Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Campbell Biology, 11th Ed chapters 11, 12
front 1 Cytokinesis often, but not always, accompanies _____. A) Telophase B) Anaphase C) Metaphase D)Interphase E) Prometaphase | back 1 A |
front 2 Chromosomes become visible during _____. A)metaphase B)interphase C) prometaphase D)anaphase E) prophase | back 2 E |
front 3 Centromeres divide and sister chromatids become full-fledged chromosomes during _____. A)metaphase B)interphase C) prometaphase D)anaphase E) prophase | back 3 D |
front 4 Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores during _____. A)metaphase B)interphase C) prometaphase D)anaphase E) prophase | back 4 C |
front 5 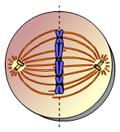 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A)metaphase B)interphase C) prometaphase D)anaphase E) prophase | back 5 D |
front 6 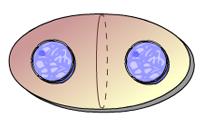 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A) cytokinesis as it occurs in animal cells B)prophase C)prometaphase D)cytokinesis as it occurs in plant cells E) metaphase | back 6 A |
front 7 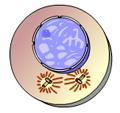 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A)metaphase B)interphase C) prometaphase D)anaphase E) prophase | back 7 E |
front 8 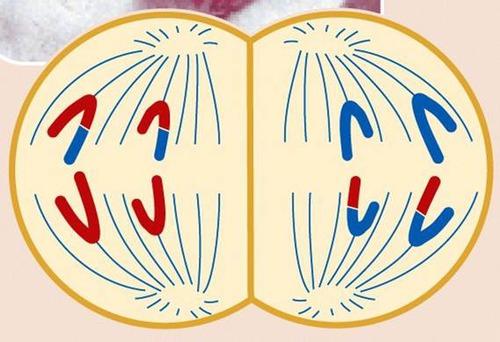 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A)anaphase I B) anaphase II C) prophase II D) interphase E)telophase I and cytokinesis | back 8 B |
front 9 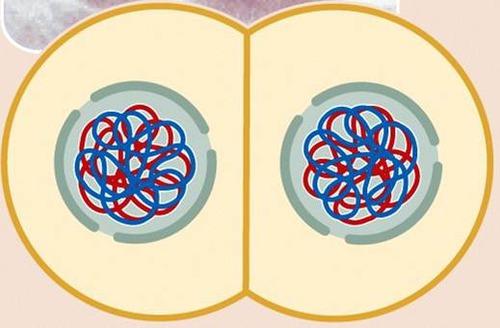 This animation illustrates the events of _____. | back 9 C |
front 10 Gametes are produced by _____. | back 10 A |
front 11 A diploid organism whose somatic (nonsex) cells each contain 32
chromosomes produces gametes containing _____ chromosomes. | back 11 A |
front 12 Meiosis I produces _____ cells, each of which is _____. | back 12 E |
front 13 Meiosis II typically produces _____ cells, each of which is _____. A) four ... diploid | back 13 D |
front 14 During prophase, a homologous pair of chromosomes consists of _____. A) ONE chromosome and two chromatids B)ONE chromosome and four chromatids C)TWO chromosomes and two chromatids D)TWO chromosomes and four chromatids E)four chromosomes and two chromatids | back 14 D |
front 15  This animation illustrates the events of _____. A) Telophase B) Anaphase C) Metaphase D)Interphase E) Prometaphase | back 15 E |
front 16  This animation illustrates the events of _____. A) Telophase B) Anaphase C) Metaphase D)cytokinesis as it occurs in plant cells E) aNaphase | back 16 D |
front 17 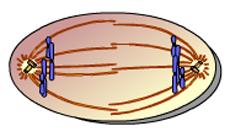 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A) Telophase B) Anaphase C) Metaphase D)Interphase E) Prometaphase | back 17 A |
front 18 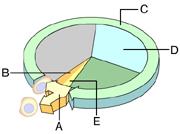 Which of these phases encompasses all of the stages of mitosis? A) B) C) D) E) | back 18 E |
front 19 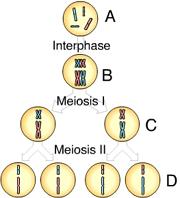 Which of these cells is (are) haploid? A) C AND D B) A AND B C)B AND A D)C AND D E)D AND B | back 19 A |
front 20 Which of the following is true of kinetochores? Which of the following is true of kinetochores? A)They interdigitate at the cell's equator and then move apart, causing the cell to elongate. B)They are the primary centromere structures that maintain the attachment of the sister chromatids prior to mitosis. C)They are sites at which microtubules attach to chromosomes. D)they attach to the ring of actin along the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane, causing the actin to contract to form the cleavage furrow E) They are located at the center of the centrosome; their function is to organize tubulin into elongated bundles called spindle fibers. | back 20 C |
front 21 In some organisms, such as certain fungi and algae, cells undergo the cell cycle repeatedly without subsequently undergoing cytokinesis. What would result from this? A)a decrease in chromosome number B)large cells containing many nuclei C)division of the organism into many cells, most lacking nuclei D)a rapid rate of gamete production E)inability to duplicate DNA | back 21 B |
