Which one of the following is correct?
A) ν + λ = c
B) ν ÷
λ = c
C) ν = cλ
D) λ = c ν
E) νλ = c
E
Of the following, ________ radiation has the shortest
wavelength.
A) X-ray
B) radio
C) microwave
D)
ultraviolet
E) infrared
A
The photoelectric effect is ________.
A) the total reflection of
light by metals giving them their typical luster
B) the
production of current by silicon solar cells when exposed to
sunlight
C) the ejection of electrons by a metal when struck with
light of sufficient energy
D) the darkening of photographic film
when exposed to an electric field
E) a relativistic effect
C
Which one of the following is considered to be ionizing
radiation?
A) visible light
B) radio waves
C)
X-rays
D) microwaves
E) infrared radiation
C
Of the following transitions in the Bohr hydrogen atom, the ________
transition results in the emission of the lowest-energy
photon.
A) n = 1 → n = 6
B) n = 6 → n = 1
C) n = 6 → n
= 3
D) n = 3 → n = 6
E) n = 1 → n = 4
C
In the Bohr model of the atom, ________.
A) electrons travel in
circular paths called orbitals
B) electrons can have any
energy
C) electron energies are quantized
D) electron paths
are controlled by probability
E) both A and C
C
According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, it is impossible
to know precisely both the position and the ________ of an
electron.
A) mass
B) color
C) momentum
D)
shape
E) charge
C
All of the orbitals in a given electron shell have the same value as
the ________ quantum number.
A) principal
B) angular
momentum
C) magnetic
D) spin
E) psi
A
The de Broglie wavelength of a ________ will have the shortest
wavelength when traveling at 30 cm/s.
A) marble
B)
car
C) planet
D) uranium atom
E) hydrogen atom
C
The uncertainty principle states that ________.
A) matter and
energy are really the same thing
B) it is impossible to know
anything with certainty
C) it is impossible to know the exact
position and momentum of an electron
D) there can only be one
uncertain digit in a reported number
E) it is impossible to know
how many electrons there are in an atom
C
All of the orbitals in a given subshell have the same value as the
________ quantum number.
A) principal
B) spin
C)
magnetic
D) A and B
E) B and C
A
Which one of the following is not a valid value for the magnetic
quantum number of an electron in a 5d subshell?
A) 2
B)
3
C) 0
D) 1
E) -1
B
Which of the subshells below do not exist due to the constraints upon
the angular momentum quantum number?
A) 2d
B) 2s
C)
2p
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A
Which of the subshells below do not exist due to the constraints upon
the angular momentum quantum number?
A) 4f
B) 4d
C)
4p
D) 4s
E) none of the above
E
An electron cannot have the quantum numbers n = ________, l =
________, ml = ________.
A) 2, 0, 0
B) 2, 1, -1
C) 3,
1, -1
D) 1, 1, 1
E) 3, 2, 1
D
An electron cannot have the quantum numbers n = ________, l =
________, ml = ________.
A) 6, 1, 0
B) 3, 2, 3
C) 3, 2,
-2
D) 1, 0, 0
E) 3, 2, 1
B
Which one of the following is an incorrect subshell notation?
A)
4f
B) 2d
C) 3s
D) 2p
E) 3d
B
Which one of the following is an incorrect orbital notation?
A)
2s
B) 3py
C) 3f
D) 4dxy
E) 4s
C
Which quantum number determines the energy of an electron in a
hydrogen atom?
A) n
B) E
C) ml
D) l
E) n and l
A
All of the following are a result from the solution of the
Schrodinger equation except ________.
A) spin
B)
principal
C) azimuthal
D) magnetic
E) angular momentum
A
Which quantum numbers must be the same for the orbitals that they
designate to be degenerate in a one-electron system (such as
hydrogen)?
A) n, l, and ml
B) n and l only
C) l and
ml
D) ml only
E) n only
E
In a px orbital, the subscript x denotes the
________.
A) energy of the electron
B) spin of the
electrons
C) probability of the shell
D) size of the
orbital
E) axis along which the orbital is aligned
E
A 4pz orbital in a many-electron atom is degenerate with
________.
A) 5s
B) 3pz
C) 4dxy
D) 4px
E) 4d2
D
Which one of the following orbitals can hold two electrons?
A)
2px
B) 3s
C) 4dxy
D) all of
the above
E) none of the above
D
Which of the quantum number(s) below represent the principal quantum
number?
A) n, l, and ml
B) n only
C) n, l, ml, and
ms
D) ms only
E) n and l only
B
Which of the following is not a valid set of four quantum numbers?
