Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
Chapter 8
a molecule of glucose
Which of the following is true for all exergonic reactions?
Chapter 8
The reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy.
A chemical reaction that has a positive ΔG is best described as
Chapter 8
endergonic.
Reactants capable of interacting to form products in a chemical reaction must first overcome a thermodynamic barrier known as the reaction's
Chapter 8
activation energy
Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true?
Chapter 8
Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy barrier.
The active site of an enzyme is the region that
Chapter 8
is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme.
When you have a severe fever, what grave consequence may occur if the fever is not controlled?
Chapter 8
change in the tertiary structure of your enzymes
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction?
Chapter 8
by changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
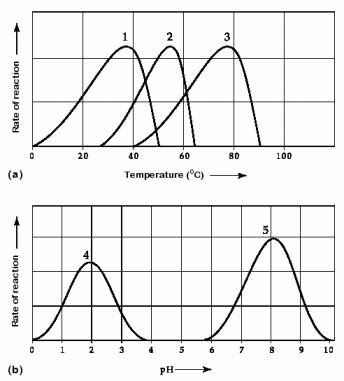
Activity of various enzymes at various temperatures (a) and at
various pH (b).
Which curve(s) on the graphs
may represent the temperature and pH profiles of an enzyme taken from
a bacterium that lives in a mildly alkaline hot springs at
temperatures of 70°C or higher?
chapter 8
curves 3 and 5
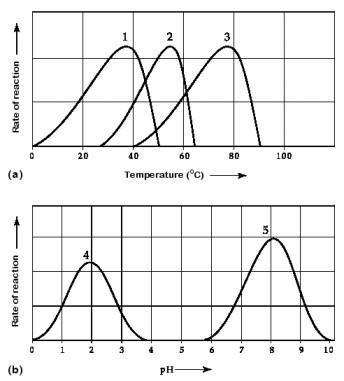
Activity of various enzymes at various temperatures (a) and at
various pH (b).
Which temperature and pH
profile curves on the graphs were most likely generated from analysis
of an enzyme from a human stomach where conditions are strongly acid?
chapter 8
curves 1 and 4
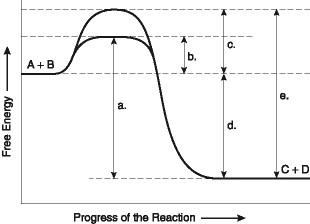
Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure?
chapter 8
exergonic, Δ G < 0

Which of the following represents the ΔG of the reaction in the figure?
chapter 8
d

The following question is based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the figure.
Which of the following in the figure would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
chapter 8
d

