What muscles if any have the ability to regenerate?
Smooth muscle
Know the different muscle types, and know what most skeletal muscles contain of these types.
Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue. Most contain smooth muscle tissue
Know what myoglobin is
Myoglobin is an iron and oxygen-binding protein found in the muscle tissue
Know the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
The major role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum is to regulate intracellular levels of Ca2+
What is the latent period? Which step is this in the process?
Ca+2 is being released from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Slack is being removed from elastic components. 1st step
What is the contraction period? Which step is this in the process?
Lasts 10-100 msec. Filaments slide past each other. 2nd step
What is the relaxation period? Which step is this in the process?
lasts 10-100 msec. Active transport of Ca+2 into SR. 3rd step
What is the refractory period? Which step is this in the process?
Muscle can not respond and has lost its excitability. 5 msec for skeletal and 300 msec for cardiac muscle. 4th step
Know the parts of a muscle twitch.
The latent, contraction, relaxation, and refractory periods
What is an isotonic contraction?
Two parts: concentric and eccentric contractions. This is moving a load
What is an isometric contraction?
A fixed position- no movement occurs
What is the function of creatine phosphate in the muscle cell.
Creatine phosphate transfers a high-energy phosphate to ADP
Know all of the steps of a muscle contraction.
ATP hydrolysis, attachment of myosin to actin to form crossbridges, power stroke, and detachment of myosin from actin.
What is endomysium?
A component of connective tissue that separates individual muscle cells
What is perimysium?
A component of connective tissue that surrounds bundles (fascicles) of 10-100 muscle cells
What is epimysium?
A component of connective tissue that surrounds the whole muscle
What is a fascicle?
A component of connective tissue that is a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium
What is rigor mortis and how does it occur.
This occurs 3-4 hours after death and lasts about 24 hours. Occurs because Ca+2 ions leak out of sarcoplasmic reticulum and allow myosin heads to bind to actin. They bind to actin until enzymes digest the decomposing cells
What is the functional unit of a skeletal muscle cell.
The functional unit is the sarcomere
What is produced during anaerobic respiration.
ATP
Know the characteristics of smooth muscle.
It is attached to hair follicles in skin, in walls of hollow organs, nonstriated in appearance, and involuntary.
What are the properties of muscles.
Excitability, conductivity, contractility, extensibility, elasticity
What is muscle tone.
Involuntary contraction of a small number of motor units (alternately active and inactive in a constantly shifting pattern)
How is acetylcholine (ACh) broken down in the synaptic cleft.
Acetylcholinesterase
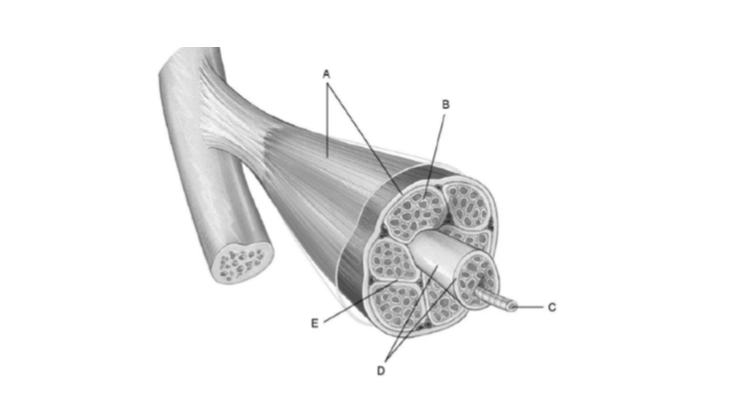
Identify these parts:
A is epimysium
B is endomysium
C is a muscle fiber/cell
D is a fascicle
E is perimysium
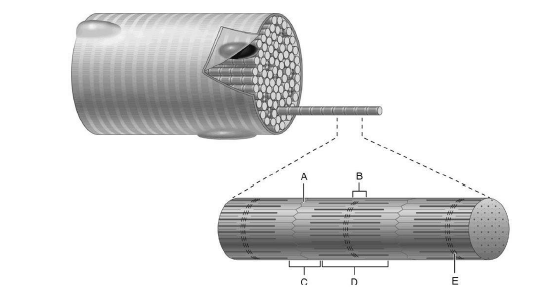
Identify the bands and structures in the picture:
A is the Z band
B is the H zone
C is the I band
D is the A band
E is the M line
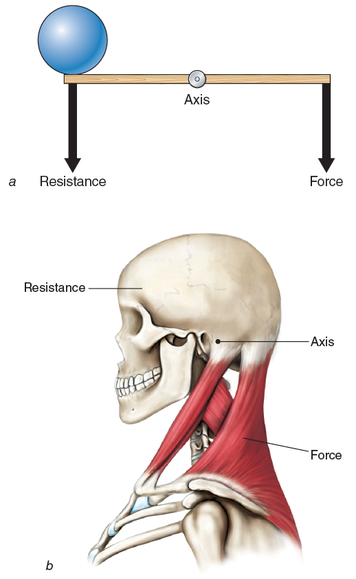
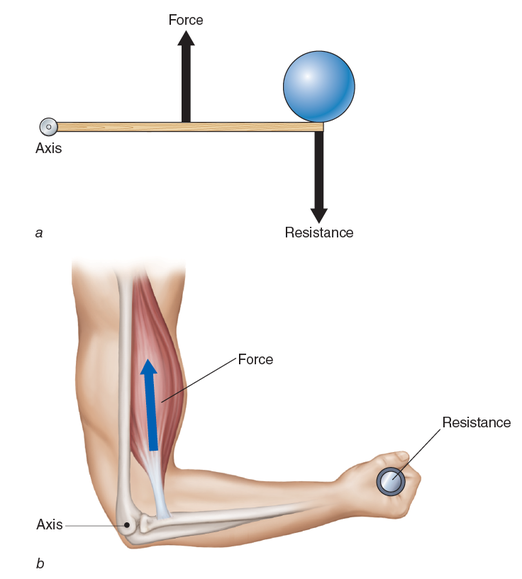
Know the different types of levers. Know the examples of each lever.
