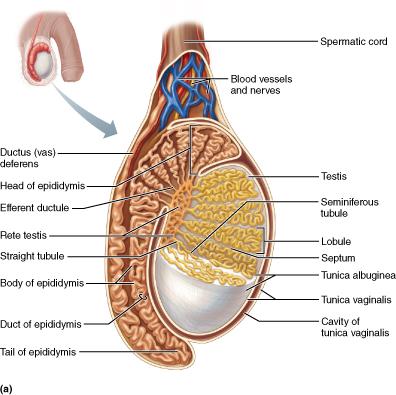
Which of the following is housed within the spermatic cord?
testicular arteries and veins
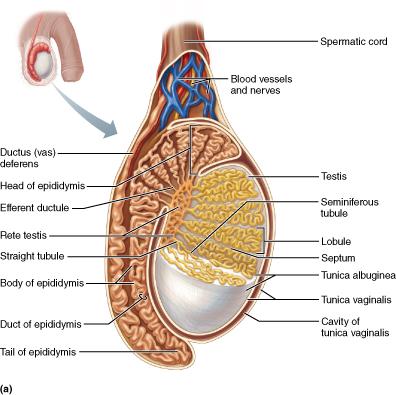
Which of the following is the site where sperm are stored until they are ejaculated?
tail of the epididymis
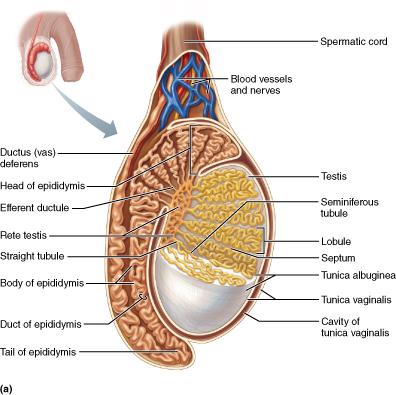
Which cells produce androgens such as testosterone?
interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells
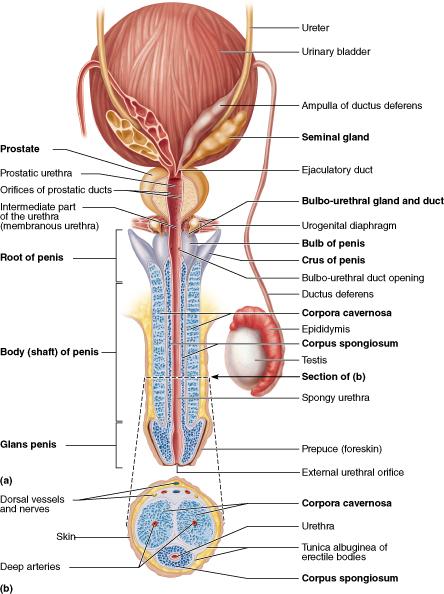
Which of these male accessory ducts transports both sperm and urine?
Urethra
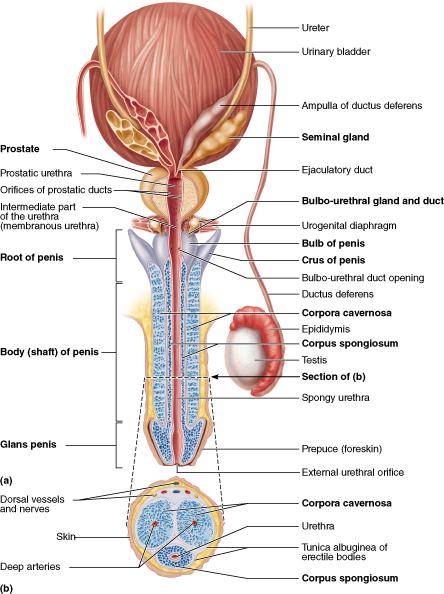
Which portion of the penis is removed through a procedure known as circumcision?
prepuce (foreskin)
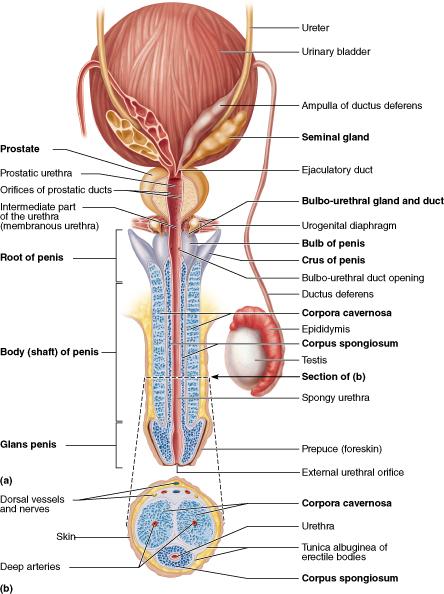
During vasectomy, what accessory duct is cut as a form of birth control?
