What are developmental genes ?
- Genes that program development control the rate, timing, and spatial pattern of changes in an organism’s form as it develops to adulthood
What is heterochrony?
- is an evolutionary change in the rate or timing of developmental events
What is this an example of ?
the contrasting shapes of human and chimpanzee skulls are the result of small changes in relative growth rates of different body parts
Heterochrony
What does heterochrony correspond to ?
various factors , regulated by gene expression
What is paedomorphosis?
- The sexually mature species may retain body features that were juvenile structures in an ancestral species
What are Homeotic genes?
- determine such basic features as where wings and legs will develop on a bird or how a flower’s parts are arranged
what do Hox genes control?
are a class of homeotic genes that provide positional information during animal embryonic development
What is this an example of ....
- in crustaceans, a swimming appendage can be produced instead of a feeding appendage
Hox genes being expressed in the wrong location
How do homeotic genes relate to Cambrian Explosion
- Evidence suggests duplication of many of these homeotic genes occurred during the time of the Cambrian explosion, and may be responsible for the incredible morphological diversity observed
What is one common way regulation of developmental genes is achieved
2 other ways this occurs....
- transcription factors
Histone modification, DNA methylation,
- Most novel biological structures evolve in many stages from previously existing structures .... what is an example of this ..
- Complex eyes have evolved from simple photosensitive cells independently many times
What are Exaptations...
are structures that evolve in one context but become co-opted for a different function
Ex ear bones orginally evolved for jaw hinge
Is evolution goal oriented
no
Why do some scientists believe that RNA, rather than DNA, was the first genetic material?
a)RNA has both information storage and catalytic properties.
b)RNA contains uracil in place of thymine.
c)RNA could have evolved into DNA.
d)RNA can replicate more accurately than DNA.
e)All the proto-cells on early Earth contained RNA.
A
Which of the following statements concerning the evolutionary origin of mammals is most likely true?
a)Radiometric dating using carbon-14 shows that synapsids existed 300 million years ago.
b)The origin of mammals cannot be known because the fossil record is incomplete.
c)Mammalian lower jaw bones and teeth changed gradually over time.
d)Modern mammals and reptiles are descendants of synapsids.
c
What features might we expect the mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells to contain if these organelles were the result of endosymbiosis of bacterial cells?
a)plasma membrane, DNA, and ribosomes
b)plasma membrane, nucleus, and ribosomes
c)nucleus, DNA, and ribosomes
d)plasma membrane, nucleus, and cilia
e)nucleus, ribosomes, and cilia
A
Photosynthetic eukaryotes contain both mitochondria and chloroplasts. Which sequence of events most likely describes the evolution of this group?
a)Ancestral anaerobic prokaryote engulfs an aerobic heterotrophic prokaryote and then engulfs a photosynthetic prokaryote.
b)Ancestral anaerobic prokaryote engulfs a photosynthetic prokaryote and then engulfs an aerobic heterotrophic prokaryote.
c)Ancestral anaerobic prokaryote engulfs an anaerobic heterotrophic prokaryote and then engulfs a photosynthetic prokaryote.
d)Ancestral anaerobic prokaryote engulfs a photosynthetic prokaryote and then engulfs an anaerobic heterotrophic prokaryote.
A
Which of the following organelles likely originated from endosymbiosis?
a)nuclear membrane and Golgi apparatus
b)ER and chloroplasts
c)chloroplasts and mitochondria
d)mitochondria and Golgi apparatus
c
How many mass extinction events have been documented in the fossil record over the past 500 million years?
a)two
b)three
c)four
d)five
d
According to geological evidence, which event may have triggered the Permian mass extinction?
a)an asteroid or comet impact off the coast of Yucatan, Mexico
b)global cooling caused by a series of ice ages
c)global cooling caused by volcanic eruptions
d)global warming caused by volcanic eruptions
d
A species of bird finds its way to the Galápagos Islands, where there are several ecological niches. This species evolves into many new species to fill all the unfilled niches. This is an example of
a)resource partitioning.
b)adaptive radiation.
c)endosymbiosis.
d)gradualism.
b
Which of the following best explains the loss of ventral spines in threespine stickleback fish?
