many histone proteins wrapped in the DNA strand? | back 105 8 |
front 106 When the cell is carrying out normal daily activity the DNA is in what form? | back 106 Extended form(chromatin) |
front 107 Deoxyribose and the phosphate group is part of what? | back 107 DNA nucleotide |
front 108 The shortest portion of interphase is what? | back 108 G2 |
front 109 During interphase the cell is doing what? | back 109 Performing its usual metabolic activities |
front 110 What is the correct sequence of bases for the complementary strand of DNA formed during replication for the DNA template bases of CGTA? | back 110 GCAT |
front 111 Shortest sequences of RNA are needed to initiate the process of replication. These RNA nucleotides are later what? | back 111 Replaced by DNA nucleotides |
front 112 The complementary strand of DNA made during replication that is synthesized in segments that are spliced together is what? | back 112 Lagging strand |
front 113 What cells do not have the ability to divide in the human adult? | back 113 Cardiac muscle cells and neurons |
front 114 What is a trigger for cells to stop dividing? | back 114 Contact inhibition |
front 115 What rise and fall in a cyclic pattern during interphase and mitosis? | back 115 Cyclin and MFP |
front 116 The longest phase of mitosis is what? | back 116 Prophase |
front 117 What is the correct sequence of events in mitosis? | back 117 Prophase, Metaphaose, Anaphase, and Telophase |
front 118 During prophase the nuclear membrane disintegrates. It reforms during what stage? | back 118 Telophase |
front 119 The phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell is what? | back 119 Anaphase |
front 120 The microtubular elements of the mitotic spindle that are attached to the centromere of the chromosomes is what? | back 120 Kinetochores |
front 121 The phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes are lined up at the equator of the cell is what? | back 121 Metaphase |
front 122 Kinetochores pulls the chromosomes to the middle of the cell. Polar microtubules push the poles of the cell which way? | back 122 apart |
front 123 Nucleoli remain visible or nonvisible thoughout mitosis? | back 123 nonvisible |
