Anatomy Exam 2
o Cardiac
Striated muscle (regular array of actin and myosin in the sarcomeres)
Each muscle has a single, centered nucleus
Cells are connected by intercalated discs
o Skeletal
Hundreds of randomly located nuclei per cell (cells fuse together in development)
Striated
o Smooth
Single nuclei
Not striated
Types of Muscle
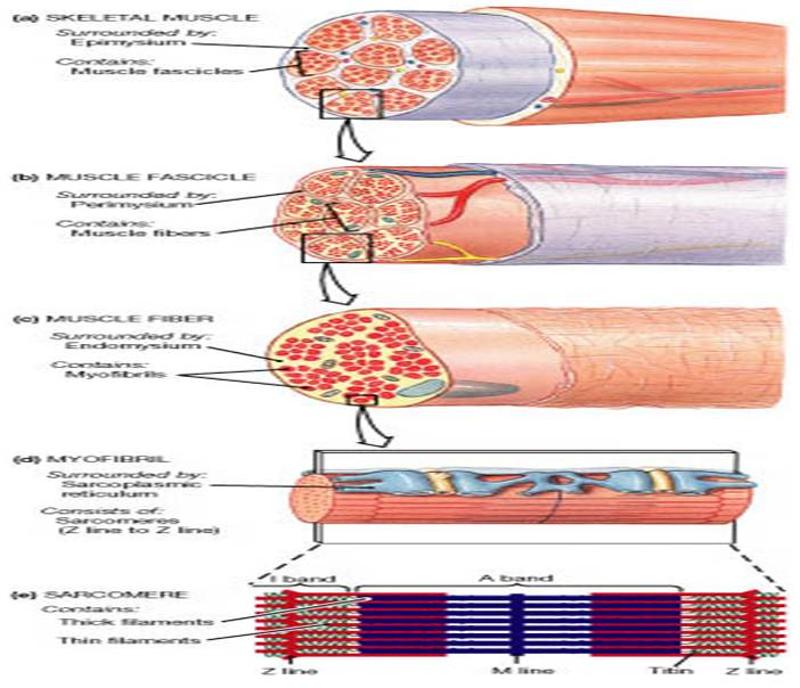
muscle covered with epimysium
made up of fascicles (bundle of cells) covered in perimysium
made up of muscle fibers (cells) covered in endomysium
myofibrils (made of molecular motors) make up each muscle fiber and sarcomeres are contained in each myofibril
blood vessels line in between the connective tissue coverings in between the fascicles
sarcolemma is the cell membrane of muscles with invaginations (t tubules) that go into the cells
sarcoplasmic reticulum stores calcium
describe the muscle levels of organization and components (largest to smallest)
epimysium- covers whole muscle (allows muscles to contract with respect to each other without friction between them)
perimysium- covers the fascicles
endomysium- covers each muscle fiber
tendons- formed by the fusion of these 3 connective tissues
Muscle Connective tissue coverings
too much calcium is released and not stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum so muscle keeps contracting and generating heat
malignant hypothermia
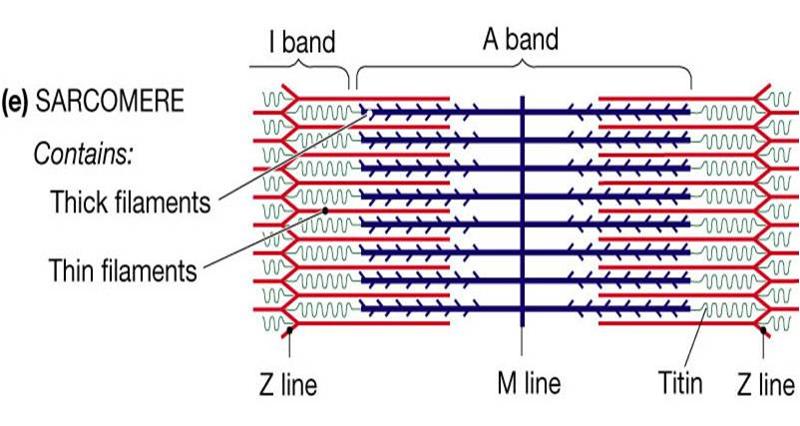
• Actin filaments (thin filaments) are held at the Z line
• Myosin (molecular motor) makes up the thick filament and is located on the A band
o I band only has thin filaments
o A band- mostly thick filaments with some areas where thick and thin filaments overlap
o Z line are thick vertical lines
o H zone/band- only thick filaments
o M line- holds thick filaments together
sarcomere construction
o The entire sarcomere decreases in width
o A band is the same width
o Z lines are closer together
o I band decreases in width
o Whole sarcomere decreases in width
What changes in a sarcomere when a muscle contracts?
