the neuron cannot respond to a second stimulus, no matter how strong
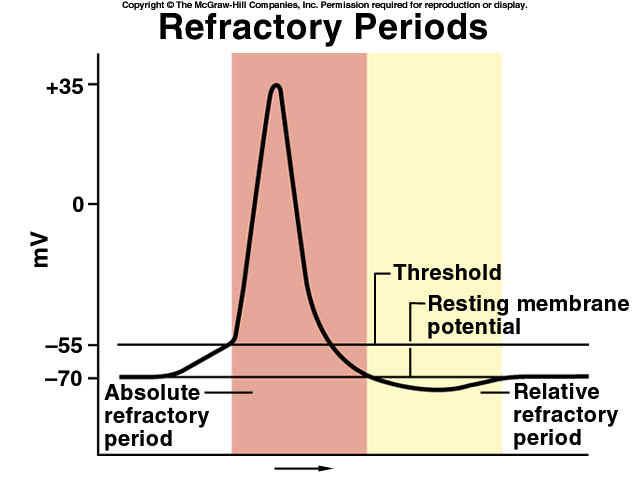
absolute refractory period
the interior of the cell becomes less negative due to an influx of sodium ions
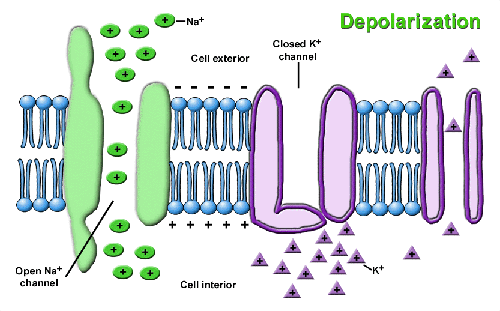
depolarrization
the specific period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron due to a change in membrane permeability
repolarizaztion
also called a nerve impulse transmitted by axons
action potential
an exceptionally strong stimulus can trigger a response
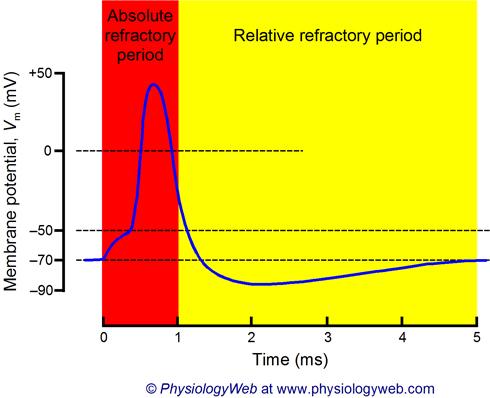
relative refractory period
area where nerve impulse in generated
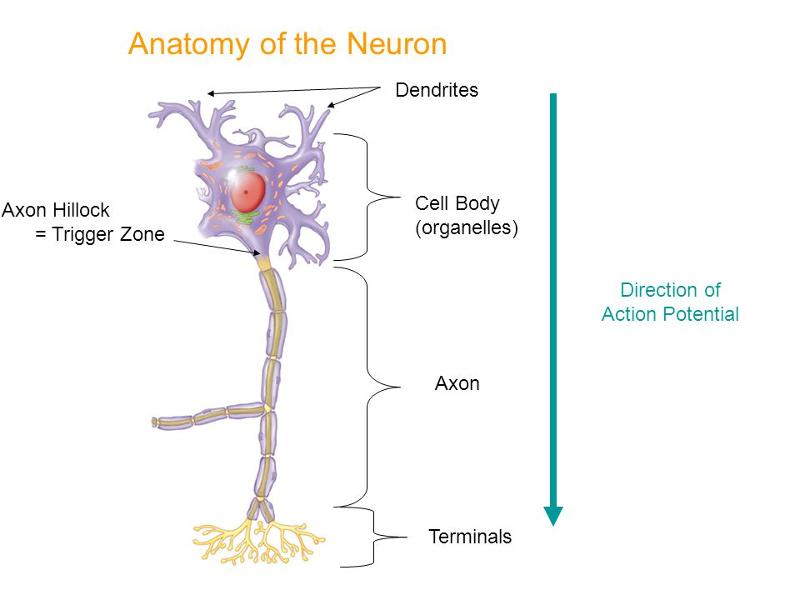
trigger zone
receives stimulus
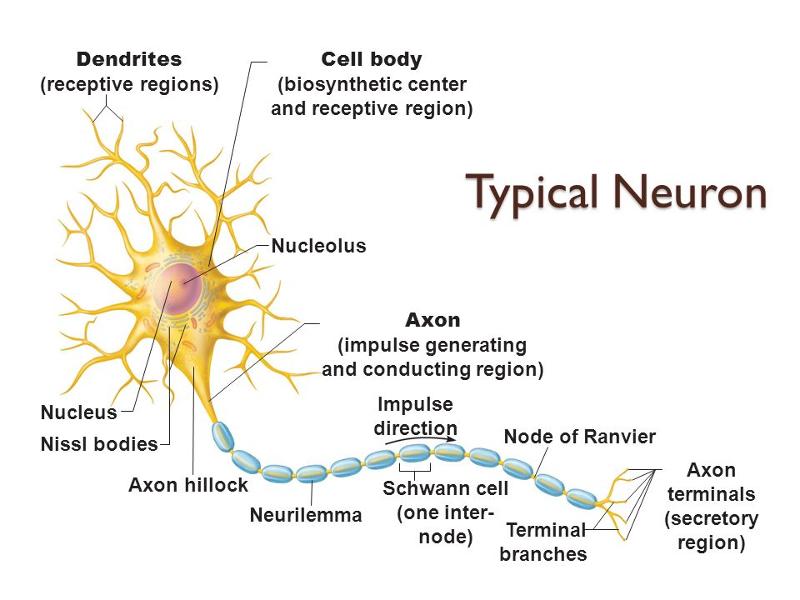
receptive region
plasma membrane exhibits voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels
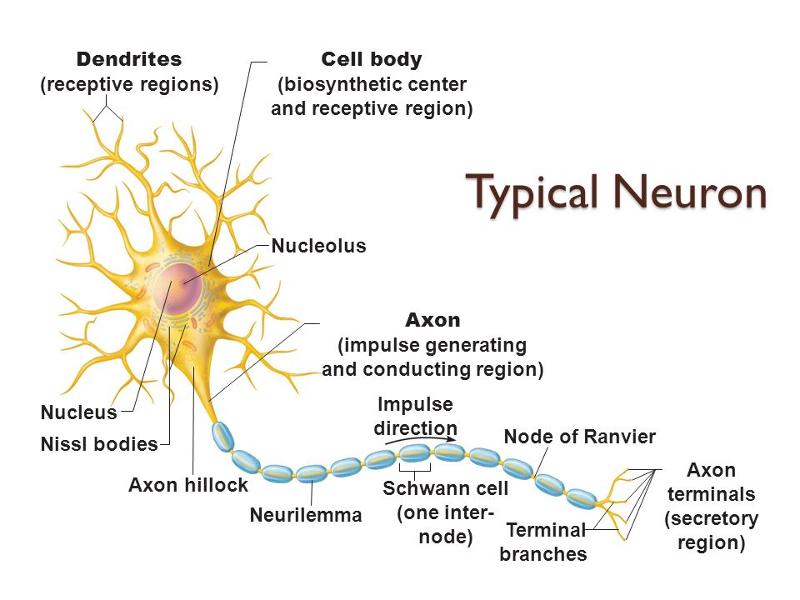
conducting region
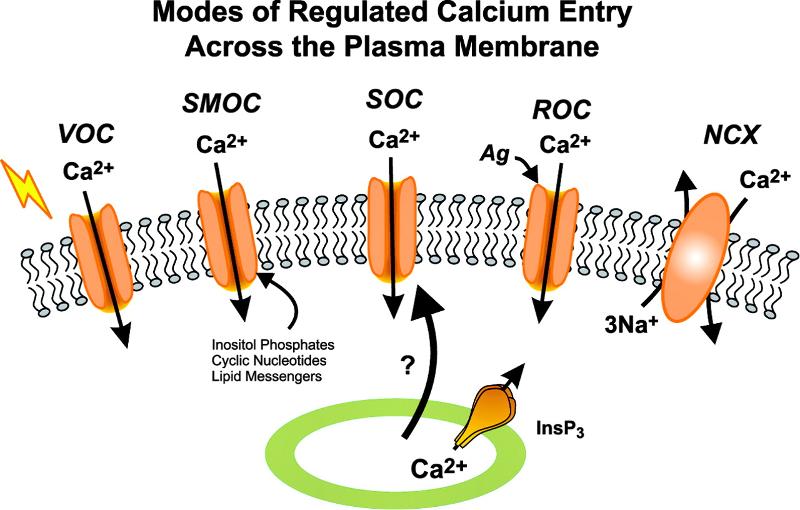
plasma membrane exhibits voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