ductus (vas) deferens
Sperm is produced in the __________ of the testes.
seminiferous tubules
Sperm are stored in the __________.
epididymis
Which of the following does NOT add substances to seminal fluid?
urethra
Viable sperm production is optimal at the body's core temperature.
FALSE
The number of chromosomes in a human gamete is __________; this is referred to as the __________ chromosome number.
23; haploid
Genetic variation of individual chromosomes occurs during __________.
prophase I
Enzymes that allow sperm to penetrate the egg are located in the __________ of the sperm cell.
Acrosome
The release of __________ encourages interstitial endocrine cells to release __________.
luteinizing hormone; testosterone
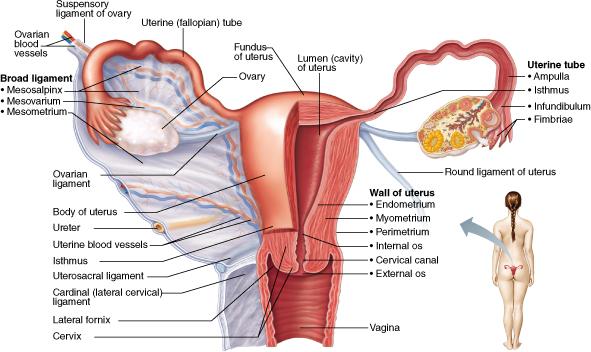
What part of the female duct system is the usual site of fertilization of the ovulated oocyte?
uterine (fallopian) tube (oviduct)
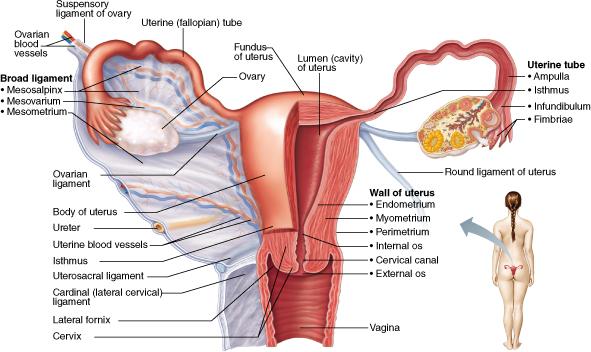
Which layer of the uterine wall is made of smooth muscle?
Myometrium
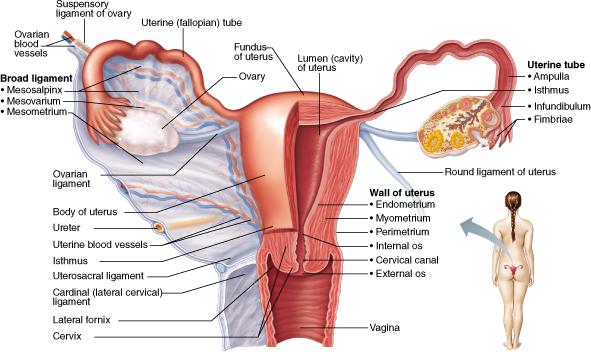
Which specific layer of the uterus is shed during menstruation, approximately every 28 days?
stratum functionalis of the endometrium
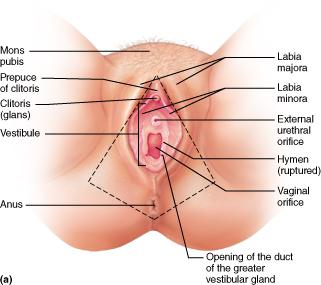
Specifically, what encloses the vestibule which houses the openings of the urethra and vagina?
labia minora
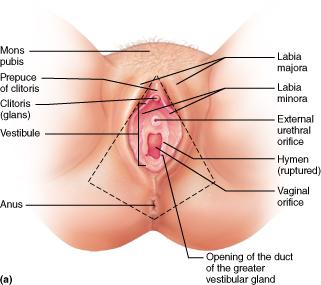
Which structure of the female's external genitalia has erectile tissue like the penis?