skeletal muscle
1- Z line
2- H zone
3- I band
4- M line
5- A band
name the tissue and label the numbers
skeletal muscle
1. Z line
2. M line
3. H zone
4. I bands
5. A band
6. Sarcomere
name the tissue and label the numbers
Actin (thin) filaments are made of G proteins with binding sites for myosin that are covered up with tropomyosin when the muscle is relaxed
sarcolemma receives an electrical impulse that releases acetylcholine which causes a change in membrane potential that travels to the t tubules that connects directly to the sarcoplasmic reticulum
sarcoplasmic reticulum then releases calcium
calcium causes a conformation change which causes tropomyosin to be released and the binding site to be uncovered
Uncovering the myosin binding site for muscle contraction
myosin binding sites are uncovered
ATP oxidation (ADP + Pi -> ATP)causes myosin to flip up in the activated position so actin can bind and begin the power stroke (pulls thin filaments in towards the center)
ATP hydrolysis (ATP-> ADP + Pi) causes ACh to be removed
sarcoplasmic reticulum recaptures calcium
myosin binding site on the actin filament are covered by tropomyosin
contraction ends
muscle contraction -> relaxation
(starting after the myosin binding site is uncovered)
no more ATP is left 8-12 hours after death to replace the ADP on the myosin head, so there is no relaxation in muscle tissues
rigormortis
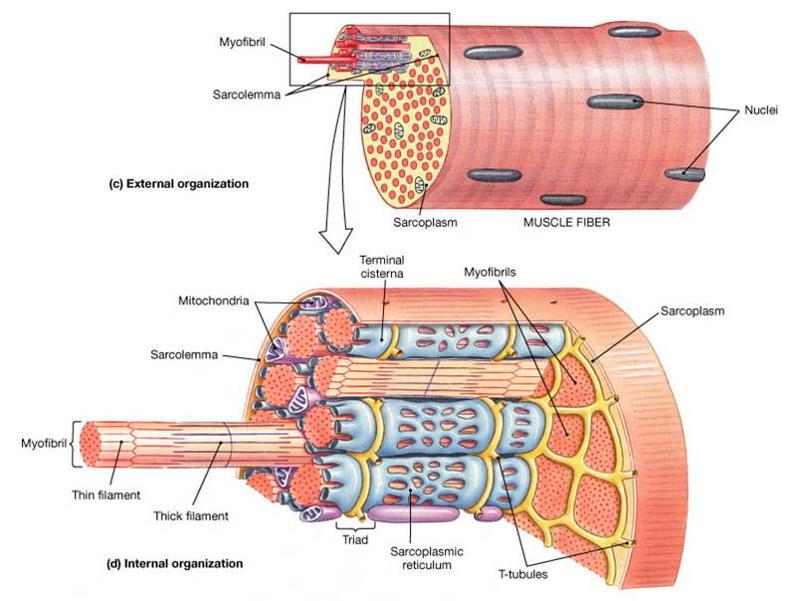
1. triad (2 terminal cisternae and a t tubule in between)
2. sarcolemma (plasma membrane)
3. myofibril (bundled thick and thin filaments, contains a chain of sarcomeres)
4. t tubule (transmit the action potential deep inside the fiber to the terminal cisternae)
5. terminal cisternae (widened sarcoplasmic reticulum that receive t tubule signals)
6. sarcoplasmic reticulum (endoplasmic reticulum that stores calcium)
7. sarcomere (smallest structural and contractile unit of a muscle myofibril)
8. thin filament (mostly actin)
9. Thick filament (mostly myosin)
label
10. actin (thin proteins)
11. tropomyosin (covers the myosin binding site until calcium releases it)
12. troponin
13. myosin crossbridges (heads project towards actin, myosin cross bridges attach to actin and pull the thin filaments past the thick filaments)
14. myosin tails
name and describe
muscles of facial expression
facial nerve
2. orbicularis oculi
3. zygomaticus
4. orbicularis oris
5. platysma
label and name the nerve that innervates them
facial nerve
to test, have the patient:
orbicularis oculi- shut their eyes tightly
zygomaticus- smile
orbicularis oris- purse their lips
buccinators- whistle (buccinator presses cheek inward)
platysma- depresses mandible (pouting)
name and the muscles of facial expression and describe how to test their nerve
2. Orbicularis Oculi (facial expression, facial nerve)
3. Zygomaticus (facial expression, facial nerve)
4. Buccinator (facial expression, facial nerve)
5. Orbicularis oris (facial expression, facial nerve)
6. Masseter (mastication, trigeminal nerve (mandibular))
7. Platysma (facial expression, facial nerve)
label each muscle, its nerve, and which muscle group it belongs to
muscles of facial expression
infrahyoid (strap) muscles (raise and lower hyoid)
abdominal muscles
splenius and semispinalis capitis (deep neck muscles that hold your head up)
erector spinae (longitudinal deep back muscles responsible for posture)
axial musculature
pectoral girdle- holds the upper extremity to the trunk
upper extremity- mostly in charge of controlling the hand
pelvic girdle- holds the lower extremity to the trunk
lower extremity
appendicular musculature
upper extremity
flexors are anterior
extensors are posterior
lower extremity
extensors are anterior
flexors are posterior
flexors and extensor organization for the upper and lower extremities
1. Temporalis (trigeminal nerve, muscles of mastication)
2. Buccinator (facial nerve, facial expression)
3. Orbicularis oris (facial nerve, facial expression)
label each muscle, its nerve, and which muscle group it belongs to
1. Sternocleidomastoid (Neck muscles)
2. Splenius Capitis (Neck Muscles)
3. Trapezius (Scapula movers and stabilizers)
4. Levator Scapulae (scapula movers and stabilizers)
5. Platysma (facial expression)
label each muscle and which muscle group it belongs to
1. Infrahyoid muscles (neck muscles)
2. Suprahyoid Muscles (neck muscles)
3. sternocleidomastoid (neck muscles)
label each muscle and which muscle group it belongs to
trigeminal nerve (mandibular)
Temporalis- elevates and retracts mandible
Masseter- elevates and retracts mandible
list the muscles of mastication, what they do, and their nerve
innervated by the cervical plexus
sternocleidomastoid (flexes head (looking down), rotates "no")
infrahyoids (depresses the hyoid bone during speaking and swallowing)
suprahyoids (elevates the hyoid bone during speaking and swallowing)
splenius capitis (holds your head up, helps to turn your neck)
list the neck muscles, what they do, and their nerve
1. Platysma (facial expression)
2. Pectoralis Major (movers of the shoulder joint)
3. Latissimus Dorsi (movers of the shoulder joint)
4. Serratus Anterior (Scapula movers and stabilizers)
5. External oblique (abdominal wall)
6. sternocleidomastoid (neck muscles)
7. Trapezius (scapula movers and stabilizers)
8. Internal intercostals (respiratory muscles)
9. External intercostals (respiratory muscles)
10. Internal Oblique (abdominal wall)
11. Transverse abdominus (abdominal wall)
12. Rectus Abdominis (abdominal wall)
label, name the muscle group
innervated by the lumbar plexus
• External oblique- most superficial side, runs down your sides (down and medially)
• Internal oblique- run up and medially under the external oblique and deeper
• Transverse abdominus-comes across (run transversely)
• rectus (straight) abdominalis- 6 pack muscles
