Where does the CCA bifurcate?
at the level of the
superior thyroid cartilage
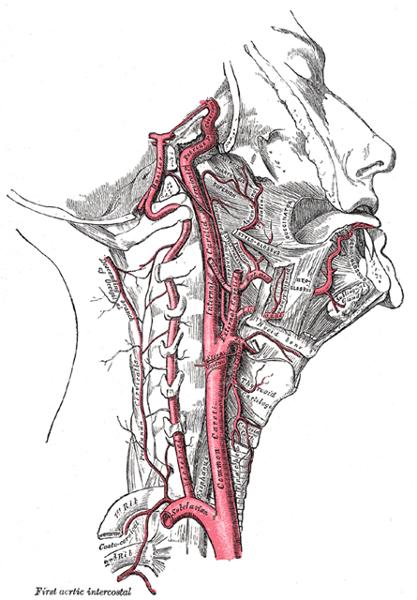
What is the first branch of the subclavian artery?
vertebral
What does systemic system on each side of the neck imply?
waveform should be the same on each side.
What is the function of the extracranial cerebrovascular system function?
Supply blood flow to
cerebral hemispheres
eyes
face muscles
forehead
scalp
Where does the vertebrals supply blood to?
- Brain stem
- Cerebellum
- Undersurface of the cerebral hemispheres
Where does the carotid artery supply blood to?
- Eyes
- Anterior 2/3 of brain
Name the branches of the aortic arch
- Right Innominate/Brachiocephalic
- Right CCA
- Right Subclavian artery
- Left CCA
- Left Subclavian artery
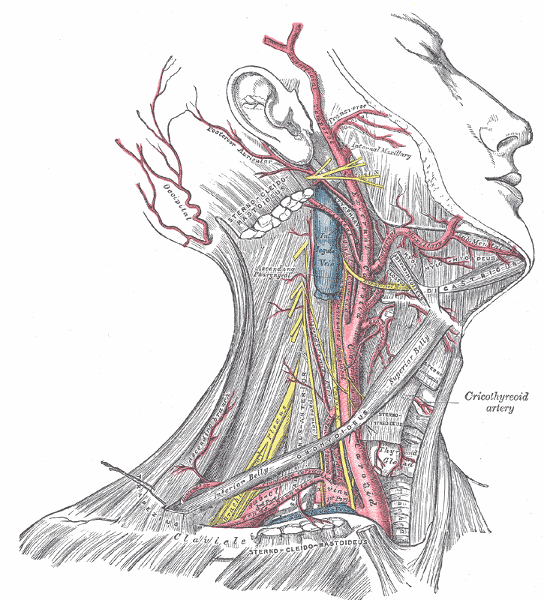
Where does the ECA supply blood to?
face
neck
scalp
Name the branches of the ECA.
- Superior thyroid
- Ascending pharyngeal
- Lingual
- Facial
- Occipital
- Posterior auricular
- Superficial temporal
- Maxillary
Name the 4 divisions of the ICA.
- Cervical
- Petrous
- Cavernous
- Cerebral
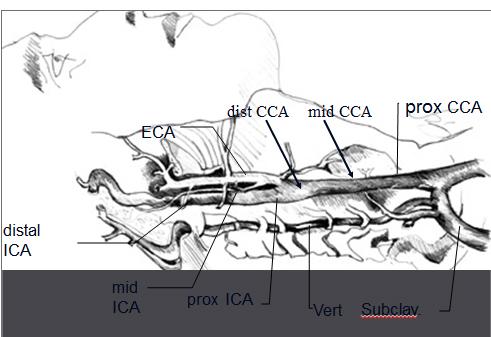
Explain the location of the ICA compared to the ECA.
posterior and lateral
What type of flow is expected in the bulb of the carotid?
turbulent
What is the flow of the vertebral arteries?
Posterior circulation
- 1st branch of the SCA
- Pass cranially through the fossae of the transverse processes of the upper 6 cervical vertebrae
- Enters the skull through the foramen magnum, joins contralateral vertebral
- Together they form the Basilar artery (intracranially)
What do the two vertebrals form?
Basilar artery
What is the diameter of the CCA?
5-6 mm
What is the diameter of the ICA?
4-5 mm
What is the diameter of the ECA?
3-4 mm
What is the diameter of the vertebral artery?
2-3 mm
How much of the carotid's blood enters the brain via the ICA?
80%
How much of the carotid's blood supplies the face and neck via the ECA?
