GSU Blood Vessels of the Lower Limb
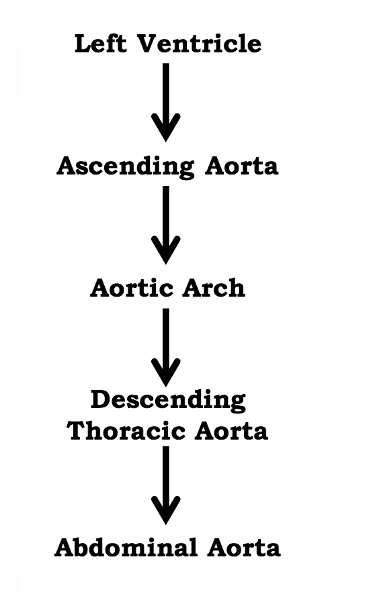
What is the pathway of blood from the heart to the aorta?
right gets deoxygenated, left gets oxygenated
Which side of the heart gets oxygenated blood and which side gets deoxygenated?
left ventricle because it is discharging oxygenated blood into the circuit of the entire body
Which is the largest chamber of the heart and why?
Draw a flowchart for pathway of blood in veins
draw a flowchart for the pathway of blood in arteries
large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart.
What is the inferior vena cava?
obturator, inferior gluteal, and superior gluteal
Which three arteries are given off by the internal iliac artery?
femoral, deep femoral, popliteal, anterior tibial, posterior tibial, and fibular
The external iliac artery gives off which five arteries?
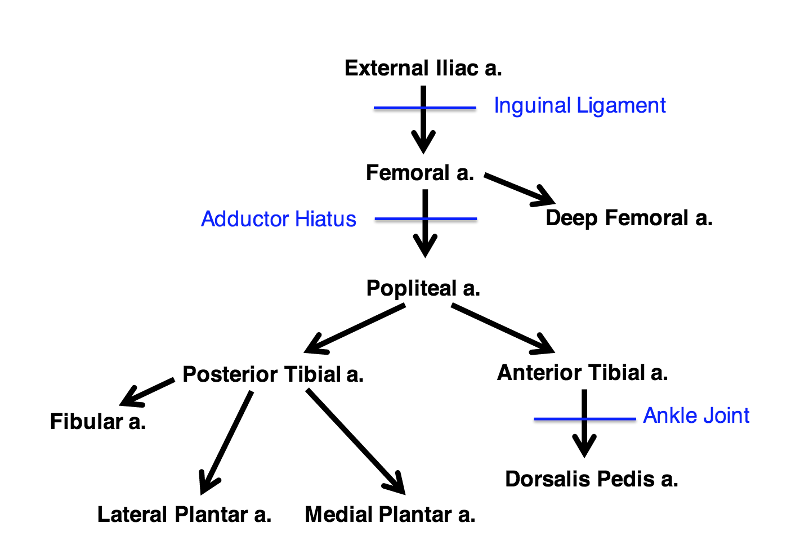
draw external iliac artery tree
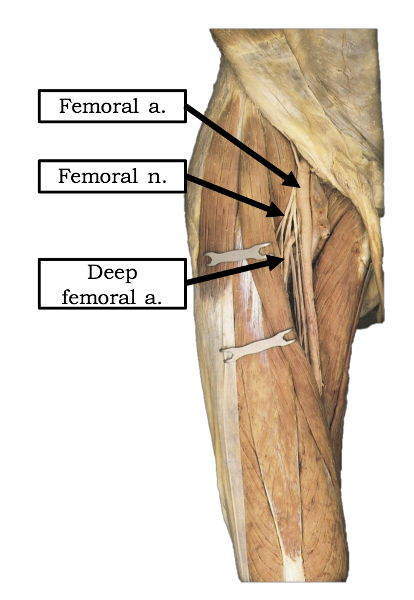
passes deep to inguinal ligament and continues into thigh as femoral artery
What is the pathway of the external iliac artery?
travels deep to sartorius in anterior thigh. becomes popliteal artery after passing posterior through adductor hiatus
What is the pathway of the femoral artery?
non terminal branch of femoral artery. continues dorsilaterally from femoral artery. reflect sartorius to see it.
What is the pathway of the deep femoral artery?
passed behind the knee in the popliteal fossa, reaches the popliteus muscle, then divides into anterior and posterior tibial artery
What is the pathway of the popliteal artery?
dorsalis pedis artery. at the ankle.
What does the anterior tibial artery become? where?
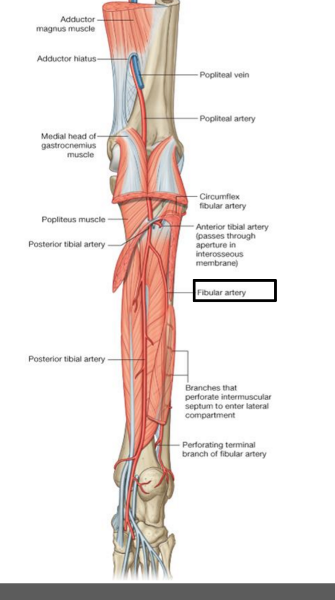
the fibular artery. lateral plantar artery, and medial plantar artery
What does posterior tibial artery branch into?
same as the arteries they accompany
how are deep veins named?
femoral v
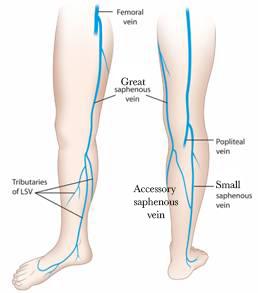
what does the greater saphenous vein drain into?
popliteal v
what does the lesser sapenous vein drain into?
the two common iliac veins
Which two veins join together to form the IVC?
lateral; medial
The lesser saphenous runs (medial/lateral) and the greater saphenous runs (medial/lateral)
medial thigh muscles
Which muscles are fed by the obturator artery?