describe the abdominal wall muscles and name their nerve
anterior: innervated by the brachial plexus
serratus anterior- abducts scapula and rotates it upward (throwing a punch), holds the scapula to the trunk, wings scapula back if it is injured
posterior
trapezius- shoulder shrugging, test by having a patient shrug their shoulders against resistance (accessory nerve)
levator scapulae- elevates scapula and rotates it downward (dorsal rami)
rhomboids- elevates and adducts scapula and rotates it downward, stabilizes scapula (dorsal rami)
describe the scapula mover and stabilizer muscles and name their nerve
all are innervated by the brachial plexus
Posterior and anterior
deltoid- powerful abductor (raises shoulder and arm away from the body, anterior medically rotates arm, posterior laterally rotated the arm)
Anterior
Pectoralis Major- flexor (moves the humerus towards the trunk), stretchs from the chest to the humerus
posterior
Teres Major- extends, adducts, and medially rotates the arm
latissimus dorsi- pulling the arm down if it is above your head (swimming)
lateral
coracobrachialis- flex and medially rotate the arm
describe the movers of the shoulder joint (not including the rotator cuff) and name their nerve
1. sternocleidomastoid (neck muscles)
2. Trapezius (scapula movers and stabilizers)
3. Deltoid (movers of the shoulder joint)
4. Infraspinatus (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
5. Teres Major (movers of the shoulder joint)
6. Latissimus Dorsi (movers of the shoulder joint)
7. External Oblique (abdominal wall)
8. Splenius Capitis (neck muscles)
9. Levator Scapulae (scapula movers and stabilizers)
10. Rhomboids (scapula movers and stabilizers)
11. Supraspinatus (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
12. Teres Minor (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
label each muscle and its muscle group
erector spinae- group of longitudinal deep back muscles, responsible for posture, helps to turn the neck
innervated by the dorsal rami
describe the vertebral column muscles and their nerve
1. Subscapularis (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
2. Teres Major (movers of the shoulder joint)
3. Coracobrachialis (movers of the shoulder joint)
4. Biceps Brachii (movers of the elbow joint)
5. Supraspinatus (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
6. Infraspinatus (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
7. Teres Minor (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
8. Triceps Brachii (movers of the elbow joint)
label each muscle and its muscle group
SITS
innervated by brachial plexus and branches
supraspinatus- posterior, assists the deltoid in abducting the arm
infraspinatus- posterior, laterally rotates and adducts the arm
teres minor- posterior, laterally extends, adducts, and rotates the arm
subscapularis- anterior, medially rotates the arm
describe the rotator cuff muscles
little branches that have motor and sensory rami (mixed spinal nerves)
only go to the deep back muscles and skin on the back
innervates the erector spinae and splenius capitis
dorsal rami
when people break their humerus they can damage thier radial nerve (part of the brachial plexus)
cannot extend their arms/wrist, everything is flexed
wrist drop
triceps brachii- major extensor of the upper extremity
biceps brachii- flexes the arm
brachialis- most powerful flexor of the forearm
brachioradialis- weak flexor of the elbow
describe the movers of the elbow joint
1- subscapularis (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff)
2- teres major (movers of the shoulder joint)
3- biceps brachii (movers of the elbow)
4- brachialis (movers of the elbow)
label the muscles and name their muscle group
1- pronator teres (movers of the wrist and fingers)
2- flexor carpi radialis (movers of the wrist and fingers)
3- brachioradialis (movers of the elbow)
4- palmaris longus (movers of the wrist and fingers)
5- flexor carpi ulnaris (movers of the wrist and fingers)
label the muscles and the muscle group
All flexors or abductors
1. biceps brachii (flexes arm)
2. brachialis (flexes forearm)
3. pronator teres (pronates and weakly flexes forearm)
4. brachioradialis (flexes forearm)
5. flexor carpi radialis (flexes wrist)
6. palmaris longus (weakly flexes wrist)
7. flexor carpi ulnaris (flexes and adducts hand)
8. flexor digitorum (flexes the digits-IMPORTANT)
9. flexor pollicis longus (flexes distal phalanx of thumb)
10. Abductor Pollicis brevis (abducts the thumb)
label and describe the muscles
1- extensor carpi radialis (extend and adduct hand)
2- extensor carpi ulnaris (extends and adducts hand)
3- extensor digitorum (extends hand and phalanges)
4- flexor carpi ulnaris (flexes and adducts hand)
label and describe the muscles
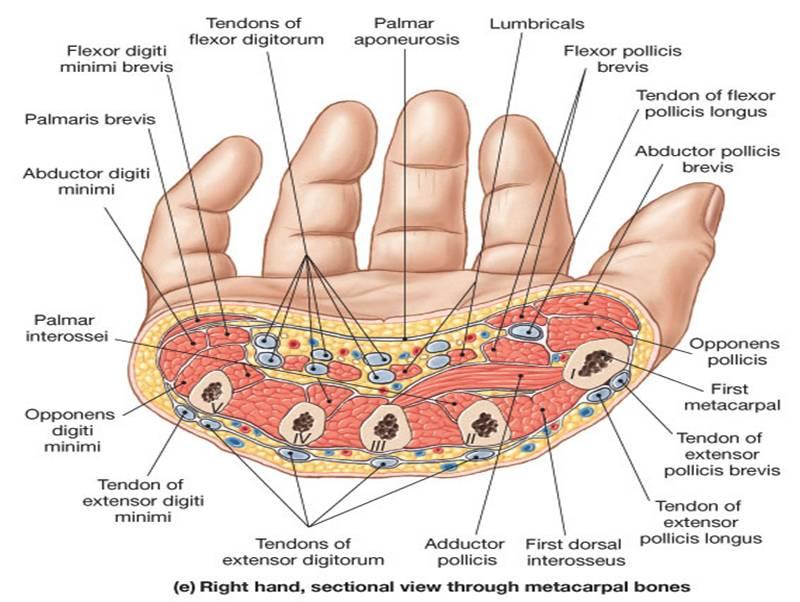
space in the wrist containing flexor digitorum tendons and median nerve
carpal tunnel syndrome- overuse of the hand causes the tendons to become inflamed which compresses the median nerve
carpal tunnel
Adductor Longus
pectineus
iliopsoas- major hip flexor
tensor fascia lata- flexes and abduct the thigh
gluteus maximus
gluteus medius
piriformis
sartorius- flexes leg and flexes, abducts and laterally rotates the thigh (allows us to cross our legs)
gracilis
describe the movers of the hip joint
changes in the hand depending on where the brachial plexus was injured
claw hand
Crutches push on the brachial plexus and can cause numbness in the hands when the brachial plexus is compressed (affects all nerves of the upper extremity)
brachial plexus injury
innervated by the brachial plexus
lumbricals- little worms, flex the metacarpal joint
abductor pollicis- abducts the thumb
flexor retinaculum- carpal tunnel is underneath
interossei- muscle group in hand
muscles of the hand
gluteus maximus- powerful extensor of the hip joint
