The ability of sperm cells to move along the ductus deferens is due to ________.
A) gravity
B) peristaltic contractions
C) enzymatic
activity
D) hormonal action
B) peristaltic contractions
Erection of the penis results from ________.
A) a sympathetic reflex
B) parasympathetic activation of the bulbourethral glands
C) dilation of the veins in the penis
D) a parasympathetic reflex
D) a parasympathetic reflex
Which is not a part of the proliferative phase of the female menstrual cycle?
A) late in this phase, cervical mucus becomes thin and crystalline
B) vesicular follicle growth
C) corpus luteum
D) development of endometrial cells
C) corpus luteum
Which of the choices below is not a function of the vagina?
A) serves as a passageway for the primary oocyte
B) serves as a passageway for menstrual flow
C) is the birth canal
D) receives semen from the penis during sexual intercourse
A) serves as a passageway for the primary oocyte
Select the correct statement about male sexual response.
A) Sympathetic impulses are responsible for causing penile arteriolar dilation, resulting in erection.
B) Erection is the result of vascular spaces in the erectile tissues filling with blood.
C) Expansion of the penile tissues results in dilation of the venous outflow.
D) Ejaculation is the result of parasympathetic stimulation.
B) Erection is the result of vascular spaces in the erectile tissues filling with blood.
Which of the choices below is not a function of testosterone?
A) stimulates the male pattern of development
B) contributes to male sexual behavior and spermatogenesis
C) stimulates protein synthesis
D) stimulates mammary gland development
D) stimulates mammary gland development
Which male hormone inhibits the secretion of FSH?
A) ACTH
B) inhibin
C) ICSH
D) testosterone
B) inhibin
During the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle ________.
A) LH reaches its highest levels
B) progesterone levels are at their highest
C) estrogen reaches its highest levels
D) the Graafian follicle forms
B) progesterone levels are at their highest
Human egg and sperm are similar in that ________.
A) about the same number of each is produced per month
B) they have the same degree of motility
C) they have the same number of chromosomes
D) they are about the same size
C) they have the same number of chromosomes
The constancy of the chromosome number from one cell generation to the next is maintained through ________.
A) mitosis
B) meiosis
C) cytokinesis
D) DNA synthesis
B) meiosis
In humans, separation of the cells at the two-cell state following fertilization may lead to the production of twins, which in this case would be ________.
A) dizygotic
B) identical
C) fraternal
D) of different sexes
B) identical
Characteristics of the mature sperm include the ________.
A) presence of two X chromosomes in approximately half the sperm
B) presence of Y chromosomes in approximately half the sperm
C) absence of an acrosome
D) absence of coiled mitochondria
B) presence of Y chromosomes in approximately half the sperm
How do the testes respond to exposure to excessive body warmth?
A) They move close to the pelvic cavity.
B) They move away from the pelvic cavity.
C) Excessive warmth has no effect on the testicles because of their location in the scrotum.
D) Excessive warmth is actually beneficial in that it speeds up the maturation of sperm.
B) They move away from the pelvic cavity.
Effects of estrogen include ________.
A) increased oiliness of the skin
B) deepening of the voice
C) growth of the breasts at puberty
D) growth of the larynx
C) growth of the breasts at puberty
Secretion of progesterone stimulates ________.
A) contraction of uterine muscles
B) preparation of the mammary glands for lactation
C) secretory activity of the uterine myometrium
D) development of the female secondary sex characteristics
B) preparation of the mammary glands for lactation
The cells that produce testosterone in the testis are called ________.
A) spermatocytes
B) spermatogonia
C) sustentacular cells
D) interstitial cells
D) interstitial cells
The most important risk for testicular cancer in young males is ________.
A) smoking
B) a diet high in fat
C) nondescent of the testes
D) sexually transmitted infections
C) nondescent of the testes
Which of the following glands are responsible for 60% of the synthesis of semen?
A) the seminal vesicles
B) the bulbourethral glands
C) the prostate
D) the pituitary
A) the seminal vesicles
Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins?
A) LH
B) FSH
C) GnRH
D) testosterone
C) GnRH
The primary function of the uterus is to ________.
A) protect the ovaries
B) synthesize female hormones
C) regulate the ovarian and menstrual cycles
D) receive, retain, and nourish a fertilized ovum
D) receive, retain, and nourish a fertilized ovum
Why is the blood-testis barrier important?
A) because spermatozoa and developing cells produce surface antigens that are recognized as foreign by the immune system
B) because some blood contents are toxic to the spermatozoa
C) because immature sperm cells lose their motility when they encounter any blood component
D) Actually, the blood-testis barrier has no function.
A) because spermatozoa and developing cells produce surface antigens that are recognized as foreign by the immune system
The structures that receive the ovulated oocyte, providing a site for fertilization, are called the ________.