Gluteus maximus, gluteus medius,gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae
Which muscles are fed by superior gluteal artery?
Gluteus maximus, piriformis
Which muscles are fed by inferior gluteal artery?
anterior compartment of thigh
What does the femoral artery feed?
posterior thigh muscles
What does the deep femoral artery feed?
popliteus muscle
what does the popliteal artery feed
anterior compartment of the leg
What does the anterior tibial artery supply blood to
the dorsal surface of the foot
what does the dorsalis pedis supply?
posterior compartment of the leg
what does the posterior tibial artery supply
the lateral compartment of the leg
what does the fibular artery supply?
abductor hallucis flexor digitorum brevis
what muscles does the medial plantar artery supply?
dorsal digital vein of great toe and dorsal venous arch of foot
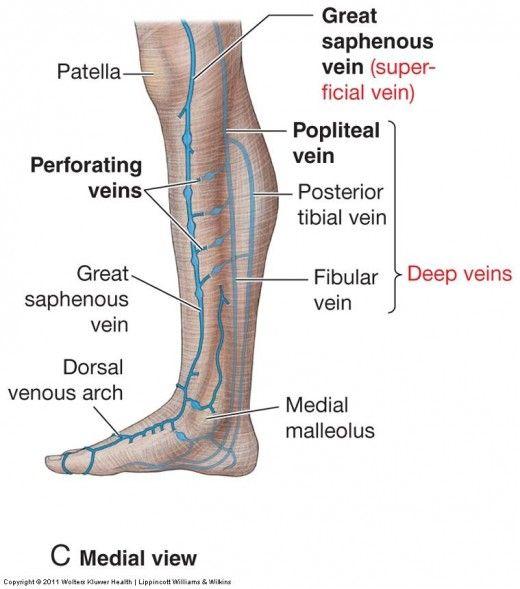
what forms the great saphenous vein?
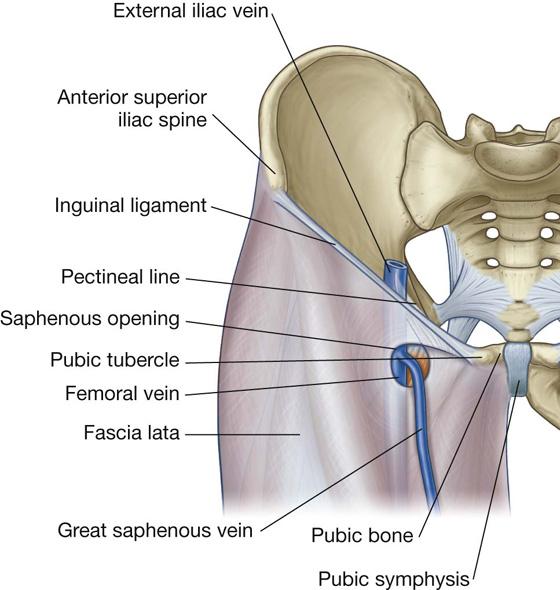
ascends anterior to medial malleolus
passes posterior to medial condyle of femur (about a hand's breadth posterior to the medial border of the patella)
transverses the saphenous opening in the fascia lata
empties into the femoral vein
Describe the pathway of the great saphenous vein, especially where it begins and empties
dorsal digital vein of the fifth digit and dorsal venous arch
what forms the small saphenous vein?
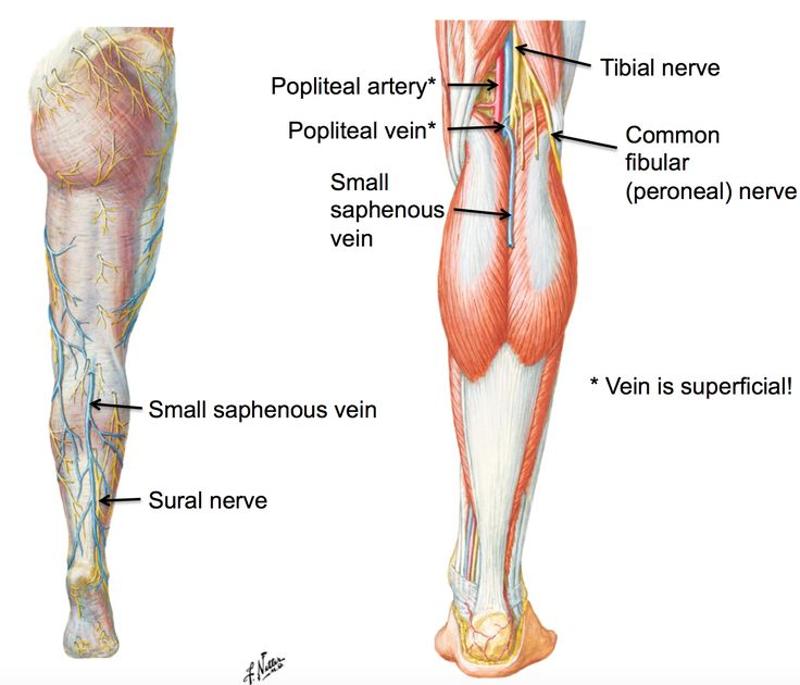
arises on the lateral side of the foot
ascends posterior to lateral malleolus as a continuation of lateral marginal vein
passes along the lateral border of the calcaneal tendon
inclines to the midline of the fibula and penetrates the deep fascia
ascends between the heads of gastroc
empties into popliteal vein in popliteal fossa
what is the pathway of the small saphenous vein
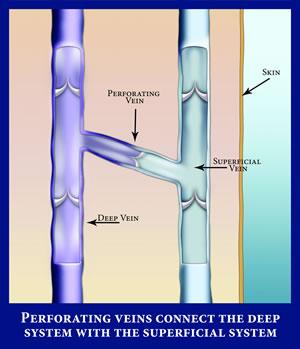
veins that connect the deep and superficial veins. blood can only flow from superficial to deep because of valves.
what are perforating veins?