front 22 22) Cells will usually divide if they receive the proper signal at a checkpoint in which phase of the cell cycle? A)G2 B)S C)M D)G1 E)CYTOKINESIS | back 22 D |
front 23 230Which of the following is true of benign tumors, but not malignant tumors? A)They migrate from the initial site of transformation to other organs or tissues. B)They remain confined to their original site C)They are the result of the transformation of normal cells. D)They can divide indefinitely if an adequate supply of nutrients is available. E)They have an unusual number of chromosomes. | back 23 B |
front 24 24)Through a microscope, you can see a cell plate beginning to develop across the middle of a cell and nuclei forming on either side of the cell plate. This cell is most likely A)a plant cell in the process of cytokinesis. B)an animal cell in the process of cytokinesis. C)a plant cell in metaphase. D)a bacterial cell dividing. E)an animal cell in the S phase of the cell cycle. | back 24 A |
front 25 25)In the cells of some organisms, mitosis occurs without cytokinesis. This will result in A)destruction of chromosomes. B)cell cycles lacking an S phase. C)cells lacking nuclei. D)cells that are unusually small. E)cells with more than one | back 25 E |
front 26 26)Which of the following does not occur during mitosis? A)condensation of the chromosomes B)separation of sister chromatids C)separation of the spindle poles D)replication of the DNA E)spindle formation | back 26 D |
front 27 27)The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the animal cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B? A)spindle formation B)cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis C)spindle attachment to kinetochores D)cell elongation during anaphase E)DNA synthesis | back 27 B |
front 28 28) Human gametes are produced by _____ A)meiosis B) asexual reproduction C)mitosis D) fertilization E) the cell cycle | back 28 A |
front 29 29)Normal human gametes carry _____ chromosomes. A)46 B)23 Pairs of C)46 pairs of D)5 E)23 | back 29 E |
front 30 30)Of the following, a receptor protein in a membrane that recognizes
a chemical signal is most similar to | back 30 D |
front 31 31)During which stage of mitosis do spindle microtubules first attach
to kinetochores? | back 31 C |
front 32 32)Which of the following best describes how chromosomes move toward
the poles of the spindle during mitosis? | back 32 A |
front 33 33)A diploid organism whose somatic (nonsex) cells each contain 32 chromosomes produces gametes containing _____ chromosomes. A)8 B)32 C)30 D)16 E)64 | back 33 D |
front 34 34)What number and types of chromosomes are found in a human somatic cell? A)45 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome B)44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes C)21 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes D)22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome E)n chromosomes | back 34 B |
front 35 35)In alternation of generations, what is the diploid stage of a plant that follows fertilization called? A)chiasmata B)gametophyte C)sporophyte D)karyotype E)spore | back 35 C |
front 36 36)How are sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes different from each other? A)They are not different. Homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids are both identical copies of each other. B)Sister chromatids are only formed during mitosis. Homologous chromosomes are formed during meiosis C)Homologous chromosomes are identical copies of each other. One sister chromatid comes from the father, and one comes from the mother. D)Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication. E)Homologous chromosomes are closely associated with each other in both mitosis and meiosis. Sister chromatids are only associated with each other during mitosis. | back 36 D |
