1) You swing a bat and hit a heavy box with a force of 1500 N. The
force the box exerts on the bat
is
A) exactly 1500 N only if
the box does not move.
B) exactly 1500 N whether or not the box
moves.
C) greater than 1500 N if the box moves.
D) less than
1500 N if the box moves.
E) greater than 1500 N if the bat
bounces back.
B
2) In order to get an object moving, you must push harder on it than
it pushes back on you.
A) True
B) False
B
3) In order to lift a bucket of concrete, you must pull up harder on
the bucket than it pulls down
on you.
A) True
B) False
B
4) Consider what happens when you jump up in the air. Which of the
following is the most
accurate statement?
A) It is the
upward force exerted by the ground that pushes you up, but this force
cannot
exceed your weight.
B) You are able to spring up
because the earth exerts a force upward on you that is
greater
than the downward force you exert on the earth.
C)
Since the ground is stationary, it cannot exert the upward force
necessary to propel you
into the air. Instead, it is the internal
forces of your muscles acting on your body itself
that propels
your body into the air.
D) When you push down on the earth with a
force greater than your weight, the earth will
push back with the
same magnitude force and thus propel you into the air.
E) When
you jump up the earth exerts a force F1 on you and you exert a force
F2 on the
earth. You go up because F1 > F2.
D
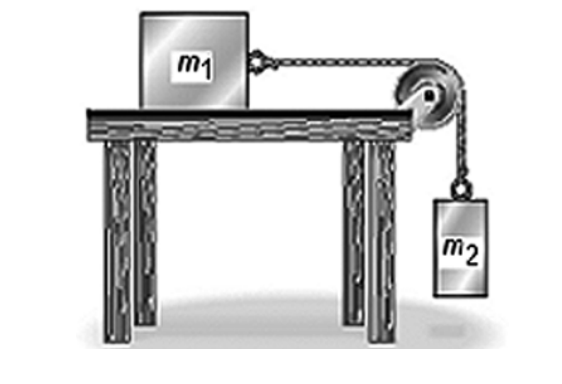
7) Two objects having masses m1 and m2 are connected to each other as
shown in the figure and
are released from rest. There is no
friction on the table surface or in the pulley. The masses of
the
pulley and the string connecting the objects are completely
negligible. What must be true
about the tension T in the string
just after the objects are released?
A) T = m2g
B) T > m2g
C) T < m2g
D) T =
m1g
E) T > m1g
C
5) A 20‐ton truck collides with a 1500‐lb car and causes a lot of
damage to the car. During the
collision
A) the force on the
truck due to the collision is slightly greater than the force on the
car.
B) the force of on the truck due to the collision is exactly
equal to the force on the car.
C) the force on the car due to the
collision is much greater than the force on the truck.
D) the car
and the truck have the same magnitude acceleration.
B
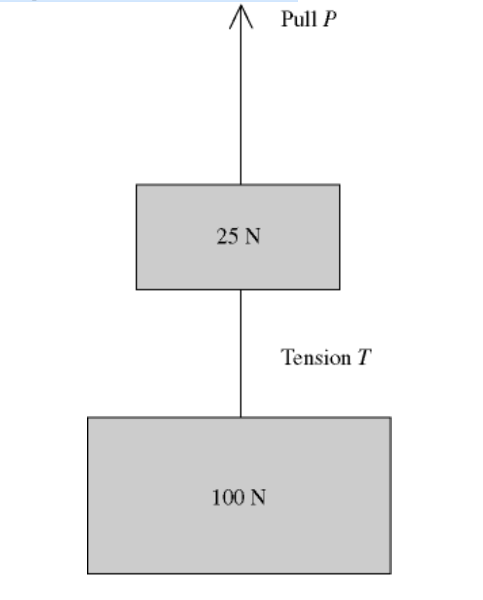
6) Two weights are connected by a massless wire and pulled upward
with a constant speed of
1.50 m/s by a vertical pull P. The
tension in the wire is T (see figure). Which one of the
following
relationships between T and P must be true?
