A localized group of organisms that belong to the same species is
called a
A) biosystem
B) community
C) population
D) ecosystem
E) family
C
Organisms interact with their environments, exchanging matter and
energy. For example, plant chloroplasts convert the energy of sunlight
into
A) the energy of motion
B) carbon dioxide and water
C) the potential energy of chemical bonds
D) oxygen
E) kinetic energy
C
The main source of energy for producers in an ecosystem is
A)
light energy
B) kinetic energy
C) thermal energy
D)
chemical energy
E) ATP
A
Which of the following types of cells utilize deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA) as their genetic material but do not have their DNA encased
within a nuclear envelope?
A) animal
B) plant
C)
archaea
D) fungi
E) protists
c
To understand the chemical basis of inheritance, we must understand
the molecular structure of DNA. This is an example of the application
of which concept to the study of biology?
A) evolution
B)
emergent properties
C) reductionism
D) the cell theory
E) feedback regulation
c
Once labor begins in childbirth, contractions increase in intensity
and frequency until delivery. The increasing labor contractions of
childbirth are an example of which type of regulation?
A) a
bioinformatic system
B) positive feedback
C) negative
feedback
D) feedback inhibition
E) enzymatic catalysis
B
When the body's blood glucose level rises, the pancreas secretes
insulin and, as a result, the blood glucose level declines. When the
blood glucose level is low, the pancreas secretes glucagon and, as a
result, the blood glucose level rises. Such regulation of the blood
glucose level is the result of
A) catalytic feedback
B)
positive feedback
C) negative feedback
D) bioinformatic
regulation
E) protein-protein interactions
C
Which branch of biology is concerned with the naming and classifying
of organisms?
A) informatics
B) schematic biology
C)
taxonomy
D) genomics
E) evolution
C
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells generally have which of the
following features in common?
A) a membrane-bounded nucleus
B) a cell wall made of cellulose
C) ribosomes
D)
flagella or cilia that contain microtubules
E) linear
chromosomes made of DNA and protein
c
Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains.
What are the domains?
A) Bacteria and Eukarya
B) Archaea
and Monera
C) Eukarya and Monera
D) Bacteria and Protista
E) Bacteria and Archaea
E
Global warming, as demonstrated by observations such as melting of
glaciers, increasing CO2 levels, and increasing average ambient
temperatures, has already had many effects on living organisms. Which
of the following might best offer a solution to this problem?
A)
Continue to measure these and other parameters of the problem.
B) Increase the abilities of animals to migrate to more suitable
habitats.
C) Do nothing; nature will attain its own balance.
D) Limit the burning of fossil fuels and regulate our loss of
forested areas.
E) Recycle as much as possible.
D
A water sample from a hot thermal vent contained a single-celled
organism that had a cell wall but lacked a nucleus. What is its most
likely classification?
A) Eukarya
B) Archaea
C)
Animalia
D) Protista
E) Fungi
B
A filamentous organism has been isolated from decomposing organic
matter. This organism has a cell wall but no chloroplasts. How would
you classify this organism?
A) domain Bacteria, kingdom
Prokaryota
B) domain Archaea, kingdom Bacteria
C) domain
Eukarya, kingdom Plantae
D) domain Eukarya, kingdom Protista
E) domain Eukarya, kingdom Fungi
E
Which of these provides evidence of the common ancestry of all life?
A) ubiquitous use of catalysts by living systems
B) near
universality of the genetic code
C) structure of the nucleus
D) structure of cilia
E) structure of chloroplasts
B
Which of the following is (are) true of natural selection?
A)
It requires genetic variation.
B) It results in descent with
modification.
C) It involves differential reproductive success.
D) It results in descent with modification and involves
differential reproductive success.
E) It requires genetic
variation, results in descent with modification, and involves
differential reproductive success.
E
Charles Darwin proposed a mechanism for descent with modification
that stated that organisms of a particular species are adapted to
their environment when they possess
A) non-inheritable traits
that enhance their survival in the local environment.
B)
non-inheritable traits that enhance their reproductive success in the
local environment.
C) non-inheritable traits that enhance their
survival and reproductive success in the local environment.
D)
inheritable traits that enhance their survival and reproductive
success in the local environment.
E) inheritable traits that
decrease their survival and reproductive success in the local environment.
D
Which of these individuals is likely to be most successful in an
evolutionary sense?
A) a reproductively sterile individual who
never falls ill
B) an organism that dies after five days of life
but leaves 10 offspring, all of whom survive to reproduce
C) a
male who mates with 20 females and fathers one offspring
D) an
organism that lives 100 years and leaves two offspring, both of whom
survive to reproduce
E) a female who mates with 20 males and
produces one offspring that lives to reproduce
B
In a hypothetical world, every 50 years people over 6 feet tall are
eliminated from the population before they reproduce. Based on your
knowledge of natural selection, you would predict that the average
height of the human population will
A) remain unchanged.
B) gradually decline.
C) rapidly decline.
D)
gradually increase.
E) rapidly increase.
B
Through time, the lineage that led to modern whales shows a change
from four-limbed land animals to aquatic animals with two limbs that
function as flippers. This change is best explained by
A)
natural philosophy.
B) creationism.
C) the hierarchy of
the biological organization of life.
D) natural selection.
E) feedback inhibition.
D
What is the major difference between a kingdom and a domain?
A)
A kingdom can include several subgroups known as domains.
B) All
eukarya belong to one domain.
C) All prokaryotes belong to one
domain.
D) The importance of fungi has led scientists to make
them the whole of one domain.
E) Only organisms that produce
their own food belong to one of the domains.
B
Which of the following best describes what occurred after the
publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species?
A) The
book received little attention except from a small scientific
community.
B) The book was banned from schools.
C) The
book was widely discussed and disseminated.
D) The book's
authorship was disputed.
E) The book was discredited by most scientists.
C
Why is Darwin considered original in his thinking?
A) He
provided examples of organisms that had evolved over time.
B) He
demonstrated that evolution is continuing to occur now.
C) He
described the relationship between genes and evolution.
D) He
proposed the mechanism that explained how evolution takes place.
E) He observed that organisms produce large numbers of offspring.
D
Darwin's finches, collected from the Galápagos Islands, illustrate
which of the following?
A) mutation frequency
B) ancestors
from different regions
C) adaptive radiation
D) vestigial
anatomic structures
E) the accuracy of the fossil record
C
Which of the following categories of organisms is least likely to be
revised?
A) kingdom
B) class
C) order
D)
phylum
E) species
E
What is the major distinguishing characteristic of fungi?
A)
gaining nutrition through ingestion
B) being sedentary
C)
being prokaryotic
D) absorbing dissolved nutrients
E)
being decomposers of dead organisms
D
What are archaea?
A) Prokaryotes characterized as extremophiles
that share some bacterial and some eukaryotic traits.
B)
Organisms that are adapted to high temperature environments, such as
in volcanic springs.
C) Single-celled organisms that are killed
by the application of antibiotics at certain concentrations.
D)
Bacteria-like organisms that can live only in extreme salt
environments.
E) Primitive protist-like creatures possessing
fewer than two chromosomes per cell.
A
According to Darwinian theory, which of the following exhibits the
greatest fitness for evolutionary success?
A) the species with
the longest life
B) the individuals within a population that
have the greatest reproductive success
C) the phylum with
members that occupy the greatest number of habitats
D) the
community of organisms that is capable of living in the most
nutrient-poor biome
E) the organism that produces its own
nutrients most efficiently
B
Similarities and differences among/between life-forms over time are
most efficiently recorded by scientists in which field(s) of study?
A) paleontology
B) paleontology and anatomy
C)
paleontology, anatomy, and taxonomy
D) paleontology, anatomy,
taxonomy, and genetics
E) paleontology, anatomy, taxonomy,
genetics, and ecology
E
Why is the theme of evolution considered to be the core theme of
biology by biologists?
A) It provides a framework within which
all biological investigation makes sense.
B) It is recognized as
the core theme of biology by organizations such as the National
Science Foundation.
C) Controversy about this theory provides a
basis for a great deal of experimental research.
D) Since it
cannot be proven, biologists will be able to study evolutionary
possibilities for many years.
E) Biologists do not subscribe to
alternative models.
A
The method of scientific inquiry that describes natural structures
and processes as accurately as possible through careful observation
and the analysis of data is known as
A) hypothesis-based
science.
B) discovery science.
C) experimental science.
D) quantitative science.
E) qualitative science.
B
Collecting data based on observation is an example of ________;
analyzing this data to reach a conclusion is an example of ________
reasoning.
A) hypothesis-based science; inductive
B) the
process of science; deductive
C) discovery science; inductive
D) descriptive science; deductive
E) hypothesis-based
science; deductive
C
When applying the process of science, which of these is tested?
A) a question
B) a result
C) an observation
D)
a prediction
E) a hypothesis
D
A controlled experiment is one in which
A) the experiment is
repeated many times to ensure that the results are accurate.
B)
the experiment proceeds at a slow pace to guarantee that the scientist
can carefully observe all reactions and process all experimental data.
C) there are at least two groups, one of which does not receive
the experimental treatment.
D) there are at least two groups,
one differing from the other by two or more variables.
E) there
is one group for which the scientist controls all variables.
C
Why is it important that an experiment include a control group?
A) The control group is the group that the researcher is in
control of, the group in which the researcher predetermines the
results.
B) The control group provides a reserve of experimental
subjects.
C) A control group is required for the development of
an "If…then" statement.
D) A control group assures
that an experiment will be repeatable.
E) Without a control
group, there is no basis for knowing if a particular result is due to
the variable being tested.
E
The application of scientific knowledge for some specific purpose is
known as
A) technology.
B) deductive science.
C)
inductive science.
D) anthropologic science.
E) pure science.
A
Which of the following are qualities of any good scientific
hypothesis?
I. It is testable.
II. It is falsifiable.
III. It produces quantitative data.
IV. It produces
results that can be replicated.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) III and IV
D
When a hypothesis cannot be written in an "If…then" format,
what does this mean?
A) It does not represent deductive
reasoning.
B) It cannot be a scientific hypothesis.
C) The
subject cannot be explored scientifically.
D) The hypothesizer
does not have sufficient information.
E) It cannot be testable.
A
In presenting data that result from an experiment, a group of
students show that most of their measurements fall on a straight
diagonal line on their graph. However, two of their data points are
"outliers" and fall far to one side of the expected
relationship. What should they do?
A) Do not show these points
but write a footnote that the graph represents the correct data.
B) Average several trials and therefore rule out the improbable
results.
C) Show all results obtained and then try to explore
the reason(s) for these outliers.
D) Throw out this set of data
and try again.
E) Change the details of the experiment until
they can obtain the expected results.
C
Which of the following is the best description of a control for an
experiment?
A) The control group is kept in an unchanging
environment.
B) The control is left alone by the experimenters.
C) The control group is matched with the experimental group
except for the one experimental variable.
D) The control group
is exposed to only one variable rather than several.
E) Only the
experimental group is tested or measured.
C
Given the cooperativity of science, which of the following is most
likely to result in an investigator being intellectually looked down
upon by other scientists?
A) Making money as the result of
studies in which a new medication is discovered.
B) Doing
meticulous experiments that show data that contradict what has been
previously reported by the scientific community.
C) Spending
most of a lifetime investigating a small and seemingly unimportant
organism.
D) Getting negative results from the same set of
experiments.
E) Being found to have falsified or created data to
better fit a hypothesis.
E
Which of these is an example of inductive reasoning?
A)
Hundreds of individuals of a species have been observed and all are
photosynthetic; therefore, the species is photosynthetic.
B)
These organisms live in sunny parts of this area so they are able to
photosynthesize.
C) If horses are always found grazing on grass,
they can be only herbivores and not omnivores.
D) If protists
are all single-celled, then they are incapable of aggregating.
E) If two species are members of the same genus, they are more
alike than each of them could be to a different genus.
A
In a high school laboratory, which of the following constitutes an
experiment?
I. learning to use a microscope by examining fixed
specimens on slides
II. being able to examine swimming protists
under a microscope
III. extracting pigments from plant leaves
and separating the types of pigments for identification
IV.
preparing root tips for examination by staining them
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E)
II, III, and IV
C
Which of the following best describes a model organism?
A) It
is often pictured in textbooks and easy for students to imagine.
B) It lends itself to many studies that are useful to beginning
students.
C) It is well studied, easy to grow, and results are
widely applicable.
D) It is small, inexpensive to raise, and
lives a long time.
E) It has been chosen for study by the
earliest biologists.
C
Why is a scientific topic best discussed by people of varying points
of view, a variety of subdisciplines, and diverse cultures?
A)
They can rectify each other's approach to make it truly scientific.
B) Robust and critical discussion between diverse groups
improves scientific thinking.
C) Scientists can explain to
others that they need to work in isolation to utilize the scientific
method more productively.
D) This is another way of making
science more reproducible.
E) Scientists need to exchange their
ideas with other disciplines and cultures so that all groups are in
consensus with the course of future research.
B
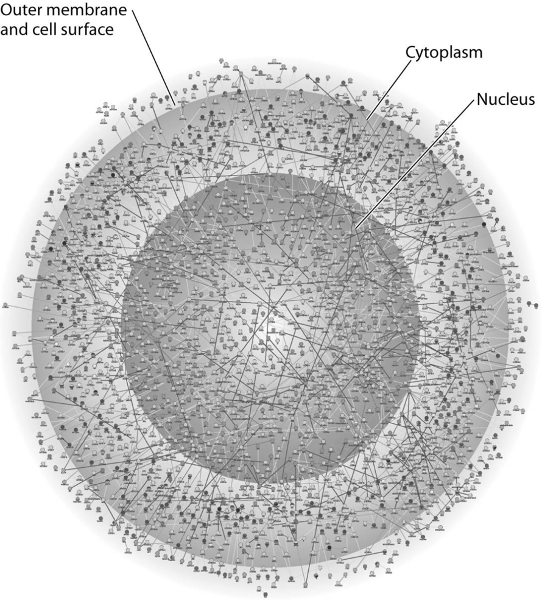
The illustration above most probably represents
A) a computer
simulation of the structure of a eukaryotic cell.
B) a map of a
network of protein interactions within a eukaryotic cell.
C) an
inventory of all the genes in a fruit fly.
D) an X-ray
diffraction image of the nucleus and cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell.
E) a computer-generated map of the interaction of genes and
cytoplasm in a prokaryotic cell.
B
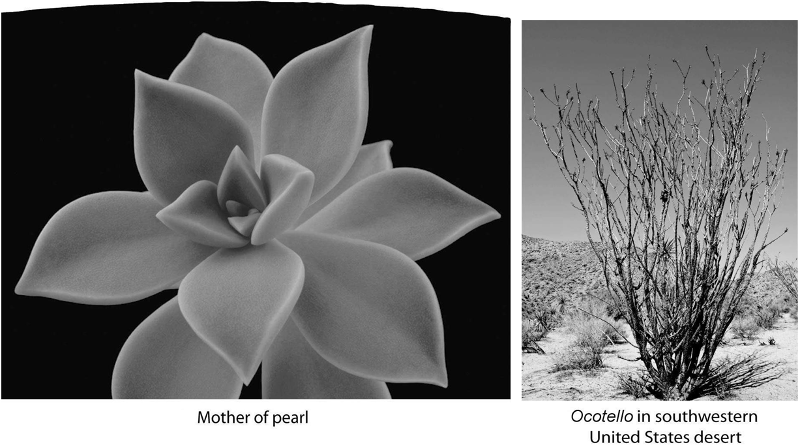
What do these two plants have in common?
A) adaptations to
extreme heat
B) adaptations to conserve water
C) identical
stem structures
D) identical flower structures
E) lack of photosynthesis
B
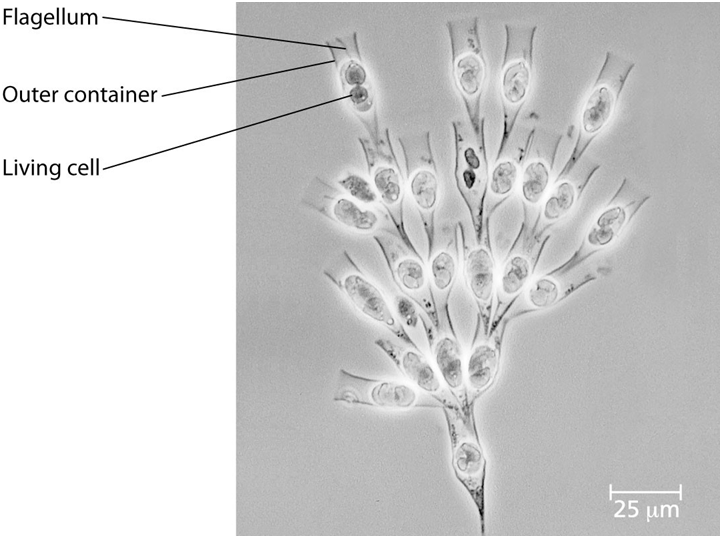
Use the following information to answer questions 47 - 50.
Golden algae are a group of protists whose color is due to
carotenoid pigments: yellow and brown. Most have two flagella and all
are photosynthetic. A group of students was given a significant sample
of one of these (Dinobryon) that is colonial. Their instructions for
the project were to design two or more experiments that could be done
with these organisms.
Since these organisms are protists, which of these
characteristics could the students assume to be true?
A) The
organisms are photosynthetic.
B) All of them are marine.
C) They are single-celled.
D) They lack membrane-bound
organelles.
E) Each has a single circular molecule of DNA.
A
The students decide that for one of their experiments, they want to
see whether the organisms can photosynthesize. Which of the following
is the best hypothesis?
A) If the Dinobryon can live > 5 days
without added food, they must be able to photosynthesize.
B) If
the Dinobryon can live without exposure to light for > 5 days, they
must be able to photosynthesize.
C) If the Dinobryon
photosynthesize, they must need no other minerals or nutrients and
will be able to live in distilled water and light alone.
D) If
the Dinobryon are kept in the dark, one-half will be expected to die
in 5 days.
E) If the Dinobryon are able to photosynthesize, the
students should be able to extract photosynthetic pigments.
E
For their second experiment, the students want to know whether the
Dinobryon have to live in colonies or can be free living. How might
they proceed?
A) Observe each day to see whether new organisms
are ever reproduced as single cells.
B) Observe whether only
specialized cells are able to divide to produce new colonies.
C)
Divide a sample into single cells and measure the length of time they
remain this way.
D) Divide a sample into single cells and
observe them.
E) Divide a sample into single cells and see
whether they come back together.
C
The students plan to gather data from the project. Which of the
following would be the best way to present what they gather from
experimental groups as opposed to controls?
A) qualitatively,
noting color, size, and so on
B) measuring the number of new
colonies formed during every 12-hour period
C) counting the
number of new colonies after a week
D) measuring the size of
each new colony in millimeters (mm) of length
E) measuring the
dry weight of all new colonies in grams
B
The following is a list of biology themes discussed in Chapter 1. Use
them to answer questions 51 - 54.
I. New properties emerge at each level in the biological
hierarchy.
II. Organisms interact with other organisms and the
physical environment.
III. Life requires energy transfer and
transformation.
IV. Structure and function are correlated at all
levels of biological organization.
V. Cells are an organism's
basic units of structure and function.
VI. The continuity of
life is based on heritable information in the form of DNA.
VII.
Feedback mechanisms regulate biological systems.
VIII. Evolution
accounts for the unity and diversity of life.
Which theme(s) is/are best illustrated by an experiment in which
a biologist seeks a medication that will inhibit pain responses in a
cancer patient?
A) II
B) VII
C) III and V
D) V
and VIII
E) VI and VII
B
Which theme(s) is/are best illustrated by a group of investigators
who are trying to classify and explain the ecology of an area known as
the Big Thicket?
