The first 28 days outside the uterus
Neonate
1-18 months
Infant
18-30 months
Toddler
30 months to 5 years
Pre-schooler
6-12 years
School age
13-18 years
Adolescence
What is the pediatric surgical team more focused on for the patient
in terms of needs
Physiological
A child less than 6 months cannot ....
Shiver
A child less than 6 months is prone to which issues (in surgery) due
to lack of temperature regulation
Hypothermia, bradycardia (slow), and acidosis
Which sinuses are present at birth
Ethmoid and maxillary
What age does the frontal sinus develop
7 years
When does the sphenoid sinus develop
After pubity
Normal heart rate for infant to 2 years
80-30 with average heart rate of 110
Normal heart rate for 2-6 year old
70-120 with average heart rate of 100
Normal heart rate for 6-10 year old
70-110 with average heart rate of 90
Normal heart rate for 10-16 year old
60-100 with average heart rate of 85
Normal respiratory rate for 1 year old
10-40 rr per min
Normal respiratory rate for 3 year old
20-30 rr per min
Normal respiratory rate for 6 year old
16-22 rr per min
Normal respiratory rate for 10 year old
16-20 rr per min
Normal respiratory rate for 17 year old
12-20 rr per min
Patients who are ...... are usually held by the anesthesia provider
during induction
2 and under
What is the appropriate out put of urine
1 to 2mL/kg/hr
A method of ECG monitoring in which the intra-arterial catheter is
inserted directly into the artery
Intra-arterial measurement
A catheter passed through a peripheral vein and ending in the
thoracic vena cava; it is used to measure venous pressure or to infuse
concentrated solutions
Central venous catheter
The standard method of monitoring blood oxygenation levels for all
age levels
Arterial blood gases
The two common types of shock seen in all age groups are
Septic and hypovolemic
A state of shock when the body is overwhelmed by the pathogenic
microorganisms and cannot adequately fight the infection. GRAM
negative within the blood.
Other causes are UTI UTI and contaminated intravascular cathetar.
Presents with reduced circulating blood volume
Septic shock
Result in decreased venous return that lowers cardiac output and
leads to poor tissue perfusion with eventual lactic acidosis.
Hypovolemic shock
What is the most common cause of hypovolemic shock in pediatric
patients and how can it be treated
Dehydration - quick fluid and blood replacement
Emergency
treatment is hypotonic solution of sodium chloride
Practically every antibiotic has been associated with the development
Pseudomembranous enterocolitis
Inflammation of the small intestine and colon
enterocolitis
What is the number one cause of death in children aged 1–15
Accidents
The most common bone fracture is of the ......., usually as a result
of shoulder dystocia
clavicle
What is the term used for difficult labor or delivery of a baby
Dystocia
Abnormal accumulation of air in the pleural cavity
Pneumothorax
What refers to patients whose body weight is 100 pounds greater than
ideal body weight
Morbid obesity
Enlargement of the heart due to the increased demands placed on the
heart, leading to congestive heart failure
Myocardial hypertrophy
What is delayed due to the poor blood supply to the adipose tissue
Healing
Obese patients are prone to an increased incidence of ......
postoperative wound infections
What is a surgical complication in which a wound ruptures along a
surgical suture
Dehiscence
What significantly improves pulmonary function in an obese patient in surgery
Reverse Trendelenburg position (Head up feet down)
What must be used with obese patients to reduce the incidence of DVT
Intermittent venous compression boots
What are the three most common complications after gastric bypass or
gastroplasty surgery
Abdominal catastrophes, internal hernia, and acute gastric distention
Often acute respiratory failure indicates peritonitis. If visceral
perforation is suspected, an exploratory laparotomy will be performed.
These can be described as ......
Abdominal catastrophes
What occur when there is protrusion of an internal organ into a
retroperitoneal fossa or a foramen
internal hernia
What occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate
in the abdomen causing its outward expansion beyond the normal girth
of the stomach and waist
acute gastric distention
What are often found during abdominal procedures on obese patients
gall stones
The pancreas produces little or no insulin, and the individual must
have daily, regular doses of insulin.