front 124 The shortest phase of mitosis is what? | back 124 Anaphase |
front 125 The term chromosomes refers to 2 chromatids connected by a centromere. Once anaphase has occurred and the individual chromatids have separated, each chromatid is now what? | back 125 termed a chromosome |
front 126 Telophase is in most ways ________ in reverse? | back 126 Prophase |
front 127 The cleavage furrow is most associated with which stage of mitosis? | back 127 Telophase |
front 128 The base pair of RNA is what? | back 128 AUCG |
front 129 The 3 base pair groupings of mRNA is what? | back 129 Codon |
front 130 The RNA that is cloverleaf-shaped and has an end for bases and an end for a specific amino acid is what? | back 130 tRNA |
front 131 The process of transcription is best described as what? | back 131 A strand of mRNA and is made from a DNA template |
front 132 What type of RNA is used in the process of translation? | back 132 tRNA, mRNA and rRNA |
front 133 Transcription factor performs what function? | back 133 Loosens the histones and binds to the promotor region of DNA |
front 134 What would be the complementary codon for a DNA template with the bases TAACGA? | back 134 AUUGCU |
front 135 What would be the complementary anticodon for a codon with the base ACG? | back 135 UGC |
front 136 What would be the anticodon for the DNA bases of ATGC? | back 136 AUGC |
front 137 The portion of pre-RNA that is removed is termed what? | back 137 introns |
front 138 The mRNA binds to what following translation? | back 138 A site |
front 139 The sequence for tRNA to the large ribosomal subunit during translation is what? | back 139 A site....P site....E site |
front 140 The basic physical unit of heredity, consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism is what? | back 140 Gene |
front 141 Complex of proteins and enzymes required for replication | back 141 Replisome |
front 142 Removes the introns from the pre-mRNA | back 142 Spliceosome |
front 143 Microtubules attached to the centrioles | back 143 Asters |
front 144 Aids in the attachment of chromatids to each other | back 144 Cohesin |