Clitoris
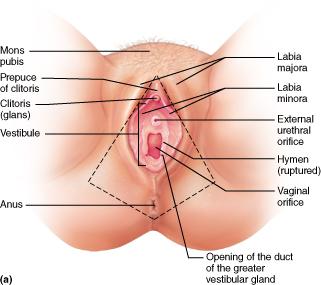
What are the two fatty, hair-covered skin folds that run posteriorly from the mons pubis?
labia majora
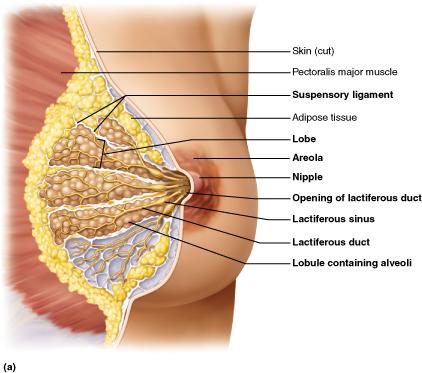
What part of the breast produces milk?
alveoli
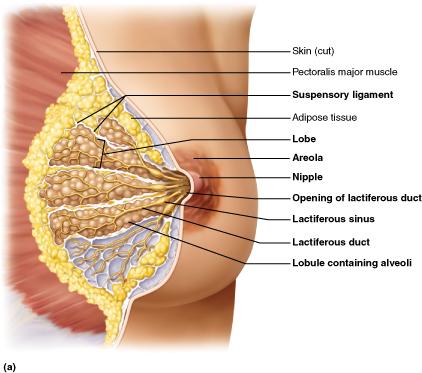
The mammary glands belong to which of the following systems?
integumentary system
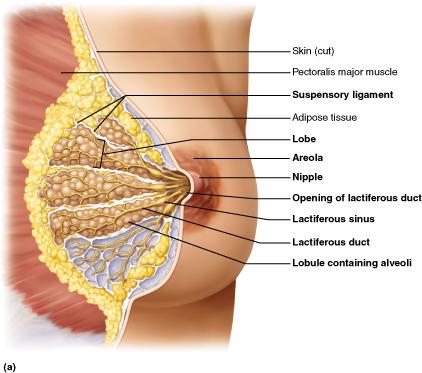
What is the pigmented ring of skin situated slightly below the center of each breast?
Areola
The __________ connects the uterus to the vagina.
Cervix
The __________, a layer of the endometrium, is shed during each menstruation and is then regenerated by the __________.
stratum functionalis; stratum basalis
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the vagina of an adult female?
The pH of the adult vagina is alkaline.
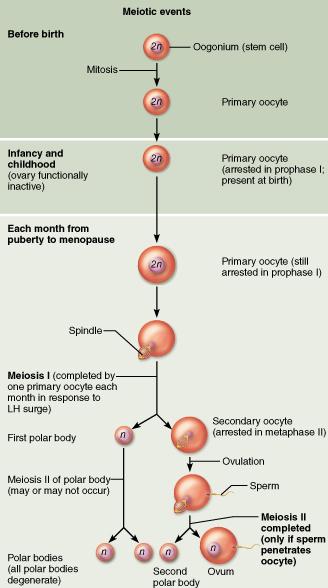
Which of the following cells is released during ovulation?
secondary oocyte
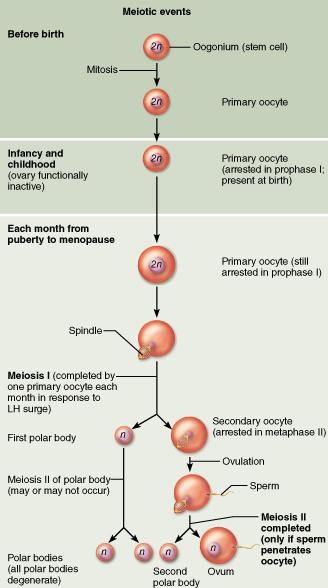
Why CAN'T polar bodies be fertilized?
Polar bodies lack nutrient-containing cytoplasm.