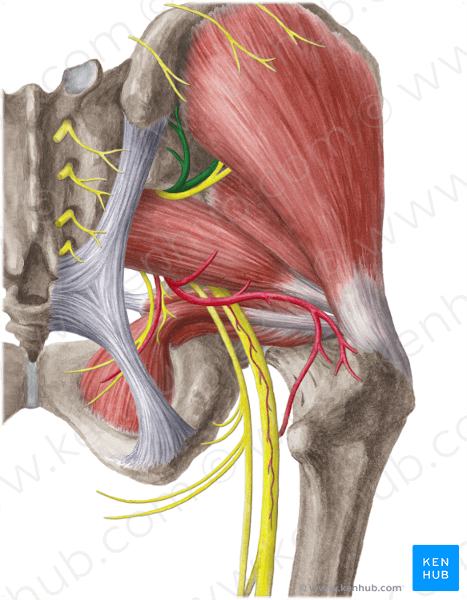
O posterior division of internal iliac artery
C leaves pelvis through greater sciatic foramen, superior to piriformis
D gluteal muscles and tensor fascia latae
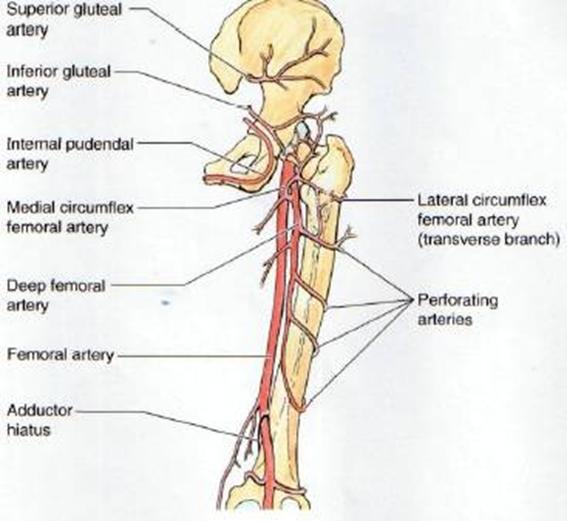
origin, course and distribution of superior gluteal artery
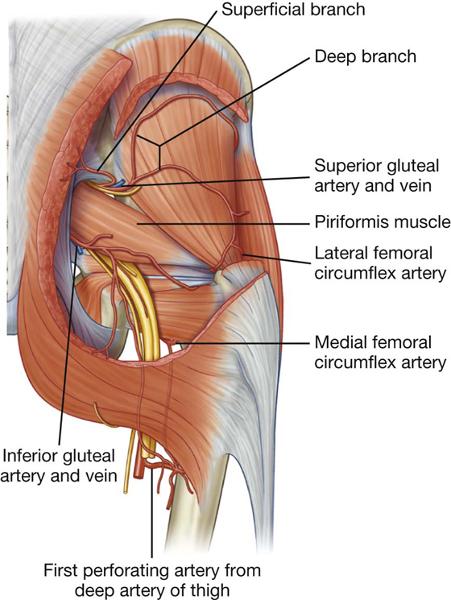
O anterior division of internal iliac artery
C leaves pelvis through greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis
D piriformis, coccygeus, levator ani, and gluteal muscles
origin course and distribution of inferior gluteal artery
O common iliac artery
C follows the iliopsoas muscle. becomes the femoral artery at the inguinal ligament. gives rise to inferior epigastric a and deep iliac circumflex a.
origin and course of external iliac artery
continuation of popliteal vein proximal to adductor hiatus
