The tryptophan operon is a repressible operon that is
- permanently turned on
- turned on only when tryptophan is present in the growth medium
- turned off only when glucose is present in the growth medium
- turned on only when glucose is present in the growth medium
- turned off whenever tryptophan is added to the growth medium
e.
Which of the following, when taken up by the cell, binds to the repressor so that the repressor no longer binds to the operator?
- ubiquitin
- inducer
- promoter
- repressor
- corepressor
b.
The lactose operon is likely to be transcribed when
- there is more glucose in the cell than lactose
- the lactose levels within the cell is low
- there is glucose but no lactose in the cell
- the lactose level is high within the cell
- the oxygen level is high and the lactose level is low
d.
For a repressible operon to be transcribed, which of the following must occur?
- a corepressor must be present
- RNA polymerase and the active repressor must be present
- RNA polymerase must bind to the promoter, and the repressor must be inactive
- RNA polymerase cannot be present, and the repressor must be inactive
- RNA polymerase must no occupy the promoter, and the repressor must be inactive.
c.
In eukaryotes, general transcription factors
- are required for the expression of specific protein-encoding genes
- bind to other proteins or to a sequence element within the promoter called the TATA box
- inhibit RNA polymerase binding to the promoter and begin transcribing
- usually lead to a high level of transcription even without additional specific transcription factors
- bind to sequences just after the start site of transcription
b.
Two potential devices that eukaryotic cells use to regulate transcription are
- DNA methylation and histone amplification
- DNA amplification and histone methylation
- DNA acetylation and methylation
- DNA methylation and histone modification
- histone amplification and DNA acetylation
d.
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- inducer
- promoter
- RNA polymerase
- repressor
- operator
RNA polymerase binds to this region to initiate transcription
b.
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- inducer
- promoter
- RNA polymerase
- repressor
- operator
Can inhibit transcription by blocking the binding of positively acting transcription factors to the DNA
d.
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- inducer
- promoter
- RNA polymerase
- repressor
- operator
Region between the promoter and the first gene which acts as an "on-off switch."
e.
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- inducer
- promoter
- RNA polymerase
- repressor
- operator
Product of the regulatory gene
d.
The host range of a virus is determined by
- the enzymes carried by the virus
- whether its nucleic acid is DNA or RNA
- the proteins in the host's cytoplasm
- the enzymes produced by the virus before it infects the cell
- the proteins on its surface and that of the host
e.
Which of the following is characteristic of the lytic cycle?
- many bacterial cells containing viral DNA are produced
- viral DNA is incorporated into the host genome
- the viral genome replicates without destroying the host
- a large number of phages are released at a time
- the virus-host relationship lasts for generations
d.
Which of the following statements describes the lysogenic cycle of lambda (λ) phage?
- after infection, the viral genes immediately turn the host cell into a lambda-producing factory, and the host cell then lyses
- most of the prophage genes are activated by the product of a particular prophage gene
- the phage genome replicates along with the host genome
- certain environmental triggers can cause the phage to exit the host genome, switching from the lytic to the lysogenic
- the phage DNA is incorporated by crossing over into any nonspecific site on the host cell's DNA
c.
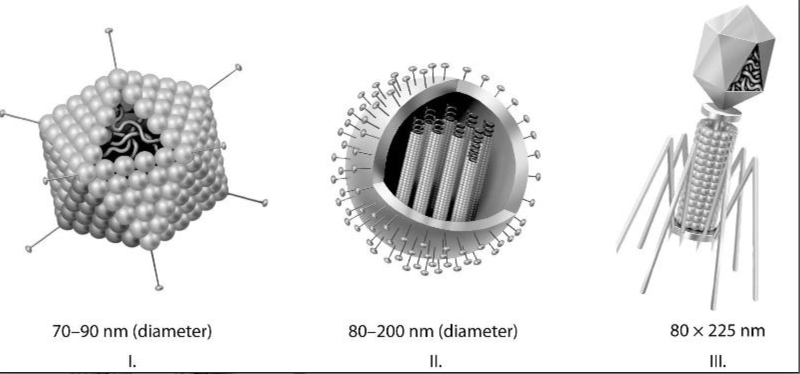
Which of the three types of viruses shown above would you expect to include glycoproteins?
