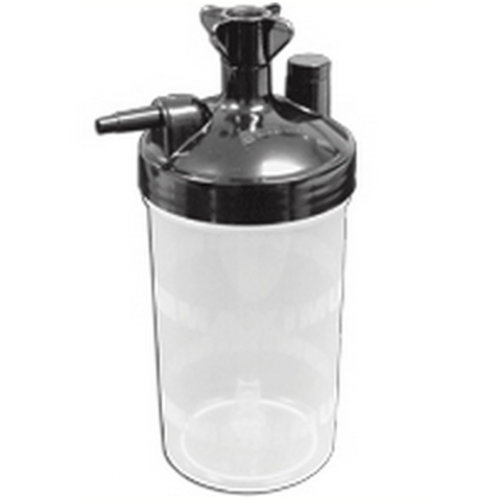

What is pictured?
A bubble humidifier.
What happens when you obstruct the bubble humidifier or kink the tubing?
The pop off valve alarm sounds, however the device still produces the same amount of bubbles.
What happens when you loosen the humidifier jar and kink a non-kinkable tubing?
The pop off valve alarm does not sound.
What happens when you kink the tubing with a bubble humidifier at a flow rate >15 L/M?
The pop off valve alarm constantly went off, the bubbles were much faster.
What are some reasons to use Humidity?
- It makes the patient more comfortable
- It's used to bypass the patients upper airway by intubation or inserting an endotracheal tube. Which provides 100% humidity at 37 degrees.
What is absolute humidity at body temperature?
It is 44 mg/ L which equals 100%
For example, if asked if a patient has 22 mg/ L , what percent humidity do they have?
They will have 50% humidity.
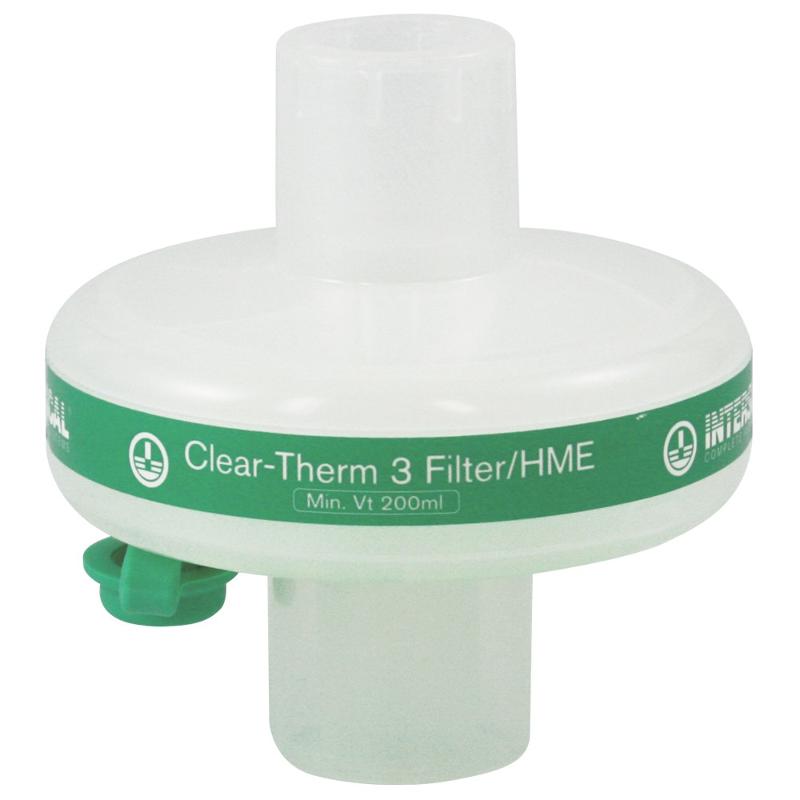

What is shown?
An HME
What does an HME do?
It is a heat and moisture exchanger which can attach to an endotracheal tube. It has an aerosol mode that only allows air in.
What are some advantages of using an HME?
1. It allows you to be out and about
2. It's cheaper
3. It decreases the chance of infection
4. It leaves no condensation
What are the limitations of using an HME?
1. The patient has to have a body temperature in the normal range.
2. Can only be used on patients with normal tidal volumes.
3. It can't be used on patients with lots of secretions
What effect does moisture have on HME function?
IT causes an increase resistance.

What is shown? What is its advantage?
A wick humidifier with heated wire technology. Does NOT produce a lot of condensation.
The temperature at the humidifier and the WYE should be the same.