Which of the following represents the activation energy required for a noncatalyzed reaction in the figure?
chapter 8
c
The mechanism in which the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step in the pathway is most precisely described as
chapter 8
feedback inhibition.
A series of enzymes catalyze the reaction X → Y → Z → A. Product A binds to the enzyme that converts X to Y at a position remote from its active site. This binding decreases the activity of the enzyme.
What is substance X?
chapter 8
a substrate
Which of the following clues would tell you if a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
chapter 6
whether or not the cell is partitioned by internal membranes
Which of the following correctly matches an organelle with its function?
chapter 6
central vacuole ... storage
But remember, plant cells have a central vacuole, whereas most animal cells have several smaller vacuoles located throughout the cytoplasm.
All of the following are part of a prokaryotic cell except
chapter 6
an endoplasmic reticulum.
Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing which of the following molecules?
chapter 6
proteins
Which one of the following statements about the endomembrane system is correct?
chapter 6
Proteins that will be secreted from the cell are likely to be found in closed spaces bounded by membranes of the endomembrane system.
Hydrolytic enzymes must be segregated and packaged to prevent general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following organelles contains these hydrolytic enzymes in animal cells?
chapter 6
lysosome
Tay-Sachs disease is a human genetic abnormality that results in cells accumulating and becoming clogged with very large, complex, undigested lipids. Which cellular organelle must be involved in this condition?
chapter 6
the lysosome
The liver is involved in detoxification of many poisons and drugs. Which of the following structures is primarily involved in this process and therefore abundant in liver cells?
chapter 6
smooth ER
Which organelle often takes up much of the volume of a plant cell?
chapter 6
vacuole
Mitochondria are found in _____.
chapter 6
plant and animal cells
Which organelle is the primary site of ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells?
chapter 6
mitochondrion
A cell has the following molecules and structures: enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, plasma membrane, and mitochondria. It could be a cell from
chapter 6
nearly any eukaryotic organism.
Which of the following functions is NOT associated with the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells?
chapter 6
Movement of RNA molecules from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
Movement of vesicles within the cell depends on what cellular structures?
chapter 6
microtubules and motor proteins
Property Microtubules (tubulin polymers) Microfilaments (actin filaments) Intermediate filaments Structure Hollow tubes; wall consists of 13 columns of tubulin molecules Two intertwined strands of actin, each a polymer of actin subunits Fibrous proteins supercoiled into thicker cables Diameter 25 nm with 15-nm lumen 7 nm 8-12 nm Main functions Cell motility Cell motility Anchorage
The differences among the three categories of cytoskeletal elements outlined in the table above would suggest that each of the following has specialized roles. Which of the following is a correct match? (All three elements are involved in the maintenance of cell shape.)
microtubules and chromosome movement
Cytochalasin D is a drug that prevents actin polymerization. A cell treated with cytochalasin D will still be able to
chapter 6
move vesicles around the cell.
Ions can travel directly from the cytoplasm of one animal cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell through
chapter 6
gap junctions
In the combined processes of glycolysis and cellular respiration, what is consumed and what is produced?
chapter 6
Glucose is consumed, and carbon dioxide is produced.
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction
chapter 9
loses electrons and loses potential energy.
Which of the following statements describes the results of this
reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy
chapter 9
C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the molecule becomes
chapter 9
oxidized.
When a molecule of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a proton), the molecule becomes
chapter 9
reduced.
Where does glycolysis take place in eukaryotic cells?
chapter 9
cytosol
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
chapter 9
accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
During glycolysis, when each molecule of glucose is catabolized to two molecules of pyruvate, most of the potential energy contained in glucose is
chapter 9
retained in the two pyruvates.
In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis?
chapter 9
NADH and pyruvate
A glucose molecule is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, but together these two processes yield only a few molecules of ATP. What happened to most of the energy that the cell obtains from the oxidation of glucose?
chapter 9
It is stored in NADH and FADH2
The electrons stripped from glucose in cellular respiration end up in which compound?
chapter 9
water
Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located?
chapter 9
mitochondrial inner membrane
In cellular respiration, the energy for most ATP synthesis is supplied by
chapter 9
a proton gradient across a membrane.
During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level?
chapter 9
FADH2
The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to
chapter 9
act as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water.
How many oxygen molecules (O2) are required each time a molecule of glucose (C6H12O6) is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water via aerobic respiration,?
chapter 9
6
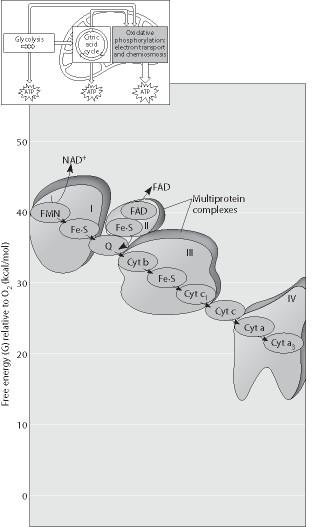
Which of the protein complexes labeled with Roman numerals in the figure will transfer electrons to O2?
chapter 9
complex IV
Which metabolic pathway is common to both cellular respiration and fermentation?
chapter 9
glycolysis
In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of
chapter 9
ATP, CO2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol).
A mutation in yeast makes it unable to convert pyruvate to ethanol. How will this mutation affect these yeast cells?
chapter 9
The mutant yeast will be unable to grow anaerobically.
The photosynthetic membranes are found in the _____ in plant cells.
chapter 9
chloroplasts
The Calvin Cycle
Carbon fixation involves the addition of carbon dioxide to _____.
RuBP
The Calvin Cycle
After 3-PGA is phosphorylated, it is reduced by _____.
NADPH
The Calvin Cycle
How many carbon dioxide molecules must be added to RuBP to make a single molecule of glucose?
6
The Calvin Cycle
In the Calvin cycle, how many ATP molecules are required to regenerate RuBP from five G3P molecules?
3
Metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules are called?
chapter 9
catabolic pathways