fed by profunda femoris vein and great saphenous vein
becomes the external iliac vein after passing posterior to inguinal ligament
in adductor canal, lies posterlaterally and posterior to the femoral artery
course of femoral vein
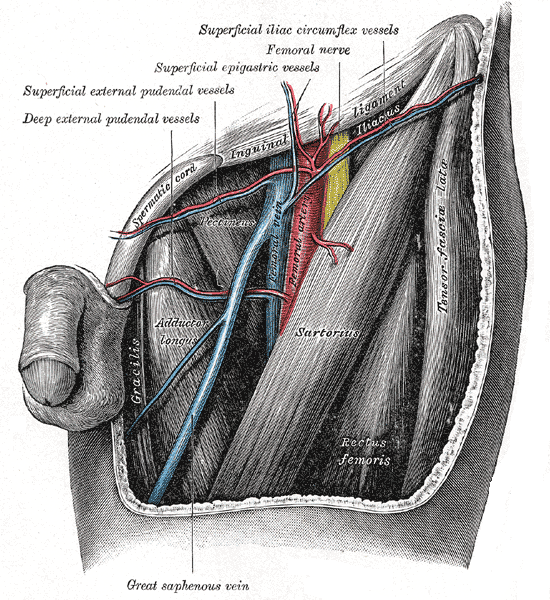
continuation of external iliac artery distal to inguinal ligament
lateral to femoral vein in femoral triangle
descends on borders of iliopsoas and pectineus
enters adductor canal deep to sartorius
exits adductor canal passing through addcutor hiatus and becomes popliteal artery
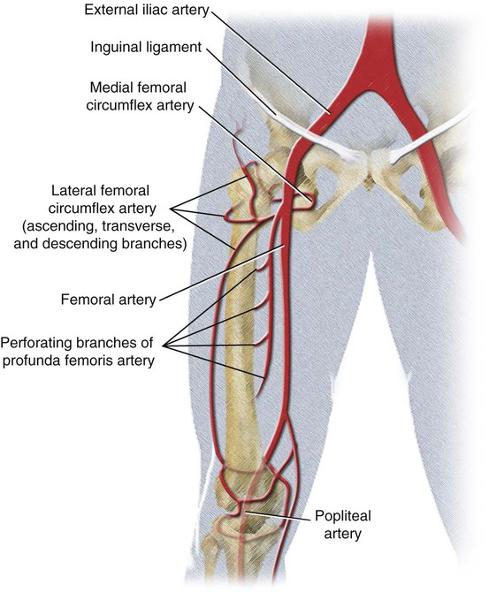
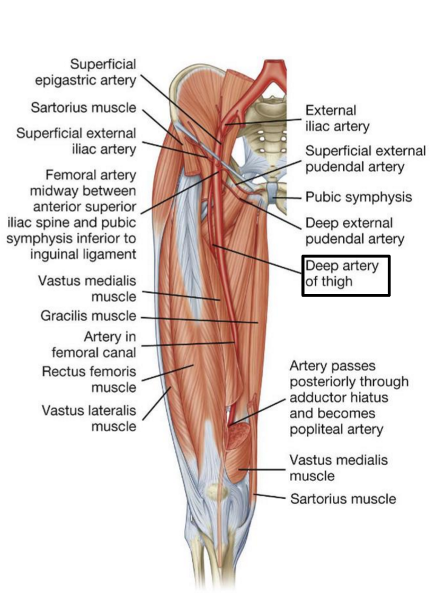
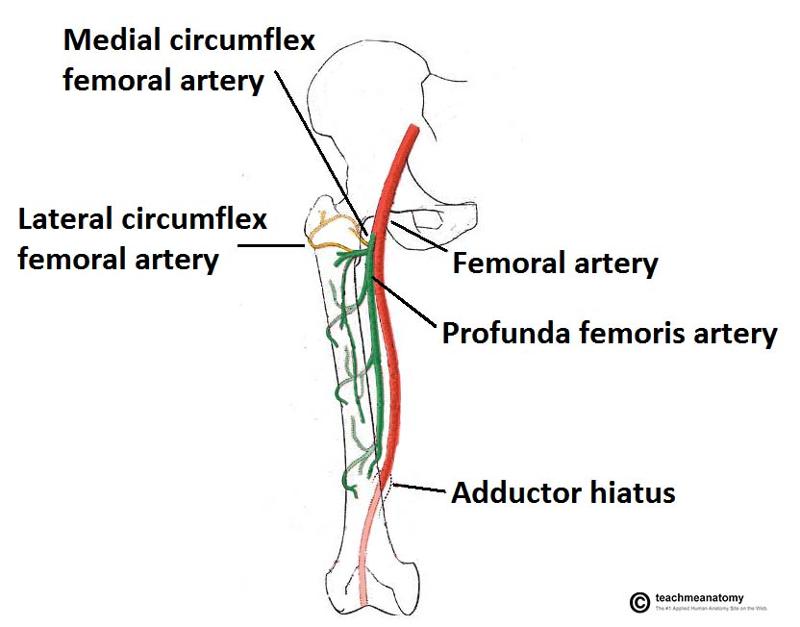
origin and course of femoral artery
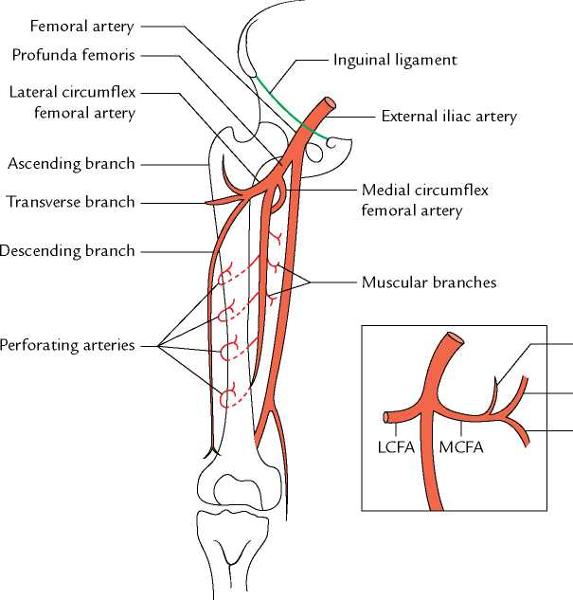
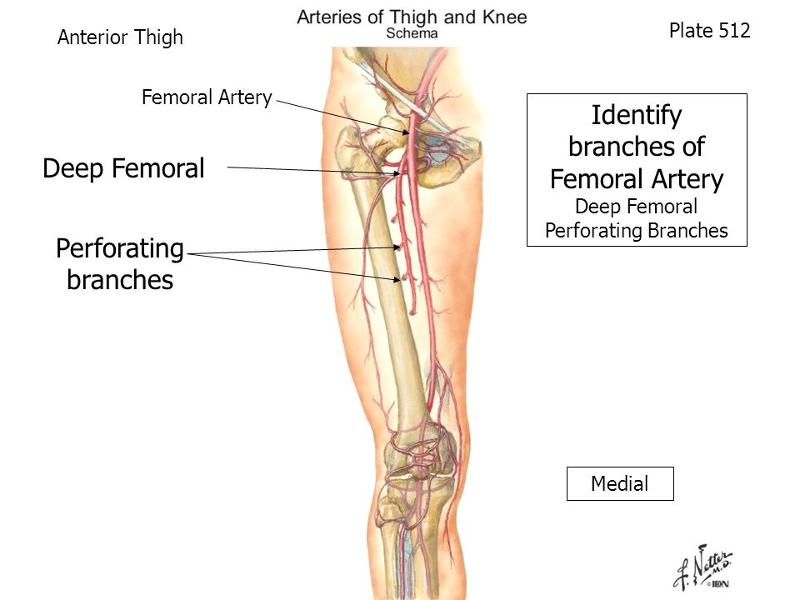