A) Graafian follicles
B) fallopian tubes
C) infundibula
D) fimbriae
B) fallopian tubes
If gametes were diploid like somatic cells, how many chromosomes would the zygote contain?
A) twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur
B) triple the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to triple and normal development would not occur
C) half the diploid number with no change in development
D) There is no relationship between gametes and somatic cells.
A) twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur
Select the correct statement about the uterine cycle.
A) The menstrual phase of the cycle is from day 1 to day 8.
B) During the secretory phase, estrogen levels are at their highest.
C) During the proliferative phase, levels of progesterone rise as the follicle begins to produce more hormone.
D) If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum is maintained by a hormone secreted by the developing embryo.
D) If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum is maintained by a hormone secreted by the developing embryo.
Normally menstruation occurs when ________.
A) blood levels of FSH fall off
B) blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease
C) blood levels of estrogen and progesterone increase
D) the corpus luteum secretes estrogen
B) blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease
The basic difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis is that ________.
A) during spermatogenesis two more polar bodies are produced
B) the mature ovum is n, while the sperm is 2n
C) in oogenesis, one mature ovum is produced, and in spermatogenesis four mature sperm are produced from the parent cell
D) spermatogenesis involves mitosis and meiosis, but oogenesis involves meiosis only
C) in oogenesis, one mature ovum is produced, and in spermatogenesis four mature sperm are produced from the parent cell
Which of the following will occur after ovulation?
A) The corpus luteum secretes estrogen only.
B) The endometrium enters its secretory phase.
C) The secretion of anterior pituitary gonadotropins is enhanced.
D) The corpus luteum prepares to become a corpus albicans.
B) The endometrium enters its secretory phase.
Why doesn’t semen enter the urinary bladder during ejaculation?
A) There is no common duct between the reproductive system and the urinary system.
B) There is no urge to urinate during sexual intercourse because of the suppression of LH by testosterone buildup in the blood.
C) The smooth muscle sphincter at the base of the urinary bladder closes.
D) Ejaculation is a parasympathetic reflex resulting in no response by urinary contraction muscles.
C) The smooth muscle sphincter at the base of the urinary bladder closes.
Which hormone is absolutely necessary for ovulation to occur?
A) LH
B) FSH
C) progesterone
D) estrogen
A) LH
Select the correct statement about testosterone control.
A) GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH release from the anterior pituitary.
B) FSH stimulates testicular production of testosterone.
C) Inhibin and testosterone exert positive feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary.
D) The pineal gland is believed to be the gland that exerts the most influence in testosterone control.
A) GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH release from the anterior pituitary.
Which of the following is a correct statement about uterine tubes?
A) The ampulla is the narrow constricted region.
B) The infundibulum is the funnel-shaped region near the ovary.
C) The isthmus is the normal site of fertilization.
D) The mesometrium supports the uterine tubes along their entire length.
B) The infundibulum is the funnel-shaped region near the ovary.
Select the correct statement about the hormonal events of the ovarian cycle.
A) Rising levels of estrogen start follicle development.
B) High estrogen levels result in a surge of LH release.
C) The follicle begins to secrete progesterone in response to estrogen stimulation.
D) The LH surge stimulates further development of the secondary oocyte.
B) High estrogen levels result in a surge of LH release.
Which of these statements about sexually transmitted infections is false?
A) Chlamydia is caused by bacteria that can often be asymptomatic or bring on a wide variety of symptoms.
B) Gonorrhea is caused by a bacterium that can bring on painful discharges in males.
C) Syphilis is caused by a virus that may lead to death if untreated.
D) Genital herpes is caused by a virus that may cause intermittent lesions.
C) Syphilis is caused by a virus that may lead to death if untreated
Match the following:
1) External sac enclosing the testes
2) Erectile tissue in the male
3) The release of oocyte
from ovary
A) Ovulation
B) Scrotum
C) Corpora cavernosa
1) B
2) C
3) A
Match the following:
1) painful urination and a yellowish discharge
2) herpes simplex virus
3) risk factor for this disease is being infected with HPV
4) organisms responsible for up to half of the diagnosed cases of pelvic inflammatory disease
5) leading cause of pelvic inflammatory disease
A) chlamydia
B) cervical cancer
C) gonorrhea
D) STI's
E) genital herpes
1) C
2) E
3) B
4) A
5) D
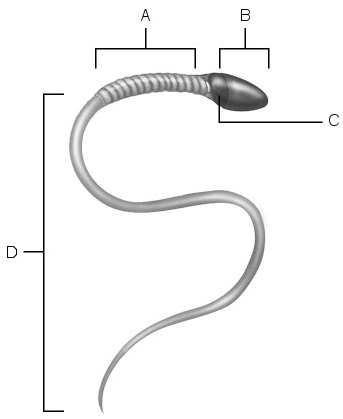
Match the following:
7) Location of mitochondria.
