What is the function of the falciform ligament?
Connects the liver to the anterior diaphragm and the anterior abdominal wall.
What is the echo texture of the liver?
homogeneous
Name the abdominal organs in order from Hyperechoic to hypoechoic
Renal sinus > Pancreas > spleen > renal cortex
Where is the porta hepatis to the caudate lobe?
lies anterior
Where is the bare area of the liver?
The bare area comes in direct contact with the diaphragm
What is riedel's lobe?
congenital variant extension of the right lobe of the liver beyond the lower pole of the right kidney.
What is the major problem with riedel's lobe?
It can be mistaken for hepatomegaly
What are the measurements of the right lobe of the liver?
20 cm / 15 cm
What are the hepatic veins key to?
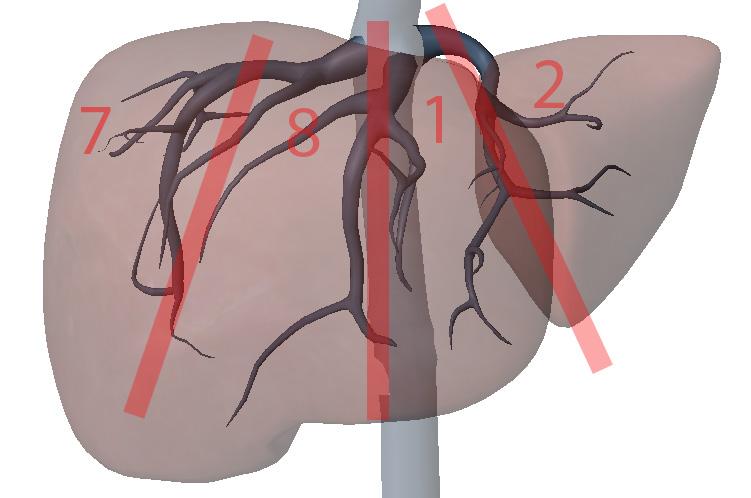
division of the liver longitudinally
What are the portal veins key to?
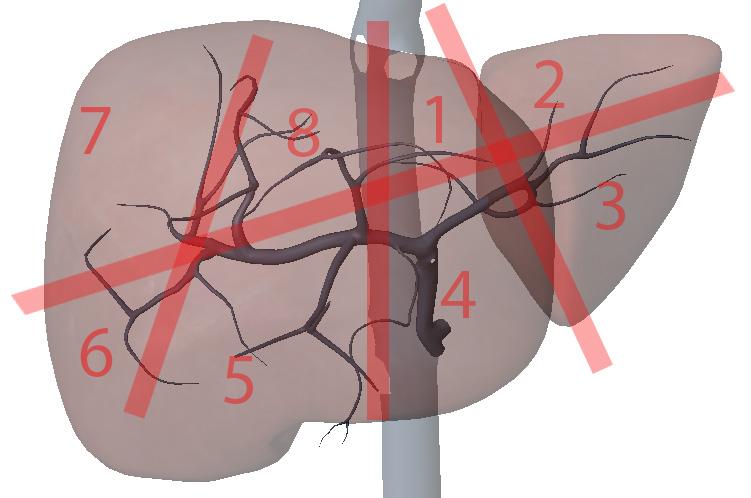
transverse division of the liver
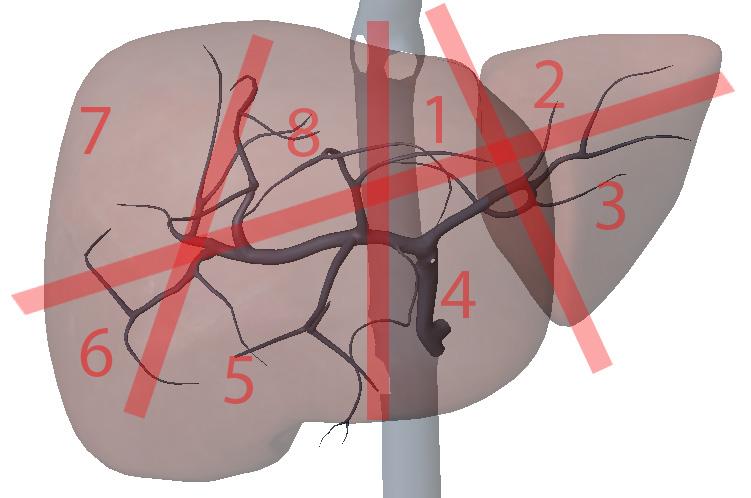
What is section 1?
Left Medial superior
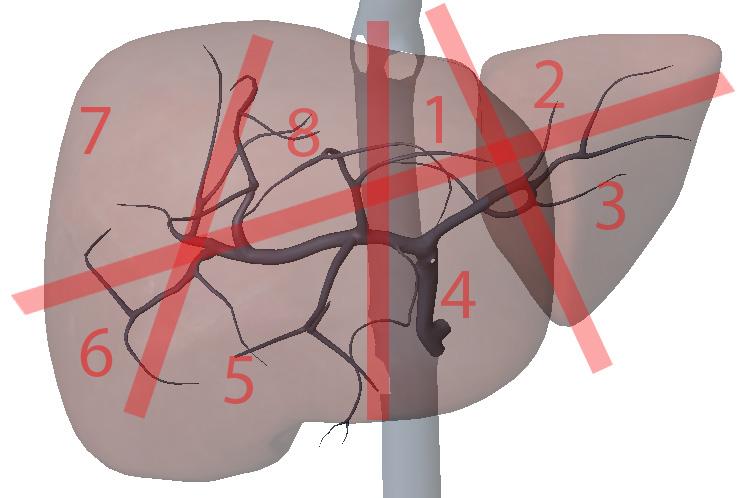
What is section 2?
Left lateral superior
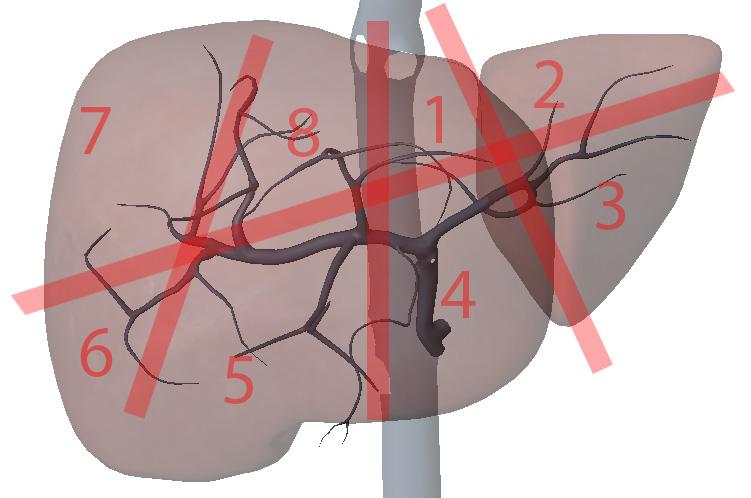
What is section 3?
Left lateral inferior
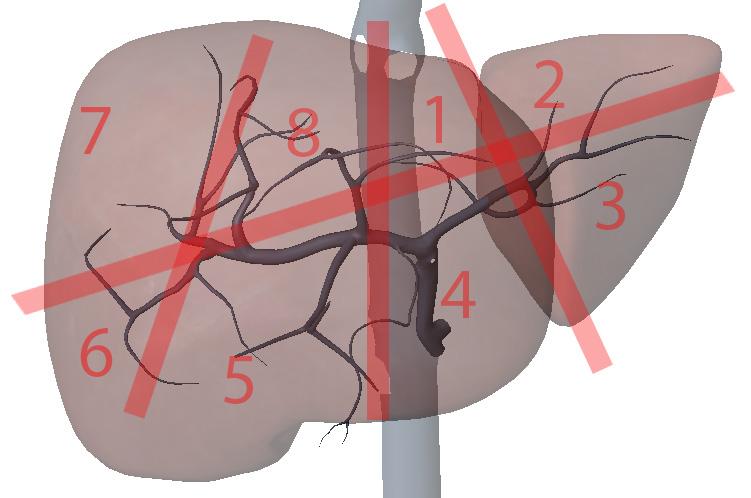
What is section 4?
Left medial inferior
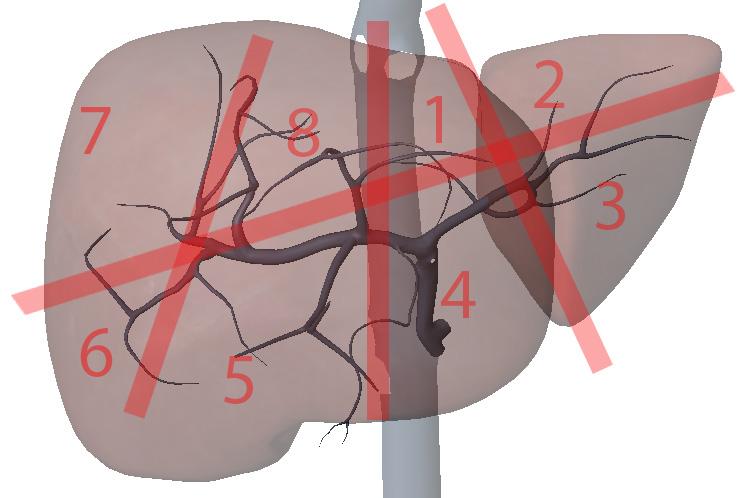
What is section 5?
Right anterior inferior
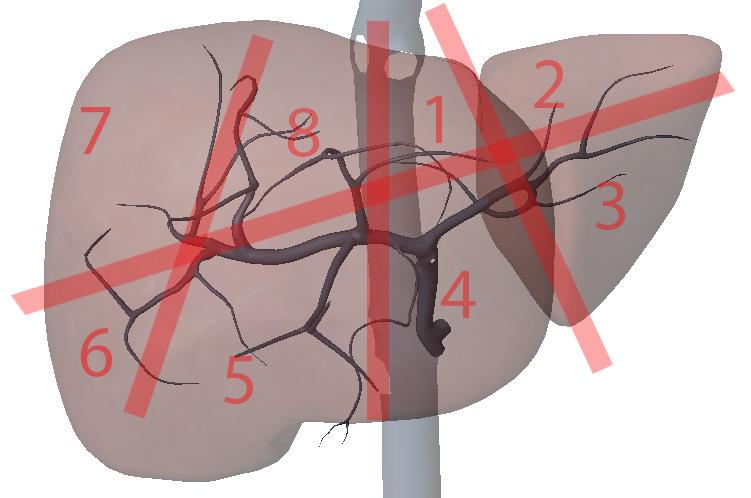
What is section 6?
Right posterior inferior
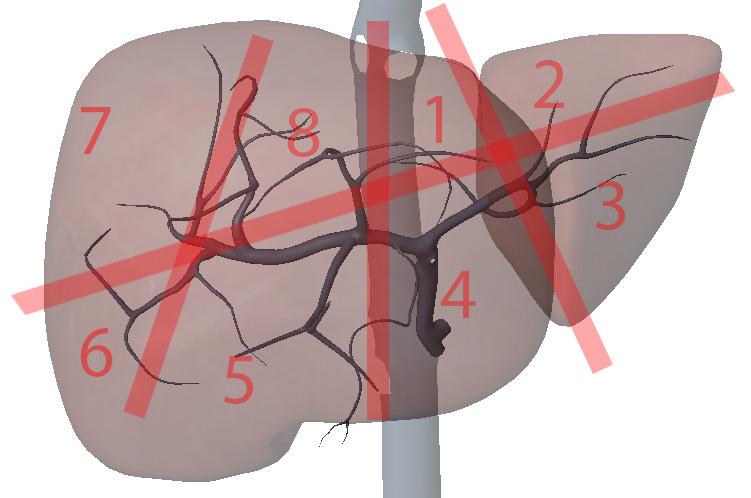
What is section 7?
Right posterior superior
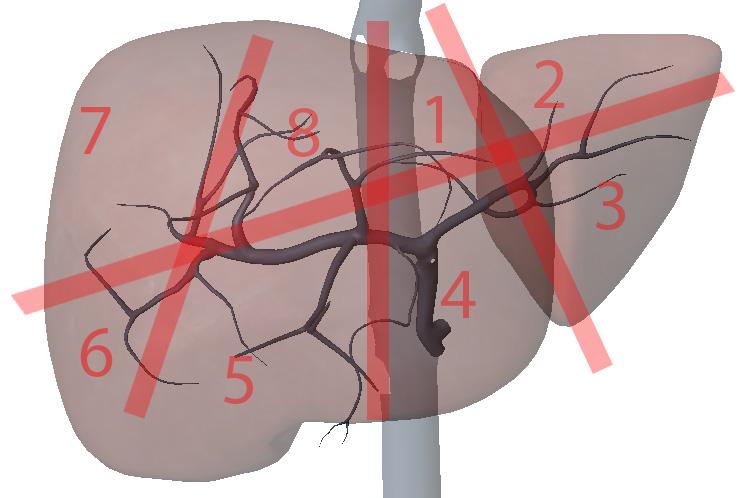
What is section 8?
Right anterior superior
Explain where the liver lies in the abdomen
right hypochondriac
epigastrium
Left hypochondriac to the left mammary line
What covers the liver?
Glisson's capsule
Fibrous peritoneum - covers all but bare area
How is the left lobe divided?
medial / lateral
How is the right lobe divided?
posterior / anterior
How is the liver oxygenated?
portal veins - 80%
Hepatic arteries - 20%
Explain the inferior liver.
sits on the mesentery
medial left lobe lies to the portal hepatis?
anterior to the portal hepatis
medial left lobe lies between?
ligament terres and the gallbladder fossa.