gluteus medius- abducts and medially rotates the thigh
test gluteal region strength by having someone sit in a chair and and stand up without using their hands or by walking up stairs
gluteal region
1- iliopsoas
2- tensor fasciae latae
3- sartorius
4- rectus femoris (Quadriceps)
5- iliotibial tract (tendon, abducts the thigh)
6- vastus lateralis (Quadriceps)
7- vastus intermedius (Quadriceps)
8- vastus medialis (Quadriceps)
9- pectineus
10- adductor longus
11- gracilis
label the anterior superficial thigh muscles
medial adductors in the groin region are innervated by the obturator nerve
adductor longus (anterior, medial adductor)
pectineus (anterior, adducts and flexes thigh)
iliopsoas (anterior, major hip flexor)
tensor fascia lata (lateral, adductor of the thigh)
gluteus maximus (posterior, powerful extensor of the hip, laterally rotates the thigh)
gluteus medius (posterior, adducts and medially rotates the thigh)
piriformis (deep posterior, laterally rotates and extends the thigh, sciatic nerve is underneath it)
sartorius (anterior, allows us to cross our legs, innervated by the femoral nerve)
gracilis (anterior, adducts and medially rotates thigh, flexes leg)
hip adductors get injured in a groin pull
describe the movers of the hip joint
largest nerve in the body
branches into the tibial nerve (posterior) and the fibular nerve (anterior)
sciatic nerve and its branches innervates mostly the whole lower extremity (except parts of the thigh)
piriformis syndrome- an overactive piriformis (sciatic nerve sits underneath the piriformis)caused a compressed sciatic nerve which causes major lower extremity problems
sciatic nerve
Quadriceps (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius)- knee extensor, innervated by the fibular nerve
hamstrings (bicep femoris, semimembranosus)- flexes knee (more important) and extends the hip
describe the movers of the knee joint
1- inguinal ligament
2- gracilis
3- adductor longus
label the anterior deep thigh muscles or ligaments
1- gluteus medius
2- gluteus maximus
3- gracilis
4- iliotibial tract (tendon, abducts the thigh)
5- semimembranosus
6- biceps femoris (hamstring)
label the thigh muscles
gastrocnemius- posterior, plantar flexes the foot and flexes the leg
soleus- posterior, plantar flexes the foot
fibularis (peroneus) longus- lateral anterior, plantar flexes and everts the foot
fibularis brevis
tibialis anterior- lateral anterior, dorsiflexes and inverts the foot (innervated by the fibular nerve)
tibialis posterior- inverts the ankle
flexor digitorum longus- posterior, flexes the toes
flexor hallucis longus- posterior, flexes the big toe
extensor digitorum- lateral anterior, dorsiflexes the foot and extends the toes (innervated by the fibular nerve)
extensor hallucis longus
anterior leg muscles dorsiflex (extend) the ankle
tibialis anterior and posterior (together) invert the ankle
deeper posterior leg muscles cause plantar flexion of toes
lateral leg muscles are everters
describe the movers of the ankle and toes
1= tibialis anterior
2= extensor digitorum
3- fibularis (peroneus) longus
4= fibularis (peroneus) brevis
5= gastrocnemius
6= soleus
7= flexor digitorum longus
label the muscles of the anterior superficial leg
1- gastrocnemius
2- soleus
3- fibularis (peroneus) longus
4- flexor hallucis longus
5- calcaneal (Achilles) tendon
label the muscles or tendons of the posterior superficial leg
1- tibialis posterior
2- flexor digitorum longus
3- flexor hallucis longus
label the muscles of the posterior deep leg
injury to the fibular nerve causes the foot to stay plantarflexed (lack of dorsiflexion, toes point down)
fibular nerve is the most commonly injured nerve in the body
foot drop
CNS- brain and spinal cord, develops from neural tube
integrates sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) information
PNS- formed from neural crest cells that migrated from the neural tube
Somatic (innervated skeletal muscle), autonomic (innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands), and sensory ganglia brings information into the nervous system
connected to receptors and effectors
Central nervous system (CNS) vs peripheral nervous system (PNS)
PNS
develop from neural crests
myelinate peripheral axons (form protective covering for all axons)
disease that affect peripheral myelin usually go away
schwann cells
cells that myelinate axons of the CNS
diseases of the CNS myelin are usually contiguous (ex. multiple sclerosis goes on and off but is usually progressive)
oligodendrocytes
motor neuron
3- dendrites
4- axon
5- axon hillock
6- cell body
7- nucleus
name and label the cell
1. axon terminal
2. schwann cell
3. node of ranvier
4. axon collateral
5. axon
6. dendrites
7. cell body
8. axon hillock
9. trigger zone
10. myelin sheath of schwann cell
name and label the parts
sensory neurons (afferent)- conduct signals from receptor to CNS when environmental changes are detected, unipolar neuron
interneuron (association)- confined to CNS, multipolar neurons
motor neuron (efferent)- conduct signals from the CNS (spinal cord) to effectors such as muscles and glands, multipolar neurons
functional classifications of neurons
1- unipolar (sensory (afferent) neuron)
2- multipolar (interneuron)
3- bipolar (motor (efferent) neuron)
classify the neuron structure
dorsal root ganglia, unipolar cells
1= process
2= satellite cells
3= nucleus
4= neuron cell body
label the cells and components
cerebral cortex, multipolar neurons
5- neuron cell body
6- nucleus
7- process
label the cells and components
1- neurolemma
2- myelin sheath
3- node of ranvier
4- axon
name the structure and label
Spinal nerves (below the neck)- sensory and motor
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS, innervates things that are automatic, spinal or cranial nerves, ex. salivation)- sympathetic and parasympathetic