8) Midpiece.
9) Location of nucleus.
10) Flagellum.
7) A
8) A
9) C
10)D
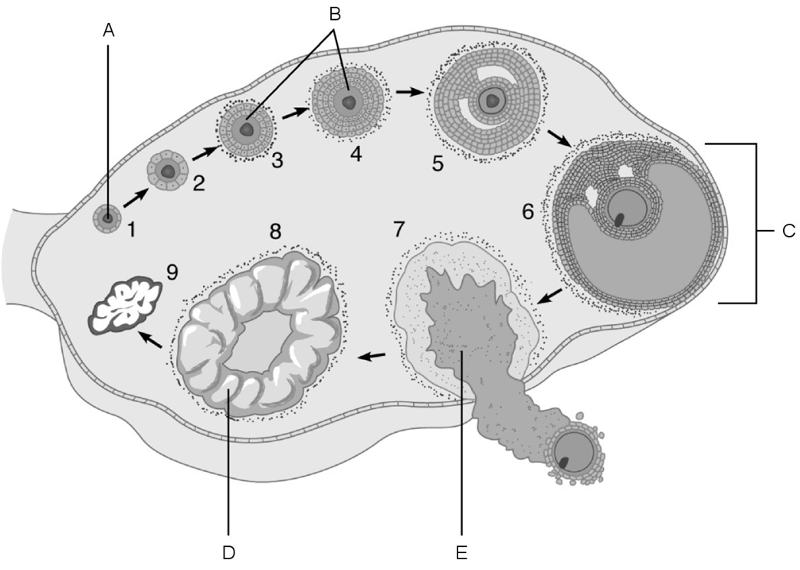
Match the following:
2) The stage called ovulation.
3) Vesicular (Graafian) follicle.
4) Primordial follicle.
5) Corpus luteum.
2) E
3) C
4) A
5) D
The dartos and cremaster muscles are important to the integrity of the male reproductive system. Which of the following is true about the role they play?
A) They contract to push sperm along the ductus deferens.
B) They regulate the temperature of the testes.
C) They are responsible for penile erection.
D) They contract to allow ejaculation.
B) They regulate the temperature of the testes.

1) Red Bone Marrow and place where T and B Cells are born at
2) Thymus and is immunocompetent with T Cells
3) Bone Marrow and is immunocompetent with B Cells
4) Lymph Nodes and help with clone selection and with both B and T cells
5) Capillaries and Recirculate
6) Area where B cells become immunocompetent.
7) Area where activated immunocompetent B and T cells recirculate.
8) Area where T cells become immunocompetent.
9)Area seeded by immunocompetent B and T cells.
10)Area where antigen challenge and clonal selection are most likely to occur.
1) A
2) B
3) C
4) D
5) E
6) C
7) E
8) B
9) D
10)D
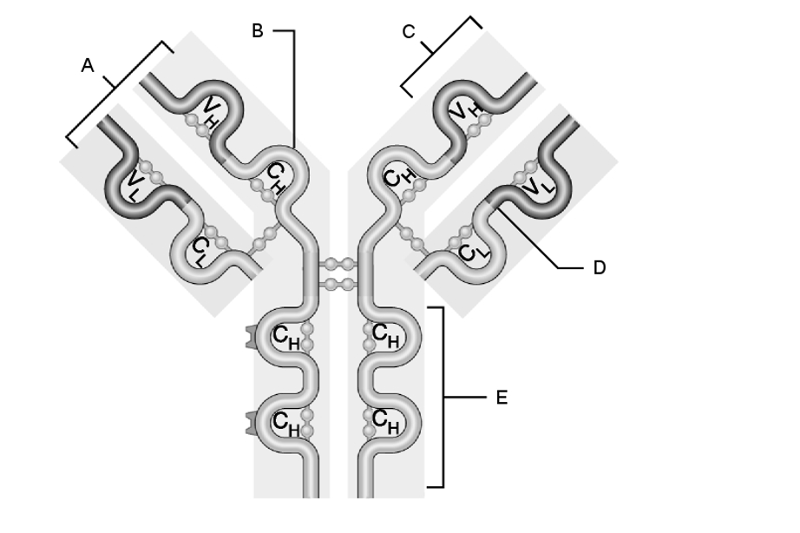
1) Heavy chain.
2) Light chain.
3) Variable region.
4) Constant region.
5) Antigen-binding site.