What lies at the anterior border of the caudate lobe?
left portal vein
What supplies the caudate lobe with blood?
hepatic artery
branches of the left portal vein
branches of the right portal vein
What drains the caudate lobe?
small veins to the IVC
What is the seagull?
Celiac axis
Explain the neonatal flow.
umbilical vein
ductus venosum
IVC
heart
Umbilical vein turns into what after birth?
ligament teres
Ductus venosum turns into what after birth?
ligament venosum
What is a possible problem with portal hypertension?
recanalization of the ligament teres
Why are portal veins echogenic?
they lie in fibrofatty tracks
Where is the ligament teres?
runs long outside of falciform ligament?
What is another name for the ligament teres?
round ligament
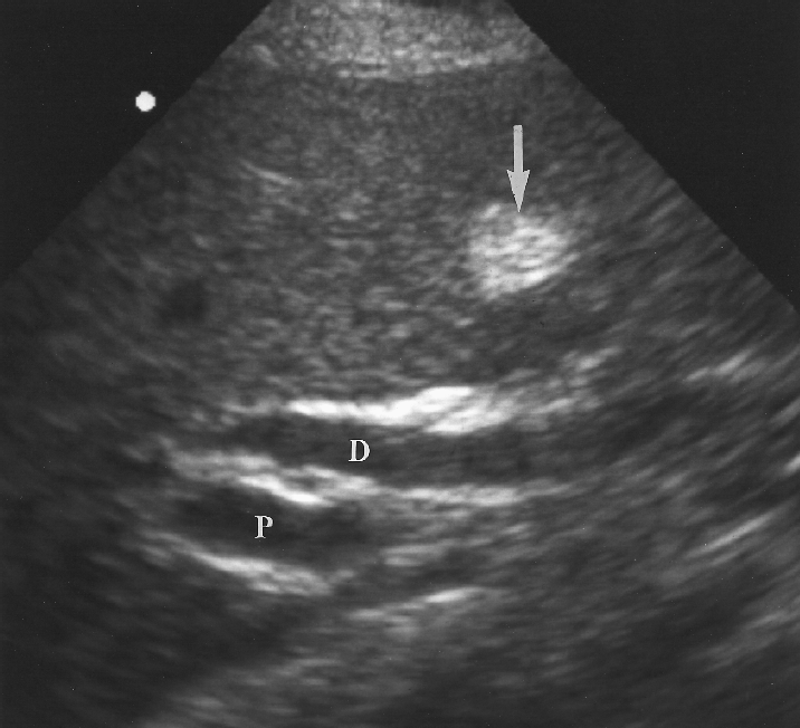
ligament teres
How do we locate the porta hepatis?
MPV kisses the IVC
Explain the direction of the main portal vein.
courses superiorly toward the right then posteriorly at the liver hylum
Main lobar fissure
A groove that divides the Rt lobe of the liver into anterior and posterior segment
Rt intersegmental fissure
Which anatomical structure is located within the Rt Intersegmental fissure?
Right hepatic vein
Which anatomical structure is located within the Lt Intersegmental fissure?
Left hepatic vein
Left Portal Vein
Ligamentum Teres
A groove that divides the Lt lobe of the liver into medial and lateral segment
Lt Intersegmental fissure
What seprates the caudate from the left liver lobe?
ligament venosum
What is the measurement of the MPV?
less than 13 mm
What is the # 1 cause of Portal Hypertension?
cirrhosis
What is possible if the MPV is more than 13 mm?
portal hypertension
Where is the right portal vein?
separates the right liver lobe into anterior and posterior sections
What does the horizontal segment of the left portal vein separate?
caudate from the medial left lobe
What does the ascending segment of the left portal vein separate?
separates the medial left lobe from the lateral left lobe.
What are the three major functions of the liver?
metabolism
detoxification
storage
What are the two types of metabolism in the liver?
gluconeogenesis
glucolysis
What is Hepatocellular?
hepatocytes are affected
treated medically
How is obstruction treated?
surgically
What does acute or chronic liver disease affect?
liver metabolism
Define metabolism.
chemical process that occur in the body that are necessary for matenance of life
catabolic - meow
anabolism - build
What happens to carbs in the liver?
catobolized to glucose to use as energy
What happens to the extra glucose not used as energy?
sent to the liver
converted to glycogen
stored
What happens to glycogen when energy is needed?
liver converts glycogen back to glucose
What is a possible cause of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia?
liver disease
What happens to fats in the liver?
converted by hepatocytes to lipoproteins
What is a lipoproteins?
fats broken down to monoglycerides and diglycerides
What makes lipoproteins so fabulous?
they are soluble in plasma and may be transported by the blood.
What happens to stored fats sent to the liver?
liver converts them to glucose and cholesterol
What happens during liver disease to monoglycerides and diglycerides?
they are unable to convert to lipoproteins
instead are converted to triglycerides
Why are triglycerides not fabulous?
they are not soluble so they get stuck in the liver
FATTY LIVER disease
What is PT
Prothrombin time - the amount of time it takes for blood to clot
What is PTT?
partial thromboplastin is the time it takes for plasma to clot
Cogulopathy
disease condition of cogulation
Does IV therapy fix liver disease?
No
What is hypoalbuminemia?
not enough albumin
What can hypoalbuminemia cause?
edema & ascites
What is the primary cause of ascites?
portal hypertension
What happens to proteins when they are digested?
they are converted to amino acids then sent to the liver
What does the liver do with amino acids?
makes proteins
What is albumin?
important protein produced in large quantities in the liver.
What is albumin responsible for?
vascular fluid pressure
What are the fat soluble vitamins?
ADEK
What is the production source of proteins for blood coagulation?
The liver
What is needed for blood coagulation?
fibrinogen
prothrombin
factors V, VII, IX, X
What do you have to do before any invasive procedure?
check labs for
PT
PTT
INR
What is INR
international normalized ratio
only used when the patient is taking blood thinner
Why is vitamin K important
precursor to the production of factors V, VII, IX, X
No K no factors V, VII, IX, X, No clotting
True or False?
liver disease can decrease production of clotting factors V, VII, IX, X.
True
What will low clotting factors cause?
inadequate coagulation which results in uncontrolable hemorrhage.
How does biliary obstruction affect coagulation?
Bile emulsifies fat
No bile = no fat will be broken down
if fat is not broken down, fat soluble vitamins are not absorbed (K)
No K = No clotting factor.
True or False?
Protein ingestion plays a role in nitrogen metabolism
True
What is the importance of hepatic enzymes?
detection of liver disease
when hepatocytes are damaged hepatic enzymes leak into the blood and can be detected with lab tests.
What is NH4 Ammonia?
toxic byproduct of nitrogen metabolism
What happens if the detoxification does not exist?
toxic levels will rise
Ex. Ammonia NH4
What happens to to Ammonia NH4?
it is converted to urea then sent to then excreted by the kidneys
What is an accumulation of ammonia called?
Fetor Hepaticus
How can we tell if a patient has Fetor Hepaticus?
fruity breath
confusion
coordination loss
coma
tremor
Fetor Hepaticus
What are the two most important lab values to look at?
BUN
creatin
What is BUN?
Blood Urea Nitrogen
What happens when drugs are not detoxified?
drug dosages may need to be lowered because they are not removed by the liver
What happens when hormones are not detoxified?
hormones rise
What happens in men with cirrhosis?
liver can't break down estrogen
gynecomastia
testicular atrophy
What is in bile?
water
bile salts
bile pigments
cholesterol
lecithin
protein
What does the Liver function test consist of?
AST
ALT
LDH
Alkaline Phosphatase
Bilirubin (direct, indirect, total)
Prothrombin time
Albumin & Globlins
Aspartase Aminotransferase
AST
present in tissue but only released in blood when tissue is damaged
What is an old name for AST
SGOT
What would be a common cause for elevation of AST?
Acute hepatitis
Cirrhosis
Infectious Mononucleosis
What can cause splenomegaly?
Infectious Mononucleosis
True or False?
AST is elevated before jaundice occurs
True
What is one draw back with AST lab?
AST is non specific
it can be produced by any organ with a high metabolism rate.
Alanine Aminotransferase
ALT
tends to be used to monitor patients after jaundice has occured
liver specific
What are some causes of low levels of ALT?
acute cirrhosis
hepatic metastasis
pancreatis
What are some causes of mid levels of ALT?
obstruction
What are some causes of high levels of ALT?
hepatocellular disease
toxic hepatitis
Lactic Acid Dehydogenase
LDH
present in tissue but not released unless there has been cell death or damage
Why is LDH not a good liver test?
detects heart attacks
elevated in myocardial infarction & pulmonary infarction
What could be the cause of elevation of Alkaline Phosphatase
obstruction caused by gallstones
What is the patient prep for a liver exam?
fast for at least 6 hours
What should be explained to the patient for a liver exam?
The sonographer should explain to the patient that the exam is being performed to visualize the liver and interdependent organs.
How should the patient be dressed for the exam?
The patient should remove any restrictive clothing above the waist. A towel should be tucked around clothing to protect them from gel.
What transducer should be used to visualize the liver?
3.25 MHz sector or curved linear array.
What transducer should be used to visualize the liver in an obese patient?
2.25 MHz sector or curved linear array.
What transducer should be used to visualize the liver on a pediatric patient?
5.0 MHz sector or curved linear array.
What transducer should be used to visualize the liver on a neonate?
7.4 MHz sector or curved linear array.
Explain the procedure of a liver exam.
Begin doing a full sweep through the liver. Starting sagittal,
slightly to the left of midline. Change to a transverse view and sweep
up and down the left lobe from a subcostal approach. Look in
transverse through the right lobe subcostally or
intercostally.
Look for:
- Parenchymal echogenicity
- Capsular contour (smooth, coarse, lobulated)
- Size
- Vascularity
- Fluid
- Masses
Start taking images.
Document the normal anatomy and
any pathology found, including measurements and vascularity if indicated.
What is important medical history?
Sex
Age
Weight
Prior Hepatic Conditions
Family History of Hepatic Conditions
What position should be used for an exam on the liver?
Supine
left lateral decubitus, left posterior oblique,
semi-erect, or prone may be used as necessary
What are the scan plans used during a liver exam?
Sagittal and Transverse
Explain the Sagittal plane for the liver exam.
The transducer may be swept under the intercostal margin to image the liver parenchyma from the anterior abdominal wall to the diaphragm.
Explain the Transverse plane for the liver exam.
The transducer should be angled in a steep cephalic direction to be as parallel to the diaphragm as possible. The transverse plan allows images of liver parenchyma, vascularity and ductal structures.
What are the Techniques used for the liver exam?
Deep inspiration and held.
Push belly out.
Alternate positions can be used to displace the bowel out of the field of view.
Place right arm above head to open intercostal spaces
Give an anatomical description of the liver.
The liver is the largest internal organ. It lies in the right upper quadrant, from the right hypochondria, extending through the epigastrum to the mammary line of the left hypochondria. Generally it lies from the diaphragm to the level of the 8th rib. Size and shape is variable. The liver is covered by the Glisson’s capsule (fibrous peritoneum), except for the bare area that is in contact with the diaphragm. The liver is dived into four lobes.
Give an anatomical description of the left liver lobe.
further divided into lateral and medial segments by the left intersegmental fissure.
Give an anatomical description of the right liver lobe.
divided from the left lobe by the main lobar fissure which passes from the gallbladder fossa to the inferior vena cava. The right lobe is further divided into anterior and posterior segments by the right intersegmental fissure.
Give an anatomical description of the caudate liver lobe.
found on the inferior, posterior side of the liver. The caudate lobe is bordered by the inferior vena cava posteriorly and the ligament venosum anteriorly. The hepatic veins run between the lobes and segments. The portal veins run centrally within the segments. The ascending portion of the left portal runs in the left intersegmental fissure.
Give an anatomical description of the medial left liver lobe.
also called the Quadrate lobe, is bordered by the porta hepatis posteriorly, laterally by the gallbladder fossa and ligament terres.
What are appropriate reasons to perform a liver exam?
Jaundice
Fatigue
Bruises
Nausea
Vomiting
Abdominal
pain
Abnormal tenderness
Anorexia
Weight loss
Decreased appetite
Dark urine
Diarrhea
Blood in
stool
Edema
Persistent fever
Bronze skin
Encephalopathy
Pruritus
Cholecystectomy
Congestive heart failure
Palpable
mass
Tremors
Bloating
Swelling in the
abdomen
Respiratory Infections
What are some appropriate history questions?
When was the last time you had something to eat or drink?
Are you in pain?
Where is your pain located?
How long have you been in pain?
How long does the pain last and does it go away?
Have you had a nausea or vomiting?
Are you experiencing any other symptoms?
Do you have a family history of cancer?
Have you had any lab work done?
What is the liver protocol?
Sagittal
Left lobe (wedge)
Left lobe W/ caudate
lobe
Left lobe W/ aorta
Right lobe W/ IVC
Right lobe W/
dome
Right lobe W/ Morrison’s pouch
Liver/kidney
comparison
Right lobe W/ gallbladder
Transverse
Left lobe (wedge)
Left lobe W/ portal
vein
Left lobe W/ ligament teres
Right lobe W/ hepatic
veins, IVC
Right lobe W/ dome
Right lobe W/ portal
veins
Right lobe W/ kidney and gallbladder
Other Images
Transverse Pancreas
-head to
tail
Abnormal findings
-Color
Doppler
-Measurements
Measurements
-right lobe if indicate
What are the normal variants of the liver?
Riedel’s lobe
Absence of left lobe
Multiple sizes
Multiple shapes
What are proper measurements for the liver exam?