20%
Explain the waveform of the CCA
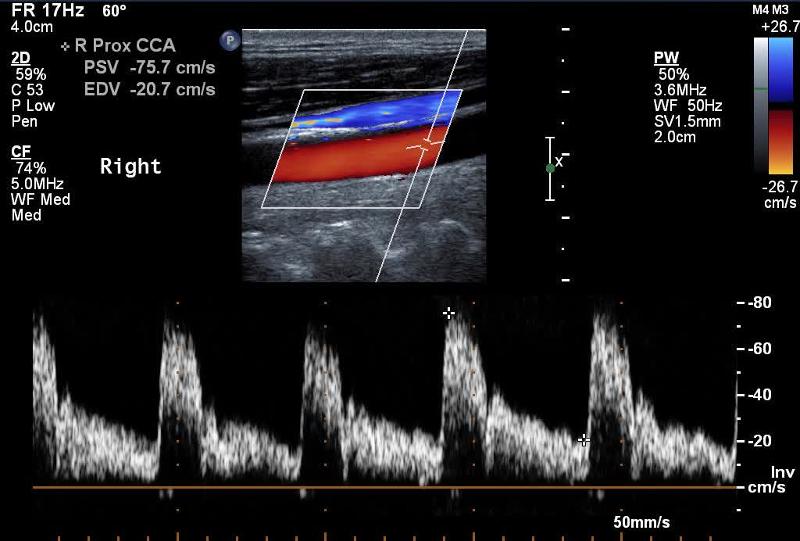
Mimics both ICA and ECA waveforms
Explain the waveform of the ICA
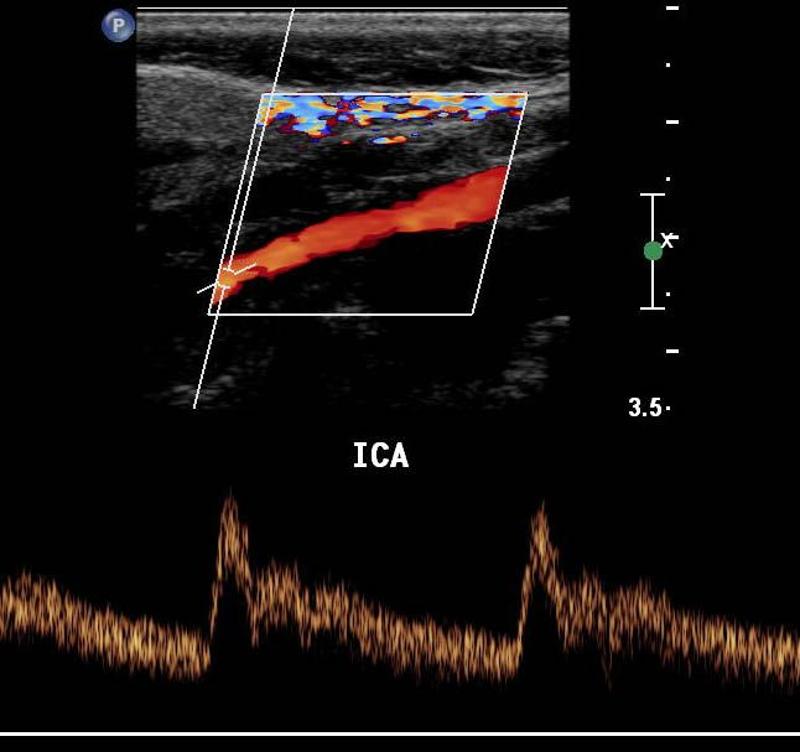
low resistant - constant forward flow
Forward flow throughout the cardiac cycle
Explain the waveform of the ECA
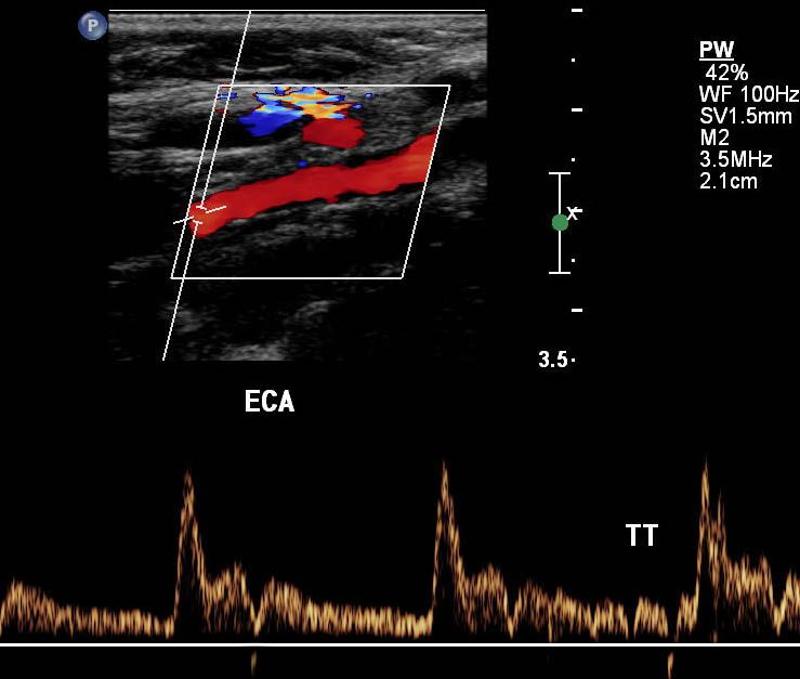
high resistant
steep forward stroke
Forward flow during systole, low or reverse diastolic component
Explain the waveform of the vertebral artery
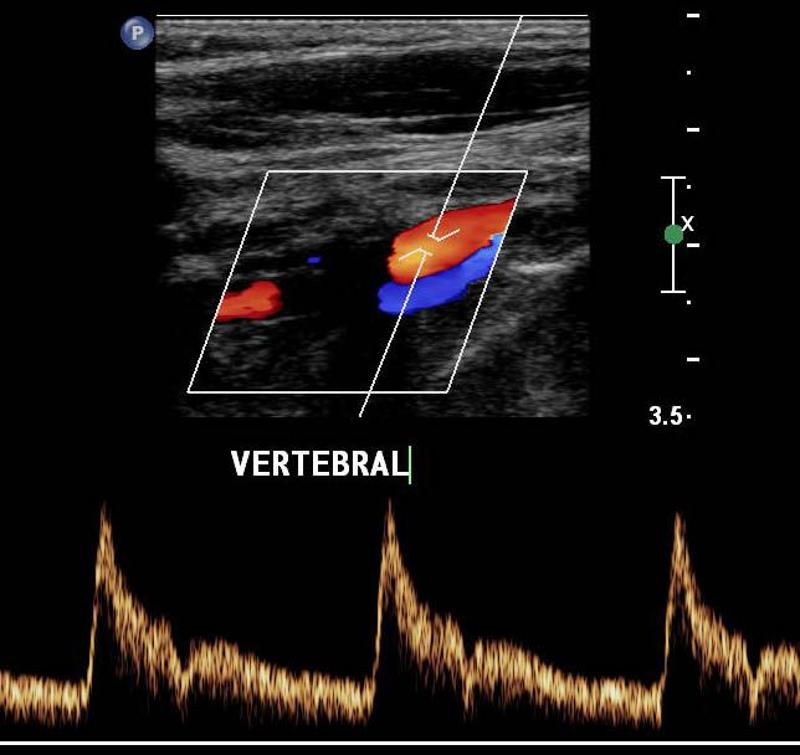
low resistant
What is resistance determined by?