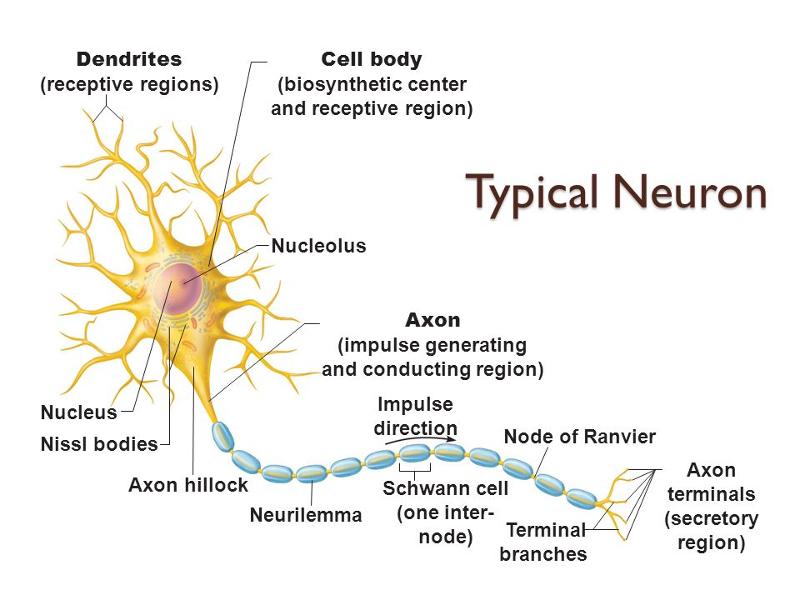
secretory region
axon terminals release neurotransmitters
secretory zone
plasma membrane exhibits chemically gated ion channels
secretory region
the all-or-none phenomenon as applied to nerve conduction states that the whole nerve cell must be stimulated for conduction to take place
false
reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli
true
efferent nerve fibers may be located in ganglia lying outside the central nervous system
true
cell bodies of sensory neurons may be located in ganglia lying outside the central nervous system
true
myelination of the nerve fibers in the central nervous system in the job of the oligodendrocytes
true
strong stimuli cause the amplitude of action potentials generated to increase
false
the oligodendrocytes can myelinate several axons
true
in myelinated axons the voltage-regulated sodium channels are concentrated at the nodes of Ranviver
true