front 145 Protective caps on the ends of chromosomes | back 145 Telomeres |
front 146 Histones wrapped together by DNA helix | back 146 Nucleosomes |
front 147 Y-shaped area site of replication | back 147 Replication fork |
front 148 Enzyme used in transcription | back 148 RNA polymerase |
front 149 Enzyme that unwinds the DNA strands during replications | back 149 Helicase |
front 150 Enzyme involved in replication by placing the correct nucleotide and creating bonds | back 150 DNA ploymerase III |
front 151 Enzyme that splices together the segments of DNA made during replication on the lagging strand | back 151 DNA ligase |
front 152 Enzyme that cleaves the cohesin holding the chromatids together | back 152 Separase |
front 153 The area surrounding the centrioles | back 153 Centrosomes |
front 154 Mitotic spindle | back 154 Centrioles |
front 155 Connects to chromatids | back 155 Centromeres |
front 156 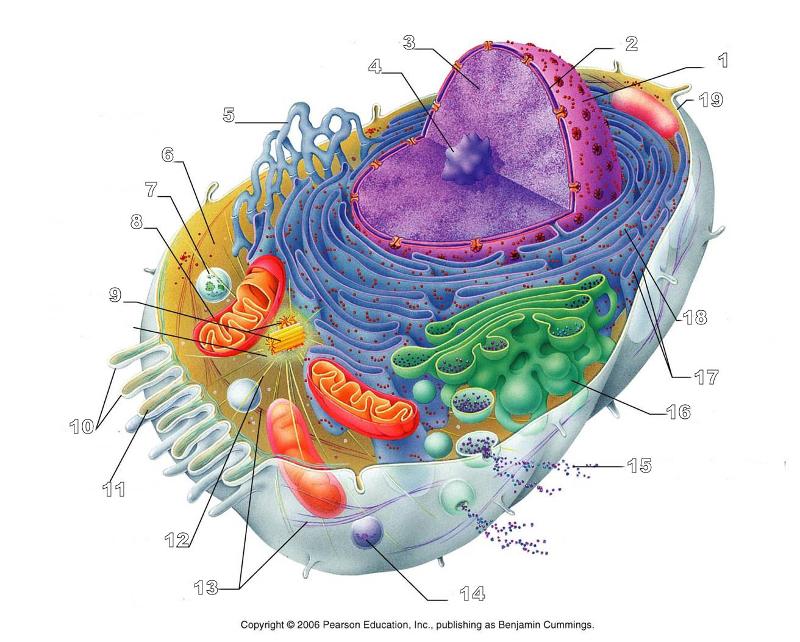 What is #1 in this picture? | back 156 Nucleus |
front 157 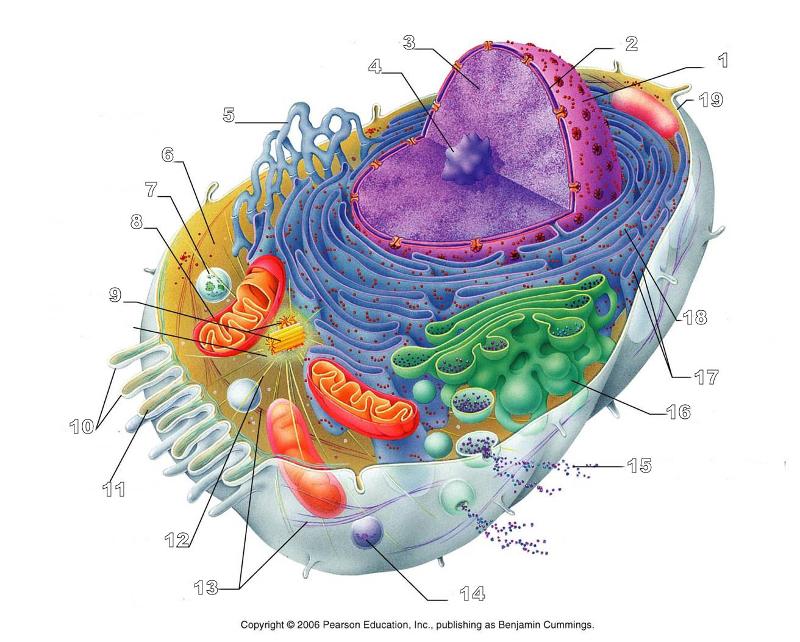 What is #2 in this picture? | back 157 Nuclear envelope |
front 158 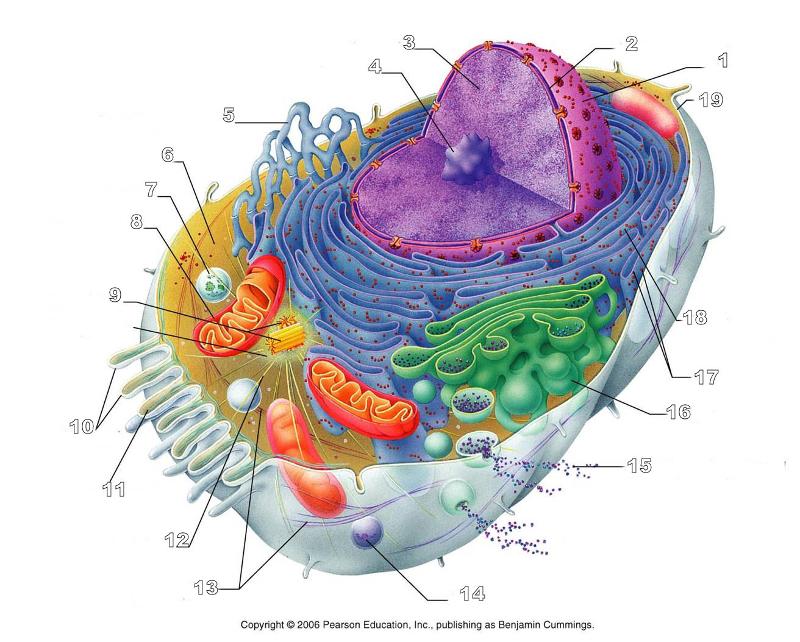 What is #3 in this picture? | back 158 Chromatin |
front 159 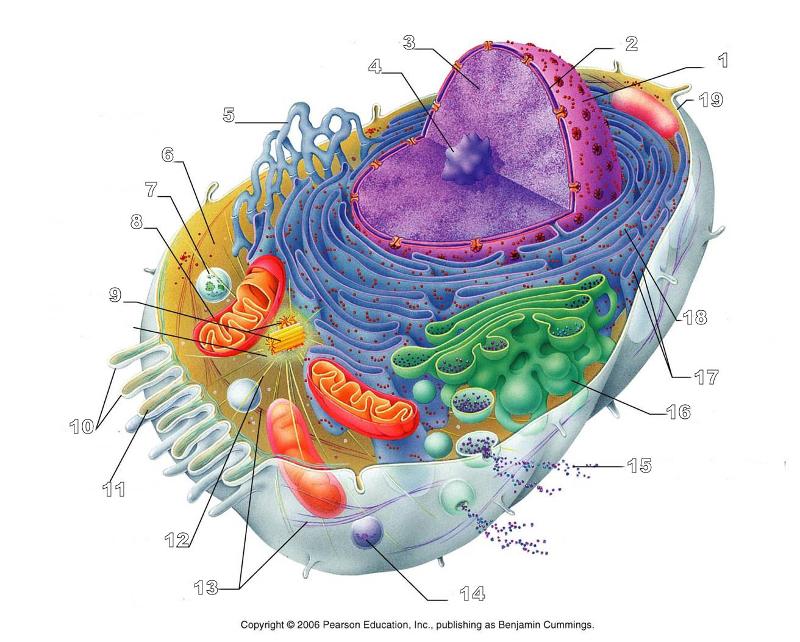 What is number #4 in this picture? | back 159 Nucleolus |
front 160 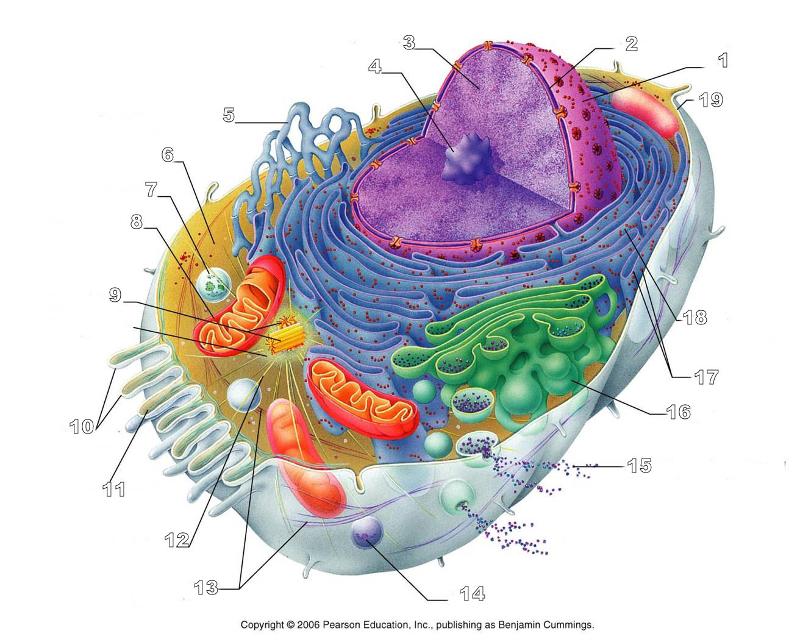 What is #5 in this picture? | back 160 Smooth ER |
front 161 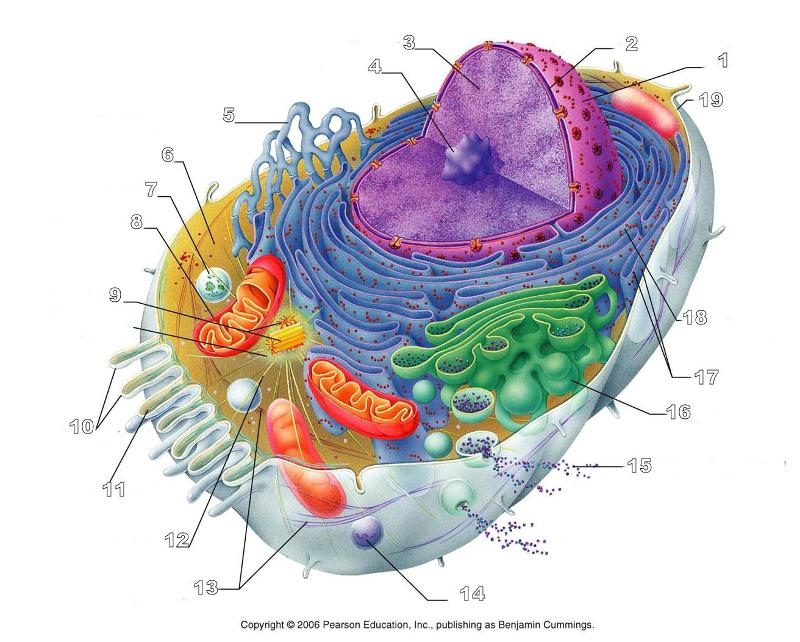 What is #6 in this picture? | back 161 Cytosol |
front 162 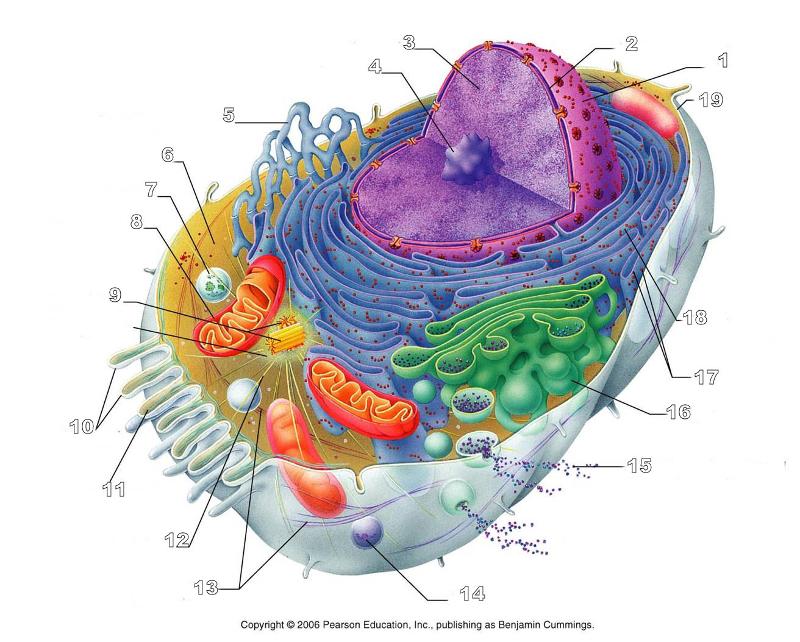 What is # 7 in this picture? | back 162 Lysosome |
front 163 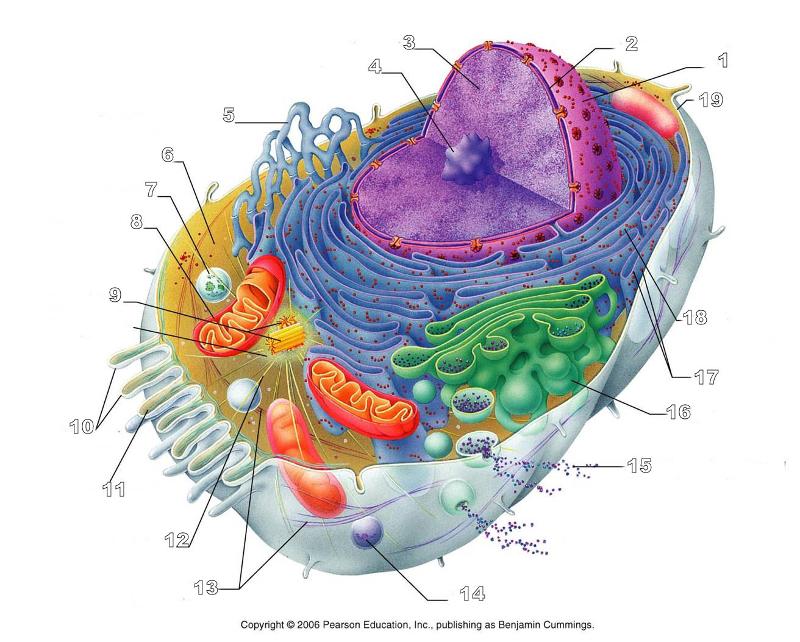 What is #8 in this picture? | back 163 Mitochondrion |
front 164 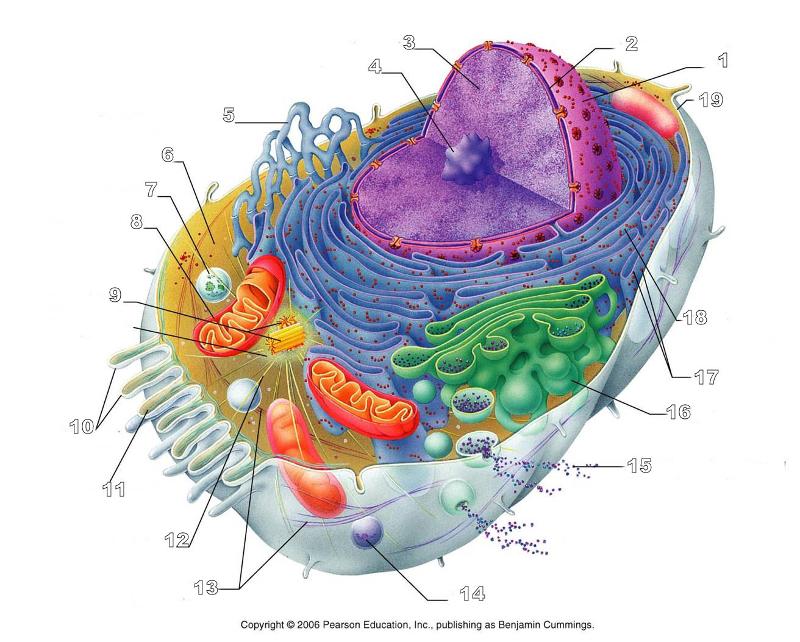 What is #9 in this picture? | back 164 Centrioles |
front 165 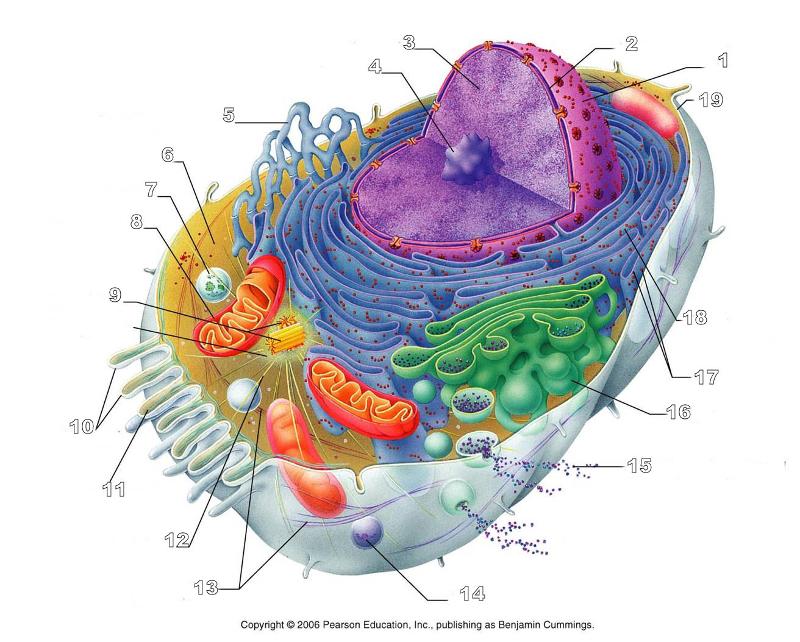 What is #10 in this picture? | back 165 Microvilli |
front 166 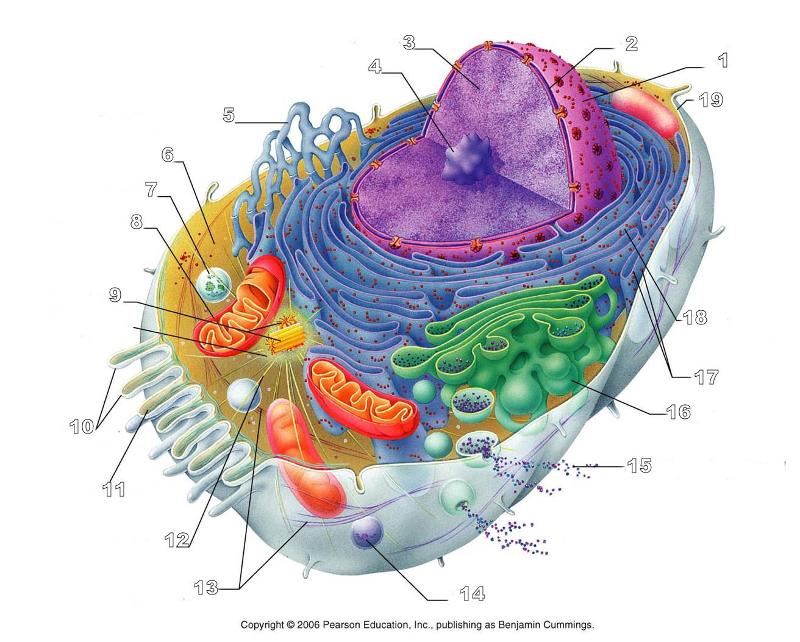 What is #11 in this picture? | back 166 Microfilament |
front 167 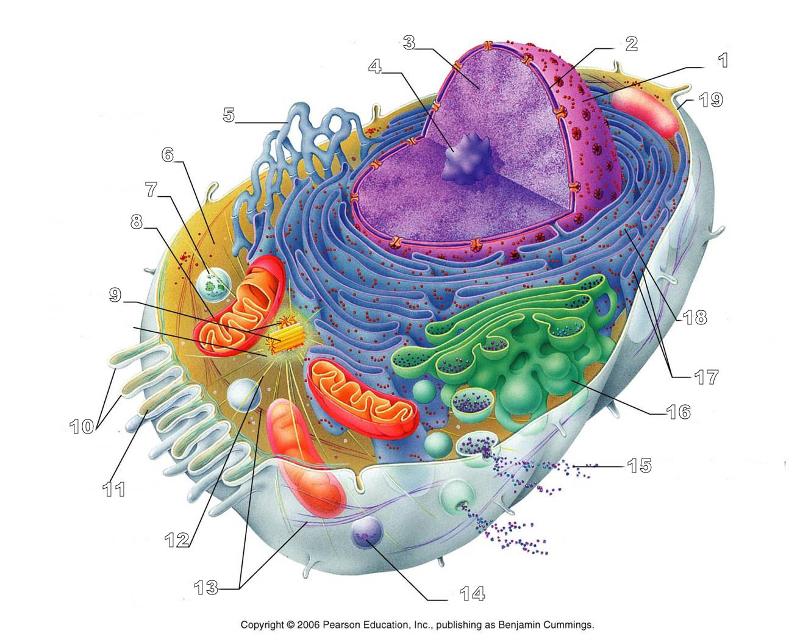 What is #13 in this picture? | back 167 Intermediate Filament |