A) T > P
B) T = P
C) P + T = 125 N
D) P = T + 25
N
E) P = T + 100 N
D
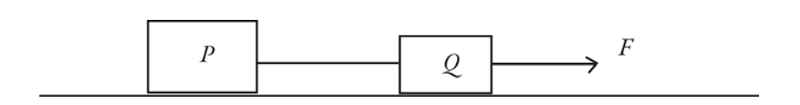
Two bodies P and Q on a smooth horizontal surface are connected by a
light cord. The mass of
P is greater than that of Q. A horizontal
force F (of magnitude F) is applied to Q as shown in
the figure,
accelerating the bodies to the right. The magnitude of the force
exerted by the
connecting cord on body P will be
A) zero.
B) less than F but not zero.
C) equal to
F.
D) greater than F.
B
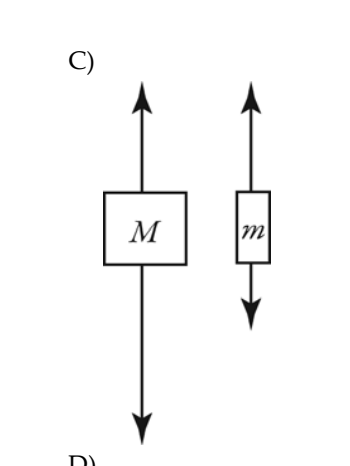
9) Two unequal masses M and m (M > m) are connected by a light
cord passing over a pulley of
negligible mass, as shown in the
figure. When released, the system accelerates. Friction
is
negligible. Which figure below gives the correct free‐body
force diagrams for the two masses
in the moving system?
C
1) The International Space Station has a mass of 1.8 × 105 kg. A
70.0-kg astronaut inside the
station pushes off one wall of the
station so she accelerates at 1.50 m/s2. What is the
magnitude of
the acceleration of the space station as the astronaut is pushing off
the wall?
Give your answer relative to an observer who is space
walking and therefore does not
accelerate with the space station
due to the push.
A) 5.8 × 10-4 m/s2
B) 1.50 m/s2
C) 4.7
× 10-4 m/s2
D) zero
E) 3.9 × 10-3 m/s2
A
On a horizontal frictionless floor, a worker of weight 0.900 kN
pushes horizontally with a force
of 0.200 kN on a box weighing
1.80 kN. As a result of this push, which statement could
be
true?
A) The box will not move because the push is less
than its weight.
B) The worker and box will both have an
acceleration of 1.08 m/s2, but in opposite
directions.
C)
The worker and box will both have an acceleration of 2.17 m/s2, but in
opposite
directions.
D) The worker will accelerate at 1.08
m/s2 and the box will accelerate at 2.17 m/s2, but in
opposite
directions.
E) The worker will accelerate at 2.17 m/s2 and the
box will accelerate at 1.08 m/s2, but in
opposite directions.
E
3) In a ballistics test, a 1.50-g bullet is fired through a 28.0-kg
block traveling horizontally
toward the bullet. In this test, the
bullet takes 11.4 ms to pass through the block as it reverses
the
blockʹs velocity from 1.75 m/s to the right to 1.20 m/s to the left
with constant acceleration.
Find the magnitude of the force that
the bullet exerts on the block during this ballistics test.
Answer: 7.25 × 103 N
4) A locomotive is pulling 19 freight cars, each of which is loaded
with the same amount of
weight. The mass of each freight car
(with its load) is 37,000 kg. If the train is accelerating
at
0.22 m/s2 on a level track, what is the tension in the
coupling between the second and third
cars? (The car nearest the
locomotive is counted as the first car, and friction is negligible.)
Answer: 140,000 N
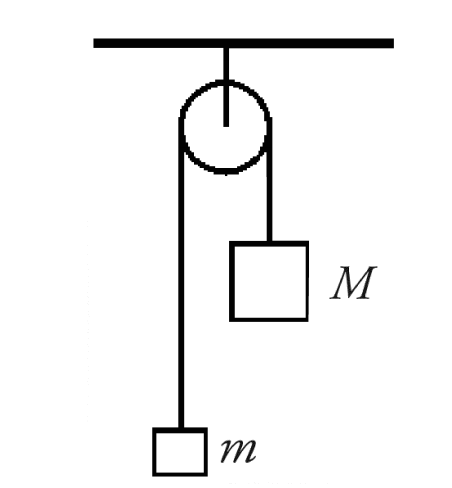
5) Two objects are connected by a very light flexible string as shown
in the figure, where M = 0.60
kg and m = 0.40 kg. You can ignore
friction and the mass of the pulley.
