Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch:8 Study Packet
front 1 1) Which of the following has eight valence electrons? A) Ti4+ B) Kr C) Cl- D) Na+ E) all of the above | back 1 E) all of the above |
front 2 2) Which of the following does not have eight valence electrons? A) Ca+ B) Rb+ C) Xe D) Br- E) All of the above have eight valence electrons. | back 2 A) Ca+ |
front 3 3) Lattice energy is ________. A) the energy required to convert a mole of ionic solid into its constituent ions in the gas phase B) the energy given off when gaseous ions combine to form one mole of an ionic solid C) the energy required to produce one mole of an ionic compound from its constituent elements in their standard states D) the sum of ionization energies of the components in an ionic solid E) the sum of electron affinities of the components in an ionic solid | back 3 A) the energy required to convert a mole of ionic solid into its constituent ions in the gas phase |
front 4 4) In ionic bond formation, the lattice energy of ions ________ as the magnitude of the ion charges _______ and the radii ________. A) increases, decrease, increase B) increases, increase, increase C) decreases, increase, increase D) increases, increase, decrease E) increases, decrease, decrease | back 4 D) increases, increase, decrease |
front 5 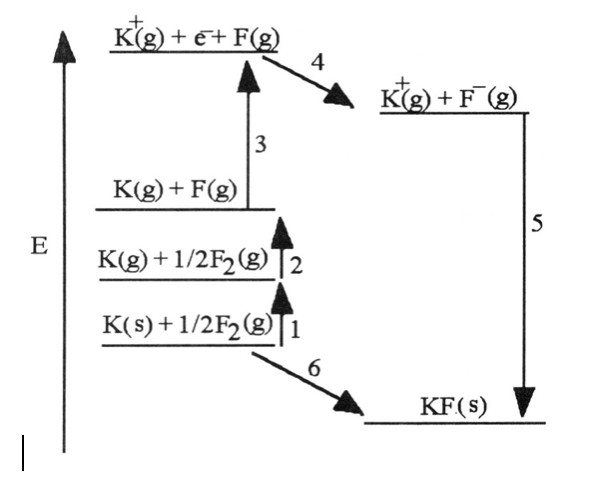 5) Which energy change corresponds to the electron affinity of fluorine? A) 2 B) 5 C) 4 D) 1 E) 6 | back 5 C) 4 |
front 6  6) Which energy change corresponds to the first ionization energy of potassium? A) 2 B) 5 C) 4 D) 3 E) 6 | back 6 D) 3 |
front 7 7) Using the Born-Haber cycle, the ΔH°f of KBr is equal to ________. A) ΔH°f [K (g)] + ΔH°f [Br (g)] + I1(K) + E(Br) + ΔHlattice B) ΔH°f [K (g)] - ΔH°f [Br (g)] - I1(K) - E(Br) - ΔHlattice C) ΔH°f [K (g)] - ΔH°f [Br (g)] + I1(K) - E(Br) + ΔHlattice D) ΔH°f [K (g)] + ΔH°f [Br (g)] - I1 - E(Br) + ΔHlattice E) ΔH°f [K (g)] + ΔH°f [Br (g)] + I1(K) + E(Br) - ΔHlattice | back 7 E) ΔH°f [K (g)] + ΔH°f [Br (g)] + I1(K) + E(Br) - ΔHlattice |
front 8 8) The type of compound that is most likely to contain a covalent bond is ________. A) one that is composed of a metal from the far left of the periodic table and a nonmetal from the far right of the periodic table B) a solid metal C) one that is composed of only nonmetals D) held together by the electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions E) There is no general rule to predict covalency in bonds. | back 8 C) one that is composed of only nonmetals |
front 9 9) In which of the molecules below is the carbon-carbon distance the shortest? A) H2C CH2 B) H-C≡C-H C) H3C—CH3 D) H2C C CH2 E) H3C—CH2—CH3 | back 9 B) H-C≡C-H |
front 10 10) Of the molecules below, the bond in ________ is the most polar. A) HBr B) HI C) HCl D) HF E) H2 | back 10 D) HF |
front 11 11) Which of the following has the bonds correctly arranged in order of increasing polarity? A) Be—F, Mg—F, N—F, O—F B) O—F, N—F, Be—F, Mg—F C) O—F, Be—F, Mg—F, N—F D) N—F, Be—F, Mg—F, O—F E) Mg—F, Be—F, N—F, O—F | back 11 B) O—F, N—F, Be—F, Mg—F |
front 12 12) The bond length in an HI molecule is 1.61 Å and the measured dipole moment is 0.44 D. What is the magnitude (in units of e) of the negative charge on I in HI? (1 debye = 3.34 × 10-30 coulomb-meters; e = 1.6 × 10-19 coulombs) A) 1.6 × 10-19 B) 0.057 C) 9.1 D) 1 E) 0.22 | back 12 B) 0.057 |
front 13 13) The Lewis structure of N2H2 shows ________. A) a nitrogen-nitrogen triple bond B) a nitrogen-nitrogen single bond C) each nitrogen has one nonbonding electron pair D) each nitrogen has two nonbonding electron pairs E) each hydrogen has one nonbonding electron pair | back 13 C) each nitrogen has one nonbonding electron pair |
