The correct sequence of preembryonic structures is _______.
zygote, morula, blastocyst
1) Human papillomavirus
2) organism responsible for up to half of the diagnosed cases of pelvic inflammatory disease
3) treponema pallidum
4) human herpes virus type 2
Answers in order
Genital warts 1
chlamydia 2
syphilis 3
Genital herpes 4
Mature follicle location
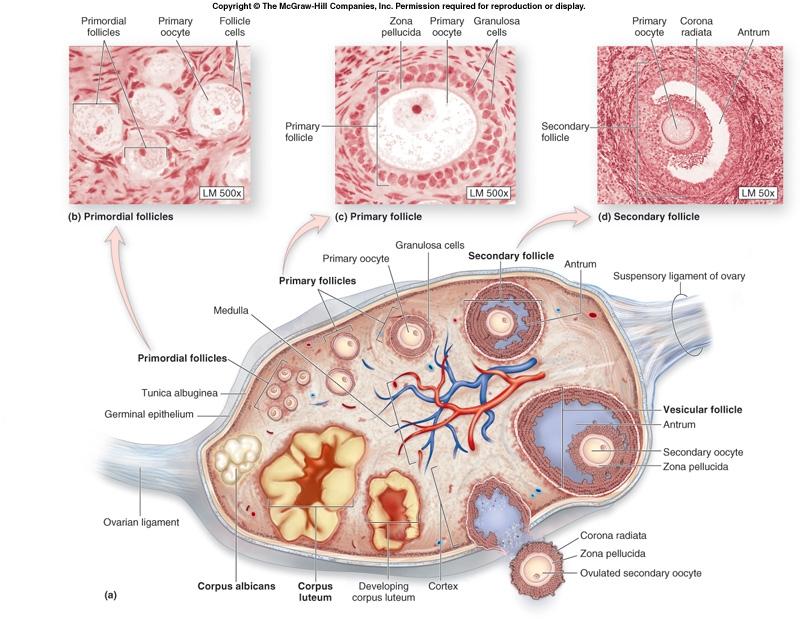
Primary follicle

The early stage of embryonic development during which rapid mitotic cell divisions occur as the zygote travels down the uterine ( fallopian ) tube is called _____.
cleavage
vesicular ( Graafian ) follicle