diastole
less diastole = high resistance
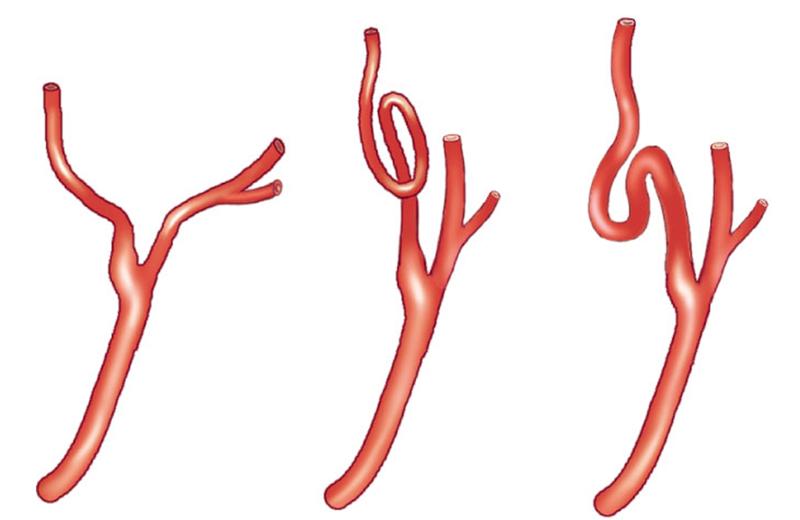
What causes tortuous vessels?
can be born this way
can happen over time as people age they shrink
*elevation can result but state that vessel was tortuous
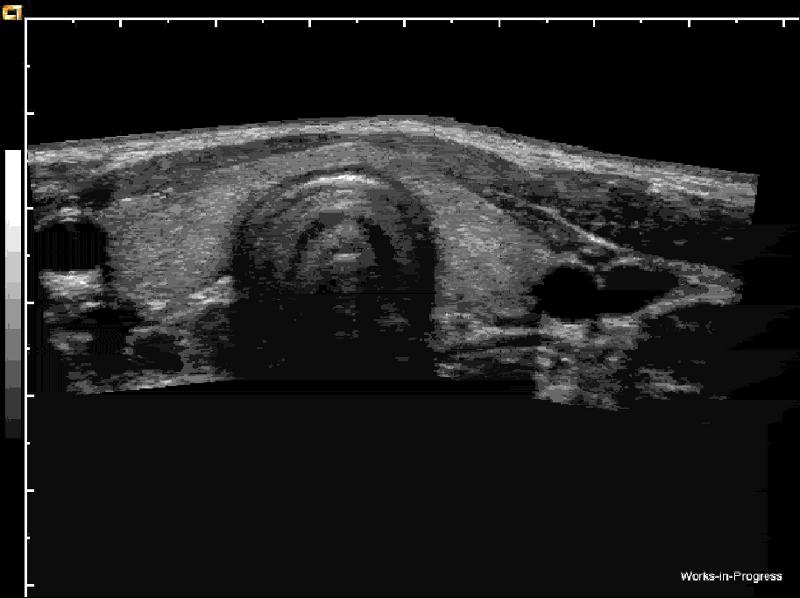
Which is the left CCA?
right
On what side is the notch in long?
superior
On what side is the notch in transverse?
patient right
Where is the notch when imaging the right cerebrovascular system in transverse,
posterior
When imaging the left cerebrovascular system in transverse, where will the notch be?
anterior
How should plaque be measured?
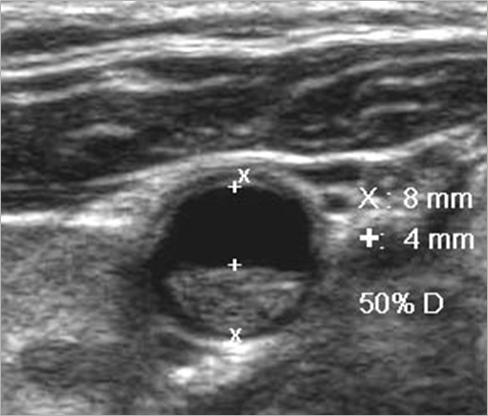
transverse measurement
lumen vs true lumen
Why is plaque measured in transverse?
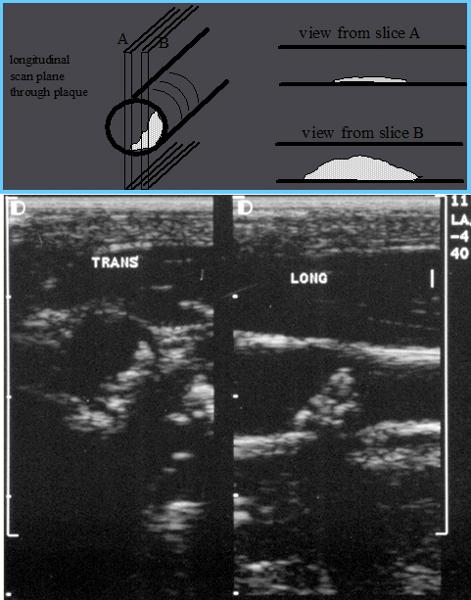
Longitudinal estimation of stenosis from B-mode image is usually unreliable, use transverse image.