a)paedomorphosis
b)duplication of the Pitx1 gene
c)changes in the Pitx1 gene sequence
d)changes in the regulatory sequences of the Pitx1 gene
d
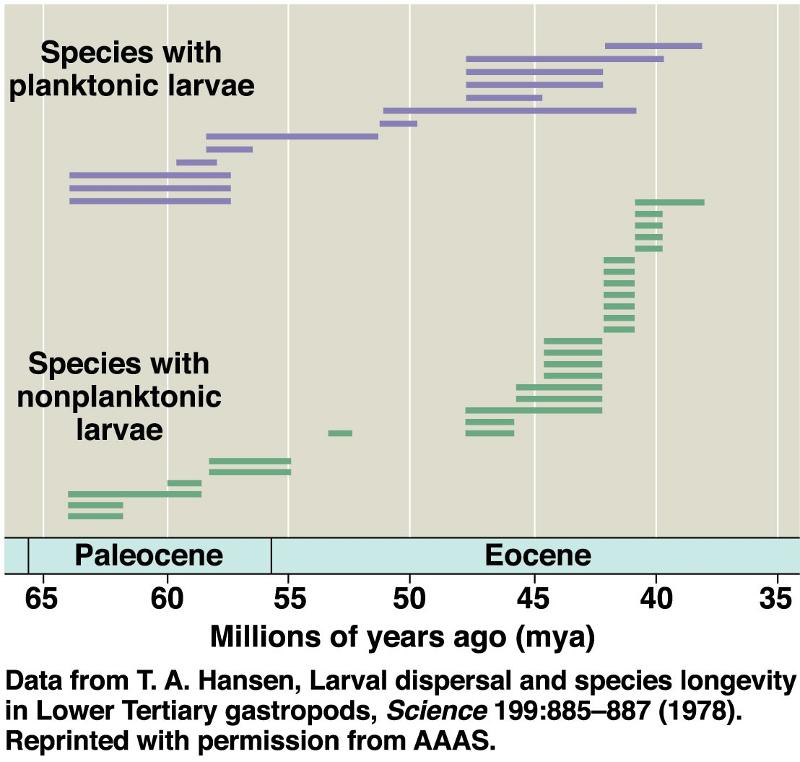
Researchers investigated whether differing modes of dispersal could explain differences in the longevity of fossil species in one taxon of marine snails, the family Volutidae. Some volute snails had planktonic larvae that could disperse over great distances on ocean currents. Other volute snails had nonplanktonic larvae, which developed directly into adults without a swimming stage. The dispersal of snails with nonplanktonic larvae was limited by the distance they can crawl as adults.
The researchers studied the distribution of volute snail fossils in outcrops of sedimentary rocks along North America’s Gulf coast. The rocks formed during the early Paleogene period, between 65 and 37 million years ago, and contain many well-preserved snail fossils. Based on features of the snail’s shell, the researchers classified each fossil species as having planktonic or nonplanktonic larvae. Each bar in the figure on the next slide shows how long a snail species persisted in the fossil record.
How many new species of snails with nonplanktonic larvae arose between 50 and 35 million years ago?
a)5 species
b)8 species
c)21 species
d)26 species
c
How many new species of snails with planktonic larvae arose between 50 and 35 million years ago?
a)5 species
b)7 species
c)8 species
d)13 species
A
Select a plausible hypothesis to explain the difference in mean longevity of snail species with planktonic and nonplanktonic larvae.
a)Snails with nonplanktonic larvae produce fewer offspring than snails with planktonic larvae.
b)Snails with nonplanktonic larvae have more limited distributions than snails with planktonic larvae.
c) Snails with nonplanktonic larvae have higher survival rates of larvae and young adults than snails with planktonic larvae
b
Carbon-14 is a commonly used isotope for radiometric dating. It
decays to nitrogen-14 with a half-life of 5,700 years. A biological
sample is found to have 1/16 as much
C-14 as there is in the
atmosphere. How old is the sample?
a)356 years
b)5,700 years
c)22,800 years
d)91,200 years
c
The Cambrian explosion marks the relatively “sudden” appearance of many animal phyla approximately 542 million years ago. Approximately what percentage of Earth’s history has occurred before the appearance of animals?
a)1%
b)13%
c)50%
d)87%
d
The following are four hypothesized stages of the origin of life.
Place them in the correct order.
1. Origin of self-replicating
molecules
2. Joining of organic monomers into polymers
3.
Abiotic synthesis of small organic monomers
4. Packaging of
molecules into membranous proto-cells
a)1, 2, 3, 4
b)3, 2, 4, 1
c)4, 2, 3, 1
d)3, 1, 2, 4
e)2, 1, 4, 3
b
Place the following geologic periods in their correct order from oldest to youngest.
a)Devonian, Jurassic, Permian, Ordovician
b)Jurassic, Devonian, Ordovician, Permian
c)Ordovician, Devonian, Permian, Jurassic
d)Permian, Ordovician, Devonian, Jurassic
e)Devonian, Permian, Jurassic, Ordovician
c
Which of the following pieces of evidence is not considered to be supportive of the endosymbiont theory?
a)Chloroplasts and mitochondria are roughly the same size as bacteria.
b)Chloroplasts and mitochondria have small, circular genomes.
c)Chloroplasts and mitochondria have double membranes.
d)Chloroplasts and mitochondria have organic molecules.
e)Chloroplasts and mitochondria have ribosomes.
d
When did the mass extinction that eliminated most dinosaurs occur?
a)542 million years ago
b)251 million years ago
c)66 million years ago
d)10 million years ago
c
The many finch species on the Galápagos Islands arose through adaptive radiation. Which piece of evidence would best support this claim?
a)The Galápagos finch species all physically resemble one another more than they do non-Galápagos finches.
b)The Galápagos finch species are more closely related to each other genetically than they are to non-Galápagos finches.
c)The Galápagos finch species all occupy similar ecological niches.
d)The Galápagos finch species are more radioactive than non-Galápagos finch species.
b
Which of the following statements helps explain the origin of new structures like eyes or wings?
a)New evolutionary structures require new genes.
b)New evolutionary structures can arise from changes in the expression of existing genes.
c)New structures can evolve in stepwise fashion.
d)Structures evolved in one context can be co-opted for another function.
e)all of the above
e
Which of the following evolutionary novelties is most consistent with being facilitated by a Hox gene?
a)honeybee social behavior
b)antibiotic resistance in bacteria
c)flowers on plants
d)wing number in insects
d