First class, second class, and third class levers.
What is a first class lever and an example of it
This has the axis(fulcrum) located between the weight(resistance) and the force. An example of this is pliers or scissors. Where this may be is the joint between the head and the first vertebra. The weight (resistance) is the head, the axis is the joint, and the force can come from any posterior muscles that attach to the skull
What is a second class lever and an example of it
This has the weight (resistance) located between the axis (fulcrum) and the force. An example of this is a wheelbarrow. Where this may be is in the lower leg when someone stands on their toes. The axis is formed by the metatarsophalangeal joints, the resistance is the weight of the body, and the force is applied to the heel by the calf muscles through the achilles tendon
What is a third class lever and an example of it
This is the most common in the body. In this, the force is applied between the resistance (weight) and the axis (fulcrum). An example is someone picking up a shovel or lifting weights. Where this is popular is in the elbow. The elbow joint is the axis (fulcrum), the resistance (weight) is the forearm, wrist, and hand, and the force is the bicep muscle when elbow is flexed.
Know the difference between a synergist, and antagonist, a fixator and an agonist (prime mover)
A synergist aids the action of agonists either by assisting with the movemnt or by reducing unnecessary movement
An antagonist opposes or reverses a movement
A fixator is a specialized synergist and it immobilizes the origin of a prime mover so all tension is at the insersion
Agonists (prime movers) are responsible for producing a particular movement
Know what the term biceps, triceps, or quadriceps that forms part of a muscle's name, what does it tell you about the muscle.
The bicep has two heads, the tricep has three heads, and the quadriceps have four heads
Be able to draw and identify the various types of levers. Make sure you know the placement of the fulcrum, the load and the effort. FIRST CLASS
Be able to draw and identify the various types of levers. Make sure you know the placement of the fulcrum, the load and the effort. SECOND CLASS

Be able to draw and identify the various types of levers. Make sure you know the placement of the fulcrum, the load and the effort. THIRD CLASS
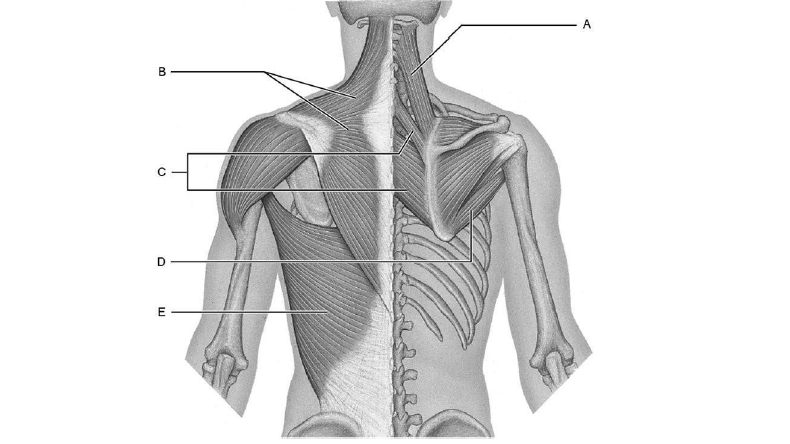
Identify the muscles
A is the levator scapulae
B is the trapezius
C is the teres major and minor
D is the infraspinatus
E is the latissimus dorsi
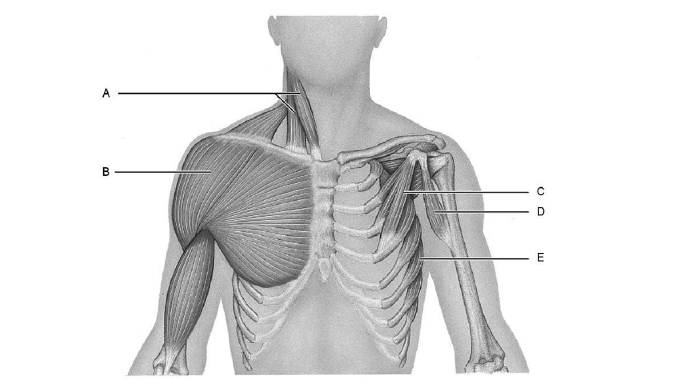
Identify the muscles
A is the sternocleidomastoid
B is the deltoid
C is the pectoral minor
D is the coracobrachialis
E is the external intercostal
Know what type of muscle assists an agonist by causing a like movement or by stabilizing a joint over which an agonist acts.
A synergist
Name the muscles of the hamstrings.
Semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris.
What is flexion? Know general location on body
This is a movement that decreases the angle between two body parts.
What is abduction? Know general location on body
This is a movement away from the midline – just as abducting someone is to take them away. For example, abduction of the shoulder raises the arms out to the sides of the body.
What is adduction? Know general location on body
This is a movement towards the mid line. Adduction of the hip squeezes the legs together.
What is extension? Know general location on body
This is a a movement that increases the angle between two body parts.
How are muscles classified?
Voluntary or involuntary. Slow twitch or fast twitch
Know what muscles make up the abdomen in order.
The rectus abdominus, the external obliques, internal obliques, and the transversus abdominus
Name the chewing muscles
The masseter, pterygoids, and the temporalis
Know what makes up the quadriceps
The rectus femorus, the vastus lateralis, the vastus medialis, and the vastus intermedius