Which part of a plant absorbs most of the water and minerals taken up from the soil?
root hairs
What is the primary function of stems?
Maximization of photosynthesis by leaves
When you eat Brussels sprouts, you are eating _____.
large axillary buds
Some of the largest leaves in the world can be found on plants near
the forest floor of dense
tropical rain forests. Which of the
following precursors for photosynthesis is most likely limited
in
these large leaves?
light
Leaf thickness represents a trade-off between _____.
water retention and carbon dioxide absorption
One important difference between the anatomy of roots and the anatomy
of leaves is that
_____.
a waxy cuticle covers leaves but is absent from roots
Which of the following was a challenge to the survival of the first land plants?
desiccation
Trichomes _____.
repel or trap insects
Which structure is correctly paired with its tissue system?
tracheid — vascular tissue
The main source of water necessary for photosynthesis to occur in the
leaf mesophyll is
_____.
soil via the xylem
The vascular bundle in the shape of a single central cylinder in a root is called the _____.
stele
Which of the following cell types retains the ability to undergo cell division?
a parenchyma cell near the root tip
Which of these is NOT an example of a parenchyma cell?
support cells near the outside of nonwoody stems
Which of the following have unevenly thickened primary walls that
support young, growing
parts of the plant?
collenchyma cells
Which of the following is correctly paired with its structure and function?
sclerenchyma — supporting cells with thick secondary walls
Which of the following occurs in vascular land plants but not charophytes (stoneworts)?
lignin
Which of the following are water-conducting cells that are dead at functional maturity?
tracheids and vessel elements
Which of the following cells transport sugars over long distances?
sieve-tube elements
Plant meristematic cells _____.
are undifferentiated cells that produce new cells
Which of the following arise, directly or indirectly, from meristematic activity?
secondary xylem, leaves, dermal tissue, and tubers
Compared to most animals, the growth of most plant structure is best described as _____.
indeterminate
What is present in a shoot apical meristem region?
I, II, and III
Shoot elongation in a growing bud is due primarily to _____.
cell elongation localized in each internode
Apical meristems of dicots are at the tips of stems. Apical meristems
of grasses are at ground
level or slightly below, concealed by
the leaves. The leaves also have an intercalary meristem at
their
bases. What does this mean when considering care of a lawn or soccer field?
If you mow two inches above ground level, both the apical and
intercalary meristems can
keep producing new cells.
In a meristematic region, the cell plate during mitosis is
perpendicular to the side of the stem.
In what direction will the
stem grow?
vertically in height
Which of the following cells or tissues arise from lateral meristem activity?
secondary xylem
Cells produced by lateral meristems are known as _____.
secondary tissues
Which of the following can be used to determine a twig’s age?
Number of apical bud scar rings
A plant that grows one year, dies back, and then grows again the
following year, produces
flowers and then dies would be
considered _____.
annual
Which of the following is the correct sequence of the zones in the
primary growth of a root,
moving from the root cap inward?
zone of cell division, zone of elongation, zone of differentiation
The driving force that pushes the root tip through the soil is primarily _____.
elongation of cells behind the root apical meristem
Mitotic activity by the apical meristem of a root makes which of the
following more
possible?
increased delivery of water to the aboveground stem
Which of the following root tissues gives rise to lateral roots?
pericycle
As a youngster, you drive a nail in the trunk of a young tree that is
3 meters tall. The nail is
about 1.5 meters from the ground.
Fifteen years later, you return and discover that the tree
has
grown to a height of 30 meters. About how many meters above
the ground is the nail?
1.5
You find a plant unfamiliar to you and observe that it has vascular
bundles scattered
throughout the stem cross section. What do you
conclude about the plant?
It is probably a monocot.
Monocot vascular bundles do not have a vascular cambium between the
xylem and phloem.
This means that monocots _____.
do not produce wood in annual rings
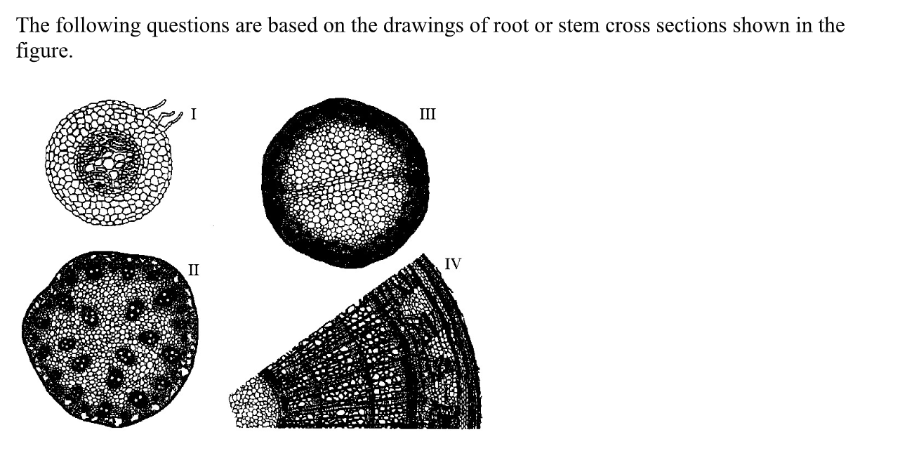
Refer to the figure above. A monocot stem is represented by _____.
II only

