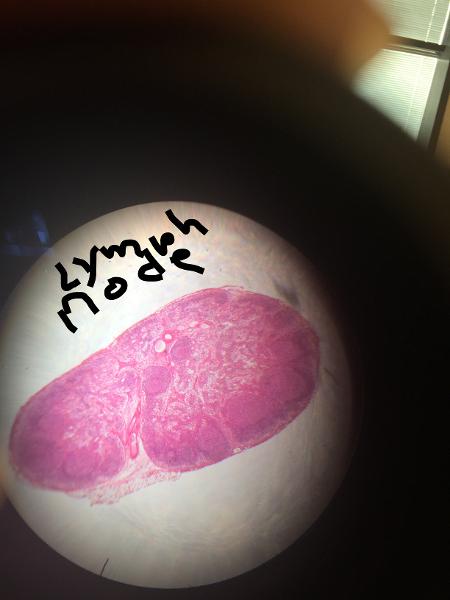
Lymph Node
Lymph Node
Capsule, Cortex, Medulla and Trabeculae of Lymph node
Medullary Cords and Medullary Sinus of Lymph Node
Lymph Follicle and Germinal Center of Lymph Node
Palatine Tonsil
Germinal Center, Tonsillar Crypt, and Lymphoid Noduled of Palatine Tonsil
Lumen and Nodule of Appendix
Germinal Center of Appendix
Overview of the Spleen
Red Pulp, White Pulp and central Artery of the spleen
Splenic Cords and Splenic Sinusoids
Spleen
Thymus
Reticular Cells and Thymic (Hassels's) Corpuscle of the Thymus
Thymus
Peyer's Patches of the Ileum
Structure of a Lymph Node (p. 756 in text book)
Figure 20.1 (p. 752 in text book)
Figure 20.2 Lymphatic System (p. 753 in text book)
Figure 20.2b (p. 753 in text book)
What promotes closure to the mini-valves associated with lymph capillaries?
Increasing pressure inside lymph capillary
___ are primary lymphoid organs.
Bone Marrow and Thymus
What areas are in a secondary lymphoid allow intimate contact between blood and the lymphocytes?
White Pulp of the Spleen
Where in the lymph node do the T- Cells first encounter antigens presented by dendritic cells?
Deep in the cortex
Collections of lymphoid tissues, called MALT (mucosa associated lymphoid tissue), are strategically placed throughout the respiratory, digestive and genitourinary system. Which one of these is located at the end of the Small Intestine?
Peyer's Patches
There is a decrease in our ability to fight infection as we age. Which lymphoid organ may have a role in this decline?
Thymus
Which of the following is NOT a pat of the lymphatic system?
A) lymphatic vessels
B) blood vessels
C) lymph nodes
D) lymph
B) blood vessels
Peyer's Patches are located ___.
wall of the small intestine
Small organs associated with lymphatic vessels are termed ___.
Lymph Nodes
The thymus is the only lymphoid organ that does not __.
directly fight antigens
T/F: Lymph Capillary permeability is due to mini-valves and protein filaments.
TRUE
Where are the lingual tonsils located?
Base of the tongue
T/F: When tissues are inflammed, lymphatic capillaries develop openings that permit uptake of large particles such as cell debris, pathogens and cancer cells.
TRUE
Which lymphatic structure drains lymph from the right side upper limb, right side of the head and right side of the thorax?
Right Lymphatic Duct
What structure delivers lymph into the junction of the internal Jugular vein and subclavian vein?
Thoracic Duct
Which lymphoid cells secrete antibodies?
Plasma Cells
Lymphoid tissue that appears as a swelling of the mucosa in the oral cavity is called a ___.
Tonsil
The thymus is most active during ___.
Childhood
T/F: Lymph arrives to the lymph nodes via efferent lymphatic vessels.
FALSE
What do collecting lymphatic vessels NOT share in common with veins of the cardiovascular system?
Thickness of the walls
The ___ are the most likely to become infected.
Palatine Tonsils
Once collected, lymph is returned to ___.
venous circulation
Which lymphoid organ provides a site for lymphocyte proliferation and immune surveillance and response and provides blood-cleansing functions?