What is shown?
A cascade with non heated wire technology. This creates tons of condensation.
What general types of humidifiers are the most effecient?
Heated humidifiers because they keep airways and secretions moist.
What are two advantages of using a continuous feed system to fill a humidifier?
You don't get any leaks
Labor savings
What are two disadvantages of using a continuous feed system to fill a humidifier?
1. Its more expensive
2. If it malfunctions you get too much water in the unit and can possible drown them with water.
Define humidity and how it differs from percent humidity?
Humidity is the amount of water in a given volume of gas. Percent humdity is dependent on temperature. For example at a body temperature of 37 degrees Celsius you have 44 mmg/L ,@ 100% humidity. at 22 mg/L you have 50% humidity.
What are two reasons for using humidifiers in the clinical setting?
1. It can make the patient feel more comfortable
2. Provides 100% humidity at 37 degrees celcius
What 3 complications can result if inadequate humidification is provided?
1. Patient can get thick, dehydrated secretions
2. Dry, non productive cough
3. Increased airway resistance
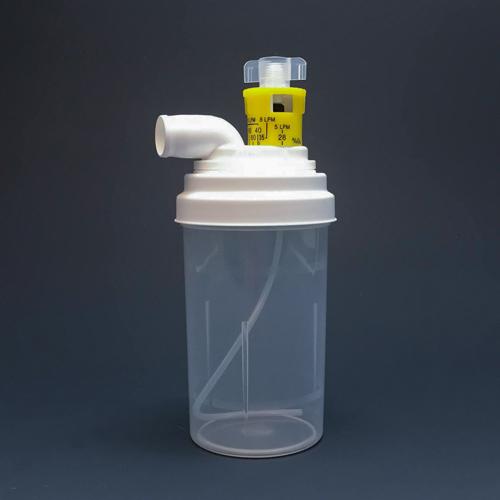

What is shown?
A Large volume nebulizer
With the LVN set at 35% and the flow meter at 10 L/M, what is the total flow being delivered?
Ratio: 5:1
(5 + 1) x (10 l/m) = 60 L/M

What is shown?
Corrugated Tubing
If you put water in the corrugated tubing attached to the LVN, what happens?
Water creates back pressure and it cant entrain room air. A water trap should be used in this cause.

What is shown? What are they used for?
An aerosol mask (used for spontaneous breathing patients)
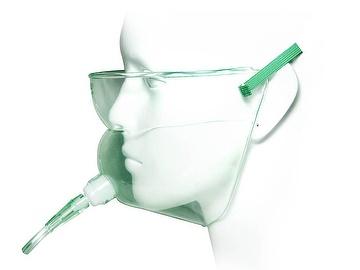
What is shown? What are they used for?
A face tent. (used for patients with injuries to the face)

What is shown? What are they used for?
Tracheotomy collar (used for spontaneous breathing trached patients.)

What is shown? What are they used for?
Briggs adapter (T piece) (used for intubated patients.)

What is shown?
A WYE
It's a valve that lets patient inhale (the valve opens.) and closes when the patient exhales (exhalation valve opens.)so they don't re-breathe their CO2.
What type of humidifier would use on a nasal cannula set at 2 L/M
None, the AARC guidelines states that a bubble bottle should be used at 4 L/M or above, there is sufficient humidity in room air to meet the patients need.
What type of humidifier would use use on a nasal cannula running at 6 L/M?
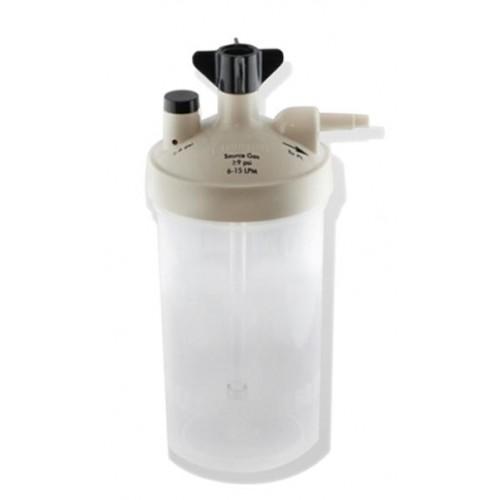