front 168 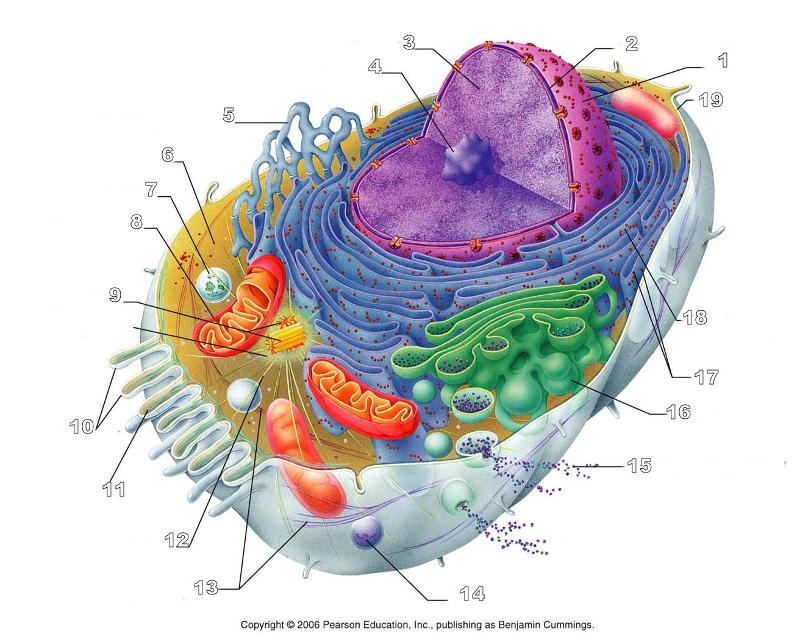 What is #14 in this picture? | back 168 Peroxisome |
front 169 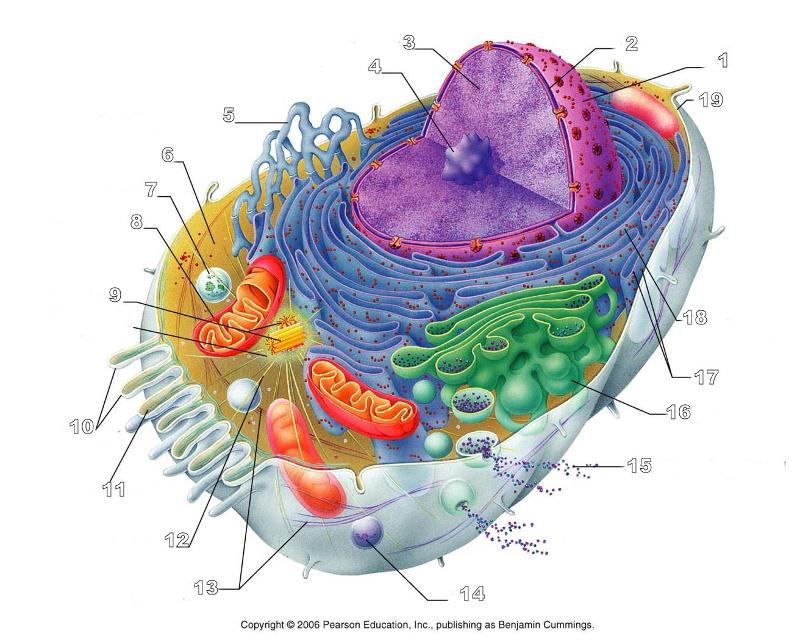 What is #15 in this picture? | back 169 Exocytosis |
front 170 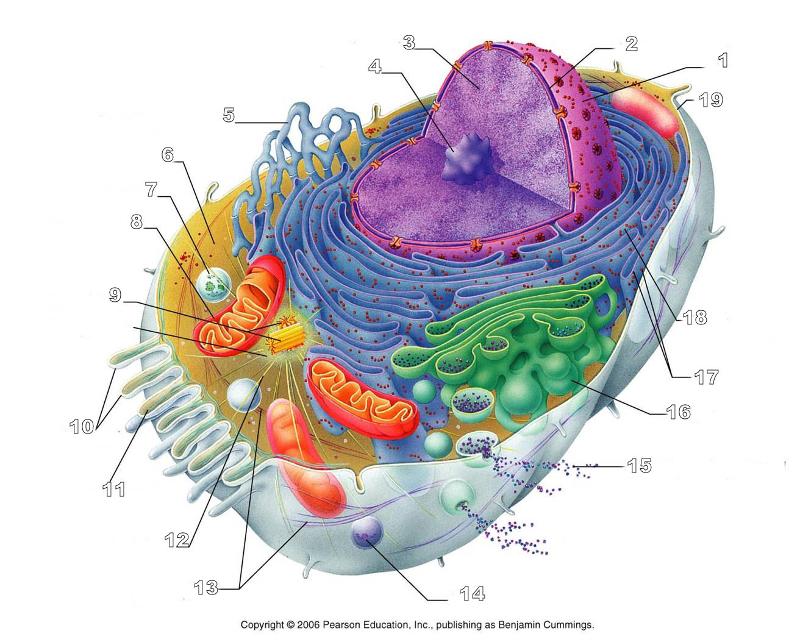 What is #16 in this picture? | back 170 Golgi Apparatus |
front 171 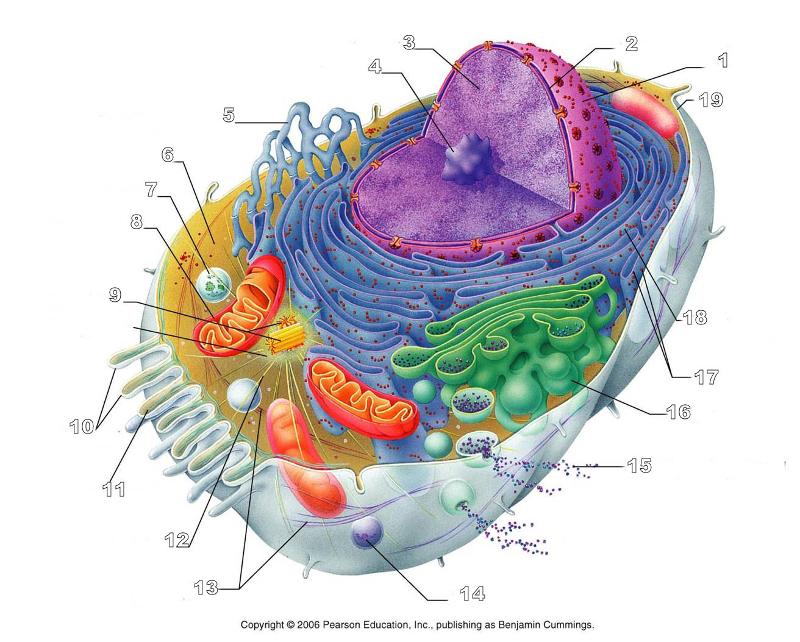 What is #17 in this picture? | back 171 Ribosomes |
front 172 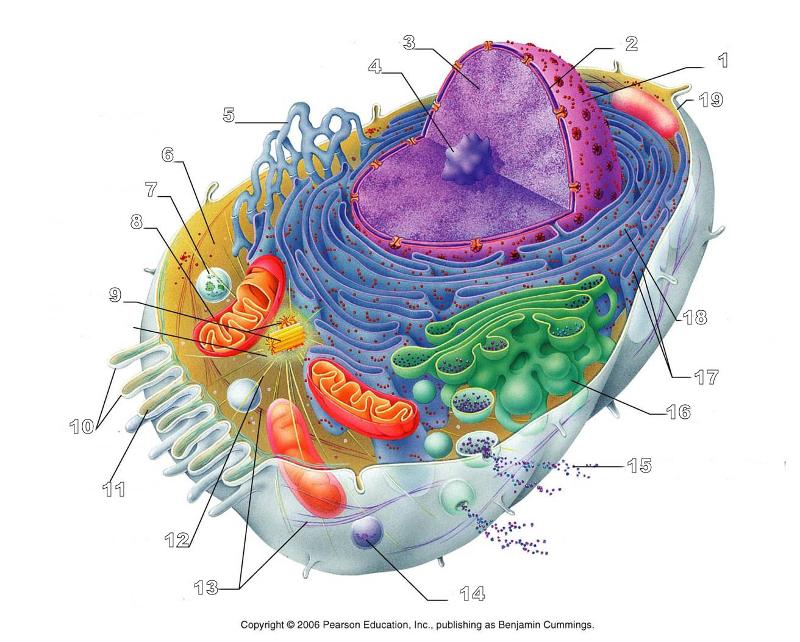 What is #18 in this picture? | back 172 Rough ER |
front 173 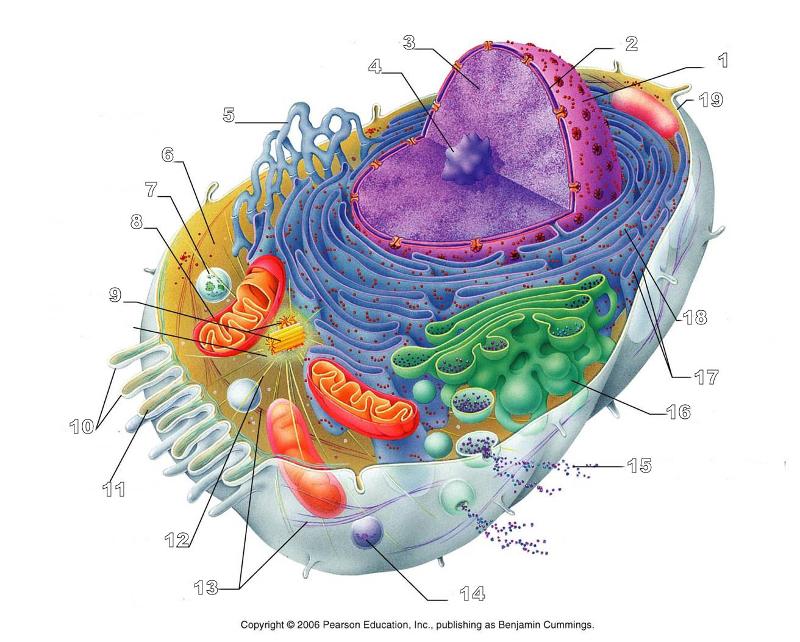 What is #19 in this picture? | back 173 Plasma Membrane |
front 174 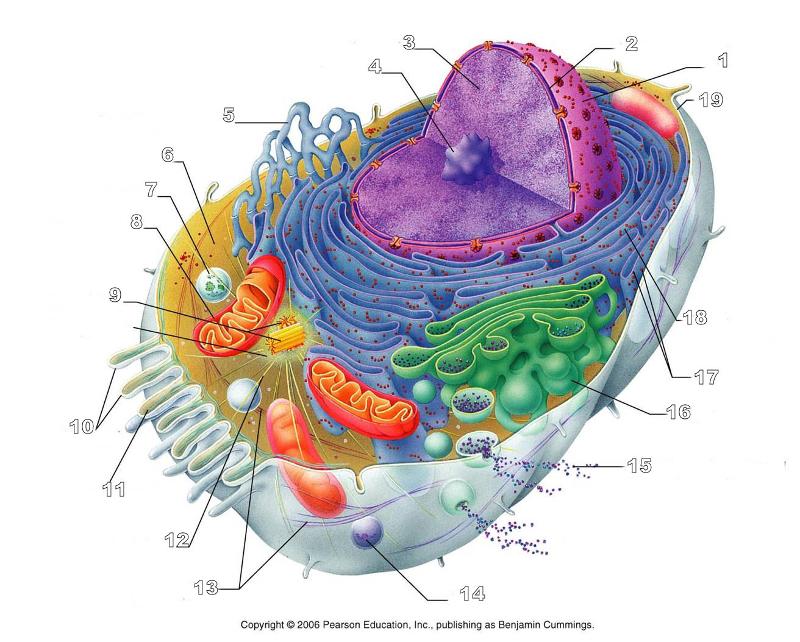 What is #12 in this picture? | back 174 Microtubules |
front 175 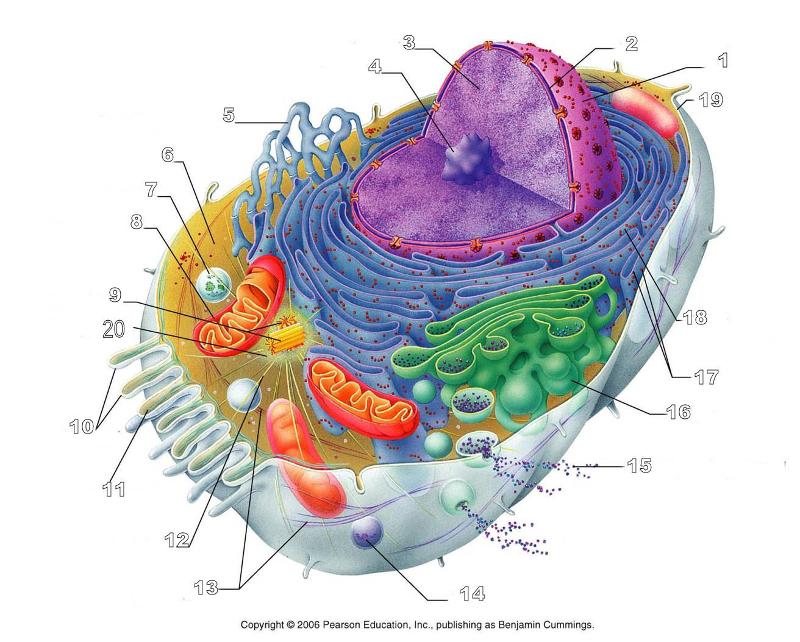 What is #20 in this picture? | back 175 Centrosome Matric |
front 176 What does pollex mean? | back 176 Thumb |
front 177 What does hallux mean? | back 177 big toe |
front 178 What does sural mean? | back 178 calf |
front 179 What does Crural mean? | back 179 (front) lower leg |
front 180 What does popliteal mean? | back 180 back side of knee |
front 181 What does palmar mean? | back 181 palm of hand |
front 182 What is a phospholipid? | back 182 1 glycerol, 2 fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group |
front 183 What % of plasma lipids do cholesterol have? | back 183 20% |
front 184 Cholesterol molecules are aligned with the phospholipid molecules where? | back 184 On both sides of the bilayer |
front 185 Glycolipids are found where? | back 185 Only in the portion of the plasma membrane that faces the extracellular fluid space |
front 186 Which one gets cut out during transcriptions Introns or exons? | back 186 Introns |
front 187 What has a cloverleaf structure? | back 187 tRNA |
front 188 What % of body mass makes up fluids in the female? | back 188 55% |
front 189 What % of body mass makes up fluids in males? | back 189 60% |
front 190 How much of the bodily fluid is in the intracellular cells? | back 190 2/3 |
front 191 How much of the bodily fluid is in the extracellular fluid? | back 191 1/3 |
front 192 In our extracellular fluid what % is in the Interstitial fluid? | back 192 80% |