Type 1—insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
The pancreas produces different amounts of insulin. The individual is
not required to take insulin and blood glucose levels are usually
controlled by diet.
Type 2—non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)
Complications associated with diabetes
Infection
Dehydration
Poor circulation
Hypertension
and myocardial infarction
Retinopathy resulting in blindness
Medical term, commonly known as a heart attack
Myocardial infarction
The normal dosage of preoperative medication is decreased since
narcotics can induce vomiting, which predisposes the patient to fluid
and electrolyte imbalance, causing a hypoglycemic reaction
Preoperative care of a diabetic patient
Monitoring is necessary to determine the patient’s needs for insulin,
glucose, or both. A glucometer is used to measure the blood glucose
level. Urine specimens are monitored for the presence of ketones.
Intraoperative care of a diabetic patient
What is one of the most common postoperative complications of
diabetes, primarily due to diminished levels of blood flow to the
affected area
Increased rate of infection
What substances are made when the body breaks down fat for energy.
Ketones
Performing surgery in the third trimester can lead to a .......
40% risk of premature labor
What can be hard to locate in a late term uterus
Anatomical landmarks
In pregnant patients, the three important items to remember are
..............when general anesthesia must be used
Increase in preterm labor, fetal death, and low birth weight
The surgical technologist should aid the surgeon by
..............during the surgical procedure to detect contractions.
palpating the uterus
When positioning a pregnant patient in the .... position, a small
rolled sheet or pad should be placed under the right hip to slightly
laterally shift the uterus to the left.
supine
For a pregnant patient the operating room table may be ...... to the
left and placed in slight ..... to aid with venous return
tilted 30 degrees, Trendelenburg position
Relief of pressure: (A) pressure on aorta and vena cava caused by
gravid uterus; (B) pressure is relieved by placing a wedge under right hip
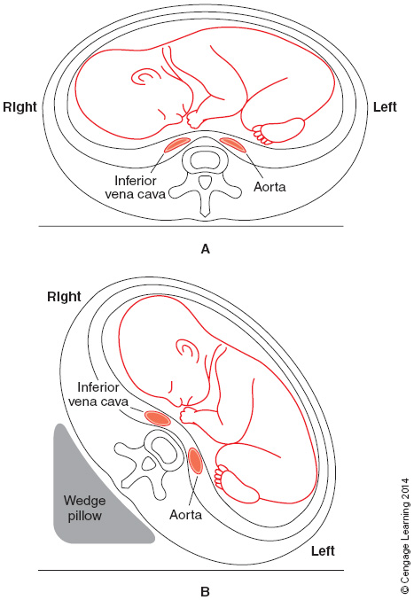
See opposite
Degree of function of an immune system that is designed to keep a
patient from infection by pathogens
Immunocompetence
Auto immune diseases include
Multiple sclerosis (debilitating - nervous system)
Lupus
erythematosus(inflammation, pain,)
Rheumatoid arthritis (chronic
joint inflammation)
What drugs are also administered to recipients of organ transplants
to prevent the recipient’s immune system from rejecting the newly
transplanted organ.
Immunosuppressant
Patients who are receiving antineoplastic agents to combat cancer are .......
Immunosuppressed.
A cancer that produces painful external and internal lesions;
internally, the lesions can cause complications, such as difficulty in
swallowing (if present in the esophagus) or bowel obstruction (when
present in the intestine)
Kaposi’s sarcoma (opportunistic in AIDS patients)
Which surgical patient may present with multiple opportunistic
infections by parasites, fungi, viruses, or bacteria; overall, the
general poor health demands special care of the patient
AIDS
For which patient should the parent(s) or legal guardian should be
present while transporting to the surgery department, and allowed in
preoperative holding and brought into PACU as soon as feasible
Patient with Down’s Syndrome
What physical traits must be taken into consideration by the
anesthesia provider and PACU personnel for a Down syndrome patient
Microgenia, muscle hypotonia, a flat nasal bridge, macroglossia, a
short neck, and excessive joint laxity.
