salivary glands
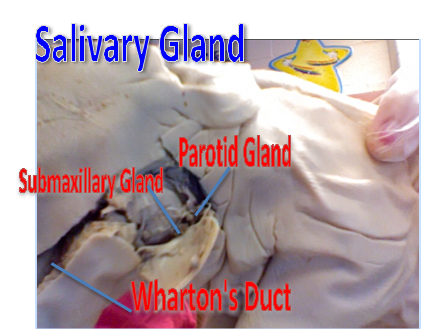
produce saliva; also helps break down carbohydrates (with salivary amylase; and lubricates the passage of food down from the oro-pharynx to the esophagus to the stomach.
parotid gland

biggest producer of saliva;
parotid duct
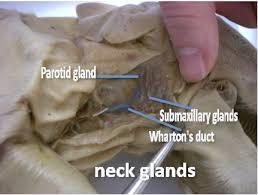
saliva travels through the gland into here
submandibular gland
salivary gland ; less fatty than parotid
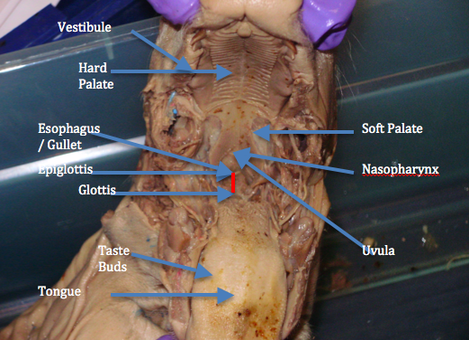
opening to nasopharynx
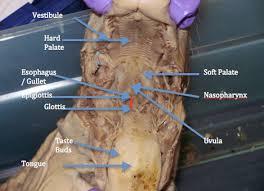
h allows a person to breathe through the nose.
hard/ soft pallete
The soft palate is moveable; closing off the nasal passages during the act of swallowing, and also for closing off the airway.
hard: help facilitate the movement of food backwards towards the larynx
auditory (eustachian tubes)
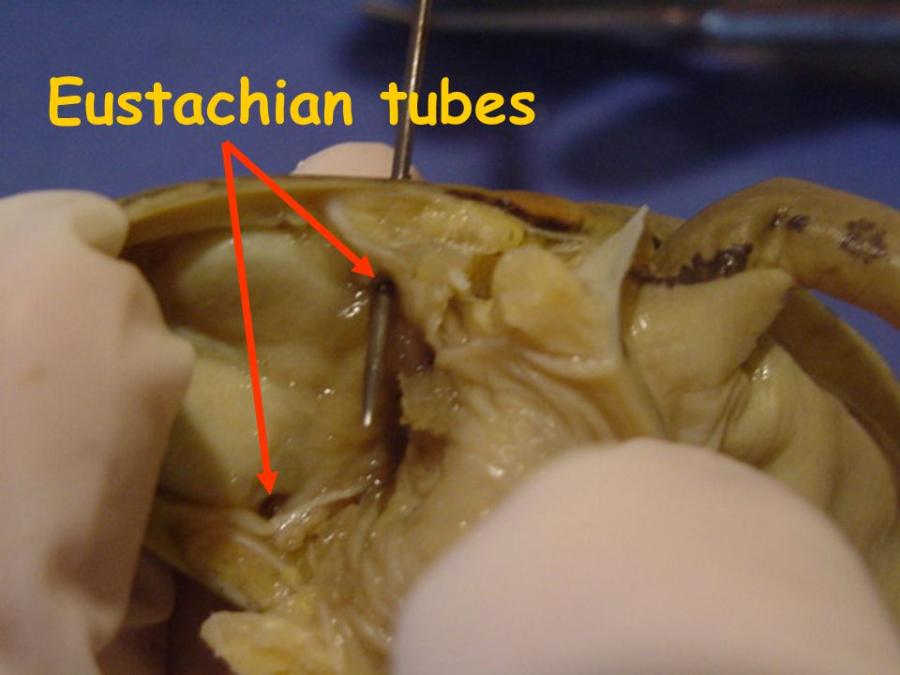
is to ventilate the middle ear space, ensuring that its pressure remains at near normal environmental air pressure
esophagus
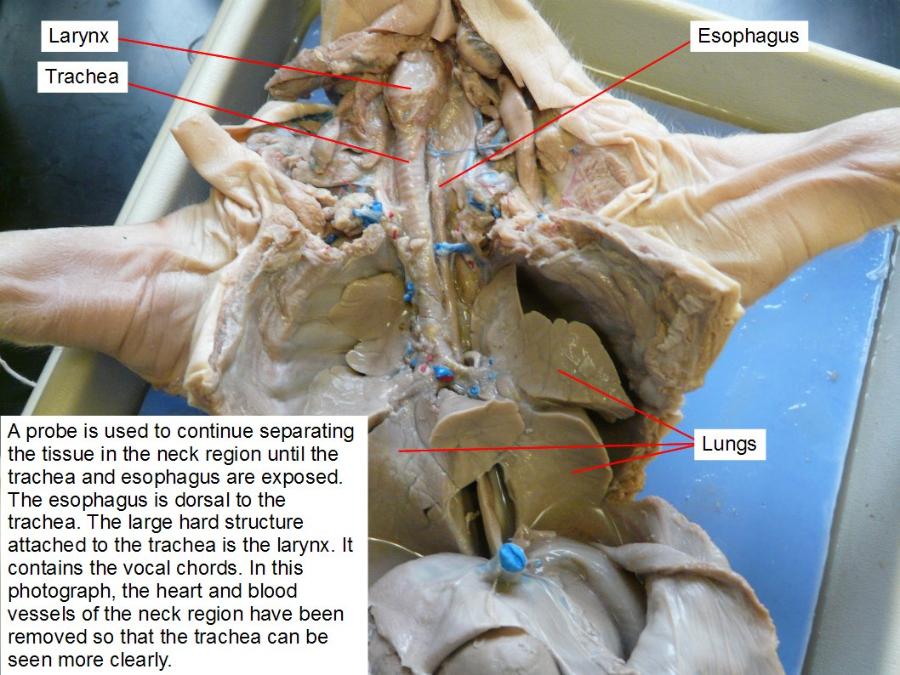
connects the pharynx (throat) to the stomach; functions as the conduit for food and liquids that have been swallowed into the pharynx to reach the stomach.
larynx

houses the vocal folds, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation
thymus
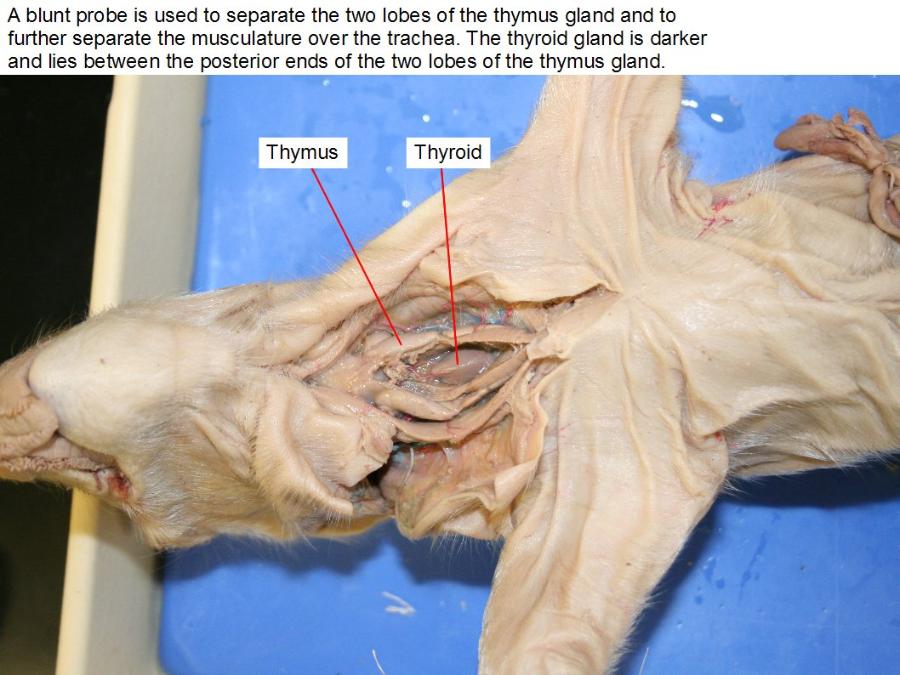
development of T-lymphocytes or T cells
trachea
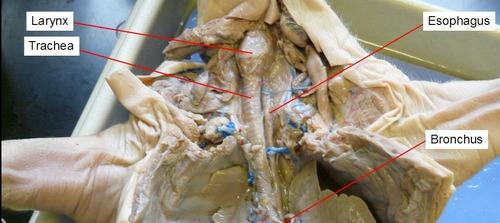
the vital function of providing air flow to and from the lungs for respiration.
glottis
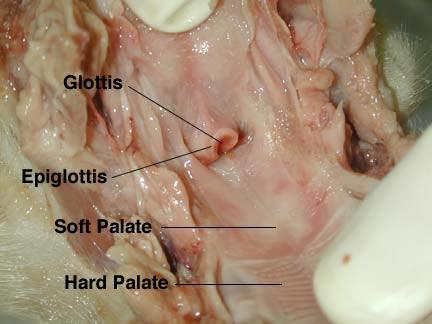
Sound production
thyroid