Liver size may be measured sagittal from the inferior tip of the liver to the dome
Length: 20 cm
Anterior Posterior: 15 cm
C/RL: <0.6
What are common pitfalls for the liver exam?
Obesity
The patient ate before the study
Metabolic disorders such as fatty infiltration will reduce detail
Shadowing
Gas
What is the liver function tests?
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): 5 – 40 units per liter of
serum
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): 7 – 56 units per liter of
serum
Lactic acid dehydrogenase (LDH): 122 – 222
U/L
Alkaline phosphatase (alk phos): 45 – 115 U/L
Bilirubin:
0.1 – 1.0 mg/dL
-Indirect: 0.2-0.7 mg/dL
-Direct: 0 – 0.3
mg/dl
-Total: 0.1 – 1.2 mg/dl
Prothrombin time: 9.5 – 13.8
seconds
Albumin: 3.5 – 5 g/dL
Globulins: 13.5 – 16.5
What are important labs used for a liver exam?
White blood count (WBC): 4,500 – 10,000
Red blood count (RBC): 4.5 – 5.5
Hemoglobin (hbg): 13.5 – 16.5
Hct: 41 – 50
Creatine: 0.5 – 1.4 mg/dl
Cholesterol: <200 mg/dl
Glucose: 60-110 mg/dl
Urinary bile and bilirubin: 1.2 mg/dl
Urinary urobilinogen: 0 – 8 mg/dl
Fecal urobilinogen: 57 to 200 mg./24 hours
Diffuse Hepatocellular disease
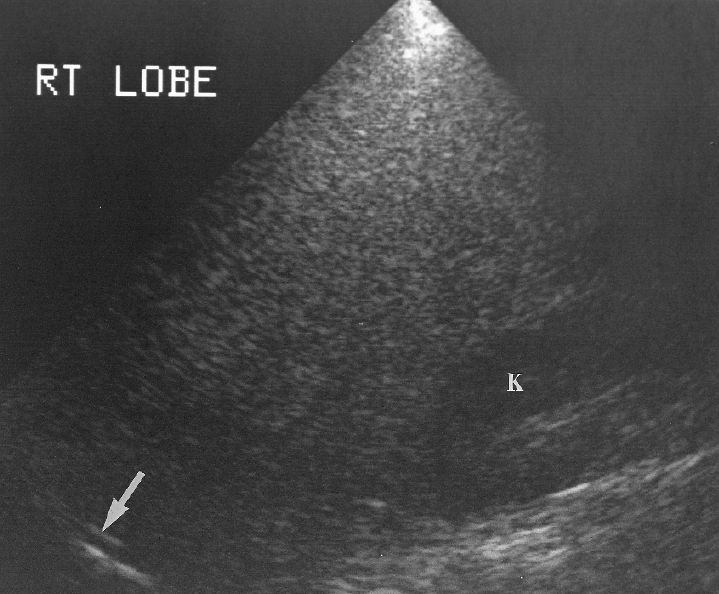
Affects the hepatocytes and interferes with liver function
What is the sonographic appearance of the Diffuse Hepatocellular disease?
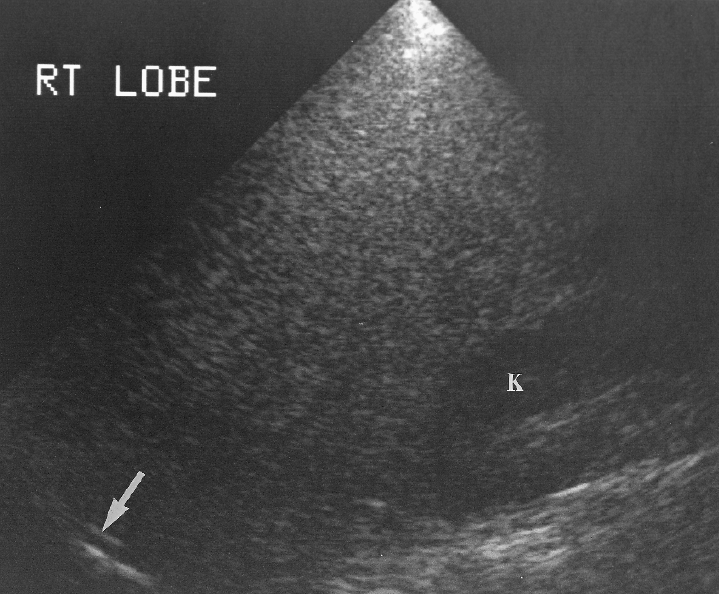
Increased echogenicity
Enlargement of affected
area
Decreased penetration
Difficult to identify liver
structures
Presentation: Asymptomatic, jaundice, nausea, vomiting
and abnormal tenderness
What are the presenting symptoms of Diffuse Hepatocellular disease?
Asymptomatic
jaundice
nausea
vomiting
abnormal tenderness
What are the presenting symptoms of acute Diffuse Hepatocellular disease?
Abnormal Liver Function Test
What is Fatty infiltration?
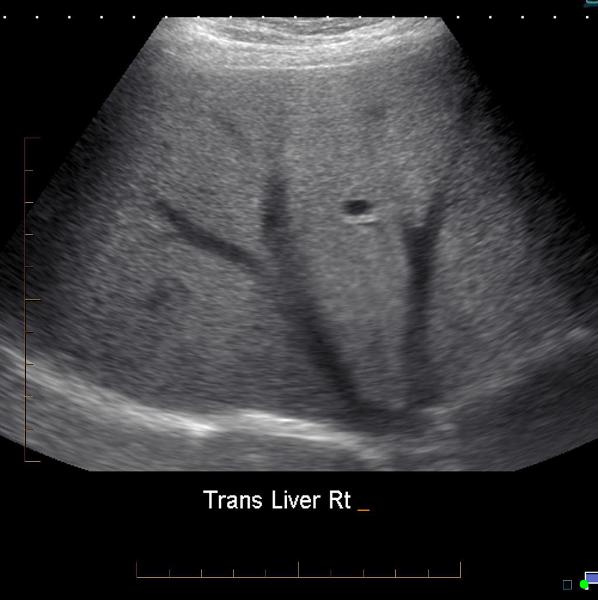
Fatty liver is an acquired but reversible disorder of metabolism. Fatty filtration implies increased lipid accumulation in the hepatocytes.
What is the sonographic appearance of fatty filtration?
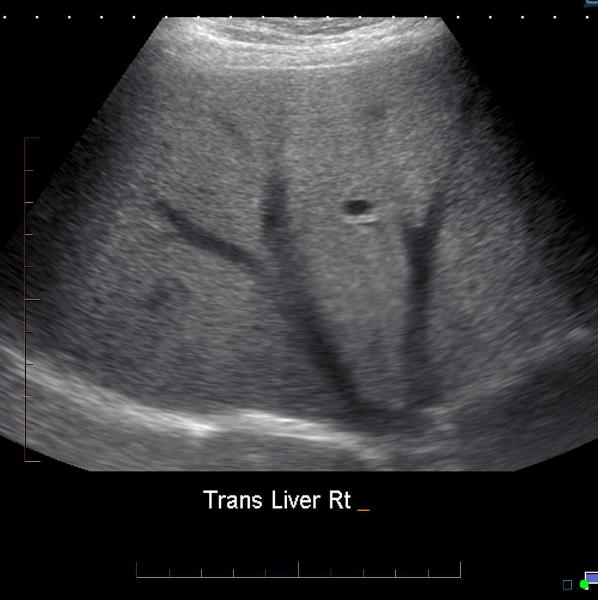
Increased echogenicity
Increased echogenicity
Enlargement
of the lobe.
Decreased penetration
Difficult to
image
Increased echo texture
What are the presenting symptoms of fatty filtration?
Asymptomatic
jaundice
nausea
vomiting
abnormal tenderness.
What lab values would suggest fatty filtration?
↑Hepatic Enzymes
↑Alk Phos
↑Direct Bilirubin
What are common causes of fatty filtration?
ETOH abuse
Diabetes Mellitis
Obsesity
steroids
What is acute hepatitis?
Inflammatory and infectious disease of the liver caused by complications of liver damage. May be mild to severe.
What is the sonographic appearance of acute hepatitis?
Mild: Normal echogenicity
Slightly increased
echogenicity
Echogenic portal radicals
Prominent portal
walls
Hepatosplenomegaly
Thickened gallbladder wall
What are the presenting symptoms of acute hepatitis?
Asymptomatic
jaundice
nausea
vomiting
abnormal tenderness.
What are the lab values that would suggest acute hepatitis?
↑AST
↑ALT
↑Bilirubin
Leukopenia
What is Chronic hepatitis?
Hepatitis becomes chronic when the inflammation lasts longer than 6 months.
What is the sonographic appearance of chronic hepatitis?
Increased echogenicity
Hypoechoic portal
triads.
Fibrosis
Soft posterior shadowing may be
apparent.
Difficult to visualize liver structures
What are the presenting symptoms of chronic hepatitis?
nausea
vomiting
anorexia
weight loss
tremors
jaundice
dark urine
fatigue
varicosities
What are the lab values that would suggest chronic hepatitis?
↑AST
↑ALT
↑Bilirubin
Leukopenia
What is Cirrhosis?
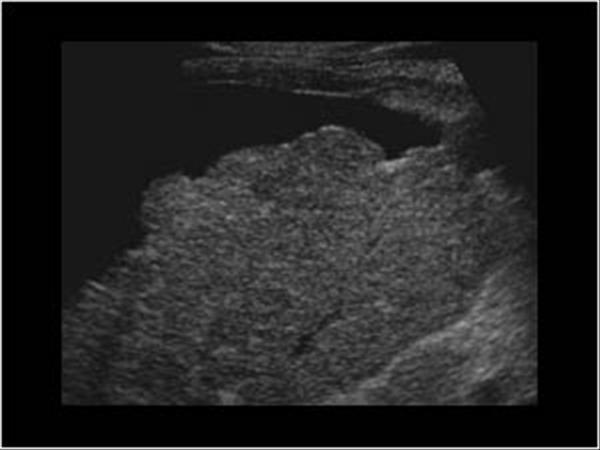
A chronic degenerative disease in which there is parenchymal necrosis, regeneration and fibrous tissue resulting in disorganization of lobular architecture. Lobules are infiltrated with fat. Commonly caused by alcoholism.
What is the sonographic appearance of Cirrhosis?
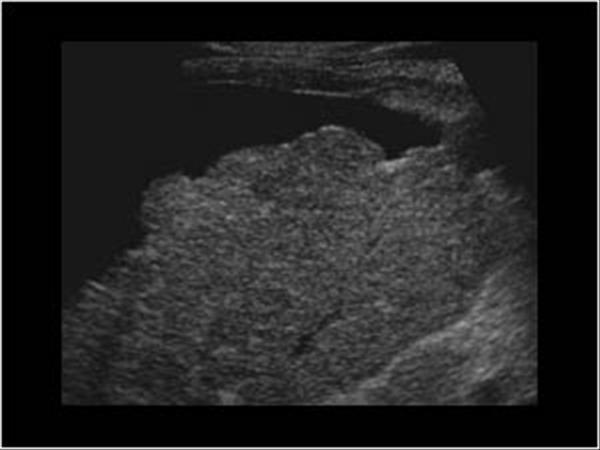
Hepatomegaly
Increased echogenicity and attenuation
Size
decrease of right lobe
Size increase of left and caudate
lobe
Nodularity
Fibrosis
Hepatospenomegaly
Ascites
Portal
hypertension
Hepatoma tumors
caudate lobe may be spared
What are the presenting symptoms of Cirrhosis?
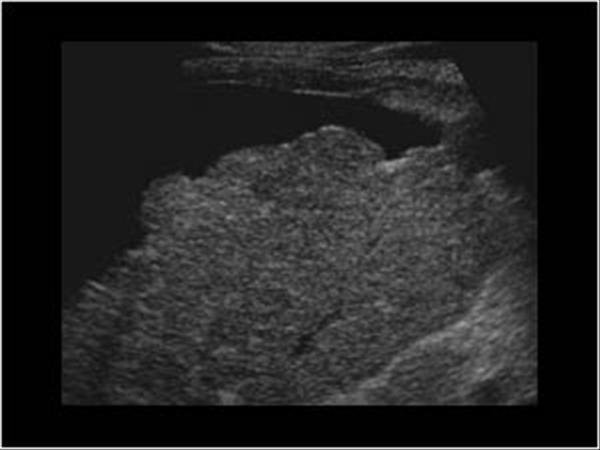
fatigue
bruises
jaundice
edema
dark urine
blood in stool
fever
Echogenic portal radicals
flatulence.
What are the lab values that would suggest Cirrhosis?
↑Alk Phos
↑Direct Bilirubin
↑AST
↑ALT
Leukopenia
What is Glycogen storage disease?
Characterized by the abnormal storage and collection of glycogen in the tissue of the liver and kidneys. Most common type I – Von Gierke’s
What is the sonographic appearance of Glycogen storage disease?
Hepatomegaly
Increased echogenicity and attenuation
Hepatic
adenomas
Focal nodular hyperplasia.
Round, homogenous,
echogenic tumors
What are the presenting symptoms of Glycogen storage disease?
Non-Specific
What are the lab values that would suggest Glycogen storage disease?
Disturbances in Acid-Base Balance
What is Hemochromatosis?
This is a rare disease involving excess iron deposits. May lead to cirrhosis and portal hypertension
What is the sonographic appearance of Hemochromatosis?
Hepatomegaly
Cirrhotic changes
Increased echogenicity
What are the presenting symptoms of Hemochromatosis?
Bronze skin
What are the lab values that would suggest Hemochromatosis?
↑Iron levels
What is Portal venous hypertension?

This is an increase in portal venous pressure (above 10mmHg) or hepatic venous gradient (above 5mmHg).