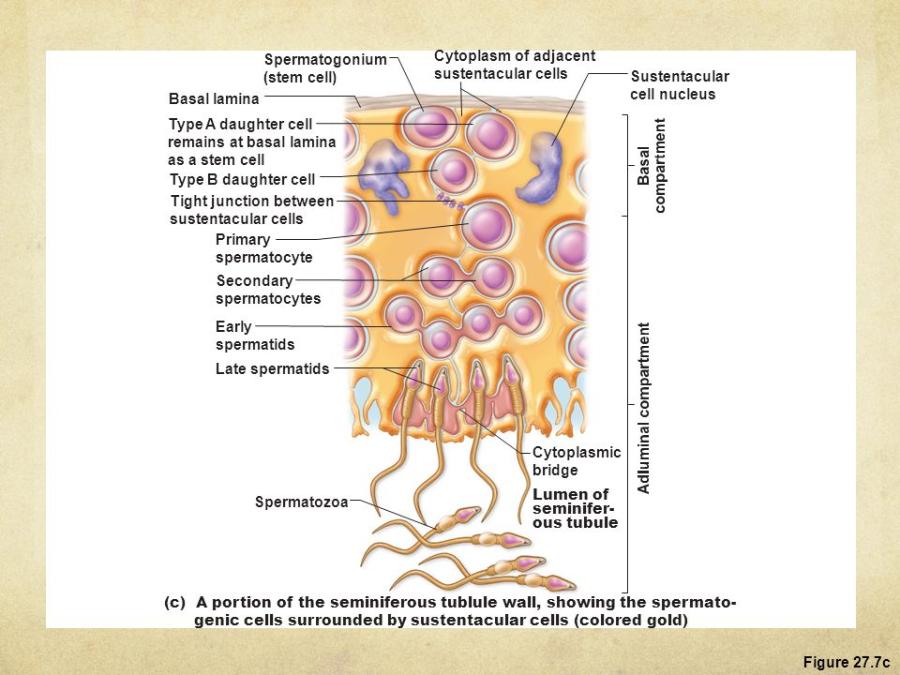
Stem cell
The presence of more oxytocin receptors in the uterus leads to weak, irregular contractions known as ____.
Braxton hicks
the fluid-filled sac surrounding the fetus is the ____.
amnion
Male sex chromosomes are represented as _____.
XY
Normally menstruation occurs when ____.
blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease
Which of the following is a correct statement about uterine tubes?
the infundibulum is the funnel-shapped region near the ovary
The pap smear is a test to detect cancerous changes in cells of the cervix
True
the ligament that anchors the anterior portion of the uterus is called the _____.
round ligament
All of the following things occur during meiosis I with the exception of one thing. Select the statement below that does not occur during meiosis I.
the sister chromatids are separated from each other
the fatty, rounded area overlying the pubic symphysis of a female is the _____.
mons pubis
the series of events that expel the infant from the uterus are referred to collectively as _____.
labor
acrosome
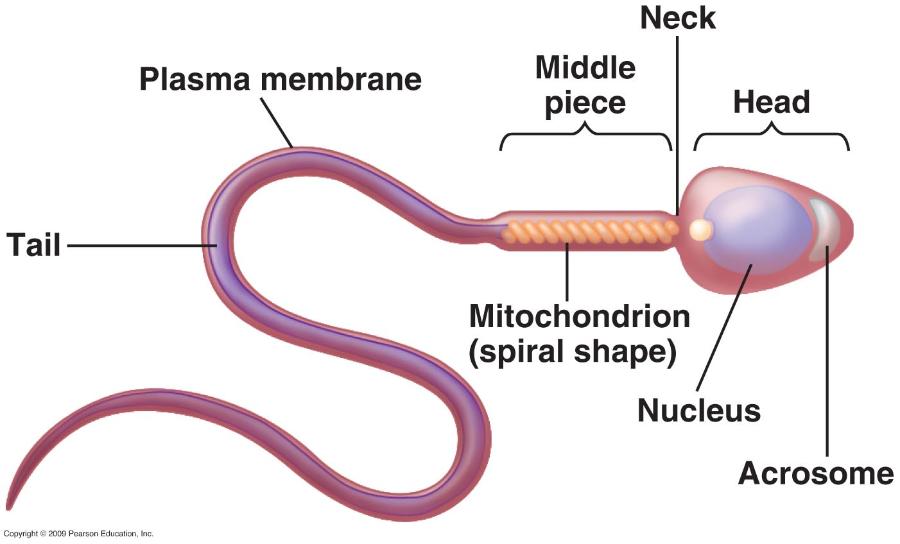
location of mitochondria

As the infants head is forced against the cervix with each contraction, the cervix effaces, which means that it
thins
trace the pathway of sperm through the duct system during ejaculation ______.
epididymis, ductus (vas) deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
which hormone is the necessary trigger for ovulation to occur?
LH
secretion of progesterone stimulates ______.
preparation of the mammary glands for lactation
the basic difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis is that _____
in oogenesis, one mature ovum is produced, and in spermatogenesis four mature sperm are produced from the parent cell
the hormone responsible for the development and maintenance of male secondary sexual characteristics is
testosterone
menopause, which ends childbirth ability, is considered to have occurred when a woman _____
has gone a year without menstuation
the placenta and its attached fetal membranes, expelled from the uterus during the placental stage of labor, are collectively referred to as ____
the after birth
flagellum

the duct system of the male reproductive system includes all but which of the following?
corpus spongiosum
which of the following is not a primary germ layer
epiderm
All but one of the following statements is true of uterine function. select the statement that is not true of uterine function.
the narrow portion of the uterus near the cervix is the most typical site of fertilization
all but one of the following statements describes the necessity of the blood testis barrier. select the one statement that does not describe a necessity of the blood testis barrier.
sperm can only be produced at temperatures lower than body temperature. inflammation in the testis could raise the temperature too high to produce sperm.
the gonads produce sex cells, also known as
gametes
the structures that receive the ovulated oocyte, providing a site for fertilization, are called the
fallopian tubes
corpus luteum

the movement of an egg cell down a uterine tube is aided by
both ciliary action and peristaltic contractions
thick, clear mucus that cleanses the urethra of acidic urine is produced by the
bulbo-urethral glands
fertilization generally occurs in the
fallopian tubes
early spermatids