(n, l, ml, ms)
A) 2, 0, 0, +1/2
B) 2, 1, 0, -1/2
C) 3,
1, -1, -1/2
D) 1, 0, 0, +1/2
E) 1, 1, 0, +1/2
E
Which of the following is a valid set of four quantum numbers? (n, l,
ml, ms)
A) 2, 1, 0, +1/2
B) 2, 2, 1, -1/2
C) 1, 0, 1,
+1/2
D) 2, 1, +2, +1/2
E) 1, 1, 0, -1/2
A
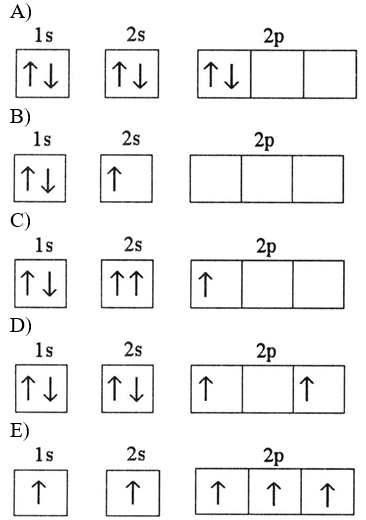
Which electron configuration represents a violation of the Pauli exclusion principle?
C
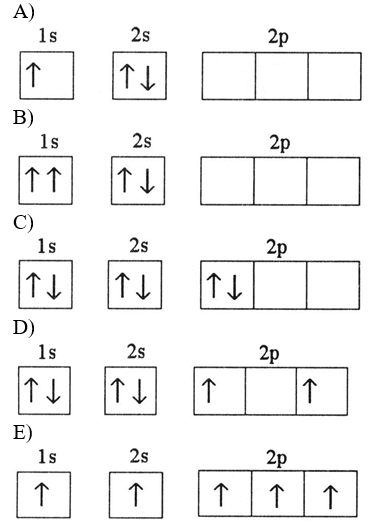
Which electron configuration represents a violation of the Pauli exclusion principle?
B
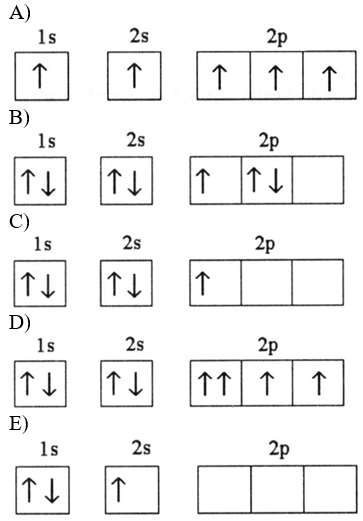
Which electron orbital diagram represents a violation of the Aufbau principle?
A

Which one of the following is the correct electron configuration for a ground-state nitrogen atom?
D
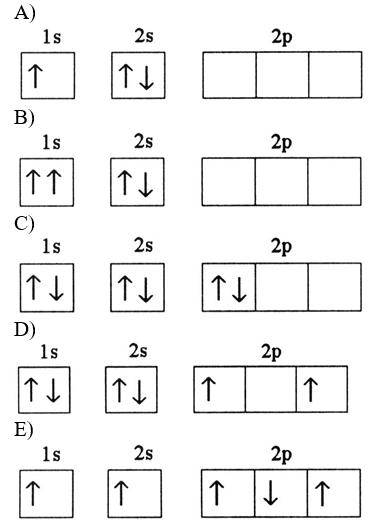
Which electron configuration denotes an atom in its ground state?
D
The ground state electron configuration of Ga is ________.
A)
1s22s23s23p64s23d104p1
B) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p1
C)
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p1
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104d1
E) [Ar]4s23d11
C
The ground-state electron configuration of the element ________ is
[Kr]5s14d5.
A) Nb
B) Mo
C) Cr
D) Mn
E) Tc
B
The ground-state electron configuration of ________ is
[Ar]4s13d5.
A) V
B) Mn
C) Fe
D) Cr
E) K
D
Which is the correct electron configuration for a nitrogen
atom?
A) 1s22s22p2
B) 1s22s22p1
C) 1s22s22p4
D)
1s22s22p3
E) [He]2s22p5
D
Which is the correct electron configuration for an oxide ion?
A)
1s22s22p3
B) 1s22s22p1
C) 1s22s22p6
D)
1s22s23s2
E) 1s22s22p2
C
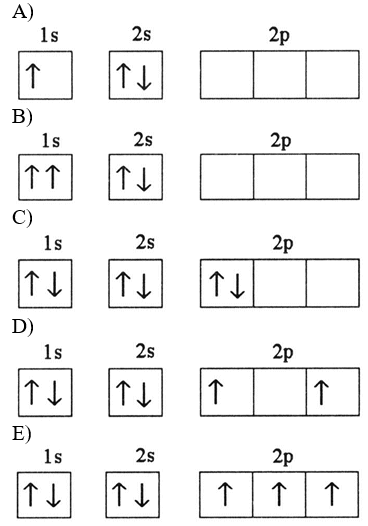
Which electron configuration represents a violation of Hund's rule for an atom in its ground state?