A bubble humidifier bottle.
Because it is an AARC requirement. A this Liter Flow it can cause patient discomfort.
What type of humidifier would use use on a post operative patient on short term mechanical ventilation?
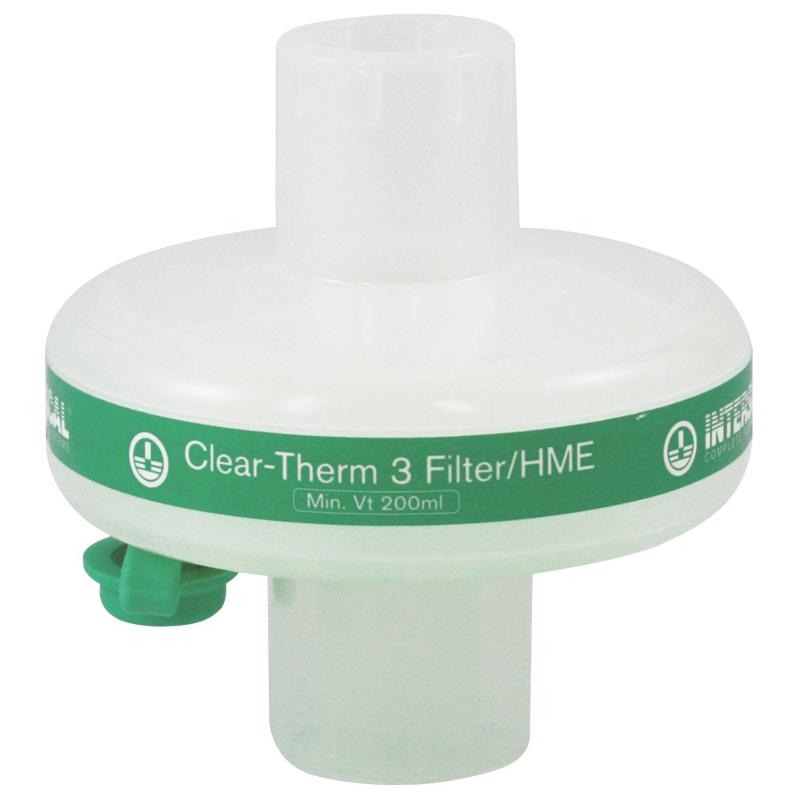

an HME.
Because it is less expensive.
What type of humidifier would use use on a long term mechanically ventilated patient with think, dry secretions.

A heated humidifier
Because it can keep the secretions moist.
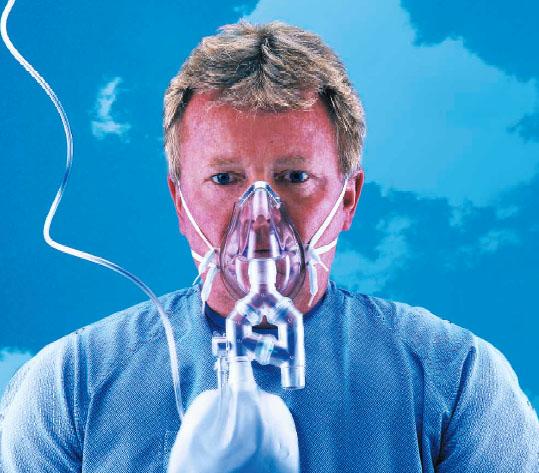
List two differences between a high flow nonrebreathing mask (HiOX) and a regular nonrebreathing mask.
1. A HiOX mask can be used in conjunction with a nebulizer to give patients treatment. A NRM can't do this.
2. A HiOx has the option to allow room air to fill the patients dead space by the sequential dilution valve, if the patient's tidal volume exceeds .75 liters and empties the reservoir.
Explain why a high FiO2 would occurs if the venturi device was covered with a sheet?
How does this effect the overall output?
This increase in FiO2 would occur because the sheet is blocking the ports, meaning that less room air is being entrained.
The overall output would decrease the total flow.
What is the formula for estimated flow demand?
Ve x 3 = Estimated Flow demand
Mrs. Lan is a 70 year old woman with COPD who is admitted to the ER wearing a nonrebreathing mask at 10 LPM. Mrs. Lan, who was awake and alert when the ambulance arrive is now extremely lethargic and somnolent. The ER physician orders you to change the oxygen delivery device to a nasal cannula.
Explain the cause for the patients lethargy.
Because Mrs. Lan is a CO2 retainer, her stimulus to breathe is the lack of oxygen. With the high FiO2 that she is receiving from the NRM, her PaO2 has risen, and her chemo-receptors are no longer telling her to breathe.
If the patient were to remain on the NRM for at least 24 hours, what complications / hazards can result from:
1. The delivery method?
2. The high oxygen concentration?
1. The patient can get pressure sores on their nose.
2. The patient may get oxygen toxicity, which can knock out the hypoxic drive in COPD patient.
A patient is on a Venti mask using an FiO2 of 28%. The patient is noted to have a minute ventilation of 15 L/M. what is the minimum liter flow, at this FiO2 required to meet the patients inspiratory flow demand?
First, we have to find the estimated flow demand.
(15 x 3 = 45 L/M)
Next: FInd the entrainment ratio for 28% = 10:1
(10+1) x ? = 45 L/M
11 x ? = 45 L/M
11 11
x = 4 L/M
Why is a minimum flow rate of 5 L/M recommended for oxygen delivery by mask?
To flush out the exhaled CO2 so the patient does not re-breathe it.
Why will an air entrainment mask never deliver 100% oxygen?
Because it always entrains room air.
You observe a patient wearing a NRM mask and note that the bag completely deflates with each inspiration. What actions should be taken?
You should increase the liter flow.
What Oxygen delivery device would you recommend to a patient who has just been resuscitated and is spontaneous breathing?
A Nonrebreathing mask.
List 3 factors that will affect the FiO2 delivered by a low flow oxygen system?
1. The patients Vt
2. The patients RR
3. The liter flow
List two advantages of using oxygen delivery devices such as the mustache reservoir or pendant cannula?
1. Saves money
2. Conserves O2
Explain how the pulse device works?
Works at the start of a patient's inhalation.
Describe an easy method of determining the number of stages in a multistage regulator?
Count the number of pressure relief valves.
Which of the following is considered a high flow (fixed performance) oxygen delivery system(s)
a. Nasal Cannula
b. Nasal catheter
c. Air entrainment
d. partial rebreathing mask
C

