Unit 8: Cell Reproduction (Meiosis)
Sexual reproduction
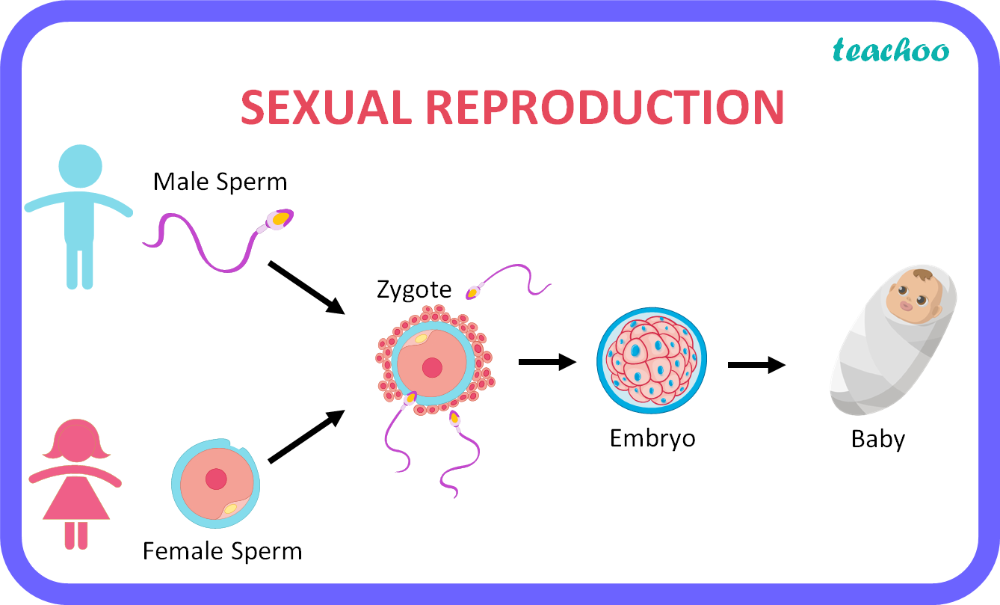
Type of reproduction that has 2 parents and results in genetically unique offspring. Sperm and egg fuse together to form a zyote.
Gametes
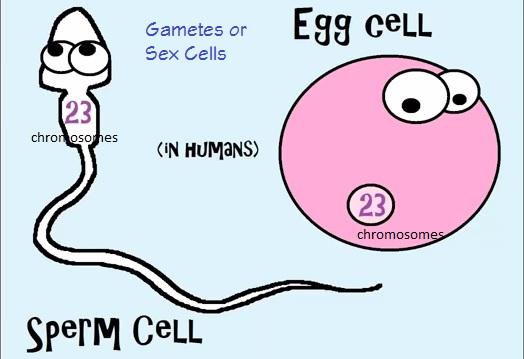
Sex cells formed through process of meiosis. Have 1/2 the number of chromosomes as body cells and are haploid.
Sperm

Male gamete
Egg

Female gamete
Fertilization
When sperm and egg fuse together to form a zygote.
Zygote
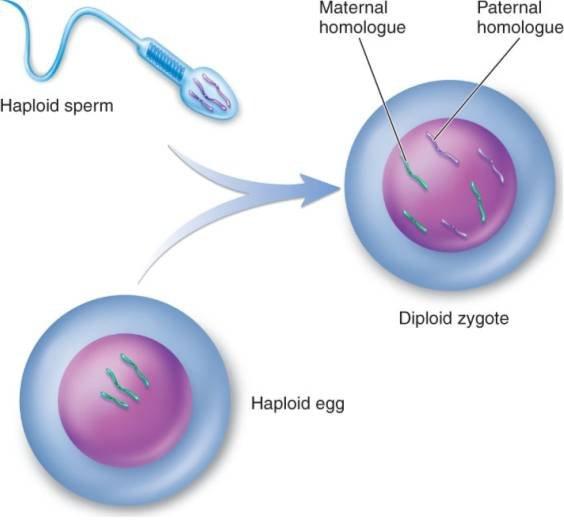
Single diploid cell formed after fertilization and develops into embryo.
Meiosis
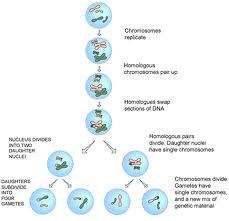
Processes that produces gametes for sexual reproduction. A diploid cell undergoes 2 divisions to half the number of chromosomes and forms 4 haploid cells that become sperm or egg.
Diploid
When a cell has 2 sets of chromosomes. In humans = 46 chromosomes
Haploid
When a cell has 1 set of chromosomes. In humans = 23 chromosomes
Interphase
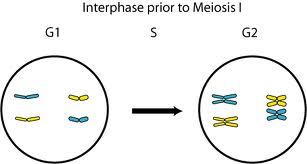
Stage before cell division where cells grow and DNA replication occurs.
Homologous Chromosomes
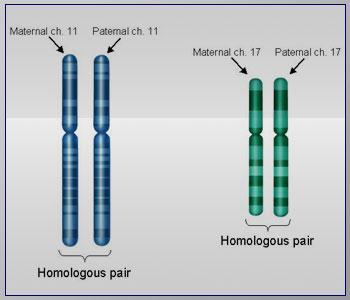
The pair of chromosomes that are the same size and carry the same types of genes - 1 comes from mom and 1 comes from dad.