Isolation precautions are based on .... guidelines
Center for Disease Control (CDC)
The primary routes of transmission of microorganisms
Contact: direct or indirect
Droplet
Airborne
Common
vehicle (food, water, medications, medical devices, and equipment)
Vector-borne (mosquitoes, flies, rats)
The wearing of protective attire is mandated by the
OSHA blood borne pathogens final rule
Who requires the wearing of a NIOSH-certified respirator through its
tuberculosis standards
CDC
What percentage of geriatric patients present with one or more
comorbid condition
80%
What pertains to a disease or other pathological process that occurs
simultaneously with another
Comorbid
Studies suggest that 30% to 80% of substance abusers suffer from .......
coexisting psychiatric illness
The presence of a ......... would benefit the surgical team to
provide assistance to the team and patient.
counselor or social worker
How do physicians often refer to the shorter the response time, the
greater is the chance for survival of the trauma patient
The “Golden Hour” and Trauma System
Concept that medical treatment of a trauma victim within the first
hour following injury improves patient outcomes
The "golden hour"
What should be given the sooner the better for a heart attack victim,
to give a greater chance that the heart rhythm will return to normal
with less damage to the heart muscle.
CPR
Can meet all needs required for treating trauma patients, including
qualified personnel and equipment on a 24-hour basis, offering a
comprehensive service and the highest level of surgical care.
Level I trauma center (Good Sam)
Can treat seriously injured or ill patients, but does not have all of
the resources that a Level I facility would have
Level II trauma center (CDH & Edward)
Most often a community or rural hospital in an area that does not
have a Level I or II facility. These centers offer limited care and
have resources for immediate care until the trauma patient is
stabilized and then transported to a Level I or II hospital.
Level III trauma center (Bolingbrook)
Available in some states, the center can provide advanced trauma life
support to stabilize the patient before the patient is transported to
a Level I or II hospital. It provides initial evaluation,
stabilization, diagnostic capabilities, and transfer to a higher level
of care.
Level IV trauma center
An attempt to understand the mechanism of injury and the action and
effect of a particular type of force on the human body, for instance a
bullet wound and knife wound will have different effects on the body
kinematics
What results from forces such as deceleration, acceleration,
compression, and shearing
Blunt trauma
Examples in which blunt trauma is sustained include
motor vehicle accidents (MVAs)
falls
assaults (hit with a
fist or blunt object)
sports injuries
What are classified as low velocity or high velocity
Bullet injuries
(bullet travels 1,000 feet per second or
slower) or high velocity (3,000 feet per second; commonly seen with
military weapons
A scoring system used to assess the severity of a traumatic wound and
to determine the condition of a patient
Revised Trauma Score
What involves the Glasgow Coma Scale, Neuro 3-15 scale, as well as
other physiological factors.
RTS
Hair, tissue, and gunpowder residue may be found on the hands of the ....
victim
What should be placed in a bag, and taped, if they do not require
surgery to preserve evidence
Hands
Vietnam veterans who have PTSD (1980) symptoms were at the time of
the war said to have
post-Vietnam syndrome
Epiphyses not closed until age 20
Bone growth plate
Male genitals
testes do not descend until 1 year old
Bodily fluid
75% water first post natal week
60% 1-2 year
Caloric requirements for pediatrics
Much higher than an adult
Physical priorities in OR/ER
Open and maintain airway
Stabilize spine
IV catheter & fluids
Obesity issues/complications
varicose veins, edema in lower extremities, liver issues, pituitary issues
Grounding pad placement on obese patient
Abdomen, thighs, buttocks
Insulin =
breakdown of sugar
Diabetic positioning priority
Pad all bony prominences
Pregnancy and surgery
2nd trimester "golden window"
Asymptomatic
No symptoms
Hearing impaired patient will need
an interpreter
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TB
Collection of bullets for evidence
Do not use serrated instruments or powdered gloves
Hypothermia
Below 35 degrees