arises from femoral artery in femoral triangle. in middle third of thigh is separated from femoral artery by adductor longus. gives off three or four perforating arteries that wrap around posterior femur and feed adductor magnus, hamstring, and vastus lateralis muscles
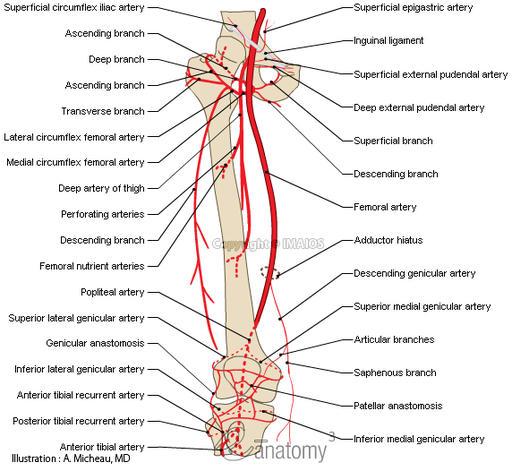
origin and course of deep femoral artery
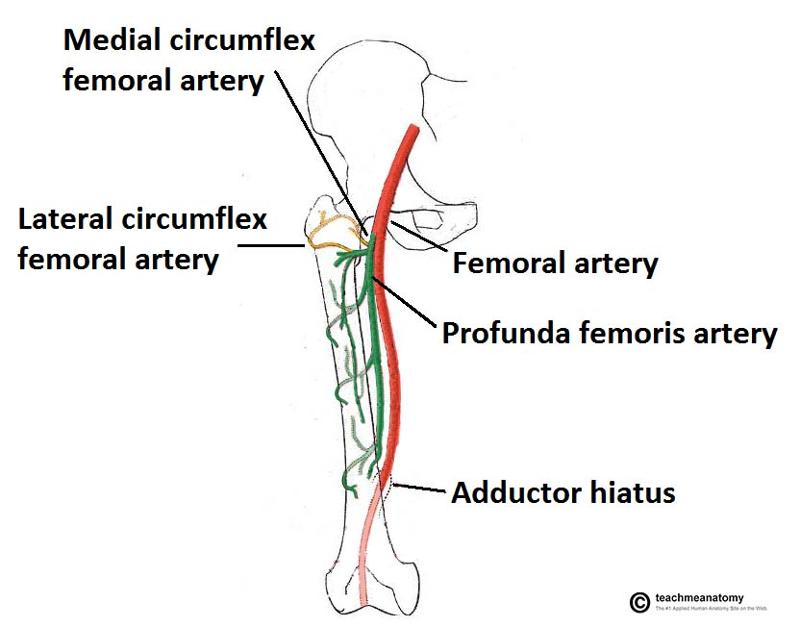
can arise from deep femoral artery or femoral artery. encircles the thigh and anastosomes with the medial circumflex artery and supplies lateral thigh muscles and proximal femur.
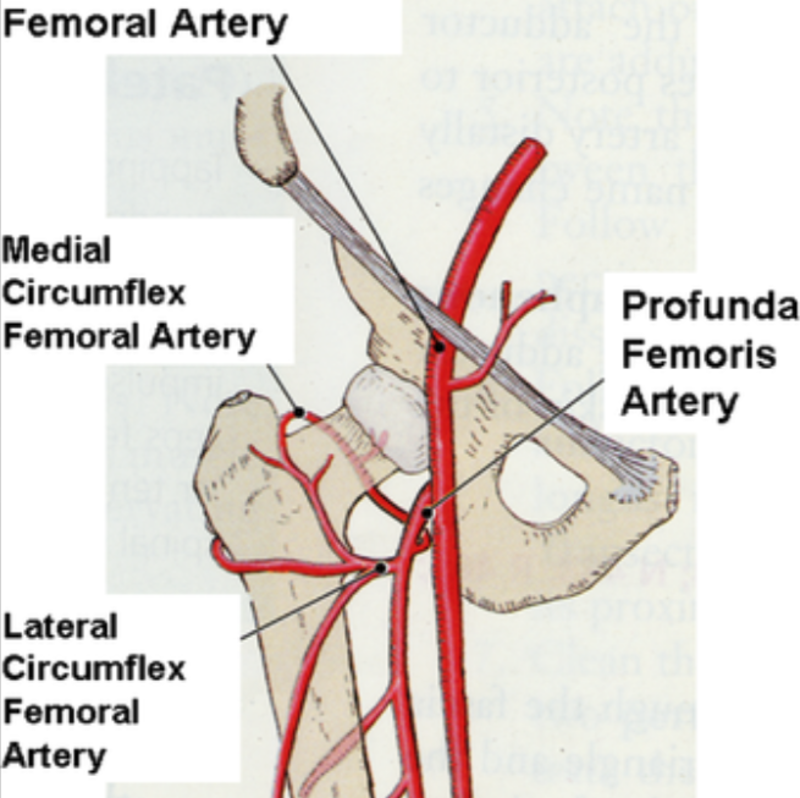
origin and course of lateral circumflex femoral artery
most likely arises from deep femoral artery but may arise from femoral artery
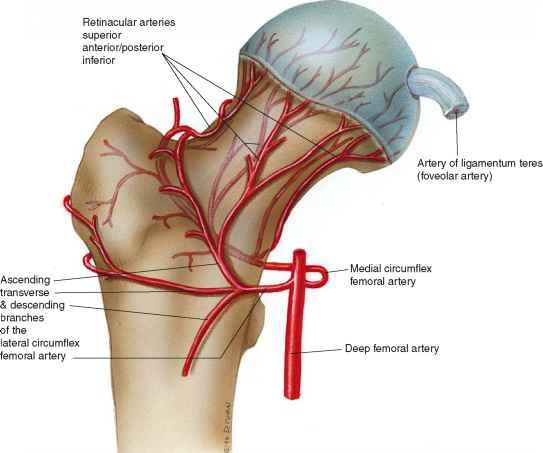
supplies most of blood to head and neck of femur. it's branches are posterior retinacular arteries.