- I only
- II only
- III only
- I and II only
- all three
d.
Viruses that infect bacteria are referred to as
- viralcidens
- bacteriocidins
- bacterialogens
- bacteriophages
d.
All viruses possess
- a capsid and an envelope
- DNA as well as RNA
- a genome and a capsid
- a nucleocapsid and envelope
c.
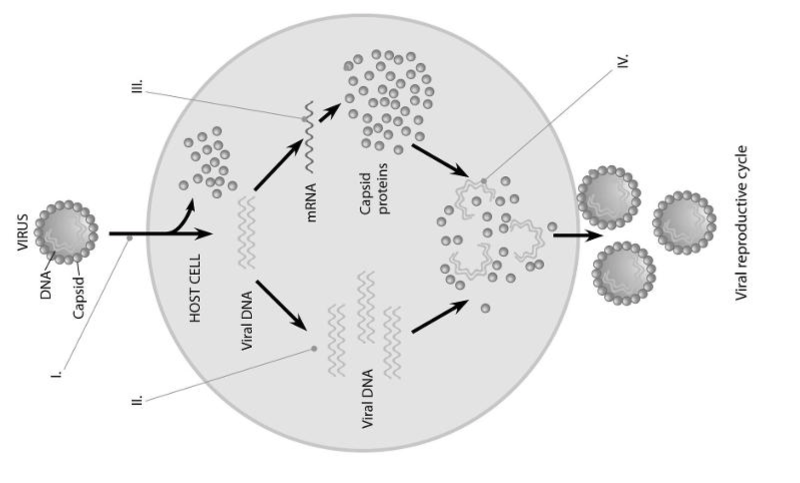
In the figure, when new viruses are being assembled (IV), what mediates the assembly?
- host cell chaperones
- assembly proteins coded for by the host nucleus
- assembly proteins coded for by the viral genes
- viral RNA intermediates
- nothing; they self-assemble
e.
As an embryo develops, new cells are produced as the result of
- differentiation
- preformation
- cell division
- morphogenesis
- epigenesis
c.
Fertilization normally
- reinstates diploidy
- follows gastrulation
- is required for parthenogensis
- merges two diploid cells into one haploid cell
- precedes ovulation
a.
Cells move to new positions as an embryo establishes its three germ tissue layers during
- determination
- cleavage
- fertilization
- induction
- gastrulation
e.
What is the most logical sequence of steps for splicing foreign DNA into a plasmid and inserting the plasmid into a bacterium?
- transform bacteria with a recombinant DNA molecule
- cut the plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes (endonuclease)
- extract plasmid DNA from bacterial cells
- hydrogen-bond the plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA fragments
- use ligase to seal plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA
- II, III, V, IV, I
- III, II, IV, V, I
- III, IV, V, I, II
- IV, V, I, II, III
b.
Which of the following uses labeled probes to visualize the expression of genes in whole tissues and organisms?
- RT-PCR
- in situ hybridization
- DNA microarrays
- RNA interference
b.
Which of the following is used to make complementary DNA (cDNA) from RNA?
- restriction enzymes
- gene cloning
- DNA ligase
- gel electrophoresis
- reverse transcriptase
e.
The reason for using Taq polymerase for PCR is that
- it is heat stable and can withstand the temperature changes of the cycler
- only minute amounts are needed for each cycle of PCR
- it binds more readily than other polymerases to primer
- it has regions that are complementary to primers
- all of these are correct
a.
DNA microarrays have made a huge impact on genomic studies because they
- can be used to eliminate the function of any gene in the genome
- can be used to introduce entire genomes into bacterial cells
- allow the expression of many or even all of the genes in the genome to be compared at once
- allow physical maps of the genome to be assembled in a very short time
- dramatically enhance the efficiency of restriction enzymes
c.
Which of the following describes the transfer of polypeptide sequences to a membrane to analyze gene expression?
- southern blotting
- northern blotting
- western blotting
- eastern blotting
- RT-PCR
c.
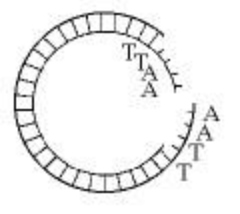
Which enzyme was used to produce the molecule in the figure above?