large-diameter nerve fibers conduct impulse much faster than small diameter fibers
true
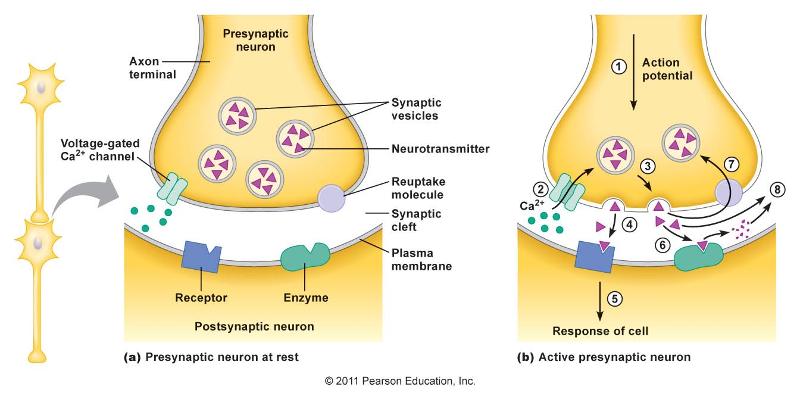
a stimulus traveling toward a synapse appears to open calcium ion channels at the presynaptic end, which in turn promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles to the axonal membrane
true
what are ciliated CNS neuroglia that play an active role in moving the cerebrospinal fluid called?
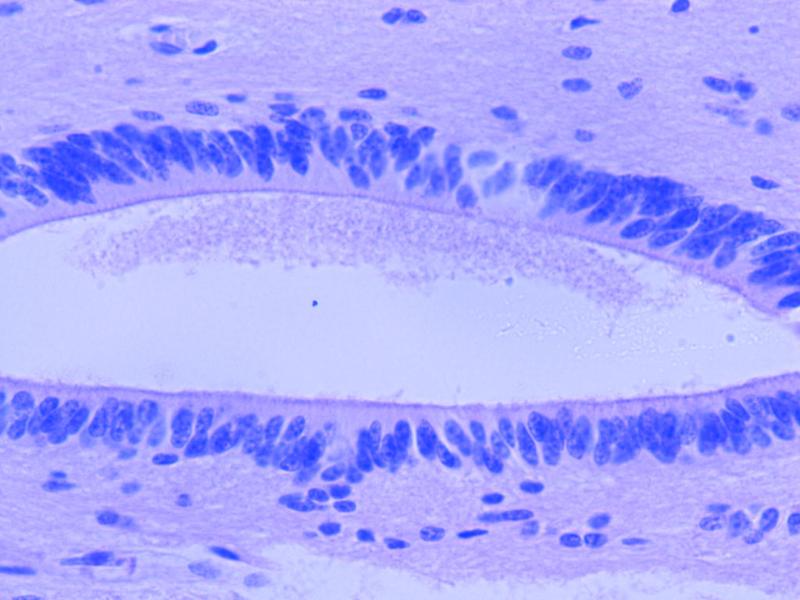
ependymal cells
which is NOT a special characteristic of neurons?
conduct impulse
extreme longevity
mitotic
exceptionally high metabolic rate
mitotic
saltatory conduction is made possible by_____
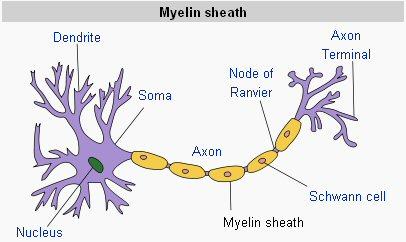
the myosin sheath
an inhibitory postnynaptic potential (IPSP) is associated with _____
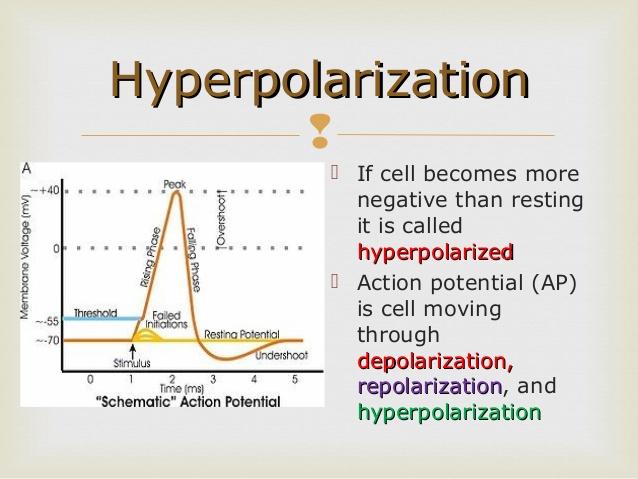
hyperpolarization
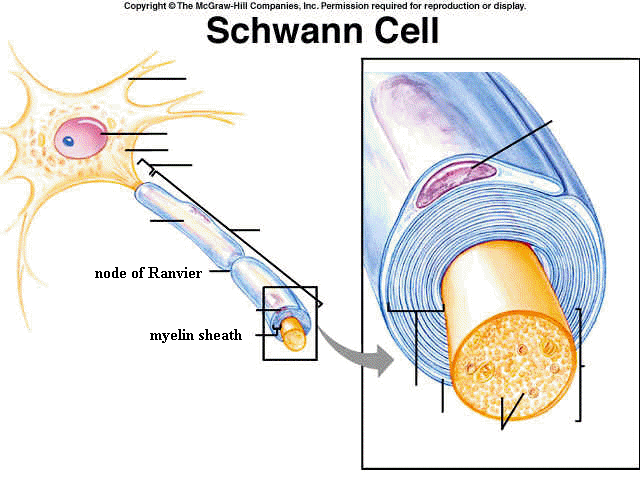
Schwann cells are functionally similar to _____
oligodendrocytes
which is NOT true for graded potentials?
