) Charles and Francis Darwin concluded from their experiments on
phototropism by grass
seedlings that the part of the seedling
that detects the direction of light is the
A) tip of the
coleoptile.
B) part of the coleoptile that bends during the
response.
C) base of the coleoptile.
D) cotyledon.
E)
phytochrome in the leaves.
A
Plants growing in a partially dark environment will grow toward light
in a response called
phototropism. Choose the incorrect statement
regarding phototropism.
A) It is caused by a chemical
signal.
B) One chemical involved is auxin.
C) Auxin causes a
growth increase on one side of the stem.
D) Auxin causes a
decrease in growth on the side of the stem exposed to light.
E)
Removing the apical meristem prevents phototropism.
D
Which of these conclusions is supported by the research of both Went
and Charles and
Francis Darwin on shoot responses to
light?
A) When shoots are exposed to light, a chemical substance
migrates toward the light.
B) Agar contains a chemical substance
that mimics a plant hormone.
C) A chemical substance involved in
shoot bending is produced in shoot tips.
D) Once shoot tips have
been cut, normal growth cannot be induced.
E) Light stimulates
the synthesis of a plant hormone that responds to light.
C
We know from the experiments of the past that plants bend toward
light because
A) they need sunlight energy for
photosynthesis.
B) the sun stimulates stem growth.
C) cell
expansion is greater on the dark side of the stem.
D) auxin is
inactive on the dark side of the stem.
E) phytochrome stimulates
florigen production.
C
Which of the following is not presently considered a major mechanism
whereby hormones
control plant development?
A) affecting
cell respiration via regulation of the citric acid cycle
B)
affecting cell division via the cell cycle
C) affecting cell
elongation through acid growth
D) affecting cell differentiation
through altered gene activity
E) mediating short-term
physiological responses to environmental stimuli
A
Evidence for phototropism due to the asymmetric distribution of auxin
moving down the
stem
A) has not been found in eudicots such
as sunflower and radish.
B) has been found in all monocots and
most eudicots.
C) has been shown to involve only IAA stimulation
of cell elongation on the dark side of
the stem.
D) can be
demonstrated with unilateral red light, but not blue light.
E) is
now thought by most plant scientists not to involve the shoot tip
A
According to modern ideas about phototropism in plants,
A) light
causes auxin to accumulate on the shaded side of a plant stem.
B)
auxin stimulates elongation of plant stem cells.
C) auxin is
produced by the tip of the coleoptile and moves downward.
D) A
and B only
E) A, B and C
E
A plant seedling bends toward sunlight because
A) auxin migrates
to the lower part of the stem due to gravity.
B) there is more
auxin on the light side of the stem.
C) auxin is destroyed more
quickly on the dark side of the stem.
D) auxin is found in
greatest abundance on the dark side of the stem.
E) gibberellins
produced at the stem tip cause phototropism.
D
The apical bud of a pine tree inhibits the growth of lateral buds
through the production of
A) abscisic acid.
B)
ethylene.
C) cytokinin.
D) gibberellin.
E) auxin
E
After some time, the tip of a plant that has been forced into a
horizontal position grows
upward. This phenomenon is related
to
A) light.
B) whether the plant is in the northern or
southern hemisphere.
C) gibberellin production by stems.
D)
auxin production in roots.
E) auxin movement toward the lower
side of the stem.
E
) Negative gravitropism of plant shoots
A) depends upon auxin
distribution.
B) depends upon the aggregation of
statoliths.
C) results from relatively rapid elongation of some
stem cells.
D) A and B only
E) A, B and C
E
The ripening of fruit and the dropping of leaves and fruit are
principally controlled by
A) auxins
B) cytokinins
C)
indole acetic acid
D) ethylene
E) carbon dioxide
concentration (in air)
D
) Which one of the following is not a direct function of either auxin
or gibberellin?
A) inducing semescence and ripening
B)
producing apical dominance
C) producing positive geotropism of
shoots
D) stimulating cell elongation
E) breaking dormancy
in seeds
A
Which of the following statements about plant hormones is
false?
A) The growth of plants in nature is probably regulated by
a combination of
growth-stimulating and growth-inhibiting
hormones.
B) Abscisic acid generally promotes growth.
C)
Gibberellins stimulate cell enlargement.
D) Cytokinins promote
cell division.
E) Ethylene contributes to the aging of plants.
B
The plant hormone involved in aging and ripening of fruit is
A)
auxin.