C
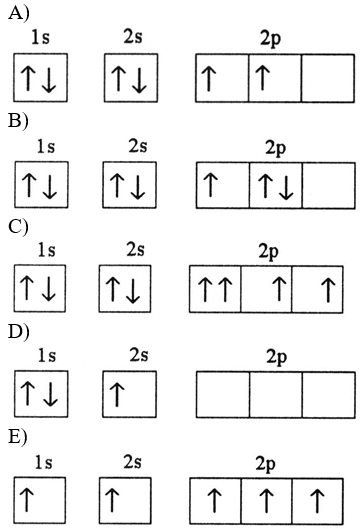
Which electron configuration represents a violation of Hund's rule for an atom in its ground state?
B
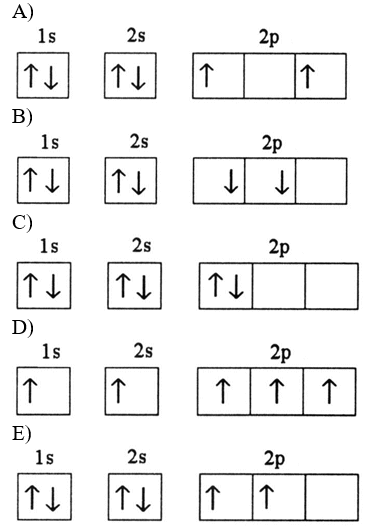
Which electron orbital diagram is written correctly for an atom without any violations?
E
The ground-state configuration of fluorine is ________.
A)
[He]2s22p2
B) [He]2s22p3
C) [He]2s22p4
D)
[He]2s22p5
E) [He]2s22p6
D
The ground-state configuration of tungsten is ________.
A)
[Ar]4s23d3
B) [Xe]6s24f145d4
C) [Ne]3s1
D)
[Xe]6s24f7
E) [Kr]5s24d105p5
B
No two electrons within the same orbtial can have the same set of
quantum numbers. This statement describes ________.
A) Planck's
constant
B) Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
C) Pauli
Exclusion Principle
D) deBroglie hypothesis
E) Hund's rule
C
Which of the following elements has a ground-state electron
configuration different from the predicted one?
A) Cu
B)
Ca
C) Xe
D) Cl
E) Ti
A
Which two elements have the same ground-state electron
configuration?
A) Pd and Pt
B) Cu and Ag
C) Fe and
Cu
D) Cl and Ar
E) No two elements have the same
ground-state electron configuration.
E
How many different principal quantum numbers can be found in the
ground-state electron configuration of nickel?
A) 2
B)
3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
C
The valence shell of the element X contains 2 electrons in a 5s
subshell. Below that shell, element X has a partially filled 4d
subshell. What type of element is X?
A) main group
element
B) chalcogen
C) halogen
D) transition
metal
E) alkali metal
D
Electromagnetic radiation travels through vacuum at a speed of
________ m/s.
A) 186,000
B) 125
C) 3.00 ×
108
D) 10,000
E) It depends on wavelength.
C
The wavelength of light that has a frequency of 1.20 ×
1013 s-1 is ________ m.
A) 25.0
B)
2.50 × 10-5
C) 0.0400
D) 12.0
E) 2.5
B
The wavelength of light that has a frequency of 1.66 × 109
s-1 is ________ m.
A) 0.181
B) 5.53
C) 2.00
× 10-9
D) 5.53 × 108
E) none of the above
A
Ham radio operators often broadcast on the 6-meter band. The
frequency of this electromagnetic radiation is ________ MHz.
A)
500
B) 200
C) 50
D) 20
E) 2.0
C
Visible light with a wavelength of 550 nm has a frequency of ________
Hz.
A) 5.5 × 105
B) 1.7 × 1011
C) 5.5 × 1014
D) 1.7 × 102
E)
5.5 × 1017
C
What is the frequency (s-1) of electromagnetic radiation that has a
wavelength of 2.3 m?
A) 1.3 × 108 s-1
B) 1.8 ×
10-9 s-1
C) 1.6 × 108 s-1
D) 1.3 ×
10-33 s-1
E) 1.3 × 1033 s-1
A
What is the frequency of light (s-1) that has a wavelength of 1.23 ×
10-6 cm?
A) 3.69
B) 2.44 × 1016
s-1
C) 4.10 × 10-17 s-1
D) 9.62 × 1012
s-1
E) 1.04 × 10-13 s-1
B
What is the frequency of light (s-1) that has a wavelength of 3.86 ×
10-5 cm?
A) 7.77 × 1014 s-1
B) 6.32 ×
10-12 s-1
C) 1.04 × 10-13 s-1
D) 9.62
× 1012 s-1
E) 2.14 × 10-16 s-1
A
What is the frequency of light (s-1) that has a wavelength of 3.12 ×
10-3 cm?
A) 3.69 s-1
B) 2.44 × 1016
s-1
C) 9.62 × 1012 s-1
D) 4.10 × 10-17
s-1
E) 1.04 × 10-13 s-1
C
What is the wavelength of light (nm) that has a frequency of 3.22 ×
1014 s-1?