passes deep between iliopsoas and pectineus to reach posterior aspect of femoral neck where it runs deep to quadratus femoris
origin and course of medial circumflex femoral artery
come from deep femoral artery
wrap around posterior aspect of femur
feed hamstrings, adductor magnus and vastus lateralis
course and distribution of perforating arteries
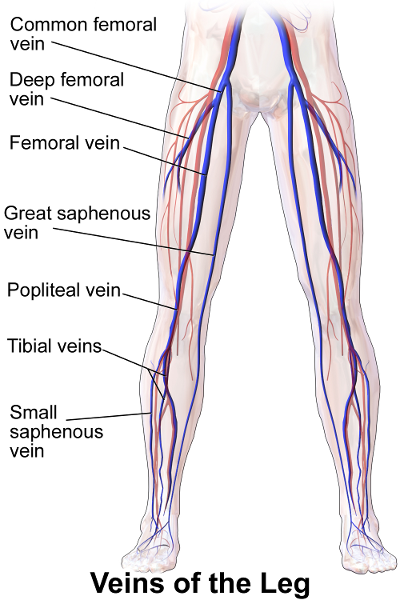
continuation of posterior tibial veins
superficial to and in the same fibrous sheath as popliteal artery throughout course
popliteal v becomes femoral vein in adductor hiatus
small saphenous enters popliteal vein in popliteal fossa
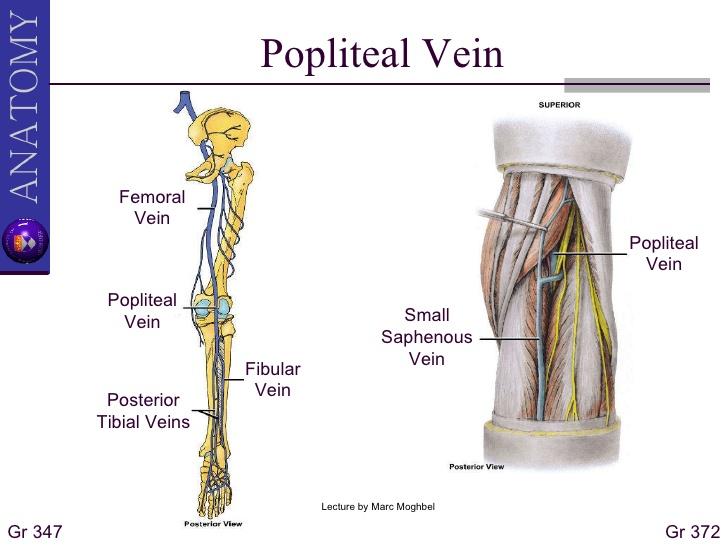
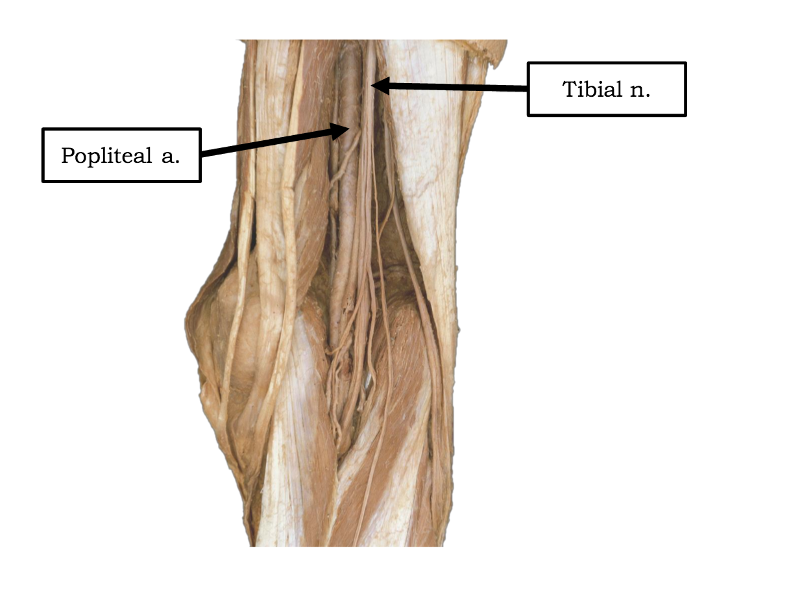
popliteal vein course
continuation of femoral artery
begins where femoral artery passes adductor hiatus
passes through popliteal fossa
ends by dividing into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
branches into genicular arteries to feed the knee joint
muscular branches feed hamstrings, gastrocnemeus, soleus and plantaris
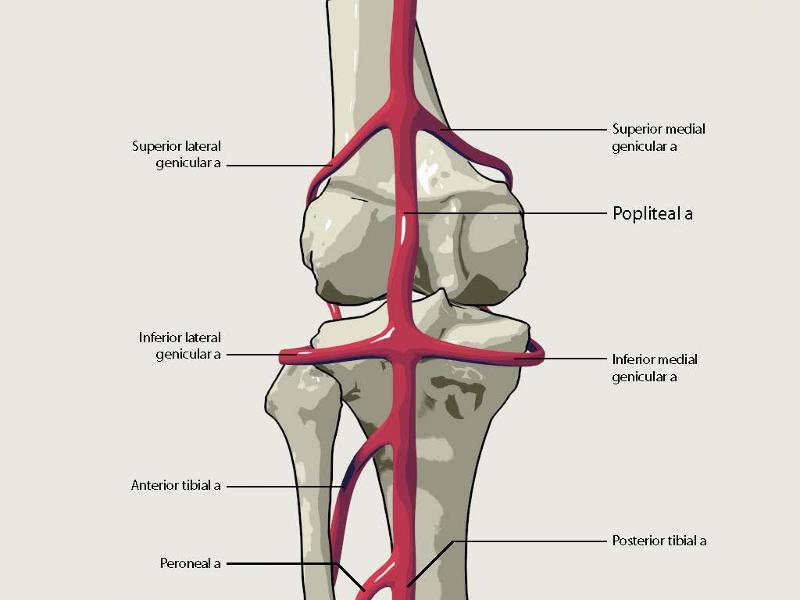
popliteal artery course and distribution
superior lateral, superior medial, inferior lateral and inferior medial genicular arteries feed the area of the knee joint capsule and ligaments.