What is the sonographic appearance of Portal venous hypertension?
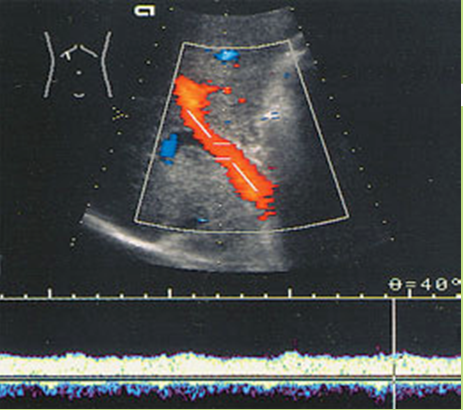
Portal vein measures greater than 13mm
Collateral
circulation
Flow reversal
Ascites
Hepatosplenomegaly
What are the presenting symptoms of Portal venous hypertension?
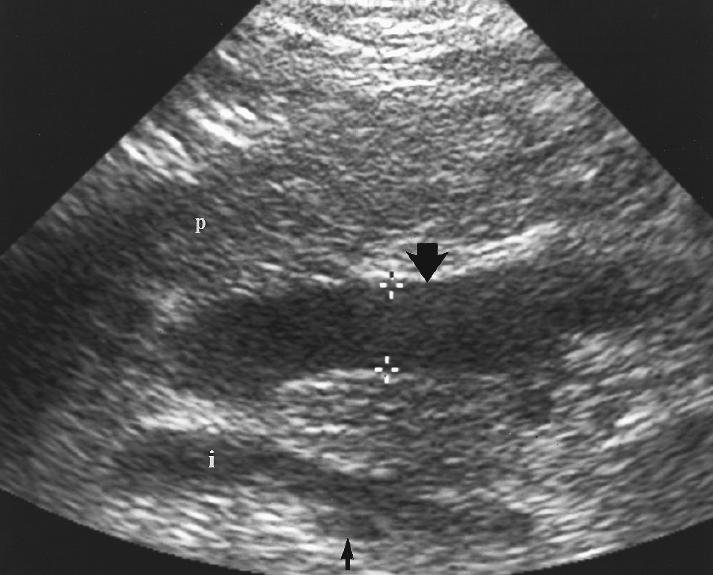
Gastrointestinal bleeding
blood in the stools
vomiting of blood
Encephalopathy
What are the lab values that would suggest Portal venous hypertension?
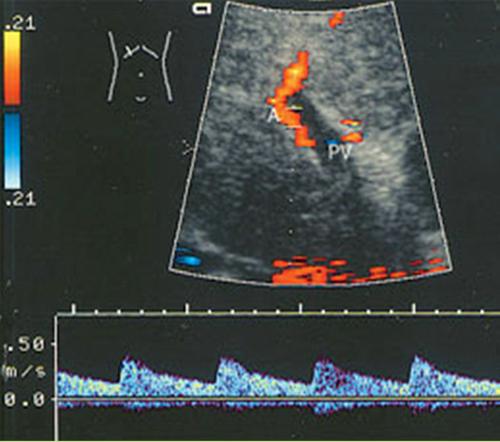
↑Liver Enzymes
↓Platelet Count
What is Portal Venous Thrombosis?
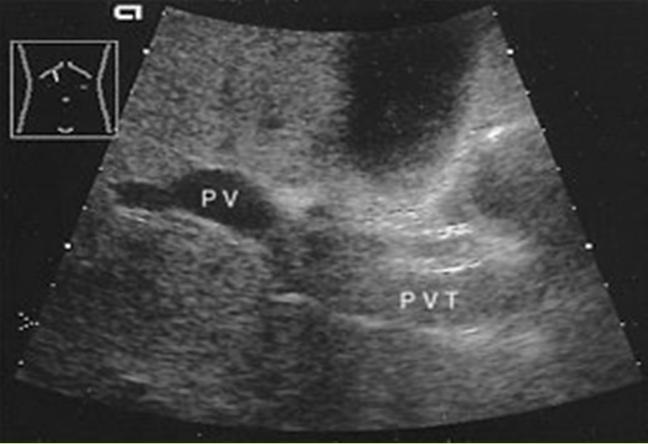
Portal Venous Thrombosis
What is the sonographic appearance of Portal Venous Thrombosis?
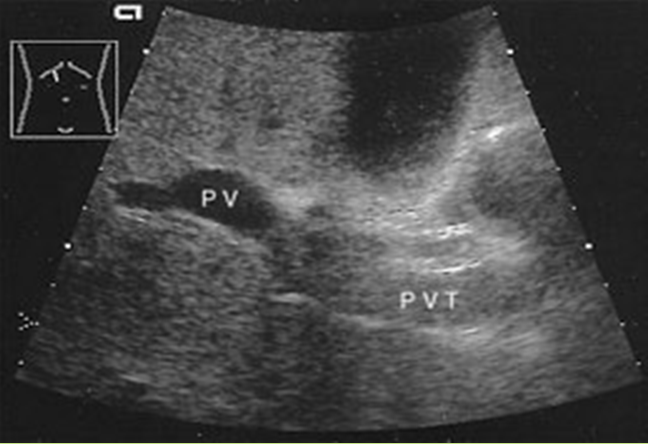
Portal flow absence
echogenic thrombosis
Worm-like
structures near porta hepatis
What are the presenting symptoms of Portal Venous Thrombosis?
vague and non-specific
What is Budd-Chiari Syndrome?
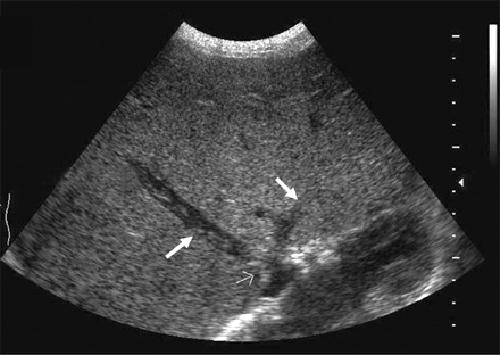
A rare disease which is caused by a thrombosis of the hepatic veins or IVC. Has a high mortality rate.
What is the sonographic appearance of Budd-Chiari Syndrome?
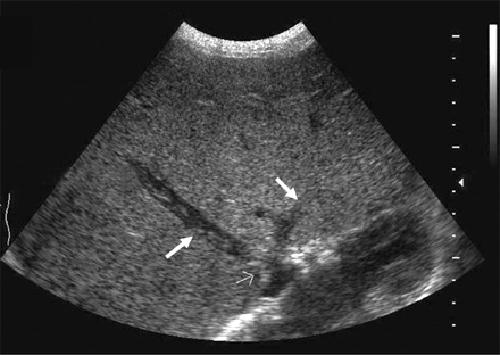
Ascites
Hepatomegaly
Enlarged caudate lobe
Atrophy of
right
lobe
Hyperechoic
Inhomogeneous
Fibrosis
Thick
Gallbladder wall
Stenosis
Disrupted flow
What are the presenting symptoms of Budd-Chiari Syndrome?
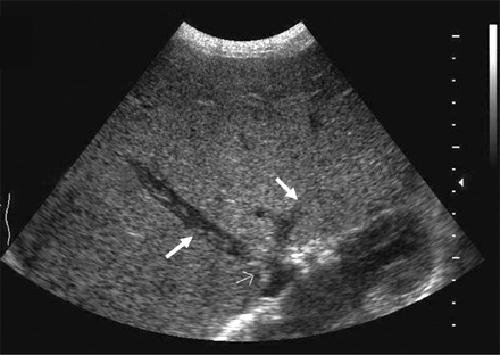
non-specific
abdominal pain
Where is Budd-Chiari syndrome most common?
asia
What are the lab values that would suggest Budd-Chiari Syndrome?
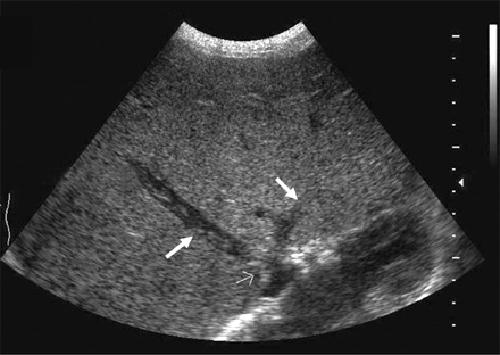
Albuminuria
↑Alk Phos
↑AFT
What is Proximal Biliary obstruction?
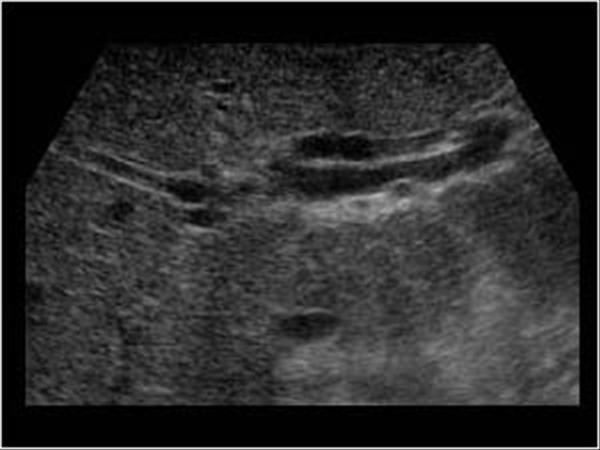
Proximal Biliary obstruction proximal to the cystic duct can be caused by gallstones.
What is the sonographic appearance of Proximal Biliary obstruction?
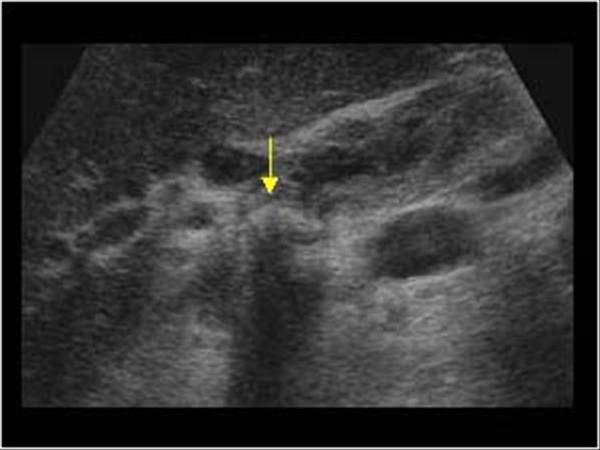
Dilated intrahepatic ducts
Carcinoma in the
CDB
Gallstones
Gallbladder normal after fatty meal
What are the presenting symptoms of Proximal Biliary obstruction?
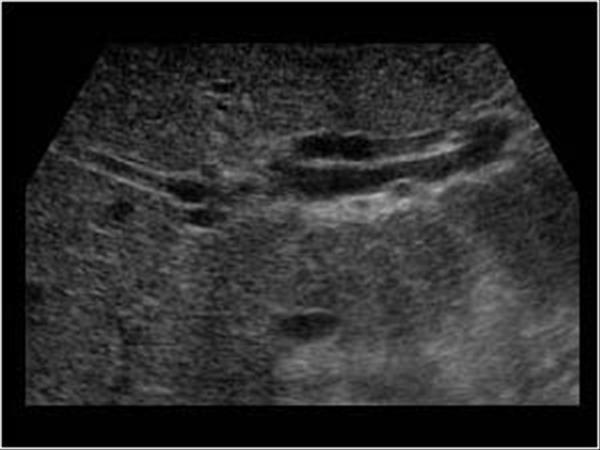
Jaundice
pruritus
What are the lab values that would suggest Biliary obstruction?
↑Direct Bilirubin
↑Alk Phos
What is Distal Biliary obstruction?
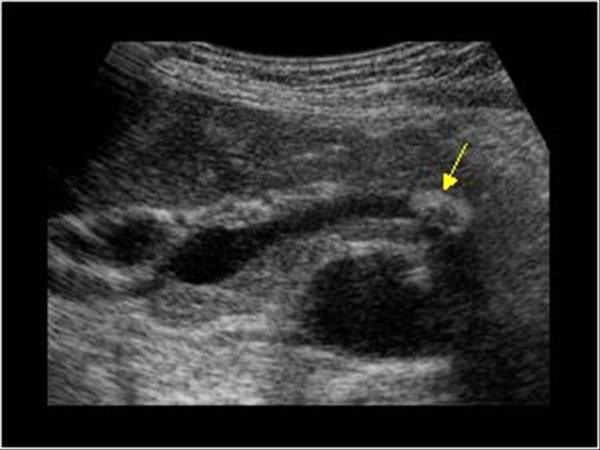
Biliary obstruction distal to the cystic duct
What is the sonographic appearance of Distal Biliary obstruction?
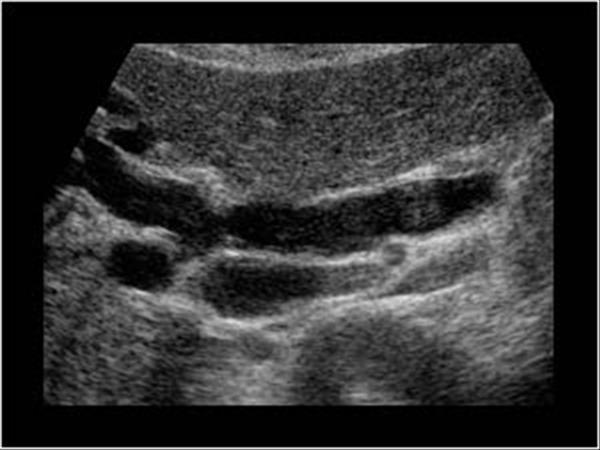
Stone in the common duct
Extrahepatic mass
Dilated
intrahepatic ducts
Gallstones
Gallbladder usually small
What are the presenting symptoms of Distal Biliary obstruction?