*This minor plaque can be made to appear more or less stenotic in longitudinal view
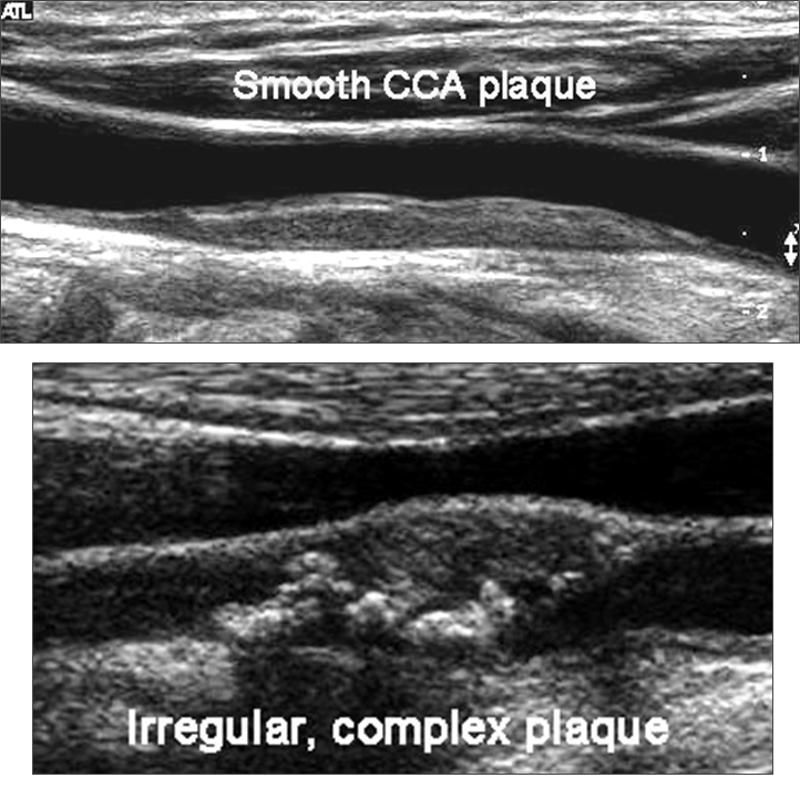
Plaque Morphology
How do you tell the difference between the ICA and ECA?
- Anatomy
- posterior position of ICA
- branches of ECA
- ICA size: not reliable when diseased
- Doppler waveforms & sounds
- ICA = low resistance
- ECA = high resistance
ICA lies _________ in the neck (95%)
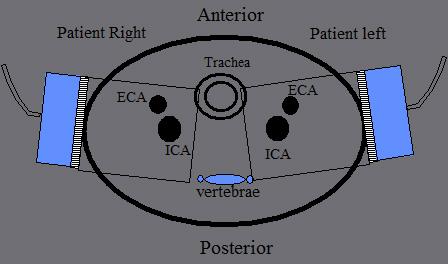
ICA lies posterior in the neck (95%)
ECA position, whether lateral, anterior or medial, is _________.
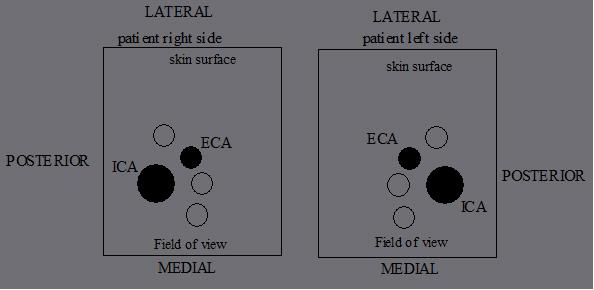
ECA position, whether lateral, anterior or medial, is variable
...
...
...
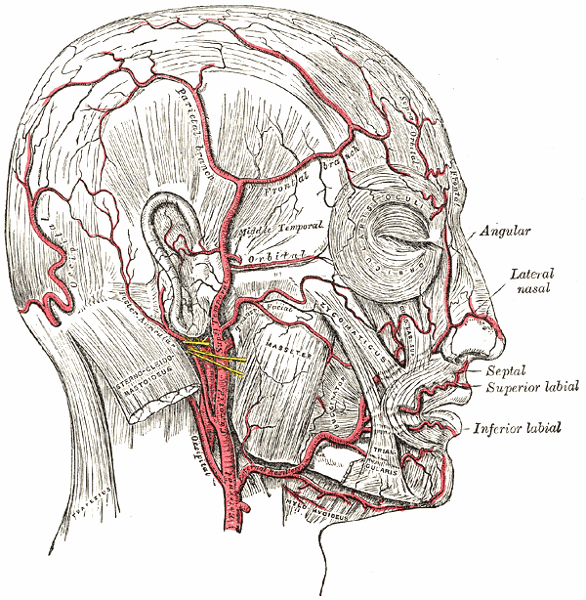
What are the four sets of the ECA branches?
Anterior
Posterior
Ascending
terminal
What are the anterior branches of the ECA?
- Superior Thyroid
- Lingual
- External Maxillary (facial)
What are the posterior branches of the ECA?
- Occipital
- Posterior Auricular
What are the ascending branches of the ECA?
Ascending Pharyngeal
What are the terminal branches of the ECA?
- Superficial Temporal
- Internal Maxillary
What is Plaque?
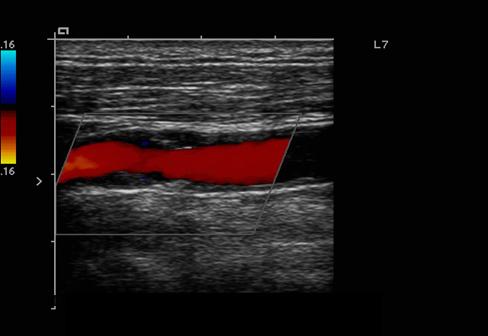
Atherosclerotic material that builds up on the walls of arteries
- It restricts flow
- It can break loose
What is a lumen?
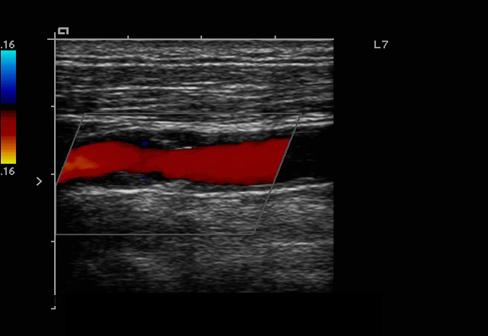
The flow space within a vessel
What is residual lumen?