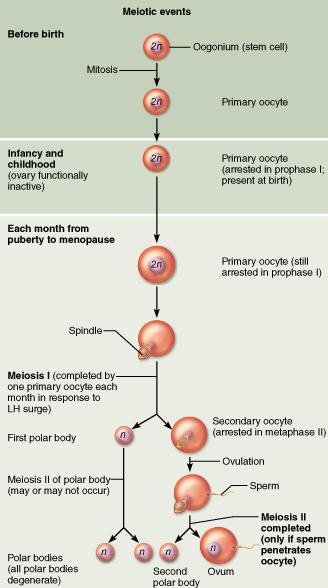
How many functional gametes are produced by oogenesis?
one functional gamete
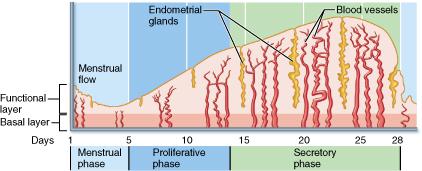
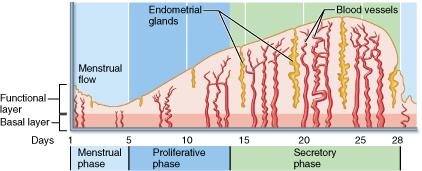
What event occurs during the proliferative phase?
ovulation
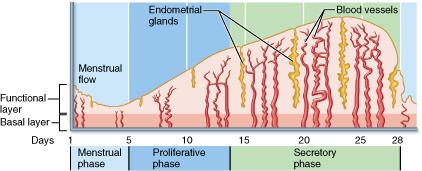
During what phase of the female's uterine (menstrual) cycle is the uterine lining shed?
menstrual phase
What hormone promotes ovulation?
luteinizing hormone (LH)
A surge in __________ directly triggers ovulation.
luteinizing hormone (LH)
During the secretory phase of the uterine cycle __________.
the endometrium prepares for implantation
Which of the following is an effect of estrogen in females?
promotes oogenesis
Which of the following is considered a primary sex organ in females?
Ovary
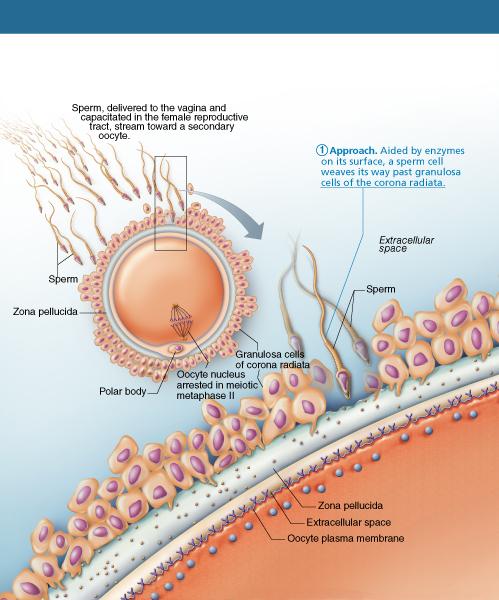
Once sperm are deposited into the vagina, sperm motility must be enhanced and they must be prepared to release hydrolytic enzymes from their acrosomes. What is this process called?
capacitation
What is the event that results when the maternal and paternal chromosomes combine?
fertilization
The fertilized egg is known as the
zygote
Sperm freshly deposited in the female vagina are incapable of fertilizing an egg. What must happen first?
Capacitation
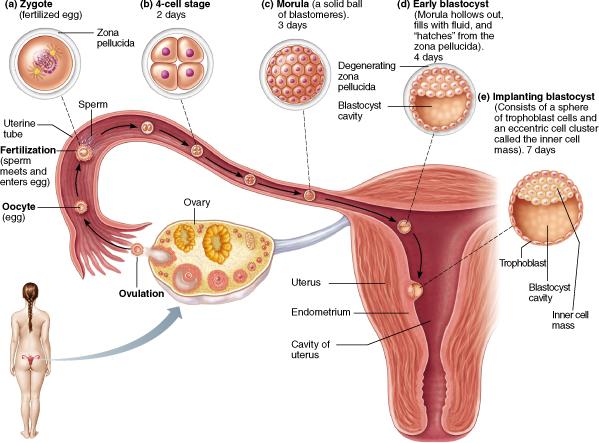
Which of the following implants in the mucosa of the endometrium?