front 14 14) The Lewis structure of the CO32- ion is ________. | back 14 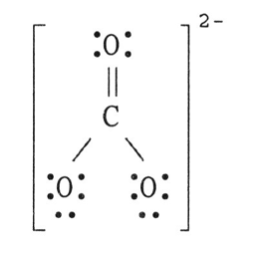 A. |
front 15 15) In the nitrite ion (NO2-), ________. A) both bonds are single bonds B) both bonds are double bonds C) one bond is a double bond and the other is a single bond D) both bonds are the same E) there are 20 valence electrons | back 15 C) one bond is a double bond and the other is a single bond |
front 16 16) Resonance structures differ by ________. A) number and placement of electrons B) number of electrons only C) placement of atoms only D) number of atoms only E) placement of electrons only | back 16 E) placement of electrons only |
front 17 17) The oxidation number of iron in Fe2O3 is ________. A) -2 B) +1 C) +3 D) +2 E) -3 | back 17 C) +3 |
front 18 18) To convert from one resonance structure to another, ________. A) only atoms can be moved B) electrons and atoms can both be moved C) only electrons can be moved D) neither electrons nor atoms can be moved E) electrons must be added | back 18 C) only electrons can be moved |
front 19 19) For resonance forms of a molecule or ion, ________. A) one always corresponds to the observed structure B) all the resonance structures are observed in various proportions C) the observed structure is an average of the resonance forms D) the same atoms need not be bonded to each other in all resonance forms E) there cannot be more than two resonance structures for a given species | back 19 C) the observed structure is an average of the resonance forms |
front 20 For the questions that follow, consider the BEST Lewis structures of the following oxyanions: (i)NO2- (ii)NO3- (iii)SO32- (iv)SO42- (v)BrO3- 20) There can be four equivalent best resonance structures of ________. A) (i) B) (ii) C) (iii) D) (iv) E) (v) | back 20 D) (iv) |
front 21 For the questions that follow, consider the BEST Lewis structures of the following oxyanions: (i)NO2- (ii)NO3- (iii)SO32- (iv)SO42- (v)BrO3- 21) In which of the ions do all X-O bonds (X indicates the central atom) have the same length? A) none B) all C) (i) and (ii) D) (iii) and (v) E) (iii), (iv), and (v) | back 21 B) all |
front 22 22) A valid Lewis structure of ________ cannot be drawn without violating the octet rule. A) NF3 B) IF3 C) PF3 D) SbF3 E) SO42- | back 22 B) IF3 |
front 23 23) Based on the octet rule, boron will most likely form a ________ ion. A) B3- B) B+ C) B3+ D) B2+ E) B2- | back 23 C) B3+ |
front 24 24) Which of the following does not have eight valence electrons? A) Cl- B) Xe C) Ti+4 D) Rb+ E) Sr+ | back 24 E) Sr+ |
front 25 25) A valid Lewis structure of ________ cannot be drawn without violating the octet rule. A) PO43- B) SiF4 C) CF4 D) SeF4 E) NF3 | back 25 D) SeF4 |
front 26 26) The central atom in ________ does not violate the octet rule. A) SF4 B) KrF2 C) CF4 D) XeF4 E) ICl4- | back 26 C) CF4 |
front 27 27) A valid Lewis structure of ________ cannot be drawn without violating the octet rule. A) ClF3 B) PCl3 C) SO3 D) CCl4 E) CO2 | back 27 A) ClF3 |
front 28 28) A valid Lewis structure of ________ cannot be drawn without violating the octet rule. A) NI3 B) SO2 C) ICl5 D) SiF4 E) CO2 | back 28 C) ICl5 |
front 29 29) A valid Lewis structure of ________ cannot be drawn without violating the octet rule. A) NF3 B) BeH2 C) SO2 D) CF4 E) SO32- | back 29 B) BeH2 |