front 193 The cytoplasm is what? | back 193 The cellular material inside the plasma membrane and outside the nucleus |
front 194 What % of the total cell volume is made up of the cytoplasm? | back 194 55% |
front 195 Major functional area of a cell where most cellular activities are accomplished | back 195 Cytoplasm |
front 196 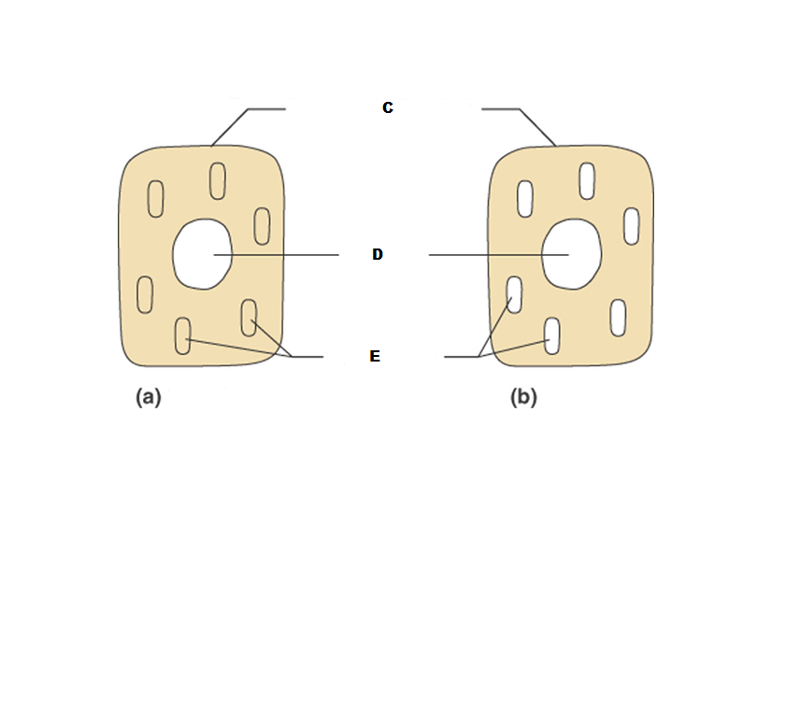 What is A in this picture? | back 196 Cytoplasm |
front 197 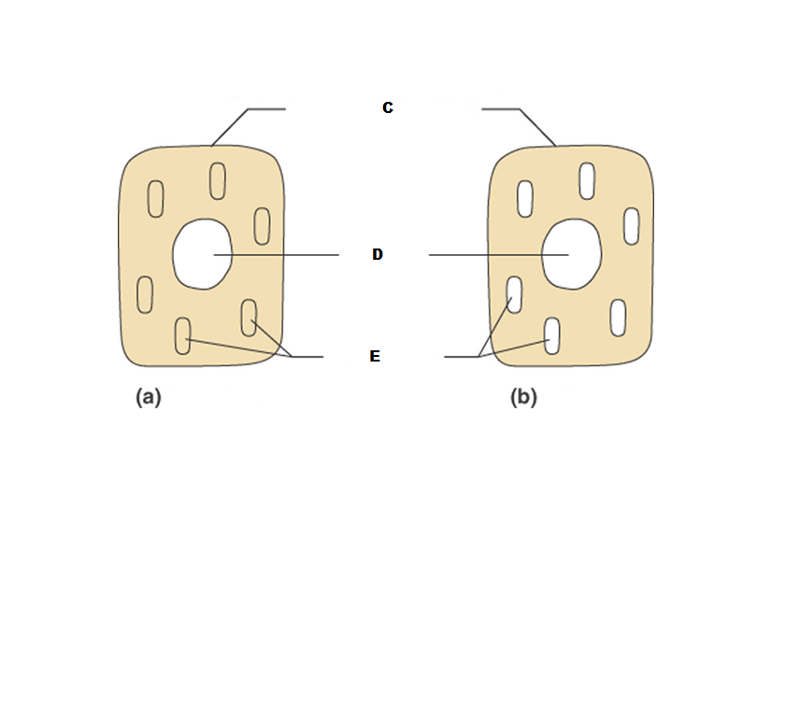 What is B in this picture? | back 197 Cytosol |
front 198 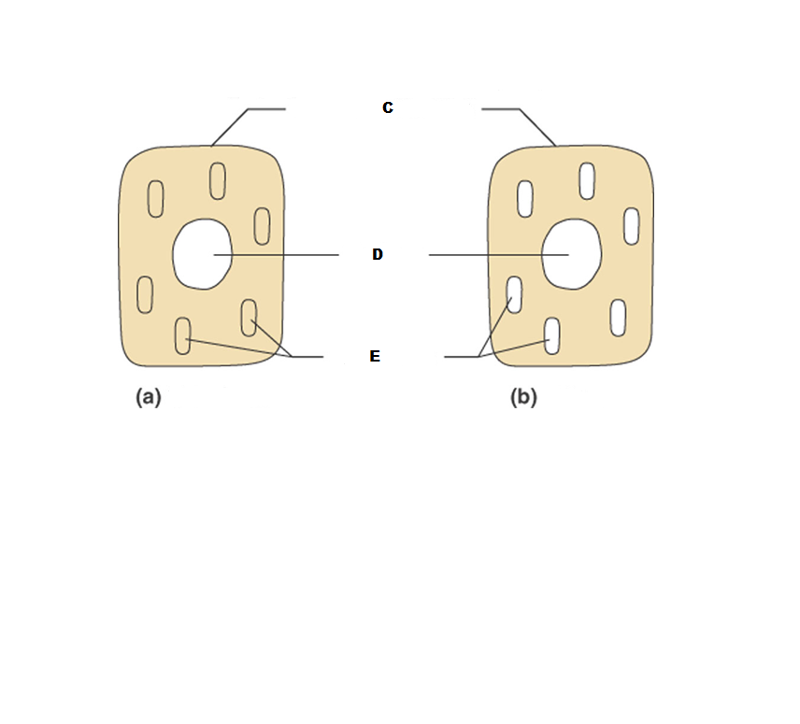 What is C in this picture? | back 198 Plasma membrane |
front 199 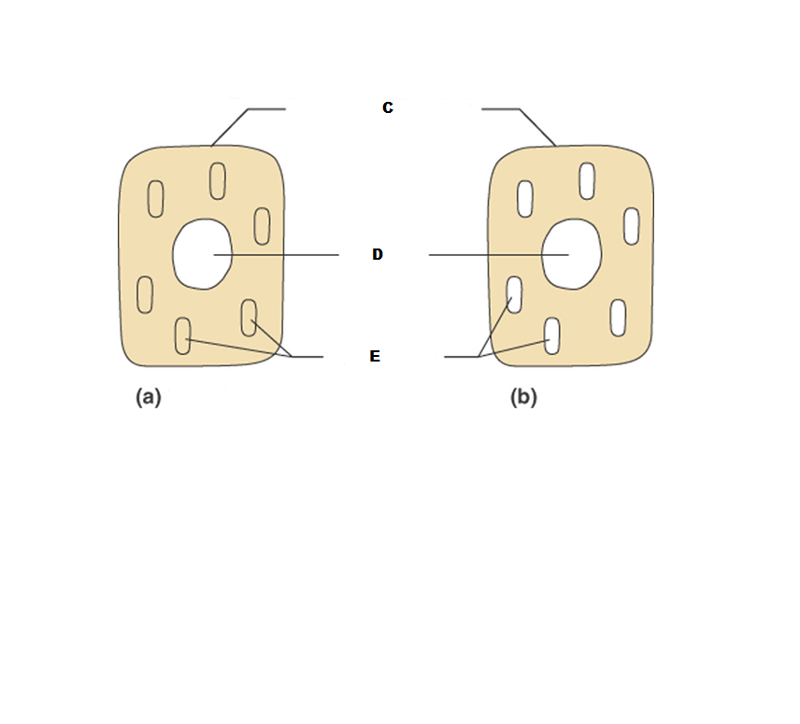 What is D in this picture? | back 199 Nucleus |
front 200 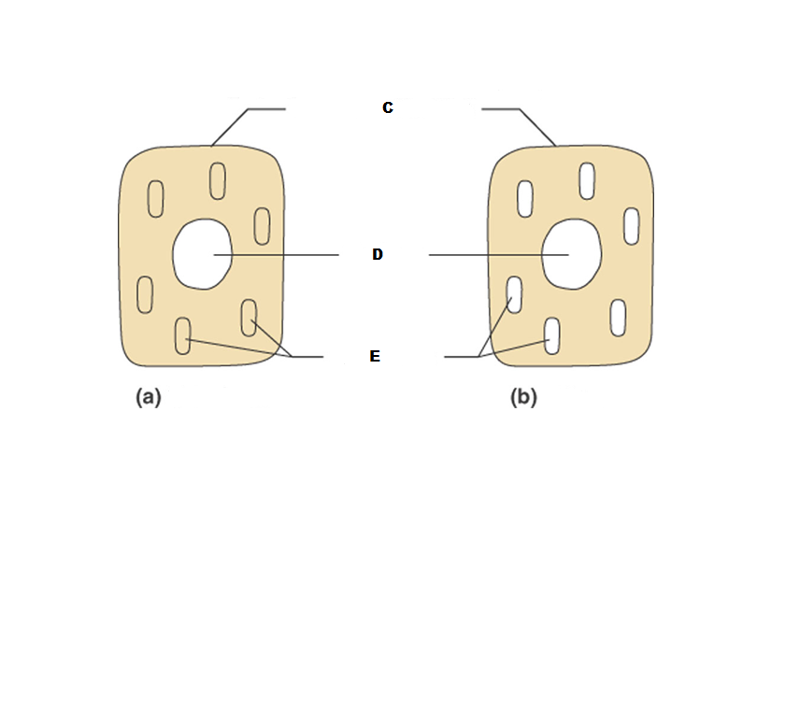 What is E in this picture? | back 200 Organelles |
front 201 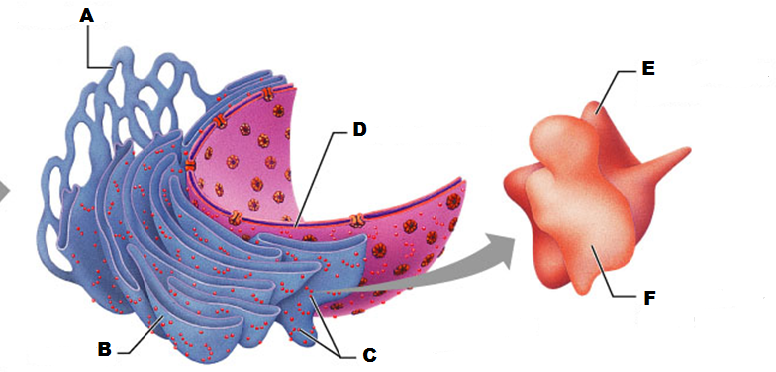 What is A in this picture | back 201 Smooth ER |
front 202 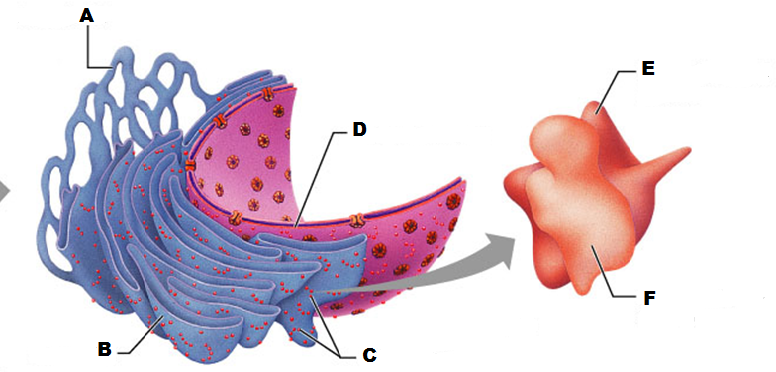 What is B in this picture? | back 202 Rough ER |
front 203 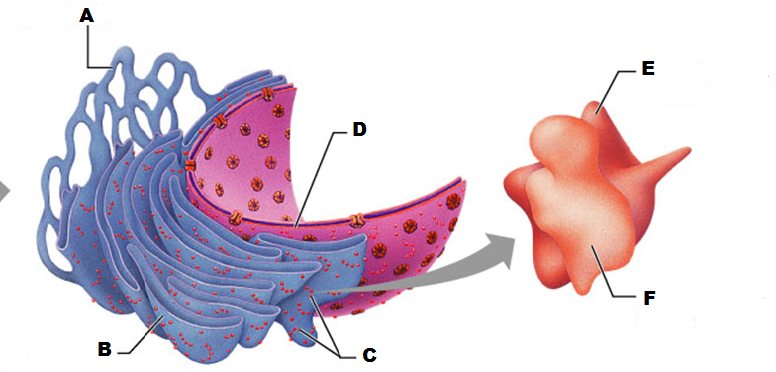 What is C in this picture? | back 203 Ribosomes |
front 204 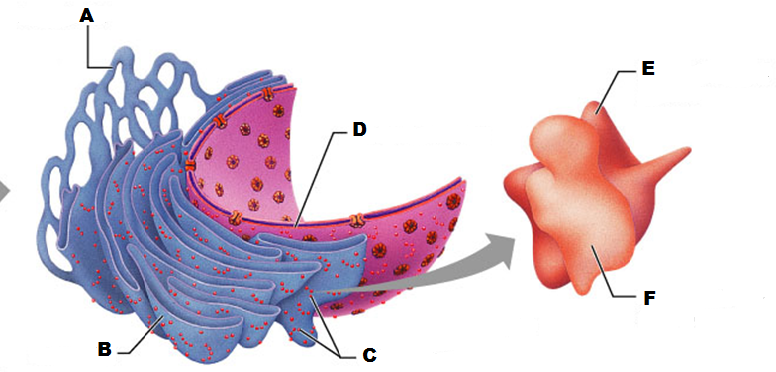 What is D in this picture? | back 204 Nuclear Envelope |
front 205 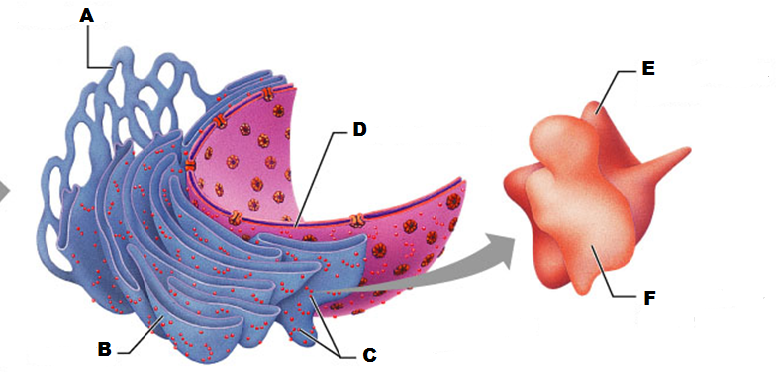 What is E in this picture? | back 205 Large ribosomal subunit |
front 206 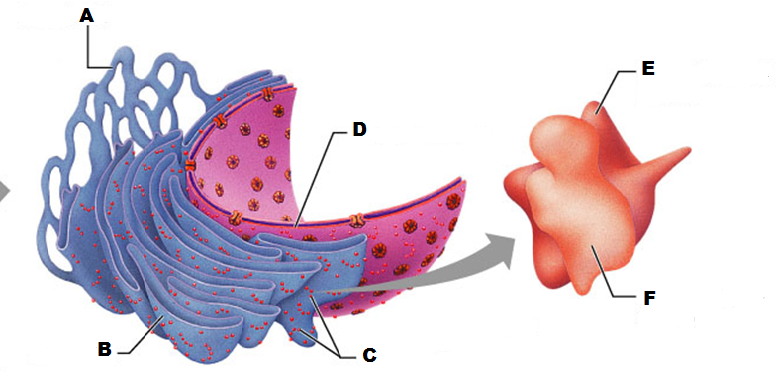 What is F in this picture? | back 206 Small ribosomal subunit |
front 207 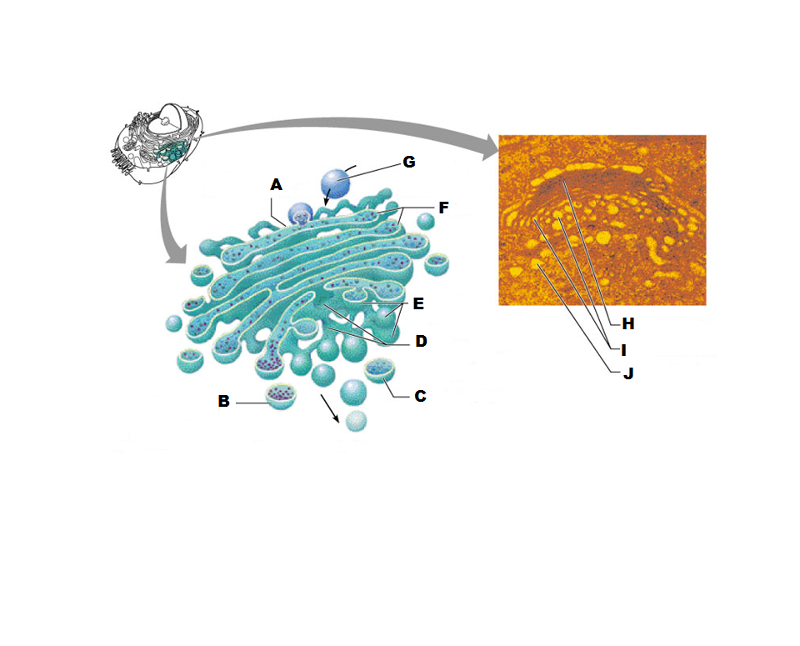 What is A in this picture? | back 207 Cis face "receiving" side of golgi apparatus |
front 208 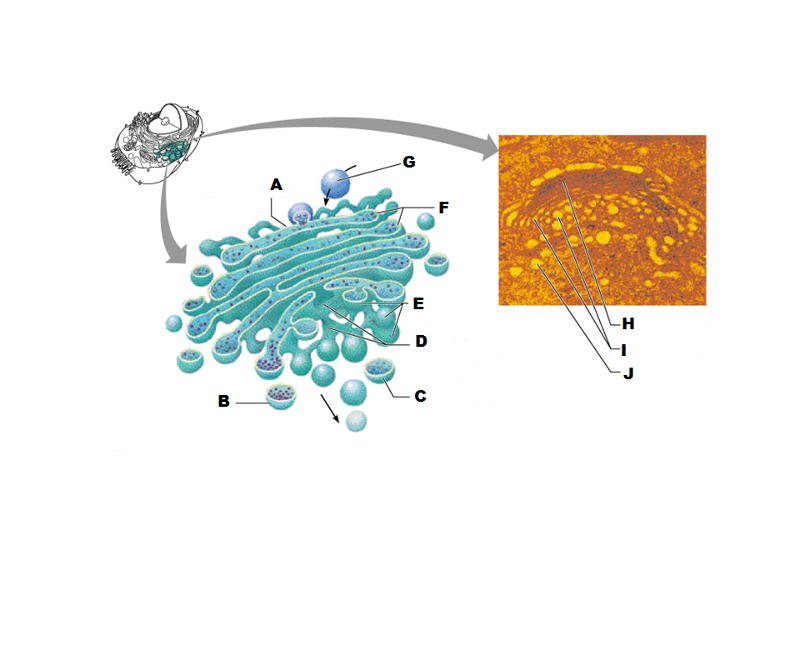 What is B in this picture? | back 208 Transport vesicle from the golgi |
front 209 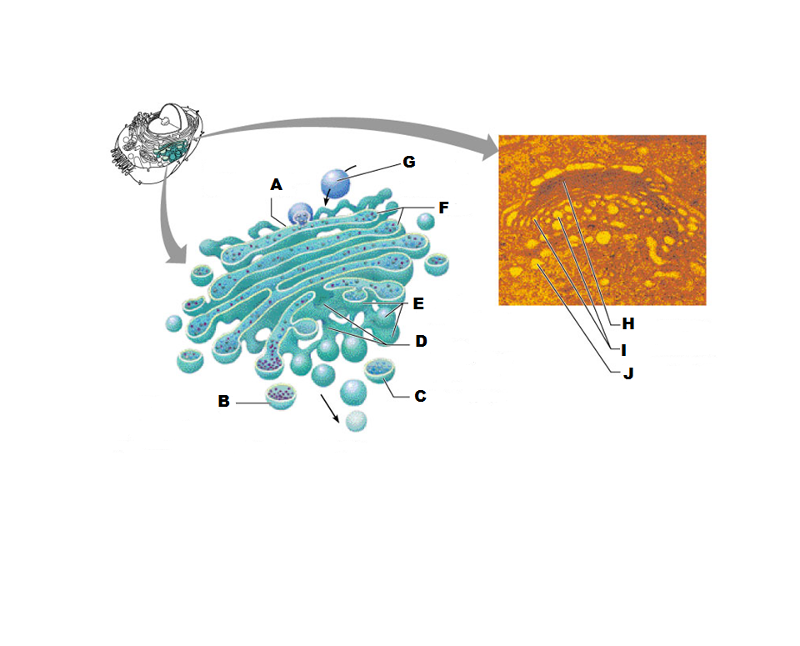 What is C in this picture? | back 209 Secretory vesicle from trans face |
front 210 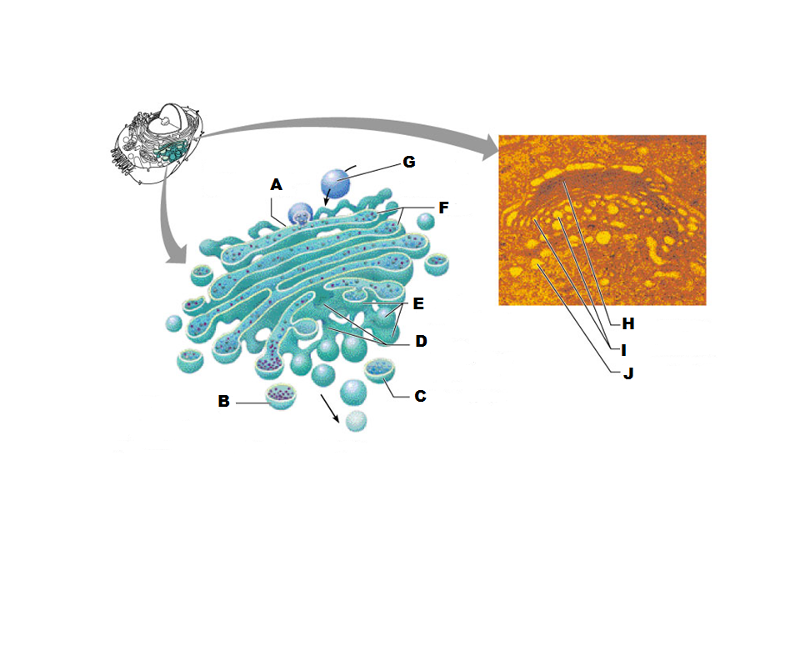 What is D in this picture? | back 210 Trans face "shipping" side of golgi apparatus |
front 211 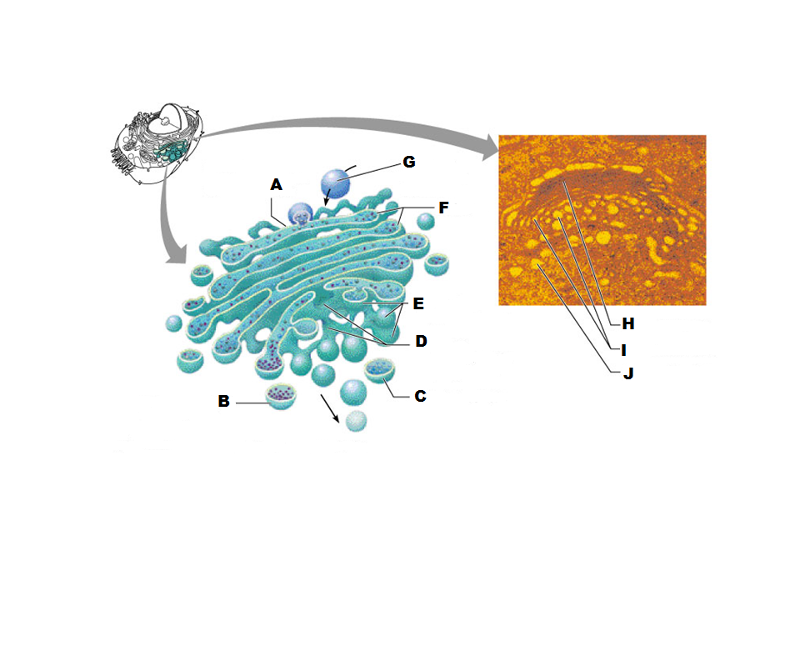 What is E in this picture? | back 211 New vesicles forming |