A) 932 nm
B) 649 nm
C) 9.66 ×
1022 nm
D) 9.32 × 10-7 nm
E) 1.07 ×
106 nm
A
What is the wavelength of light (nm) that has a frequency of 6.44 ×
1013 s-1?
A) 4660 nm
B) 6490 nm
C) 4.66 ×
10-8 nm
D) 6.49 × 10-8 nm
E) 932 nm
A
What is the wavelength of light (nm) that has a frequency 4.62 ×
1014 s-1?
A) 932 nm
B) 649 nm
C) 1.39 ×
1023 nm
D) 1.54 × 10-3 nm
E) 1.07 ×
106 nm
B
The wavelength of a photon that has an energy of 6.33 ×
10-18 J is ________ m.
A) 3.79 × 10-7
B) 3.10 × 10-8
C) 2.38 × 1023
D) 4.21 × 10-24
E) 9.55 × 1015
B
The energy of a photon of light is ________ proportional to its
frequency and ________ proportional to its wavelength.
A)
directly, directly
B) inversely, inversely
C) inversely,
directly
D) directly, inversely
E) indirectly, not
D
The wavelength of a photon that has an energy of 5.25 ×
10-19 J is ________ m.
A) 3.79 × 10-7
B) 2.64 × 106
C) 2.38 × 1023
D) 4.21 ×
10-24
E) 3.79 × 107
A
The energy of a photon that has a wavelength of 9.0 m is ________
J.
A) 2.2 × 10-26
B) 4.5 × 1025
C) 6.0 × 10-23
D) 2.7 × 109
E) 4.5 × 10-25
A
The energy of a photon that has a wavelength of 8.33 ×
10-6 m is ________ J.
A) 2.20 × 10-26
B) 3.60 × 1013
C) 2.39 × 10-20
D) 2.7 × 109
E) 4.5 × 10-25
C
The frequency of a photon that has an energy of 3.7 ×
10-18 J is ________ s-1.
A) 5.6 × 1015
B) 1.8 × 10-16
C) 2.5 × 10-15
D) 5.4 × 10-8
E) 2.5 × 1015
A
The frequency of a photon that has an energy of 8.5 ×
10-12 J is ________ s-1.
A) 1.3 × 1022
B) 1.8 × 10-16
C) 2.5 × 10-15
D) 5.4 × 10-8
E) 2.5 × 1015
A
What is the energy of a photon (J) that has a wavelength of 105
nm?
A) 1.89 × 10-13
B) 1.89 × 10-32
C) 1.89 × 10-18
D) 1.89 × 10-36
E) 1.89 × 10-27
C
The energy of a photon that has a wavelength of 13.2 nm is ________
J.
A) 9.55 × 10-25
B) 1.62 × 10-17
C) 1.99 × 10-25
D) 4.42 × 10-23
E) 1.51 × 10-17
E
What is the energy of a photon (J) that has a frequency of 4.39 ×
1019 Hz?
A) 2.91 × 10-14
B) 2.91 ×
1020
C) 6.83 × 10-12
D) 2.91 ×
10-52
E) 2.91 × 1054
A
The energy of a photon that has a frequency of 1.821 ×
1016 s-1 is ________ J.
A) 5.44 × 10-18
B) 1.99 × 10-25
C) 3.49 × 10-48
D) 1.21 × 10-17
E) 5.46 × 10-24
D
What is the frequency (s-1) of a photon that has an energy of 4.38 ×
10-18 J?
A) 436 s-1
B) 6.61 × 1015
s-1
C) 1.45 × 10-16 s-1
D) 2.30 × 107
s-1
E) 1.31 × 10-9 s-1
B
What is the wavelength (angstroms) of a photon that has an energy of
4.38 × 10-18 J?
A) 45.4 angstroms
B) 2.30 ×
107 angstroms
C) 6.89 × 1015
angstroms
D) 1.45 × 10-16 angstroms
E) 1.31 ×
10-9 angstroms
A
A photon that has an energy of 8.63 × 10-12 J would emit
light at which wavelength (m)?
A) 230
B) 2.30 ×
10-14
C) 2.30
D) 3.48 × 1019
E) 2.30 × 10-5
B
A mole of red photons of wavelength 725 nm has ________ kJ of
energy.
A) 2.74 × 10-19
B) 4.56 ×
10-46
C) 6.05 × 10-3
D) 165
E) 227
D
A mole of yellow photons of wavelength 527 nm has ________ kJ of
energy.
A) 165
B) 227
C) 4.56 × 10-46
D) 6.05 × 10-3
E) 2.74 × 10-19
B
Of the following, ________ radiation has the longest wavelength and
________ radiation has the greatest energy.
gamma ultraviolet visible
A) ultraviolet, gamma
B) visible, ultraviolet
C) gamma,
gamma
D) visible, gamma
E) gamma, visible
D
What color of visible light has the longest wavelength?