front 30 30) Why don't we draw double bonds between the Be atom and the Cl atoms in BeCl2? A) That would give positive formal charges to the chlorine atoms and a negative formal charge to the beryllium atom. B) There aren't enough electrons. C) That would result in more than eight electrons around beryllium. D) That would result in more than eight electrons around each chlorine atom. E) That would result in the formal charges not adding up to zero. | back 30 A) That would give positive formal charges to the chlorine atoms and a negative formal charge to the beryllium atom. |
front 31 31) Which atom can accommodate an octet of electrons, but doesn't necessarily have to accommodate an octet? A) N B) C C) H D) O E) B | back 31 E) B |
front 32 32) Bond enthalpy is ________. A) always positive B) always negative C) sometimes positive, sometimes negative D) always zero E) unpredictable | back 32 A) always positive |
front 33 33) Given that the average bond energies for C-H and C-Br bonds are 413 and 276 kJ/mol, respectively, the heat of atomization of bromoform (CHBr3) is ________ kJ/mol. A) 1241 B) 689 C) -689 D) 1378 E) -1378 | back 33 A) 1241 |
front 34 34) Of the bonds C-C, C C, and C≡C, the C-C bond is ________. A) strongest/shortest B) strongest/longest C) weakest/longest D) weakest/shortest E) intermediate in both strength and length | back 34 C) weakest/longest |
front 35 35) Of the bonds C-N, C N, and C≡N, the C-N bond is ________. A) strongest/shortest B) strongest/longest C) weakest/shortest D) weakest/longest E) intermediate in both strength and length | back 35 D) weakest/longest |
front 36 36) As the number of covalent bonds between two atoms increases, the distance between the atoms ________ and the strength of the bond between them ________. A) increases, increases B) decreases, decreases C) increases, decreases D) decreases, increases E) is unpredictable | back 36 D) decreases, increases |
front 37 37) Of the possible bonds between carbon atoms (single, double, and triple), ________. A) a triple bond is longer than a single bond B) a double bond is stronger than a triple bond C) a single bond is stronger than a triple bond D) a double bond is longer than a triple bond E) a single bond is stronger than a double bond | back 37 D) a double bond is longer than a triple bond |
front 38 38) Most explosives are compounds that decompose rapidly to produce ________ products and a great deal of ________. A) gaseous, gases B) liquid, heat C) soluble, heat D) solid, gas E) gaseous, heat | back 38 E) gaseous, heat |
front 39 39) Dynamite consists of nitroglycerine mixed with ________. A) potassium nitrate B) damp KOH C) TNT D) diatomaceous earth or cellulose E) solid carbon | back 39 D) diatomaceous earth or cellulose |
front 40 40) Dynamite ________. A) was invented by Alfred Nobel B) is made of nitroglycerine and an absorbent such as diatomaceous earth C) is a much safer explosive than pure nitroglycerine D) is an explosive E) all of the above | back 40 E) all of the above |
front 41 41) Based on the octet rule, magnesium most likely forms a ________ ion. A) Mg2+ B) Mg2- C) Mg6- D) Mg6+ E) Mg- | back 41 A) Mg2+ |
front 42 42) The electron configuration of the phosphide ion (P3-) is ________. A) [Ne]3s2 B) [Ne]3s23p1 C) [Ne]3s23p3 D) [Ne]3p2 E) [Ne]3s23p6 | back 42 E) [Ne]3s23p6 |
front 43 43) The electron configuration of the sulfide ion (S2-) is ________. A) [Ne]3s2 B) [Ne]3s23p1 C) [Ne]3s23p4 D) [Ne]3p2 E) [Ne]3s23p6 | back 43 E) [Ne]3s23p6 |
front 44 44) The halogens, alkali metals, and alkaline earth metals have ________ valence electrons, respectively. A) 7, 4, and 6 B) 1, 5, and 7 C) 8, 2, and 3 D) 7, 1, and 2 E) 2, 7, and 4 | back 44 D) 7, 1, and 2 |
front 45 45) The only noble gas without eight valence electrons is ________. A) Ar B) Ne C) He D) Kr E) All noble gases have eight valence electrons. | back 45 C) He |