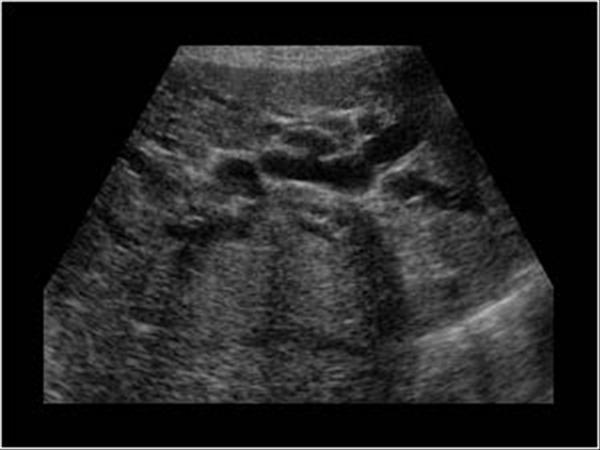
Jaundice
pruritus
What are the lab values that would suggest Distal Biliary obstruction?
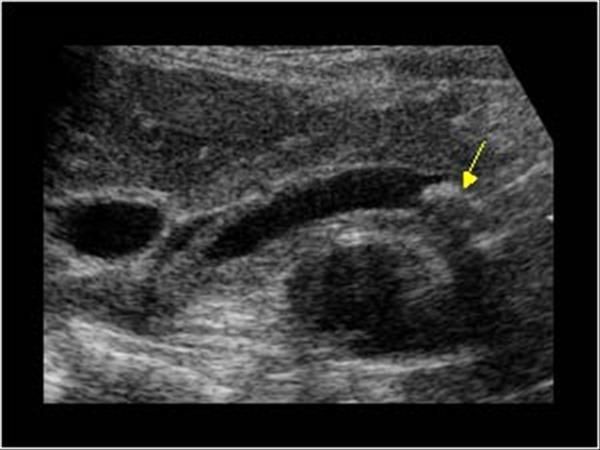
↑Direct Bilirubin
↑Alk Phos
What is Extrahepatic mass?
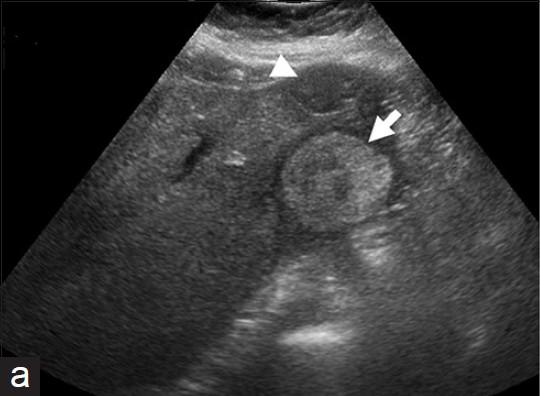
A mass in the area of the porta hepatis
What is the sonographic appearance of Extrahepatic mass??
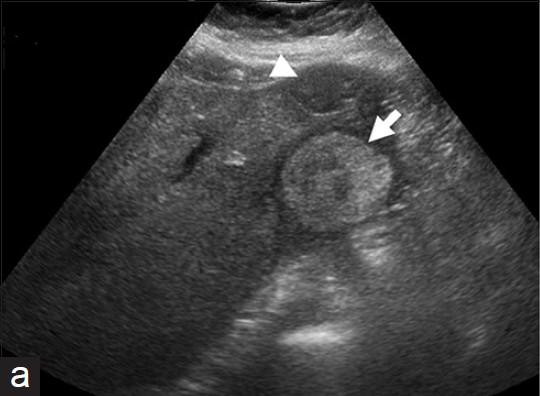
Stone in the common duct
Extrahepatic mass
Dilated
intrahepatic ducts
Gallstones
Gallbladder usually small
What are the presenting symptoms of Extrahepatic mass??
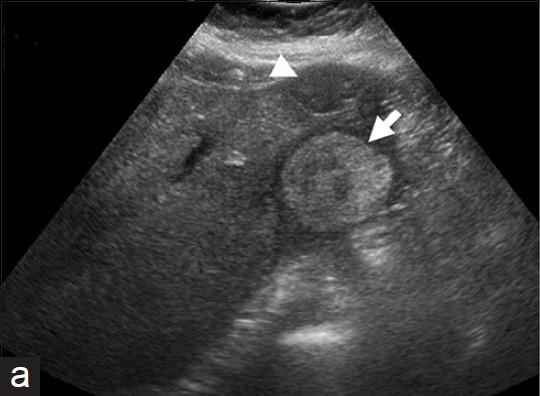
Jaundice
pruritus
What are the lab values that would suggest Extrahepatic mass??
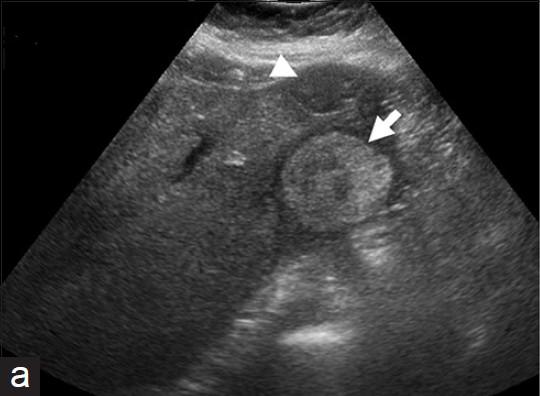
↑Direct Bilirubin
↑Alk Phos
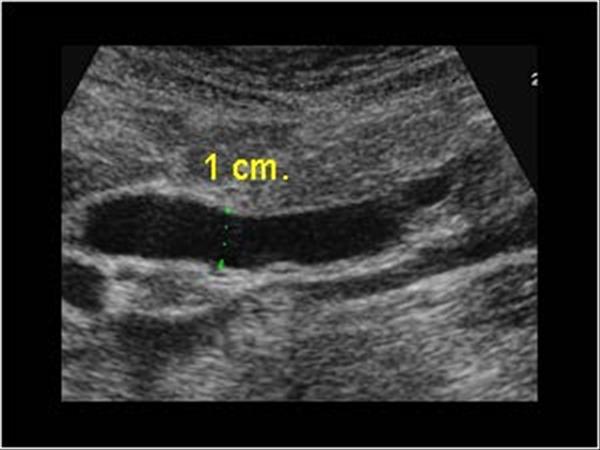
What is Common Duct Stricture?

Sonographic Appearance:
What is the sonographic appearance of Common Duct Stricture?
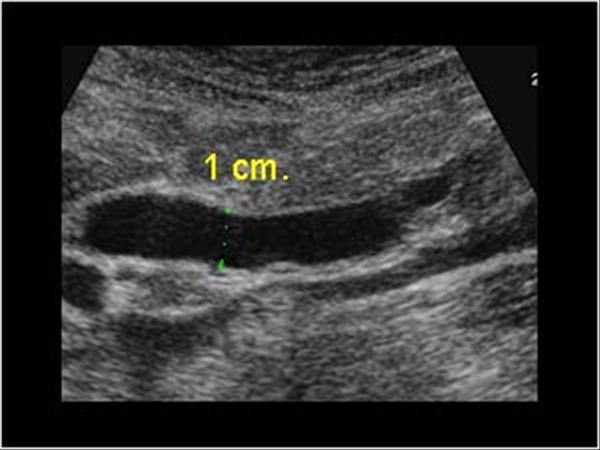
Common Duct Stricture
What are the presenting symptoms of Common Duct Stricture?
jaundice
past cholecystectomy
increase in direct bilirubin
What are the lab values that would suggest Common Duct Stricture?

↑Direct Bilirubin
↑Alk Phos
What is Passive hepatic congestion?
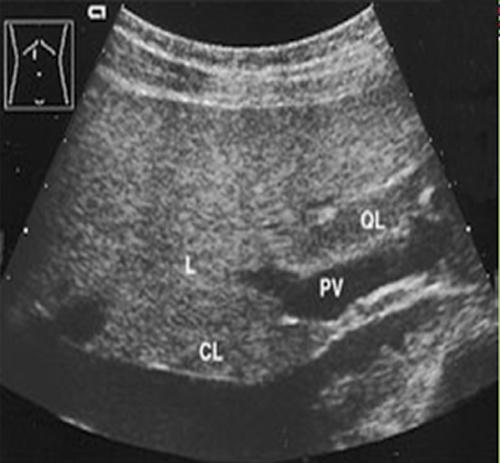
develops secondary to congestive heart failure.
What is the sonographic appearance of Passive hepatic congestion?
Dilated IVC, SMV, Portal and Splenic veins
Hepatomegaly
What are the presenting symptoms of Passive hepatic congestion?
congestive heart failure.
What are the lab values that would suggest Passive hepatic congestion?
↑ LFT
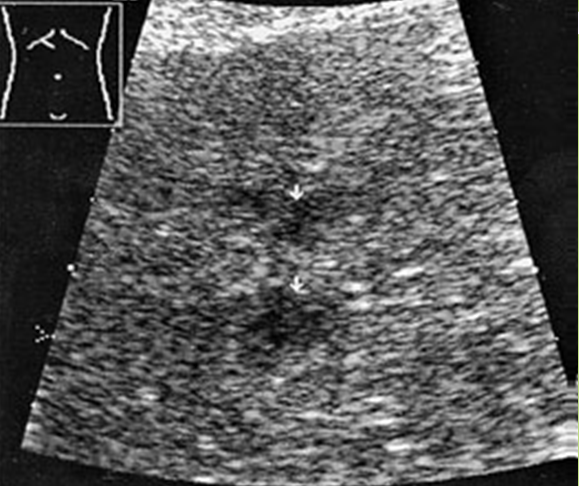
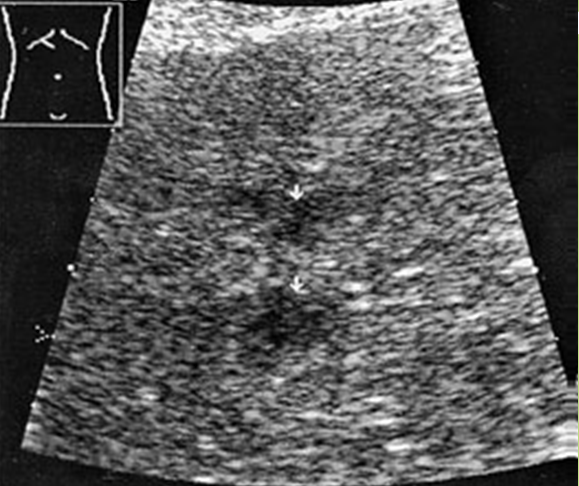
What is Simple hepatic cysts?
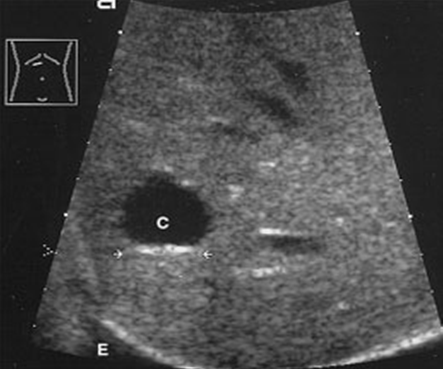
A hepatic cyst is usually a solitary, non-parasitic cyst of the liver. solitary or multiple. More common in females.
What is the sonographic appearance of hepatic cysts?
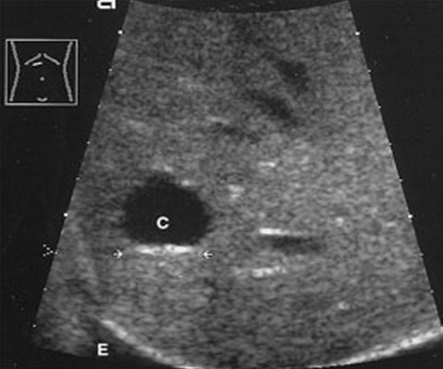
Solitary or multiple
Thin well-defined
walls
Anechoic
Posterior enhancement
Rarely fine,
linear internal septa, Calcification
What are the presenting symptoms of hepatic cysts?
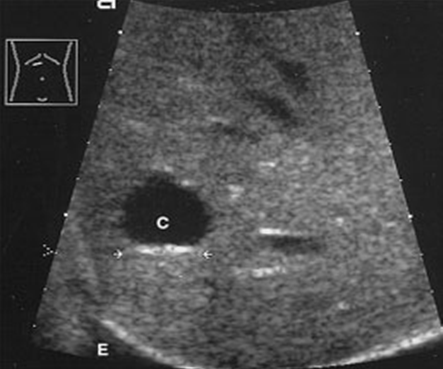
Asymptomatic
localized pain
What is Congenital hepatic cysts?