1) b
2) d
3) c
4) e
5) a
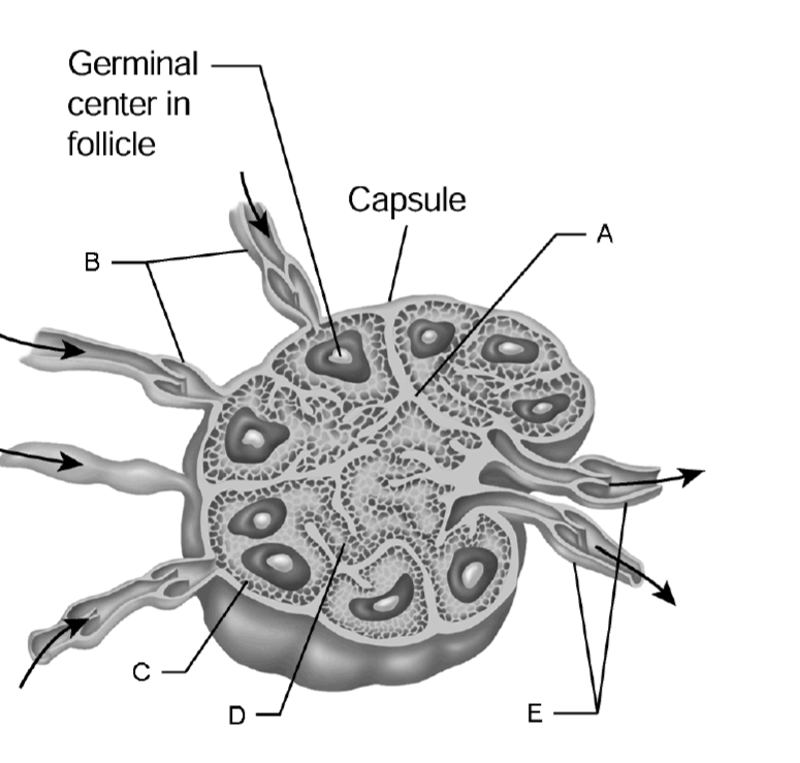
1) Cortex
2) Medulla
3) Medullary cord
4) Efferent vessels
5) Trabecula
1) C
2) d
3) d
4) e
5) a
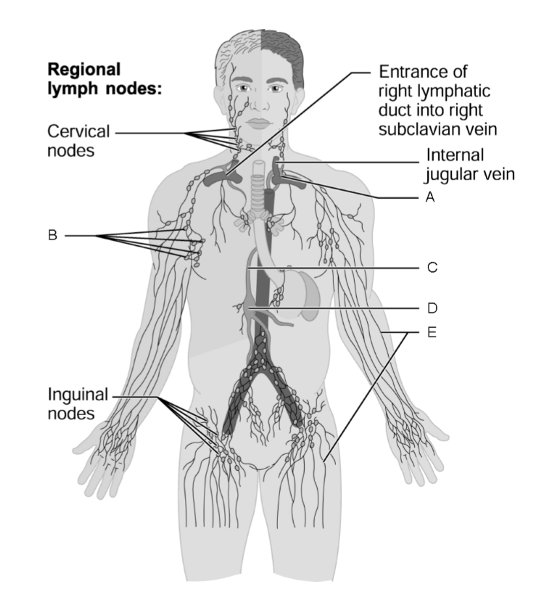
1) Entrance of thoracic duct into subclavian vein
2) Lymphatic collecting vessels
3) Cisterna chyli
4) Axillary node(s)
5) Thoracic duct
1) a
2) e
3) d
4) b
5) c
1) Protein-containing fluid within lymphatic vessels.
2) Receives lymph from most of the body.
3) Isolated clusters of lymph follicles found in the wall of the small intestine.
4) Small organs intimately associated with lymphatic vessels.
5) Largest lymphatic organ.
6) Stores blood platelets.
A) Lymph
B) Peyer's patches
C) Spleen
D) Thoracic duct
E) Lymph nodes
1) a
2) d
3) b
4) e
5) c
6) c
Matching:
1) Involved in allergies.
2) Present the double activation signal to T cells.
3) Stimulate the proliferation of other lymphocytes
4) Dampen the activity of both T cells and B cells
5) Activates complement.
A) IgE
B) Regulatory T cells
C) helper T cells
D) APCs
E) IgM
1) a
2) d
3) c
4) b
5) e
11) Second line of defense
12) Main antibody of both primary and secondary immune response.
13) Protects mucosal barriers.
14) First line of defense
15) Small proteins secreted by virus-containing cells
J) Inflammatory response
K) IgA
L) IgG
M) intact skin & mucous membranes
N) interferon
11)j
12)L
13)k
14)m
15)n
6) Along with IgM, this is a B cell receptor
7) Third line of defense.
8) Adaptive defense system
9) Innate defense system.
10) Major innate mechanism that mediates destruction of foreign substances in the body.
F) IgD
G) Inflammatory response & skin & mucous membranes
H) Immune response
I) Complement
6) f
7) h
8) h
9) g
10)I