hormones;Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body which can absorb iodine.
diaphragm
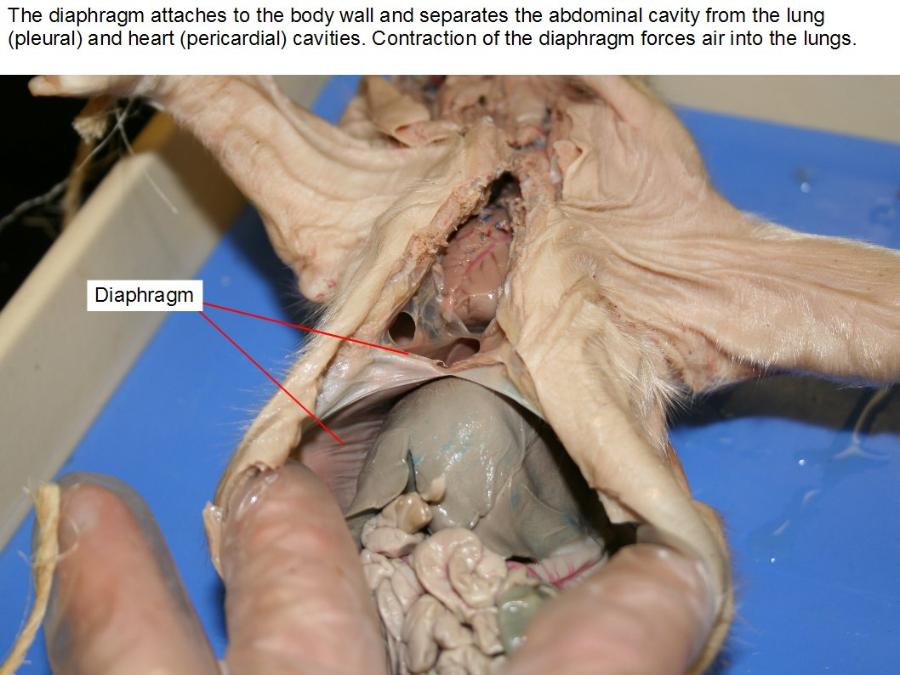
is the primary muscle used in the process of inspiration, or inhalation
lungs
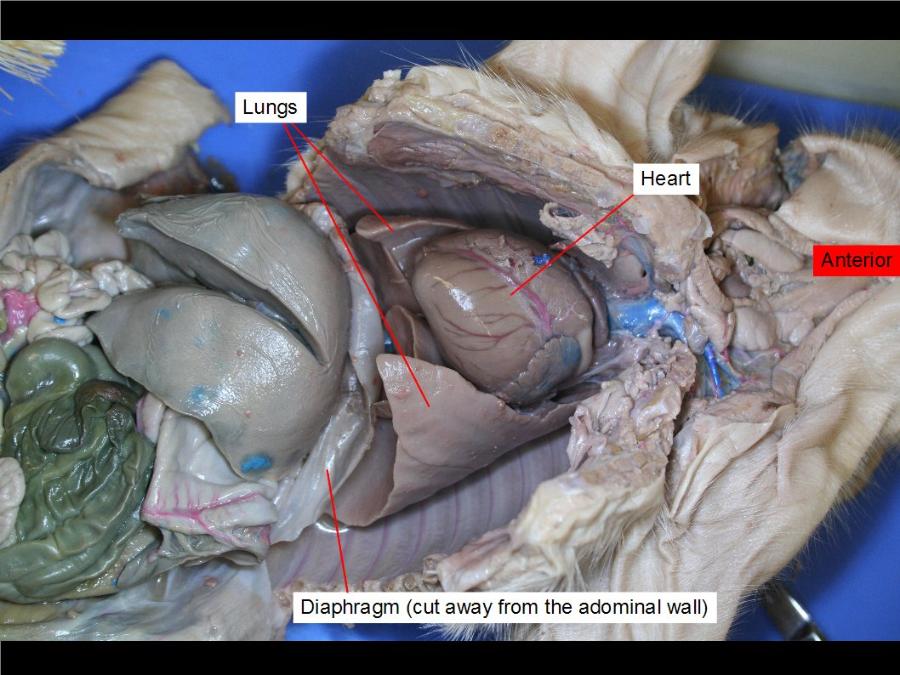
breathing bitch!
o2 --> co2
peritoneum- parietal / visceral
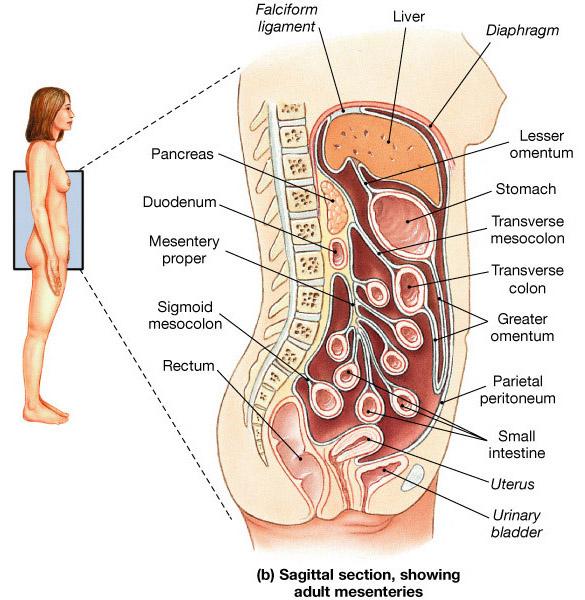
is that portion that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
pleura - parietal / visceral
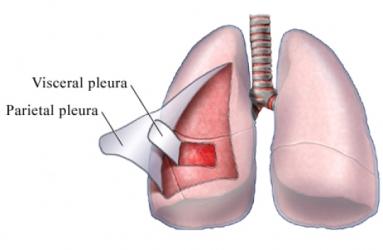
P: lines pleural cavity
v: covers surface of the lungs
bronchi
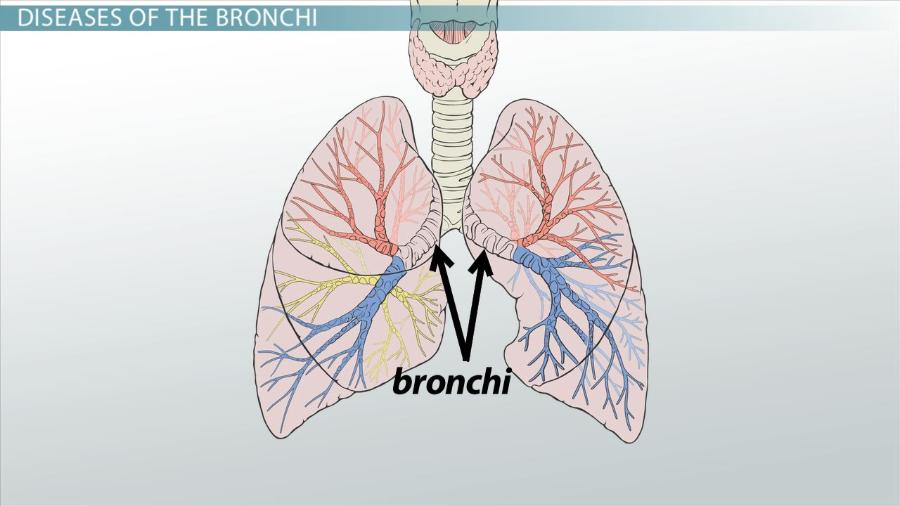
are the main passageway into the lungs
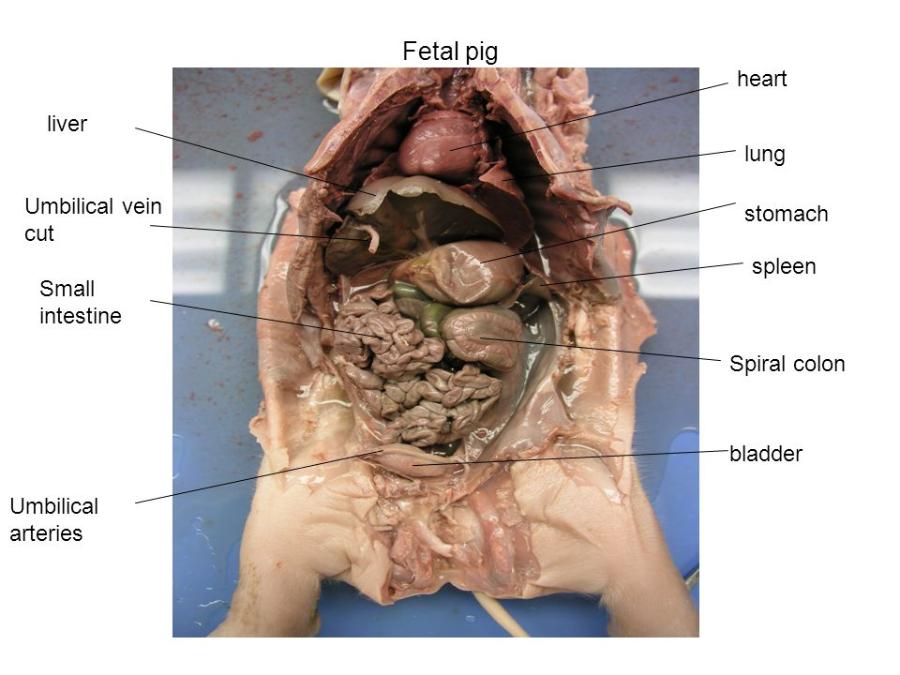
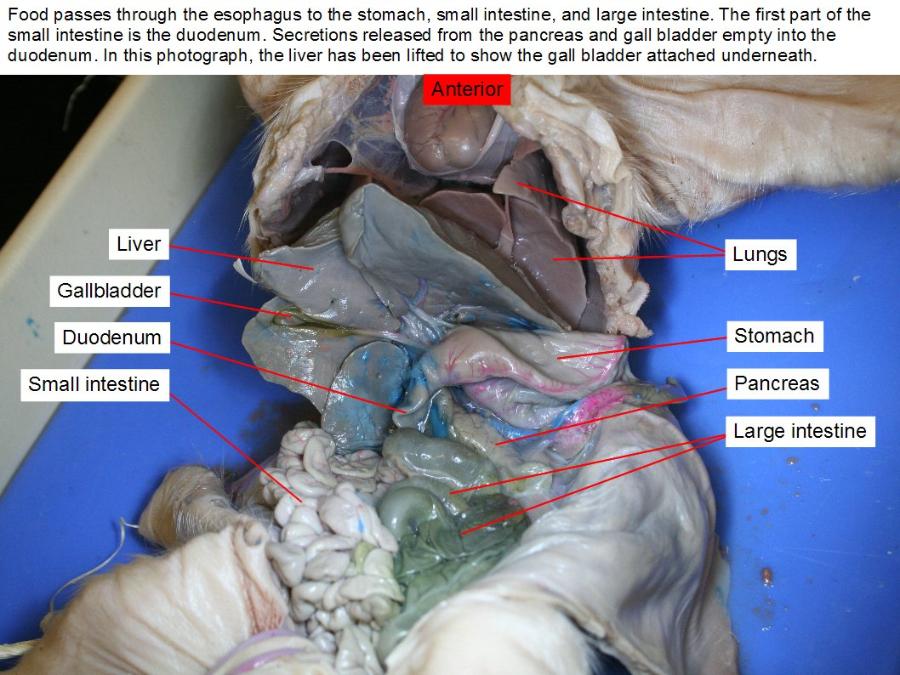
liver
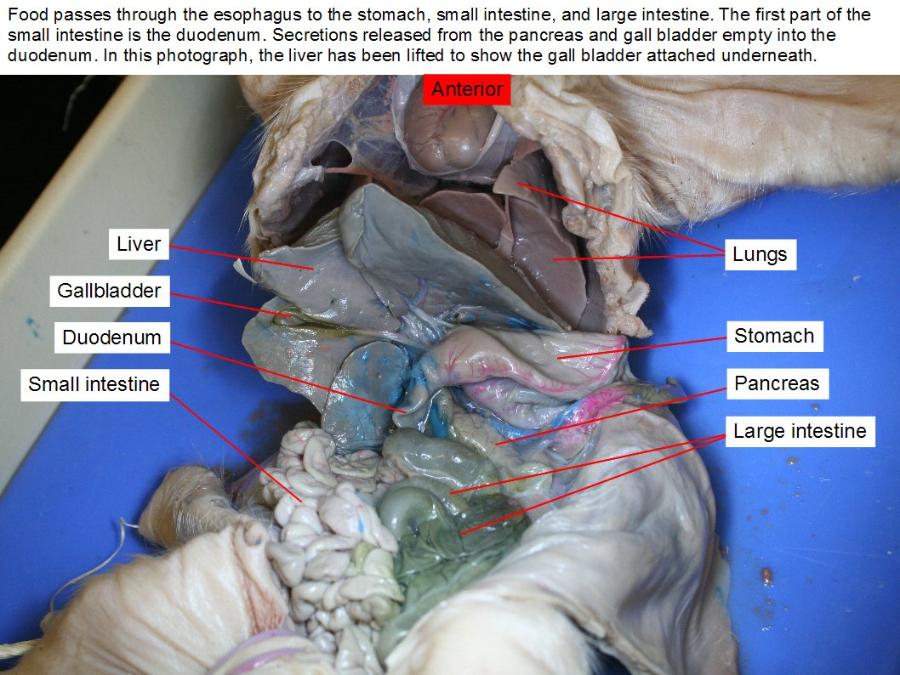
making proteins and blood clotting factors, manufacturing triglycerides and cholesterol, glycogen synthesis, and bile production.
spleen
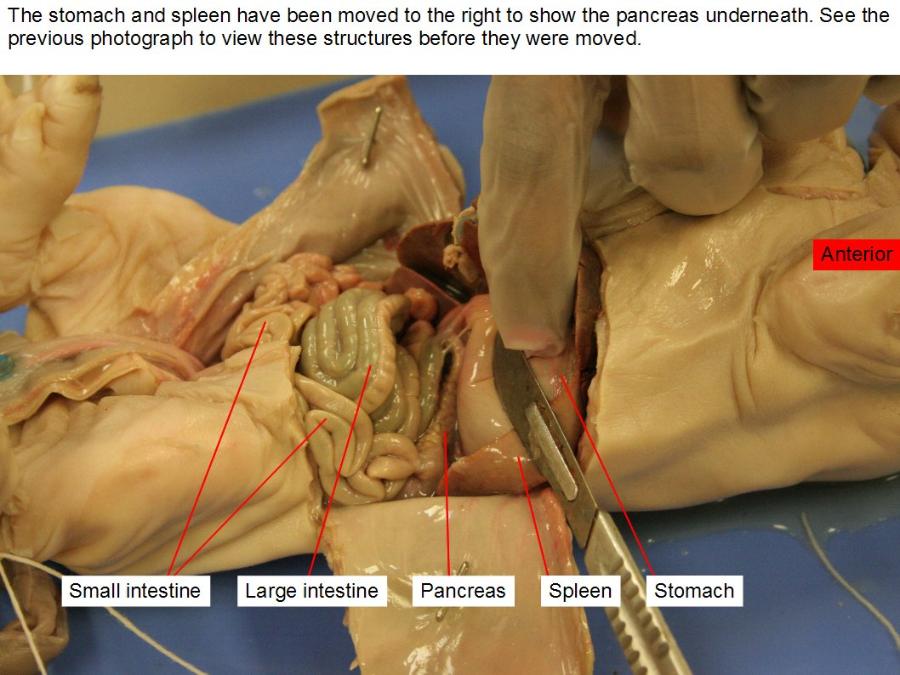
It acts as a filter for blood as part of the immune system.
duodenum