Refer to the figure above. A woody eudicot is represented by _____.
IV only

Refer to the figure above. A plant that is at least three years old is represented by _____.
IV only
Canada thistle is a dicot that spreads via growth from lateral roots.
You want to use a root
miner insect for weed control. What would
you need to observe in the underground growth to
verify that this
weed spreads via lateral roots and not by underground stems?
a vascular bundle in the center surrounded by parenchyma tissue
A student examining leaf cross sections under a microscope finds many
loosely packed cells
with relatively thin cell walls. The cells
have numerous chloroplasts. What type of cells are they?
parenchyma
The veins of leaves are _____.
I) composed of xylem and
phloem
II) continuous with vascular bundles in the stem and
roots
III) finely branched to be in close contact with
photosynthesizing cells
I, II, and III

The main function associated with structure X is _____.
retention of water

The main function associated with structure Y is _____.
absorption of carbon dioxide
Increasing the number of stomata per unit surface area of a leaf when
atmospheric carbon
dioxide levels decline is most analogous to a
human _____.
putting more red blood cells into circulation when atmospheric oxygen levels decline
Where is primary growth occurring in an old tree?
in young branches where leaves are forming
What tissue makes up most of the wood of a tree?
secondary xylem
A plant has the following characteristics: a taproot system, several
growth rings evident in a
cross section of the stem, and a layer
of bark around the outside. Which of the following best
describes
the plant?
woody eudicot
If you were able to walk into an opening cut into the center of a
large redwood tree, when
you exited from the middle of the trunk
(stem) outward, you would cross, in order, _____.
the annual rings, new xylem, vascular cambium, phloem, and bark
Heartwood and sapwood consist of _____.
secondary xylem
Two examples of lateral meristems in plants are _____.
vascular cambium, producing secondary xylem; cork cambium, producing cork
Additional vascular tissue produced as secondary growth in a root
originates from which
cells?
vascular cambium
Girdling is a procedure to kill unwanted tress by cutting a groove
into the bark of the tree.
The groove must completely encircle
the trunk and should penetrate into the wood to a depth of
at
least 1/2-inch on small trees, and 1-3/2 inches on larger trees. Why
does this procedure cause
tree death?
No sugars can be transported from the leaves to the roots.
Where are the youngest wood and the youngest bark in a tree trunk?
Youngest wood is toward the outside, near the vascular cambium;
youngest bark is the inner
part, next to the vascular cambium.
The polarity of a plant is established when _____.
the shoot-root axis is established in the embryo
Growth and development of plant parts involves _____.
I) cell
division to produce new cells
II) enlargement and elongation of
cells
III) specialization of cells into tissues
I, II, and III
Totipotency is a term used to describe a cell's ability to
give rise to a complete new
organism. In plants, this means that _____.
cell differentiation depends largely on the control of gene expression
Which of the following statements is true?
Homeotic genes often control morphogenesis.
The phase change of an apical meristem from the juvenile to the
mature vegetative phase is
often revealed by _____.
a change in the morphology of the leaves produced