B) ethylene.
C) florigen.
D) abscisic
acid.
E) gibberellin.
B
When growing plants in culture, IAA is used to stimulate cell
enlargement. Which plant
growth regulator has to now be added to
stimulate cell division?
A) ethylene
B) indoleacetic
acid
C) gibberellin
D) cytokinin
E) abscisic acid
D
Why do coleoptiles grow toward light?
A) Auxin is destroyed by
light.
B) Gibberellins are destroyed by light.
C) Auxin
synthesis is stimulated in the dark.
D) Auxin moves away from the
light to the shady side.
E) Gibberellins move away from the light
to the shady side.
D
Plant growth regulators can be characterized by all of the following
except that they
A) may act by altering gene expression.
B)
have a multiplicity of effects.
C) function independently of
other hormones.
D) control plant growth and development.
E)
affect division, elongation, and differentiation of cells.
C
) Plant hormones produce their effects by
A) altering the
expression of genes.
B) modifying the permeability of the plasma
membrane.
C) modifying the structure of the nuclear envelope
membrane.
D) both A and B
E) B and C only
D
Why might animal hormones function differently from plant
hormones?
A) Animals move rapidly away from negative stimuli, and
most plants donʹt.
B) Plant cells have a cell wall that blocks
passage of many hormones.
C) Plants must have more precise timing
of their reproductive activities.
D) Plants are much more
variable in their morphology and development than animals.
E)
Both A and D are correct.
E
Buds and sprouts often form on tree stumps. Which of the following
hormones would you
expect to stimulate their formation?
A)
auxin
B) cytokinins
C) abscisic acid
D)
ethylene
E) gibberellins
B
Plant hormones can have different effects at different
concentrations. This explains how
A) some plants are long-day
plants and others are short-day plants.
B) signal transduction
pathways in plants are different from those in animals.
C) plant
genes recognize pathogen genes.
D) auxin can stimulate cell
elongation in apical meristems, yet will inhibit the growth
of
axillary buds.
E) they really donʹt fit the definition of ʺhormone.ʺ
D
Auxins (IAA) in plants are known to affect all of the following
phenomena except
A) geotropism of shoots.
B) maintenance of
dormancy.
C) phototropism of shoots.
D) inhibition of
lateral buds.
E) fruit development.
B
How does indoleacetic acid affect fruit development?
A)
preventing pollination
B) inhibiting formation of the
ovule
C) promoting gene expression in cambial tissue
D)
promoting rapid growth of the ovary
E) inducing the formation of brassinosteroids
D
) Oat seedlings are sometimes used to study auxins because
A)
they are a readily accessible monocot, and auxins affect only
monocots.
B) they have a stiff coleoptile.
C) they green
rapidly in the light.
D) their coleoptile exhibits a strong
positive phototropism.
E) monocots inactivate synthetic auxins.
D
Auxin triggers the acidification of cell walls that results in rapid
growth, but also stimulates
sustained, long-term cell elongation.
What best explains how auxin brings about this dual
growth
response?
A) Auxin binds to different receptors in different
cells.
B) Different concentrations of auxin have different
effects.
C) Auxin causes second messengers to activate both
proton pumps and certain genes.
D) The dual effects are due to
two different auxins.
E) Other antagonistic hormones modify
auxinʹs effectS
C
Which plant hormones might be used to enhance stem elongation and
fruit growth?
A) brassinosteroids and oligosaccharides
B)
auxins and gibberellins
C) abscisic acid and phytochrome
D)
ethylene and cytokinins
E) phytochrome and flowering hormone
B
Which of the following has not been established as an aspect of
auxinʹs role in cell
elongation?
A) Auxin instigates a
loosening of cell wall fibers.
B) Auxin increases the quantity of
cytoplasm in the cell.
C) Through auxin activity, vacuoles
increase in size.
D) Auxin activity permits an increase in turgor
pressure.
E) Auxin stimulates proton pumps.
B
Cells elongate in response to auxin. All of the following are part of
the acid growth
hypothesis except
A) Auxin stimulates proton
pumps in cell membranes.
B) Lowered pH results in the breakage of
cross-links between cellulose microfibrils.
C) The wall fabric
becomes looser (more plastic).
D) Auxin-activated proton pumps
stimulate cell division in meristems.
E) The turgor pressure of
the cell exceeds the restraining pressure of the loosened
cell
wall, and the cell takes up water and elongates.