A) I only
B) II only
C) VIII only
D) IV and VI
E) I and II
E
Which theme(s) is/are illustrated when a group of students is trying
to establish which phase of cell division in root tips happens most
quickly?
A) IV only
B) V only
C) VII only
D)
IV, V, and VI
E) V, VI, and VII
D
Which theme(s) is/are illustrated when a biology class is comparing
the rates of photosynthesis between leaves of a flowering plant
species (Gerbera jamesonii) and a species of fern (Polypodium
polypodioides)?
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III
D) I and VII
E) I, III, and V
E
Questions 55 - 64 are from the end-of-chapter "Test Your
Understanding" section in Chapter 1 of the textbook.
All the organisms on your campus make up
A) an ecosystem.
B) a community.
C) a population.
D) an experimental
group.
E) a taxonomic domain.
B
Which of the following is a correct sequence of levels in life's
hierarchy, proceeding downward from an individual animal?
A)
brain, organ system, nerve cell, nervous tissue
B) organ system,
nervous tissue, brain
C) organism, organ system, tissue, cell,
organ
D) nervous system, brain, nervous tissue, nerve cell
E) organ system, tissue, molecule, cell
D
Which of the following is not an observation or inference on which
Darwin's theory of natural selection is based?
A) Poorly adapted
individuals never produce offspring.
B) There is heritable
variation among individuals.
C) Because of overproduction of
offspring, there is competition for limited resources.
D)
Individuals whose inherited characteristics best fit them to the
environment will generally produce more offspring.
E) A
population can become adapted to its environment over time.
A
Systems biology is mainly an attempt to
A) analyze genomes from
different species.
B) simplify complex problems by reducing the
system into smaller, less complex units.
C) understand the
behavior of entire biological systems.
D) build high-throughput
machines for the rapid acquisition of biological data.
E) speed
up the technological application of scientific knowledge.
C
Protists and bacteria are grouped into different domains because
A) protists eat bacteria.
B) bacteria are not made of
cells.
C) protists have a membrane-bounded nucleus, which
bacterial cells lack.
D) bacteria decompose protists.
E)
protists are photosynthetic.
C
Which of the following best demonstrates the unity among all
organisms?
A) matching DNA nucleotide sequences
B) descent
with modification
C) the structure and function of DNA
D)
natural selection
E) emergent properties
C
A controlled experiment is one that
A) proceeds slowly enough
that a scientist can make careful records of the results.
B)
tests experimental and control groups in parallel.
C) is
repeated many times to make sure the results are accurate.
D)
keeps all variables constant.
E) is supervised by an experienced scientist.
B
Which of the following statements best distinguishes hypotheses from
theories in science?
A) Theories are hypotheses that have been
proved.
B) Hypotheses are guesses; theories are correct answers.
C) Hypotheses usually are relatively narrow in scope; theories
have broad explanatory power.
D) Hypotheses and theories are
essentially the same thing.
E) Theories are proved true;
hypotheses are often falsified.
C
Which of the following is an example of qualitative data?
A)
The temperature decreased from 20°C to 15°C.
B) The plant's
height is 25 centimeters (cm).
C) The fish swam in a zigzag
motion.
D) The six pairs of robins hatched an average of three
chicks.
E) The contents of the stomach are mixed every 20 seconds.
C
Which of the following best describes the logic of scientific
inquiry?
A) If I generate a testable hypothesis, tests and
observations will support it.
B) If my prediction is correct, it
will lead to a testable hypothesis.
C) If my observations are
accurate, they will support my hypothesis.
D) If my hypothesis
is correct, I can expect certain test results.
E) If my
experiments are set up right, they will lead to a testable hypothesis.
D
About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to
life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of
living matter?
A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen
B)
carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen
C) oxygen, hydrogen,
calcium, nitrogen
D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
E)
carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium
D
Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute
quantities. Which of the following is a trace element that is required
by humans and other vertebrates, but not by other organisms such as
bacteria or plants?
A) nitrogen
B) calcium
C) iodine
D) sodium
E) phosphorus
C
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the most abundant elements of
living matter.
B) Some trace elements are very abundant on
Earth.
C) Virtually all organisms require the same elements in
the same quantities.
D) Iron is an example of an element needed
by all organisms.
E) Other than some trace elements, animals are
mostly made up of the same elements as plants, in similar proportions.
C
What factors are most important in determining which elements are
most common in living matter?
A) the relative abundances of the
elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere
B) the emergent
properties of the simple compounds made from these elements
C)
the reactivity of the elements with water
D) the chemical
stability of the elements
E) both the relative abundances of the
elements and the emergent properties of the compounds made from these elements
E
Why is each element unique and different from other elements in
chemical properties?
A) Each element has a unique atomic mass.
B) Each element has a unique atomic weight.
C) Each
element has a unique number of protons in its nucleus.
D) Each
element has a unique number of neutrons in its nucleus.
E) Each
element has different radioactive properties.
C
Knowing just the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about
which of the following?
A) the chemical properties of the
element
B) the number of protons in the element
C) the
number of neutrons in the element
D) the number of protons plus
neutrons in the element
E) both the number of protons and the
chemical properties of the element
D
In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the
same?
A) They have the same number of protons.
B) They
have the same number of neutrons.
C) They have the same number
of electrons.
D) They have the same number of electrons in their
valence shell.
E) They have the same number of electron shells.
D
Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 and a mass number of 16. Thus, what
is the atomic mass of an oxygen atom?
A) exactly 8 grams
B) exactly 8 daltons
C) approximately 16 grams
D)
approximately 16 daltons
E) 24 amu (atomic mass units)
D
The nucleus of a nitrogen atom contains 7 neutrons and 7 protons.
Which of the following is a correct statement concerning nitrogen?
A) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7
daltons and an atomic mass of 14.
B) The nitrogen atom has a
mass number of approximately 14 daltons and an atomic mass of 7.
C) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of 14 and an atomic mass
of 7 grams.
D) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of 7 and an
atomic number of 14.
E) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of
14 and an atomic mass of approximately 14 daltons.
E
Molybdenum has an atomic number of 42. Several common isotopes exist,
with mass numbers of 92, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, and 100. Therefore, which
of the following can be true?
A) Molybdenum atoms can have
between 50 and 58 neutrons.
B) The isotopes of molybdenum have
different electron configurations.
C) The isotopes of molybdenum
can have between 50 and 58 protons.
D) The isotopes of
molybdenum have between 50 and 58 neutrons and have different electron
configurations.
E) The isotopes of molybdenum have between 50
and 58 protons and have different electron configurations.
A
Carbon-12 is the most common isotope of carbon, and has an atomic
mass of 12 daltons. A mole of carbon in naturally occurring coal,
however, weighs slightly more than 12 grams. Why?
A) The atomic
mass does not include the mass of electrons.
B) Some carbon
atoms in nature have an extra proton.
C) Some carbon atoms in
nature have more neutrons.
D) Some carbon atoms in nature have a
different valence electron distribution.
E) Some carbon atoms in
nature have undergone radioactive decay.
C
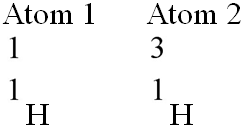
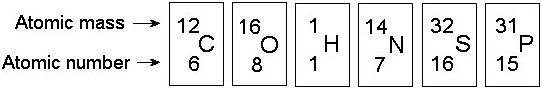
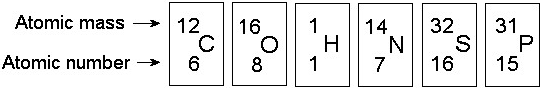
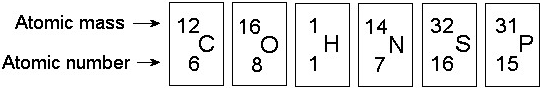
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the
atoms described below? [SEE IMAGE]
A) They are isomers.
B)
They are polymers.
C) They are isotopes.
D) They contain 1
and 3 protons, respectively.
E) They each contain 1 neutron.
C
The precise weight of a mole of some pure elements like silicon (Si)
can vary slightly from the standard atomic mass, or even from sample
to sample. Why?
A) The element may undergo radioactive decay.
B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic
particles.
C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with
each other, and that changes the weight of the element.
D) The
element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic
composition may vary from sample to sample.
E) The amount of
energy absorbed by the element affects the mass of its electrons, and
thus the atomic mass can vary slightly.
D
One difference between carbon-12 (12/6 C) is that carbon-14 (14/6 C)
has
A) two more protons than carbon-12.
B) two more
electrons than carbon-12.
C) two more neutrons than carbon-12.
D) two more protons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
E) two more electrons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
C
An atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. How many unpaired
electrons does it have?
A) 0
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 2 or 4
B
The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 is heavier than
nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains how
many neutrons?
A) 6
B) 7
C) 8
D) 12
E) 14
C
Electrons exist only at fixed levels of potential energy. However, if
an atom absorbs sufficient energy, a possible result is that
A)
an electron may move to an electron shell farther away from the
nucleus.
B) an electron may move to an electron shell closer to
the nucleus.
C) the atom may become a radioactive isotope.
D) the atom would become a positively charged ion, or cation,
and become a radioactive isotope.
E) the atom would become a
negatively charged ion, or anion.
A
The atomic number of neon is 10. Therefore, which of the following is
most correct about an atom of neon?
A) It has 8 electrons in its
outer electron shell.
B) It is inert.
C) It has an atomic
mass of 10 daltons.
D) It has 8 electrons in its outer electron
shell and it is inert.
E) It has 8 electrons in its outer
electron shell, it is inert, and it has an atomic mass of 10 daltons.
D
From its atomic number of 15, it is possible to predict that the
phosphorus atom has
A) 15 neutrons.
B) 15 protons.
C) 15 electrons.
D) 8 electrons in its outermost electron
shell.
E) 15 protons and 15 electrons.
E
Atoms whose outer electron shells contain 8 electrons tend to
A)
form ions in aqueous solutions.
B) form hydrogen bonds in
aqueous solutions.
C) be stable and chemically nonreactive, or
inert.
D) be gaseous at room temperature.
E) be both
chemically inert and gaseous at room temperature.
E
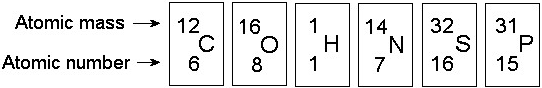
The atomic number of each atom is given to the left of each of the
elements below. Which of the atoms has the same valence as carbon
(12/6 C)?
A) ₇N nitrogen
B) ₉F flourine
C) ₁₀Ne neon
D) ₁₂Mg magnesium
E) ₁₄Si silicon
E
Two atoms appear to have the same mass number. These atoms
A)
must have the same atomic number.
B) must have the same number
of electrons.
C) must have the same chemical properties.
D) must have the same number of protons + neutrons.
E)
must have the same atomic number, the same number of protons +
neutrons, the same number of electrons, and the same chemical properties.
D
Fluorine has an atomic number of 9 and a mass number of 19. How many
electrons are needed to complete the valence shell of a fluorine atom?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 0
D) 7
E) 9
A
What is the maximum number of electrons in a single 2 p orbital of an
atom?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
B
The organic molecules in living organisms have a measurably lower
ratio of carbon-13/carbon-12, two stable isotopes of carbon that
comprise approximately 1.1% and 98.9% of atmospheric carbon,
respectively. What is a reasonable explanation for this phenomenon?
A) Photosynthesis preferentially uses carbon dioxide molecules
with carbon-12, and the lower carbon-13/carbon-12 ratio propagates
through the food chain.
B) Carbon dioxide molecules with
carbon-13 stay in the upper atmosphere and are less available to
terrestrial plants and algae.
C) Carbon-13 has a different
valence electron configuration and is therefore less chemically
reactive than carbon-12.
D) Oxygen atoms preferentially react
with carbon-13, thereby enriching the atmosphere with carbon dioxide
molecules containing carbon-13 atoms.
E) Carbon dioxide
molecules containing carbon-13 are heavier and sink into the ocean
depths, making them less available to living organisms.
A
Phosphorus-32, a radioactive isotope of phosphorus-31 (atomic number
15), undergoes a form of radioactive decay whereby a neutron turns
into a proton and emits radiation in the form of an electron. What is
the product of such radioactive decay of phosphorus-32?
A)
phosphorus-31
B) a positively charged phosphorus-31 ion
C)
a negatively charged phosphorus-32 ion
D) sulfur-32 (atomic
number 16)
E) the conversion of the phosphorus-32 atom into pure energy
D
An atom with atomic number 12 would have what type of chemical
behavior in bonding with other elements?
A) It would form ions
with a +1 charge.
B) It would form ions with a +2 charge.
C) It would form ions with a -1 charge.
D) It would form
ions with a -2 charge.
E) It would form two covalent bonds with
other atoms.
B
If a salamander relied on hydrogen bonds to cling to surfaces, what
type of surface would cause the most problems for this animal?
A) a surface coated with a thin film of water
B) a surface
made with carbon and hydrogen atoms covalently bonded together
C) a surface made with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
covalently bonded together
D) a surface made with carbon,
hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms covalently bonded together
E) a surface made with silicon and oxygen atoms covalently
bonded together
B
A covalent chemical bond is one in which
A) electrons are
removed from one atom and transferred to another atom so that the two
atoms become oppositely charged.
B) protons and neutrons are
shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms.
C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to
satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms.
D)
outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner
electron shell of another atom.
E) an electron occupies a hybrid
orbital located between the nuclei of two atoms.
C
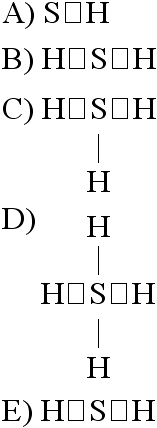
If an atom of sulfur (atomic number 16) were allowed to react with
atoms of hydrogen (atomic number 1), which of the molecules below
would be formed?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
B
What is the maximum number of covalent bonds an element with atomic
number 8 can make with hydrogen?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6
B
Nitrogen (N) is much more electronegative than hydrogen (H). Which of
the following statements is correct about the atoms in ammonia (NH₃)?
A) Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge; the
nitrogen atom has a partial negative charge.
B) The nitrogen
atom has a strong positive charge; each hydrogen atom has a strong
positive charge.
C) Each hydrogen atom has a slight negative
charge; the nitrogen atom has a strong positive charge.
D) The
nitrogen atom has a slight positive charge; each hydrogen atom has a
slight negative charge.
E) There are covalent bonds between the
hydrogen atoms and polar bonds between each hydrogen atom and the
nitrogen atom.
A
When two atoms are equally electronegative, they will interact to
form
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) van der Waals interactions.
C) polar covalent bonds.
D) nonpolar covalent bonds.
E) ionic bonds.
D
What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms?
A) a nonpolar covalent bond
B) a polar covalent bond
C) an ionic bond
D) a hydrogen bond
E) a hydrophobic interaction
B
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when
A) one of the atoms
sharing electrons is much more electronegative than the other atom.
B) the two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative.
C) oxygen is one of the two atoms sharing electrons.
D)
one of the atoms has absorbed more energy than the other atom.
E) the two atoms sharing electrons are different elements.
A
Which of the following molecules contains the most polar covalent
bond?
A) H₂
B) O₂
C) CO₂
D) H₂O
E) CH₄
D
In comparing covalent bonds and ionic bonds, which of the following
would you expect?
A) An atom can form covalent bonds with
multiple partner atoms, but only a single ionic bond with a single
partner atom.
B) Covalent bonds and ionic bonds occupy opposite
ends of a continuous spectrum, from nearly equal to completely unequal
sharing of electrons.
C) Both involve electrical attraction
between the electrons of one atom and the nucleus of the other atom.
D) Ionic interactions remain when covalent bonds are broken in
water. Ionic bonds are much stronger than covalent bonds.
B
What is the difference between covalent bonds and ionic
bonds?
A) Covalent bonds are formed between atoms to form
molecules; ionic bonds are formed between atoms to form compounds.
B) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons
between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons
between atoms.
C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of
electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction
between atoms.
D) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of
electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of protons
between atoms.
E) Covalent bonds involve the transfer of
electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of electrons
between atoms.
C
In ammonium chloride salt (NH₄Cl) the anion is a single chloride ion,
Cl. What is the cation of NH₄Cl?
A) N, with a charge of +1
B) NH, with a charge of +1
C) H₃, with a charge of +1
D) NH₄, with a charge of +1
E) NH₄, with a charge of +4
D
The atomic number of chlorine is 17. The atomic number of magnesium
is 12. What is the formula for magnesium chloride?
A) MgCl
B) MgCl₂
C) Mg₂Cl
D) Mg₂Cl₂
E) MgCl₃
B
How many electron pairs are shared between carbon atoms in a molecule
that has the formula C₂H₄?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
C
Which bond or interaction would be difficult to disrupt when
compounds are put into water?
A) covalent bond
B) hydrogen
bond
C) van der Waals interaction
D) ionic bond
E)
either covalent bonds or ionic bonds
A
Which of the following explains most specifically the attraction of
water molecules to one another?
A) nonpolar covalent bond
B) polar covalent bond
C) ionic bond
D) hydrogen
bond
E) hydrophobic interaction
D
Van der Waals interactions result when
A) hybrid orbitals
overlap.
B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a
molecule.
C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water.
D) two polar covalent bonds react.
E) a hydrogen atom
loses an electron.
B
What bonding or interaction is most likely to occur among a broad
array of molecules of various types (polar, nonpolar, hydrophilic,
hydrophobic)?
A) covalent bonding
B) polar covalent
bonding
C) ionic bonding
D) hydrogen bonding
E) van
der Waals interactions
E
Which of the following is not considered to be a weak molecular
interaction?
A) a covalent bond
B) a van der Waals
interaction
C) an ionic bond in the presence of water
D) a
hydrogen bond
E) both a hydrogen bond and a covalent bond
A
Which of the following would be regarded as compounds?
A) H₂O,
O₂, and CH₄
B) H₂O and O₂
C) O₂ and CH₄
D) CH₄ and
O₂, but not H₂O
E) H₂O and CH₄, but not O₂
E
What is the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can be covalently
bonded in a molecule containing two carbon atoms?
A) 2
B)
3
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
D
Which of the following is true for this reaction?
3 H₂ + N₂ ↔ 2
NH₃
A) The reaction is nonreversible.
B) Hydrogen and
nitrogen are the reactants of the reverse reaction.
C) Hydrogen
and nitrogen are the products of the forward reaction.
D)
Ammonia is being formed and decomposed.
E) Hydrogen and nitrogen
are being decomposed.
D
Which of the following correctly describes chemical equilibrium?
A) Forward and reverse reactions continue with no effect on the
concentrations of the reactants and products.
B) Concentrations
of products are higher than the concentrations of the reactants.
C) Forward and reverse reactions have stopped so that the
concentration of the reactants equals the concentration of the
products.
D) Reactions stop only when all reactants have been
converted to products.
E) There are equal concentrations of
reactants and products, and the reactions have stopped.
A
Which of the following correctly describes any reaction that has
reached chemical equilibrium?
A) The concentration of the
reactants equals the concentration of the products.
B) The rate
of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
C) All of the reactants have been converted to the products of
the reaction.
D) All of the products have been converted to the
reactants of the reaction.
E) Both the forward and the reverse
reactions have stopped with no net effect on the concentration of the
reactants and the products.
B
Which of these systems is least likely to be at chemical equilibrium?