blastocyst
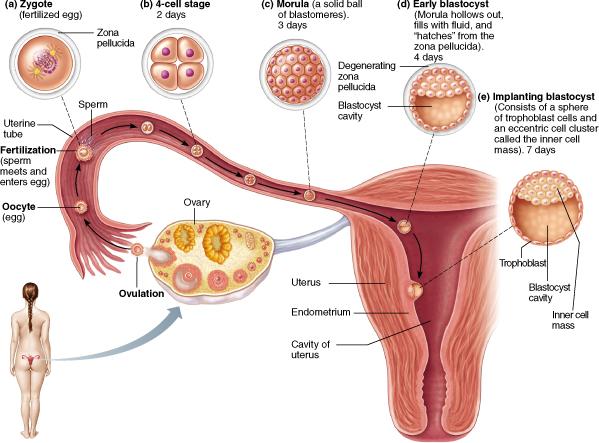
What is the 16-cell stage known as?
Morula
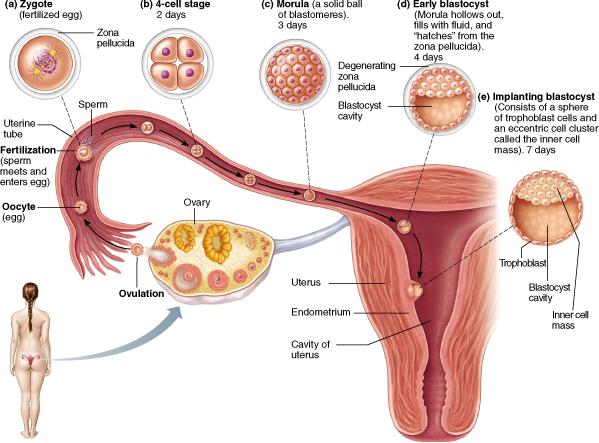
How much time passes after fertilization until implantation occurs?
7 days

What releases human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)?
?
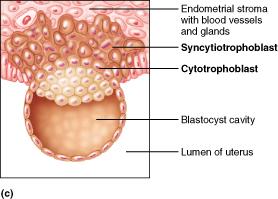
What membrane does the trophoblast form after implantation?
chorion
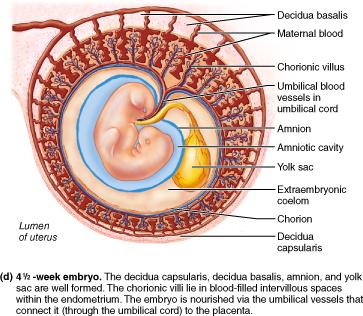
What is the function of the placenta?
The placenta functions as a nutritive, respiratory, excretory, and endocrine organ for the developing embryo.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of development from zygote to embryo?
cleavage, morula, blastocyst, gastrula
What structure(s) ultimately form(s) the placenta?
decidua basalis and chorionic villi
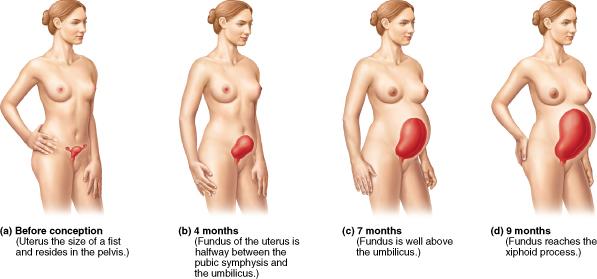
What does the hormone relaxin promote?
Relaxin promotes the relaxation, widening, and increased flexibility of the pelvic ligaments and pubic symphysis.
While human chorionic gonadotropin levels spike and sharply decline to reach a low value by four months, estrogen and progesterone levels steadily increase over the course of the pregnancy.
TRUE
The sole responsibility of the placenta is to supply the fetus with oxygen and nutrients.
FALSE

What role does oxytocin play in promoting labor?
Oxytocin stimulates the uterus to contract.
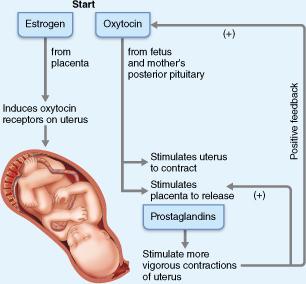
Which of the following serves as the trigger to begin the vigorous, rhythmic contractions of true labor?
prostaglandins
During pregnancy, which hormone is responsible for stimulating maturation of the breast for lactation?
human placental lactogen (hPL)
__________ extends from the last menstrual period until birth, which is approximately 280 days.
A gestation period