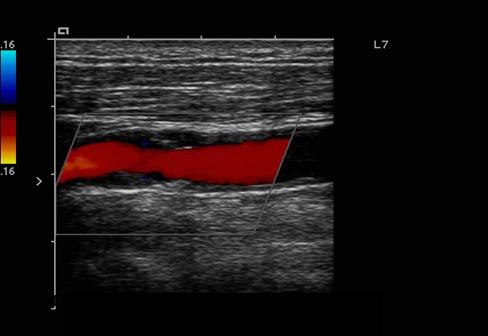
amount of flow space after accounting for the plaque
What is a Bifurcation?
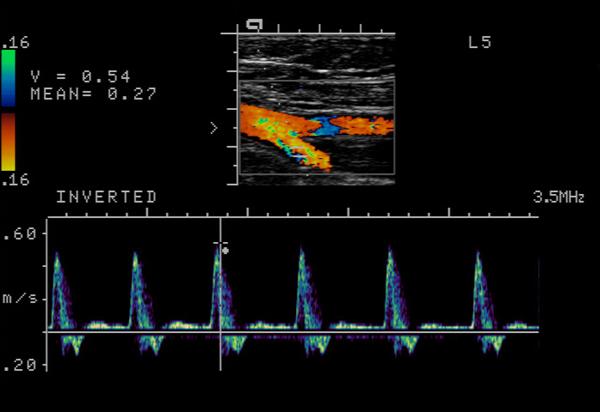
The point of vessel division
- can be a common site of stenosis
What are Collateral Circulation?
- Alternate pathways for blood flow that become functional after obstruction.
- Detours
What is an Embolus?
An object traveling through the circulation that can cause occlusion
What are the different types of an Embolus?
air
tumor
fat
bullets
foam
clot
What is hemodynamics?
blood flow characteristics
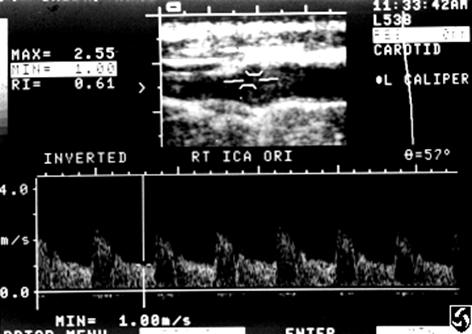
What is the Doppler angle?
The angle of the Doppler beam with respect to the angle of blood flow
Angle of Incidence
Angle theta q
What is the best Doppler angle?
0 o
What is the Optimal Doppler angle?
45o to 60o
What is the worst Doppler angle?
90o
...
Explain angle correct?
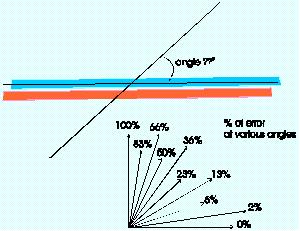
Visually adding a correction factor to the Doppler angle so that correct velocities can be calculated
What is Spectral Analysis?
- Plotting of returned Doppler signals
- frequency shifts on the vertical axis
- amplitude on the “Z” axis
- Time on the horizontal axis
Explain velocity?
- The speed of blood
- Calculated from Doppler frequency shift & Doppler angle
- velocity is proportional to frequency shift
- Expressed as cm or m / second
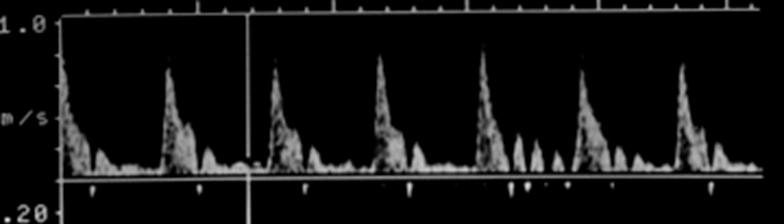
Where is peak systole?
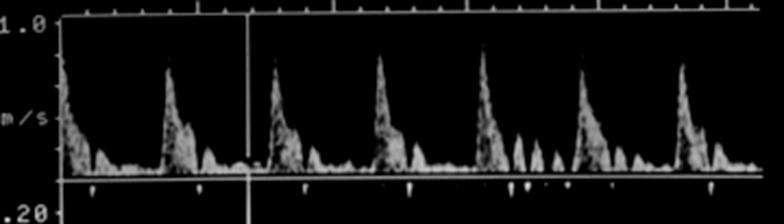
The highest point on the wave form
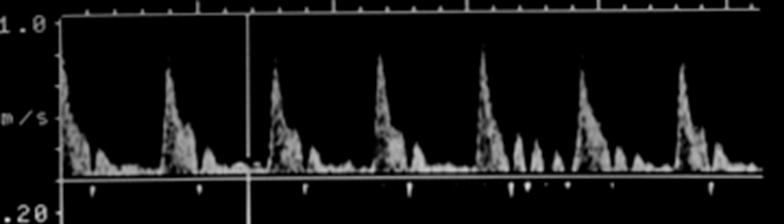
Where is end diastole?
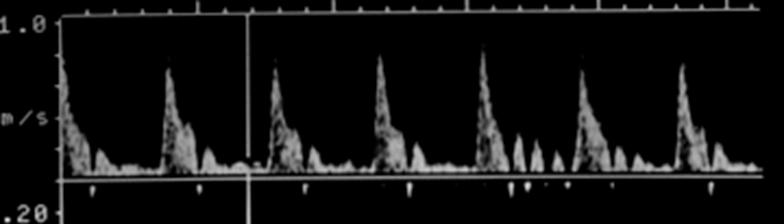
The point just prior to the systolic upstroke
Beam Steering
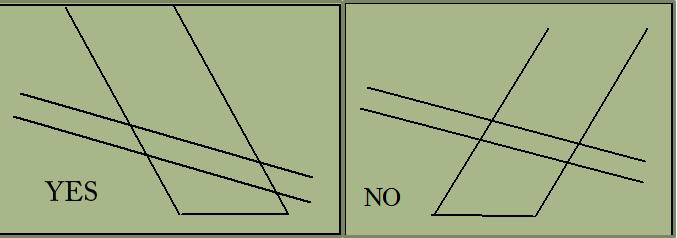
Depth penetration may be improved by _____________________ .