front 212 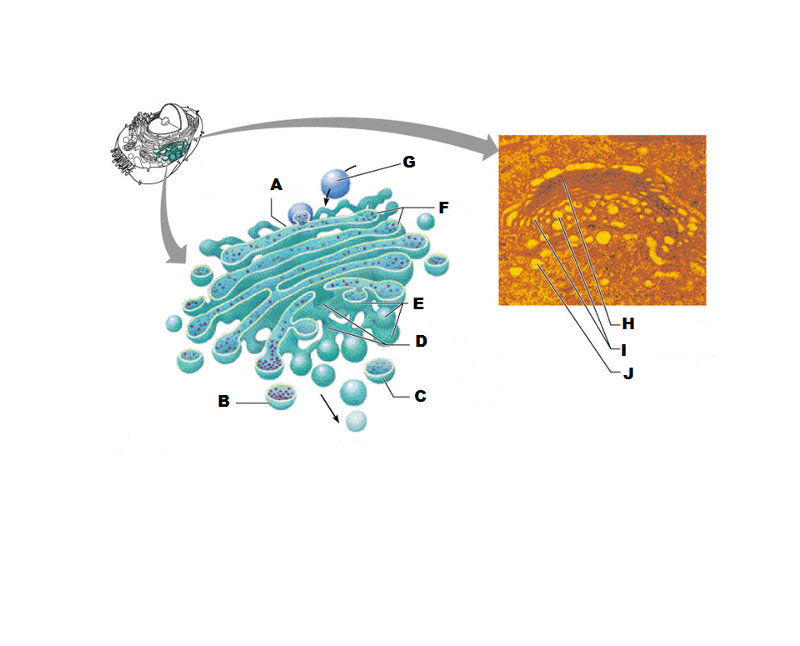 What is F in this picture? | back 212 Cisternae |
front 213 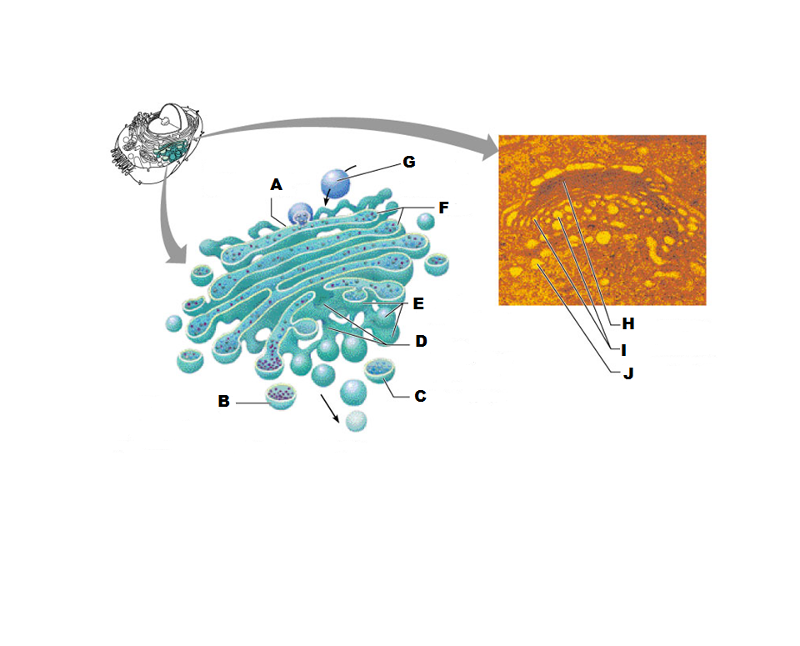 What is G in this picture? | back 213 Transport vesicle from rough ER |
front 214 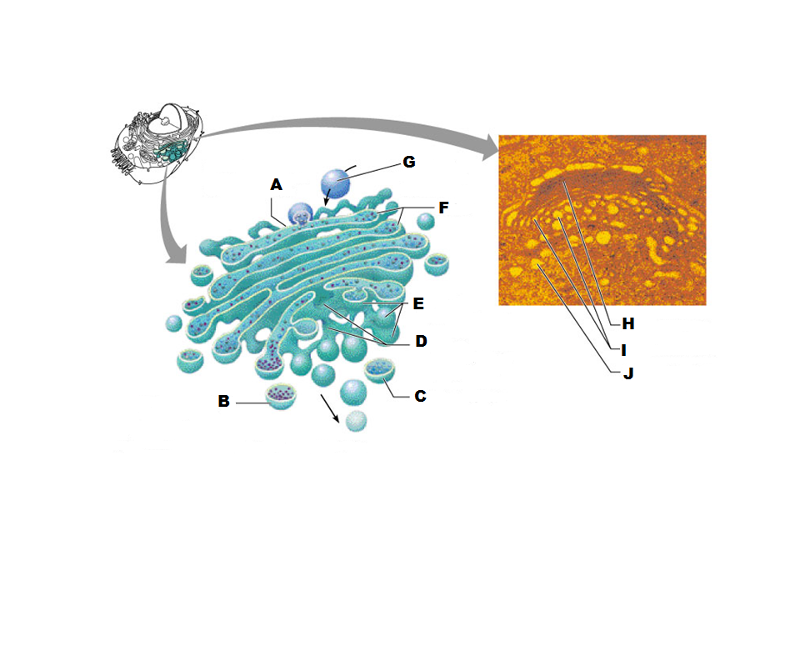 What is H in this picture? | back 214 Golgi apparatus |
front 215 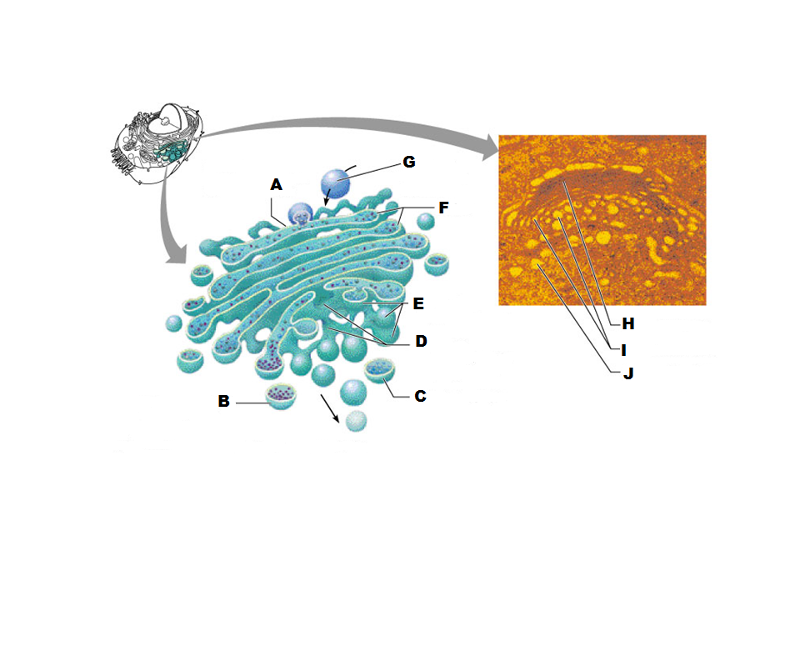 What is I in this picture? | back 215 New Vesicles forming |
front 216 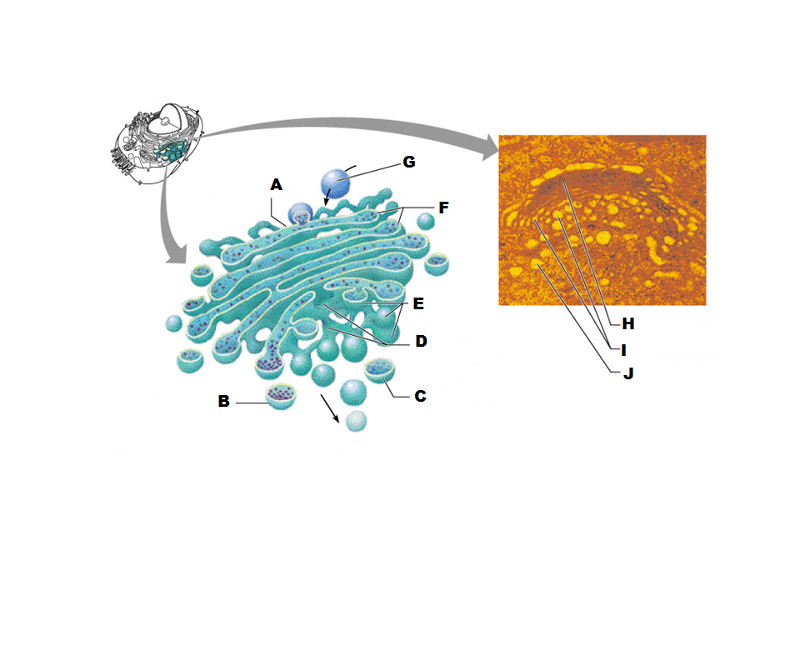 What is J in this picture? | back 216 Transport vesicle from the golgi |
front 217 What does the Cis face do? | back 217 Receives proteins from the rough ER |
front 218 What does the medial cisternae do? | back 218 Adds carbohydrates to proteins to form glycoproteins
|
front 219 What does the trans face do? | back 219 Modifies the proteins further and packages them in vesicles for transport |
front 220 What contains proteins to be exported from the cell? | back 220 Secretory vesicles |
front 221 What delivers proteins to the cell plasma membrane to be incorporated there? | back 221 Membrane vesicles |
front 222 What carries proteins to another location in the cell other than the plasma membrane? | back 222 Transport Vesicles |
front 223 How many different kinds of enzymes are their in lysosomes? | back 223 60 |
front 224 Lysosomes work best in what kind of environment? | back 224 acidic |
front 225 What do lysosomes contain? | back 225 Digestive and hydrolytic enzymes |
front 226 What do peroxisome's do? | back 226 Removes hydrogen from organic compounds such as fatty acids and amino acids
|
front 227 What does peroxisomes contain? | back 227 Oxidases and catalases |
front 228 Where do you find more mitochondria cells? | back 228 Muscle cells, liver and kidney
|
front 229 Mitochondria do what kind of replicating? | back 229 self-replicating |
front 230 What kind of DNA do Mitochondria have? | back 230 their own distinct kind |
front 231 How many genes do Mitochondria have and what pattern is the DNA? | back 231 37 genes and the DNA is circular |
front 232 Where does Mitochondrial DNA come from? | back 232 mother |
front 233 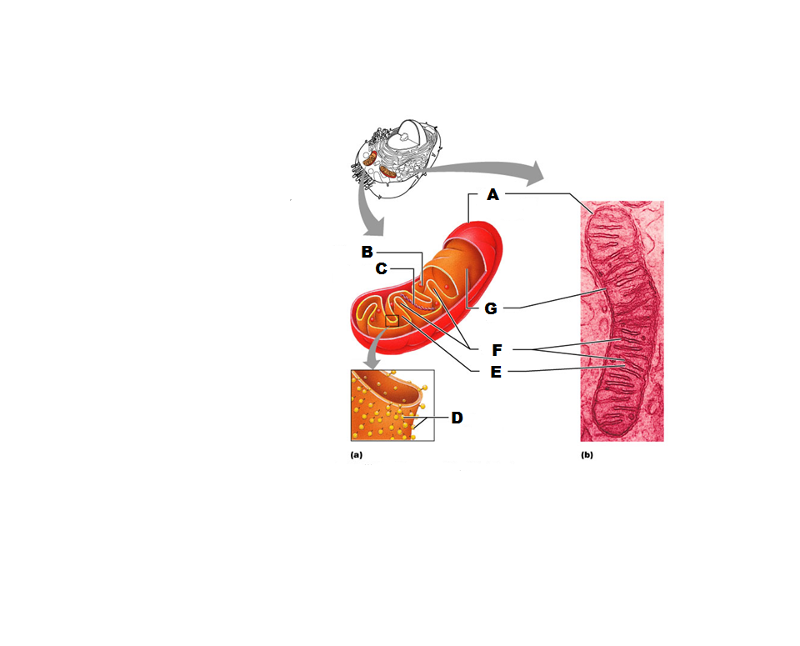 What is A in this picture? | back 233 Outer mitochondrial membrane |