A)
blue
B) violet
C) red
D) yellow
E) green
C
Which of the following radiation sources from the electromagnetic
spectrum has the shortest wavelength and greatest energy?
A)
radio
B) microwave
C) gamma
D) visible
E) ultraviolet
C
What color of visible light has the highest energy?
A)
violet
B) blue
C) red
D) green
E) yellow
A
Using Bohr's equation for the energy levels of the electron in the
hydrogen atom, determine the energy (J) of an electron in the n = 4
level.
A) -1.36 × 10-19
B) -5.45 ×
10-19
C) -7.34 × 1018
D) -1.84 ×
10-29
E) +1.84 × 10-29
A
An electron in a Bohr hydrogen atom with a n = 4 value would have an
energy of ________.
A) 1.362 × 10-19 J
B) -1.362
× 10-16 J
C) -1.362 × 1019 J
D) 1.362
× 1019 J
E) -1.362 × 10-19 J
E
The energy (J) required for an electronic transition in a Bohr
hydrogen atom from n = 2 to n = 3 is ________ J.
A) 4.00 ×
10-19
B) 3.00 × 10-19
C) -3.00 ×
10-19
D) -7.90 × 10-19
E) 4.60 × 1014
B
The energy (J) required for an electronic transition in a Bohr
hydrogen atom from n = 1 to n = 3 is ________ J.
A) -8.90 ×
10-1
B) 3.00 × 10-19
C) -3.00 ×
10-19
D) 1.94 × 10-18
E) 8.90 × 10-1
D
An electron transition from n = 2 to n = 5 in a Bohr hydrogen atom
would correspond to the following energy.
A) 4.9 ×
10-19 J
B) 4.9 × 1019 J
C) -4.9 ×
10-19 J
D) -4.9 × 1019 J
E) 4.9 ×
10-16 J
A
The frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to promote an
electron from n = 2 to n = 4 in a Bohr hydrogen atom is ________
Hz.
A) 4.13 × 10-19
B) 6.17 × 1014
C) 5.46 × 10-19
D) 8.22 × 1014
E) 4.13 × 1019
B
A spectrum containing only ________ wavelengths is called a line
spectrum.
A) Rydberg
B) specific
C) continuous
D)
visible
E) invariant
B
When the electron in a hydrogen atom moves from n = 6 to n = 1, light
with a wavelength of ________ nm is emitted.
A) 487
B)
411
C) 434
D) 93.8
E) 657
D
What is the wavelength (nm) of light emitted when an electron in a
hydrogen atom moves from n = 4 to n = 2?
A) -486
B) 2.06 ×
1015
C) 486
D) 2.06 × 106
E)
4.86 × 10-7
C
The n = 2 to n = 6 transition in the Bohr hydrogen atom corresponds
to the ________ of a photon with a wavelength of ________ nm.
A)
emission, 410
B) absorption, 410
C) absorption, 660
D)
emission, 94
E) emission, 390
B
The n = 5 to n = 3 transition in the Bohr hydrogen atom corresponds
to the ________ of a photon with a wavelength of ________ nm.
A)
absorption, 657
B) absorption, 1280
C) emission, 657
D)
emission, 1280
E) emission, 389
D
A transition in the Bohr hydrogen atom from n = 4 to n = 2 occurs in
the ________ region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
A)
infrared
B) microwave
C) ultraviolet
D) visible
E) X-ray
D
A transition in the Bohr hydrogen atom from n = 6 to n = 1 occurs in
the ________ region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
A)
radio
B) ultraviolet
C) infrared
D) X-ray
E) microwave
B
The de Broglie wavelength of a particle is given by ________.
A)
h + mv
B) hmv
C) h/mv
D) mv/c
E) mv
C
What is the de Broglie wavelength (m) of a 2.0-kg object moving at a
speed of 50 m/s?
A) 6.6 × 10-36 m
B) 1.5 ×
1035 m
C) 5.3 × 10-33 m
D) 2.6 ×
10-35 m
E) 3.8 × 1034 m
A
A 934 g object is traveling at a velocity of 35.0 m/s. What is the de
Broglie wavelength of this object?
A) 2.03 × 10-38
m
B) 2.03 × 10-32 m
C) 2.03 × 1033
m
D) 2.03 × 10-35 m
E) 2.03 × 1036 m
D
A 13 kg object is traveling at a velocity of 12.0 m/s. What is the de
Broglie wavelength of this object?
A) 4.25 × 10-36
m
B) 4.25 × 1037 m
C) 4.25 × 1034
m
D) 4.25 × 10-39 m
E) 4.25 × 10-33 m
A
At what speed (m/s) must a 10.0-mg object be moving to have a de
Broglie wavelength of 3.3 × 10-41 m?
A) 4.1
m/s
B) 1.9 × 10-11 m/s
C) 2.0 × 1012
m/s
D) 3.3 × 10-42 m/s
E) 1.9 × 1013 m/s
C
A 34.0 mg object with a de Broglie wavelength of is traveling at what
speed?