plays a vital role in the chemical digestion of chyme in preparation for absorption in the small intestine.
jejunum
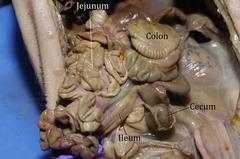
Most of the nutrients present in food are absorbed by the jejunum before being passed on to the ileum for further absorption.
ileum

is mainly to absorb whatever products of digestion were not absorbed by the jejunum.
pancreas

an exocrine function that helps in digestion and an endocrine function that regulates blood sugar.
gall bladder

is to store and concentrate bile, a yellow-brown digestive enzyme produced by the liver
common bile duct
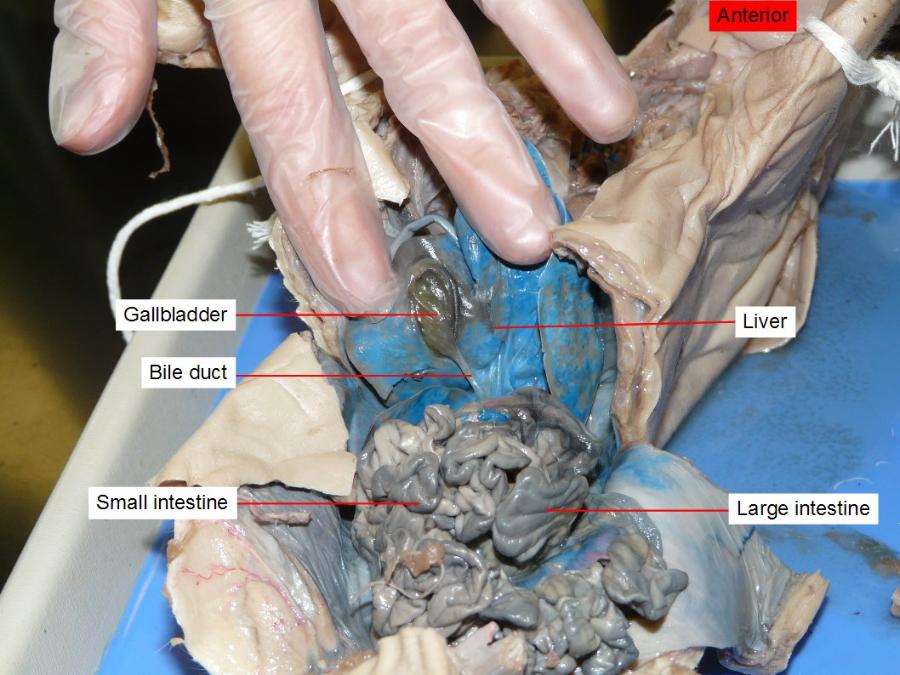
carry bile from thegallbladder and empty it into the upper part of the small intestine
cystic duct
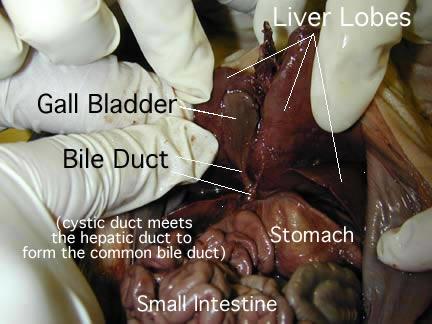
It then joins the common bile duct, which meets pancreatic duct before it empties into the duodenum
hepatic duct
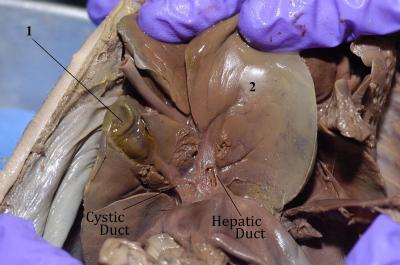
drains bile from the liver
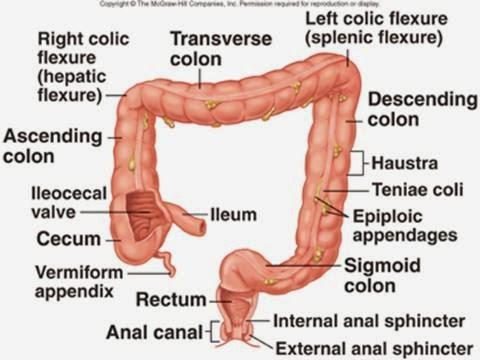
colon - all parts
reabsorb fluids and process waste products from the body and prepare for its elimination
caecum
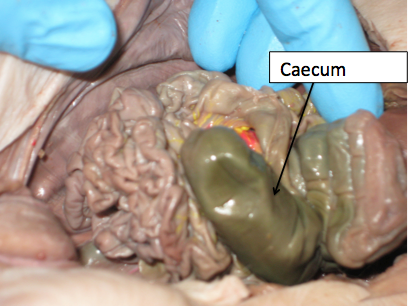
absorb fluids and salts that remain after completion of intestinal digestion
rectum
acts as a temporary storage site for feces
anus
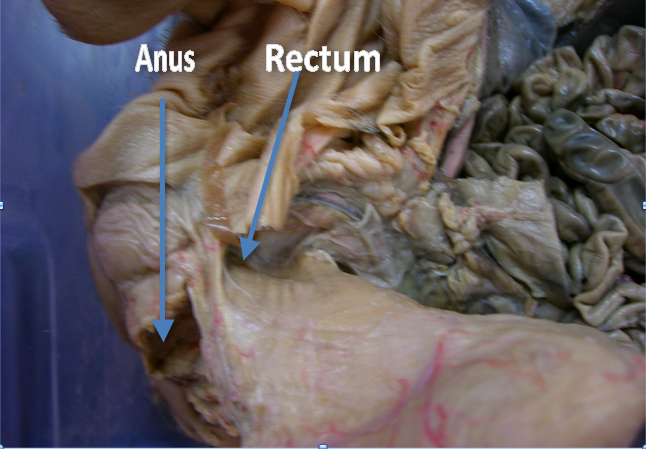
is the last part of the digestive tract. is specialized to detect rectal contents. It lets you know whether the contents are liquid, gas, or solid.
large intestine
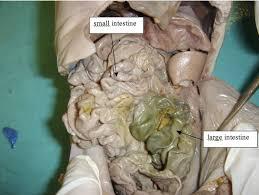
is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and transmit the useless waste material from the body
small intestine

where 90% of the digestion and absorption of food occurs, the other 10% taking place in the stomach and large intestine.
stomach - all parts