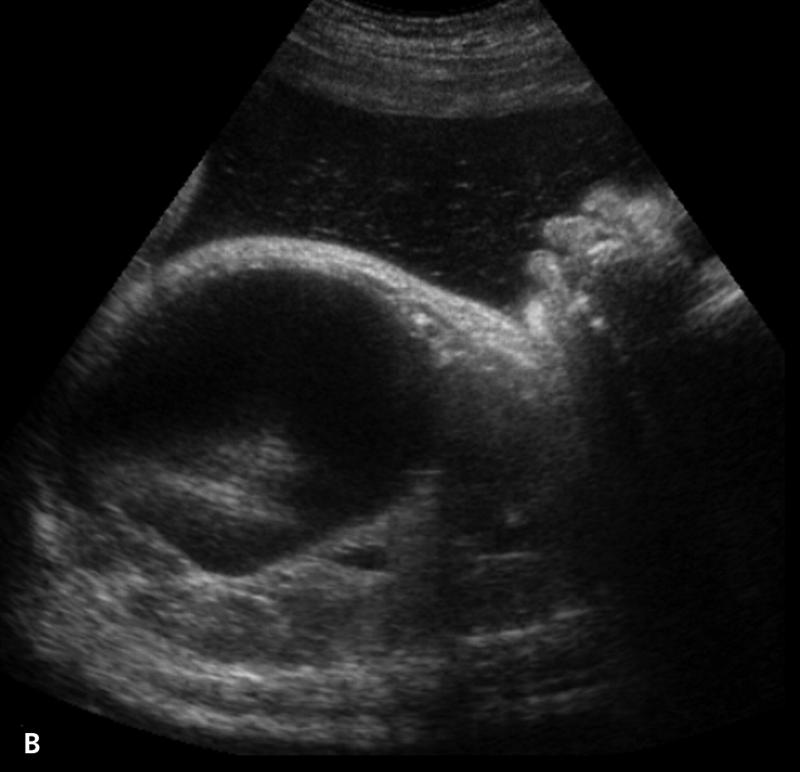
A rare lesion that caused by developmental defects in the formation of bile ducts.
What is the sonographic appearance of Congenital hepatic cysts?
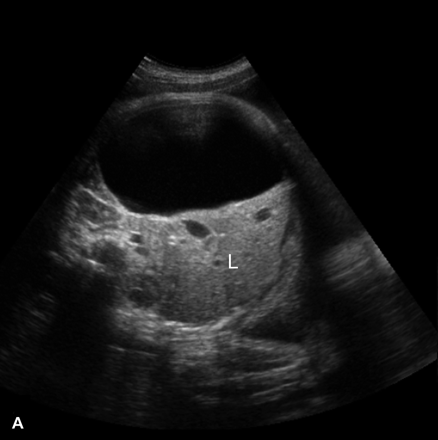
Usually solitary
Varying size
Thin well-defined
walls
Anechoic
Posterior enhancement
Generally right
lobe lesion
What is Peribiliary Cysts?
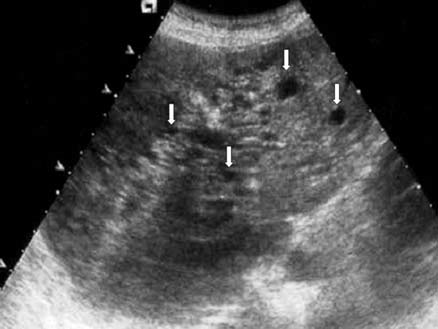
Very small cysts that range from .2 to 2.5 cm. They are most common in patients with severe liver disease.
What is the sonographic appearance of Peribiliary Cysts?
clusters with a tubular appearance
thin septations that run
parallel to the bile ducts and portal veins
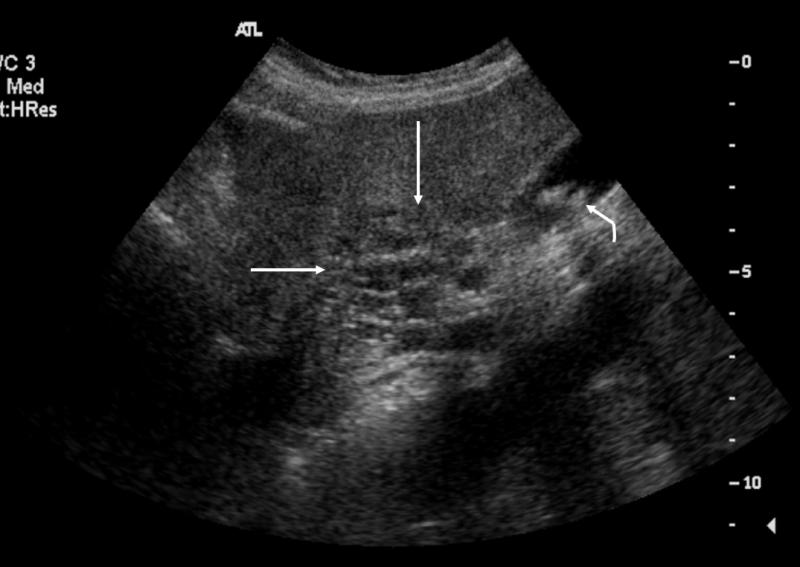
What is Polycystic liver disease?
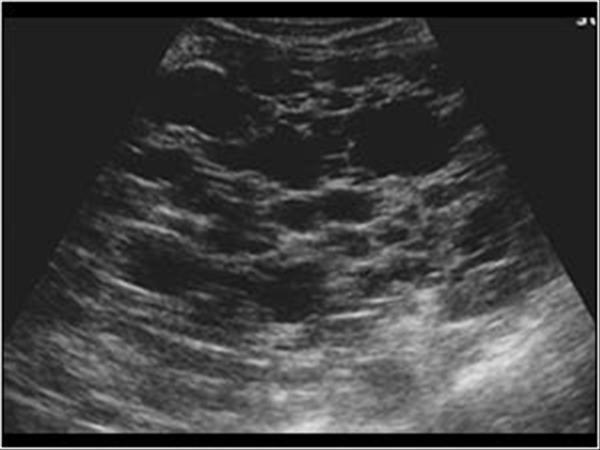
This is an autosomal dominant genetic disease in which multiple small cysts cover the liver. 60% of patients with polycystic liver disease will have polycystic kidney disease.
What is the sonographic appearance of Polycystic liver disease?
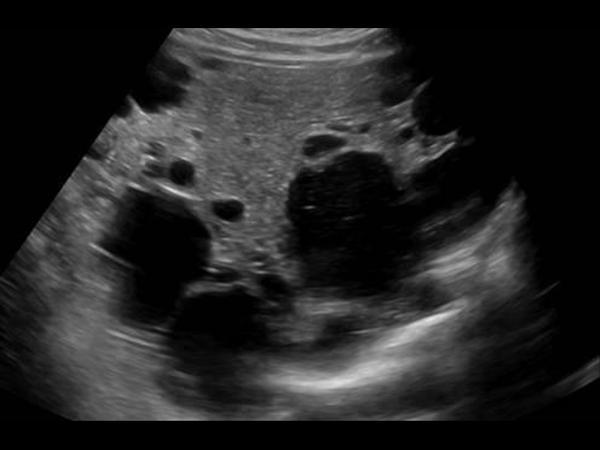
Anechoic
Thin well-defined walls
Posterior
enhancement
Multiple
Varying in small size
What are the presenting symptoms of Polycystic liver disease?
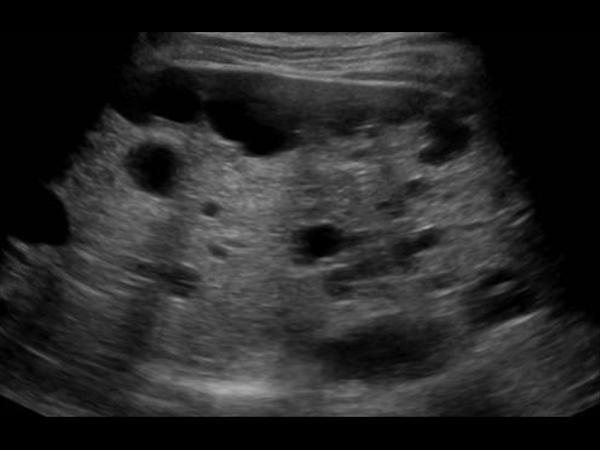
abdominal pain
bloating or swelling in the abdomen
feeling full
What are the lab values that would suggest Polycystic liver disease?
↑WBC
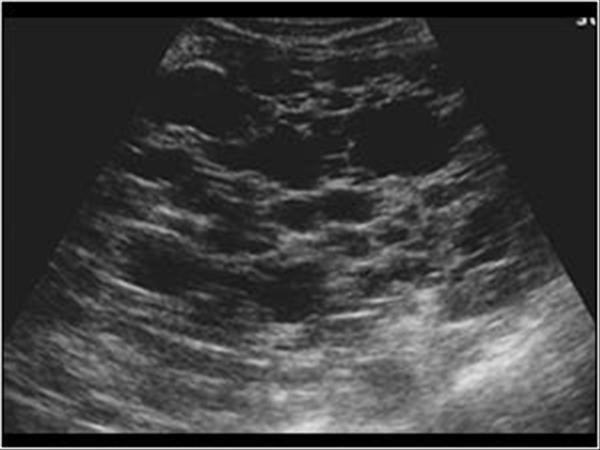
What is Pyogenic abscess?
A pus-forming abscess caused by bacteria. The most common bacteria is Escherichia coli and anaerobes.
The most frequent organism causing the infection is Escherichia coli or anaerobes
What is the sonographic appearance of Pyogenic abscess?
Sonographic Appearance:
Varying size
hyperechoic
round
or oval margins
Internal debris
Posterior
enhancement
Shadowing
Presentation: fever, pain, pleutitis,
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Elevated liver function tests,
leukocytosis, and anemia. The most frequent organism causing the
infection is Escherichia coli or anaerobes
Lab Values: ↑WBC, LFT
What are the presenting symptoms of Pyogenic abscess?
fever
pain
pleutitis
nausea
vomiting
diarrhea
What are the lab values that would suggest Pyogenic abscess?
↑WBC
LFT
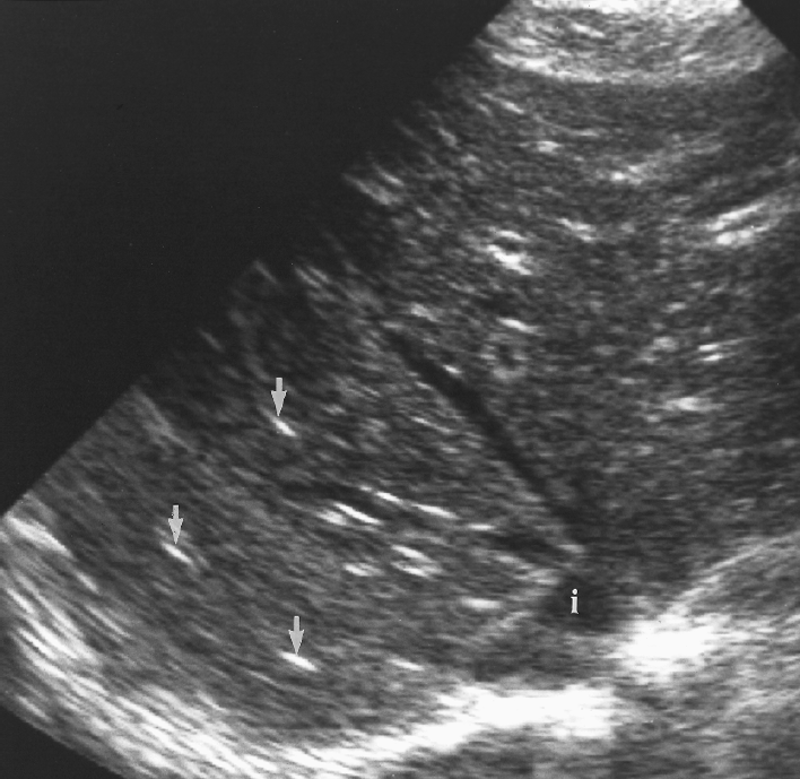
What is Hepatic candidiasis?
This is caused by a type of Candida fungus usually in immunocompromised patients.
What is the sonographic appearance of Hepatic candidiasis?
Multiple
small
bull’s-eyes or target
lesions
Hypoechoic mass
echogenic core
What are the presenting symptoms of Hepatic candidiasis?
persistent fever and localized pain
What are the lab values that would suggest Hepatic candidiasis?
↑WBC
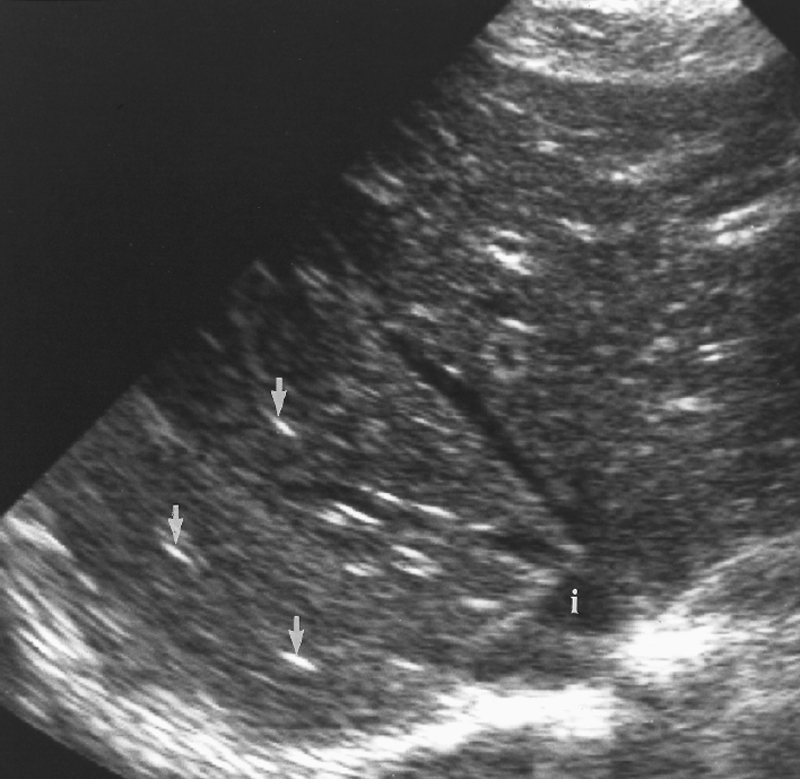
What is Chronic granulomatous disease?
a genetic disorder in which phagocytes are unable to kill certain bacteria.