front 37 37)During _____ sister chromatids separate. A)interphase B)prophase I C)metaphase I D)prophase II E)anaphase II | back 37 E |
front 38 38)During _____ a spindle forms in a haploid cell. | back 38 B |
front 39 39)During ____ the chromosomes finish their journey and two haploid
daughter cells are produced, each chromosome still consists of two
sister chromatids. | back 39 D |
front 40 40)At the end of _____ and cytokinesis, haploid cells contain
chromosomes that each consist of two sister chromatids. | back 40 B |
front 41 41)At the end of _____ and cytokinesis, haploid cells contain
chromosomes that each consist of two sister
chromatids. | back 41 C |
front 42 42)Synapsis occurs during _____. | back 42 C |
front 43 43)During _____ chromosomes align single file along the equator of a
haploid cell. | back 43 A |
front 44 44)Homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles during
_____. | back 44 B |
front 45 45)Mitosis results in the formation of how many cells; meiosis results in the formation of how many cells? A)two diploid cells ... two diploid cells B)four diploid cells ... four haploid cells C)two diploid cells ... four haploid cells D)four haploid cells ... two diploid cells E)two diploid cells ... two haploid cells | back 45 C |
front 46 46)Which of the following occurs during meiosis but not during mitosis? A)Synapsis occurs. B)A spindle apparatus forms. C)Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate D)Chromosomes condense E)Chromosomes migrate to opposite poles | back 46 A |
front 47 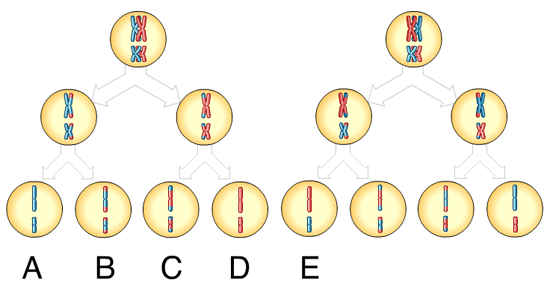 47)Which of these gametes contains one or more recombinant chromosomes? A) A and B B) B and C C) A and D D) D and E E) A and C | back 47 B |
front 48 48)A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is
| back 48 A |
front 49 49)Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing
cell during | back 49 B |
front 50 50)Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that | back 50 A |
front 51 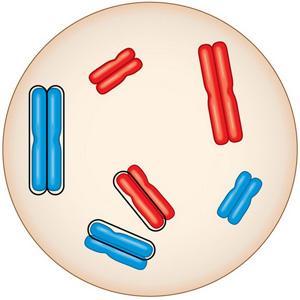 51)Look at the cell in the figure. Based on this figure, which of the following statements is true? A)This cell is haploid. B)This cell is diploid. C)It is impossible to tell whether the cell is haploid or diploid. | back 51 B |
front 52 52)Which life cycle stage is found in plants but not animals? A)gamete B)multicellular haploid C)zygote D)multicellular diploid E)unicellular diploid | back 52 B |
front 53 53)Why do some species employ both mitosis and meiosis, whereas other species use only mitosis? A)A single-celled organism only needs mitosis. B)They need meiosis if the cells are producing organs such as ovaries C)They need only meiosis if they produce egg cells. D)They need only mitosis to make large numbers of cells such as sperm. E)They need both if they are producing animal gametes. | back 53 E |
front 54 54) Nucleoli are present during _____. A)metaphase B)prophase C)interphase D)prometaphase E)anaphase | back 54 C |
front 55 55)During _____ both the contents of the nucleus and the cytoplasm are divided. A)G2 B)the mitotic phase C)mitosis D)G1 E)S | back 55 B |
front 56 56)During _____ the cell grows and replicates both its organelles and its chromosomes. A)cytokinesis B)interphase C)mitosis D)G1 E)S | back 56 B |
front 57 57)Which of the following correctly matches a phase of the cell cycle with its description? A)M: duplication of DNA B)G1: follows cell division C)G2: cell division D)S: immediately precedes cell division E)All of the above are correctly matched. | back 57 B |
front 58 58)One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is that cancer cells A)cannot function properly because they are affected by density-dependent B)are arrested at the S phase of the cell cycle. C)are always in the M phase of the cell cycle. D)are unable to synthesize DNA. E)continue to divide even when they are tightly packed together. | back 58 E |