Cranial nerves (generally innervate the things in the head, ex. salivation)- come off the brain but innervate structures outside of the CNS
Peripheral Nervous system (PNS)
(“horse’s tail”)= nerve roots at the lower part of the spinal cord (lumbar and sacrum)
At birth the spinal cod has equal length as the vertebra (spinal cord and spinal nerve labels match their places in the vertebral column)
As an adult the spinal cord ends at the L1/L2 vertebrae since the spinal cord grows much slower then the vertebral column. Vertebrae pulls nerve roots down with it during development so the nerve roots still exit at their appropriate vertebrae
best place for a Lumbar puncture/spinal tap
cauda equina
Best place to get cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) is between L4 or L5 in the cauda equina because you can get CSF without puncturing the spinal cord since there is lots of CSF and only small nerve roots (like sticking a fork into cooking spaghetti)
lumbar puncture/spinal tap
1. posterior root
2. lateral white column
3. central canal
4. posterior median sulcus
5. posterior white column
6. posterior gray horn
7. posterior root ganglion
8. anterior root
9. anterior gray horn
10. anterior white column
11. Gray commissure
12. Anterior median fissure
name the structure and label the parts
cross section of spinal cord
1- pia mater- delicate covering where small blood vessels are located
2- dura mater- tough, plastic like outer covering
3- epidural space- space in between the dura mater and vertebral bone where epidural anesthesia is injected for pelvis and lower extremity surgeries
4- subarachnoid space- where cerebral spinal fluid is located
5- arachnoid matter- spider web-like covering
name the structure and label and describe each number
cross section of spinal cord
1- spinal nerve
2- posterior root ganglion
3- posterior root
4- posterior median sulcus
5- central canal
6- anterior root
7- anterior median fissure
8- white matter
9- gray matter
name the structure and label each number
5- sympathetic ganglion
6- spinal nerve
7- intervertebral foramen
8- anterior ramus
9- posterior ramus
10- rami communicantes
label the diagram
1- sacral plexus
2- lumbar plexus
3- brachial plexus
4- cervical plexus
5- cervical nerve
6- thoracic nerve
7- lumbar nerve
8- sacral nerve
9- coccygeal nerve
label the spinal plexi
1- axillary nerve
2- musculocutaneous nerve
3- median nerve
4- ulnar nerve
5- radial nerve
6- phrenic nerve
label the nerves that come from the cranial and brachial plexuses
1- obturator nerve
2- pudendal
3- femoral nerve
4- sciatic
5- tibial
6- common fibular
label the nerves that cam from the lumbar and sacral plexuses
1- cerebrum
2- cerebellum
3- diencephalon
4- brain stem
label the 4 major brain regions
1- olfactory bulb
2- olfactory tract
3- pituitary gland
4- optic tract
5- mammillary body
6- cerebellar peduncles
7- olive
8- pyramids
9- spinal nerve C1
10- spinal cord
11- cerebrum
12- cerebral peduncle of midbrain
13- pons
14- medulla oblongata
15- cerebellum
label the inferior side of the brain
blood vessels that run between the dura mater and the skull
if one breaks they bleed between the dura and the skull- epidural hematoma (creating a space that shouldn't be there, arterial bleed so it compresses the brain pretty rapidly)
Middle meningeal artery- between the dura and the temporal bone
• Artery that breaks if someone gets hit in the temporal part of the head
meningeal arteries
normally occurring and blood drains from bridging veins from the brain and the subarachnoid space into these sinuses that eventually form the jugular vein
If a brain shrinks (can happen with aging and dementia) then the bridging veins stretch and if someone hits their head, then the veins will rupture and cause a subdural hematoma
• Subdural hematoma- slow bleed, person becomes confused, major problems later, serious but difficult to diagnose
• Bleeds into the subdural space
duravenus sinuses
o Arteiries in brain also travel through the subarachnoid space
Artery break- subarachnoid hematoma
• Weakness in walls of arteries of high blood pressure
subarachnoid hematoma
consists of the midbrain (processes visual and auditory data), pons (relays sensory information to cerebellum and thalamus) and medulla (relays sensory information to thalamus)
origin of all cranial nerves (except I and II)
many nervous pathways travel through the brainstem
brain stem
31 levels of the spinal cord (each level gives off mixed spinal nerves (motor and sensory))
8 cervical spinal cord levels (7 cervical vertebrae)
12 thoracic spinal cord levels (1 for each rib)
5 lumbar levels
5 sacral levels
1-2 coccygeal levels (usually considered to have 1)
levels of the spinal cord
White matter (axons) are on the outside of the spinal cord carrying sensory info up to the brains and motor info down to the limbs
Gray matter-cell bodies (sensory info enters at the dorsal root via the dorsal horn (dorsal root ganglia are sensory cell bodies), ventral part of gray matter contains motor neuron cell bodies that exit the spinal cord at the ventral root)
white vs gray matter in the spinal cord
Dorsal root ganglia- sensory cell bodies
Dorsal root- bringing info into the spinal cord (sensory neurons, unipolar)
Ventral root- axons of motor neurons, goes directly to muscles
Mixed spinal nerves- signals to and from the goal location (everywhere neck down), travel in the same nerve in opposite directions like a highway, made by dorsal and ventral roots joining, split into dorsal and ventral rami
Dorsal rami-only innervates deep back muscles, erector spinae muscles, skin of midline of the back
Ventral rami- much larger than dorsal, innervates everything else that isn’t covered by dorsal rami (neck and below), can go off on their own or form plexi (how upper and lower extremities are innervated)
Spinal cord nerve roots