Depth penetration may be improved by not steering the Doppler
...
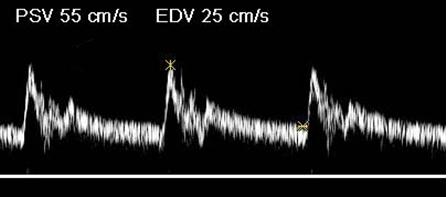
Where is the waveform?
ICA
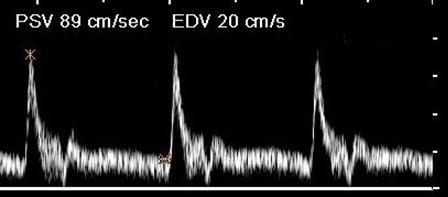
Where is the waveform?
CCA
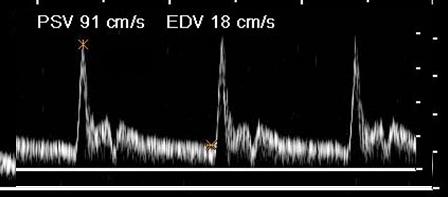
Where is the waveform?
ECA
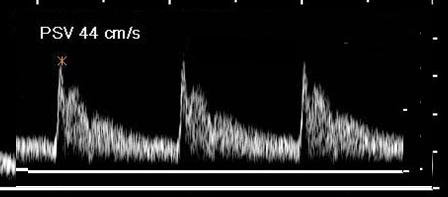
Where is the waveform?
vertebral
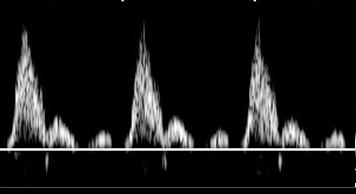
Where is the waveform?
subclavian
Hypoechoic / Anechoic
Dark or black areas on the image caused by objects with little or no reflectivity
Echodense/ Echogenic
Bright areas on the image caused by highly reflective material
Distal / Proximal Limits
The farthest and closest region that can be visualized
Plaque
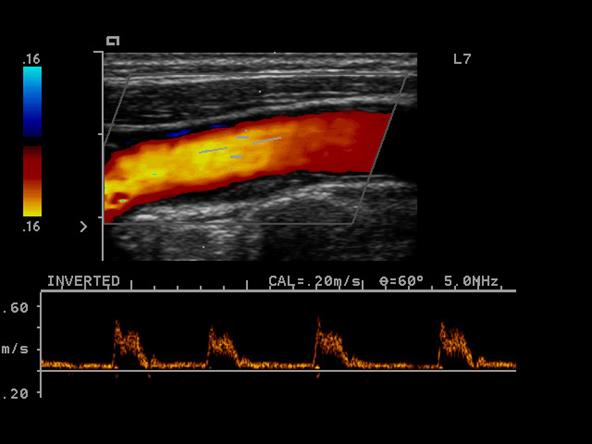
A swollen area of the lining of an artery formed by the deposition of lipids
Calcific Plaque
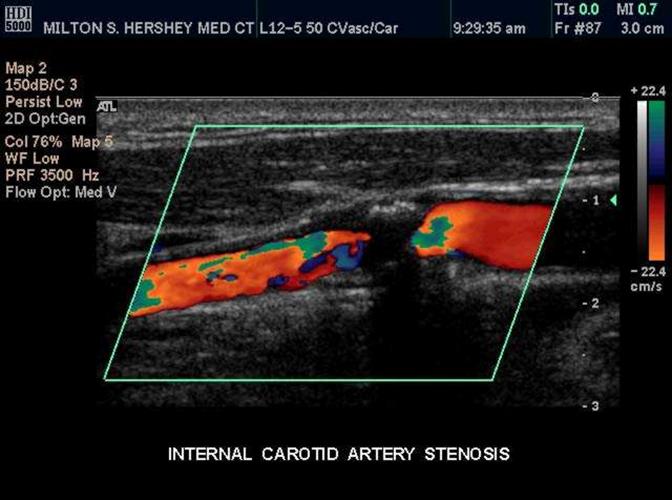
Bright echogenic plaque which creates shadowing
Dense Plaque
Bright echogenic plaque which does not produce shadowing
Soft / Fibrous Plaque or Thrombus
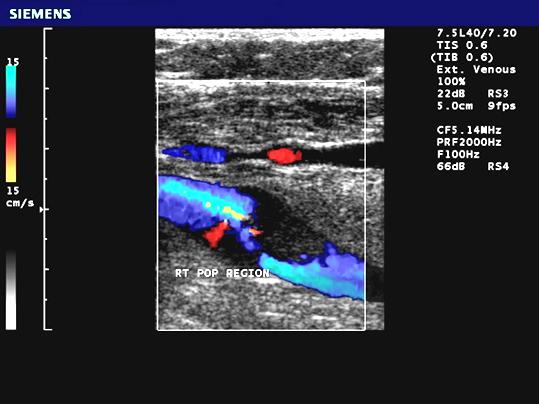
Plaque which produces echoes (not hypoechoic) but not as bright as dense or calcific plaque
Intimal thickening or Fatty streak
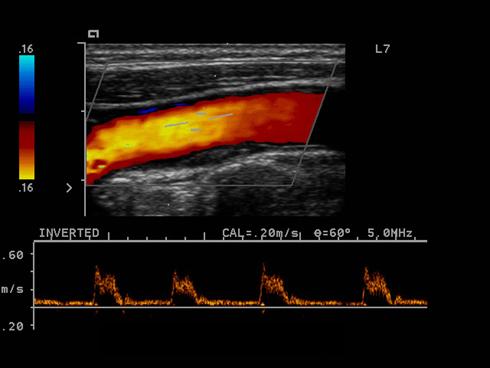
Plaque that is along the wall of the vessel as a minimal amount
What is minimal degree of plaque?
10%
What is moderate degree of plaque?
60%
What is severe degree of plaque?
90%
What is Circumferential plaque?