D
According to the acid growth hypothesis, auxin works by
A)
dissolving sieve plates, permitting more rapid transport of
nutrients.
B) dissolving the cell membranes temporarily,
permitting cells that were on the verge of
dividing to divide
more rapidly.
C) changing the pH within the cell, which would
permit the electron transport chain to
operate more
efficiently.
D) increasing wall plasticity and allowing the
affected cell walls to elongate.
E) greatly increasing the rate
of deposition of cell wall material.
D
Which of the following hormones would be most useful in promoting the
rooting of plant
cuttings?
A) oligosaccharins
B)
abscisic acid
C) cytokinins
D) gibberellins
E) auxins
E
Which plant hormone(s) is (are) most closely associated with cell
division?
A) ethylene
B) cytokinin
C) abscisic
acid
D) phytochrome
E) brassinosteroids
B
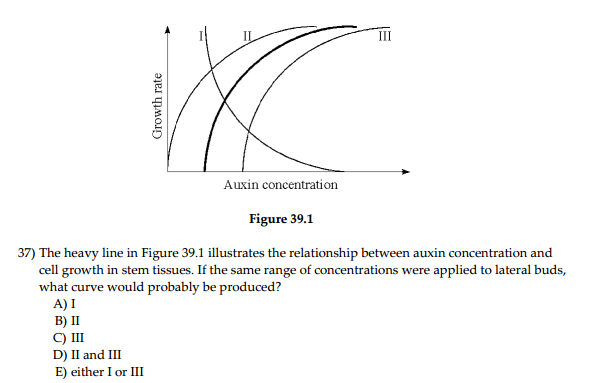
A
The synthesis of which of the following hormones would be a logical
first choice in an
attempt to produce normal growth in mutant
dwarf plants?
A) indoleacetic acid
B) cytokinin
C)
gibberellin
D) abscisic acid
E) ethylene
C
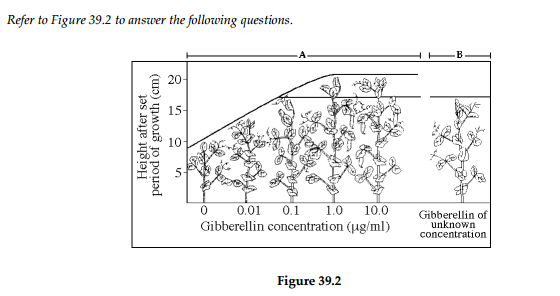
The results of this experiment, shown on the left of the graph (area
A), may be used to
A) show that these plants can live without
gibberellin.
B) show that gibberellin is necessary in positive
gravitropism.
C) show that taller plants with more gibberellin
produce fruit (pods).
D) show a correlation between plant height
and gibberellin concentration.
E) study phytoalexins in plants.
D

This experiment suggests that the unknown amount of gibberellin in
the experimental plant
(B) is approximately
A) zero.
B)
0.01 μg/mL.
C) 0.1 μg/mL.
D) 1.0 μg/mL.
E) equal to the
amount of gibberellin in the shortest plant.
C
One effect of gibberellins is to stimulate cereal seeds to
produce
A) RuBP carboxylase.
B) lipids.
C) abscisic
acid.
D) starch.
E) amylase
E
In attempting to make a seed break dormancy, one logically could
treat it with
A) IAA.
B) 2, 4-D.
C) CO2.
D)
gibberellins.
E) abscisic acid.
D
Ethylene, as an example of a plant hormone, may have multiple effects
on a plant,
depending on all of the following except the
A)
site of action within the plant.
B) developmental stage of the
plant.
C) concentration of ethylene.
D) altered chemical
structure of ethylene from a gas to a liquid.
E) readiness of
cell membrane receptors for the ethylene.
D
If you were shipping green bananas to a supermarket thousands of
miles away, which of
the following chemicals would you want to
eliminate from the plantsʹ environment?
A) CO2
B)
cytokinins
C) ethylene
D) auxin
E) gibberellic acids
C
Which of the following is currently the most powerful method of
research on plant
hormones?
A) comparing of photoperiodic
responses
B) comparing tropisms with turgor movements
C)
subjecting plants to unusual stresses
D) studying
phytochromes
E) analyzing mutant plants
E
We tend to think of plants as immobile when, in fact, they can move
in many ways. All of
the following are movements plants can
accomplish except
A) growth movements up or down in response to
gravity.
B) folding and unfolding of leaves using muscle-like
tissues.