front 59 59)A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in a mitotically active tissue. The cell in question is most likely in A)metaphase. B)anaphase. C)G2 D)G1 E)prophase | back 59 D |
front 60 60)The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the animal cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B? A)DNA synthesis B)spindle formation C)cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis D)spindle attachment to kinetochores E)cell elongation during anaphase | back 60 c |
front 61 61)Asexual reproduction _____. A)produces offspring genetically identical to the parent B)requires both meiosis and mitosis C)is limited to plants D)is limited to single-cell organisms E)leads to a loss of genetic material | back 61 A |
front 62 62)For what purpose(s) might a karyotype be prepared? A)for prenatal screening, to determine if a fetus has the correct number of chromosomes B)to determine whether a fetus is male or female C)to detect the possible presence of chromosomal abnormalities such as deletions, inversions, or translocations D)The first and second answers are correct E)The first three answers are correct. | back 62 E |
front 63 63)In alternation of generations, what is the diploid stage of a
plant that follows fertilization called? | back 63 C |
front 64 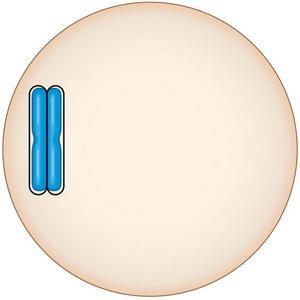 64)This chromosome has two chromatids, joined at the centromere. What process led to the formation of the two chromatids? A)The two chromatids were formed by synapsis and the formation of a synaptonemal complex. B)The two chromatids were formed by fertilization, bringing together maternal and paternal chromatids. C)The two chromatids were formed by duplication of a chromosome. | back 64 C |
front 65 65)Two sister chromatids are joined at the centromere prior to meiosis. Which statement is correct A)These chromatids make up a diploid chromosome. B) The cell that contains these sister chromatids must be haploid. C)Barring mutation, the two sister chromatids must be identical | back 65 C |
front 66 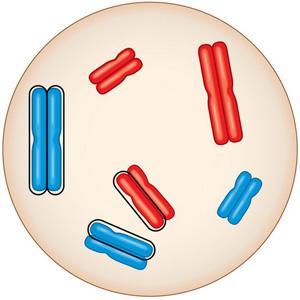 What is the best evidence telling you whether this cell is diploid or haploid? A)The cell is haploid because the chromosomes are not found in pairs. B)The cell is diploid because it contains two sets of chromosomes. C)The cell is diploid because each chromosome consists of two chromatids | back 66 B |
front 67 67)Identify all possible products of meiosis in plant and animal life cycles. A)Gametes B)Spores C)Multicellular adult organisma D) A AND B | back 67 D |
front 68 81)What is crossing over? | back 68 E |
front 69 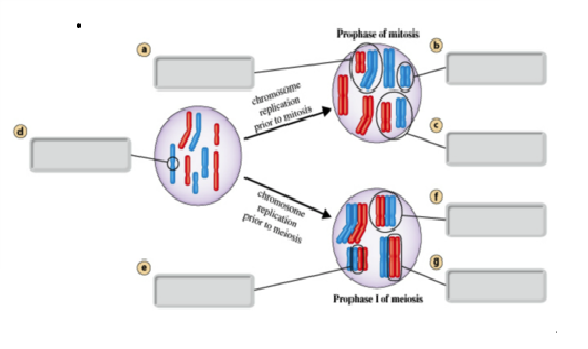 82)non-homologous chromosomes A) B) C) D) E) | back 69 A |
front 70  83) sister chromatids A)B, G B)C,F C)A,B D)F,C E)E,A | back 70 A |
front 71  84)homologous chromosomes A)B, G B)C,F C)A,B D)F,C E)E,A | back 71 B |
front 72  85) centromere A) B) C) D) E) | back 72 D |
front 73  86)nonsister chromatids A) B) C) D) E) | back 73 E |
front 74 87)Which of the following defines a genome? | back 74 B |
front 75 88)Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome
number of 2n = 16? | back 75 E |
front 76 89)Assume that an organism exists in which crossing over does not occur, but that all other processes associated with meiosis occur normally. Consider how the absence of crossing over would affect the outcome of meiosis. If crossing over did not occur, which of the following statements about meiosis would be true? Select all that apply. A)The two sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome would no longer be identical. B)Independent assortment of chromosomes would not occur. C)There would be less genetic variation among gametes. D)The two daughter cells produced in meiosis I would be identical. | back 76 C |
front 77 90)The shuffling of chromosomes that occurs during both fertilization and _____ can lead to genetic variation. A)natural selection B)mutation C)meiosis D)genetic drift E)mitosis | back 77 C |