secretes acid and enzymes that digest food. Ridges of muscle tissue called rugae line thestomach. The stomach muscles contract periodically, churning food to enhance digestion. The pyloric sphincter is a muscular valve that opens to allow food to pass from the stomach to the small intestine
ileo- cecal valve
limit the reflux of colonic contents into the ileum
pancreatic duct
supply pancreatic juice provided from the exocrine pancreas which aids in digestion
pyloric sphincter
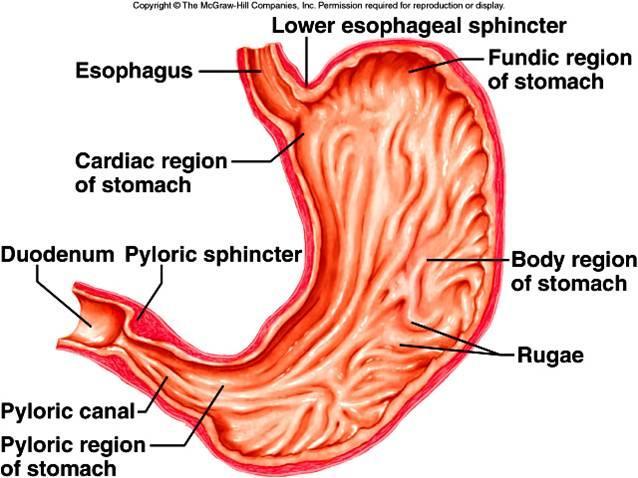
acts as a valve to controls the flow of partially digested food from the stomach to the small intestine
mesentery
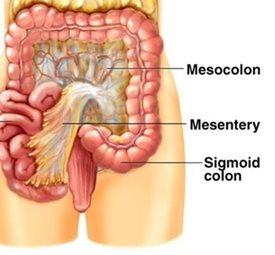
attaches your intestines to the wall of your abdomen and holds them in place
anterior (superior, cephalic) vena cava
s- brings deox blood from body to heart. veins from head feed into it... then will empty into right atrium of heart
posterior (inferior, caudial) vena cava
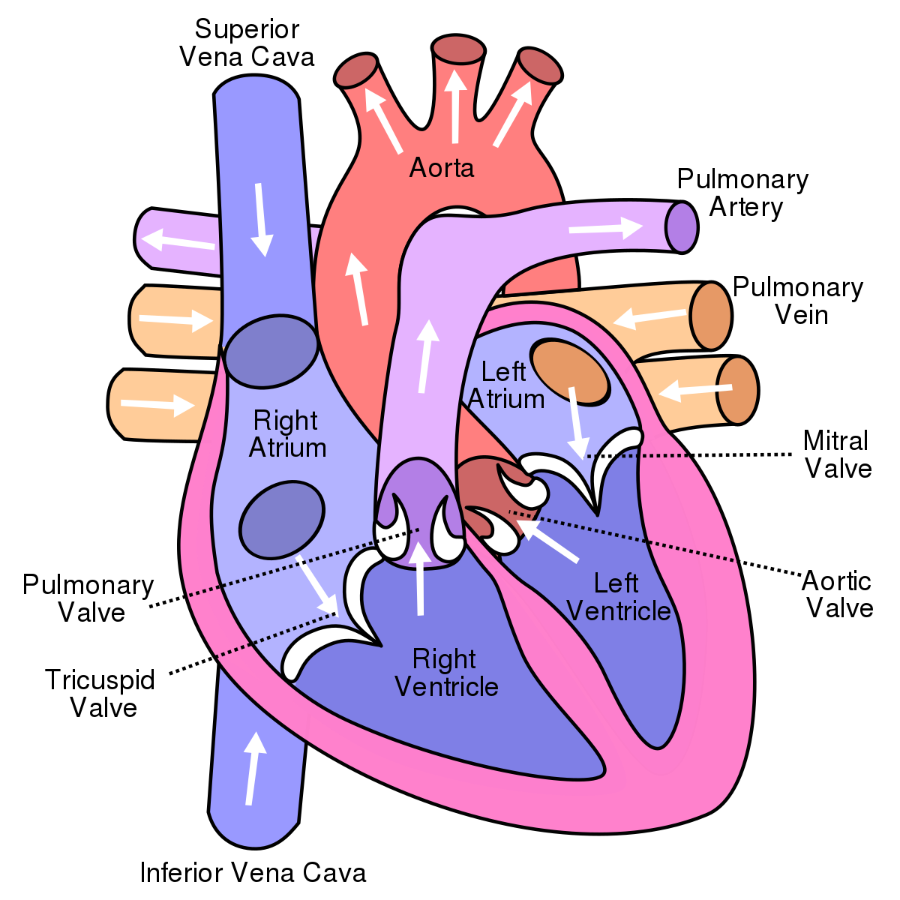
carries deox blood from lower body to heart
subclavian artery and vein
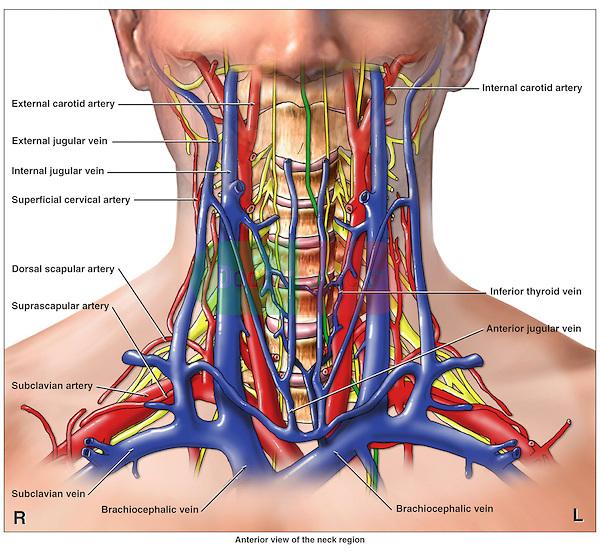
empty blood from the upper extremities and then carry it back to the heart
internal thoracic artery and vein
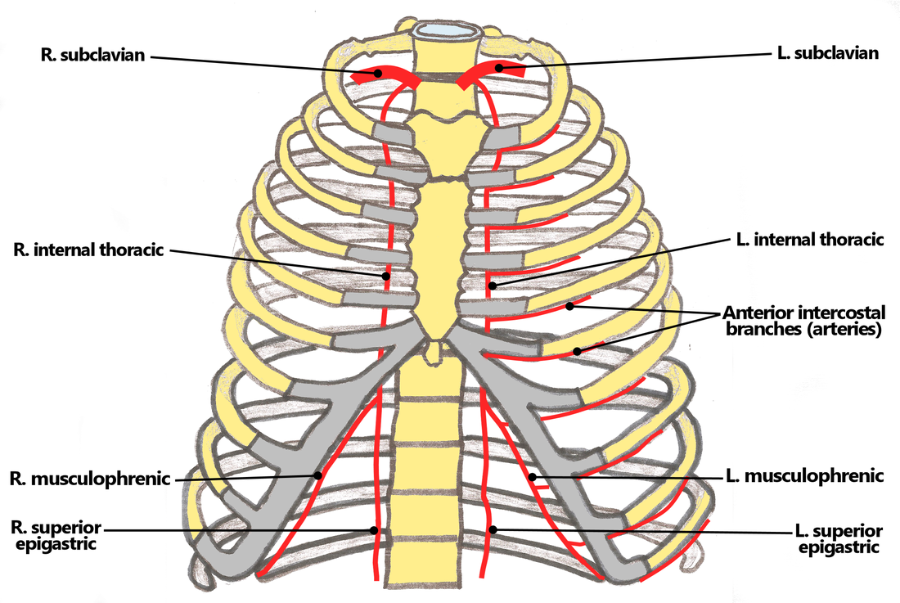
is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts
brachiocephalic artery
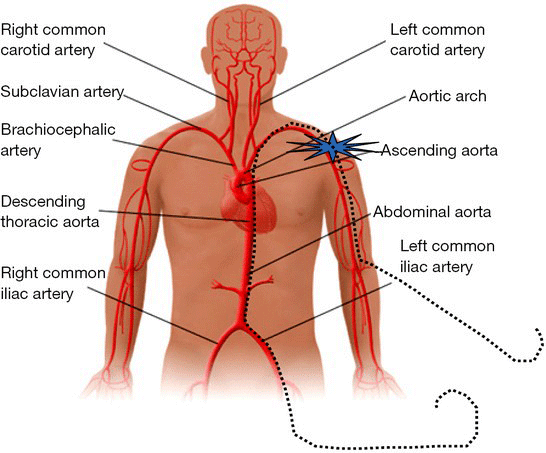
supplies oxygenated blood to the head, neck and arm regions of the body.
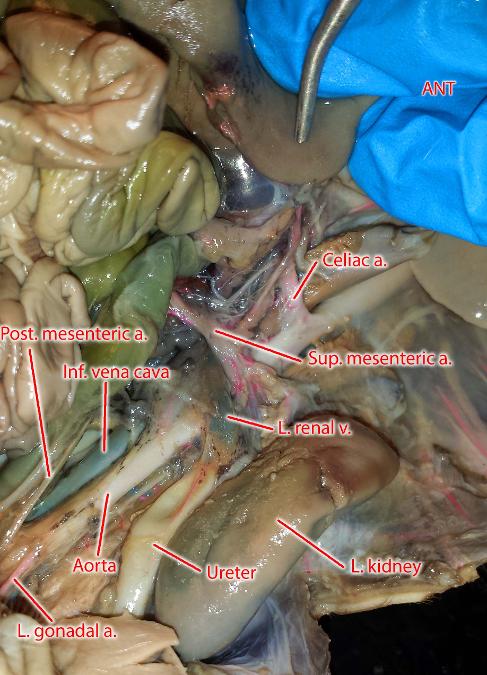
coeliac artery
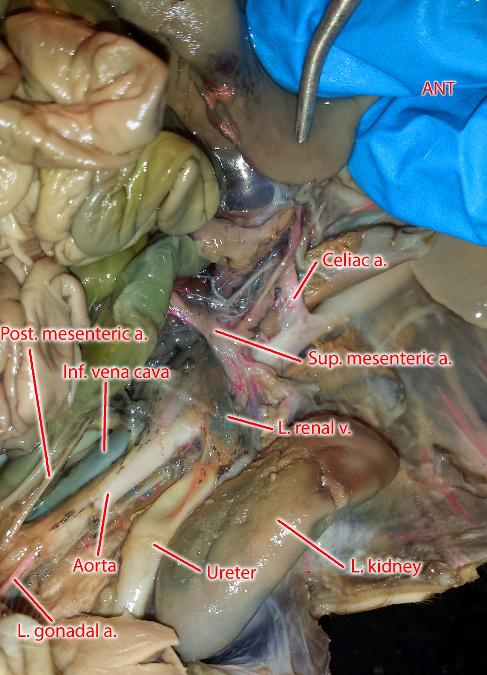
supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas.
mesenteric artery