list the genicular arteries and area of the body
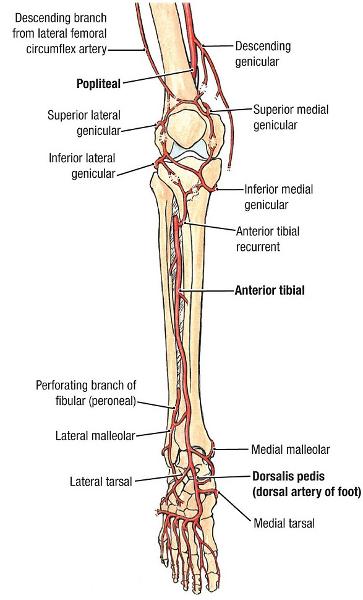
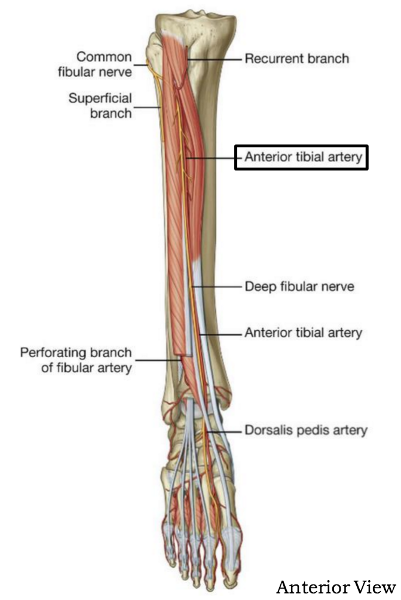
anterior branch of popliteal artery - smaller than posterior branch
supplies anterior compartment of the leg
begins at inferior border of popliteus m. and pierces interosseus membrane
becomes dorsalis pedis artery
course and distribution of anterior tibial a
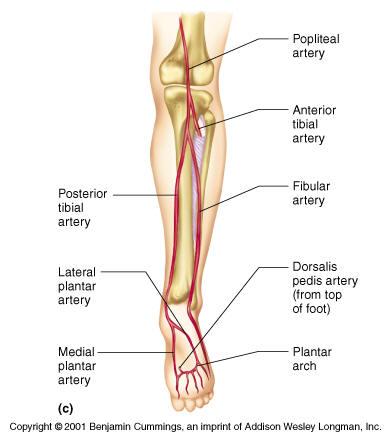
supplies posterior compartment of leg and plantar area of foot
larger branch of popliteal artery
after if gives off fibular artery, passes inferomedially on posterior surface of tibialis posterior and then runs posterior to medial malleolus.
divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries
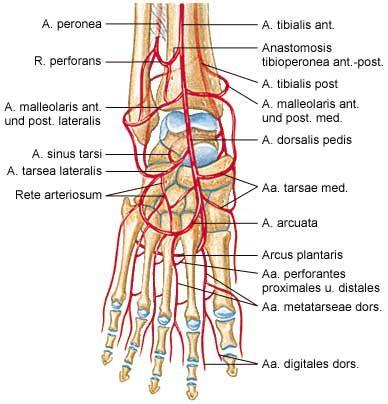
course and distribution of posterior tibial a.
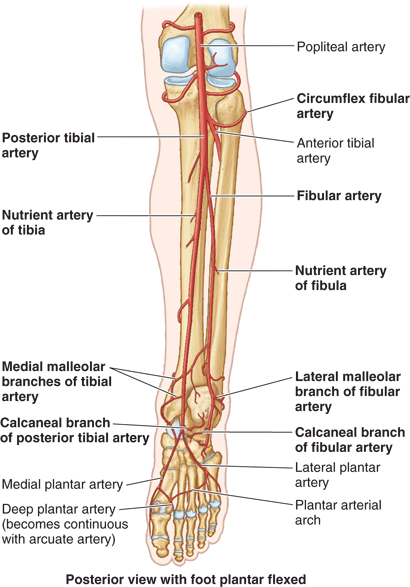
largest branch of posterior tibial a. Arises near distal border of popliteus
descends obliquely toward fibula, usually through flexor hallucis longus
gives off muscular branches to posterior and lateral compartment of leg, nutrient artery of the fibula, and perforating branch of fibular artery which pierces the interosseus membrane and goes to the dorsum of the foot
course and distribution of fibular artery
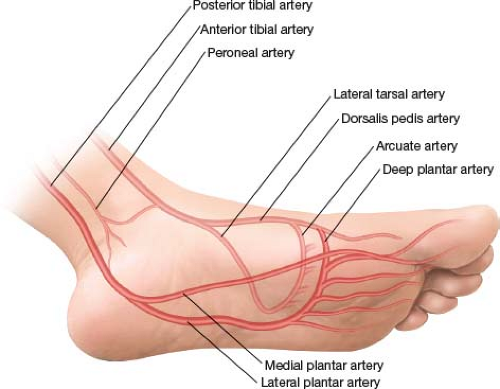
from posterior tibial artery
courses laterally between first and second layer of plantar muscles continues into deep plantar arch
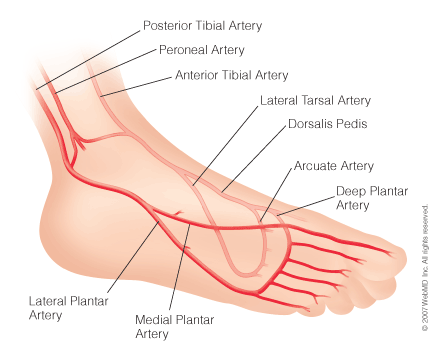
course of lateral plantar artery
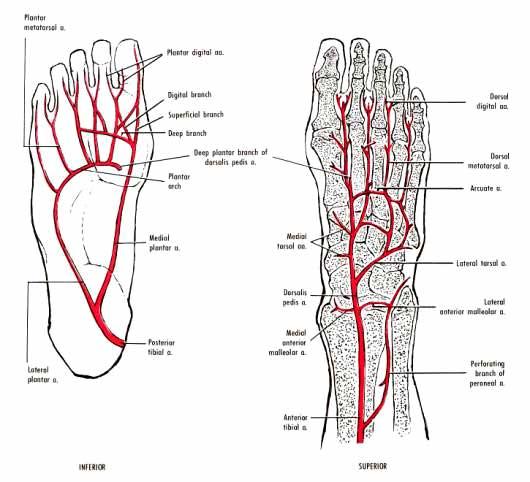
beings at base of fifth metatarsal as continuation of lateral plantar artery
courses between third and fourth muscle layers
unites lateral plantar artery and deep plantar artery (branch of dorsal artery)
deep plantar arch gives rise to four plantar metatarsal arteries, three perforating branches and branches to skin, fascia, and muscles in the sole
course of plantar arch
feeds the muscles of the great toes and skin on the medial side of the sole
branch of posterior tibial artery
branches common plantar digitial a --> proper plantar digital a.