short lived
can form on receptor ending
increase amplitude as move away from stimulus point
increase amplitude as move away from stimulus point
second nerve impulse CANNOT be generated until
membrane potential has been reestablished
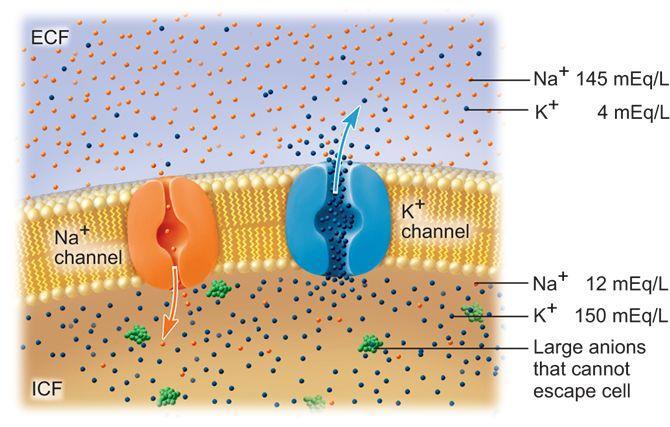
interior surface of a cell membrane of a resting (nonconducting) neuron differ from the external environment? the inferior is ____
negatively charged and contains less sodium
if a motor neuron in the body were stimulated by an electrode placed about midpoint along the length of axon
the impulse would spread bidirectionally
major relay station for sensory information ascending to primary sensory area of the cerebral cortex. contains many nuclei
thalamus
brain area that associates experiences necessary for the production of abstract ideas, and conscience
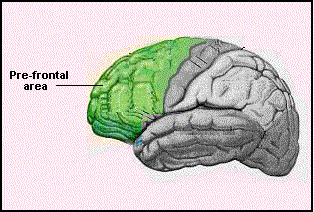
prefrontal area
axon from this area form major pyramidal tract
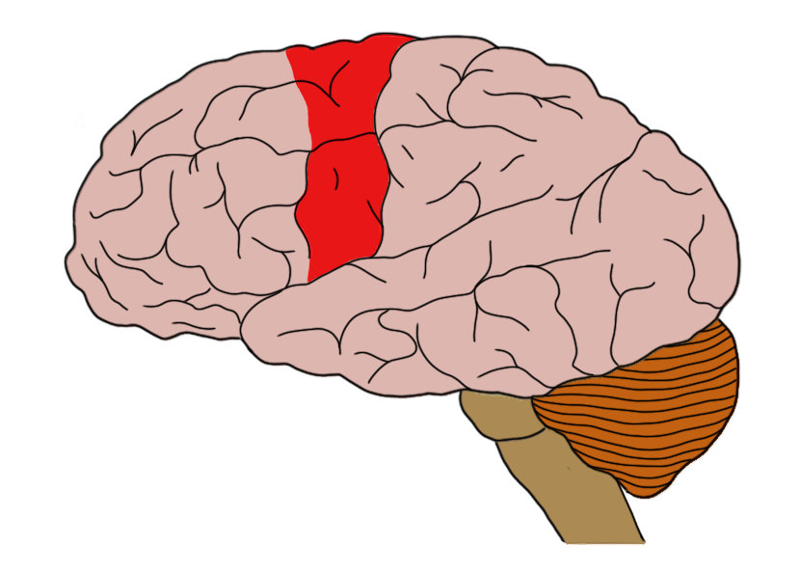
primary motor cortex
this area is maintain the main visceral control of the body
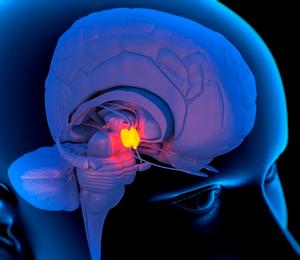
hypothalamus