major blood vessel in the digestive system
genital arteries
supplies ox blood to genitals/ bladder region
external iliac artery

provides the main blood supply to the legs
common iliac vein

They drain blood from the pelvis and lower limbs.
hepatic portal vein
is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver
ductus venosus
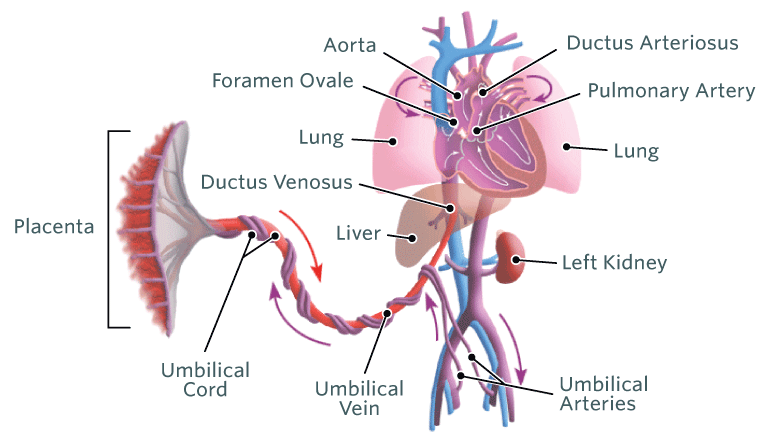
it allows oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the liver
ductus arteriosus
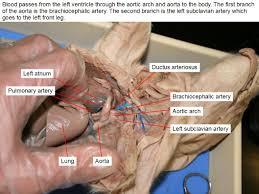
It allows most of the blood from the right ventricle to bypass the fetus's fluid-filled non-functioning lungs.
jugular (external and internal)
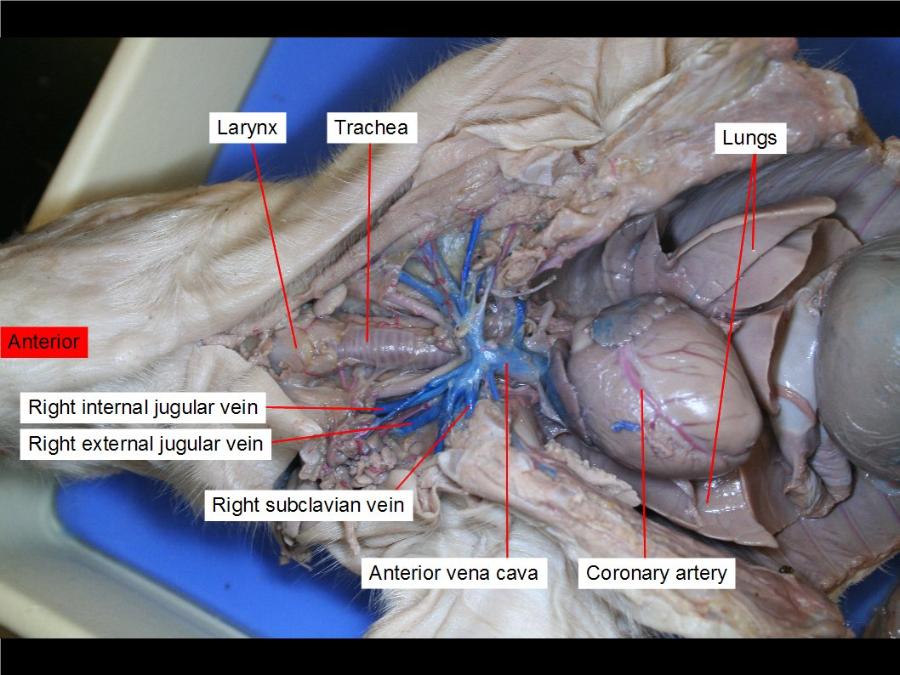
e-receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the craniumand the deep parts of the face
i-collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck
carotid (common, external, internal, and carotid body)

These arteries transfer blood to the structures inside and outside of the skull.
brachial vien
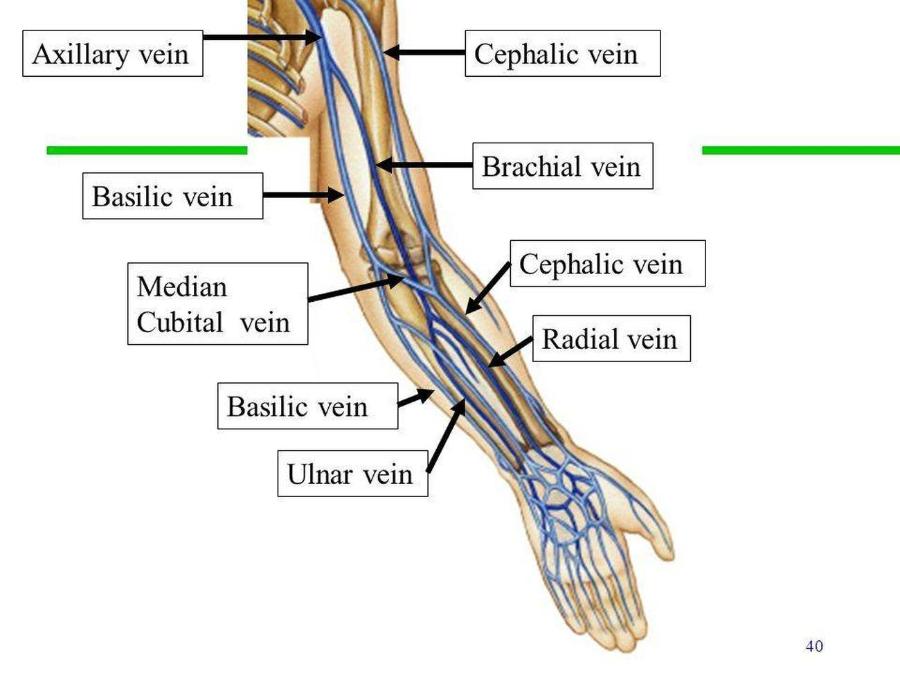
blood to bicep/tricep area
renal artery and vein
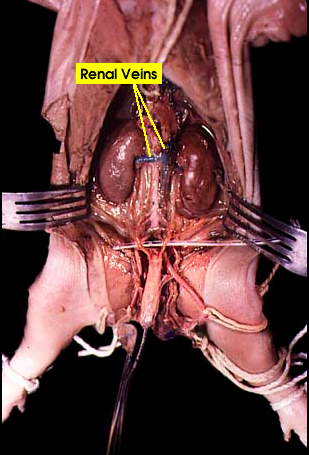
a-carries oxygenated blood to your kidneys.
v-drain oxygen-depleted blood from the kidneys
umbilical arteries and vein
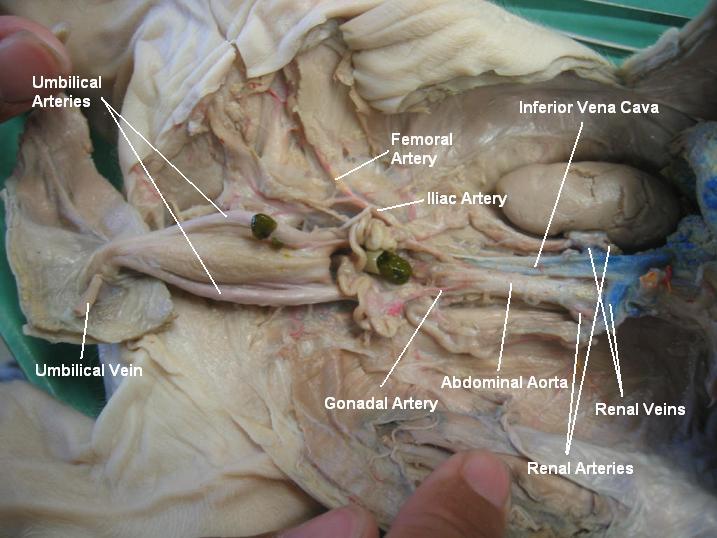
The umbilical vein carries oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta to the fetus, and the umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood from the fetus to the placenta
aorta (arch and dorsal)
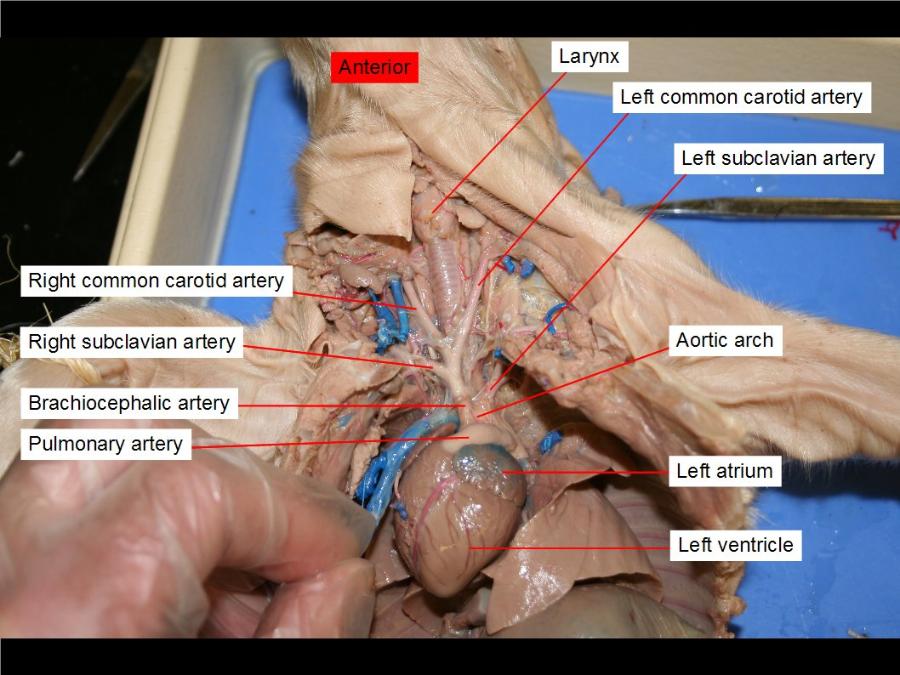
a-distributes blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the rest of the body
d-give branches to the yolk-sac, and are continued backward through the body-stalk as the umbilical arteries to the villi of the chorion
hemiazygos vein
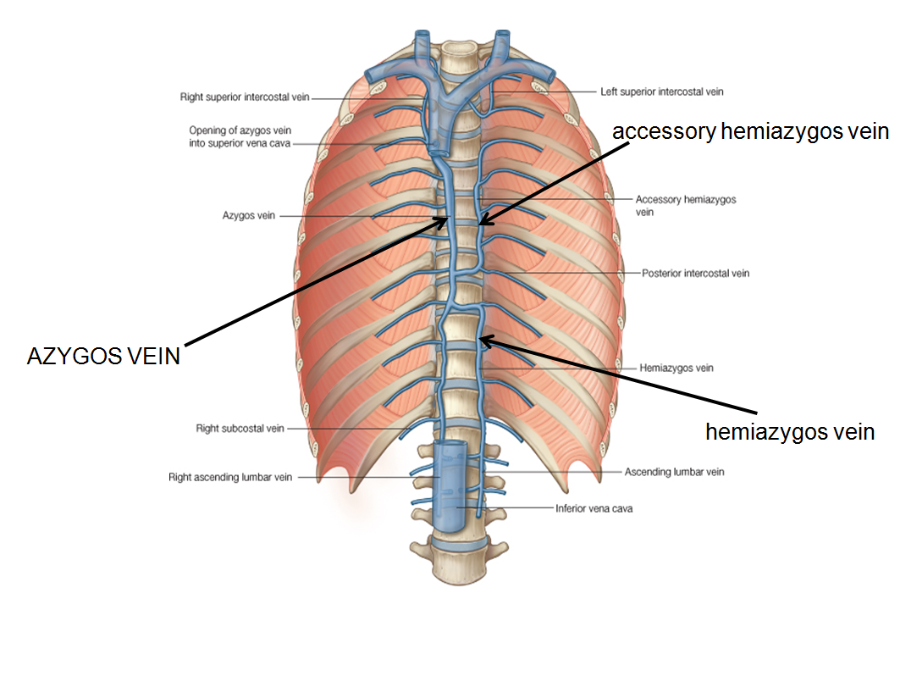
is a veinrunning superiorly in the lower thoracic region
scattered lymph nodes
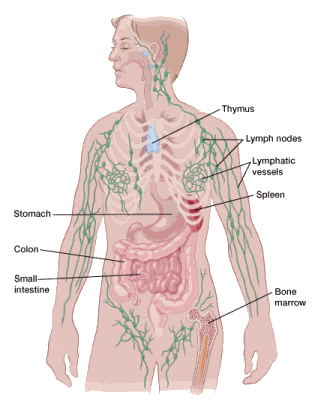
It is involved in protecting the body against infection, by delivering immune cells, known as lymphocytes
pulmonary arteries and veins