- ligase
- a restriction enzyme (endonuclease)
- RNA polymerase
- DNA polymerase
b.
In 1997, Dolly the sheep was cloned. Which of the following processes was used?
- replication and dedifferentiation of adult stem cells from sheep bone marrow
- separation of an early stage blastula into separate cells, one of which was incubated in a surrogate ewe
- fusion of an adult cell's nucleus with an enucleated sheep egg, followed by incubation in a surrogate
- isolation of stem cells from a lamb embryo and production of a zygote equivalent
c.
Which of the following is in the correct order for one cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
- denature DNA; add fresh enzyme; anneal primers; add dNTPs; extend primers
- anneal primers; denature DNA; extend primers
- extend primers; anneal primers; denature DNA
- denature DNA; anneal primers; extend primers
d.
Genetically engineered plants ___
- are more difficult to develop than genetically engineered animals
- include transgenic rice plants that can grow in water of high salinity
- are used in research but not yet in commercial agricultural production
- are banned throughout the world
b.
Scientists developed a set of guidelines to address the safety of DNA technology. Which of the following is one of the adopted safety measure?
- microorganisms used in recombinant DNA experiments are genetically crippled to ensure that they cannot survive outside of the laboratory
- genetically modified organisms are not allowed to be part of our food supply
- transgenic plants are engineered so that the plant genes cannot hybridize
- experiments involving HIV or other potentially dangerous viruses have been banned
a.
Plasmids are used as vectors in plant and bacterial genetic engineering. However, there is a major difference in the fate of genes introduced into bacteria on most bacterial plasmids and into plants on tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmids. What is this difference?
- in bacteria genes are stably expressed; in plants, gene expression is always lost quickly
- gene expression tends to decrease rapidly and unpredictably in bacteria; gene expression is much more stable in plants
- bacterial plasmids are circular DNAs; Ti plasmid DNA is linear
- bacterial plasmids and the genes they carry usually are not integrated into the chromosome; Ti plasmids and the genes they carry are integrated into the chromosome
d.
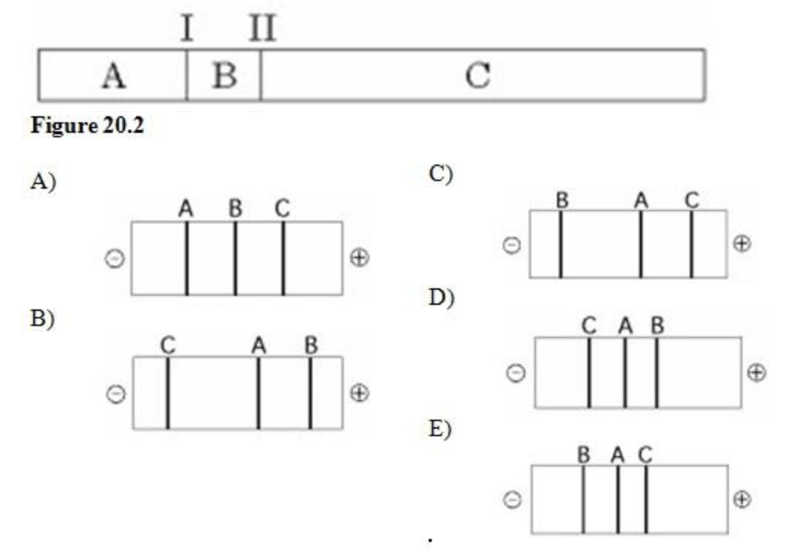
The segment of DNA shown in the figure above has restriction sites I and II, which create restriction fragments A, B, and C. Which of the gels produced by electrophoresis shown below best represents the separation and identity of these fragments?
- A, B, C
- C, A, B
- B, A, C
- C, A, B
b.
In a hypothetical situation, the genes for sex pills construction and for tetracycline resistance are located together on the same plasmid within a particular bacterium. If this bacterium readily performs conjugation involving a copy of this plasmid, then the result should be
- a bacterium that has undergone transduction
- the rapid spread of tetracycline resistance to other bacteria in that habitat
- the subsequent loss of tetracycline resistance from this bacterium
- the production of endospores among the bacterium's progeny
- the temporary possession by this bacterium of a completely diploid gene
b.