A) 8.12 × 10-7 m/s
B) 2.76 ×
10-14 m/s
C) 2.76 × 10-11 m/s
D) 8.12
× 10-10 m/s
E) 8.12 × 10-13 m/s
A
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron is 8.7 × 10-11 m.
The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10-31 kg. The velocity of
this electron is ________ m/s.
A) 8.4 × 103
B)
1.2 × 10-7
C) 6.9 × 10-5
D) 8.4 ×
106
E) 8.4 × 10-3
D
What is the de Broglie wavelength (m) of a 1.0 × 109 kg
train car traveling at 95 km/hr?
A) 2.51 × 10-41
B) 2.51 × 10-47
C) 6.97 × 10-45
D) 2.51 × 10-44
E) 6.97 × 10-48
D
What is the de Broglie wavelength (m) of a 1.00 × 103 kg
race car traveling at 145 mi/hr?
A) 1.02 × 10-41
B) 1.02 × 10-35
C) 1.02 × 10-38
D) 4.57 × 10-39
E) 4.57 × 10-42
C
The wavelength of an electron whose velocity is 1.7 × 104
m/s and whose mass is 9.1 × 10-28 g is ________ m.
A)
4.3 × 10-11
B) 12
C) 4.3 × 10-8
D) 2.3 × 107
E) 2.3 × 10-7
C
The ________ quantum number defines the shape of an orbital.
A)
spin
B) magnetic
C) principal
D) angular
momentum
E) psi
D
There are ________ orbitals in the third shell.
A) 25
B)
4
C) 9
D) 16
E) 1
C
The ________ subshell contains only one orbital.
A) 5d
B)
6f
C) 4s
D) 3d
E) 1p
C
There are ________ orbitals in the second shell.
A) 1
B)
2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 9
C
The angular momentum quantum number is 3 in ________
orbitals.
A) s
B) p
C) d
D) f
E) a
D
The n = 1 shell contains ________ p orbitals. All the other shells
contain ________ p orbitals.
A) 3, 6
B) 0, 3
C) 6,
2
D) 3, 3
E) 0, 6
B
The lowest energy shell that contains f orbitals is the shell with n
= ________.
A) 3
B) 2
C) 4
D) 1
E) 5
C
The principal quantum number of the first d subshell is
________.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 0
C
The total number of orbitals in a shell is given by ________.
A)
I2
B) n2
C) 2n
D) 2n + 1
E) 2l + 1
B
In a hydrogen atom, an electron in a 1s orbital can ________ a
photon, but cannot ________ a photon.
A) accept, absorb
B)
absorb, accept
C) absorb, emit
D) emit, absorb
E) emit, accept
C
________-orbitals are spherically symmetrical.
A) s
B)
p
C) d
D) f
E) g
A
Each p-subshell can accommodate a maximum of ________
electrons.
A) 6
B) 2
C) 10
D) 3
E) 5
A
Each d-subshell can accommodate a maximum of ________
electrons.
A) 6
B) 2
C) 10
D) 3
E) 5
C
How many quantum numbers are necessary to designate a particular
electron in an atom?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 2
D) 1
E) 5
B
Which orbital is degenerate with a 3dz 2 in a
many-electron atom?
A) 3dyz
B) 5dz
2
C) 4dz 2
D)
3dzz
E) 4dxz
A
The 3p subshell in the ground state of atomic xenon contains ________
electrons.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 36
B
The 3p subshell in the ground state of atomic silicon contains
________ electrons.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 36
A
The first shell in the ground state of a krypton atom can contain a
maximum of ________ electrons.
A) 6
B) 36
C) 8
D)
18
E) 2
E
The 4d subshell in the ground state of atomic xenon contains ________
electrons.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 36
D
[Ar]4s23d104p3 is the electron configuration of a(n) ________
atom.
A) As
B) V
C) P
D) Sb
E) Sn
A
[Ne]3s23p3 is the electron configuration of a(n) ________
atom.
A) As
B) V
C) P
D) Sb
E) Sn
C
There are ________ unpaired electrons in a ground state fluorine
atom.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
B
The electron configuration of a ground-state Ag atom is
________.
A) [Ar]4s24d9
B) [Kr]5s14d10
C)
[Kr]5s23d9
D) [Ar]4s14d10
E) [Kr]5s24d10
B
The ground-state electron configuration for Zn is ________.
A)
[Kr]4s23d10
B) [Ar]4s23d10
C) [Ar]4s13d10
D)
[Ar]3s23d10
E) [Kr]3s23d10
B
What is the correct ground state electron configuration for
copper?
A) [Ar]4s24d9
B) [Ar]4s14d10
C)
[Ar]4s13d10
D) [Ar]4s23d10
E) [Ar]4s23d9
C
What is the correct ground state electron configuration for
chromium?