A) a test tube of living cells
B) a test tube of organic
molecules, kept in the freezer
C) a test tube of dry organic
molecules, kept at room temperature
D) a test tube of organic
molecules dissolved in water, kept at room temperature
E) a test
tube of dead cells in water, kept at room temperature
A
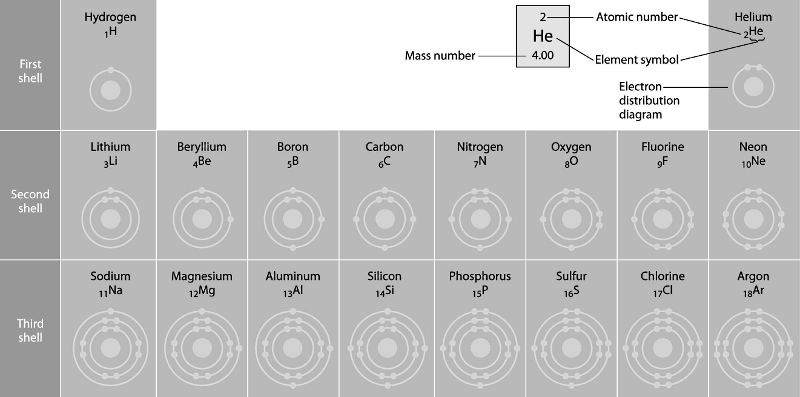
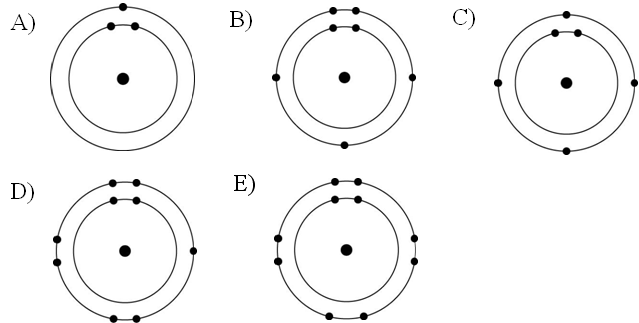
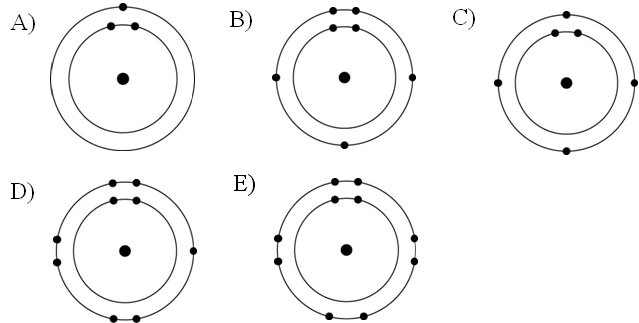
Refer to the figure above (first three rows of the periodic table).
If life arose on a planet where carbon is absent, which element might
fill the role of carbon?
A) boron
B) silicon
C)
nitrogen
D) aluminum
E) phosphorus
B
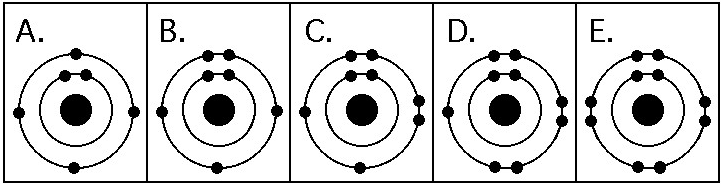
Which drawing in the figure above depicts the electron configuration
of an element with chemical properties most similar to Helium (₂He)?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E
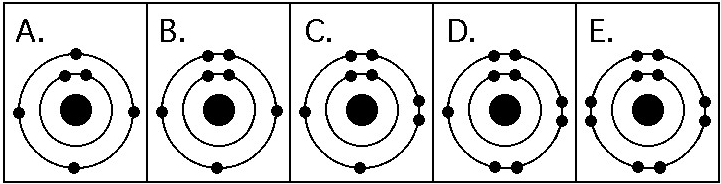
Which drawing in the figure above depicts the electron configuration
of an atom that can form covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
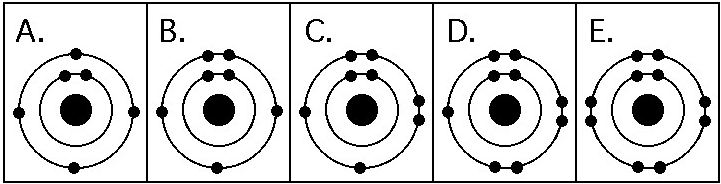
Which drawing in the figure above depicts the electron configuration
of an atom capable of forming three covalent bonds with other atoms?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
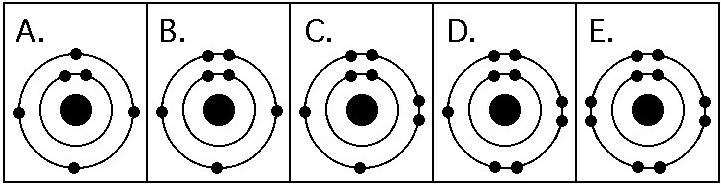
Which drawing in the figure above is of the electron configuration of
a sodium ₁₁Na⁺ ion?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E
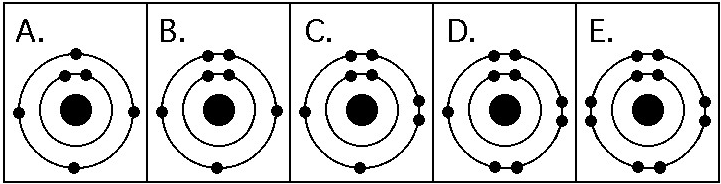
Which drawing in the figure above depicts the most electronegative
atom?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
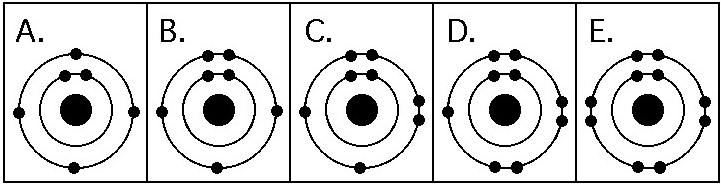
Which drawing in the figure above depicts an atom with a valence of 3?
B
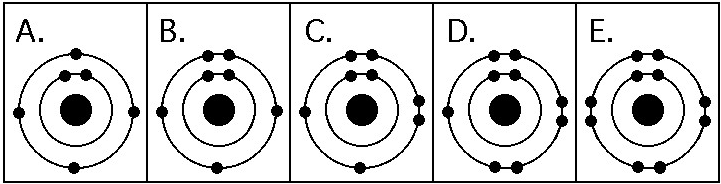
Which drawing in the figure above depicts an atom with a valence of
2?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
In the figure above, how many electrons does nitrogen have in its
valence shell?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 7
D) 8
E) 14
B
In the figure above, how many unpaired electrons does phosphorus have
in its valence shell?
A) 15
B) 2
C) 3
D) 7
E) 5
C
How many neutrons are present in the nucleus of a phosphorus-32 (³²P)
atom (see the figure above)?
A) 5
B) 15
C) 16
D) 17
E) 32
D
How many electrons does an atom of sulfur have in its valence shell
(see the figure above)?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 16
E) 32
B
Based on electron configuration, which of these elements in the
figure above would exhibit a chemical behavior most like that of
oxygen?
A) carbon
B) hydrogen
C) nitrogen
D)
sulfur
E) phosphorus
D
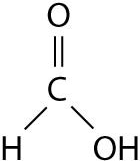
The illustration above shows a representation of formic acid. A
formic acid molecule
A) will form hydrogen bonds with water
molecules.
B) has a tetrahedral configuration of hybrid electron
orbitals for the carbon atom.
C) consists of largely nonpolar
covalent bonds.
D) is held together by hydrogen bonds.
E)
has a tetrahedral shape and will form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
A
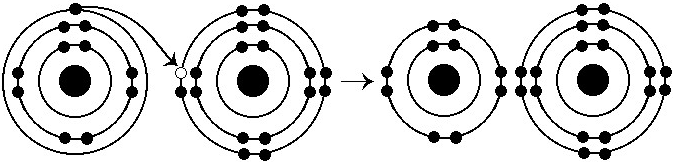
What results from the chemical reaction illustrated above?
A) a
cation with a net charge of +1
B) a cation with a net charge of
-1
C) an anion with a net charge of +1
D) an anion with a
net charge of -1
E) a cation with a net charge of +1 and an
anion with a net charge of -1
E
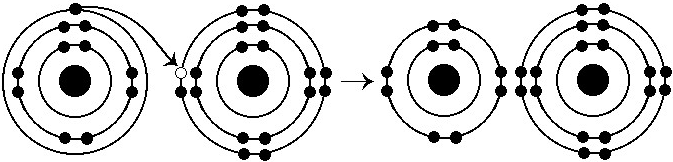
What is the atomic number of the cation formed in the reaction
illustrated above?
A) 1
B) 8
C) 10
D) 11
E) 16
D
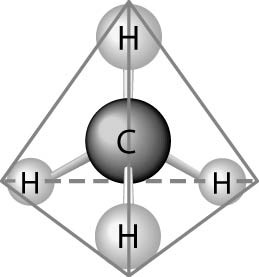
What causes the shape of the molecule shown above?
A) the
configuration of the 2 p orbitals in the carbon atom
B) the
configuration of the 1 s orbital in the carbon atom
C) the
configuration of the sp hybrid orbitals of the electrons shared
between the carbon and hydrogen atoms
D) the packing of the
carbon and hydrogen atoms in a crystal lattice
E) hydrogen
bonding configurations between the carbon and hydrogen atoms
C
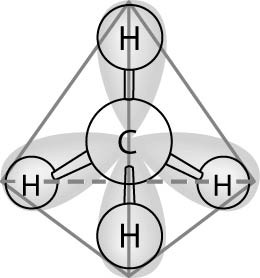
In the methane molecule shown in the figure above, bonds have formed
that include both the s orbital valence electrons of the hydrogen
atoms and the p orbital valence electrons of the carbon. The electron
orbitals in these bonds are said to be
A) double orbitals.
B) tetrahedral orbitals.
C) complex orbitals.
D)
hybrid orbitals.
E) polar orbitals.
D
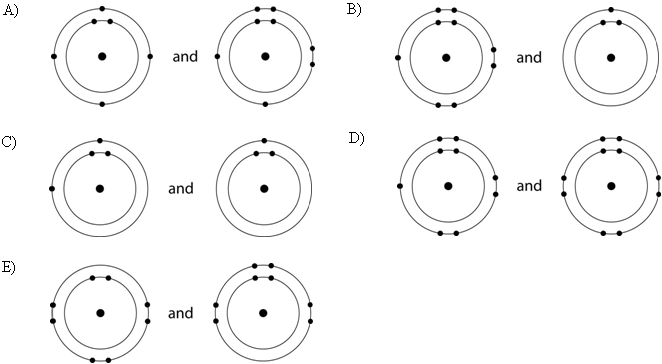
Which one of the atoms shown would be most likely to form a cation
with a charge of +1?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
A
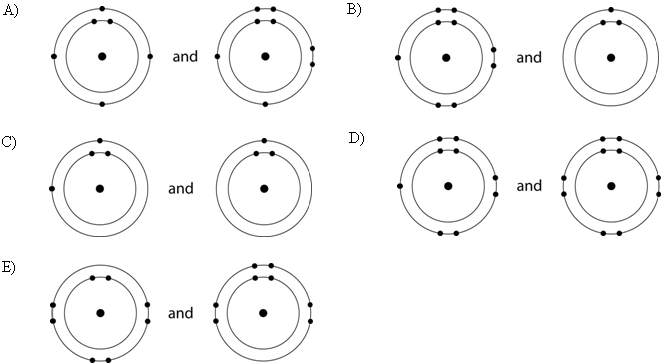
Which one of the atoms shown would be most likely to form an anion
with a charge of -1?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
D
Which of the following pairs of atoms would be most likely to form a
polar covalent bond?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
A
Which of the following pairs of atoms would be most likely to form an
ionic bond?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
B
A group of molecular biologists is trying to synthesize a new
artificial compound to mimic the effects of a known hormone that
influences sexual behavior. They have turned to you for advice. Which
of the following compounds is most likely to mimic the effects of the
hormone?
A) a compound with the same number of carbon atoms as
the hormone
B) a compound with the same molecular mass (measured
in daltons) as the hormone
C) a compound with the same
three-dimensional shape as part of the hormone
D) a compound
with the same number of orbital electrons as the hormone
E) a
compound with the same number of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms as the hormone
C
In the term trace element, the modifier trace means that
A) the
element is required in very small amounts.
B) the element can be
used as a label to trace atoms through an organism's metabolism.
C) the element is very rare on Earth.
D) the element
enhances health but is not essential for the organism's long-term
survival.
E) the element passes rapidly through the organism.
A
Compared with ³¹P, the radioactive isotope ³²P has
A) a
different atomic number.
B) a different charge.
C) one
more proton.
D) one more electron.
E) one more neutron.
E
The reactivity of an atom arises from
A) the average distance
of the outermost electron shell from the nucleus.
B) the
existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shell.
C) the sum
of the potential energies of all the electron shells.
D) the
potential energy of the valence shell.
E) the energy difference
between the s and p orbitals.
B
Which statement is true of all atoms that are anions?
A) The
atom has more electrons than protons.
B) The atom has more
protons than electrons.
C) The atom has fewer protons than does
a neutral atom of the same element.
D) The atom has more
neutrons than protons.
E) The net charge is 1-.
A
Which of the following statements correctly describes any chemical
reaction that has reached equilibrium?
A) The concentrations of
products and reactants are equal.
B) The reaction is now
irreversible.
C) Both forward and reverse reactions have halted.
D) The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal.
E) No reactants remain.
D
We can represent atoms by listing the number of protons, neutrons,
and electrons: for example,
2p⁺; 2n⁰; 2e⁻ for helium. Which of
the following represents the 18O isotope of oxygen?
A) 6p⁺, 8n⁰,
6e⁻
B) 8p⁺, 10n⁰, 8e⁻
C) 9p⁺, 9n⁰, 9e⁻
D) 7p⁺, 2n⁰,
9e⁻
E) 10p⁺, 8n⁰, 9e⁻
B
The atomic number of sulfur is 16. Sulfur combines with hydrogen by
covalent bonding to form a compound, hydrogen sulfide. Based on the
number of valence electrons in a sulfur atom, predict the molecular
formula of the compound:
A) HS
B) HS₂
C) H₂S
D) H₃S₂
E) H₄S
C
What coefficients must be placed in the following blanks so that all
atoms are accounted for in the products?
C₆H₁₂O₆ → ____ C₂H₆O +
____ CO₂
A) 1; 2
B) 3; 1
C) 1; 3
D) 1; 1
E) 2; 2
E
In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a
single oxygen atom by
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) nonpolar
covalent bonds.
C) polar covalent bonds.
D) ionic bonds.
E) van der Waals interactions.
C
The slight negative charge at one end of one water molecule is
attracted to the slight positive charge of another water molecule.
What is this attraction called?
A) a covalent bond
B) a
hydrogen bond
C) an ionic bond
D) a hydrophilic bond
E) a van der Waals interaction
B
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because
A) the oxygen atom acquires an additional electron.
B) the
electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time
around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus.
C) the oxygen atom has two pairs of electrons in its valence
shell that are not neutralized by hydrogen atoms.
D) the oxygen
atom forms hybrid orbitals that distribute electrons unequally around
the oxygen nucleus.
E) one of the hydrogen atoms donates an
electron to the oxygen atom.
B
Sulfur is in the same column of the periodic table as oxygen, but has
electronegativity similar to carbon. Compared to water molecules,
molecules of H₂S
A) will ionize more readily.
B) will have
greater cohesion to other molecules of H₂S.
C) will have a
greater tendency to form hydrogen bonds with each other.
D) will
have a higher capacity to absorb heat for the same change in
temperature.
E) will not form hydrogen bonds with each other.
E
Water molecules are able to form hydrogen bonds with
A)
compounds that have polar covalent bonds.
B) oils.
C)
oxygen gas (O₂) molecules.
D) chloride ions.
E) any
compound that is not soluble in water.
A
Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface
tension of water?
A) Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite
low temperatures.
B) A water strider can walk across the surface
of a small pond.
C) Organisms resist temperature changes,
although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D)
Evaporation of sweat from the skin helps to keep people from
overheating.
E) Water flows upward from the roots to the leaves
in plants.
B
Which of the following takes place as an ice cube cools a drink?
A) Molecular collisions in the drink increase.
B) Kinetic
energy in the drink decreases.
C) A calorie of heat energy is
transferred from the ice to the water of the drink.
D) The
specific heat of the water in the drink decreases.
E)
Evaporation of the water in the drink increases.
B
A dietary Calorie equals 1 kilocalorie. Which of the following
statements correctly defines 1 kilocalorie?
A) 1,000 calories,
or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of
water by 1,000°C
B) 100 calories, or the amount of heat required
to raise the temperature of 100 g of water by 1°C
C) 10,000
calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1
kg of water by 1°F
D) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat
required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C
E)
1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the
temperature of 100 g of water by 100°C
D
The nutritional information on a cereal box shows that one serving of
a dry cereal has 200 kilocalories. If one were to burn one serving of
the cereal, the amount of heat given off would be sufficient to raise
the temperature of 20 kg of water how many degrees Celsius?
A)
0.2°C
B) 1.0°C
C) 2.0°C
D) 10.0°C
E) 20.0°C
D
Liquid water's high specific heat is mainly a consequence of the
A) small size of the water molecules.
B) high specific
heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
C) absorption and release of
heat when hydrogen bonds break and form.
D) fact that water is a
poor heat conductor.
E) higher density of liquid water than
solid water (ice).
C
Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize?
A)
ionic bonds
B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds
C)
polar covalent bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
E) both polar
covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
D
Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of
water is most directly responsible for this phenomenon?
A) the
change in density when it condenses to form a liquid or solid
B)
reactions with other atmospheric compounds
C) the release of
heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds
D) the release of heat
by the breaking of hydrogen bonds
E) the high surface tension of water
C
Why does evaporation of water from a surface cause cooling of the
surface?
A) The breaking of bonds between water molecules
absorbs heat.
B) The water molecules with the most heat energy
evaporate more readily.
C) The solute molecules left behind
absorb heat.
D) Water molecules absorb heat from the surface in
order to acquire enough energy to evaporate.
E) The expansion of
water vapor extracts heat from the surface.
B
Why does ice float in liquid water?
A) The high surface tension
of liquid water keeps the ice on top.
B) The ionic bonds between
the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C) Ice always
has air bubbles that keep it afloat.
D) Hydrogen bonds stabilize
and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules
of liquid water.
E) The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to
be denser than liquid water.
D
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are
A) nonpolar
substances that repel water molecules.
B) nonpolar substances
that have an attraction for water molecules.
C) polar substances
that repel water molecules.
D) polar substances that have an
affinity for water.
E) charged molecules that hydrogen-bond with
water molecules.
A
One mole (mol) of glucose (molecular mass = 180 daltons) is
A)
180 × 10²³ molecules of glucose.
B) 1 kg of glucose dissolved in
1 L of solution.
C) the largest amount of glucose that can be
dissolved in 1 L of solution.
D) 180 kilograms of glucose.
E) both 180 grams of glucose and 6.02 × 10²³ molecules of glucose.
E
How many molecules of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆ molecular mass = 180 daltons)
would be present in 90 grams of glucose?
A) 90 × 10²³
B)
(6.02/180) × 10²³
C) (6.02/90) × 10²³
D) (90 x 6.02) ×
10²³
E) (90/180) × 6.02 × 10²³
E
How many molecules of glycerol (C₃H₈O₃; molecular mass = 92) would be
present in 1 L of a 1 M glycerol solution?