Spleen
Antibodies that act against a particular foreign substance are released by __.
Plasma Cells
___ is not a normal component of lymph.
Red blood cells
Where are worn-out erythrocytes found in the spleen?
Red Pulp
Lymphatic vessels ____.
return tissue fluid to the bloodstream
The first lymphoid organ to appear during fetal development is the ___.
Thymus
Which lymphoid organ serves as the site where T-Lymphocytes become immunocompetent T-Cells?
Thymus Gland
___ tissue is predominantly reticular connective tissue.
Lymphoid
___ is NOT a lymphatic cell.
Eosinophil
Which is not a function of lymph nodes?
produce lymph fluid and cerebrospinal fluid
Lymph nodes are surrounded by a capsule from which connective tissue strands extend inward to divide the node into compartments. What is the name of these strands?
Trabeculae
Which tonsil is located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx and is referred to as the adenoids if it is enlarged?
Pharyngeal Tonsil
Of the following lymphoid organs, which are structurally simplest and lack a complete capsule?
Tonsils
Lymph from what regions of the body are drained into the right lymphatic duct?
Right upper limb, right side of the head and thorax
___ is not a lymphoid organ or tissue.
Bone Marrow
Antibodies are produced by ___.
Plasma cells
Which of the following statements about the thymus is NOT true?
It has follicles similar to those of the spleen
What is the name of the enlarged sac to which the lumbar trunks and the intestinal trunk returns lymph?
Cisterna Chyli
Which of the following would not be classified as a lymphatic structure?
A) Tonsils
B) Spleen
C) Pancreas
D) Peyer's Patches
C) Pancreas
Which part of the spleen is the site of immune function?
White Pulp
What is the role of the mini-valves in lymph capillaries?
Increases permeability
Which of the following is NOT a part of MALT?
a) Tonsils
b) Lymph Nodes
c) Peyer's Patches
d) Appendix
b) Lymph Nodes
The lymphatic capillaries are ___.
more permeable than blood capillaries
Peyer's patches are found in the ___.
Ileum of the small intestine
Lymphatic collecting vessels are most closely associated with ___.
Capillary beds
Which of the following is not a part of the lymphatic system?
a) Erythrocytes
b) Lymph Nodes
c) Lymph
d) Lymphatic Vessels
a) Erythrocytes
Lymph capillaries are are absent in all except ___.
a) CNS
b) Digestive Organs
c) Bones and Teeth
d) Bone Marrow
b) digestive organs
Large clusters of lymph nodes occur in all of the following locations except ___.
lower extremities
___ returns lymph to the right lymphatic duct.
Right Jugular Trunk
T/F: The Cisterna Chyli collects lymph from the lumbar trunks, draining the upper limbs and from the intestinal trunk draining the digestive organs.
FALSE
Functions of the spleen include all of the following except ___.
a) storage of blood platelets
b) storage of iron
c) forming crypts that trap bacteria
d) removal of old or defective blood cells from the blood
c) forming crypts that trap bacteria
Lymph transport involves all but which of the following?
a) milking action of active muscle fibers
b) lymph capillary mini-valve action
c) thorax pressure changes during breathing
d) smooth muscle contraction in the lymph capillary walls
d) smooth muscle contraction in the lymph capillary walls
Which lymphoid organ serves in immune surveillance and in filtering lymph?
Lymph Nodes
Which of the following is a role of lymph nodes?
a) they produce lymph
b) the return lymph to circulation
c) they filter lymph
d) they produce red blood cells
c) they filter lymph
___ is NOT a function of the lymphatic system.
Transporting respiratory gases
___ lacks lymph capillaries.
Bones and teeth
___ are functions of lymphoid tissue.
Furnish an ideal surveillance vantage point for lymphocytes and macrophages
House and provide a proliferation site for lymphocytes
___ does not contain MALT tissue.
Thymus
Digestive tract associated lymphatic tissue includes all of the following except ___.
Islets of Langerhans
Which lymphoid organ is primarily active during the early years of life?
Thymus