What is the sonographic appearance of granulomatous disease?
Sonographic Appearance:
Poor borders
hypoechoic
mass
Posterior enhancement
Calcifications
shadowing
What are the presenting symptoms of granulomatous disease?
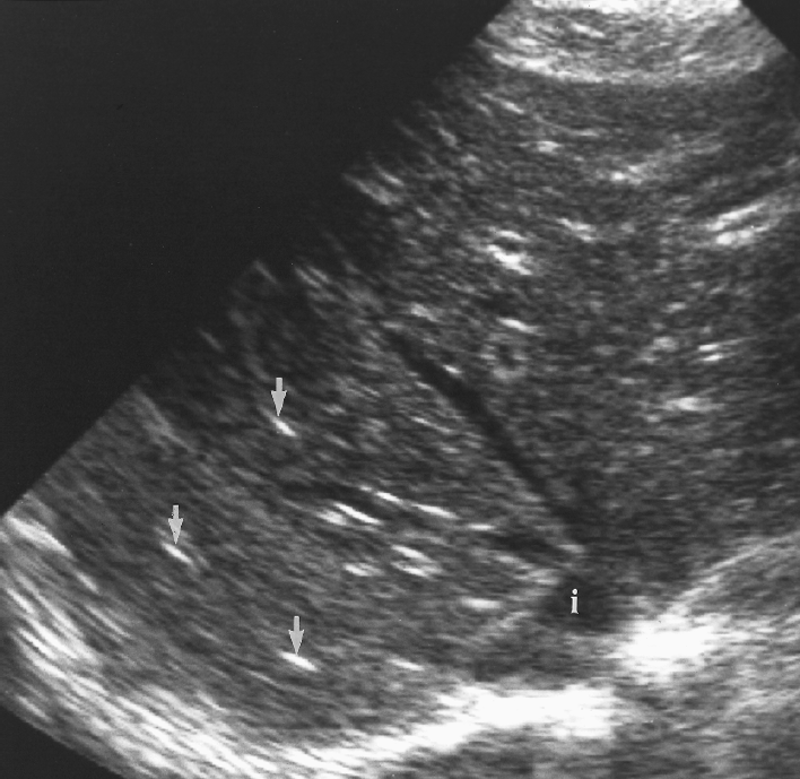
reoccurring respiratory infections
What are the lab values that would suggest granulomatous disease?
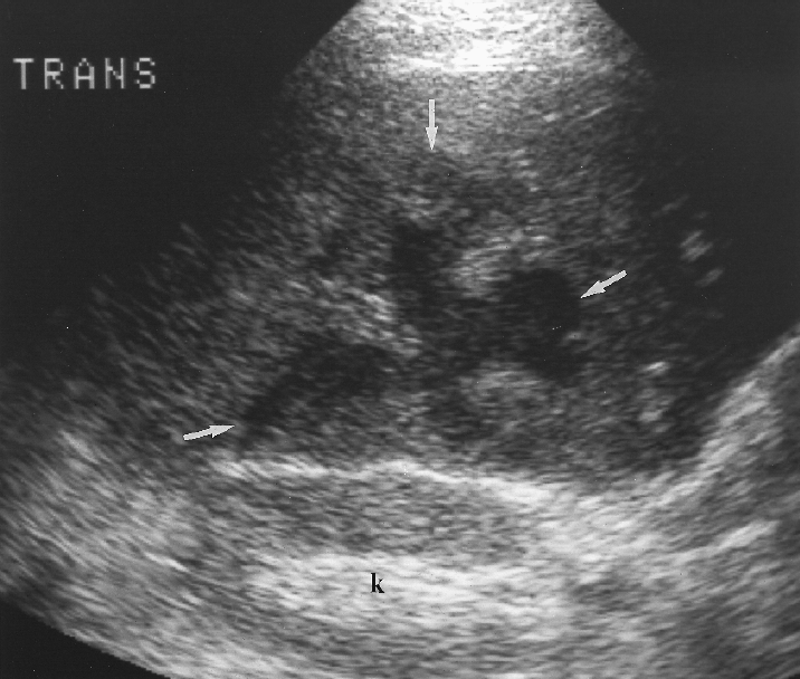
What is Amebic abscess?

A collection of pus formed by disintegrated tissue. Primarily a disease of the colon
What is the sonographic appearance of Amebic abscess?
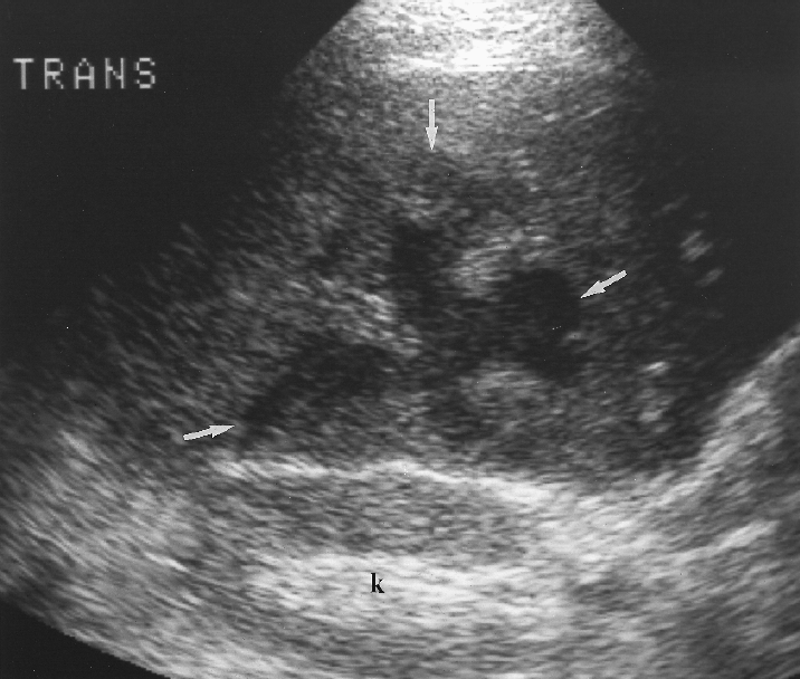
Hypoechoic
Ill-defined walls
Round or oval
Internal
echoes
Posterior enhancement
What are the presenting symptoms of Amebic abscess?

asymptomatic
abdominal pain
diarrhea leukocytosis
fever.
What are the lab values that would suggest Amebic abscess?
↑Leukocytes
What is Echinococcal cyst?
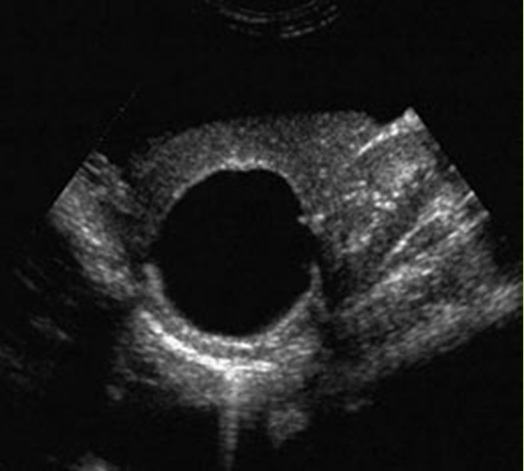
Infectious cystic disease common in sheep herders, a tapeworm that infects.
What is the sonographic appearance of Echinococcal cyst?

Simple
Complex cyst
Posterior
enhancement
Round
oval
Calcifications
Septations
Water
lily sign (cyst within cyst)
What are the presenting symptoms of Echinococcal cyst?
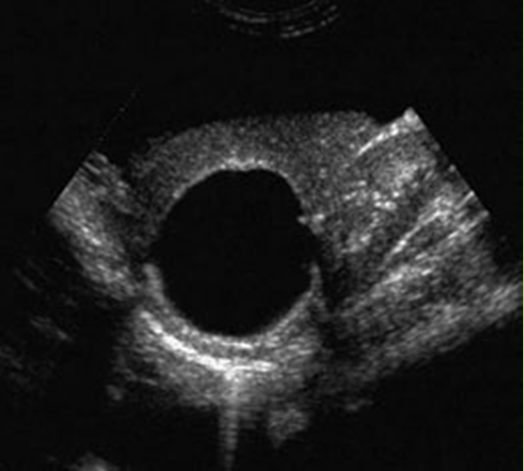
asymptomatic
abdominal pain
abnormal abdominal tenderness
hepatomegaly
abdominal mass
jaundice
fever
anaphylactic reaction
What are the lab values that would suggest Echinococcal cyst?
↑WBC
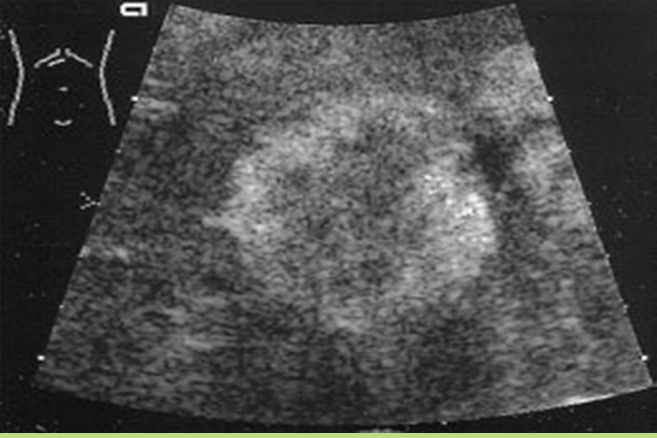
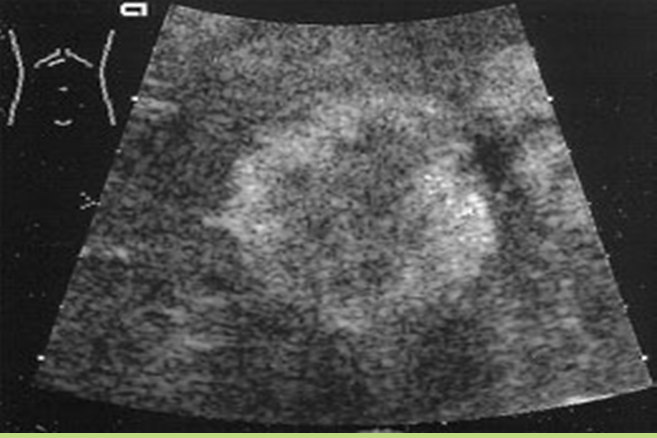
What is Cavernous hemangioma?
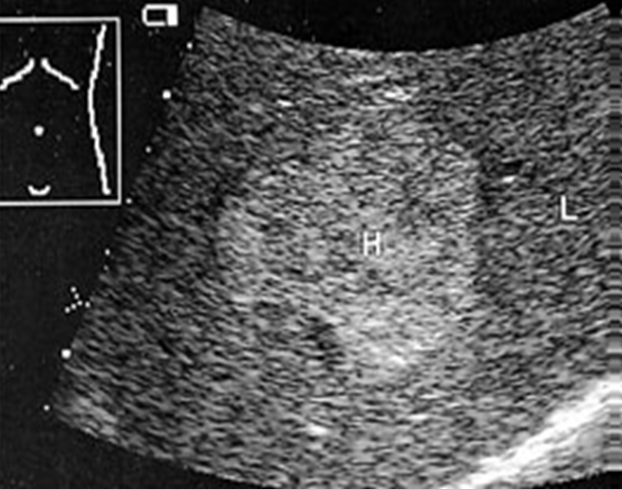
Benign congenital tumor of the liver. Most common and most frequent in females.
What is the sonographic appearance of hemangioma?
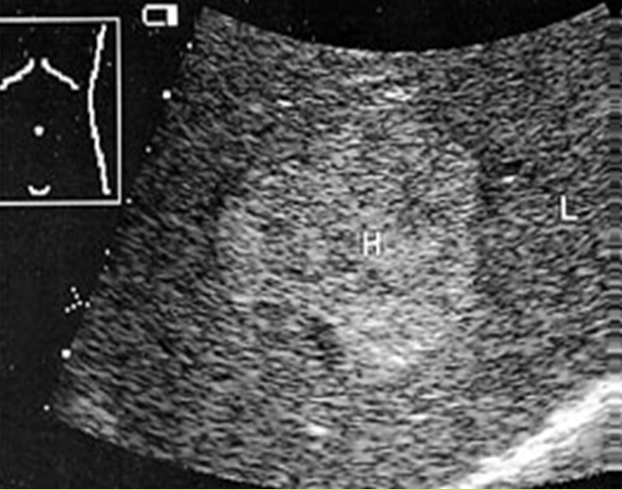
Hyperechoic
Posterior enhancement
Round, oval or
lobulated
Well-defined walls
Mixed echogenicity from necrosis
Heterogeneous
Calcifications
What are the presenting symptoms of hemangioma?
RUQ pain
What are the lab values that would suggest hemangioma?