a- carries blood from right ventircle to lungs
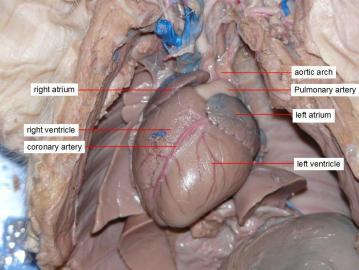
coronary arteries and veins
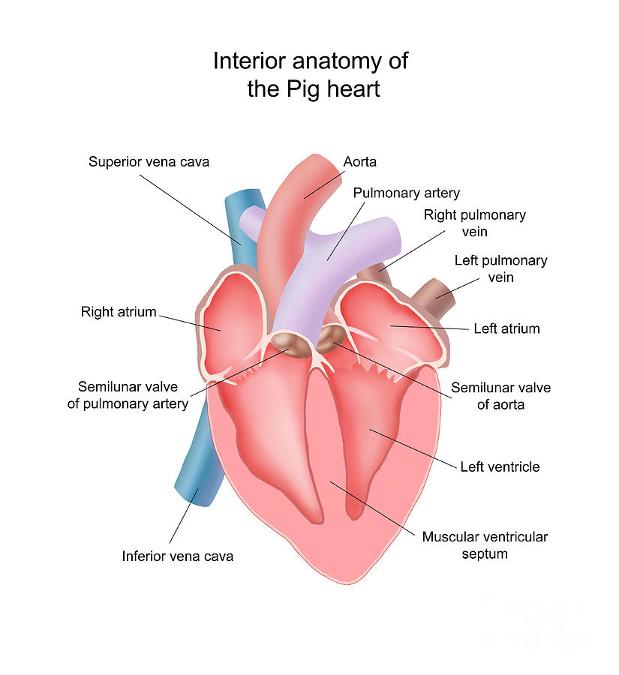
supply blood to/away the heart muscle
right and left auricles (atria)
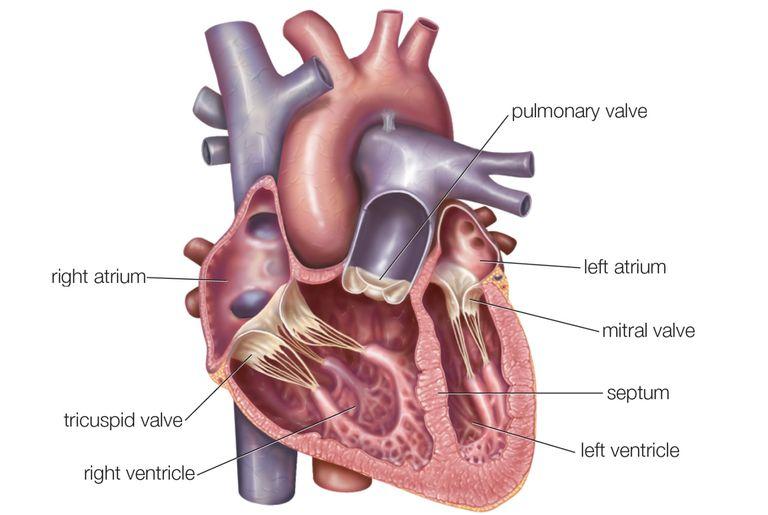
is the chamber where incoming blood from the major vein of the circulatory system (vena cava) brings deoxygenated blood into the heart. The right atrium (auricle) receives the blood and pushes it into the the right ventricle, which then transports the blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
l-collect this blood and pump it to the left ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to the body's tissues
right and left ventricles

r- responsible for pumping deox blood to lungs
l- recieves ox blood from left atrium
pericardium- parietal and visceral
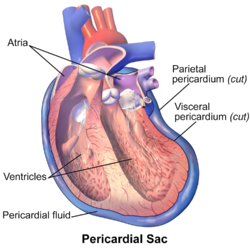
Both of these layers function in lubricating the heart to prevent friction during heart activity
ovaries
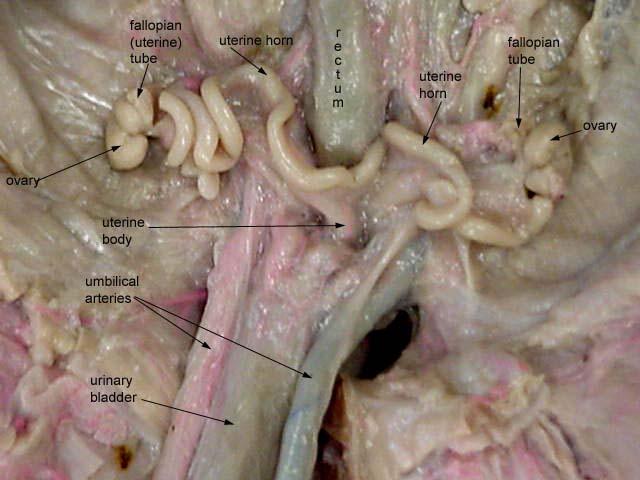
They produce oocytes (eggs) for fertilisation and they produce the reproductive hormones, oestrogen and progesterone.
uterine (fallopian tubes) aka oviducts

is the tube that links the ovary to the uterus and which the ovulated oocyte travels down to become fertilised by sperm present in the female tract
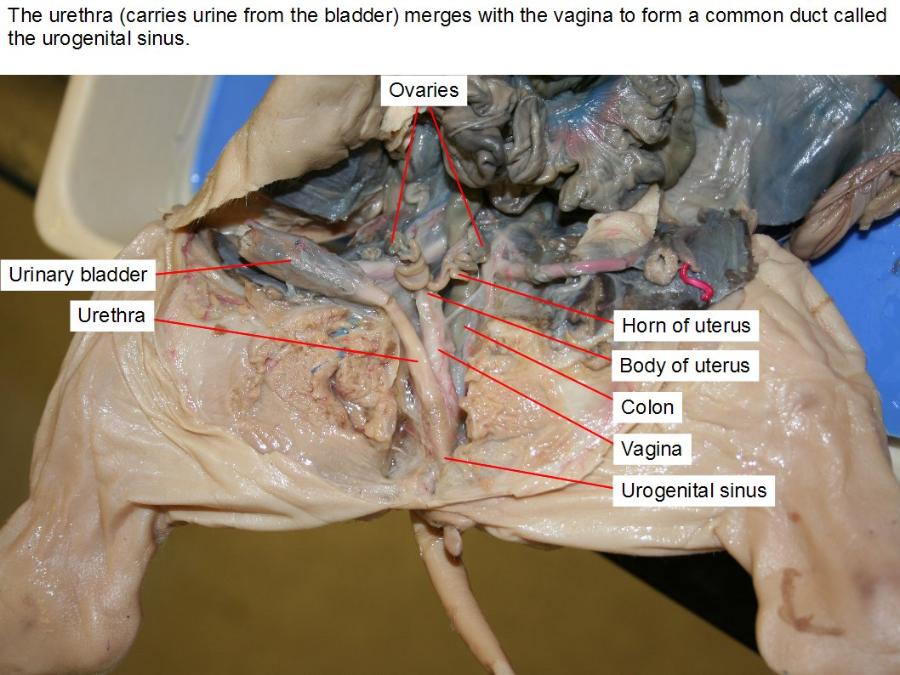
uterus (horns and body)