the stage when vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature) each their lowest normal levels
stage 4
indicated by movement of the eyes under lids, dreaming occurs
REM
theta and beta waved begin to appear
stage 3
easy to awake; EEG
show alpha wages; may even deny asleep
typified by sleep spindle
stage 2
begin bout 90 min after onset of sleep
REM
necessary for emotional health; may contribute neutral "debugging"
REM
gateway to the cerebrum
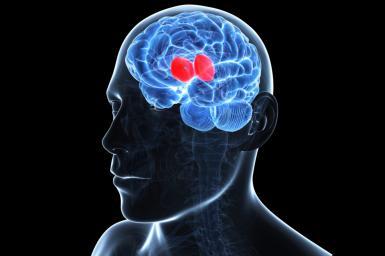
thalamus
motor command center
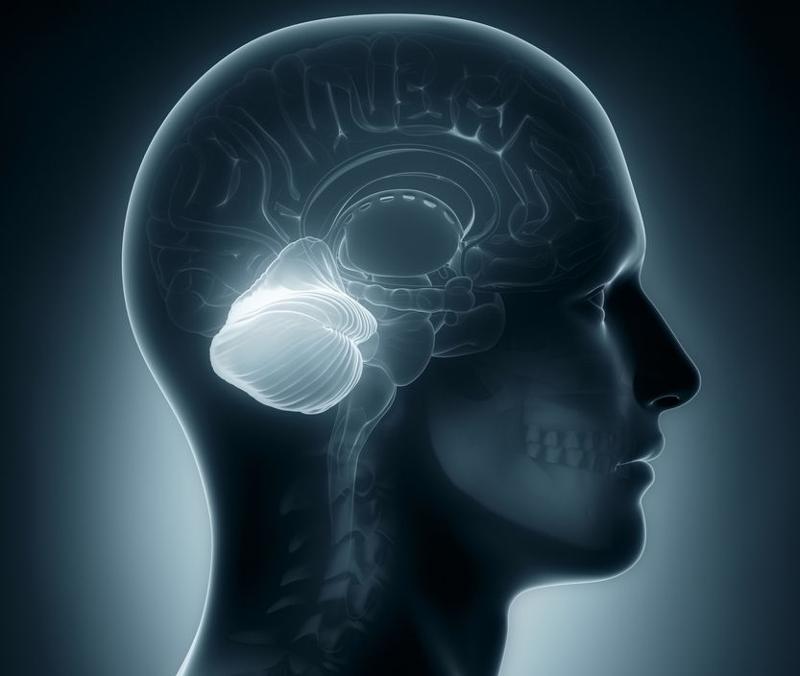
cerebellum
survival center
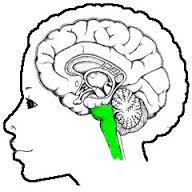
brain stem
executive suite
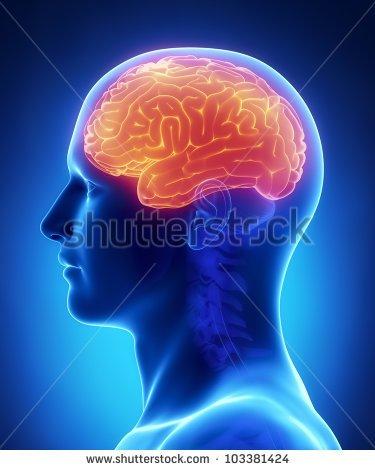
cerebrum
visceral command center
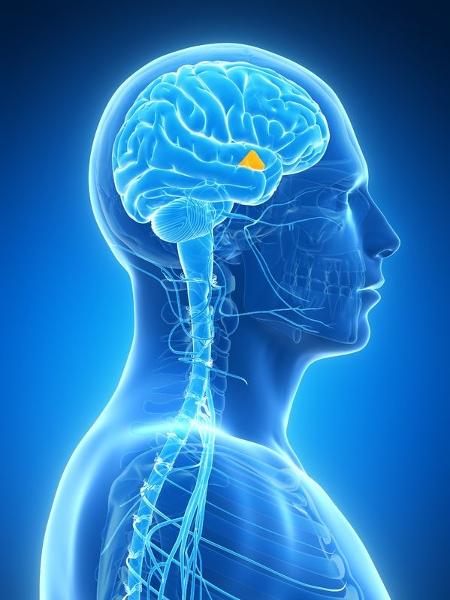
hypothalamus
NREM sleep normally exhibits 4 distinct stages, which appear to alternate
true
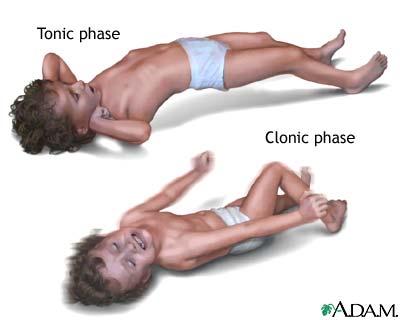
petit mal seizures found in children generally go away with age
true
specific motor and sensory functions are localized in specific area called domains, whereas memory and language overlapping domains
false
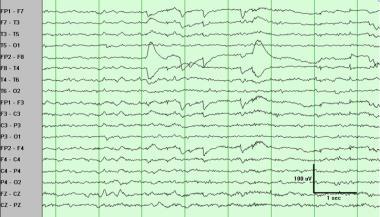
flat EEG is good indication of deep sleep
true