course and distribution of medial plantar artery
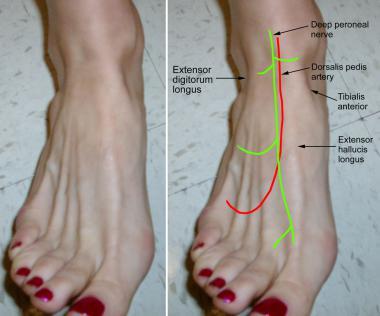
direct continuation of dorsalis pedis artery
begins midway between the malleoli and runs anteromedially deep to inferior extensor retinaculum between extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus tendons on the foot
feeds the forefoot
gives off lateral tarsal artery, arcuate a, deep plantar a, and dorsal metatarsal a.
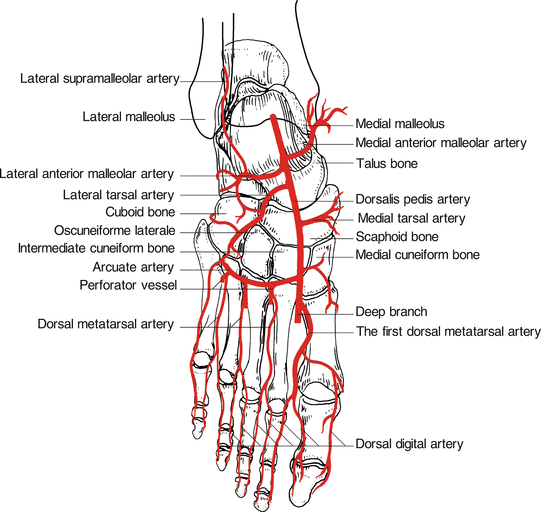
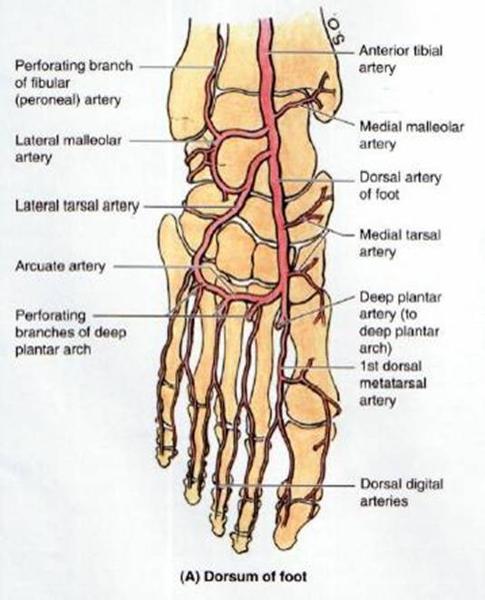
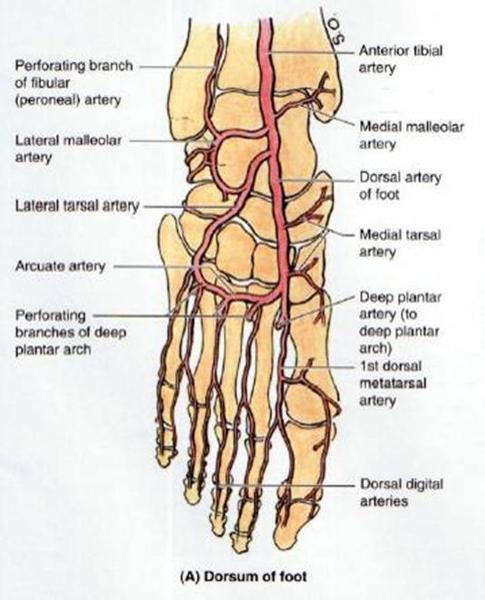
course and distribution of dorsalis pedis
branch of dorsalis pedis artery
deep to extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis
supplies extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis and articulations o the tarsus
course and distribution of lateral tarsal artery
branch of dorsalis pedis a
it passes laterally, over the bases of the lateral four metatarsal bones, beneath the tendons of the extensor digitorum brevis
terminates in lateral tarsal artery
communicates with plantar arteries through perforating arteries of the foot
course and distribution of arcuate artery
branch of dorsalis pedis
passes deeply between the heads of the first dorsal interosseous muscle to enter the sole of the foot where it joints the lateral plantar artery to form the deep plantar arch
course and distribution of deep plantar artery
branches of dorsalis pedis.
each dorsal metatarsal arteries run to the cleft of the toe where they divide into two dorsal digital arteries
course of dorsal metatarsal arteries
branches of dorsal metatarsal arteries
run along each side of phalanges
course of dorsal digital arteries