(a) Draw free-body diagrams for each object.
(b) Calculate the
magnitude of the acceleration of each object.
(c) Calculate the
tension in the string.
(a) The force of gravity acts downward and tension acts upward on
each object.
(b) 2.0 m/s2
(c) 4.7 N
6) Three boxes in contact rest side-by-side on a smooth, horizontal
floor. Their masses are
5.0-kg, 3.0-kg, and 2.0-kg, with the
3.0-kg box in the center. A force of 50 N pushes on the
5.0-kg
box, which pushes against the other two boxes.
(a) Draw the
free-body diagrams for each of the boxes.
(b) What magnitude
force does the 3.0-kg box exert on the 5.0-kg box?
(c) What
magnitude force does the 3.0-kg box exert on the 2.0-kg box?
(a) The following forces act on the 5.0-kg box: the force due to
gravity, normal force,
contact force between 5.0-kg mass and
3.0-kg mass, the force of 50 N pushing on the
box. The following
forces act on the 3.0-kg box: the force due to gravity, normal
force,
contact force between the 5.0-kg box and the 3.0-kg box,
the contact force between the
3.0-kg box and the 2.0-kg box. The
following forces act on the 2.0-kg box: the force
due to gravity,
normal force, contact force between the 3.0-kg box and the 2.0-kg
box.
(b) 25 N
(c) 10 N
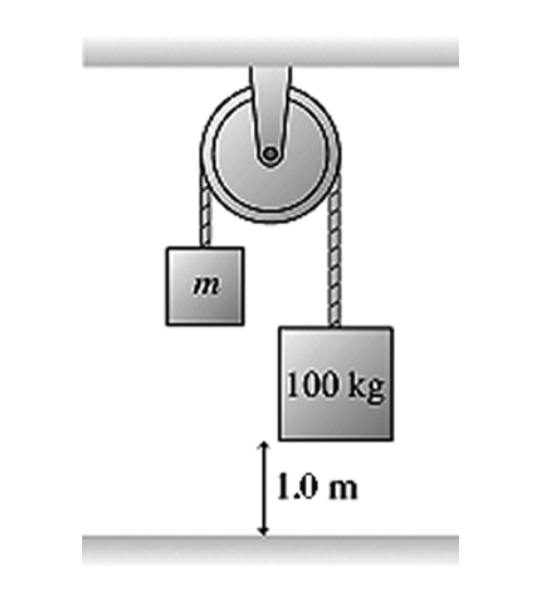
The figure shows a 100-kg block being released from rest from a
height of 1.0 m. It then takes
it 0.90 s to reach the floor. What
is the mass m of the other block? The pulley has no
appreciable
mass or friction.
A) 60 kg
B) 54 kg
C) 48 kg
D) 42 kg
A
A wooden block A of mass 4.0 kg slides on a frictionless table when
pulled using a massless
string and pulley array by a hanging box
B of mass 5.0 kg, as shown in the figure. What is
the
acceleration of block A as it slides on the frictionless
table? Hint: Think carefully about the
acceleration constraint.
A) 4.1 m/s2
B) 3.5 m/s2
C) 3.1 m/s2
D) 2.7 m/s2
A
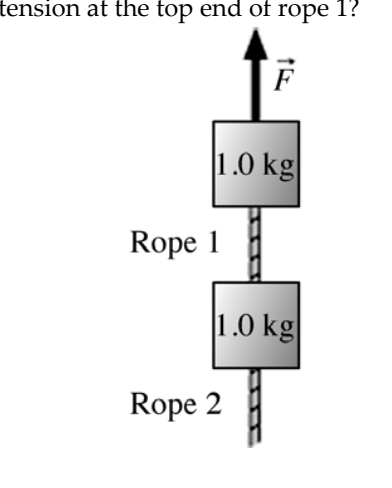
The figure shows two 1.0 kg-blocks connected by a rope. A second rope
hangs beneath the
lower block. Both ropes have a mass of 250 g.
The entire assembly is accelerated upward at 2.3
m/s2 by force F
. What is the tension at the top end of rope 1?