corpora quadrigemina and superior colliculi are auditory reflex center
true
cell body of somatic motor neurons of spinal nerve are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
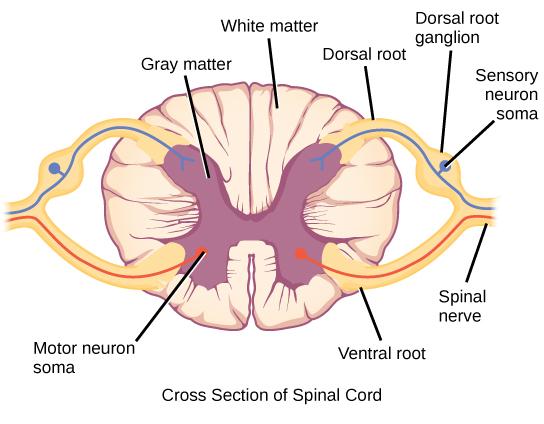
true
meningitis is the most accurate term for inflammation of neurons
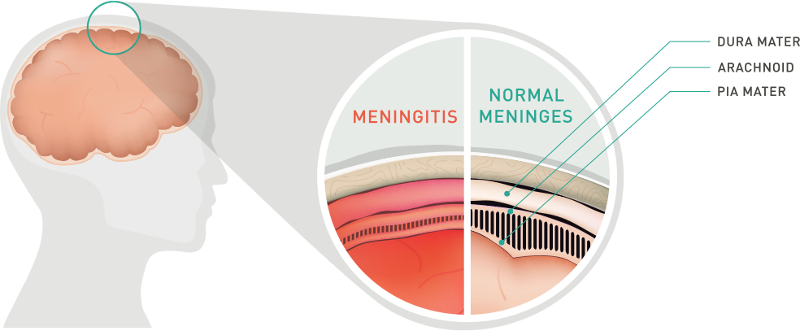
true
adult spinal cord ends between L1 and L2
true
cerebrospinal fluid circulates within the ventricles of the brain and in the subarachnoid space
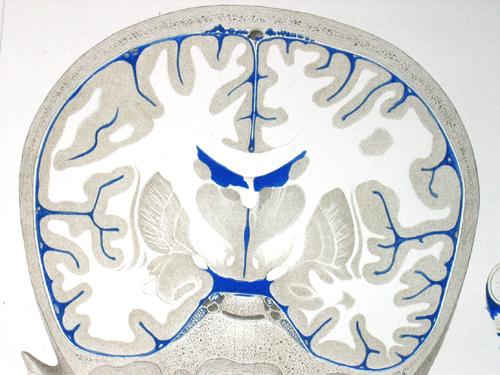
true
the term fainting and syncope described the same thing
true
1st obvious sign that the nervous system is forming in the embryo is the thickening of the surface ectoderm to form the neural plate
true
the left cerebral hemisphere is usually dominant
true
the limbic system acts as your emotional, or effective, brain
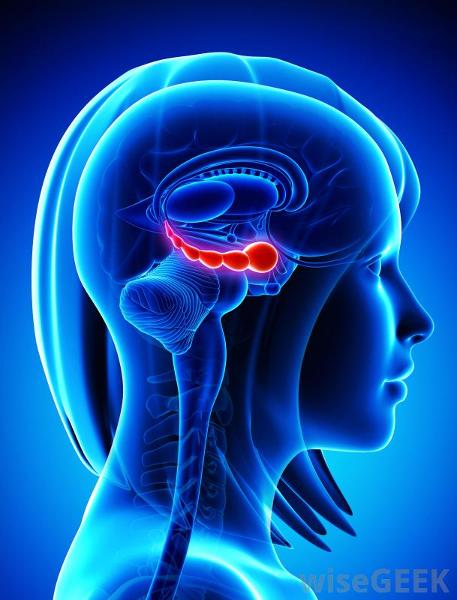
true
disturbance of posture, muscle tremors at rest, and uncontrolled muscle contraction are all symptoms of damage to the basal nuclei
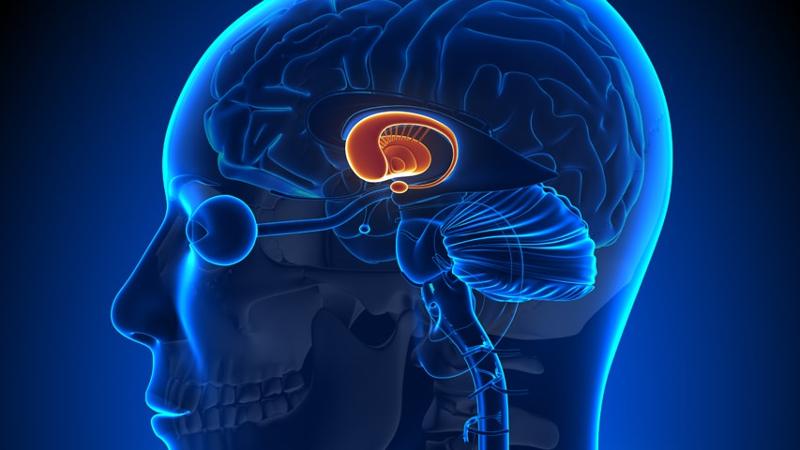
true
most of the ascending pathways to and from the brain cross over from one side of the body to other.