A) 1 × 10⁶
B)
14 × 6.02 × 10²³
C) 92 × 6.02 × 10²³
D) 6.02 × 10²⁶
E) 6.02 × 10²³
E
When an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (NaCl) is placed in
water, the component atoms of the NaCl crystal dissociate into
individual sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻). In contrast, the
atoms of covalently bonded molecules (e.g., glucose, sucrose,
glycerol) do not generally dissociate when placed in aqueous solution.
Which of the following solutions would be expected to contain the
greatest number of solute particles (molecules or ions)?
A) 1 L
of 0.5 M NaCl
B) 1 L of 0.5 M glucose
C) 1 L of 1.0 M NaCl
D) 1 L of 1.0 M glucose
E) 1 L of 1.0 M NaCl and 1 L of
1.0 M glucose will contain equal numbers of solute particles.
C
The molar mass of glucose is 180 g/mol. Which of the following
procedures should you carry out to make a 1 M solution of glucose?
A) Dissolve 1 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
B) Dissolve
180 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
C) Dissolve 180 g of glucose
in 180 g of water.
D) Dissolve 180 milligrams (mg) of glucose in
1 L of water.
E) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 0.8 L of water,
and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
E
The molar mass of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is 180 g/mol. Which of the
following procedures should you carry out to make a 0.5 M solution of
glucose?
A) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in a small volume of
water, and then add more water until the total volume of solution is 1
L.
B) Dissolve 90 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and
then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
C) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and
then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
D) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
E) Dissolve
180 g of glucose in 0.5 L of water.
B
You have a freshly prepared 0.1 M solution of glucose in water. Each
liter of this solution contains how many glucose molecules?
A)
6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 ×
10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
E
The molecular weight of water is 18 daltons. What is the molarity of
1 liter of pure water? (Hint: What is the mass of 1 liter of pure
water?)
A) 55.6 M
B) 18 M
C) 37 M
D) 0.66 M
E) 1.0 M
A
You have a freshly prepared 1 M solution of glucose in water. You
carefully pour out a 100 mL sample of that solution. How many glucose
molecules are included in that 100 mL sample?
A) 6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
E
A strong acid like HCl
A) ionizes completely in an aqueous
solution.
B) increases the pH when added to an aqueous solution.
C) reacts with strong bases to create a buffered solution.
D) is a strong buffer at low pH.
E) both ionizes
completely in aqueous solutions and is a strong buffer at low pH.
A
Which of the following ionizes completely in solution and is
considered to be a strong base (alkali)?
A) NaCl
B) HCl
C) NH₃
D) H₂CO₃
E) NaOH
E
A 0.01 M solution of a substance has a pH of 2. What can you conclude
about this substance?
A) It is a strong acid that ionizes
completely in water.
B) It is a strong base that ionizes
completely in water.
C) It is a weak acid.
D) It is a weak
base.
E) It is neither an acid nor a base.
A
A given solution contains 0.0001(10⁻⁴) moles of hydrogen ions [H⁺]
per liter. Which of the following best describes this solution?
A) acidic: will accept H⁺ from both strong and weak acids
B) basic: will accept H⁺ from both strong and weak acids
C) acidic: will give H⁺ to weak acids, but accept H+ from strong
acids
D) basic: will give H⁺ to weak acids, but accept H⁺ from
weak acids
E) acidic: will give H⁺ to both strong and weak acids
C
A solution contains 0.0000001(10⁻⁷) moles of hydroxyl ions [OH⁻] per
liter. Which of the following best describes this solution?
A)
acidic: H⁺ acceptor
B) basic: H⁺ acceptor
C) acidic: H⁺
donor
D) basic: H⁺ donor
E) neutral
E
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxyl ion [OH⁻] concentration
of 10⁻¹² M?
A) pH 2
B) pH 4
C) pH 10
D) pH 12
E) pH 14
A
What is the pH of a 1 millimolar NaOH solution?
A) pH 3
B) pH 8
C) pH 9
D) pH 10
E) pH 11
E
Which of the following solutions would require the greatest amount of
base to be added to bring the solution to neutral pH?
A) gastric
juice at pH 2
B) vinegar at pH 3
C) tomato juice at pH 4
D) black coffee at pH 5
E) household bleach at pH 12
A
What is the hydrogen ion [H⁺] concentration of a solution of pH 8?
A) 8 M
B) 8 x 10⁻⁶ M
C) 0.01 M
D) 10⁻⁸ M
E) 10⁻⁶ M
D
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 9 to 8, it means that the
A) concentration of H⁺ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it
was at pH 9.
B) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold (10X)
compared to what it was at pH 9.
C) concentration of OH⁻ has
increased tenfold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
D)
concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at
pH 9.
E) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold (10X) and the
concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what they were
at pH 9.
E
If the pH of a solution is increased from pH 5 to pH 7, it means that
the
A) concentration of H⁺ is twice (2X) what it was at pH 5.
B) concentration of H⁺ is one-half (1/2) what it was at pH 5.
C) concentration of OH⁻ is 100 times greater than what it was at
pH 5.
D) concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth (0.01X) what it
was at pH 5.
E) concentration of H⁺ is 100 times greater and the
concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth what they were at pH 5.
C
One liter of a solution of pH 2 has how many more hydrogen ions (H⁺)
than 1 L of a solution of pH 6?
A) 4 times more
B) 16
times more
C) 40,000 times more
D) 10,000 times more
E) 100,000 times more
D
One liter of a solution of pH 9 has how many more hydroxyl ions (OH⁻)
than 1 L of a solution of pH 4?
A) 5 times more
B) 32
times more
C) 50,000 times more
D) 10,000 times more
E) 100,000 times more
E
Which of the following statements is true about buffer solutions?
A) They maintain a constant pH when bases are added to them but
not when acids are added to them.
B) They maintain a constant pH
when acids are added to them but not when bases are added to them.
C) They maintain a relatively constant pH of approximately 7
when either acids or bases are added to them.
D) They maintain a
relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them.
E) They are found only in living systems and biological fluids.
D
Buffers are substances that help resist shifts in pH by
A)
releasing H⁺ to a solution when acids are added.
B) donating H⁺
to a solution when bases are added.
C) releasing OH⁻ to a
solution when bases are added.
D) accepting H⁺ from a solution
when acids are added.
E) both donating H⁺ to a solution when
bases are added, and accepting H⁺ when acids are added.
E
One of the buffers that contribute to pH stability in human blood is
carbonic acid (H₂CO₃). Carbonic acid is a weak acid that dissociates
into a bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻) and a hydrogen ion (H⁺). Thus,
H₂CO₃ ↔ HCO₃⁻ + H⁺
If the pH of the blood drops, one would expect
A) a
decrease in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and an increase in the
concentration of HCO₃⁻.
B) the concentration of hydroxide ion
(OH⁻) to increase.
C) the concentration of bicarbonate ion
(HCO₃⁻) to increase.
D) the HCO₃⁻ to act as a base and remove
excess H⁺ with the formation of H₂CO₃.
E) the HCO₃⁻ to act as an
acid and remove excess H⁺ with the formation of H₂CO₃.
D
One of the buffers that contribute to pH stability in human blood is
carbonic acid (H₂CO₃). Carbonic acid is a weak acid that, when placed
in an aqueous solution, dissociates into a bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻ and
a hydrogen ion (H⁺). Thus,
H₂CO₃ ↔ HCO₃⁻ + H⁺
If the pH of the blood increases, one would expect
A) a
decrease in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and an increase in the
concentration of HCO₃⁻.
B) an increase in the concentration of
H₂CO₃ and a decrease in the concentration of HCO₃⁻.
C) a
decrease in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and an increase in the
concentration of H⁺.
D) an increase in the concentration of
HCO₃⁻ and a decrease in the concentration of OH⁻.
E) a decrease
in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and an increase in the concentration of
both HH₂CO₃ and H⁺.
A
Assume that acid rain has lowered the pH of a particular lake to pH
4.0. What is the hydroxyl ion concentration of this lake?
A) 1 ×
10⁻¹⁰ mol of hydroxyl ion per liter of lake water
B) 1 × 10⁻⁴
mol of hydroxyl ion per liter of lake water
C) 10.0 M with
regard to hydroxyl ion concentration
D) 4.0 M with regard to
hydroxyl ion concentration
E) 1 × 10⁻⁴ mol of hydroxyl ion per
liter of lake water and 4.0 M with regard to hydrogen ion concentration
A
Research indicates that acid precipitation can damage living
organisms by
A) buffering aquatic systems such as lakes and
streams.
B) decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and
streams.
C) increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and
streams.
D) washing away certain mineral ions that help buffer
soil solution and are essential nutrients for plant growth.
E)
both decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams and
increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
D
Consider two solutions: solution X has a pH of 4; solution Y has a pH
of 7. From this information, we can reasonably conclude that
A)
solution Y has no free hydrogen ions (H⁺).
B) the concentration
of hydrogen ions in solution X is 30 times as great as the
concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
C) the
concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y is 1,000 times as great
as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X.
D) the
concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 3 times as great as
the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
E) the
concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 1,000 times as great
as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
E
If a solution has a pH of 7, this means that
A) there are no H⁺
ions in the water.
B) this is a solution of pure water.
C)
the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water equals the concentration of
OH⁻ ions in the water.
D) this is a solution of pure water, and
the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water is 10⁻⁷ M.
E) this is
a solution of pure water, and the concentration of H⁺ ions equals the
concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
C
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is readily soluble in water, according to the
equation CO₂ + H₂O ↔ H₂CO₃. Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) is a weak acid.
Respiring cells release CO₂ into the bloodstream. What will be the
effect on pH of blood as that blood first comes in contact with
respiring cells?
A) Blood pH will decrease slightly.
B)
Blood pH will increase slightly.
C) Blood pH will remain
unchanged.
D) Blood pH will first increase, then decrease as CO₂
combines with hemoglobin.
E) Blood pH will first decrease, then
increase sharply as CO₂ combines with hemoglobin.
A
A beaker contains 100 mL of NaOH solution at pH = 13. A technician
carefully pours into the beaker 10 mL of HCl at pH = 1. Which of the
following statements correctly describes the results of this mixing?
A) The concentration of Na⁺ ion rises.
B) The
concentration of Cl⁻ ion will be 0.1 M.
C) The concentration of
undissociated H₂O molecules remains unchanged.
D) The pH of the
beaker's contents will be neutral.
E) The pH of the beaker's
contents falls.
E
Equal volumes (5 mL) of vinegar from a freshly opened bottle are
added to each of the following solutions. After complete mixing, which
of the mixtures will have the highest pH?
A) 100 mL of pure
water
B) 100 mL of freshly brewed coffee
C) 100 mL of
household cleanser containing 0.5 M ammonia
D) 100 mL of freshly
squeezed orange juice
E) 100 mL of tomato juice
C
Increased atmospheric CO₂ concentrations might have what effect on
seawater?
A) Seawater will become more acidic, and bicarbonate
concentrations will decrease.
B) Seawater will become more
alkaline, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
C) There
will be no change in the pH of seawater, because carbonate will turn
to bicarbonate.
D) Seawater will become more acidic, and
carbonate concentrations will decrease.
E) Seawater will become
more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will increase.
D
How would acidification of seawater affect marine organisms?
A)
Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and
promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
B)
Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and
promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
C)
Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and
hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
D)
Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and
hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
E)
Acidification would increase dissolved bicarbonate concentrations, and
cause increased calcification of corals and shellfish.
D
One idea to mitigate the effects of burning fossil fuels on
atmospheric CO₂ concentrations is to pipe liquid CO₂ into the ocean at
depths of 2,500 feet or greater. At the high pressures at such depths,
CO₂ is heavier than water. What potential effects might result from
implementing such a scheme?
A) increased photosynthetic carbon
fixation because of the increased dissolved carbon dioxide in the deep
water
B) increased carbonate concentrations in the deep waters
C) reduced growth of corals from a change in the
carbonate—bicarbonate equilibrium
D) no effect because carbon
dioxide is not soluble in water
E) both increased acidity of the
deep waters and changes in the growth of bottom-dwelling organisms
with calcium carbonate shells
E
If the cytoplasm of a cell is at pH 7, and the mitochondrial matrix
is at pH 8, this means that
A) the concentration of H⁺ ions is
tenfold higher in the cytoplasm than in the mitochondrial matrix.
B) the concentration of H⁺ ions is tenfold higher in the
mitochondrial matrix than in the cytoplasm.
C) the concentration
of H⁺ ions in the cytoplasm is 7/8 the concentration in the
mitochondrial matrix.
D) the mitochondrial matrix is more acidic
than the cytoplasm.
E) the concentration of H⁺ ions in the
cytoplasm is 8/7 the concentration in the mitochondrial matrix.
A
Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the
solute molecule depicted here is most likely
A) positively
charged.
B) negatively charged.
C) without charge.
D) hydrophobic.
E) nonpolar.
A
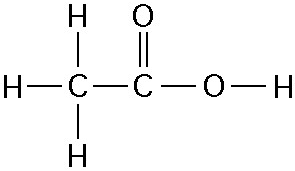
How many grams would be equal to 1 mol of the compound shown in the
figure above?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
A)
29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
C
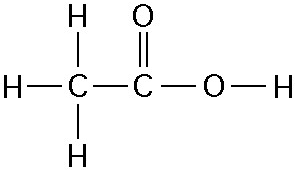
How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required
to make 1 L of a 0.5 M solution?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16,
hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
B
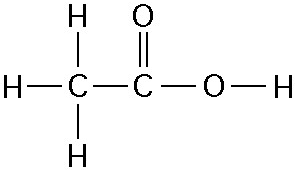
How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required
to make 2.5 L of a 1 M solution?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16,
hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
D
A small birthday candle is weighed, then lighted and placed beneath a
metal can containing 100 mL of water. Careful records are kept as the
temperature of the water rises. Data from this experiment are shown on
the graph. What amount of heat energy is released in the burning of
candle wax?
A) 0.5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
B)
5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
C) 10 kilocalories per
gram of wax burned
D) 20 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
E) 50 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
A
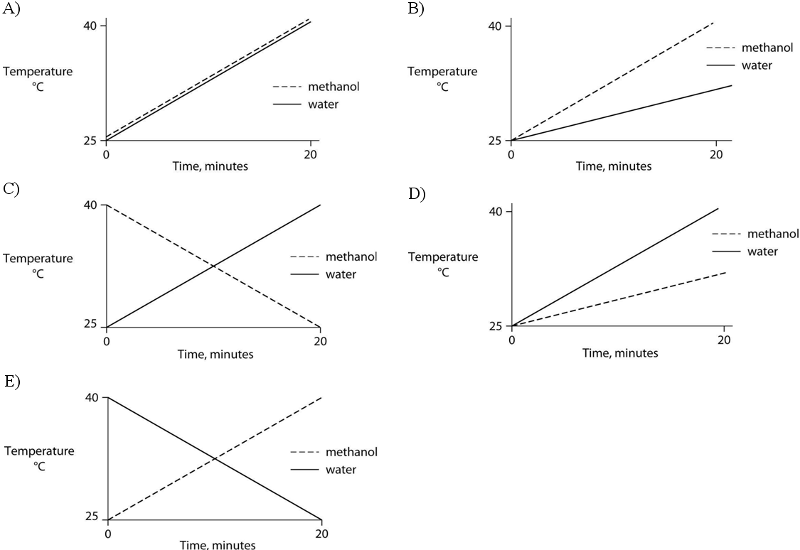
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on identical containers of
water and methanol (wood alcohol), so that each liquid absorbs the
same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol
molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol
molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will
happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
B
Which of these molecules would be soluble in water?
B
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is readily soluble in water, according to the equation CO₂ + H₂O ↔ H₂CO₃. Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) is a weak acid. If CO₂ is bubbled into a beaker containing pure, freshly distilled water, which of the following graphs correctly describes the results?
B
You have two beakers. One contains pure water, the other contains
pure methanol (wood alcohol). The covalent bonds of methanol molecules
are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules.
You pour crystals of table salt (NaCl) into each beaker. Predict what
will happen.
A) Equal amounts of NaCl crystals will dissolve in
both water and methanol.
B) NaCl crystals will NOT dissolve in
either water or methanol.
C) NaCl crystals will dissolve readily
in water but will not dissolve in methanol.
D) NaCl crystals
will dissolve readily in methanol but will not dissolve in water.
E) When the first crystals of NaCl are added to water or to
methanol, they will not dissolve; but as more crystals are added, the
crystals will begin to dissolve faster and faster.
C
You have two beakers. One contains a solution of HCl at pH = 1.0. The
other contains a solution of NaOH at pH = 13. Into a third beaker, you
slowly and cautiously pour 20 mL of the HCl and 20 mL of the NaOH.
After complete stirring, the pH of the mixture will be
A) 2.0.
B) 12.0.
C) 7.0.
D) 5.0.
E) 9.0.
C
Many mammals control their body temperature by sweating. Which
property of water is most directly responsible for the ability of
sweat to lower body temperature?
A) water's change in density
when it condenses
B) water's ability to dissolve molecules in
the air
C) the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen
bonds
D) the absorption of heat by the breaking of hydrogen
bonds
E) water's high surface tension
D
The bonds that are broken when water vaporizes are
A) ionic
bonds.
B) hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
C)
covalent bonds between atoms within water molecules.
D) polar
covalent bonds.
E) nonpolar covalent bonds.
B
Which of the following is a hydrophobic material?
A) paper
B) table salt
C) wax
D) sugar
E) pasta
C
We can be sure that a mole of table sugar and a mole of vitamin C are
equal in their
A) mass in daltons.
B) mass in grams.
C) volume.
D) number of atoms.
E) number of molecules.
E
Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is
the hydrogen ion concentration of the lake?
A) 4.0 M
B)
10⁻¹⁰ M
C) 10⁻⁴ M
D) 10⁴ M
E) 4%
C
Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is
the hydroxide ion concentration of the lake?
A) 10⁻¹⁰ M
B)
10⁻⁴ M
C) 10⁻⁷ M
D) 10⁻¹⁴ M
E) 10 M
A
A slice of pizza has 500 kcal. If we could burn the pizza and use all
the heat to warm a 50-L container of cold water, what would be the
approximate increase in the temperature of the water? (Note: A liter
of cold water weighs about 1 kg.)
A) 50°C
B) 5°C
C)
1°C
D) 100°C
E) 10°C
E
How many grams of acetic acid (C₂H₄O₂) would you use to make 10 L of
a 0.1 M aqueous solution of acetic acid? (Note: The atomic masses, in
daltons, are approximately 12 for carbon, 1 for hydrogen, and 16 for
oxygen.)
A) 10 g
B) 0.1 g
C) 6.0 g
D) 60 g
E) 0.6 g
D
The element present in all organic molecules is
A) hydrogen.
B) oxygen.
C) carbon.
D) nitrogen.
E) phosphorus.
C
The complexity and variety of organic molecules is due to
A)
the chemical versatility of carbon atoms.
B) the variety of rare
elements in organic molecules.
C) the fact that they can be
synthesized only in living organisms.
D) their interaction with
water.
E) their tremendously large sizes.
A
The experimental approach taken in current biological investigations
presumes that
A) simple organic compounds can be synthesized in
the laboratory from inorganic precursors, but complex organic
compounds like carbohydrates and proteins can only be synthesized by
living organisms.
B) a life force ultimately controls the
activities of living organisms and this life force cannot be studied
by physical or chemical methods.
C) although a life force, or
vitalism, exists in living organisms, this life force cannot be
studied by physical or chemical methods.
D) living organisms are
composed of the same elements present in nonliving things, plus a few
special trace elements found only in living organisms or their
products.
E) living organisms can be understood in terms of the
same physical and chemical laws that can be used to explain all
natural phenomena.
E
Differences among organisms are caused by
A) large differences
in elemental composition from organism to organism.