front 234 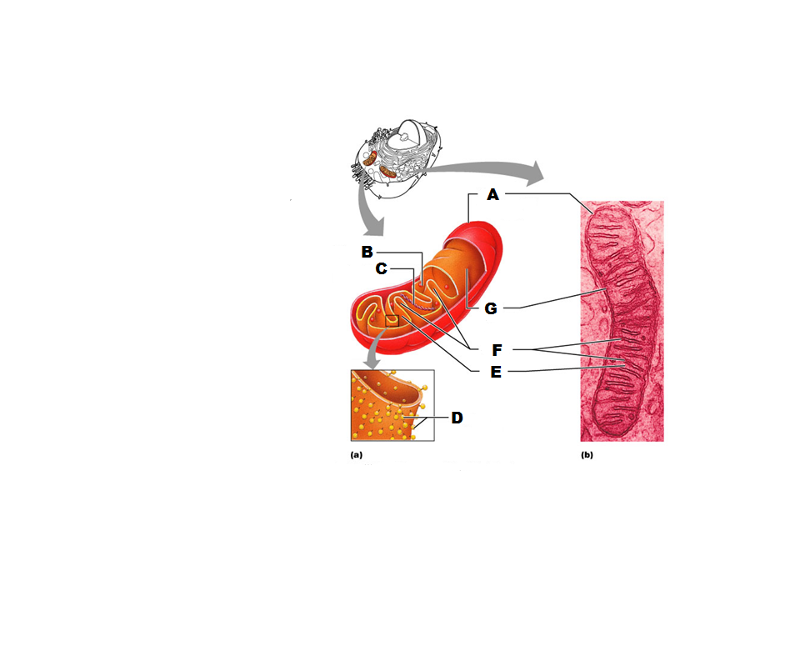 What is B in this picture? | back 234 Ribosome |
front 235 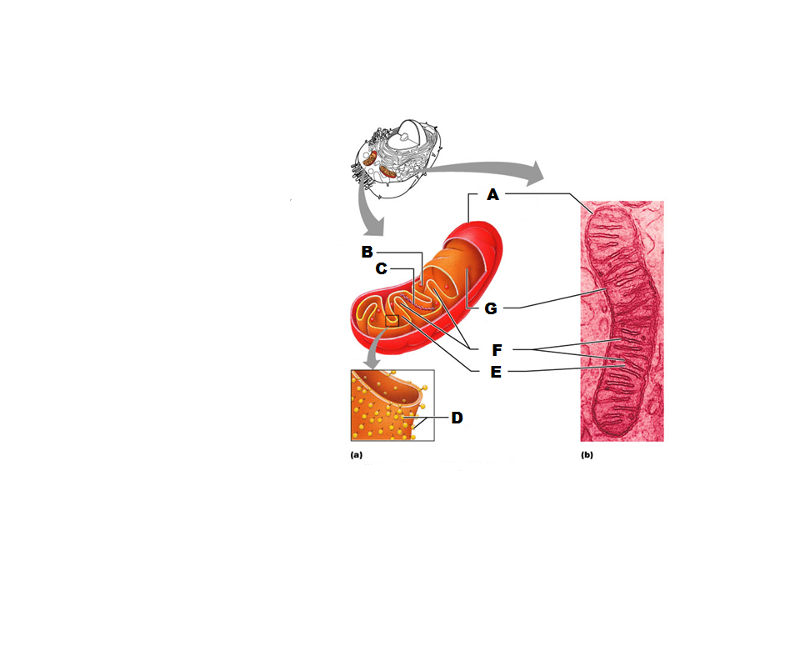 What is C in this picture? | back 235 Mitochondrial DNA |
front 236 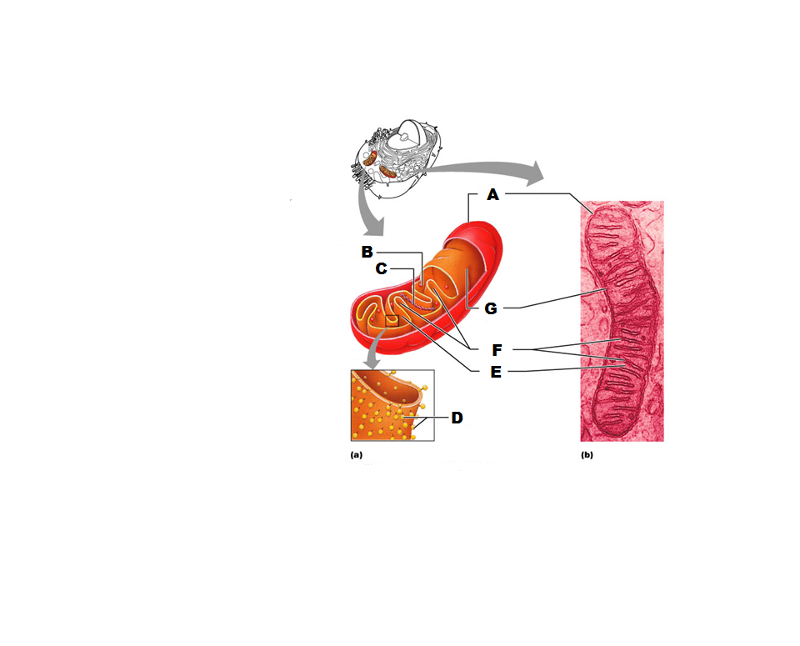 What is D in this picture? | back 236 Enzymes |
front 237 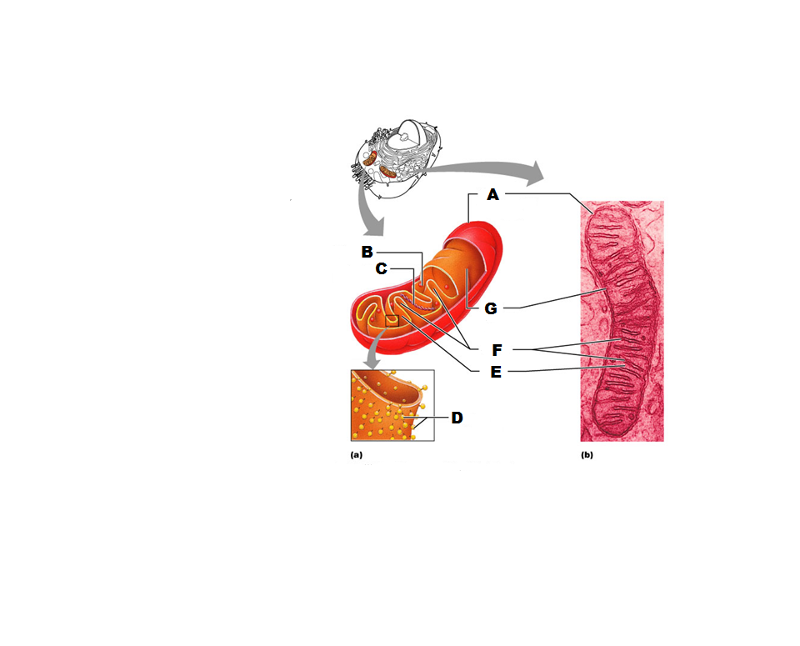 What is E in this picture? | back 237 Matrix |
front 238 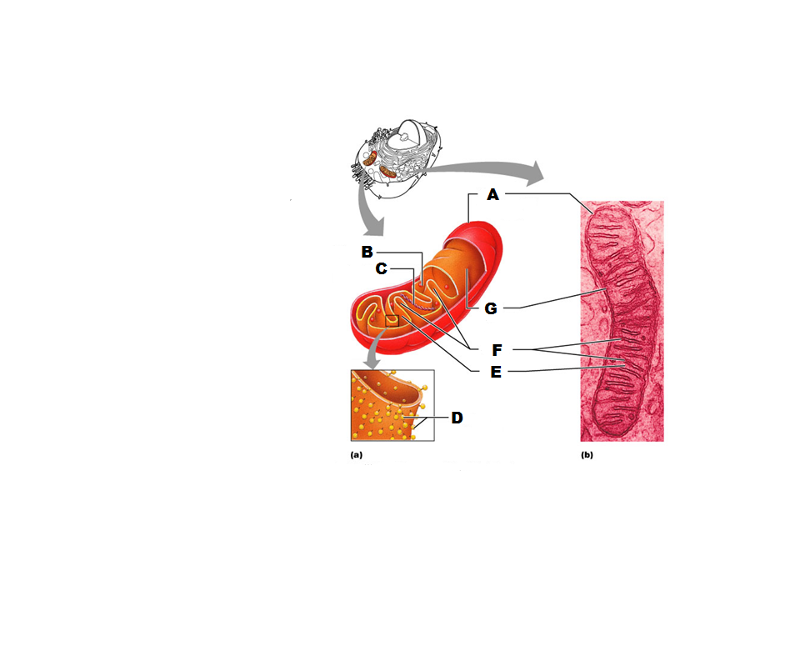 What is F in this picture? | back 238 Cristae |
front 239 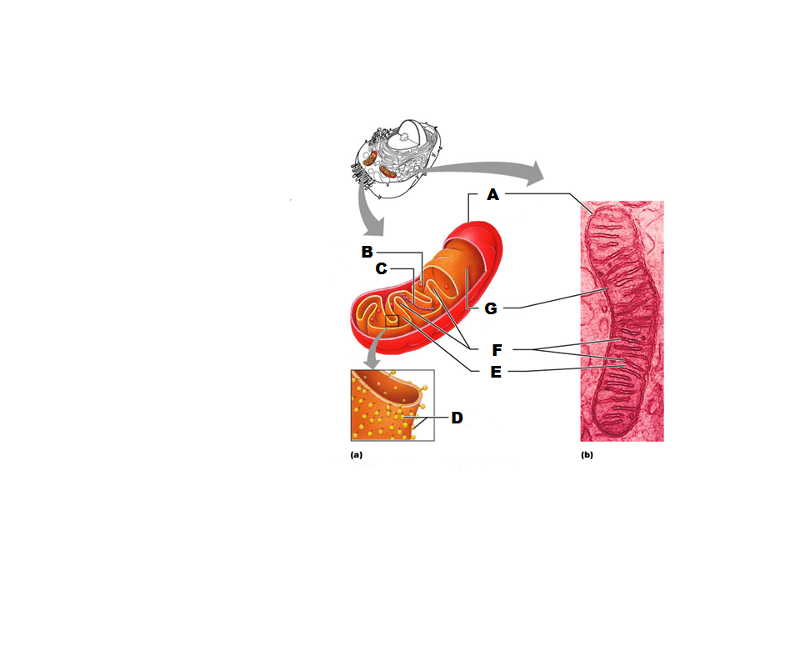 What is G in this picture? | back 239 Inner mitochondrial membrane |
front 240 What detoxifies toxins such as alcohol in liver cells | back 240 Smooth ER |
front 241 What synthesizes fatty acids and steroids such as Estrogen and testosterone | back 241 Smooth ER |
front 242 Structural framework for cell shape and for movement of organelles within the cell, chromosomes during mitosis and phagocytosis | back 242 Cytoskeleton |
front 243 What forms the mitotic spindle? | back 243 Centrioles |
front 244 What is the centrosome? | back 244 Cellular location of the centrioles |
front 245 How many clusters of triplets do centrioles have? | back 245 9 |
front 246 How many centrioles do each cell have and how are they located? | back 246 2 pairs perpendicular to each other |
front 247 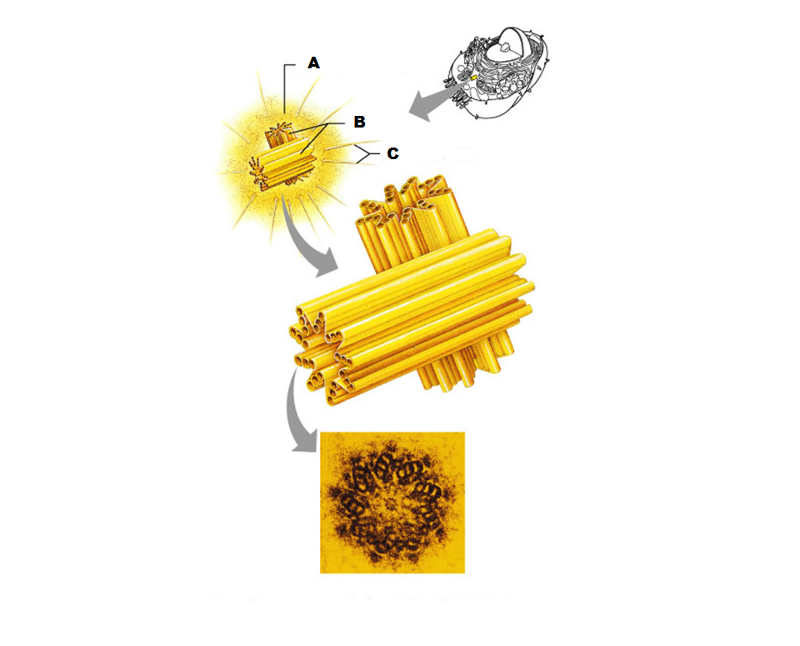 What is A in this picture? | back 247 Centrosome matrix |
front 248 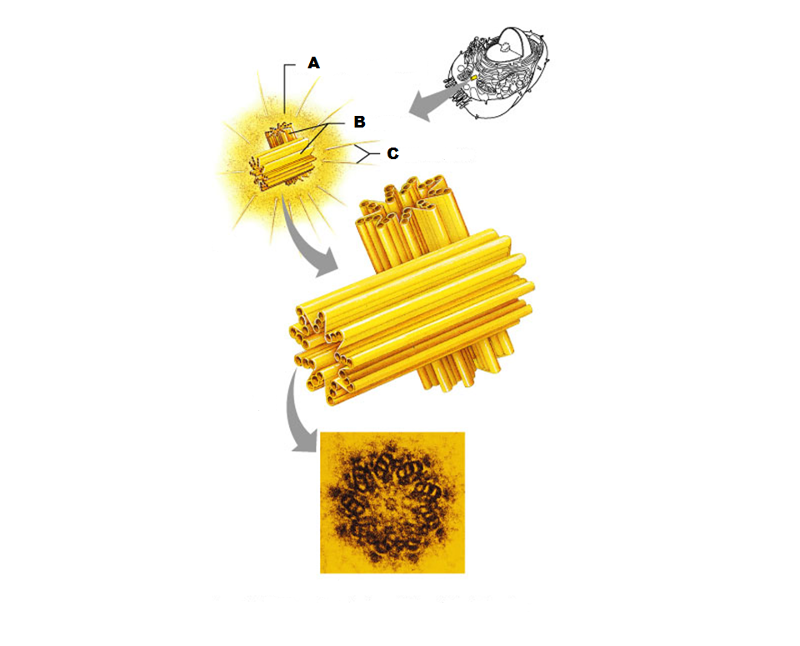 What is B in this picture? | back 248 Centrioles |
front 249 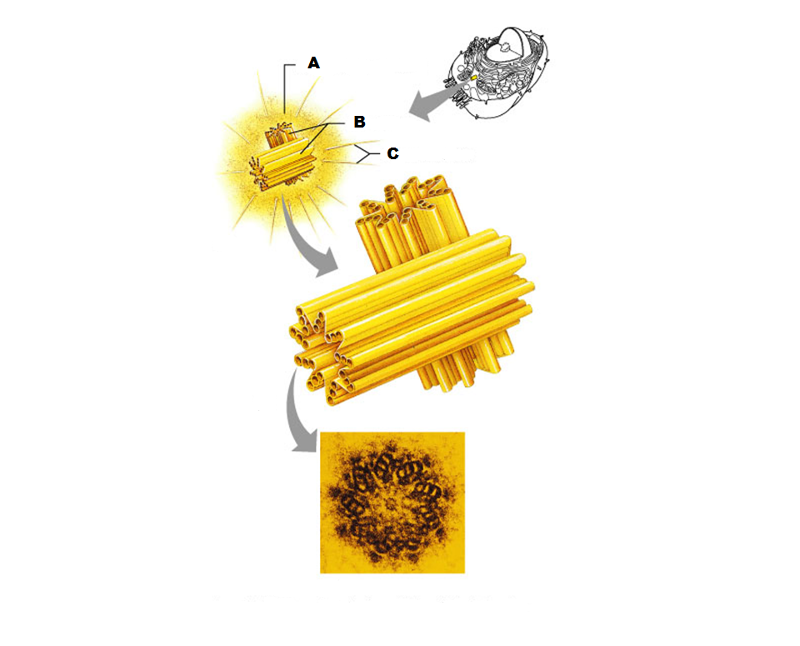 What is C in this picture? | back 249 Microtubules |
front 250 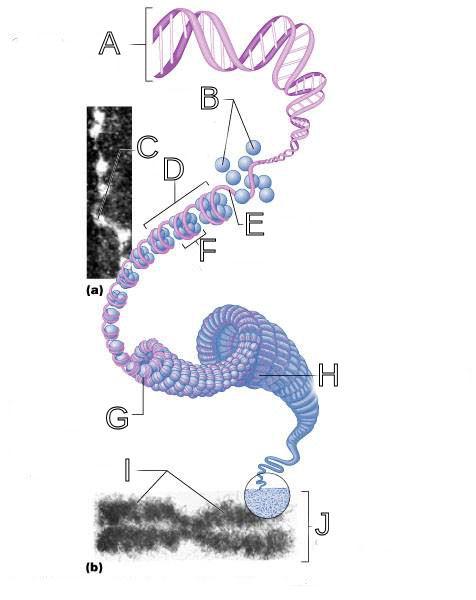 What is A labeled in this picture? | back 250 DNA double helix |
front 251 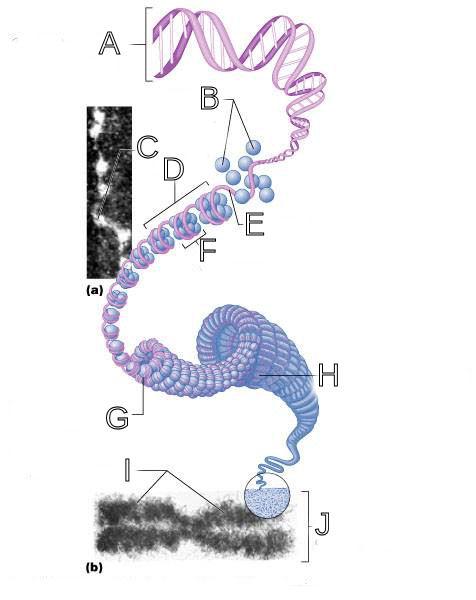 What is B labeled in this picture? | back 251 Histones |
front 252 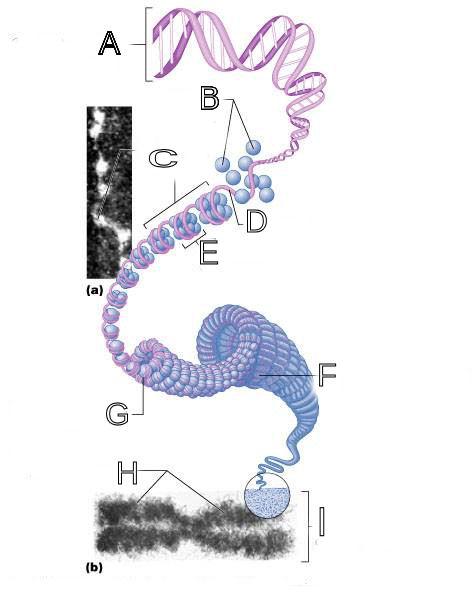 What is C labeled in this picture? | back 252 Chromatid " beads on a string" |
front 253 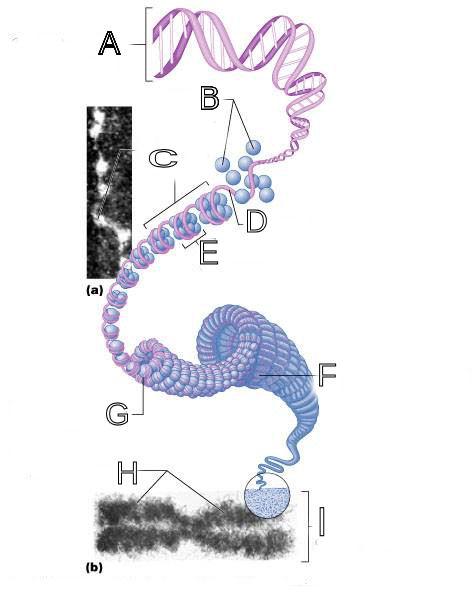 What is D labeled in this picture? | back 253 Linker DNA |