Match
1) forms the mothers part of the placenta
2) becomes the embryonic disc
3) surrounds the uterine cavity face of the implanted embryo
4) forms the chorion
Answers in order
decidua basalis 1
inner cell mass 2
decidua capsularis 3
trophoblast 4
which of the choices below occurs if implantation is successful
the corpus luteum is maintained until the placenta takes over its hormone-producing functions.
the dartos and cremaster muscles are important to the integrity of the male reproductive system. which of the following is true about the role they play?
they regulate the temperature of the testes
by the end of the embryonic period, at 8 weeks, all the adult organ systems are recognizable
true
the process by which the acrosome membranes of sperm break down is known as
the acrosomal reaction
select the correct statement about the hormonal events of the ovarian cycle
high estrogen levels result in a surge of LH release
select the correct statement about male sexual response
erection is the result of vascular spaces in the erectile tissues filling with blood
meiosis occurs during
both spermatogenesis and oogenesis
Days 6-14 of the uterine (menstrual) cycle are known as the ____ phase. this phase concludes with ovulation
proliferative
Match
1) leads to the development of a morula and then a blastocyst
2) leads to the formation of the first cell of the new individual
3) leads to the establishment of the three primary germ layers
4) leads to enhancement of sperm motility and increasing membrane fragility to enable enzyme release from acrosomes
5) embedding of the blastocyst in the uterine wall
Answers in order
cleavage 1
fertilization 2
gastrulation 3
capacitation 4
implantation 5
the infant is delivered during the second stage of labor known as the _____stage
expulsion
ovarian follicles contain mature eggs
false
human egg and sperm are similar in that
they have the same number of chromosomes
in the block to polyspermy, entry of the sperms contents causes _____ levels in the oocytes cytoplasm to rise, triggering the cortical reaction
calcium ion
failure of the testes to descend into the scrotum is a condition known as _____
cryptorchidism
an episiotomy is an incision made to widen the vaginal orifice, aiding fetal expulsion
true
the stage called ovulation

which of the following statements about spermatogenesis is not true
each spermatid forms two sperm
the innermost mucosa layer of the uterus is called the
endometrium
which is not a part of the proliferative phase of the female menstrual cycle
corpus luteum
which of the following female structures is homologous to the male scrotum
labia majora
in fetal circulation, one way in which blood bypasses the nonfunctional lungs is by way of the foramen ovale
true
the constancy of the chromosome number from one cell generation to the next is maintained through
meiosis
first cells with n number of chromosomes

cells of the _____ gather around the notochord and neural tube and produce the vertebra and rib at their associated level
sclerotome
which of the following glands are responsible for 70% of the synthesis of semen
the seminal vesicles
select the correct statement about testosterone control
GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH release from the anterior pituitary
of the three germ layers, the mesoderm forms the most body parts
true
the most important risk for testicular cancer in young males is
failure of the testis to make their normal decent
Milk ejection ( the letdown reflex ) is stimulated by which of the following hormones associated with pregnancy
oxytocin
which of the following refers to the transfer of sperm and harvested oocytes together into the woman's uterine tubes in the hopes that fertilization will take place there
gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
primary spermatocyte

Undifferentiated spermatogenic cells are called
spermatogonia
the enlarged tip of the penis is called the
glans penis
primordial follicle

which of the choices below is not a function of the vagina
serves as a passageway for the primary oocyte
the male and female reproductive systems
transport sex cells to sites of fertilization
secrete hormones for developing secondary sex characteristics
produce sex cells
secrete hormones for maintaining secondary sex characteristics
(Answer) All of the above
women athletes sometimes experience disturbances in their reproductive cycles because of
decreased synthesis of estrogens
the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis
involves FSH and LH release
all but one of the following statements are true regarding the differences between early and late spermatids. select the answer below that does not reflect a difference between early and late spermatids
early spermatids have not undergone meiosis and are still diploid
type B spermatogonia

androgens are
male sex hormones
the first major event in organogenesis is
neurulation
the genetic determinate for male reproductive development is
the SRY gene
Follicle-stimulating hormone causes a primordial follicle to start the maturation process
true
the amount of testosterone and sperm produced by the testes is dependent on the influence of FSH alone.
false
the hormone mainly responsible for the development and maintenance of female secondary sexual characteristics is
estrogen
the pigmented area of a females breast that surrounds the nipple is the
areola
it is necessary for the testes to be kept below body temperature for abundant, viable sperm formation
true