true
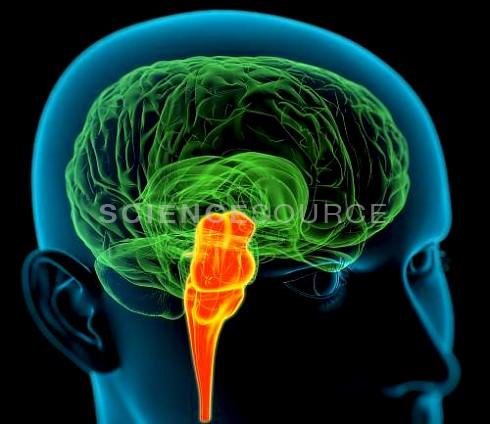
one functional center found within the medulla oblongata is a respiratory center involved in the control of the rate and depth of breathing
true
embryonic damage to the mesencephalon could result in improper formation of the midbrain
true
the arbor vitae refers to
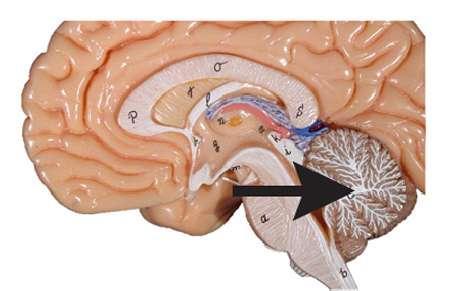
cerebellar white matter
brain stem consists of the_____
midbrain, medulla, and pons
primary auditory cortex is located in the ____
temporal lope
what cells line the vetricles of the brain?
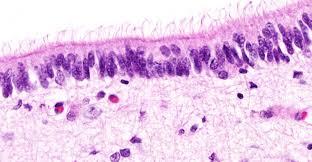
ependymal cells
subarachnoid space lies between what two layers of meninges?
arachnoid and pia
vital centers for the control of heart rate, respiration and blood pressure are located in the _____
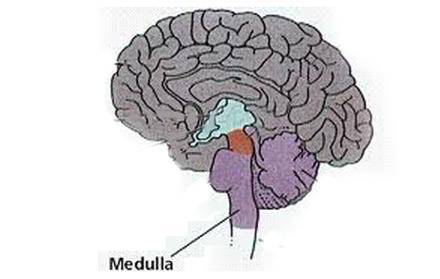
medullla
cell bodies of the sensory neurons of the spinal nerves are located in _____
dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord
which fissure separates the cererbral hemipheres?
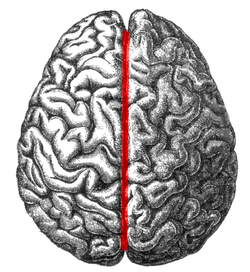
longitudinal fissure
a shallow groove on the surface of the cortex is called ___
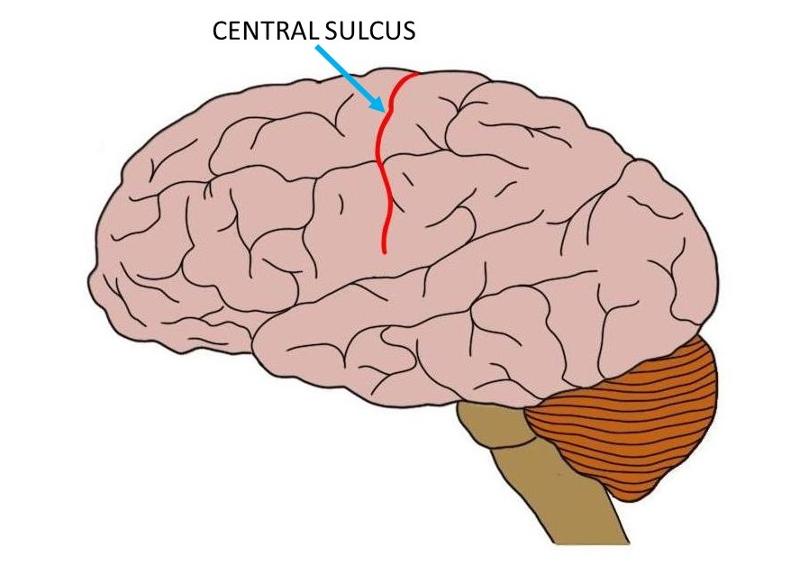
sulcus
the white matter of the spinal cord contains ____
myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers
an individual accidentally transected the spinal cord between T1 and L1
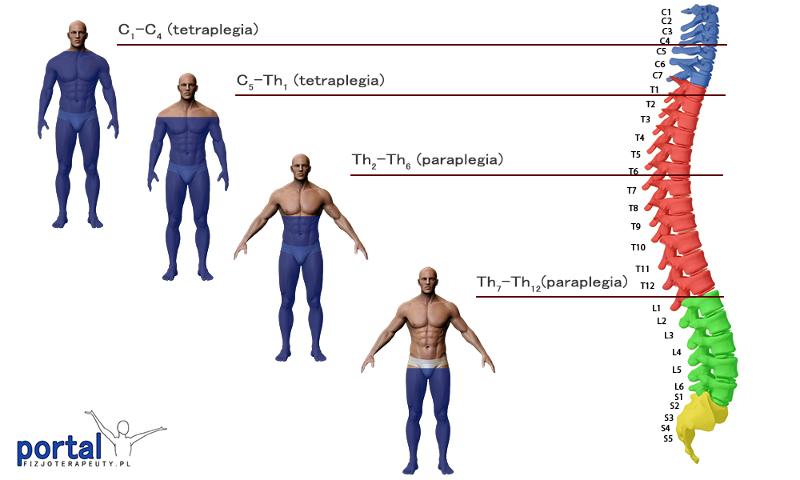
paeaplegia
Broca's area
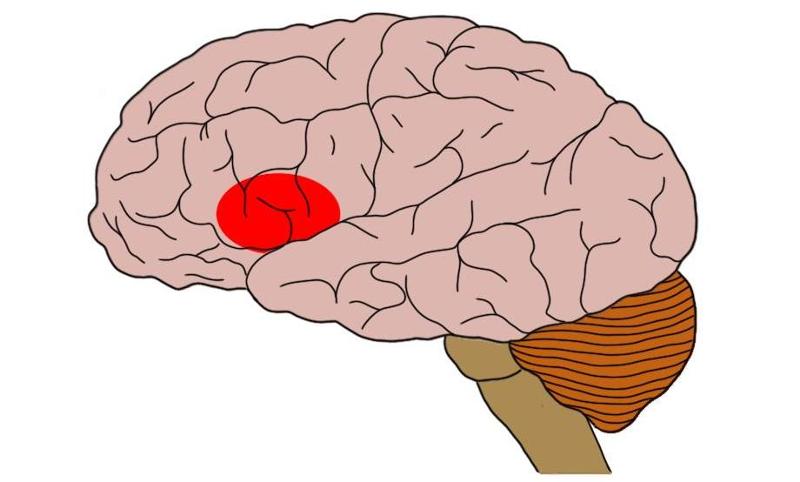
is considered a motor speech area
tests both uper and lower motor pathways. the sole of the foot is stimulated with a dull in strument
plantar
consists of an ipsilateral withdrawal reflexes and a contralateral extensor reflex, importantmaintaining balance
crossed-extensor
produce a rapid withdrawal of the body part form a painful stimulus; ipsilateral
flexor
prevents muscle overstretching and maintains muscle tone
stretch
produces muscle relaxation and lengthening in response to tension; the contracting muscle relaxes as its antagonist activated
golgi tendon
obturator and femoral nerves branch from this plexus
lumbar plexus
striking the "funny bone" (ulnar nerve) may cause injury to a nerve of this plexus
branchial pelxus
trauma to a nerve of this plexus may cause wrist drop
branchial plexus
a fall or improper administration of an injection to the buttocks may injure a nerve of this flexus
sacral plexus
the phrenic nerve branches from this plexus
golgi tendon
TRUE OR FALSE
there are 41 pairs of spinal nerve
false
TRUE OR FALSE
the glossopharyngeal nerve is the only cranial nerve that contains sensory fibers