C) growth movements toward or away from light.
D)
changes in plant growth form in response to wind or touch.
E)
rapid responses using action potentials similar to those found in the
nervous tissue of
animals.
B
Auxin is responsible for all of the following plant growth responses
except
A) phototropism.
B) formation of adventitious
roots.
C) apical dominance.
D) the detection of
photoperiod.
E) cell elongation
D
Incandescent light bulbs, which have high output of red light, are
least effective in
promoting
A) photosynthesis.
B) seed
germination.
C) phototropism.
D) flowering.
E)
entrainment of circadian rhythms.
C
) Both red and blue light are involved in
A) stem
elongation.
B) photoperiodism.
C) positive
phototropism.
D) tracking seasons.
E) all of the above
A
) Seed packets give a recommended planting depth for the enclosed
seeds. The most likely
reason some seeds are to be covered with
only 1/4 inch of soil is that the
A) seedlings do not produce a
hypocotyl.
B) seedlings do not have an etiolation
response.
C) seeds require light to germinate.
D) seeds
require a higher temperature to germinate.
E) seeds are very
sensitive to waterlogging
C
A short-day plant will flower only when
A) days are shorter than
nights.
B) days are shorter than a certain critical
value.
C) nights are shorter than a certain critical
value.
D) nights are longer than a certain critical
value.
E) days and nights are of equal length.
D
A flash of red light followed by a flash of far-red light given
during the middle of the night
to a short-day plant will
likely
A) cause increased flower production.
B) have no
effect upon flowering.
C) inhibit flowering.
D) stimulate
flowering.
E) convert florigen to the active form
B
Many plants flower in response to day-length cues. Which statement
concerning flowering
is false?
A) As a rule, short-day
plants flower in the spring or fall.
B) As a rule, long-day
plants flower in the summer.
C) Long-day plants flower in
response to long days, not short nights.
D) Flowering in
day-neutral plants is not influenced by day length.
E) Flowering
in short-day plants is controlled by photochrome.
C
Which of the following does not reduce the level of the Pfr form of
phytochrome?
A) exposure to far-red light
B) exposure to red
light
C) long dark period
D) destruction of
phytochrome
E) synthesis of phosphorylating enzymes
B
) Most plants close their stomata at night. What color of light would
be most effective in
promoting stomatal opening in the middle of
the night?
A) red
B) far-red
C) blue
D) red
followed by far-red
E) far-red followed by blue
C
The houseplants in a windowless room with only fluorescent lights
begin to grow tall and
leggy. Which of the following treatments
would promote more normal growth?
A) Leave the lights on at night
as well as during the day.
B) Add additional fluorescent tubes to
increase the light output.
C) Add some incandescent bulbs to
increase the amount of red light.
D) Set a timer to turn on the
lights for 5 minutes during the night.
E) Turn off the lights for
5 minutes during the day.
C
) In legumes, it has been shown that ʺsleepʺ movements are correlated
with
A) positive thigmotropisms.
B) rhythmic opening and
closing of K+ channels in motor cell membranes.
C) senescence
(the aging process in plants).
D) flowering and fruit
development.
E) ABA-stimulated closing of guard cells caused by
loss of K+.
B
Biological clocks cause organisms to perform daily activities on a
regular basis. Which of
the following is a false statement about
this kind of ʺcircadian rhythmʺ?
A) It may have the same signal
transduction pathway in all organisms.
B) It must be reset on a
daily basis.
C) It may help to cause photoperiodic
responses.
D) Once set, it is independent of external
signals.
E) The exact mechanism of biological clocks remains unknown
D
The biological clock controlling circadian rhythms must
ultimately
A) depend on environmental cues.
B) affect gene
transcription.
C) stabilize on a 24-hour cycle.
D) speed up
or slow down with increasing or decreasing temperature.
E) do all
of the above.
B
Plants often use changes in day length (photoperiod) to trigger
events such as dormancy
and flowering. It is logical that plants
have evolved this mechanism because photoperiod
changes
A)
are more predictable than air temperature changes.
B) alter the
amount of energy available to the plant.
C) are modified by soil
temperature changes.
D) can reset the biological clock.
E)
are correlated with moisture availability
A
If the range of a species of plants expands to a higher latitude,
which of the following
processes is the most likely to be
modified by natural selection?