B)
differences in the types and relative amounts of organic molecules
synthesized by each organism.
C) differences in the elements
that bond with carbon in each organism.
D) differences in the
sizes of the organic molecules in each organism.
E) differences
in inorganic compounds present in each organism.
B
Which of the following people was the first to synthesize an organic
compound, urea, from inorganic starting materials?
A) Stanley
Miller
B) Jakob Berzelius
C) Friedrich Wohler
D)
Hermann Kolbe
E) August Kekulé
C
Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments proved that
A) life arose on
Earth from simple inorganic molecules.
B) organic molecules can
be synthesized abiotically under conditions that may have existed on
early Earth.
C) life arose on Earth from simple organic
molecules, with energy from lightning and volcanoes.
D) the
conditions on early Earth were conducive to the origin of life.
E) the conditions on early Earth were conducive to the abiotic
synthesis of organic molecules.
B
Hermann Kolbe's synthesis of an organic compound, acetic acid, from
inorganic substances that had been prepared directly from pure
elements was a significant milestone for what reason?
A) It
solved an industrial shortage of acetic acid.
B) It proved that
organic compounds could be synthesized from inorganic compounds.
C) It disproved the concept of vitalism.
D) It showed that
life originated from simple inorganic chemicals.
E) It proved
that organic compounds could be synthesized from inorganic compounds
and disproved the concept of vitalism.
E
Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments assumed that early Earth's
atmosphere contained
A) hydrogen cyanide, formaldehyde, hydrogen
gas, and water vapor.
B) ammonia, methane, hydrogen gas, and
water vapor.
C) ammonia, methane, oxygen gas, and water vapor.
D) amino acids, methane, hydrogen cyanide, and water vapor.
E) methane, formaldehyde, ammonia, and carbon dioxide.
B
When Stanley Miller applied heat and electrical sparks to a mixture
of simple inorganic compounds such as methane, hydrogen gas, ammonia,
and water vapor, what compounds were produced?
A) mostly amino
acids
B) only simple organic compounds such as formaldehyde and
cyanide
C) mostly hydrocarbons
D) only simple inorganic
compounds
E) both simple organic compounds and more complex
organic compounds such as amino acids and hydrocarbons
E
How many electron pairs does carbon share in order to complete its
valence shell?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
D
A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other
atoms?
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) covalent
D)
covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
E) ionic bonds, covalent
bonds, and hydrogen bonds
C
Which of the following statements best describes the carbon atoms
present in a seed-eating bird?
A) They were incorporated into
organic molecules by plants.
B) They were processed into sugars
through photosynthesis.
C) They are ultimately derived from
carbon dioxide.
D) They were incorporated into organic molecules
by plants, and they are ultimately derived from carbon dioxide.
E) They were incorporated into organic molecules by plants, they
were processed into sugars through photosynthesis, and they are
ultimately derived from carbon dioxide.
E
Which of the following statements best describes the carbon atoms
present in a seed-eating bird?
A) Inorganic carbon atoms in the
seeds were incorporated into organic molecules by the bird.
B)
The carbon atoms ultimately came from the soil.
C) The carbon
atoms are ultimately derived from coal.
D) The carbon atoms
ultimately came from carbon dioxide incorporated into sugars through
photosynthesis.
E) The carbon atoms ultimately came from simple
organic compounds that formed abiotically from inorganic carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms.
D
Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water?
A) The majority of
their bonds are polar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
B)
The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen
linkages.
C) They are hydrophilic.
D) They exhibit
considerable molecular complexity and diversity.
E) They are
lighter than water.
B
How many structural isomers are possible for a substance having the
molecular formula C₄H₁₀?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 3
E) 11
B
Which of the following statements correctly describes cis-trans
isomers?
A) They have variations in arrangement around a double
bond.
B) They have an asymmetric carbon that makes them mirror
images.
C) They have the same chemical properties.
D) They
have different molecular formulas.
E) Their atoms and bonds are
arranged in different sequences.
A
Research indicates that ibuprofen, a drug used to relieve
inflammation and pain, is a mixture of two enantiomers; that is,
molecules that
A) have identical chemical formulas but differ in
the branching of their carbon skeletons.
B) are mirror images of
one another.
C) exist in either linear chain or ring forms.
D) differ in the location of their double bonds.
E) differ
in the arrangement of atoms around their double bonds.
B
What determines whether a carbon atom's covalent bonds to other atoms
are in a tetrahedral configuration or a planar configuration?
A)
the presence or absence of bonds with oxygen atoms
B) the
presence or absence of double bonds between the carbon atom and other
atoms
C) the polarity of the covalent bonds between carbon and
other atoms
D) the presence or absence of bonds with nitrogen
atoms
E) the solvent that the organic molecule is dissolved in
B
Compared to a hydrocarbon chain where all the carbon atoms are linked
by single bonds, a hydrocarbon chain with the same number of carbon
atoms, but with one or more double bonds, will
A) be more
flexible in structure.
B) be more constrained in structure.
C) be more polar.
D) have more hydrogen atoms.
E)
have fewer structurally distinct isomers.
B
Organic molecules with only hydrogens and five carbon atoms can have
different structures in all of the following ways except
A) by
branching of the carbon skeleton.
B) by varying the number of
double bonds between carbon atoms.
C) by varying the position of
double bonds between carbon atoms.
D) by forming a ring.
E) by forming enantiomers.
E
A compound contains hydroxyl groups as its predominant functional
group. Which of the following statements is true concerning this
compound?
A) It lacks an asymmetric carbon, and it is probably a
fat or lipid.
B) It should dissolve in water.
C) It should
dissolve in a nonpolar solvent.
D) It won't form hydrogen bonds
with water.
E) It is hydrophobic.
B
Which of the following is a false statement concerning amino groups?
A) They are basic in pH.
B) They are found in amino acids.
C) They contain nitrogen.
D) They are nonpolar.
E)
They are components of urea.
D
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
A)
ketone and methyl
B) carbonyl and amino
C) carboxyl and
amino
D) amino and sulfhydryl
E) hydroxyl and carboxyl
C
Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional
group?
A) amino
B) carbonyl
C) carboxyl
D)
phosphate
E) hydroxyl
C
A carbon skeleton is covalently bonded to both an amino group and a
carboxyl group. When placed in water it
A) would function only
as an acid because of the carboxyl group.
B) would function only
as a base because of the amino group.
C) would function as
neither an acid nor a base.
D) would function as both an acid
and a base.
E) is impossible to determine how it would function.
D
Which functional groups can act as acids?
A) amino and
sulfhydryl
B) carbonyl and carboxyl
C) carboxyl and
phosphate
D) hydroxyl and aldehyde
E) ketone and amino
C
Testosterone and estradiol are
A) soluble in water.
B)
structural isomers of each other.
C) proteins.
D) lipids.
E) enantiomers of each other.
B
Testosterone and estradiol are male and female sex hormones,
respectively, in many vertebrates. In what way(s) do these molecules
differ from each other?
A) Testosterone and estradiol are
structural isomers but have the same molecular formula.
B)
Testosterone and estradiol are cis-trans isomers but have the same
molecular formula.
C) Testosterone and estradiol have different
functional groups attached to the same carbon skeleton.
D)
Testosterone and estradiol have distinctly different chemical
structures, with one including four fused rings of carbon atoms, while
the other has three rings.
E) Testosterone and estradiol are
enantiomers of the same organic molecule.
C
Which of the following people used this apparatus to study the
formation of organic compounds?
A) Stanley Miller
B) Jakob
Berzelius
C) Friedrich Wohler
D) Hermann Kolbe
E)
August Kekulé
A
The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
A) optical isomers.
B) enantiomers.
C) structural
isomers.
D) cis-trans isomers.
E) chain length isomers.
C
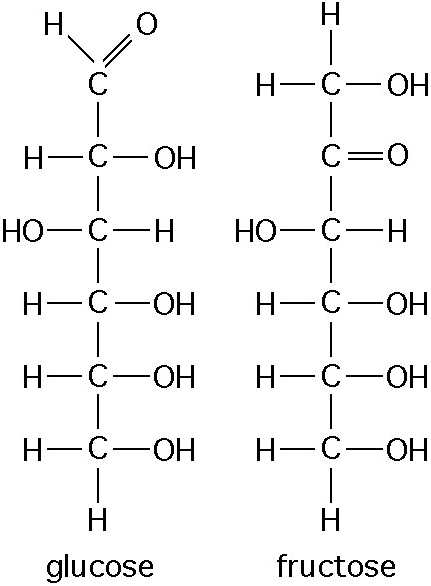
The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose. These
two molecules differ in the
A) number of carbon, hydrogen, and
oxygen atoms.
B) types of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
C) arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
D)
number of oxygen atoms joined to carbon atoms by double covalent
bonds.
E) number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; the
types of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; and the arrangement of
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
C
The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose. These
two molecules are
A) geometric isotopes.
B) enantiomers.
C) cis-trans isomers.
D) structural isomers.
E)
nonisotopic isomers.
D
The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
A) enantiomers.
B) radioactive isotopes.
C)
structural isomers.
D) nonisotopic isomers.
E) cis-trans isomers.
E
Three or four of the following illustrations depict different
structural isomers of the organic compound with molecular formula
C₆H₁₄. For clarity, only the carbon skeletons are shown; hydrogen
atoms that would be attached to the carbons have been omitted. Which
one, if any, is NOT a structural isomer of this compound?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
C
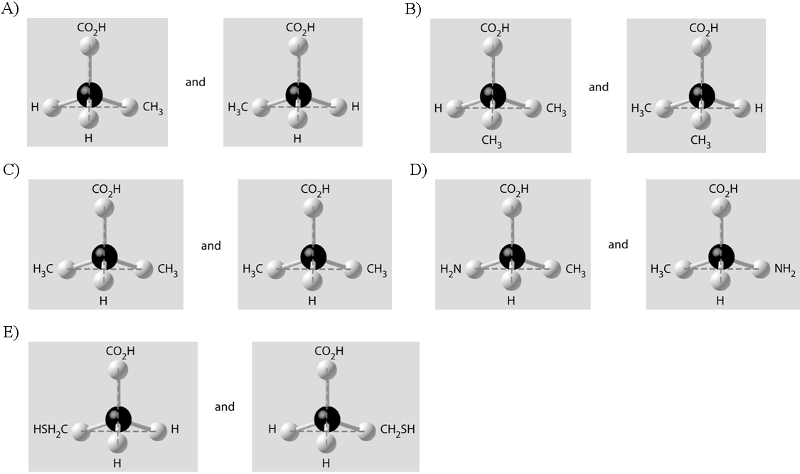
Which of the pairs of molecular structures shown below depict
enantiomers (enantiomeric forms) of the same molecule?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
D
Which of the pairs of molecular structures shown below do NOT depict
enantiomers (enantiomeric forms) of the same molecule?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
C
Which pair of molecules shown below are not enantiomers of a single
molecule?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
B
Thalidomide and L-dopa, shown below, are examples of pharmaceutical
drugs that occur as enantiomers, or molecules that
A) have
identical three-dimensional shapes.
B) are mirror images of one
another.
C) are structural isomers.
D) are mirror images
of one another and have the same biological activity.
E) are
cis-trans isomers.
B
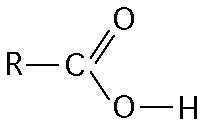
What is the name of the functional group shown in the figure above?
A) carbonyl
B) ketone
C) aldehyde
D) carboxyl
E) hydroxyl
D
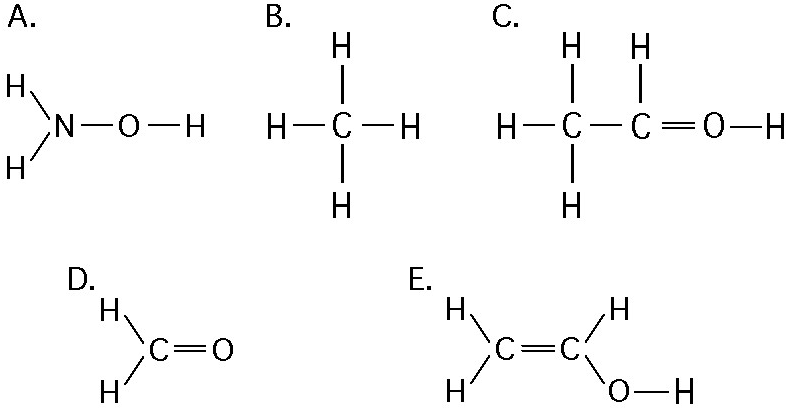
Which of the structures illustrated above is an impossible covalently
bonded molecule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
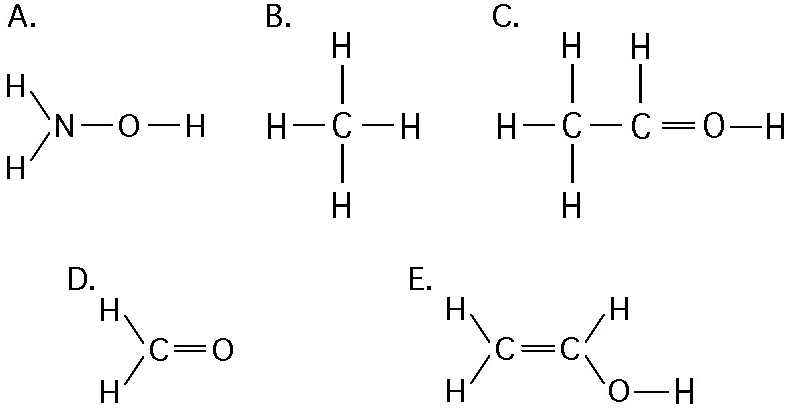
Which of the structures illustrated above contain(s) a carbonyl
functional group?
A) A
B) C and D
C) C
D) D
E) C and E
D
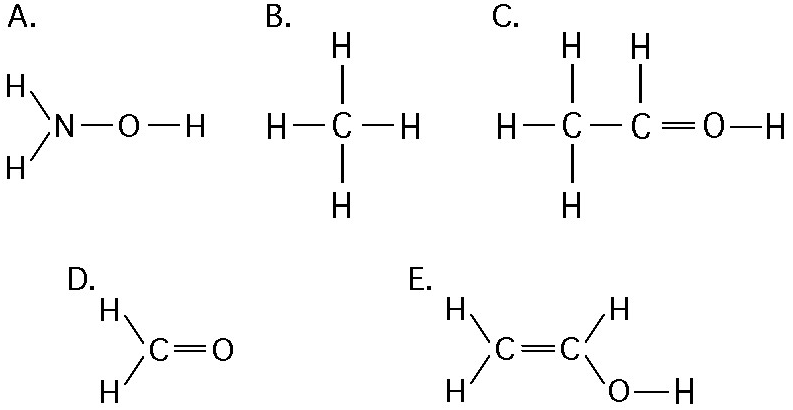
In which of the structures illustrated above are the atoms bonded by
ionic bonds?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) C, D, and E
only
E) none of the structures
E
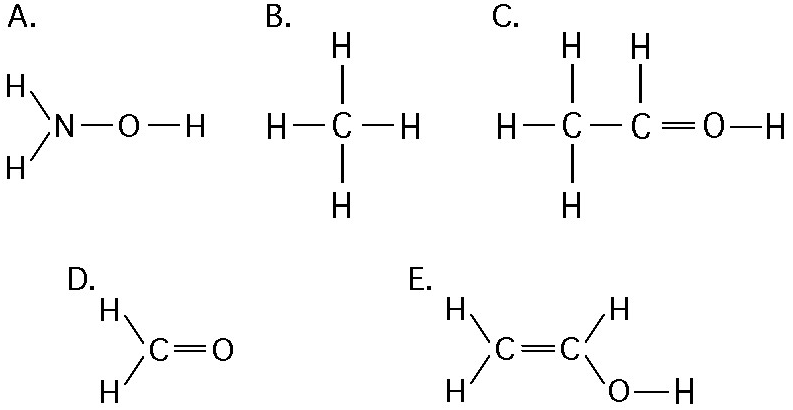
Which of the structures illustrated above cannot form hydrogen bonds
with water molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
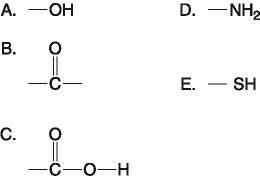
Which functional group shown above is characteristic of alcohols?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A
Which functional group(s) shown above is (are) present in all amino
acids?
A) A and B
B) B and D
C) C only
D) D
only
E) C and D
E
Which of the groups shown above is a carbonyl functional group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
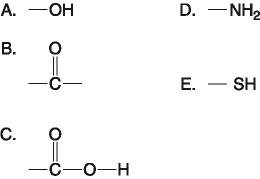
Which of the groups shown above is a functional group that helps
stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between
protein molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E
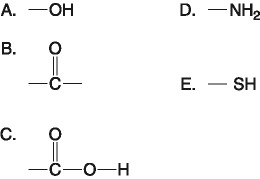
Which of the groups above is a carboxyl functional group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
Which of the groups above is an acidic functional group that can
dissociate and release H⁺ into a solution?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
Which of the groups above is a basic functional group that can accept
H⁺ and become positively charged?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
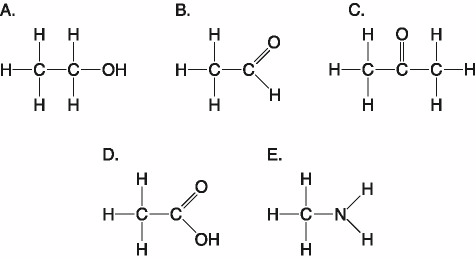
Which molecule shown above would have a positive charge in aqueous
solution at pH 7?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E
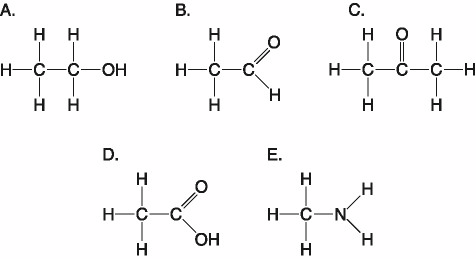
Which molecule(s) shown above is (are) ionized in aqueous solution at
pH 7?
A) A
B) B and D
C) D and E
D) D
E) E
A
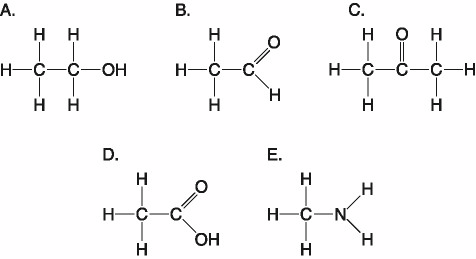
Which molecules shown above contain a carbonyl group?
A) A and
B
B) B and C
C) B, C, and D
D) D and E
E) E
and A
B
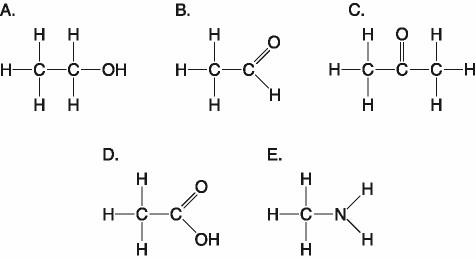
Which molecule shown above has a carbonyl functional group in the
form of a ketone?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
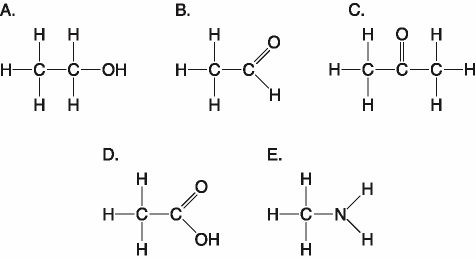
Which molecule shown above has a carbonyl functional group in the
form of an aldehyde?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
Which molecule shown above contains a carboxyl group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
Which molecule shown above can increase the concentration of hydrogen
ions in a solution and is therefore an organic acid?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
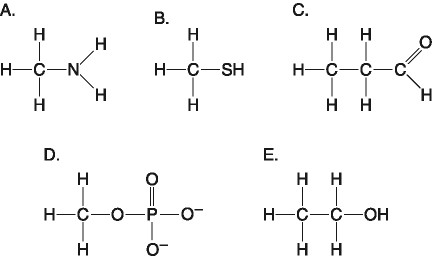
Which molecule shown above can form a dimer linked by a covalent
bond?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
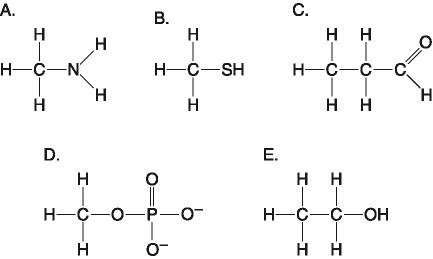
Which molecules shown above will form hydrogen bonds with water?