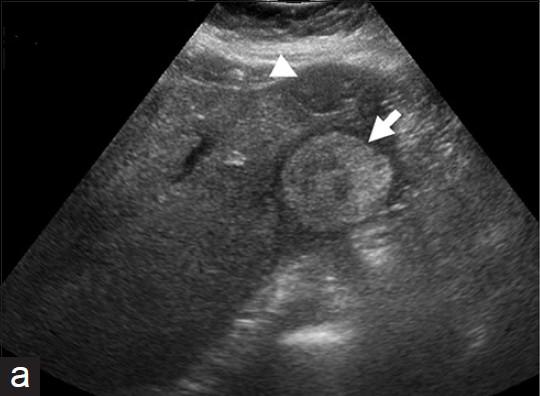
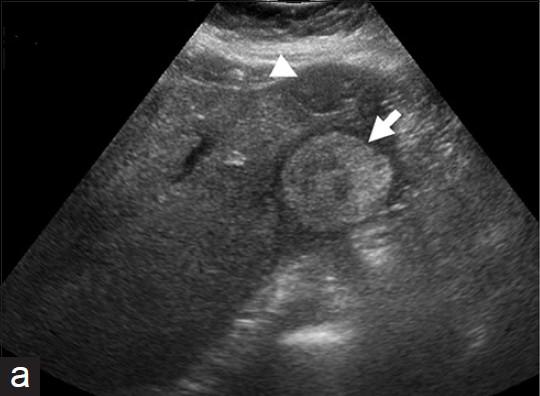
What is Liver cell adenoma?
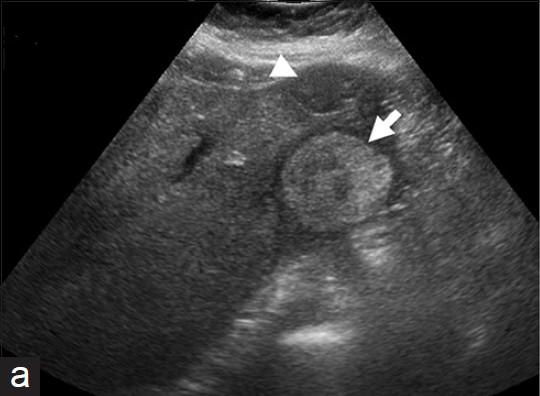
tumor of glandular epithelial tissue. More commonly in women taking oral contraceptives.
What is the sonographic appearance of Liver cell adenoma?
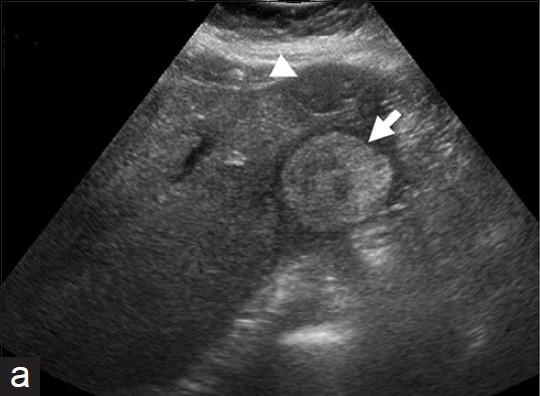
Sonographic Appearance:
Well defined
Hyperechoic with
central hypoechoic area
Solitary
Multiple
Fluid may be present
What are the presenting symptoms of Liver cell adenoma?
RUQ pain
What are the lab values that would suggest Liver cell adenoma?
What is Hepatic cystadenoma?
rare neoplasm in middle aged women
What is the sonographic appearance of Hepatic cystadenoma?
Multi – loculated lesion
mucinous fluid
What are the presenting symptoms of Hepatic cystadenoma?
palpable mass
What are the lab values that would suggest Hepatic cystadenoma?
...
What is Focal nodular hyperplasia?
This is the second most common benign liver mass in women over 40 years of age.
What is the sonographic appearance of Focal nodular hyperplasia?
Sonographic Appearance:
Subtle contour
abnormalities
Hyperechoic to linear areas
Multiple nodule
What are the presenting symptoms of Focal nodular hyperplasia?

Asymptomatic
What are the lab values that would suggest Focal nodular hyperplasia?
What is Hepatocellular carcinoma?
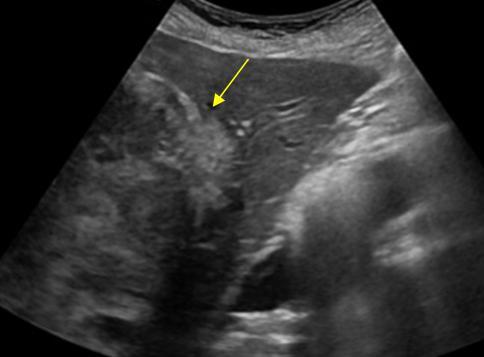
HCC - This is the most common primary malignant neoplasm.
What is the sonographic appearance of Hepatocellular carcinoma?
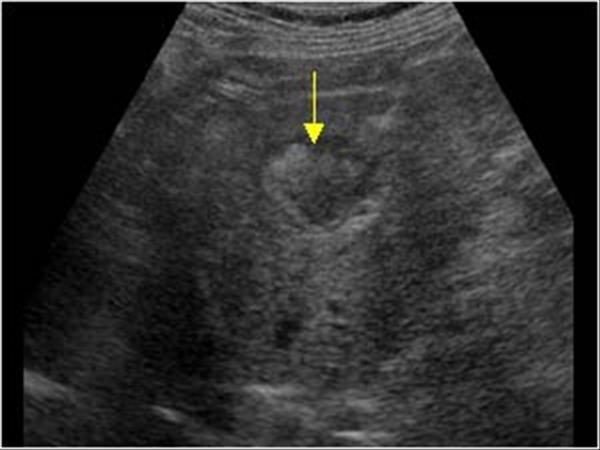
Sonographic Appearance:
hepatomegaly
Appearance
varies
Solitary
Multiple
Hypoechoic
Hyperechoic
Vessel
with tumor invasion
What are the presenting symptoms of Hepatocellular carcinoma?
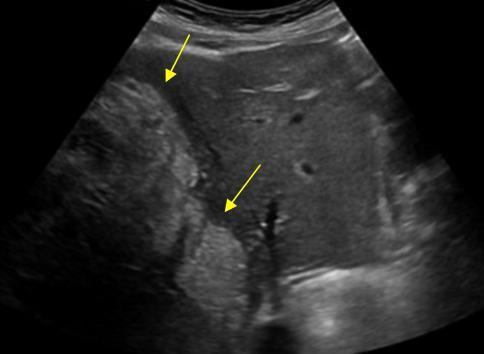
palpable mass
appetite disorder
fever
What are the lab values that would suggest Hepatocellular carcinoma?
↑alpha-protein test
Liver function test
↑Alk Phos
↑Direct Bilirubin
↑AST, ↑ALT
Leukopenia
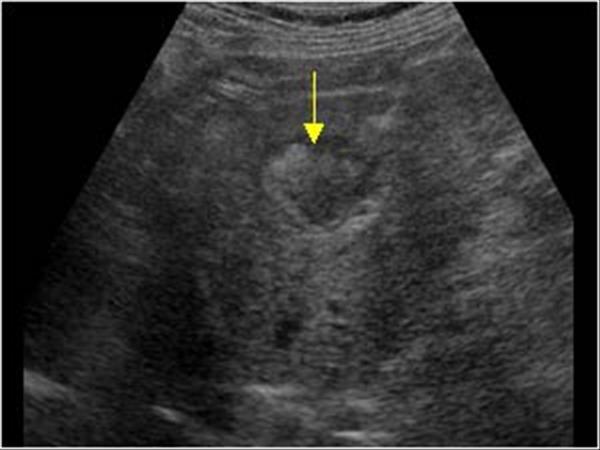
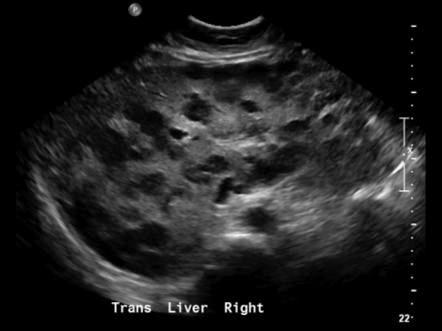
What is Metastatic disease?
This is the most common form of neoplastic involvement of the liver. The primary sites include colon, breast, and lung.
What is the sonographic appearance of Metastatic disease?
Appearance varies
Multiple nodes
Solitary
Well
defined
Echogenic to hypoechoic mass
Homogenous
Calcification
Necrosis
What are the presenting symptoms of Metastatic disease?
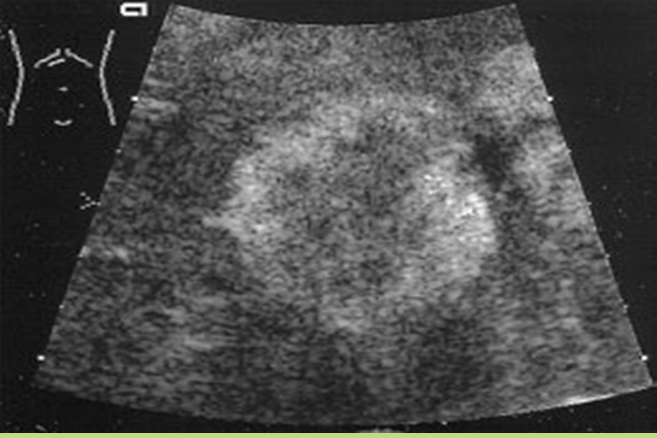
jaundice
hepatomegaly
weight loss
decreased appetite
What are the lab values that would suggest Metastatic disease?
Abnormal LFT
What is Lymphoma?
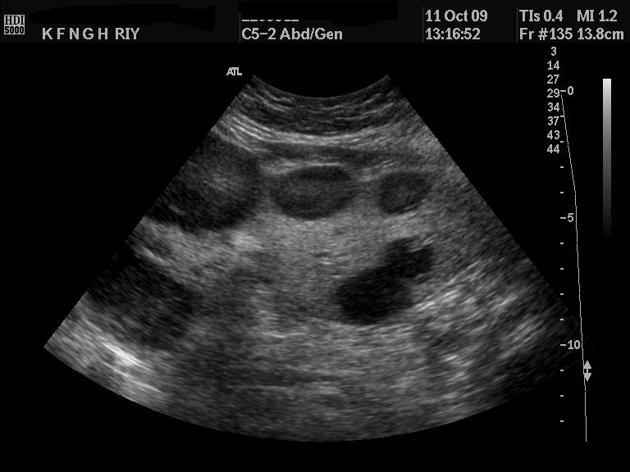
This is a malignant neoplasm which involves a rapid increase of lymphocytes in the lymph nodes. Hodgkins, and Non-Hodgkins lymphoma.
What is the sonographic appearance of Lymphoma?
hepatomegaly
Hypoechoic target lesions
Anechoic
Solid
with no enhancement
Hepatosplenomegaly
What are the lab values that would suggest Lymphoma?
abnormal LFTs
What is Hepatic trauma?
injury
What is the sonographic appearance of Hepatic trauma?
Hyperechoic hematomas
Hyperechoic to anechoic
Unilateral
fluid along laceration
Septations
varies
What are the presenting symptoms of Hepatic trauma?
varies
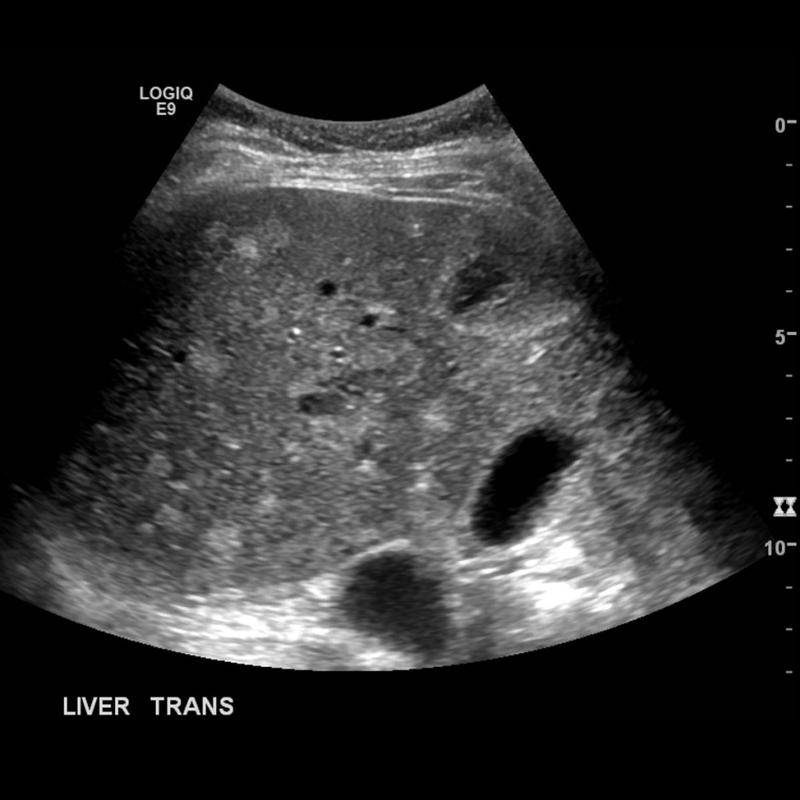
What is Liver transplantation?

A liver transplant is performed when other conventional and surgical methods have failed the patient. The most common reason for a transplant is cirrhosis.
Scans should be performed 24, 48, and biweekly post operative
What is the sonographic appearance of transplantation?

Examine the portal venous system, hepatic arteries, the IVC, and
parenchymal patterns
Examine the kidneys and the
spleen
Asses the biliary system
Asses the vascular flow
What is the cause of the most common complication of a liver transplant?
hepatic arteries
What are the lab values that would suggest transplantation?
...
What is lymphadenopathy?
Swollen lymph nodes
What is lymphosarcoma?
lymphadenopathy in multiple organs
Pediatrics
What is Neuroblastomeas?
tumor of the adrenal
densely reflective
Pediatrics
What is Wilms tumor?
reflective with central lucency from necrosis
Pediatrics
What is Leukemia?
cancer of blood
reflective with central lucency from necrosis