A) circadian rhythm
B)
photoperiodic response
C) phototropic response
D) biological
clock
E) thigmomorphogenesis
B
In nature, poinsettias bloom in early March. Research has shown that
the flowering process
is triggered three months before blooming
occurs. In order to make poinsettias bloom in
December, florists
change the length of the light-dark cycle in September. Given
the
information and clues above, which of the following is a
false statement about poinsettias?
A) They are short-day
plants.
B) They require a light period shorter than some set
maximum.
C) They require a longer dark period than is available
in September.
D) The dark period can be interrupted without
affecting flowering.
E) They will flower even if there are brief
periods of dark during the daytime.
D
A botanist exposed two groups of the same plant species to two
photoperiods–one with 14
hours of light and 10 hours of dark and
the other with 10 hours of light and 14 hours of
dark. Under the
first set of conditions, the plants flowered, but they failed to
flower under
the second set of conditions. Which of the following
conclusions would be consistent with
these results?
A) The
critical night length is 14 hours.
B) The plants are short-day
plants.
C) The critical day length is 10 hours.
D) The
plants can convert phytochrome to florigen.
E) The plants flower
in the spring
E
What does a short-day plant need in order to flower?
A) a burst
of red light in the middle of the night
B) a burst of far-red
light in the middle of the night
C) a day that is longer than a
certain length
D) a night that is longer than a certain
length
E) a higher ratio of Pr to Pfr.
D
If a short-day plant has a critical night length of 15 hours, then
which of the following
24-hour cycles will prevent
flowering?
A) 8 hours light/16 hours dark
B) 4 hours
light/20 hours dark
C) 6 hours light/2 hours dark/light flash/16
hours dark
D) 8 hours light/8 hours dark/light flash/8 hours
dark
E) 2 hours light/20 hours dark/2 hours light
D
A long-day plant will flower if
A) the duration of continuous
light exceeds a critical length.
B) the duration of continuous
light is less than a critical length.
C) the duration of
continuous darkness exceeds a critical length.
D) the duration of
continuous darkness is less than a critical length.
E) it is kept
in continuous far-red light.
D
Plants that have their flowering inhibited by being exposed to bright
lights at night are
A) day-neutral plants.
B) short-night
plants.
C) devoid of phytochrome.
D) short-day
plants.
E) long-day plants.
D
) Plants that have their flowering inhibited by being exposed to
bright lights at night are
A) day-neutral plants.
B)
short-night plants.
C) devoid of phytochrome.
D) short-day
plants.
E) long-day plants.
D
Classic experiments suggested that a floral stimulusFlorigencould
move across a graft
from an induced plant to a noninduced plant
and trigger flowering. Recent evidence using
Arabidopsis has
recently shown that florigen is probably
A) a phytochrome
molecule that is activated by red light.
B) a protein that is
synthesized in leaves and travels to the shoot apical meristem
and
initiates flowering.
C) a membrane signal that travels
through the symplast from leaves to buds.
D) a second messenger
that induces Ca++ ions to change membrane potential.
E) a
transcription factor that controls the activation of florigen specific genes.
B
In general, which of the following is not a plant response to
herbivores?
A) domestication, so that humans can protect the
plant
B) attracting predatory animals, such as parasitoid
wasps
C) chemical defenses, such as toxic compounds
D)
physical defenses, such as thorns
E) production of volatile molecules
A
) In order for a plant to initiate chemical responses to
herbivory,
A) the plant must be directly attacked by an
herbivore.
B) volatile ʺsignalʺ compounds must be
perceived.
C) gene-for-gene recognition must occur.
D)
phytoalexins must be released.
E) all of the above must happen.
B
Plants are affected by an array of pathogens. Which of the following
is not a plant defense
against disease?
A) cells near the
point of infection destroying themselves to prevent the spread of
the
infection
B) production of chemicals that kill
pathogens
C) acquiring gene-for-gene recognition that allows
specific proteins to interact so that
the plant can produce
defenses against the pathogen
D) a waxy cuticle that pathogens
have trouble penetrating
E) All of the above are plant defenses
against disease.
E
A pathogenic fungus invades a plant. What does the infected plant
produce in response to
the attack?
A) antisense RNA
B)
phytoalexins
C) phytochrome
D) statoliths
E) thickened
cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall
B
) Which of the following are defenses that some plants use against
herbivory?
A) production of the unusual amino acid
canavanine
B) release of volatile compounds that attract
parasitoid wasps
C) association of plant tissues with
mycorrhizae
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C
D
The transduction pathway that activates systemic acquired resistance
in plants is initially
signaled by
A) antisense RNA.