A) Only D will form hydrogen bonds with water.
B) All of
these molecules will form hydrogen bonds with water.
C) None of
these molecules will form hydrogen bonds with water.
D) All of
these molecules except B will form hydrogen bonds with water.
E)
Only C, D, and E will form hydrogen bonds with water.
D
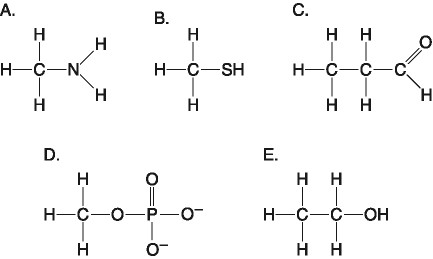
Which molecule shown above contains an amino functional group, but is
not an amino acid?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A
Which molecule shown above is a thiol?
A) A
B) B
C)
C
D) D
E) E
B
Which molecule shown above contains a functional group that cells use
to transfer energy between organic molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
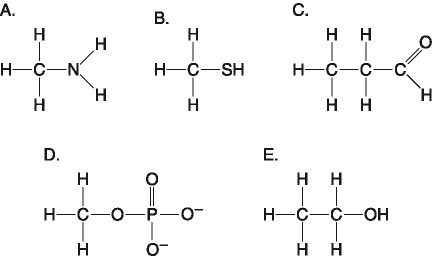
Which molecule shown above can function as a base?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A
A chemist wishes to make an organic molecule less acidic. Which of
the following functional groups should be added to the molecule in
order to do so?
A) carboxyl
B) sulfhydryl
C)
hydroxyl
D) amino
E) phosphate
D
Organic chemistry is currently defined as
A) the study of
compounds made only by living cells.
B) the study of carbon
compounds.
C) the study of vital forces.
D) the study of
natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
E) the study of hydrocarbons.
B
Which functional group is not present in this molecule?
A)
carboxyl
B) sulfhydryl
C) hydroxyl
D) amino
B
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic
molecule behaving as a base?
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) carboxyl
D) amino
E) phosphate
D
Which of the following hydrocarbons has a double bond in its carbon
skeleton?
A) C₃H₈
B) C₂H₆
C) CH₄
D) C₂H₄
E) C₂H₂
D
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between
these two sugar molecules:
A) structural isomers
B)
cis-trans isomers
C) enantiomers
D) isotopes
A
Identify the asymmetric carbon in this molecule.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
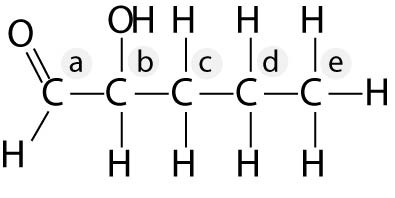
Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
A) the replacement
of the OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
B) the addition of a
thiol to a hydroxyl
C) the addition of a hydroxyl to a phosphate
D) the replacement of the nitrogen of an amine with
oxygen
E) the addition of a sulfhydryl to a carboxyl
A
Humans and mice differ because
A) their cells have different
small organic molecules.
B) their cells make different types of
large biological molecules.
C) their cells make different types
of lipids.
D) their cells have some differences in the sequence
of nucleotides in their nucleic acids.
E) their cells make
different types of proteins.
D
Molecules with which functional groups may form polymers via
dehydration reactions?
A) hydroxyl groups
B) carbonyl
groups
C) carboxyl groups
D) either carbonyl or carboxyl
groups
E) either hydroxyl or carboxyl groups
E
Which of these molecules is not formed by dehydration reactions?
A) fatty acids
B) disaccharides
C) DNA
D)
protein
E) amylose
A
In animal metabolism, most of the monomers released by digestion of
food macromolecules are metabolized to provide energy. Only a small
portion of these monomers are used for synthesis of new
macromolecules. The net result is that
A) water is generated by
animal metabolism.
B) water is consumed by animal metabolism.
C) the water consumed is exactly balanced by the water
generated, to maintain homeostasis.
D) water is consumed during
homeostasis, but water is generated during periods of growth.
E)
water is generated during homeostasis, but water is consumed during
periods of growth.
B
Which of these classes of biological molecules consist of both small
molecules and macromolecular polymers?
A) lipids
B)
carbohydrates
C) proteins
D) nucleic acids
E)
lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids all consist of only
macromolecular polymers
B
Which of the following is not a polymer?
A) glucose
B)
starch
C) cellulose
D) chitin
E) DNA
A
What is the chemical reaction mechanism by which cells make polymers
from monomers?
A) phosphodiester linkages
B) hydrolysis
C) dehydration reactions
D) ionic bonding of monomers
E) the formation of disulfide bridges between monomers
C
How many molecules of water are needed to completely hydrolyze a
polymer that is 11 monomers long?
A) 12
B) 11
C) 10
D) 9
E) 8
C
Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between
dehydration reactions and hydrolysis?
A) Dehydration reactions
assemble polymers, and hydrolysis reactions break down polymers.
B) Dehydration reactions eliminate water from lipid membranes,
and hydrolysis makes lipid membranes water permeable.
C)
Dehydration reactions can occur only after hydrolysis.
D)
Hydrolysis creates monomers, and dehydration reactions break down
polymers.
E) Dehydration reactions ionize water molecules and
add hydroxyl groups to polymers; hydrolysis reactions release hydroxyl
groups from polymers.
A
Which of the following polymers contain nitrogen?
A) starch
B) glycogen
C) cellulose
D) chitin
E) amylopectin
D
The molecular formula for glucose is C₆H₁2O₆. What would be the
molecular formula for a molecule made by linking three glucose
molecules together by dehydration reactions?
A) C₁₈H₃₆O₁₈
B) C₁₈H₃₂O₁₆
C) C₆H₁₀O₅
D) C1₈H₁₀O₁₅
E) C₃H₆O₃
B
The enzyme amylase can break glycosidic linkages between glucose
monomers only if the monomers are the α form. Which of the following
could amylase break down?
A) glycogen
B) cellulose
C) chitin
D) glycogen and chitin only
E) glycogen,
cellulose, and chitin
A
On food packages, to what does the term insoluble fiber refer?
A) cellulose
B) polypeptides
C) starch
D)
amylopectin
E) chitin
A
A molecule with the chemical formula C₆H₁₂O₆ is probably a
A)
carbohydrate.
B) lipid.
C) monosaccharide
D)
carbohydrate and lipid only.
E) carbohydrate and monosaccharide only.
E
Lactose, a sugar in milk, is composed of one glucose molecule joined
by a glycosidic linkage to one galactose molecule. How is lactose
classified?
A) as a pentose
B) as a hexose
C) as a
monosaccharide
D) as a disaccharide
E) as a polysaccharide
D
All of the following are polysaccharides except
A) lactose.
B) glycogen.
C) chitin.
D) cellulose.
E) amylopectin.
A
Which of the following is true of both starch and cellulose?
A)
They are both polymers of glucose.
B) They are cis-trans isomers
of each other.
C) They can both be digested by humans.
D)
They are both used for energy storage in plants.
E) They are
both structural components of the plant cell wall.
A
Which of the following is true of cellulose?
A) It is a polymer
composed of enantiomers of glucose.
B) It is a storage
polysaccharide for energy in plant cells.
C) It is digestible by
bacteria in the human gut.
D) It is a major structural component
of plant cell walls.
E) It is a polymer composed of enantiomers
of glucose, it is a storage polysaccharide for energy in plant cells,
it is digestible by bacteria in the human gut, and it is a major
structural component of plant cell walls.
D
Humans can digest starch but not cellulose because
A) the
monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is
galactose.
B) humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the β
glycosidic linkages of starch but not the α glycosidic linkages of
cellulose.
C) humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the α
glycosidic linkages of starch but not the β glycosidic linkages of
cellulose.
D) humans harbor starch-digesting bacteria in the
digestive tract.
E) the monomer of starch is glucose, while the
monomer of cellulose is glucose with a nitrogen-containing group.
C
Which of the following statements concerning saturated fats is not
true?
A) They are more common in animals than in plants.
B) They have multiple double bonds in the carbon chains of their
fatty acids.
C) They generally solidify at room temperature.
D) They contain more hydrogen than unsaturated fats having the
same number of carbon atoms.
E) They are one of several factors
that contribute to atherosclerosis.
B
A molecule with the formula C₁₈H3₆O₂ is probably a
A)
carbohydrate.
B) fatty acid.
C) protein.
D) nucleic
acid.
E) hydrocarbon.
B
Which of the following statements is true for the class of biological
molecules known as lipids?
A) They are insoluble in water.
B) They are made from glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphate.
C) They contain less energy than proteins and carbohydrates.
D) They are made by dehydration reactions.
E) They contain nitrogen.
A
The label on a container of margarine lists "hydrogenated
vegetable oil" as the major ingredient. What is the result of
adding hydrogens to vegetable oil?
A) The hydrogenated vegetable
oil has a lower melting point.
B) The hydrogenated vegetable oil
stays solid at room temperature.
C) The hydrogenated vegetable
oil has more "kinks" in the fatty acid chains.
D) The
hydrogenated vegetable oil has fewer trans fatty acids.
E) The
hydrogenated vegetable oil is less likely to clog arteries.
B
Which of the following is true regarding saturated fatty acids?
A) They are the predominant fatty acid in corn oil.
B)
They have double bonds between carbon atoms of the fatty acids.
C) They are the principal molecules in lard and butter.
D)
They are usually liquid at room temperature.
E) They are usually
produced by plants.
C
Large organic molecules are usually assembled by polymerization of a
few kinds of simple subunits. Which of the following is an exception
to this statement?
A) a steroid
B) cellulose
C) DNA
D) an enzyme
E) a contractile protein
A
Which modifications of fatty acids will best keep triglycerides solid
at warmer temperatures?
A) creating cis double bonds to the
fatty acids
B) adding hydrogens to the fatty acids
C)
creating trans double bonds to the fatty acids
D) adding
hydrogens and trans double bonds to the fatty acids
E) adding
cis double bonds and trans double bonds to the fatty acids
D
Why are human sex hormones considered to be lipids?
A) They are
essential components of cell membranes.
B) They are not soluble
in water.
C) They are made of fatty acids.
D) They are
hydrophilic compounds.
E) They contribute to atherosclerosis.
B
All of the following contain amino acids except
A) hemoglobin.
B) cholesterol.
C) antibodies.
D) enzymes.
E) insulin.
B
The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule
requires
A) the release of a water molecule.
B) the
release of a carbon dioxide molecule.
C) the addition of a
nitrogen atom.
D) the addition of a water molecule.
E) the
release of a nitrous oxide molecule.
A
There are 20 different amino acids. What makes one amino acid
different from another?
A) different side chains (R groups)
attached to a carboxyl carbon
B) different side chains (R
groups) attached to the amino groups
C) different side chains (R
groups) attached to an α carbon
D) different structural and
optical isomers
E) different asymmetric carbons
C
The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule
requires which of the following?
A) removal of a water molecule
B) addition of a water molecule
C) formation of a
glycosidic bond
D) formation of a hydrogen bond
E) both
removal of a water molecule and formation of a hydrogen bond
A
Polysaccharides, triacylglycerides, and proteins are similar in that
they
A) are synthesized from monomers by the process of
hydrolysis.
B) are synthesized from subunits by dehydration
reactions.
C) are synthesized as a result of peptide bond
formation between monomers.
D) are decomposed into their
subunits by dehydration reactions.
E) all contain nitrogen in
their monomer building blocks.
B
Dehydration reactions are used in forming which of the following
compounds?
A) triacylglycerides
B) polysaccharides
C) proteins
D) triacylglycerides and proteins only
E) triacylglycerides, polysaccharides, and proteins
E
Upon chemical analysis, a particular polypeptide was found to contain
100 amino acids. How many peptide bonds are present in this protein?
A) 101
B) 100
C) 99
D) 98
E) 97
C
What aspects of protein structure are stabilized or assisted by
hydrogen bonds?
A) primary structure
B) secondary
structure
C) tertiary structure
D) quaternary structure
E) secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures, but not
primary structure
E
How many different kinds of polypeptides, each composed of 12 amino
acids, could be synthesized using the 20 common amino acids?
A)
4¹²
B) 12²⁰
C) 240
D) 20
E) 20¹²
E
Which bonds are created during the formation of the primary structure
of a protein?
A) peptide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C)
disulfide bonds
D) phosphodiester bonds
E) peptide bonds,
hydrogen bonds, and disulfide bonds
A
What maintains the secondary structure of a protein?
A) peptide
bonds
B) hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one peptide
bond and the carboxyl group of another peptide bond
C) disulfide
bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) hydrogen bonds
between the R groups
B
Which type of interaction stabilizes the α helix and the β pleated
sheet structures of proteins?
A) hydrophobic interactions
B) disulfide bonds
C) ionic bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
E) peptide bonds
D
Which level of protein structure do the α helix and the β pleated
sheet represent?
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
B
The amino acids of the protein keratin are arranged predominantly in
an α helix. This secondary structure is stabilized by
A)
covalent bonds.
B) peptide bonds.
C) ionic bonds.
D)
polar bonds.
E) hydrogen bonds.
E
The tertiary structure of a protein is the
A) bonding together
of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds.
B) order in which
amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain.
C) unique
three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide.
D)
organization of a polypeptide chain into an α helix or β pleated
sheet.
E) overall protein structure resulting from the
aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits.
C
What type of covalent bond between amino acid side chains (R groups)
functions in maintaining a polypeptide's specific three-dimensional
shape?
A) ionic bond
B) hydrophobic interaction
C)
van der Waals interaction
D) disulfide bond
E) hydrogen bond
D
At which level of protein structure are interactions between the side
chains (R groups) most important?
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) all of the above
C
The R group or side chain of the amino acid serine is –CH₂–OH. The R
group or side chain of the amino acid leucine is –CH₂–CH–(CH₃)₂. Where
would you expect to find these amino acids in a globular protein in
aqueous solution?
A) Serine would be in the interior, and
leucine would be on the exterior of the globular protein.
B)
Leucine would be in the interior, and serine would be on the exterior
of the globular protein.
C) Both serine and leucine would be in
the interior of the globular protein.
D) Both serine and leucine
would be on the exterior of the globular protein.
E) Both serine
and leucine would be in the interior and on the exterior of the
globular protein.
B
Misfolding of polypeptides is a serious problem in cells. Which of
the following diseases are associated with an accumulation of
misfolded polypeptides?
A) Alzheimer's only
B) Parkinson's
only
C) diabetes mellitus only
D) Alzheimer's and
Parkinson's only
E) Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and diabetes mellitus
D
Changing a single amino acid in a protein consisting of 325 amino
acids would
A) alter the primary structure of the protein, but
not its tertiary structure or function.
B) cause the tertiary
structure of the protein to unfold.
C) always alter the
biological activity or function of the protein.
D) always alter
the primary structure of the protein and disrupt its biological
activity.
E) always alter the primary structure of the protein,
sometimes alter the tertiary structure of the protein, and affect its
biological activity.
E
Normal hemoglobin is a tetramer, consisting of two molecules of β
hemoglobin and two molecules of α hemoglobin. In sickle-cell disease,
as a result of a single amino acid change, the mutant hemoglobin
tetramers associate with each other and assemble into large fibers.
Based on this information alone, we can conclude that sickle-cell
hemoglobin exhibits
A) altered primary structure.
B)
altered secondary structure.
C) altered tertiary structure.
D) altered quaternary structure.
E) altered primary
structure and altered quaternary structure; the secondary and tertiary
structures may or may not be altered.
E
What methods may be used to elucidate the structures of purified
proteins?
A) X-ray crystallography
B) bioinformatics
C) analysis of amino acid sequence of small fragments
D)
NMR spectroscopy
E) both X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy
E
In a normal cellular protein, where would you expect to find a
hydrophobic amino acid like valine?
A) in the interior of the
folded protein, away from water
B) on the exterior surface of
the protein, interacting with water
C) in the transmembrane
portion interacting with lipid fatty acid chains
D) in the
interior of the folded protein, away from water, or in a transmembrane
portion interacting with lipid fatty acid chains
E) anywhere in
the protein, with equal probability
D
Which of the following techniques uses the amino acid sequences of
polypeptides to predict a protein's three-dimensional structure?
A) X-ray crystallography
B) bioinformatics
C)
analysis of amino acid sequence of small fragments
D) NMR
spectroscopy
E) high-speed centrifugation
B
If cells are grown in a medium containing radioactive ³⁵S, which of
these molecules will be labeled?
A) phospholipids
B)
nucleic acids
C) proteins
D) amylose
E) both
proteins and nucleic acids
C
What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the
proper folding of other proteins?
A) tertiary protein
B)
chaperonin
C) enzyme protein
D) renaturing protein
E) denaturing protein
B
DNAase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the covalent
bonds that join nucleotides together. What would first happen to DNA
molecules treated with DNAase?
A) The two strands of the double
helix would separate.
B) The phosphodiester bonds between
deoxyribose sugars would be broken.
C) The purines would be
separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
D) The pyrimidines would
be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
E) All bases would be
separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
B
Which of the following statements about the 5' end of a
polynucleotide strand of DNA is correct?
A) The 5' end has a
hydroxyl group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose.
B) The
5' end has a phosphate group attached to the number 5 carbon of
ribose.
C) The 5' end has phosphate attached to the number 5
carbon of the nitrogenous base.
D) The 5' end has a carboxyl
group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose.
E) The 5' end
is the fifth position on one of the nitrogenous bases.
B
One of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to
A) transmit
genetic information to offspring.
B) function in the synthesis
of proteins.
C) make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic
continuity.
D) act as a pattern or blueprint to form DNA.
E) form the genes of higher organisms.
B
If ¹⁴C-labeled uridine triphosphate is added to the growth medium of
cells, what macromolecules will be labeled?
A) phospholipids
B) DNA
C) RNA
D) both DNA and RNA
E) proteins
C
Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules
known as nucleotides?
A) a nitrogenous base and a phosphate
group
B) a nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar
C) a
nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar
D) a
phosphate group and an adenine or uracil
E) a pentose sugar and
a purine or pyrimidine
C
Which of the following are nitrogenous bases of the pyrimidine type?
A) guanine and adenine
B) cytosine and uracil
C)
thymine and guanine
D) ribose and deoxyribose
E) adenine
and thymine
B
Which of the following are nitrogenous bases of the purine type?
A) cytosine and guanine
B) guanine and adenine
C)
adenine and thymine
D) thymine and uracil
E) uracil and cytosine
B
If a DNA sample were composed of 10% thymine, what would be the
percentage of guanine?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 80
E) impossible to tell from the information given
C
A double-stranded DNA molecule contains a total of 120 purines and
120 pyrimidines. This DNA molecule could be composed of
A) 120
adenine and 120 uracil molecules.