What is shown? what three monitors does this system include? Where are these gases sampled?

an INOmaxDS *for nitric oxide therapy.
It has an oxygen, nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide monitor.
The gases are sampled right before the patients WYE.

What are 5 reasons to utilize heliox therapy?
1. To manage asthmatic patients w/ acute respiratory failure
2. Treat postextubation stridor
3.Adjunct with the treatment of refractory croup
4. To administer anesthetic gases to patients with small dia tubes
5. TO provide support for patients with severe airway obstruction
What conclusion can you make about the density of this mixture? What type of flow does it produce and how can it be delivered to the patient.
Heliox is less dense then oxygen. It can create, smooth laminar flow and can be delivered to an intubated patient or one who is using a non rebreathing mask.
What are the ratios for an:
80/20
70/30
60/40
1.8 (brown body, green shoulder)
1.6 (green body brown shoulder.)
1.4 (two separate cylinders.)
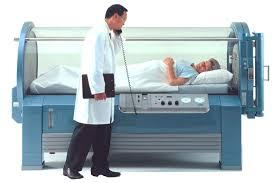
What does a hyperbaric oxygen expose the patient to?
What 10 conditions does it treat?
It exposes the patient to greater than atmospheric pressure and 100% oxygen.
- decompression sickness (divers surface to quickly.)
- Air embolism
- CO poisoning
- Smoke inhalation
- Wound healing
- Gas Gangrene
- Thermal injuries
-Refractory Osteomylitis
-Cyanide Poisoning
- Anaerobic infections
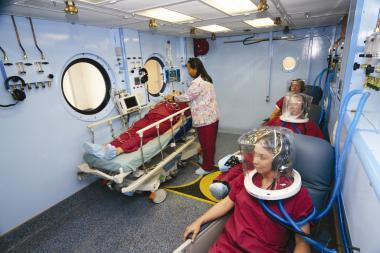
What is shown?
What gas compresses the chamber?
What gas does the patient breathe in?
A multiplace chamber
Room air compresses the chamber
The patient breathes in 100% oxygen
Advantage: Caregivers are able to get pressured and get inside to help multiple patients.
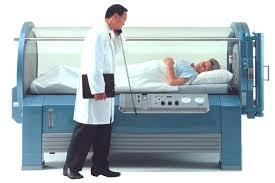
What is shown?
What gas compresses the chamber?
What gas does the patient breathe in?
A monoplace chamber
oxygen compresses the chamber
the patient breathes in 100% oxygen
What are the contraindications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
- Congenital spherocytosis
- High fevers
- Hypercapnia (>60 mmHg)
- Obstructive Airway disease
- Optic Neuritis
- Pneumothorax
- Seizure disorders
- Sinusitis
- Upper Resp. Infections
- Viral infections