front 254 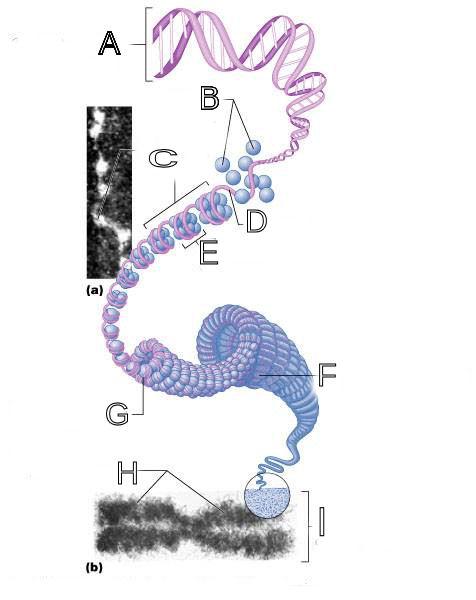 What is E labeled in this picture? | back 254 Nucleosomes |
front 255 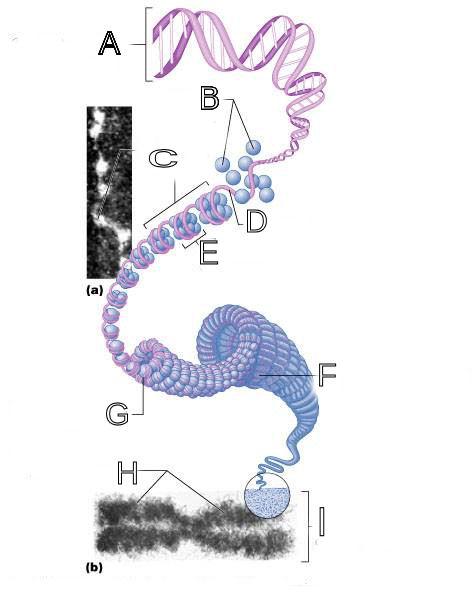 What is F labeled in this picture? | back 255 Super coiled structure |
front 256 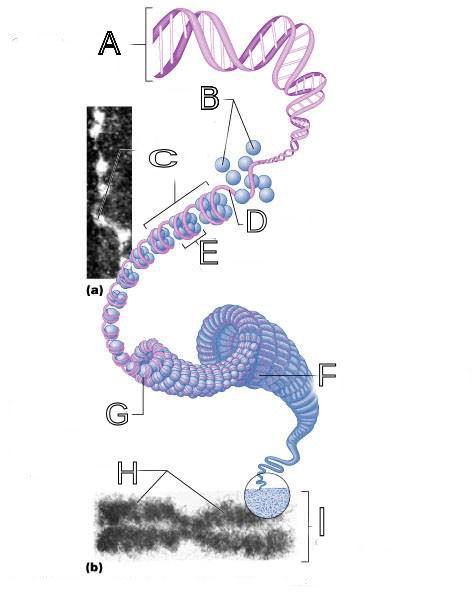 What is G labeled in this picture? | back 256 Tight Helical fiber |
front 257 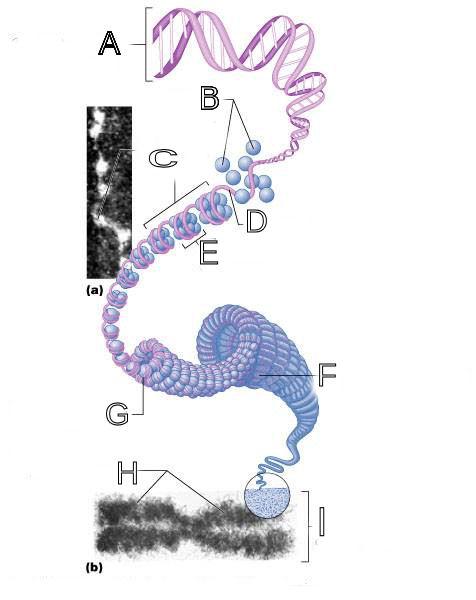 What is H labeled in this picture? | back 257 Chromatid |
front 258 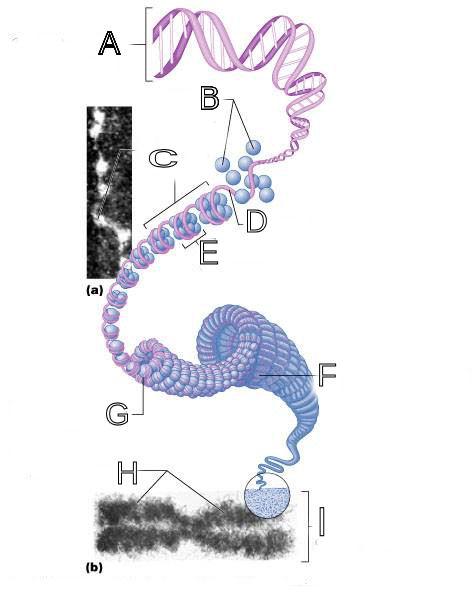 What is I labeled in this picture? | back 258 Metaphase chromosome |
front 259 DNA base pairs are:
| back 259 Adinene to Thymine
|
front 260 RNA base pairs are:
| back 260 Adinene to Thymine
|
front 261 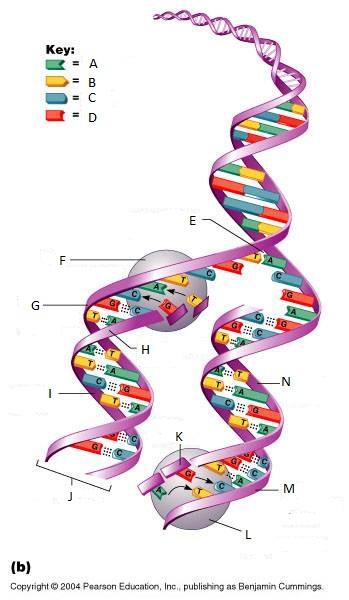 What is A in this picture? | back 261 Adenine |
front 262 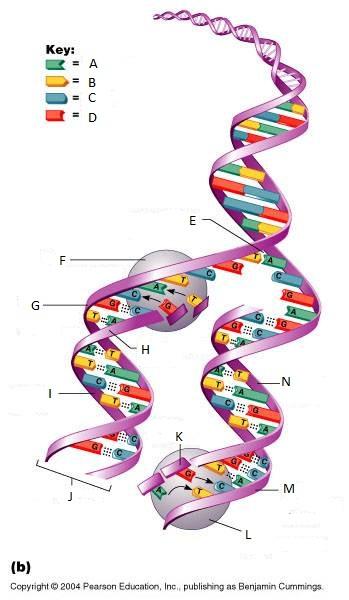 What is B in this picture? | back 262 Thymine |
front 263 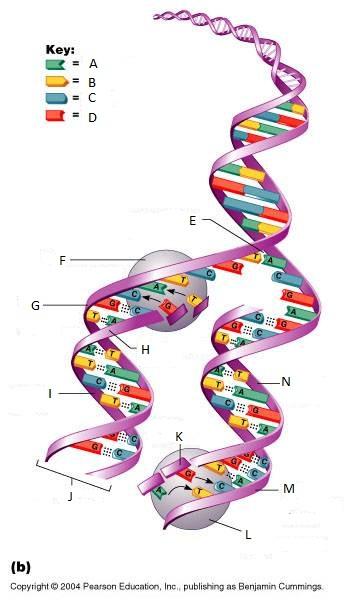 What is C in this picture? | back 263 Cytosine |
front 264 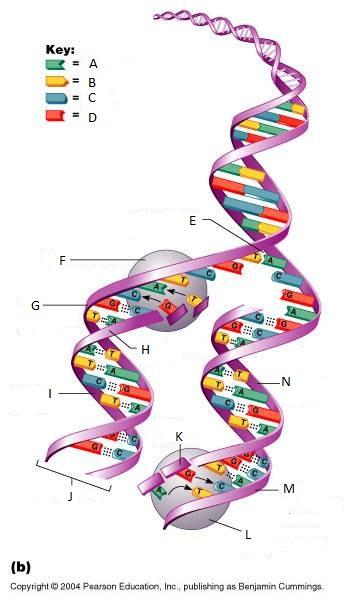 What is D in this picture? | back 264 Guanine |
front 265 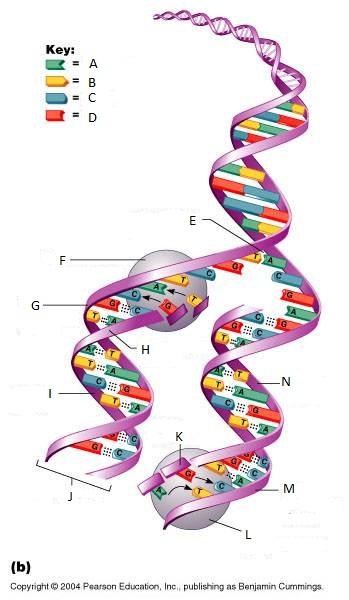 What is E in this picture? | back 265 Replication fork |
front 266 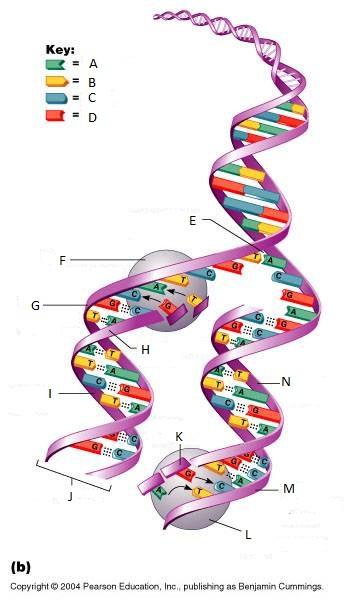 What is F in this picture? | back 266 DNA Polymerase III |
front 267 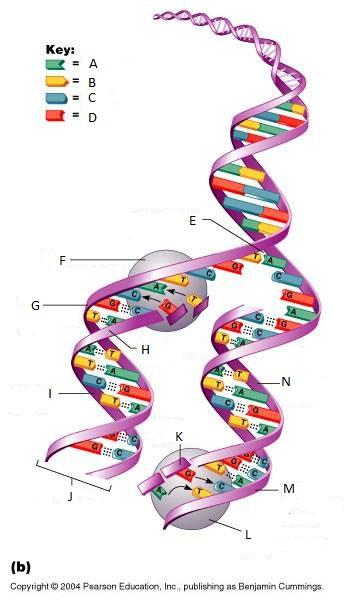 What is G in this picture? | back 267 Old template strand |
front 268 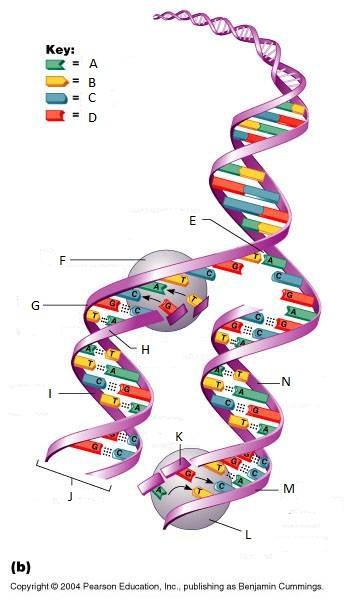 What is H in this picture? | back 268 Newly made strand |
front 269 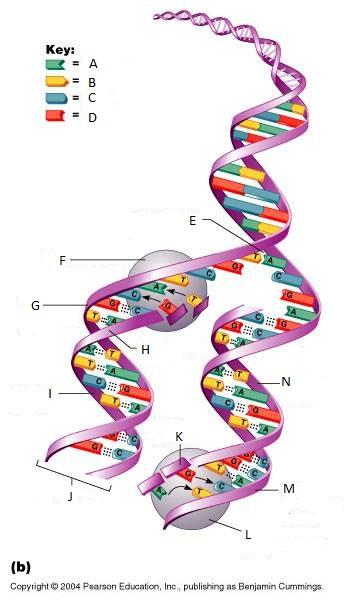 What is I in this picture? | back 269 Leading strand |
front 270 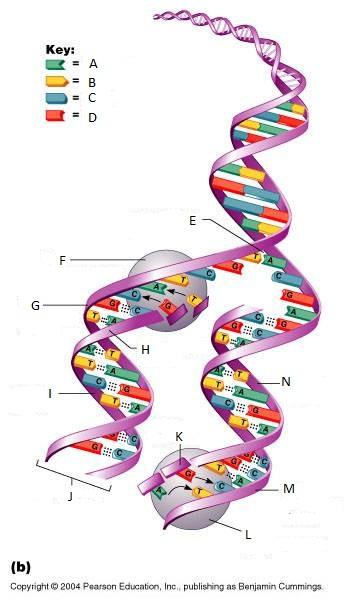 What is J in this picture? | back 270 DNA One chromatid |
front 271 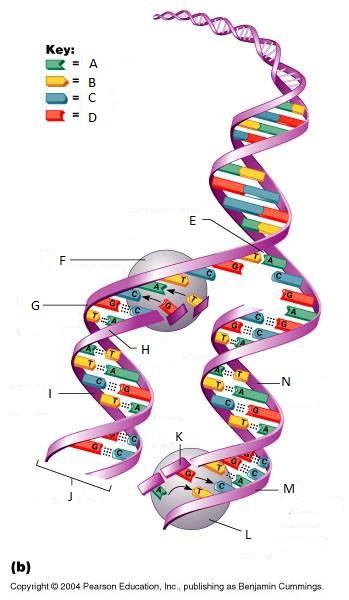 What is K in this picture? | back 271 New strand forming |
front 272 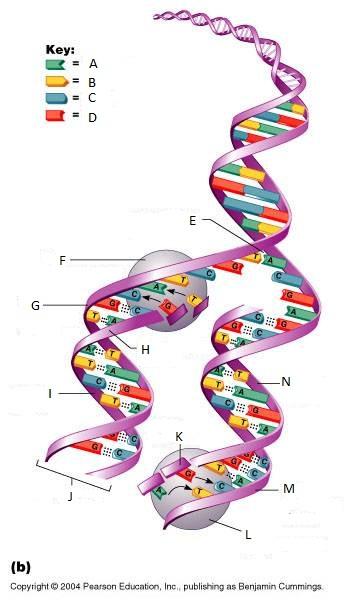 What is L in this picture? | back 272 DNA Polymerase III |
front 273 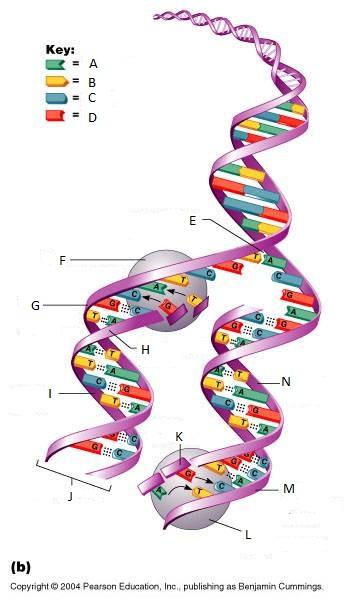 What is M in this picture? | back 273 Old template strand |
front 274 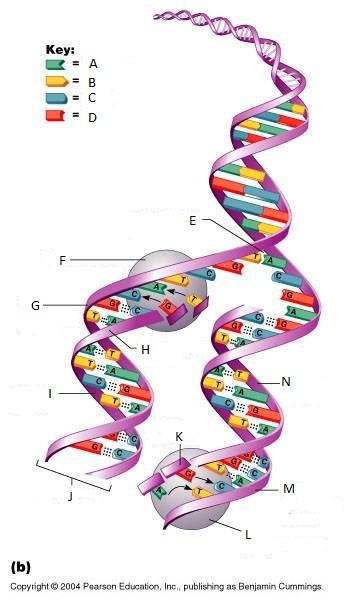 What is N in this picture? | back 274 Lagging strand |