Which of these statements about prokaryotes is correct?
- bacterial cells conjugate to mutually exchange genetic material
- their genetic material is confined within vesicles known as plasmids
- they divide by binary fission, without mitosis or meiosis
- the persistence of bacteria throughout evolutionary time is due to their genetic homogeneity (in other words, sameness..)
- genetic variation in bacteria is not known to occur, because of their asexual mode of reproduction
c.
An R plasmid encodes
- antibiotics resistance in bacteria
- rates of metabolic pathways
- repressor for gene expression
- regulation of an operon
- reverse transcriptase in HIV
a.
In Fred Griffith's experiments, harmless R strain pneumococcus became lethal S strain pneumococcus as the result of which of the following?
- horizontal gene transfer
- transduction
- conjugation
- transformation
- genetic recombination
- 2 only
- 4 only
- 2 and 5
- 1, 3, and 5
- 1, 4, and 5
e.
Use the following answers for the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- transduction
- transposition
- translation
- transformation
- conjugation
External DNA is taken up by a cell
d.
Use the following answers for the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- transduction
- transposition
- translation
- transformation
- conjugation
DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by bacteriophage
a.
Use the following answers for the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- transduction
- transposition
- translation
- transformation
- conjugation
A plasmid is exchanged between bacteria through a pilus
e.
In which feature(s) should one be able to locate a complete chromosome of a bacterium?
- nucleolus
- prophage
- endospore
- nucleoid
- 4 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 2 and 3
c.
From earliest to latest, the overall sequence of early development proceeds in which of the following sequences?
- first cell division --> synthesis of embryo's DNA begins --> acrosomal reaction --> cortical reaction
- cortical reaction --> synthesis of embryo's DNA begins -> acrosomal reaction --> first cell division
- cortical reaction --> acrosomal reaction --> first cell division --> synthesis of embryo's DNA begins
- acrosomal reaction --> cortical reaction --> synthesis of embryo's DNA begins --> first cell division
d.
Which of the following are characteristic of the lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle respectively?
- Lytic: viral DNA is incorporated into the host genome. Lysogenic: kills the host cell and many are released
- Lytic: the viral genome replicates without destroying the host. Lysogenic: kills the host cell and many are released.
- Lytic: a large number of phages are released at a time by budding. Lysogenic: after infection, the viral genes immediately turn the host cell into a lambda-producing factory, doing which the host cell lyses and dies.
- Lytic: a large number of phages are released at a time by killing the host cell. Lysogenic: the phage genome replicates along with the host genome and can switch to lytic form when conditions are not favorable.
- I
- II
- IV
- III
c.
Which statements regarding the lac and trp operons are correct?
- The lac operon is repressible because its default is "on." This means that its genes are almost always being expressed.
- The lac operon is inducible, and the trp operon is repressible.
- The trp operon is repressible because its default is "on." This means that its genes are almost always being expressed.
- The inducible operon is turned on by the presence of the end product, and the repressible operon is turned off by the presence of the substrate.
- The signal molecule (i.e. the molecule that binds to the repressor) for the trp operon is tryptophan, and the signal molecule for the lac operon is allolactose.
- The signal molecule (i.e. the molecule that binds to the repressor) for the trp operon is tryptophan, and the signal molecule for the lac operon is lactose.
- The inducible operon is turned on by the presence of substrate (allolactose), and the repressible operon is turned off by the presence of the end product (tryptophan)
- V, VI, VII, VIII
- I, IV, VI, VII
- I, III, IV, VI
- II, III, IV, VI
- II, III, V, VIII
b.
What are the main ways that a bacterium can gain new DNA?
- Conjugation in which a plasmid is exchanged between bacteria through a pilus
- Transformation, in which a plasmid is exchanged between bacteria through a pilus
- Transformation, during which DNA is assimilated from the surrounding environment by a bacterium/cell
- Transduction, during which DNA is assimilated from the surrounding environment by a bacterium/cell
- Transduction, in which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus
- Conjugation, in which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus
- II, V, VI
- I, III, V
b.