false
TRUE OR FALSE
the musculocutaneous nerve is the major nerve of the brachial plexus
true
TRUE OR FALSE
the second cranial nerve forms a chaisma at the base of the brain for partial crossover of the neutral fibers
true
TRUE OR FALSE
the only cranial nerve form to extend beyond the head and neck region are the vagus nerves
true
TRUE OR FALSE
the dorsal ramus consists only of motor fiber bringing information to theh spinal cord
false
TRUE OR FALSE
dermatomes are skin segments that relate to sensory innervation to the spinal nerves
true
TRUE OR FALSE
b/c the Autonomic Nervous System is visceral motor system, afferent pathways are of no importance and actually are rarely found
false
TRUE OR FALSE
splanchnic nerves are mixed motor and sensory nerves
false
TRUE OR FALSE
most disorders of the autonomic system reflect abnormalities of smooth muscle control
true
TRUE OR FALSE
the adrenal medulla is considered a "misplaced" sympathetic ganglion by some
true
TRUE OR FALSE
most blood vessels are innervated by the sympathetic division alone
true
TRUE OR FALSE
the structures that specifically exhibit vasomotor tone are mostly under sympathetic control
true
TRUE OR FALSE
b/c parasympathetic fibers never run in spinal nerves, rami communicates are associated only with the sympathetic division
true
TRUE OR FALSE
cranial nerves III, VII, and IX supply the entire parasympathetic innervation of the head; however, only the preganglionic fibers lie within these 3 pair of cranial nerves
true
NOT an exteroceptor ?
tough
pressure
pain
temperature
baroreceptor
baroreceptor
spinal nerves exiting the cord from the level of L4 to S4 form the ______
sacral plexus
inborn or intrinsic reflexes are ______
involuntary, yet may be modified by learned behavior
a drug that might be used specifically to reduce heart rate in cardiac patients could be _____
a beta-blocker
over 90% of all parasympathetic fibers are derived from cranial nerve number _____
X
the "resting and digesting" division of the autonomic nervous system is the _______
parasympathetic division
which is NOT a result of parasympathetic stimulation?
salivation
dilation of pupils
increased peristalsis of the digestive viscera
elimination of urine
dilation of pupils
sympathetic responses generally are widespread b/c _____
NE and epinephrine are secreted into blood as partof the sympathetic response
autonomic ganglia contain _____
the cell bodies of motor neurons
which if the following is NOT a plexus of the vagus nerve?
cardiac
pulmonary
celiac
esophageal
celiac