A) [Ar]4s13d5
B) [Ar]4s14d5
C)
[Ar]4s23d4
D) [Ar]4s24d5
E) [Kr]4s13d5
A
All of the ________ have a valence shell electron configuration
ns1.
A) noble gases
B) halogens
C) chalcogens
D)
alkali metals
E) alkaline earth metals
D
The elements in the ________ period of the periodic table have a
core-electron configuration that is the same as the electron
configuration of neon.
A) first
B) second
C)
third
D) fourth
E) fifth
C
Elements in group ________ have a np6 electron configuration in the
outer shell.
A) 4A
B) 6A
C) 7A
D) 8A
E) 5A
D
Which group in the periodic table contains elements with the valence
electron configuration of ns2np1?
A) 1A
B) 2A
C)
3A
D) 4A
E) 8A
C
Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 640 nm appears as
orange light to the human eye. The frequency of this light is ________
s-1.
A) 4.688 × 1014
B) 4.688 × 105
C) 1.920 × 102
D) 1.920 × 1011
E) 2.133 × 10-15
A
The wavelength of light emitted from a traffic light having a
frequency of 2.74 × 1014 Hz is ________ nm.
A)
1090
B) 109
C) 54.7
D) 36.5
E) 50.0
A
An FM radio station broadcasts electromagnetic radiation at a
frequency of 89.7 MHz. The wavelength of this radiation is ________
m.
A) 3.34 × 106
B) 3.34
C) 2.69 ×
1016
D) 2.69 × 1010
E) 0.299
B
Calculate the energy (J) found in one photon of visible light if the
wavelength is 589 nm.
A) 3.37 × 10-19
B) 1.17 ×
10-31
C) 1.17 × 10-22
D) 3.37 ×
10-28
E) 2.96 × 1018
A
Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 641 nm appears as
orange light to the human eye. The energy of one photon of this light
is 3.10 × 10-19 J. Thus, a laser that emits 1.3 x
10-2 of energy in a pulse of light at this wavelength
produces ________ photons in each pulse.
A) 2.4 ×
10-17
B) 6.3 × 10-24
C) 2.7 ×
1019
D) 4.2 × 1016
E) 6.5 × 1013
D
Calculate the longest wavelength of light (nm) that can be used to
remove electrons from metal surfaces if 245 kJ/mol is required to
eject electrons.
A) 233
B) 488
C) 725
D)
552
E) 165
B
A radio station broadcasts at 99.5 MHz. The wavelength of the signal
is ________ m.
A) 3.10
B) 3.02
C) 2.90
D)
2.75
E) 4.71
B
When the electron in a hydrogen atom moves from n = 5 to n = 2, light
with a wavelength of ________ nm is emitted.
A) 93.8
B)
410
C) 487
D) 657
E) 434
E
Of the following transitions in the Bohr hydrogen atom, the ________
transition results in the emission of the highest-energy
photon.
A) n = 6 → n = 4
B) n = 2 → n = 7
C) n = 4 → n
= 6
D) n = 1 → n = 4
E) All transitions emit photons of
equivalent energy
A
Of the following transitions in the Bohr hydrogen atom, the ________
transition results in the absorption of the highest-energy
photon.
A) n = 2 → n = 5
B) n = 4 → n = 2
C) n = 3 → n
= 2
D) n = 5 → n = 2
E) All transitions absorb photons of
equivalent energy.
A
What is the de Broglie wavelength (m) of an electron traveling at a
velocity of 6.10 × 106 m/s?
A) 1.19 × 10-10
B) 8.39 × 109
C) 8.39 × 1012
D) 1.19 × 10-16
E) 1.19 × 10-13
A
A 77.67 gram object traveling at a velocity of 386.7 m/s has a de
Broglie wavelength of ________ m.
A) 2.206 × 10-36
B) 2.206 × 10-37
C) 2.206 × 10-38
D) 1.990 × 10-32
E) 2.206 × 10-35
E
The de Broglie wavelength of a 0.02900 gram bullet traveling at the
speed of 647.4 m/s is ________ m.
A) 3.529 × 10-32
B) 3.529 × 10-33
C) 3.529 × 10-34
D) 3.529 × 10-35
E) 1.244 × 10-35
A
The symbol for the spin magnetic quantum number is ________.
A)
ms
B) n
C) l
D) ml
E) sm
A
The angular momentum quantum number (l) value of 2 indicates the
________ subshell.
A) d
B) f
C) s
D) p
E) +1/2
A
At maximum, an d-subshell can hold ________ electrons.