They are one of the points of attachment for the round ligament of uterus
cervix
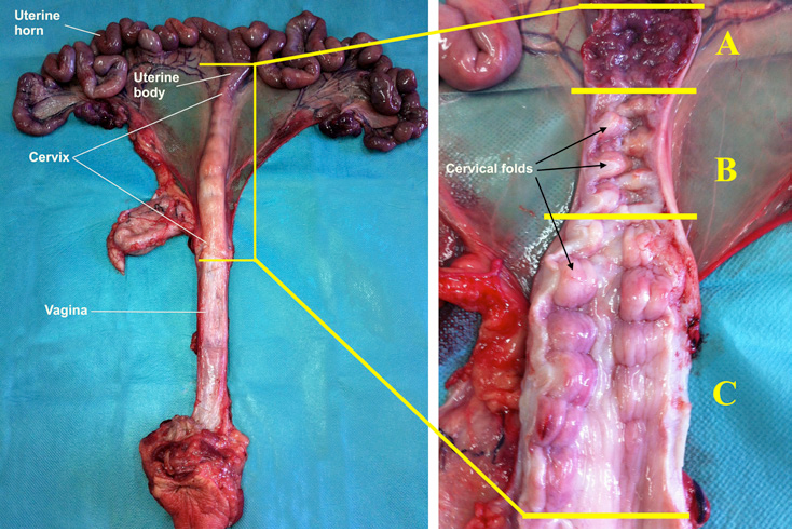
allow flow of menstrual blood from the uterus into the vagina, and direct the sperms into the uterus during intercourse
vagina
receives the penis during sexual intercourse and also serves as a conduit for menstrual flow from the uterus. During childbirth, the baby passes through the vagina
urogenital sinus

he ventral part of the cloaca after its separation from the rectum, giving rise to the lower part of the bladder in both sexes, to the prostatic portion of the male urethra, and to the urethra and vestibule in the female.
urogenital papilla
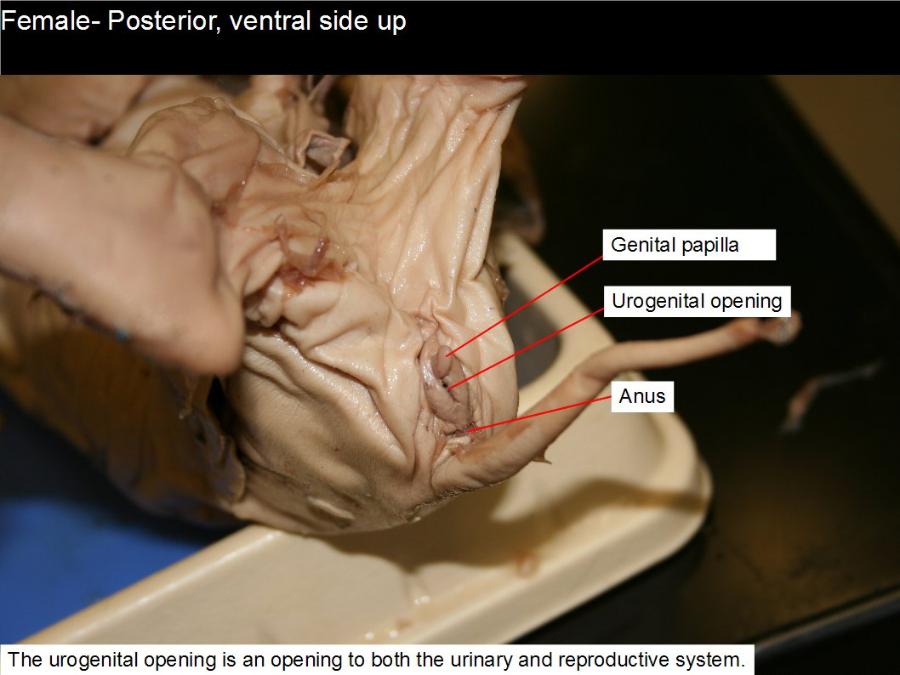
covers the opening of the vagina.
testes
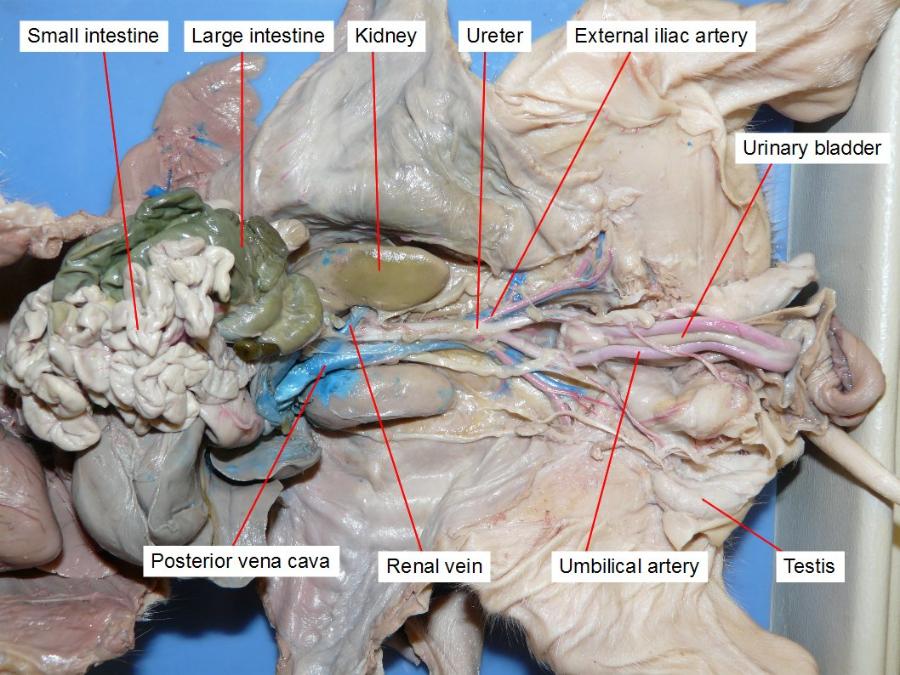
are the male gonads — the primary male reproductive organs.
scrotal sac
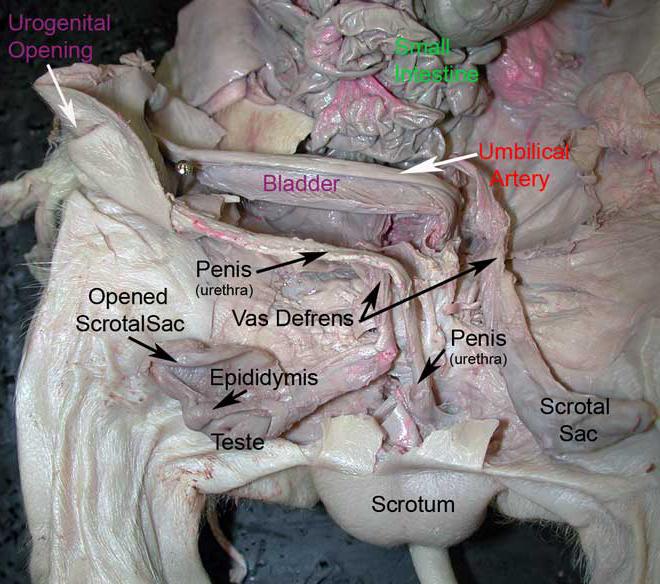
It contains the testicles (also called testes), as well as many nerves and blood vessels. The scrotum has a protective function and acts as a climate control system for the testes.
gubernaculum
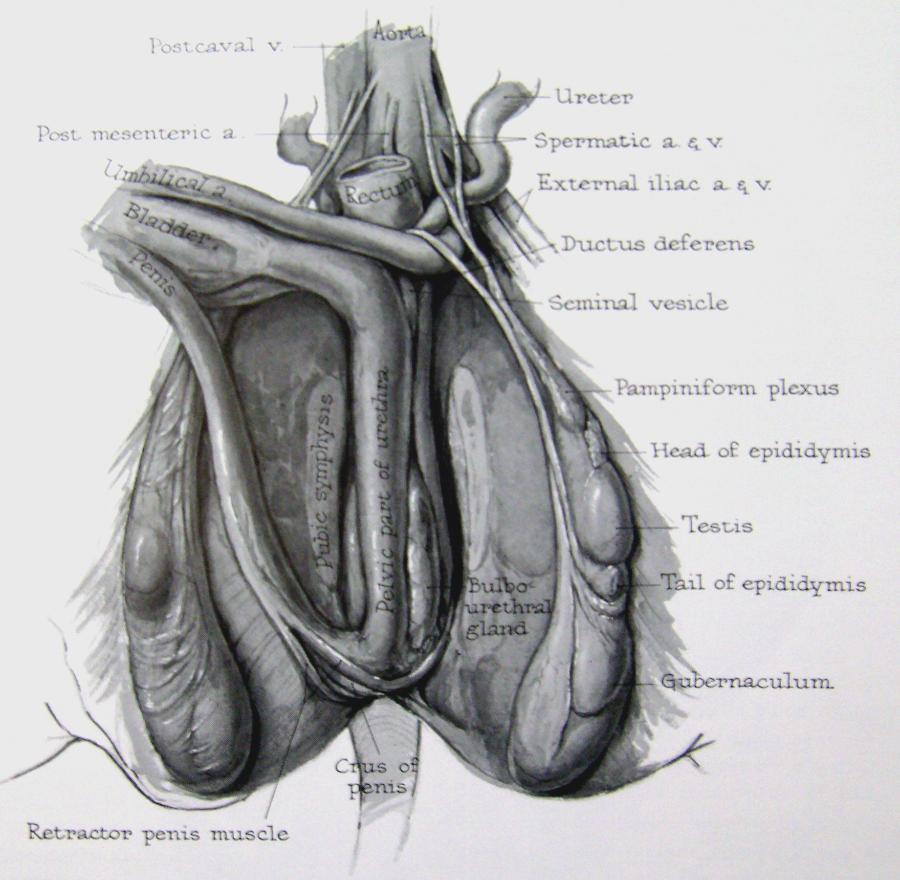
aids in the descent of the gonads (both testes and ovaries).
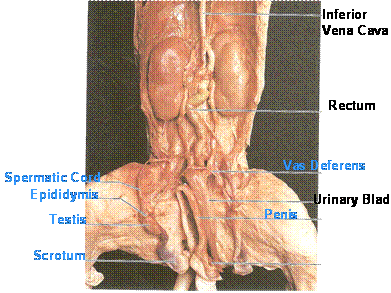
epididymis
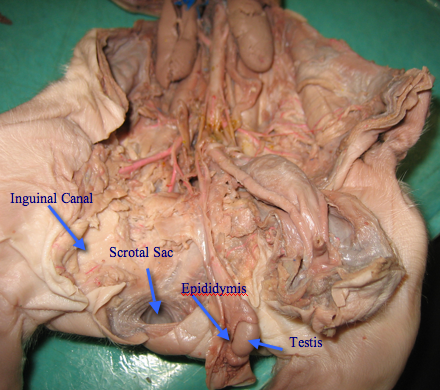
carries sperm from the testes to the ductus deferens in the male reproductive system
vas (ductus) deferens
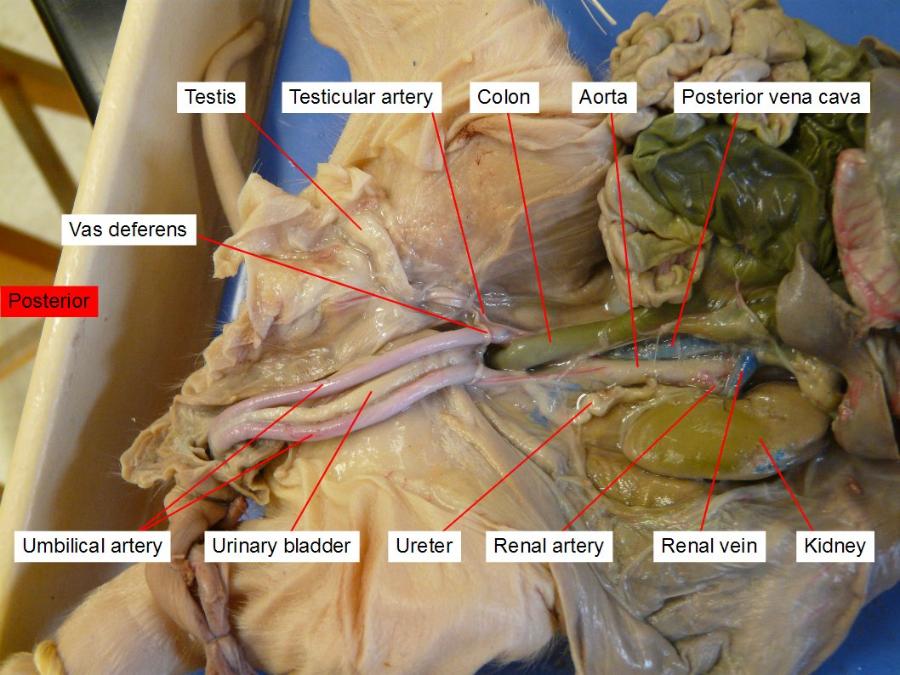
their purpose is to carry ejaculatory sperm out of the epididymis. To do this
inguinal canal