B) 120 thymine and 120 adenine
molecules.
C) 120 cytosine and 120 thymine molecules.
D)
120 adenine and 120 cytosine molecules.
E) 120 guanine and 120
thymine molecules.
B
The difference between the sugar in DNA and the sugar in RNA is that
the sugar in DNA
A) is a six-carbon sugar and the sugar in RNA
is a five-carbon sugar.
B) can form a double-stranded molecule.
C) is an aldehyde sugar and the sugar in RNA is a keto sugar.
D) is in the α configuration and the sugar in RNA is in the β
configuration.
E) contains one less oxygen atom.
E
Which of the following statements best summarizes the differences
between DNA and RNA?
A) DNA encodes hereditary information,
whereas RNA does not.
B) The bases in DNA form base-paired
duplexes, whereas the bases in RNA do not.
C) DNA nucleotides
contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides.
D) DNA contains
the base uracil, whereas RNA contains the base thymine.
E) DNA
encodes hereditary information, whereas RNA does not; the bases in DNA
form base-paired duplexes, whereas the bases in RNA do not; and DNA
nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides.
C
If one strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence of bases 5'ATTGCA3',
the other complementary strand would have the sequence
A)
5'TAACGT3'.
B) 5'TGCAAT3'.
C) 5'UAACGU3'.
D)
3'UAACGU5'.
E) 5'UGCAAU3'.
B
What is the structural feature that allows DNA to replicate?
A)
sugar-phosphate backbone
B) complementary pairing of the
nitrogenous bases
C) disulfide bonding (bridging) of the two
helixes
D) twisting of the molecule to form an α helix
E)
three-component structure of the nucleotides
B
A new organism is discovered in the forests of Costa Rica. Scientists
there determine that the polypeptide sequence of hemoglobin from the
new organism has 72 amino acid differences from humans, 65 differences
from a gibbon, 49 differences from a rat, and 5 differences from a
frog. These data suggest that the new organism
A) is more
closely related to humans than to frogs.
B) is more closely
related to frogs than to humans.
C) evolved at about the same
time as frogs, which is much earlier than primates and mammals.
D) is more closely related to humans than to rats.
E) is
more closely related to frogs than to humans and also evolved at about
the same time as frogs, which is much earlier than primates and mammals.
B
Which of the following is an example of hydrolysis?
A) the
reaction of two monosaccharides, forming a disaccharide with the
release of water
B) the synthesis of two amino acids, forming a
peptide with the release of water
C) the reaction of a fat,
forming glycerol and fatty acids with the release of water
D)
the reaction of a fat, forming glycerol and fatty acids with the
consumption of water
E) the synthesis of a nucleotide from a
phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base with the production
of a molecule of water
D
If cells are grown in a medium containing radioactive ³²P-labeled
phosphate, which of these molecules will be labeled?
A)
phospholipids
B) nucleic acids
C) proteins
D)
amylose
E) both phospholipids and nucleic acids
E
If cells are grown in a medium containing radioactive ¹⁵N, which of
these molecules will be labeled?
A) fatty acids only
B)
nucleic acids only
C) proteins only
D) amylase only
E) both proteins and nucleic acids
E
How will brief heating (to 95°C) affect macromolecular structures in
aqueous solution?
A) DNA duplexes will unwind and separate.
B) Proteins will unfold (denature).
C) Starch will
hydrolyze into monomeric sugars.
D) Proteins will hydrolyze into
amino acids.
E) DNA duplexes will unwind and separate, and
proteins will unfold (denature).
E
Which of the following is not a monomer/polymer pairing?
A)
monosaccharide/polysaccharide
B) amino acid/protein
C)
triglyceride/phospholipid bilayer
D) deoxyribonucleotide/DNA
E) ribonucleotide/RNA
C
If two molecules of the general type shown in Figure 5.1 were linked
together, carbon-1 of one molecule to carbon-4 of the other, the
single molecule that would result would be
A) maltose.
B)
fructose.
C) glucose.
D) galactose.
E) sucrose.
A
Which of the following descriptors is true of the molecule shown in
Figure 5.1?
A) hexose
B) fructose
C) glucose
D) hexose and fructose only
E) hexose and glucose only
E
Which of the following statements is true regarding the molecule
illustrated in Figure 5.2?
A) It is a saturated fatty acid.
B) A diet rich in this molecule may contribute to
atherosclerosis.
C) Molecules of this type are usually liquid at
room temperature.
D) It is a saturated fatty acid and a diet
rich in this molecule may contribute to atherosclerosis.
E) It
is a saturated fatty acid, a diet rich in this molecule may contribute
to atherosclerosis, and molecules of this type are usually liquid at
room temperature.
D
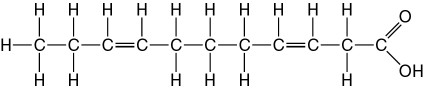
Which of the following statements is true regarding the molecule
illustrated in Figure 5.3?
A) It is a saturated fatty acid.
B) A diet rich in this molecule may contribute to
atherosclerosis.
C) Molecules of this type are usually liquid at
room temperature.
D) It is a saturated fatty acid and a diet
rich in this molecule may contribute to atherosclerosis.
E) It
is a saturated fatty acid, a diet rich in this molecule may contribute
to atherosclerosis, and molecules of this type are usually liquid at
room temperature.
C
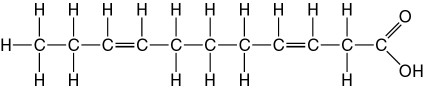
The molecule shown in Figure 5.3 is a
A) polysaccharide.
B) polypeptide.
C) saturated fatty acid.
D)
triacylglycerol.
E) unsaturated fatty acid.
E
What is the structure shown in Figure 5.4?
A) pentose molecule
B) fatty acid molecule
C) steroid molecule
D)
oligosaccharide molecule
E) phospholipid molecule
C
Which of the following statements is/are true regarding the chemical
reaction illustrated in Figure 5.5?
A) It is a hydrolysis
reaction.
B) It results in a peptide bond.
C) It joins two
fatty acids together.
D) It is a hydrolysis reaction and it
results in a peptide bond.
E) It is a hydrolysis reaction, it
results in a peptide bond, and it joins two fatty acids together.
B
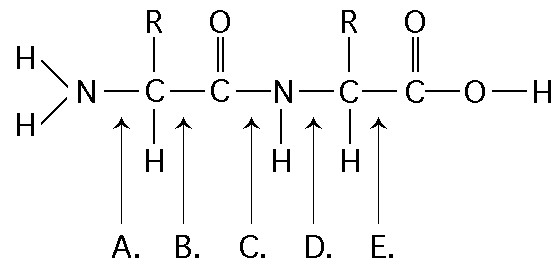
At which bond would water need to be added to achieve hydrolysis of
the peptide, back to its component amino acid?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
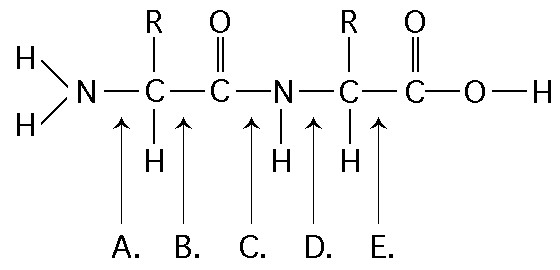
Which bond is a peptide bond?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
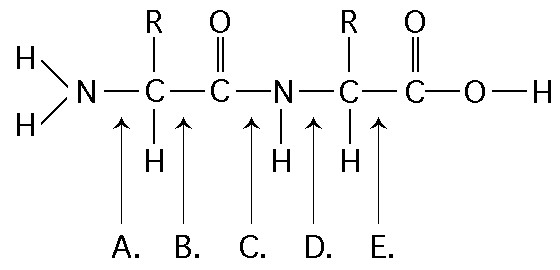
Which bond is closest to the amino terminus of the molecule?
A)
A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A
The structure depicted in Figure 5.7 shows the
A) 1-4 linkage
of the α glucose monomers of starch.
B) 1-4 linkage of the β
glucose monomers of cellulose.
C) double-helical structure of a
DNA molecule.
D) α helix secondary structure of a polypeptide.
E) β pleated sheet secondary structure of a polypeptide.
D
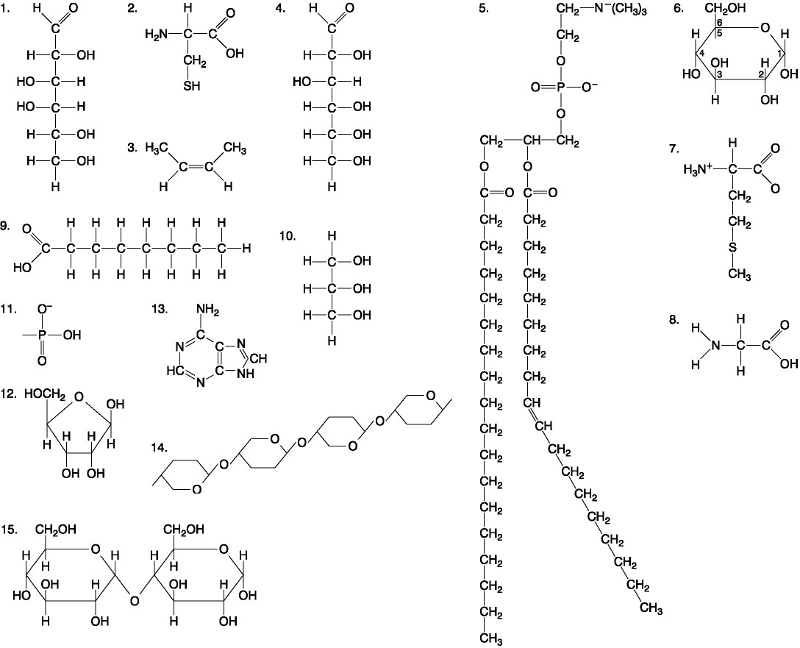
Which molecule has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties and
would be found in plasma membranes?
A) 1
B) 5
C) 6
D) 12
E) 14
B
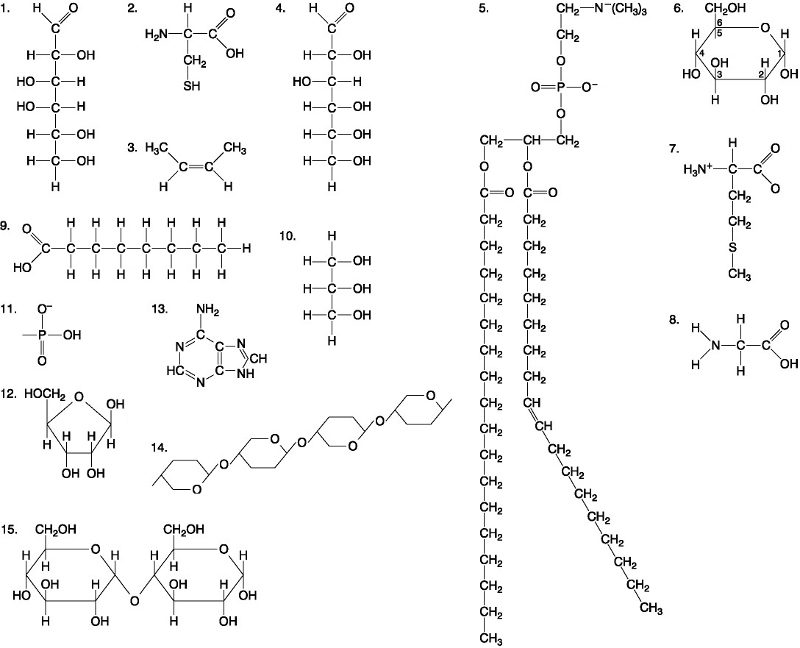
Which of the following combinations could be linked together to form
a nucleotide?
A) 1, 2, and 11
B) 3, 7, and 8
C) 5,
9, and 10
D) 11, 12, and 13
E) 12, 14, and 15
D
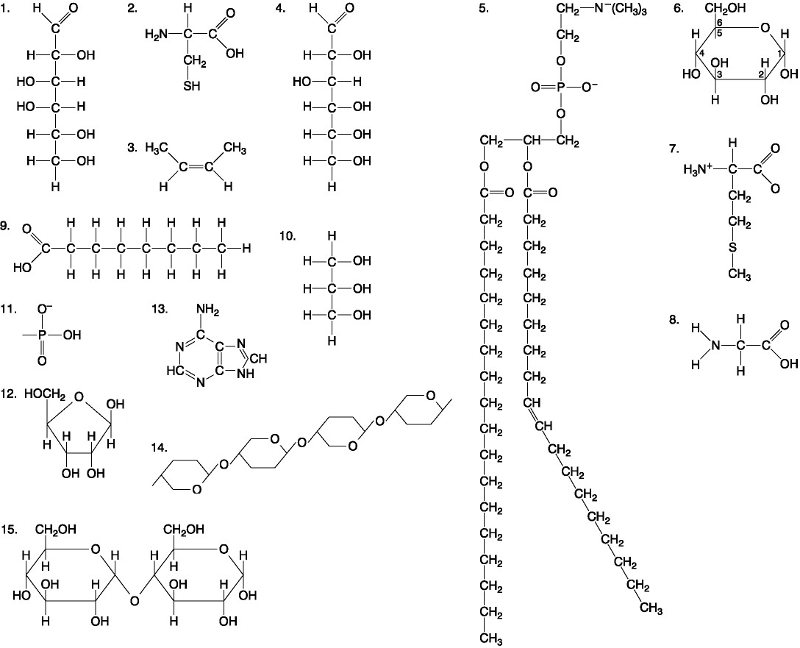
Which of the following molecules contain(s) an aldehyde type of
carbonyl functional group?
A) 1
B) 4
C) 8
D)
10
E) 1 and 4
E
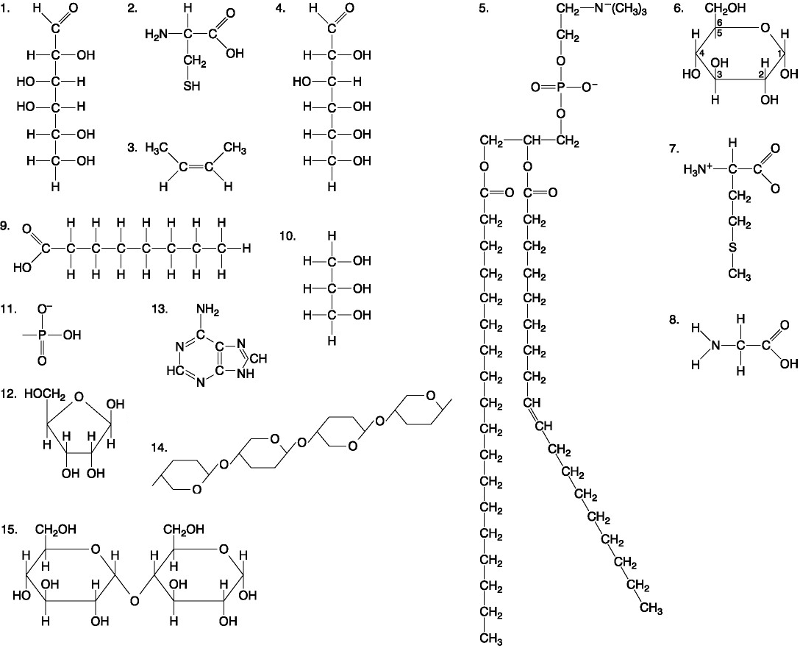
Which molecule is glycerol?
A) 1
B) 6
C) 10
D) 14
E) 15
C

Which molecule is a saturated fatty acid?
A) 1
B) 5
C) 6
D) 8
E) 9
E
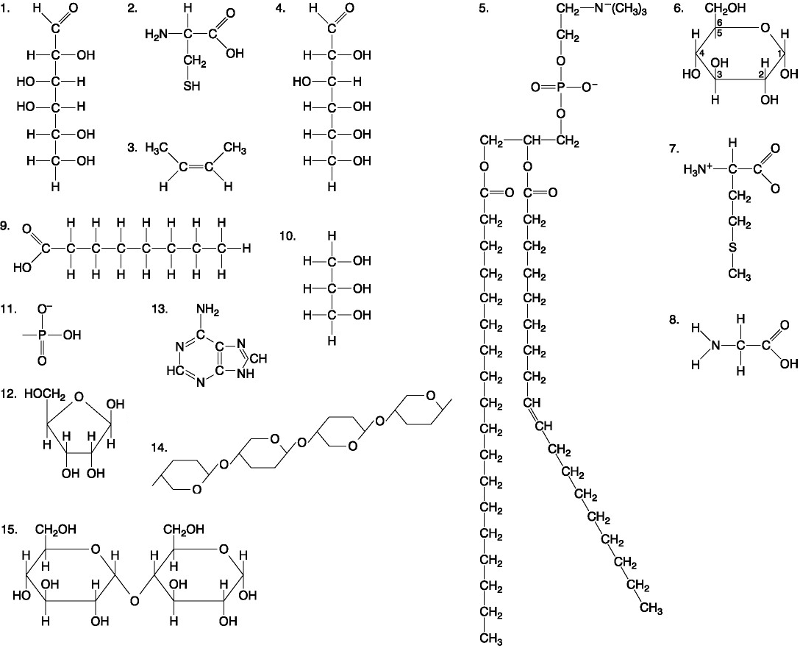
Which of the following molecules is a purine type of nitrogenous
base?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 5
D) 12
E) 13
E
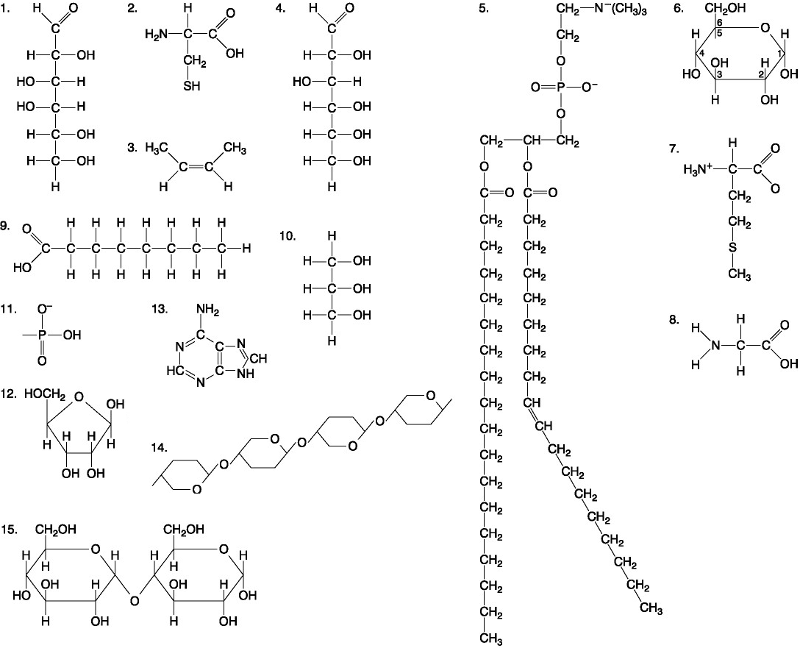
Which of the following molecules act as building blocks (monomers) of
polypeptides?