all from the brachial plexus
musculocutaneous- flexors of arm (biceps and brachialis)
median- most flexors of the wrist, lateral phalanges, most thumb muscles. passes through the carpal tunnel
ulnar- some flexor of the wrist, all flexors of medial phalanges (funny bone, medial side of humerus)
radial- all extensors of the upper extremity
axillary- deltoid and part of the rotator cuff
upper extremity nerves
o dermatome- sensory information from a single dorsal root
If you injure a dorsal root you get a dermatome pattern of sensory losses
shingles-the virus lives in a dorsal root and becomes activated and comes out of a dorsal root to cause painful symptoms along a dermatome (single stripe pattern on skin)
dermatomes
all are made from ventral rami
cervical plexus: C1-C5, innervates strap muscles
brachial plexus: C5-T1, innervates the entire upper extremity, has 5 branch nerves
T2-T12 we don't form plexi, just intercostal nerves
Lumbar plexus: L1-L5, innervates abdominal muscles
Sacral Plexus: S1-S4
Lumbosacral plexus- gives rise to sciatic nerve which innervates the entire lower extremity
major nerve plexi and what they innervate
five rise to the following nerves
femoral nerve- innervates quadriceps
obturator nerve- innervates adductors
sciatic nerve- L4 to S3 (largest nerve in the body)
innervates hamstrings
gives rise to: tibial nerve (innervates all flexors), and fibular nerve (innervates all extensors)
sacral nerve damage- bladder and bowel problems due to parasympathetic innervations
Lumbar and sacral plexi
all glands and smooth muscle innervations and cardiac muscle
parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems
both parasymp and symp divisions have 2 motor neurons between the spinal cord and the effectors (the first motor neuron (preganglionic) synapses with the second motor neuron (postganglionic) in the ANS ganglia
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Sympathetic- go everywhere (innervated sweat glands in skin that are located everywhere), preganglionic sympathetics located in 14 thoracolumbar (T1-L2 in CNS), in chain that extends the entire length of the trunk, Every spinal nerve from C1 to coccygeal must have sympathetic innervations
Parasympathetic- in head in places that drip [pupil of eye, lacrimal gland (tears), salivary gland], vagus nerve (heart, lungs), sacral nerve (bowel and bladder)
go to oculomotor nerve (constrict pupils) and facial nerve (glands(
parasympathetic vs sympathetic nervous systems
motor fibers for muscle
postganglionic sympathetic fibers to innervate sweat glands in skin
sensory fibers for sensation
3 things every spinal nerve has
brainstem (formed by 6,7,8)
6- midbrain
7- pons
8- medulla oblongata
9-spinal cord
label the inferior portions of the brain and name the part of the brain formed by 6, 7, and 8
cerebellum
1- cerebellar hemispheres
2- vermis
3- folia
4- superior colliculus
5- inferior colliculus
6- arbor vitae (white matter)
7- cerebellar cortex (gray matter)
8- pons
9- medulla oblongata
name the part of the brain and label
1- pineal gland
2- thalamus
3- hypothalamus
4- diencephalon
5- cerebrum
6- cerebellum
7- spinal cord
8- midbrain
9- pons
10-medulla oblongata
11- brainstem
label the parts of the sagittal brain
diencephalon
5- mammillary body
6- pineal gland
7- thalamus
8- intermediate mass of thalamus
9- hypothalamus
10- infundibulum
11- pituitary gland
12- optic chiasm
label that parts and name the structure
cerebrum
1- internal capsule
2- cerebral cortex
3- white matter
4- corpus callosum
5- fornix
6- basal nuclei
name the part of the brain and label
1- central sulcus (shallow groove separating the frontal lobe and parietal lobe)
2- postcentral gyrus (elevation located just posterior to the central sulcus)
3- parietal lobe
4- occipital lobe
5- transverse fissure (deep groove separating the cerebrum from the cerebellum in the posterior/ inferior part of the brain)
6- precentral gyrus (elevation located just anterior to the central sulcus)
7- frontal lobe
8- insula (inner lobe deep to the lateral cerebral fissure)
9- temporal lobe (cut)
label
1- Broca's speech area
2- primary gustatory area
3- primary motor area
4- central sulcus
5- primary somatosensory area
6- primary visual area
7. Wernicke's area
8. primary auditory area
label the functional areas of the cerebral cortex
1- subarachnoid space
2- arachnoid villus
3- falx cerebri
4- white matter
5- superior sagittal sinus
6- parietal bone
7- dura mater
8- arachnoid mater
9- pia mater
10- cerebral cortex
label the cranial meninges
8- lateral ventricles
9- interventricular foramen
10- 3rd ventricle
11- cerebral aqueduct
12- 4th ventricle
13- central canal of the spinal cord
label the ventricles of the brain
14-superior sagittal sinus
15- arachnoid villus
16- subarachnoid space
17- lateral ventricle
18- choroid plexus
19- 3rd ventricle
20- cerebral aqueduct
21- 4th ventricle
22- central canal
label
groove that separates the frontal and parietal lobes
central sulcus
part of the motor areas to the cerebral cortex
located in the precentral gyrus of each frontal lobe
controls impulses to muscles
• A lot of cortex controls the face, fingers
• Medially controls toes and lower extremities
• Lateral cerebral cortex stroke- effects of facial expression, speech (left side), movements of hands and fingers
o Problems with motor control on the opposite side
Premotor (or motor association) cortex- programs of motor movement are made
primary motor cortex
part of the motor areas to the cerebral cortex
located anterior to the primary motor cortex
initiates impulses that result in speech
• Lateral cerebral cortex stroke- effects of facial expression, speech (left side), movements of hands and fingers
broca's speech area
part of the sensory areas to the cerebral cortex
determines where on the body the sensory stimulation occurred