Function. The structures which pass through the canals differ between males and females: in males: the spermatic cord and its coverings + the ilioinguinal nerve. in females: the round ligament of the uterus + the ilioinguinal nerve.
prostate gland
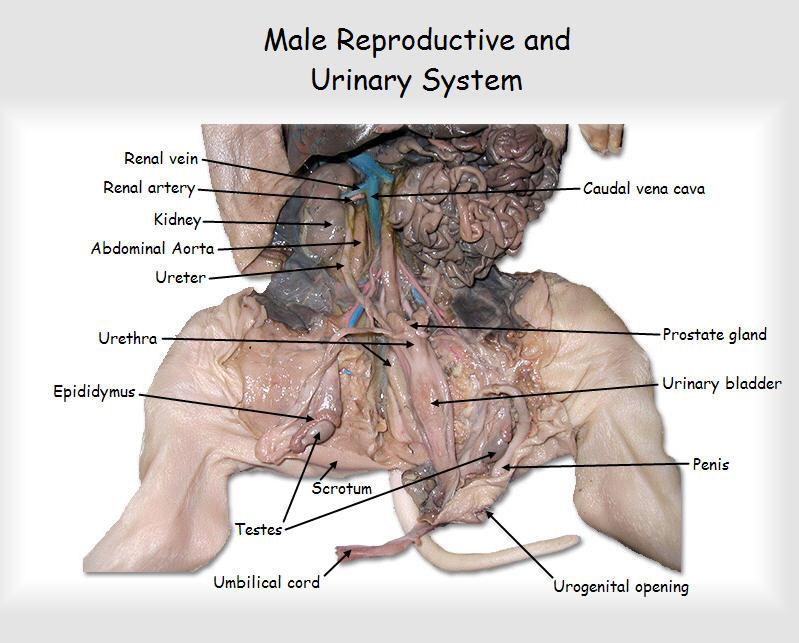
The prostate secretes fluid that nourishes and protects sperm
seminal vesicles
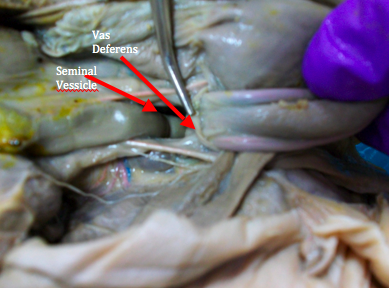
Semen combines fluid elements from the epididymis, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and vas deferens.
bulbo- urethral glands
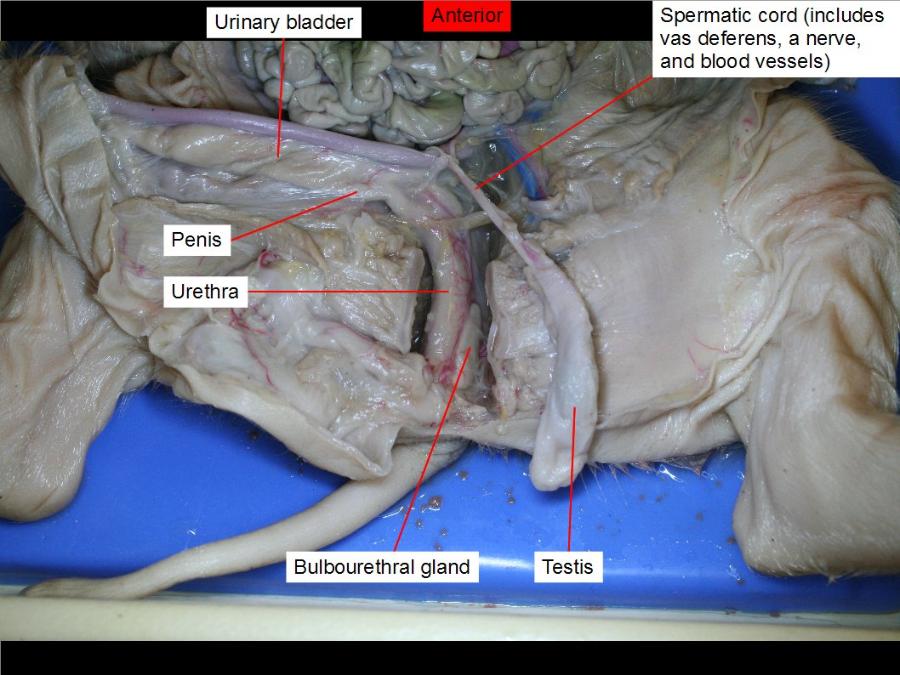
makes the precum
penis

fuckinggggg
urinary bladder

stores urine
kidneys

filtration
ureters

is a tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
urethra

The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body
adrenal gland
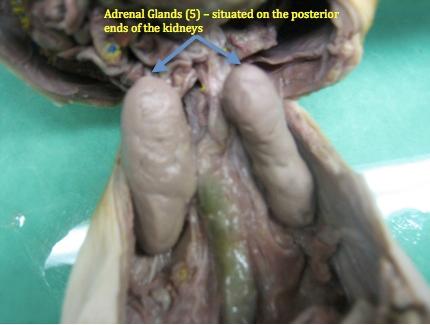
Located at the top of each kidney, the adrenal glands produce hormones that help the body control blood sugar, burn protein and fat, react to stressors like a major illness or injury, and regulate blood pressure.
head
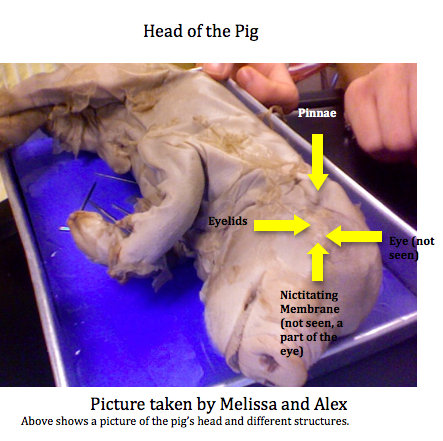
nose

tongue
external ear

eye with lids

vestigal nictitating membrane

that protects and moisten the eye without losing visibility.
cervical region
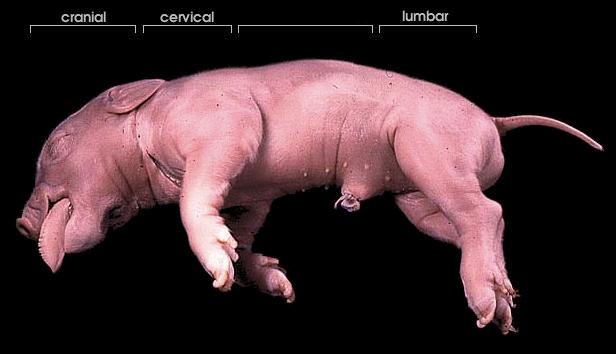
thoracic region
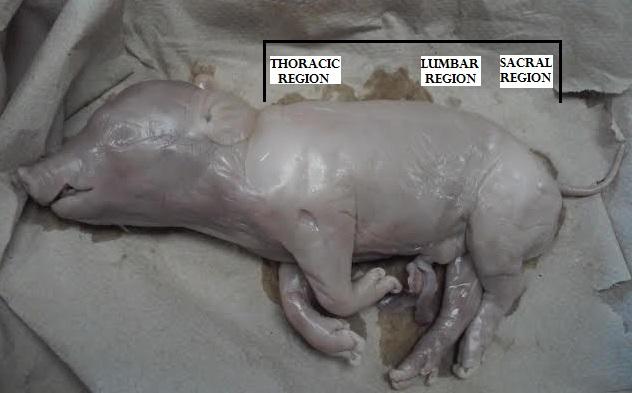
lumbar region

sacral region

caudal region
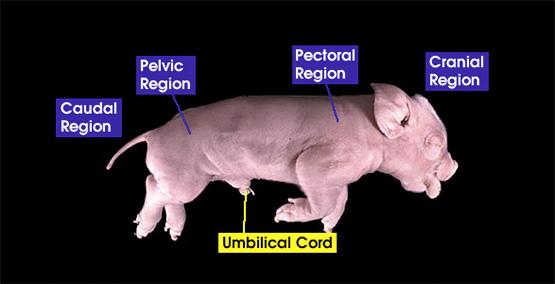
umbilical cord region