Plaque along the entire lumen - all the way around
What is extensive plaque?
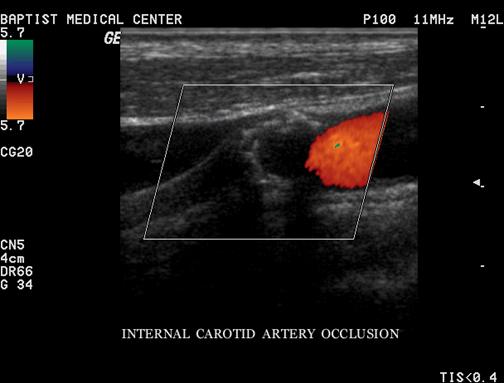
Plaque along a lengthy segment of the artery
What is scattered plaque?
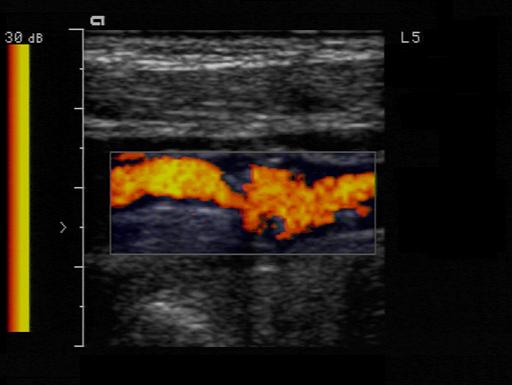
Plaque found at several locations which are not connected
True Lumen
True Lumen is the original internal diameter of the vessel
Residual Lumen
Residual Lumen is the current internal diameter of the vessel
- What’s left over after the plaque has taken over; where the blood flow is flowing
Homogenous plaque
less likely to ulcerate
- Uniform in echo texture
Heterogeneous plaque
more likely to ulcerate
- Nonuniform in echotexture
Smooth vs Irregular plaque
- Talking about the surface of the plaque and it’s probability of ulcerating
Ulcerative Plaque
A scooped out appearance
shelf like projections
Occlusion
Complete blockage
- Best used with the terms probable & total
- Complete filling of the vessel internal area with heterogeneous material
- No blood flow
What must one do in calling an occlusion
sensitize the equipment before doing so
Decrease PRF
Increase color gain, use power Doppler
laminar flow
Orderly
non-turbulent
Sharp flow
Indicating a swift upstroke
Sharp peaks
Damped flow
Slow upstroke
Rounded Peaks
Monophasic
One upstroke within one cardiac cycle
Multiphasic
Multiple upstrokes within one cardiac cycle
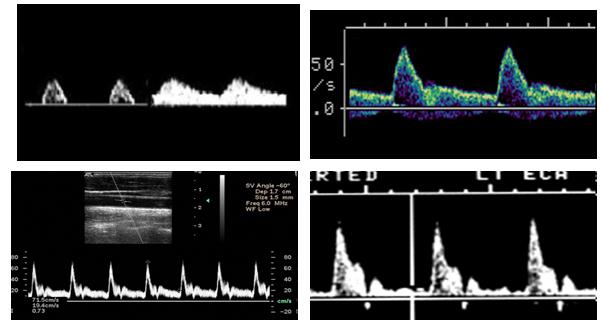
Which is monophasic?

Antegrade
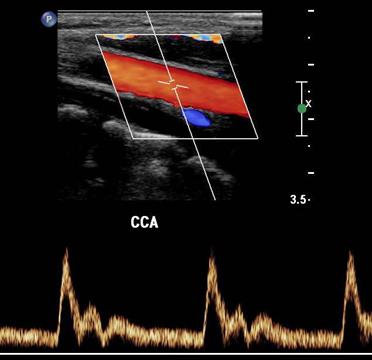
Flow in the direction that is expected from that specific vessel
Retrograde
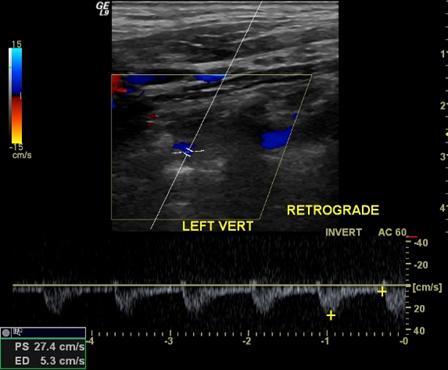
Flow that is reversed from the expected direction for that vessel
Characterization of flow disturbances
Turbulence
Spectral Broadening
Disturbed flow
Window Filling
Gross Turbulence
Aliasing
A Spectral Doppler Artifact of Pulsed Doppler systems
Spectral Doppler displays the peaks wrapped in the reverse direction
Color Doppler displays as a reversed color
Mosaic
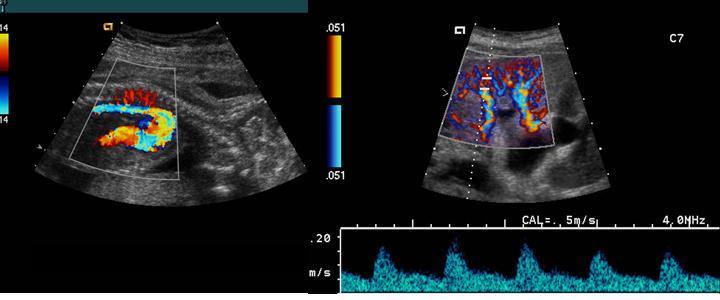
A mottled appearance caused by turbulent flow
Jet
A localized area of higher flow through and after an area high grade stenosis
Diploplia
double vision
Drop attack
falling to the ground without other symptoms
Syncope
transient loss of consciousness
Bruits
abnormal flow sounds caused by turbulent patterns
Subclavian steal
abnormal flow direction into the subclavian from the vertebral artery caused by stenosis of the subclavian
- Subclavian artery has a severe stenosis or occlusion
- Vertebral artery must compensate for the reduction of flow
- Becomes a collateral pathway to the extremity
- RETROGRADE flow or abnormal flow present in the vertebral arter
What side does subclavian steal syndrome usually occur?
left
Amaurosis fugax
temporary partial or total blindness
Homonymous hemianopia
Blindness in the outer half of the visual field
Vertigo
difficulty in maintaining equilibrium
movement that is not real
Ataxia
inability to control gait or touch an article
Paresis
weakness or slight paralysis on one side of the body
Paresthesia
numbness or lack of feeling
Dysphasia
impaired speech
Aphasia
inability to speak
What is a Carotid body tumor?