mostly devoted to hands and face
primary somatosensory cortex
part of the sensory areas to the cerebral cortex
in the temporal lobe
interprets auditory stimuli from auditory receptors
primary auditory area
part of the sensory areas to the cerebral cortex
receives impulses from taste receptors
primary gustatory area
judgement and decision making
prefrontal cortex
in occipital lobe
part of the sensory areas to the cerebral cortex
receive information from the retina and interprets the visual stimulu
primary visual area
located on in the temporal lobe
part of the sensory areas to the cerebral cortex
receives impulses from olfactory receptors
primary olfactory area
part of the association areas to the cerebral cortex
recognize spoken words, translates words into thoughts, and possibly helps us sound out strange or new words
wernicke's area
part of the association areas to the cerebral cortex
adjacent to their corresponding sensory cortex
integrate sensory information from the sensory cortex with past experiences
somatosensory, visual, and auditory association areas
crossing pathways from one side of the brain to the other
o Corpus callosum (connects 2 cerebral hemispheres)- major commissure
Almost everything in the right cortex contributes info to the left cortex via crossing fibers
o Optic chiasm is another example
commissural pathways
o Projects from higher to lower
o Like for your cerebral cortex (motor cortex) to tell your muscles what to do you need fibers that go from the cortex to the spinal cord (motor neurons for muscles are in the spinal cord, for these neurons to fire they need a signal from the cortex)
o Projection pathways- north to south or south to north
projection pathways
connect parts of our brain on the same side
ex. seeing and interpreting what your hand is writing
association pathways
huntington's disease
the patient cannot suppress unwanted movements
• Basal ganglia (deeper nuclei, gray matter)- suppresses unwanted movement
basal ganglia disease
2 hemispheres with the vermis connecting them
regulates posture and balance, smooths and coordinates skilled skeletal muscle movements
cerebellum
2 main regions: thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
thalamus- gets all sensory infor except olfaction (olfaction needs to be faster for survival)
suppresses unwanted sensory infor- allows for focus, selects what sensory info is important and sends it to the cerebral cortex
hypothalamus- control many bodily functions and homeostasis
contains the optic chiasm- where the optic nerve crosses
epithalamus- contains some glands
diencephalon
head trauma (brain swelling, broken artery) causes the brain to squish to the only space available which compresses the oculomotor nerve
uncus is a piece of the temporal lobe that herniates if the brain swells which pushes on the oculomotor nerve
o Pupils cannot compress and stay dilated and are not responsive to light
epidural hematoma
tumor of Schwann cells (peripheral nervous system cells), compresses nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear and facial VII), and can affect the cerebellopontine angle (angle between the cerebellum (important for coordination) and the pons)
• Nerve damage causes uncoordinated gate, droopy face, hearing loss, ringing in the ears can only all happen together at the cerebellopontine angle
acoustic schwannoma
CSF leaks out of the choroid plexus blood vessels
ependymal cells with cilia push the CSF in one direction into the lateral ventricle
the CSF then moves into the 3rd ventricle then into the 4th ventricle via cerebral aqueducts
the CSF then goes into the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain and spinal cord (CSF follows the central canal of the spinal cord then goes back into the subarachnoid space)
CSF it then returned to the blood through arachnoid villi located at the superior sagittal sinus
path of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
I Olfactory
II Optic
III Oculomotor
IV Trochlear
V Trigeminal (Ophthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular)
VI Abducens
VII Facial
VIII Vestibulocochlear
IX Glossopharyngeal
X Vagus
XI Accessory
XII Hypoglossal
Oh, Oh, Oh To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet, AH
list all the cranial nerves in order
1. olfactory
2. optic
3. Oculomotor
4. Trochlear
5. Trigeminal (Ophthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular)
6. Abducens
7. Facial
8. Vestibulocochlear
9. Glossopharyngeal
10. Vagus
11. Accessory
12. Hypoglossal
label the cranial nerves
• Usually if you have a problem with one olfactory nerve then the other one will take over
You may regenerate olfactory neurons (but not any others)
Olfactory nerves are tiny branches that are attached to receptors, axons go through the cribriform plate then form into the olfactory nerve
What we often call the olfactory nerve is actually the olfactory tract (CNS)
Test by having a patient smell something through one nostril at a time
purely sensory
goes straight to the cerebrum for processing (only sensory nerve that doesn't go through the thalamus)
olfactory nerve I
Optic nerve starts in the retina ((retinal ganglion cells give rise to the optic nerve [myeleinated by an oligodendrocyte which speeds up conduction in the CNS]). Optic nerve is very fast conducting nerve
Actually a CNS tract
Right visual field process on the left side of the brain, visa versa
Tested using visual fields, doctors move fingers from lateral to medial parts of visual fields
optic nerve II
CNS disease affecting myelination and oligodendrocytes
deteriorates CNS myelin and is first noticed in the optic nerve since conduction is usually so fast
multiple sclerosis
when the optic nerve crossed over in the brain above the pituitary gland (commissure). Optic nerve comes from the lateral part of your visual field.