Crossing Over
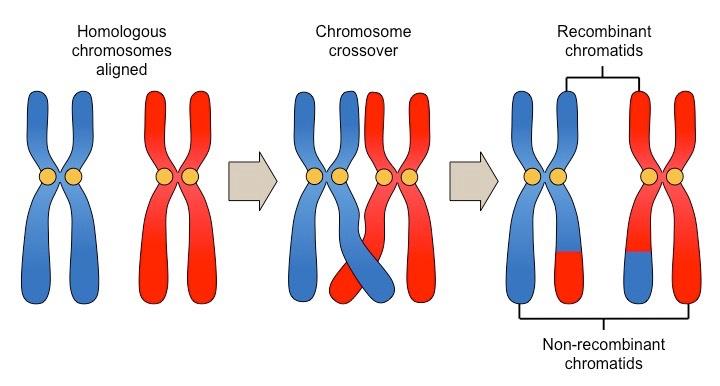
Occurs during Prophase I of meiosis where homologous chromosomes exchange parts to increase genetic variation.
Meiosis I
First division of meiosis that separates the homologous chromosomes resulting in 2 haploid cells. Includes:
- Prophase I - nuclear envelope dissolves, chromosomes condense, homologous chromosomes pair up and crossing over occurs.
- Metaphase I - homologous pairs line up at the middle of the cell.
- Anaphase I - homologous pairs are pulled apart to the opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase I - nuclear envelope reforms around the 2 sets of chromosomes and chromosomes unwind.
- Cytokinesis I - cytoplasm divides resulting in 2 haploid cells with replicated DNA.
Meiosis II
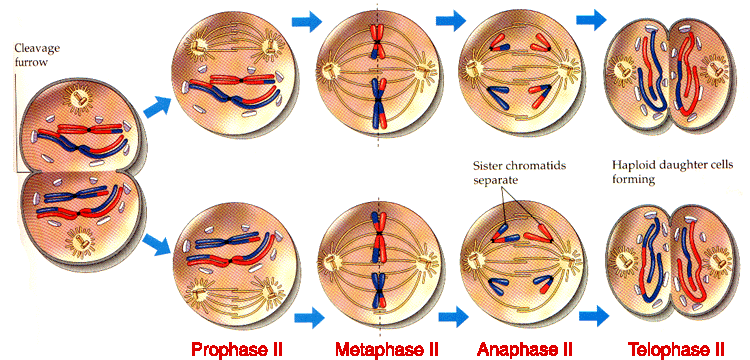
Second division of meiosis where the 2 cells at the end of meiosis one separates the sister chromatids resulting in 4 haploid cells. Includes:
- Prophase II: nuclear envelope dissolves, chromosomes condense
- Metaphase II: chromosomes line u p at the middle of the cell
- Anaphase II: sister chromatids pull apart to opposite ends of the cell
- Telophase II: nuclear envelope reforms around the 2 sets of chromosomes and chromosomes unwind.
- Cytokinesis II: cytoplasm divides resulting in 4 haploid cells.
Nondisjunction
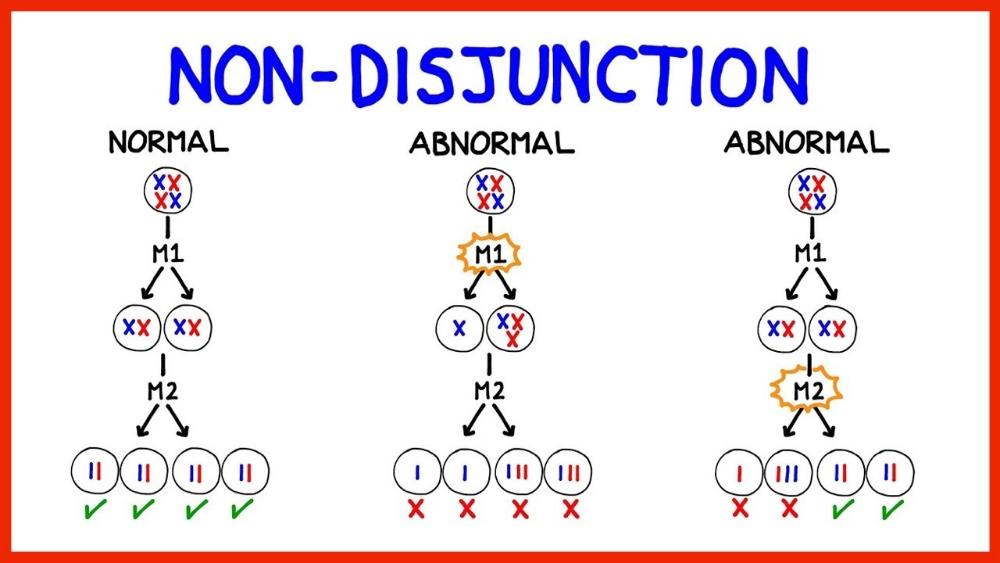
Mutation that can occur during Anaphase I or Anaphase II of meiosis where the chromosomes do not separate properly resulting in cells with either too many chromosomes or not enough chromosomes.