A small mass of vascular tissue that adjoins the carotid sinus. It functions as a chemoreceptor sensitive to changes in oxygen tension of the blood and signals necessary changes in respiratory activity
Nonatherosclerotic lesions
Trauma
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD)
- dysplasia of the media with overgrowth of collagen
- beadlike appearance on angiography
- Seen in young women
Collagen vascular connective tissue disorders
Where does a Nonatherosclerotic lesions usually occur?
mid to distal
renal or carotid
What are the Mechanisms of disease?
- Stenosis
- Embolism
- Thrombosis
- Aneurysm
- Nonatherosclerotic lesions
- Carotid body tumor
What are the Risk Factors &
contributing diseases?
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Hyperlipidemia
What is a Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)?
Produces a permanent neurological deficit
What is an acute CVA?
symptoms of sudden onset
unstable
What is a Stroke in evolution?
symptoms come and go
unstable
What is a Completed stroke?
No progression or resolution of the symptoms
stable
What are the symptoms of Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency?
- Bilateral symptoms
- Visual blurring
- Paresthesia
- Vertigo
- Ataxia
- Drop attacks
What is a Reversible Ischemic Neurologic Deficit (RIND)?
- Lasts longer than a TIA
- Deficits resolve in time
What is a TIA?
Transient Ischemic Attack - TIA
A fleeting neurological dysfunction without lasting effects
What are the symptoms of a TIA?
last minutes - hours
never more than 24 hours
sensory, motor, speech impairment, monocular visual disturbance
What is the Etiology of a TIA?
heart or carotid artery emboli
What is NASCET?
North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial
What is ECET?
European Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (ECET)
What is ACAS?
Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Trial (ACAS)
What was the endpoint for all 3 Carotid Endarterectomy Trials?
Reduction of hemispheric stroke & death
In the Carotid Endarterectomy Trials what showed long term benefits?
surgery in pt’s with >60 – 70% stenosis
for both symptomatic & asymptomatic over medical treatment
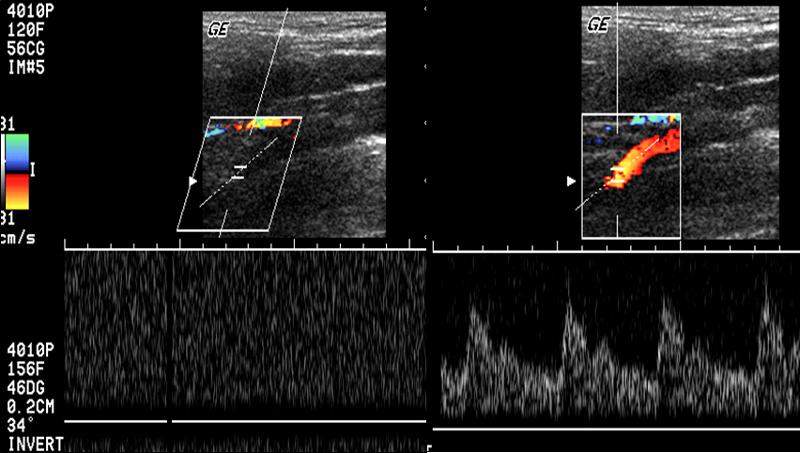
What are the key points of spectral broadening?
- Spectral broadening is proportional to stenosis
- Filled spectral window suggests >50% diameter
- >70% stenosis has poor spectral border, high amplitude and low frequency
- Spectral broadening may be the only sign of stenosis
What can we expect from post stenotic flow?
turbulent – nonlaminar
- Although objective measurements have been created - - clinically spectral broadening is graded subjectively
What Factors cause abnormal Low PSV?
- Collateralization
- Low BP
- Decreased cardiac output
What Factors cause abnormal High PSV?
Hypertension
Why do we calculate Systolic Velocity Ratio?
- Physiological factors can change the absolute systolic velocities
- By comparing the CCA to the ICA we remove the Physiological factors affect.
Why do we take the End Diastolic Velocity?
- It becomes valuable in high grade stenosis
- Will not show change below 50% stenosis
When does the PSV drop off?
Stenosis starts to exceed Approximately 90 %
What affects the PSV
length of the stenosis
- A range of velocities are possible with variable stenosis - - - Precise velocity stenosis is not possible
What are the Cardinal Doppler Parameters?
Peak Systole
End Diastole
ICA/CCA Ratio
- Critical that measurements are taken at the highest velocity
Explain the velocity increase in a stenosis.
The amount of velocity increase is small until the stenosis exceeds 50%
What is velocity proportional to?
Velocity will be proportional to the amount of stenosis.
By measuring the velocity we measure the stenosis
In vascular what is everything weighed by?
Everything that we do in Vascular is weighed by the velocity more so than the Bmode measurement
What happens when no cause of asymmetry can be found?
other modalities should be used to find the cause.
Major asymmetry between right & left should be a red flag
If the CCA is normal what do we say about the waveform?
Should be low resistance
If the Distal CCA is obstructed what happens to the waveform?
High resistance
ECA waveform
If the proximal CCA is obstructed what happens to the waveform?
Dampened Waveform
- Best method of quantification is
What is the best method of Best method of quantification of the CCA
comparison with the contralateral side
CCA Pulsatility
- Normally the Pre-stenotic Area
- Stenosis can also occur at the CCA origin
- CCA waveforms may appear pre-stenotic or post stenotic
What are the three critical areas?
- Prestenotic Area
- Stenotic Area
- Post Stenotic Area