A) 1, 4, and 6
B) 2, 7, and 8
C) 7, 8,
and 13
D) 11, 12, and 13
E) 12, 13, and 15
B
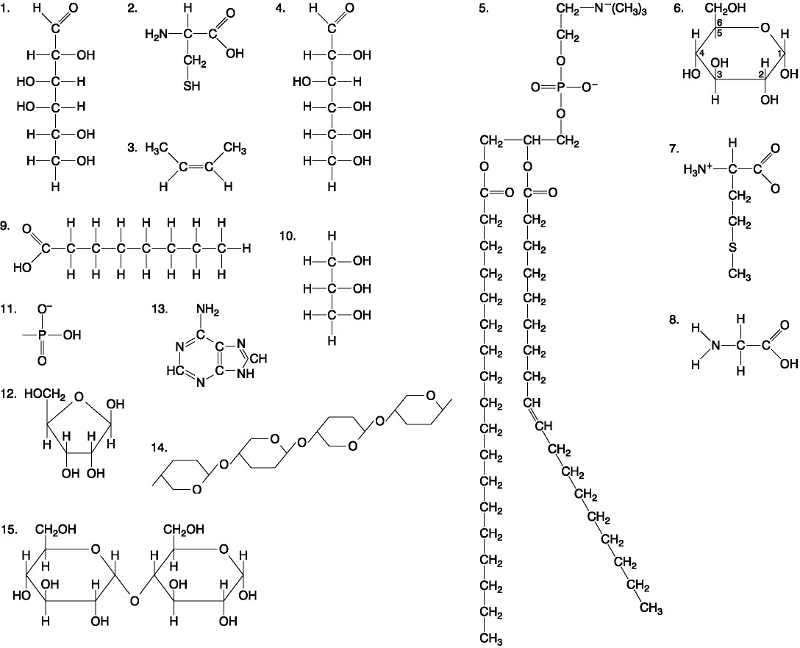
Which of the following molecules is an amino acid with a hydrophobic
R group or side chain?
A) 3
B) 7
C) 8
D) 12
E) 13
B
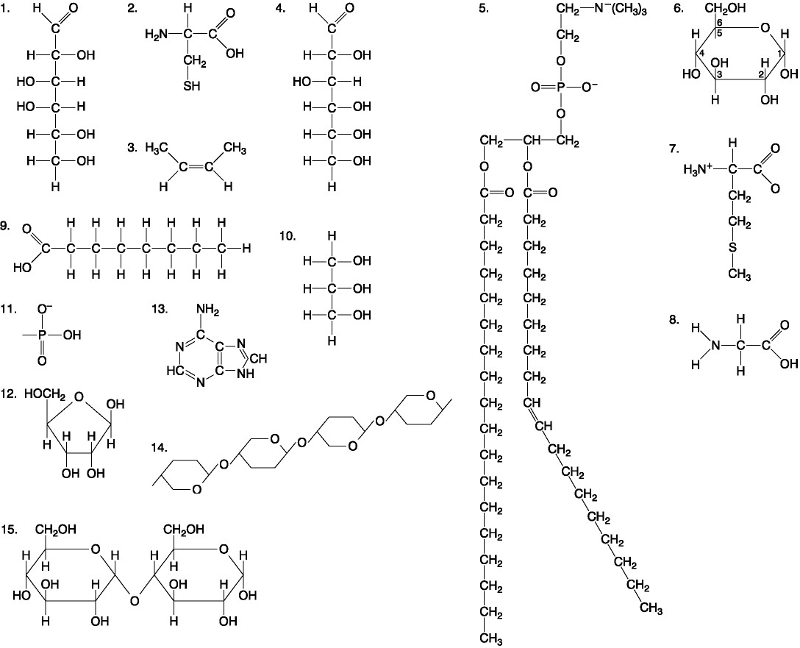
Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a
peptide bond as a result of a dehydration reaction?
A) 2 and 3
B) 3 and 7
C) 7 and 8
D) 8 and 9
E) 12 and 13
C
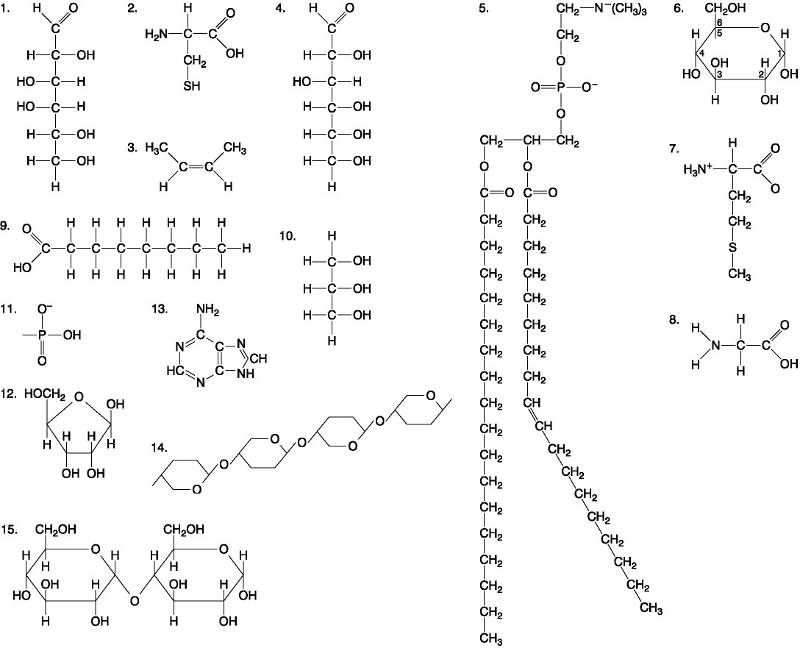
A fat (or triacylglycerol) would be formed as a result of a
dehydration reaction between
A) one molecule of 9 and three
molecules of 10.
B) three molecules of 9 and one molecule of 10.
C) one molecule of 5 and three molecules of 9.
D) three
molecules of 5 and one molecule of 9.
E) one molecule of 5 and
three molecules of 10.
B
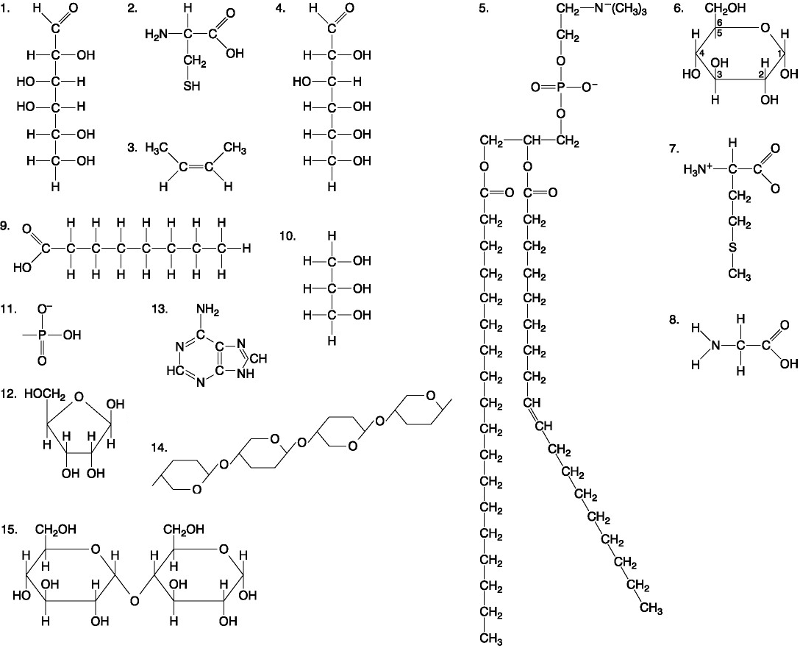
Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a
phosphodiester type of covalent bond?
A) 3 and 4
B) 3 and
8
C) 6 and 15
D) 11 and 12
E) 11 and 13
D
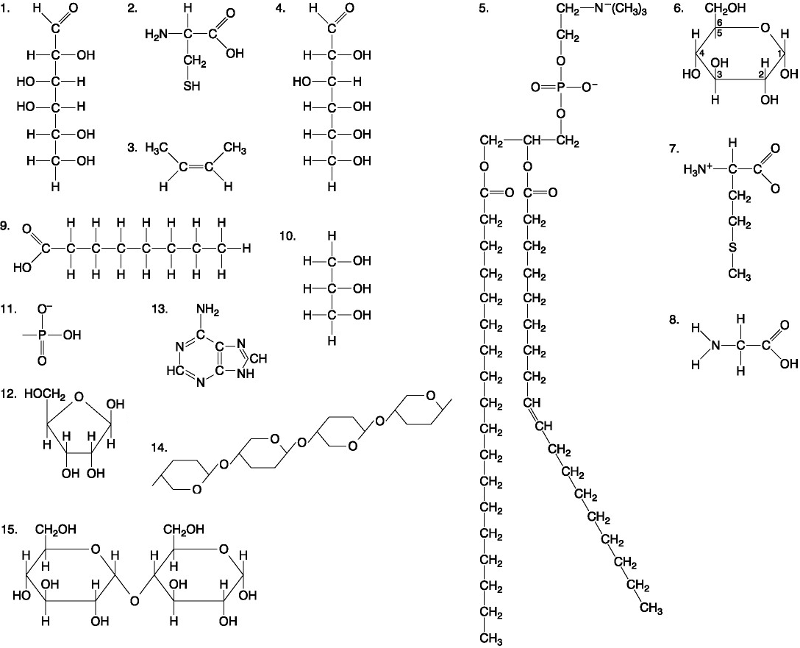
Which of the following molecules is the pentose sugar found in RNA?
A) 1
B) 4
C) 6
D) 12
E) 13
D
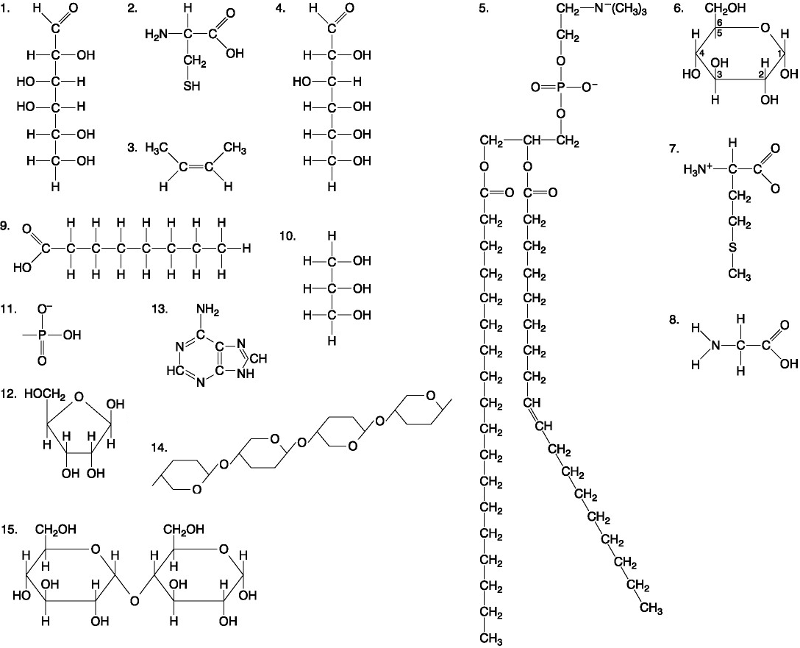
Which of the following molecules contains a glycosidic linkage type
of covalent bond?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 12
D) 13
E) 15
E
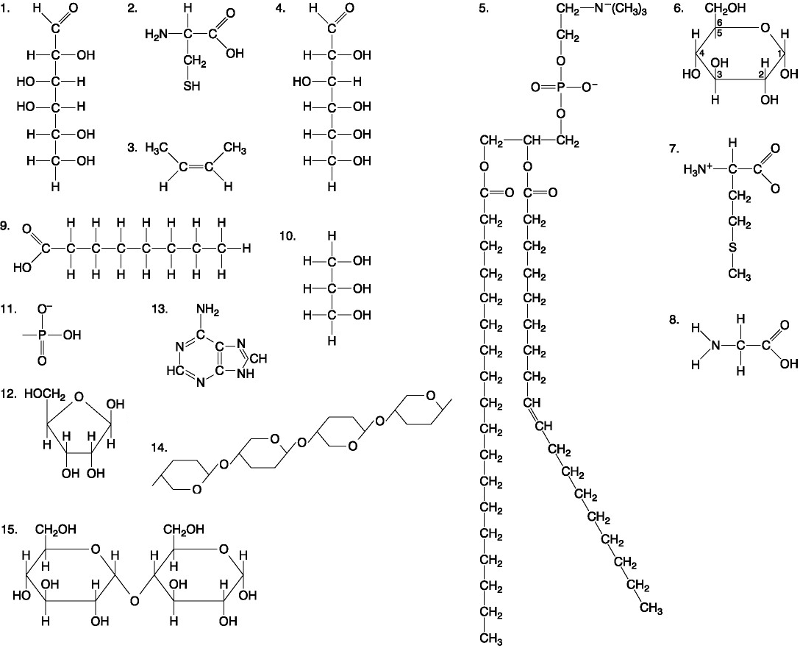
Which of the following molecules has a functional group that
frequently forms covalent bonds that maintain the tertiary structure
of a protein?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 7
D) 8
E) 9
A
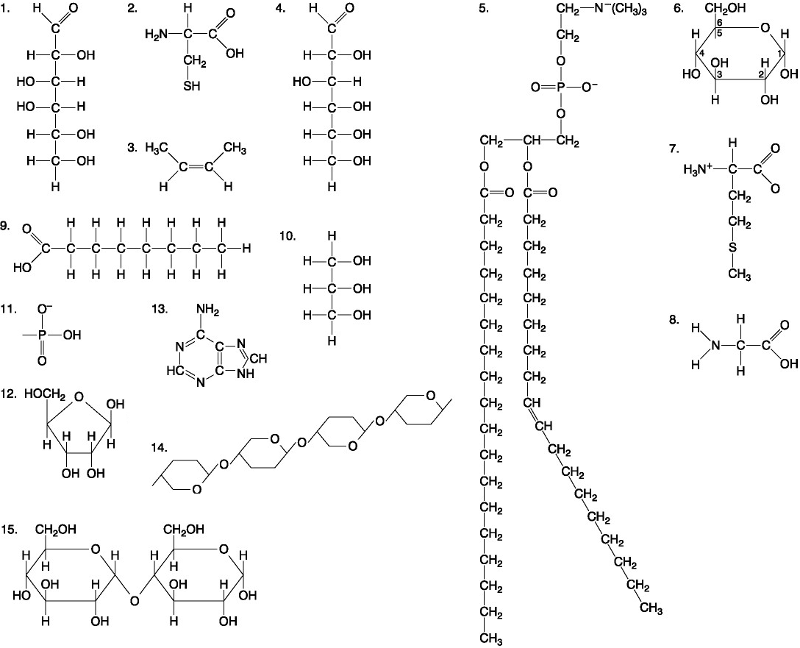
Which of the following molecules consists of a hydrophilic
"head" region and a hydrophobic "tail" region?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 7
D) 9
E) 11
B
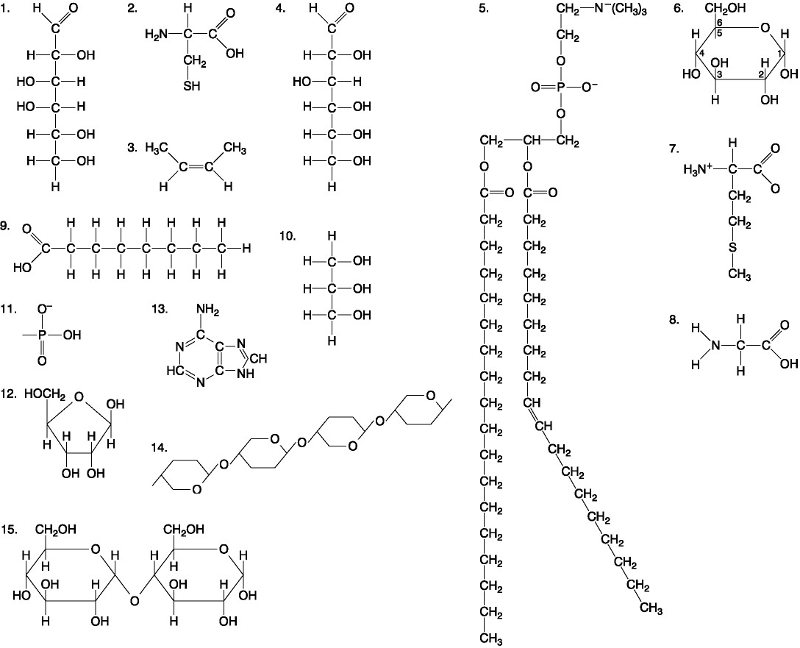
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Molecules 1 and
4 could be joined together by a glycosidic linkage to form a
disaccharide.
B) Molecules 9 and 10 could be joined together by
ester bonds to form a triacylglycerol.
C) Molecules 2 and 7
could be joined together to form a short peptide.
D) Molecules
2, 7, and 8 could be joined together to form a short peptide.
E)
Molecules 14 and 15 could be joined together to form a polypeptide.
E
Approximately 32 different monomeric carbohydrate subunits are found
in various natural polysaccharides. Proteins are composed of 20
different amino acids. DNA and RNA are each synthesized from four
nucleotides.
Among these biological polymers, which has the least structural
variety?
A) polysaccharides
B) proteins
C) DNA
D) RNA
C
Which class of biological polymer has the greatest functional
variety?
A) polysaccharides
B) proteins
C) DNA
D) RNA
B
Professor Jamey Marth at the University of California, Santa Barbara,
identified 70 molecules that are used to build cellular macromolecules
and structures. These include at least 34 saccharides, 8 nucleosides,
and 20 amino acids. In theory, then, which class of biological polymer
has the greatest information-coding capacity?
A) polysaccharides
B) proteins
C) DNA
D) RNA
A
Which of the following categories includes all others in the list?
A) monosaccharide
B) disaccharide
C) starch
D)
carbohydrate
E) polysaccharide
D
The enzyme amylase can break glycosidic linkages between glucose
monomers only if the monomers are in the α form. Which of the
following could amylase break down?
A) glycogen, starch, and
amylopectin
B) glycogen and cellulose
C) cellulose and
chitin
D) starch and chitin
E) starch, amylopectin, and cellulose
A
Which of the following statements concerning unsaturated fats is
true?
A) They are more common in animals than in plants.
B) They have double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty
acids.
C) They generally solidify at room temperature.
D)
They contain more hydrogen than do saturated fats having the same
number of carbon atoms.
E) They have fewer fatty acid molecules
per fat molecule.
B
The structural level of a protein least affected by a disruption in
hydrogen bonding is the
A) primary level.
B) secondary
level.
C) tertiary level.
D) quaternary level.
E)
All structural levels are equally affected.
A
Enzymes that break down DNA catalyze the hydrolysis of the covalent
bonds that join nucleotides together. What would happen to DNA
molecules treated with these enzymes?
A) The two strands of the
double helix would separate.
B) The phosphodiester linkages of
the polynucleotide backbone would be broken.
C) The purines
would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
D) The
pyrimidines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
E)
All bases would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
B
The molecular formula for glucose is C₆H₁₂O₆. What would be the
molecular formula for a polymer made by linking ten glucose molecules
together by dehydration reactions?
A) C₆₀H₁₂₀O₆₀
B)
C₆H₁₂O₆
C) C₆₀H₁₀₂O₅₁
D) C₆₀H₁₀₀O₅₀
E) C₆₀H₁₁₁O₅₁
C
Which of the following pairs of base sequences could form a short
stretch of a normal double helix of DNA?
A)
5'-purine-pyrimidine-purine-pyrimidine-3' with
3'-purine-pyrimidine-purine-pyrimidine-5'
B) 5'-AGCT-3' with
5'-TCGA-3'
C) 5'-GCGC-3' with 5'-TATA-3'
D) 5'-ATGC-3'
with 5'-GCAT-3'
E) All of these pairs are correct.
D