A)
10
B) 6
C) 2
D) 8
E) 14
A
If an electron has a principal quantum number (n) of 7 and an angular
momentum quantum number (l) of 3, the subshell designation is
________.
A) 7f
B) 7s
C) 7p
D) 3f
E) 3d
A
Which one of the following represents an acceptable set of quantum
numbers for an electron in an atom? (arranged as n, l, ml, and ms
)
A) 3, 2, -2, -1/2
B) 3, 3, -4, 1/2
C) 3, 4, 6,
-1/2
D) 3, 2, 0, 0
E) 3, 3, 3, -1/2
A
Which one of the following represents an acceptable set of quantum
numbers for an electron in an atom? (arranged as n, l, ml, and
ms)
A) 3, 0, 0, -1/2
B) 3, -1, -4, 1/2
C) 3, -3, 1,
-1/2
D) 0, 2, 1, 0
E) 3, 3, 4, 3
A
Which one of the following represents an impossible set of quantum
numbers for an electron in an atom? (arranged as n, l, ml, and
ms)
A) 4, 3, 0, 0
B) 4, 3, -3, 1/2
C) 4, 3, 3,
-1/2
D) 4, 3, 0, +1/2
E) 4, 2, -2, -1/2
A
Which set of three quantum numbers (n, l, ml) corresponds to a 4s
orbital?
A) 4,0,1
B) 4,0,2
C) 4,0,0
D)
4,1,0
E) 4,1,1
C
How many p-orbitals are occupied in a O atom?
A) 5
B)
6
C) 0
D) 3
E) 1
D
The element that corresponds to the electron configuration
1s22s22p2 is ________.
A)
lithium
B) beryllium
C) boron
D) nitrogen
E) carbon
E
There are ________ unpaired electrons in a ground state chlorine
atom.
A) 4
B) 3
C) 2
D) 1
E) 0
D
The ground-state electron configuration of V is ________.
A)
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3
B) 1s22s22p63s23p63d5
C)
1s22s22p63s23p11
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4
E) None of the above
A
The complete electron configuration of sulfur, element 16, is
________.
A) 1s22s22p63s23p4
B) 1s22s22p103s2
C)
1s42s42p63s2
D) 1S42s42p8
E) 1S62s62p23s2
A
The complete electron configuration of vanadium, element 23, is
________.
A) 1s22s22p103s23p7
B) 1s22s22p63s23p63d34s2
C) 1s42s42p63s43p5
D) 1s42s42p103s43p1
E)
1s42s42p83s43p3
Answer: B
B
In a ground-state copper atom, the ________ subshell is partially
filled.
A) 3s
B) 4s
C) 4p
D) 3d
E) 4d
D
What is the principal quantum number for the outermost electrons in a
Te atom in the ground state?
A) 5
B) 3
C) 4
D)
6
E) 7
A
What is the angular momentum quantum number for the outermost
electrons in a manganese atom in the ground state?
A) -1
B)
1
C) 3
D) 2
E) 0
D
The condensed electron configuration of argon, element 18, is
________.
A) [Ne]3s4
B) [Ar]3s23p2
C) [Ne]3s23p6
D) [He]2s42p10
E) [He]3s4
C
The condensed electron configuration of titanium, element 22, is
________.
A) [Ar]3s23p6
B) [Ne]3s4
C) [Ar]3s43p4
D) [Ar]3d24s2
E) [Ne]3s43p2
D
The element that has a valence configuration of 2s2 is
________.
A) Be
B) Mg
C) Ca
D) Sr
E) Ba
A
The element that has a valence configuration of 5s25p6 is
________.
A) Xe
B) Rn
C) Ne
D) Ar
E) Kr
A
The element that has a valence configuration of 2s1 is
________.
A) Li
B) Na
C) K
D) Rb
E) Cs
A
What is the maximum angular momentum quantum number in the ground
state electron configuration of iodine?
A) 3
B) 6
C)
7
D) 4
E) 5
D
A 750 nm wavelength light corresponds to which color within the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum?
red
In the de Broglie formula describing the movement of an electron about the nucleus, the quantity "mv" is called its ________.
momentum
A line spectrum contains radiation of ________ wavelengths.
specific
The shape of an orbital is defined by the angular momentum quantum number which is represented as letter ________.
1
The maximum angular momentum quantum number in the ground state electron configuration of carbon is ________.
1
The maximum angular momentum quantum number in the ground state electron configuration of argon is ________.
2
The ground state electron configuration of scandium is ________.
[Ar]4s23d1
Which group is represented by a ns2np1 valence shell electron configuration?
3A
Which group is represented by a ns2np6 valence shell electron configuration?
8A
The ground state electron configuration of copper is ________.
[Ar]4s13d10
The wavelength of radio waves can be longer than a football field.
true
High energy and low wavelength light has the ability to eject electrons from metal surfaces.
true
If a hydrogen atom electron jumps from the n=6 orbit to the n=2 orbit, energy is released.
true
The square of Schrodinger's wave equation is called an orbital.
true
The electron density of the 5s orbital is symmetric.
true
The larger the principal quantum number of an orbital, the lower is the energy of the electrons in that orbital.
false
When the value of n is greater than or equal to 3, electrons can reside in d orbitals.
true
An NMR spectrum results from photon irradiation in which the electron spin alignment is flipped.
false