front 78 91)Heritable variation is required for which of the following? A)mitosis | back 78 b |
front 79 92)Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing
cell during | back 79 A |
front 80 93)Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that | back 80 D |
front 81  94)We can see that the chromosomes are duplicated and lined up by homologous pair. A)the start of mitosis B)just before mitosis C)just before mitosis D)the start of meiosis II E)the start of meiosis I | back 81 E |
front 82 95)Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into
newly forming DNA and, therefore, can be assayed to track their
incorporation. In a set of experiments, a studentfaculty research team
used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of
dividing human cells at specific times. A)infection causes cell cultures in general to reproduce more rapidly B)infection causes lymphocytes to divide more rapidly C)infection causes lymphocyte cultures to skip some parts of the cell cycle D)the presence of the pathogen made the experiments too contaminated to trust the results | back 82 B |
front 83 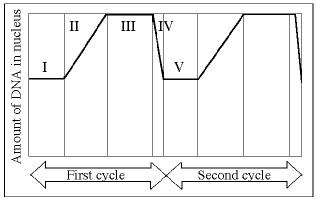 96)In the figure above, which number represents DNA synthesis? A)I B)II C)III D)IV | back 83 B |
front 84  97)In the figure above, at which of the numbered regions would you
expect to find cells at metaphase | back 84 C |
front 85 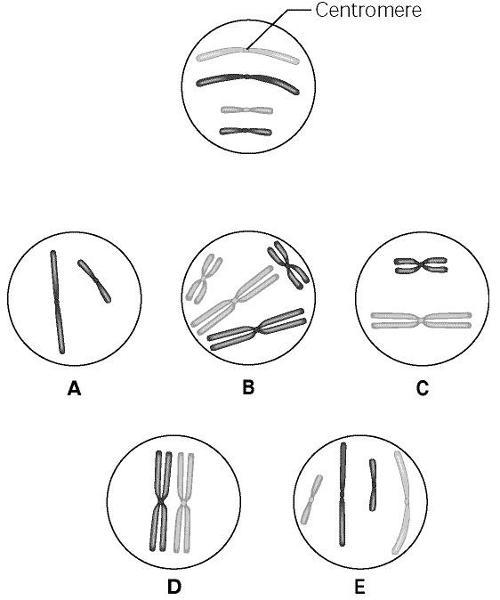 98)The unlettered circle at the top of the figure shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes that have not yet replicated. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is black, and the other is gray. The circles labeled A to E show various combinations of these chromosomes. 25) What is the correct chromosomal condition at prometaphase of mitosis? A) B B) C C) D D) E | back 85 A |
front 86  99)The unlettered circle at the top of the figure shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes that have not yet replicated. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is black, and the other is gray. The circles labeled A to E show various combinations of these chromosomes. 26) What is the correct chromosomal condition for one daughter nucleus at telophase of mitosis? A) B B) C C) D D) E | back 86 D |
front 87 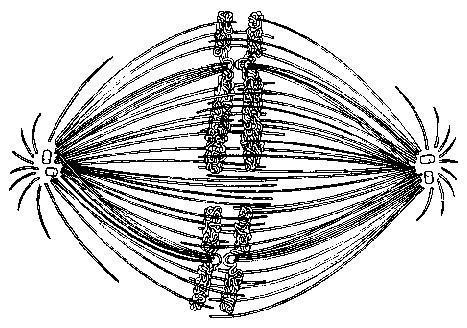 100)If the cell whose nuclear material is shown in the accompanying figure continues toward completion of mitosis, which of the following events would occur next? A) spindle fiber formation B) nuclear envelope breakdown C) formation of telophase nuclei D) synthesis of chromatids | back 87 C |
front 88 88)A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms would be found at the end of S and the end of G2? A) 8; 8 B) 8; 16 C) 16; 8 D) 16; 16 | back 88 D |
front 89 89)Metaphase is characterized by _____. A) aligning of chromosomes on the equator B) splitting of the centromeres C) cytokinesis D) separation of sister chromatids | back 89 A |
front 90 90)If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis? A) 10 B) 20 C) 40 D) 80 | back 90 A |
front 91 91)Taxol is an anticancer drug extracted from the Pacific yew tree. In animal cells, Taxol disrupts microtubule formation. Surprisingly, this stops mitosis. Specifically, Taxol must affect _____. A) the structure of the mitotic spindle B) anaphase C) formation of the centrioles D) chromatid assembly | back 91 A |
front 92 92)Which of the following are primarily responsible for cytokinesis in plant cells but not in animal cells? A) kinetochores B) Golgi-derived vesicles C) actin and myosin D) centrioles and centromeres | back 92 B |
front 93 93)Measurements of the amount of DNA per nucleus were taken on a large number of cells from a growing fungus. The measured DNA levels ranged from 3 to 6 picograms per nucleus. In which stage of the cell cycle did the nucleus contain 6 picograms of DNA? A) G1 B) S C) G2 D) M | back 93 C |