Pituitary gland tumors causes “tunnel vision” which limits your vision into the center of your visual field due to damage to the optic chiasm, damages the crossing fibers
optic chiasm
Always tested together, more extra-ocular muscles
Oculomotor- innervates the levator palpebrae (oculomotor lesion would cause trouble elevating the eyelid) and 4 extra ocular muscles and pupil (parasympathetic, constrict)
Oculomotor Damage- causes droopy eyelid (ptosis) and a dilated pupil
Trochlear lesion- Can’t look down and in (trouble reading)
Abducens- abducts the eye, cannot abduct both eyes are the same time (one abducts and the other stays neutral)
test these by observing eyelids (ptosis is abnormal), moving eye in different directions, and making sure pupil constricts
Oculomotor, Trochlear, and Abducens (III, IV, and VI) cranial nerves
main sensory nerve to the head, motor to muscles of mastication (gives you sensation on your face)
• Ophthalmic nerve (afferent, corneal blink reflex with facial nerve)- innervates forehead and cornea
o Test afferent by putting a whisp of cotton on their eye to get them to blink or tap forhead
o Afferent=ophthalmic, efferent=facial -> V-VII reflex
• Maxillary nerve- innervates the upper teeth, cheek, around the nose (purely sensory)
• Mandibular division- lower teeth, chin, motor component
o Trigeminal motor component- muscles of mastication (chewing, temporalis, masseter)
test by tapping chin
trigeminal nerves (V)
motor to muscles of facial expression, taste, anterior 2/3 of tongue, ANS to lacrimal submandibular and (sublingual)salivary glands
Innervates muscles of facial expression- test it by having the patient make faces or by testing the corneal blink reflex
Carries taste, autonomic to the lacrimal gland and 2 of the salivary glands
corneal blink refllex (V-VII)
shutting the eye is a muscle (nerve VII) for facial expression (open with III-oculomotor), puff of air causes patient to blink which tests facial nerve
facial nerve (VII)
purely sensory
Tumor on VII cranial nerve- dizziness, ringing in ears, hearing loss
Acoustic Schwannomas
vestibulocochlear (VIII) nerve
sensory to pharynx (back or throat, or motor to 1 small pharynx muscle)
taste, posterior 1/3 of tongue
visceral sensory
Test using the gag reflex (IX-X reflex)- sticks a tongue depressor on the tongue to push it down and see the back of the throat and make you gag
Afferant- IX (vagus), constricts pharynx
Efferent- causes gag (X)
glossopharyngeal (IX)
Motor:larynx and pharynx
ANS: visceral organs
Sensory:visceral organs
Taste
Vagabond: wanders out of the head to innervate the pharynx and larynx (swallowing and speaking)
Parasympathetic to all the organs down to the the small intestine
Tested using the gag reflex (IX-X reflex)
vagus nerve (X)
Accessory (XI)- innervates sternocleidomastoid (test by having the look from side to side) and trapezius (check by putting hands on pts shoulder and having them shrug against resistance)
Hypoglossal (XII)- innervates the muscles on the tongue, test by sticking the tongue out and having the patient move it from side to side, damage on one side has the tongue pointed towards the side of the lesion
Accessory and hypoglossal nerves (XI and XII)
1. interneuron
2. sensory neuron (afferent)
3. sensory receptor
4. preganglionic motor neuron
5. autonomic ganglion
6. postganglionic motor neuron
7. visceral effector
label
1. superior oblique
2. superior rectus
3. lateral rectus
4. medial rectus
5. inferior oblique
6. inferior rectus
label the muscles
1. scleral venous sinus
2. ciliary muscle
3. ciliary process
4. ciliary body
5. choroid
6. sclera
7. retina
8. cornea
9. pupil
10. iris
11. suspensory ligaments
12. ora serrata
label the parts of the eye
retina
1. macula lutea
2. central fovea
3. blood vessel
4. optic disc
label the tissue and the numbers
6. cornea
7. pupil
8. iris
9. ciliary body
10. lens
11. choroid
12. sclera
13. retina
14. optic disc
15. optic nerve
label the eye
retina
name the tissue
1. lobule
2. auricle
3. helix
4. external ear
5. malleus
6. incus
7. stapes attached to oval window
8. middle ear
9. internal ear
10. auditory tube
11. tympanic membrane
12. external auditory canal
label the ear
1. anterior semicircular canal
2. posterior semicircular canal
3. lateral semicircular canal
4. ampulla of semicircular canal and duct
5. utricle
6. saccule
8. membranous semicircular duct
9. vestibule
10. round window
11. cochlea
12. cochlear duct
label the internal ear
fibrous (cornea=clear layer, sclera= opaque layer)
choroid (highly vascular, gives rise to iris and ciliary body)
retinal layer (inner, sensory (photo) receptors)
3 coats of the eye
connective tissue layer that lines the eyelid, makes a bend and reflects over the sclera, does not go over the cornea (or you wouldn’t be able to see)
Contact lenses can get stuck behind the ledge
conjunctiva
o Light goes through the cornea, through the anterior chamber of the eye through fluid, through the pupil, through the lens where its focused, through the vitreous (eye jelly) then to the retina
path of light through the eye
o Aqueous humor- circulating fluid, produced by cells in Ciliary body, circulated then is reabsorbed in the canal of schlemm
If the canal of schlemm is blocked then pressure builds in the eye and causes glaucoma
aqueous humor
o Middle ear has ossicles (tiny bones) that vibrate with sound waves and that vibration is transduced to pressure waves which is then transduced to an electrical signal in the cochlea
o Hair cells run against the tectorial membrane to transmit sound
o 2 tiny muscles (tensor tipany, )that are in the ear that contract with very large sounds to dampen the sound and damaging the cochlea
ear
• innervated by the cranial nerves III (oculomotor), IV (trochlear), VI (abducens)
• ocular motor nerve- droopy eye lid, opens the eye (lavatory palpebrae)
• lateral rectus- abducens nerve, that abducts, lets the eye move laterally
extra-ocular muscles
axon terminals on a neuromuscular junction
arrows point to motor end plates
name the structure and what the arrows are pointing to
cochlea
name the structure
ganglion
name the structure
neuron
arrow pointing to nissl substance
name the structure and what the arrow is pointing to
peripheral nerve in cross section
arrow is pointing to perneurium
name the structure and what the arrow is pointing to
spinal cord
1. dorsal horn (gray matter)
2. white matter
3. Ventral horn (gray matter)
name the structure and label
lumbodorsal (thoracolumbar) fascia (tendon)
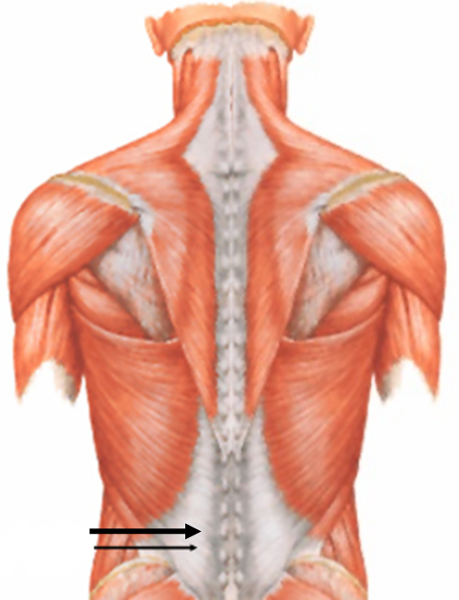
name the tendon indicated by the arrow
central tendon of the diaphragm
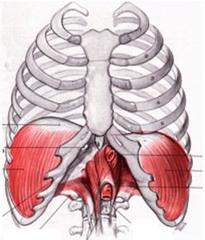
name the white part of the muscle
1. flexor retinaculum of the wrist (tendon)
2. median (nerve)
name the tendon and nerve