B)
Pfr phytochrome.
C) salicylic acid.
D) abscisic
acid.
E) red, but not far-red, light.
C
Which of the following are examples or parts of plantsʹ systemic
acquired resistance against
infection?
A)
phytoalexins
B) salicylic acid
C) alarm hormones
D) A
and B only
E) A, B, and C
E
A plant will recognize a pathogenic invader
A) if it has many
specific plant disease resistance (R) genes.
B) when the pathogen
has an R gene complementary to the plantʹs antivirulence
(Avr)
gene.
C) only if the pathogen and the plant have the
same R genes.
D) if it has the specific R gene that corresponds
to the pathogen molecule encoded by an
Avr gene.
E) when the
pathogen secretes Avr protein.
D
What is the probable role of salicylic acid in the defense responses
of plants?
A) destroy pathogens directly
B) activate
systemic acquired resistance of plants
C) close stomata, thus
preventing the entry of pathogens
D) activate heat-shock
proteins
E) sacrifice infected tissues by hydrolyzing cells
B
When an arborist prunes a limb off a valuable tree, he or she usually
paints the cut surface.
The primary purpose of the paint is
to
A) minimize water loss by evaporation from the cut
surface.
B) improve the appearance of the cut surface.
C)
stimulate growth of the cork cambium to ʺhealʺ the wound.
D)
block entry of pathogens through the wound.
E) induce the
production of phytoalexins.
D
Which of the following is not a typical component of a signal
transduction pathway?
A) production of more signal
B)
production of second messengers such as cGMP
C) expression of
specific proteins
D) activation of protein kinases
E)
phosphorylation of transcription factors
A
Auxin enhances cell elongation in all of these ways except
A)
increased uptake of solutes.
B) gene activation.
C)
acidification of the cell wall, causing denaturation of
growth-inhibiting cell wall
proteins.
D) increased activity
of plasma membrane proton pumps.
E) cell wall loosening.
C
Charles and Francis Darwin discovered that
A) auxin is
responsible for phototropic curvature.
B) auxin can pass through
agar.
C) light destroys auxin.
D) light is perceived by the
tips of coleoptiles.
E) red light is most effective in causing
phototropic curvatures.
D
Which hormone is incorrectly paired with its function?
A)
auxinpromotes stem growth through cell elongation
B)
cytokininsinitiate programmed cell death
C)
gibberellinsstimulate seed germination
D) abscisic acidpromotes
seed dormancy
E) ethyleneinhibits cell elongation
B
) The hormone that helps plants respond to drought is
A)
auxin.
B) gibberellin.
C) cytokinin.
D)
ethylene.
E) abscisic acid.
E
) The chemical signal for flowering could be released earlier than
normal in a long-day plant
exposed to flashes of
A) far-red
light during the night.
B) red light during the night.
C)
red light followed by far-red light during the night.
D) far-red
light during the day.
E) red light during the day.
B
If a long-day plant has a critical night length of 9 hours, which
24-hour cycle would
prevent flowering?
A) 16 hours light/8
hours dark
B) 14 hours light/10 hours dark
C) 15.5 hours
light/8.5 hours dark
D) 4 hours light/8 hours dark/4 hours
light/8 hours dark
E) 8 hours light/8 hours dark/light flash/8
hours dark
B
If a scientist discovers an Arabidopsis mutant that does not store
starch in plastids but has
normal gravitropic bending, what
aspect of our understanding would need to be
reevaluated?
A)
the role of auxin in gravitropism
B) the role of calcium in
gravitropism
C) the role of statoliths in gravitropism
D)
the role of light in gravitropism
E) the role of differential
growth in gravitropic bending
C
How may a plant respond to severe heat stress?
A) by orienting
leaves toward the sun, increases evaporative cooling
B) by
producing ethylene, which kills some cortex cells and creates air
tubes for
ventilation
C) by producing salicylic acid, which
initiates a systemic acquired resistance response
D) by
increasing the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes
reducing
their fluidity
E) by producing heat-shock proteins,
which may protect the plantʹs proteins from
denaturing
E
In systemic acquired resistance, salicylic acid probably
A)
destroys pathogens directly.
B) activates defenses throughout the
plant before infection spreads.
C) closes stomata, thus
preventing the entry of pathogens.
D) activates heat-shock
proteins.
E) sacrifices infected tissues by hydrolyzing cells.
B