A) 18 N
B) 15 N
C) 2.9 N
D) 3.5 N
A
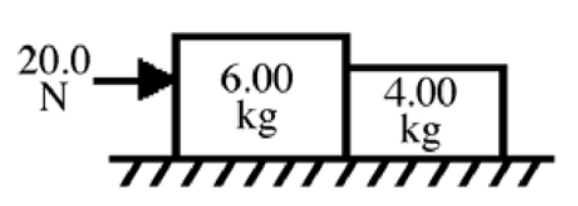
A 6.00-kg block is in contact with a 4.00-kg block on a horizontal
frictionless surface as shown
in the figure. The 6.00-kg block is
being pushed by a horizontal 20.0-N force as shown. What
is the
magnitude of the force that the 6.00-kg block exerts on the 4.00-kg block?
A) 6.00 N
B) 20.0 N
C) 8.00 N
D) 4.00 N
E) 10.0 N
C
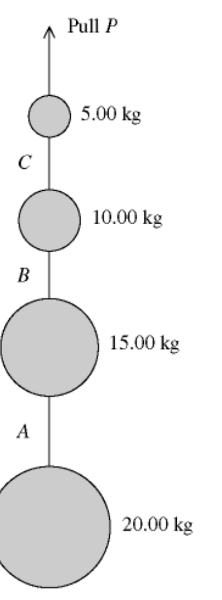
A series of weights connected by very light cords are given an upward
acceleration of 4.00
m/s2 by a pull P, as shown in the figure. A,
B, and C are the tensions in the connecting cords.
The pull P is
closest to
A) 690 N.
B) 490 N.
C) 290 N.
D) 200 N.
E) 50 N.
A
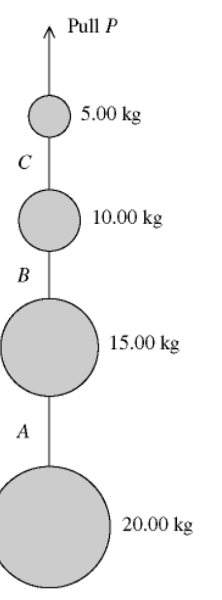
A series of weights connected by very light cords are given an upward
acceleration of 4.00
m/s2 by a pull P, as shown in the figure. A,
B, and C are the tensions in the connecting cords.
The SMALLEST
of the three tensions, A, B, and C, is closest to
C
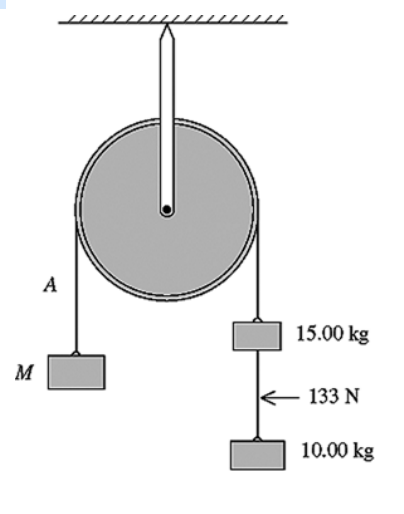
Three objects are connected by massless wires over a massless
frictionless pulley as shown in
the figure. The tension in the
wire connecting the 10.0-kg and 15.0-kg objects is measured to
be
133 N. What is the mass M?
A) 8.33 kg
B) 33.9 kg
C) 35.0 kg
D) 52.8 kg
E)
95.0 kg
D
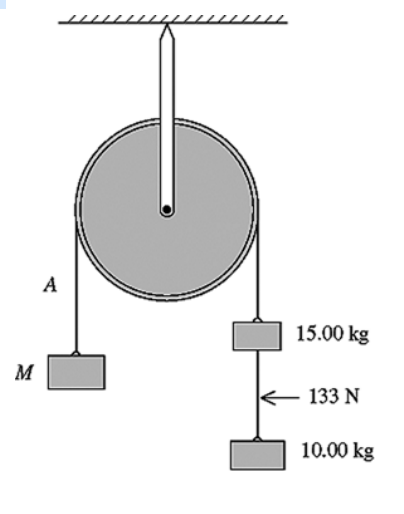
Three objects are connected by massless wires over a massless
frictionless pulley as shown in
the figure. The tension in the
wire connecting the 10.0-kg and 15.0-kg objects is measured to
be
133 N. What is the tension in wire A?
A) 87.5 N
B) 245 N
C) 280 N
D) 333 N
E) 517 N
D
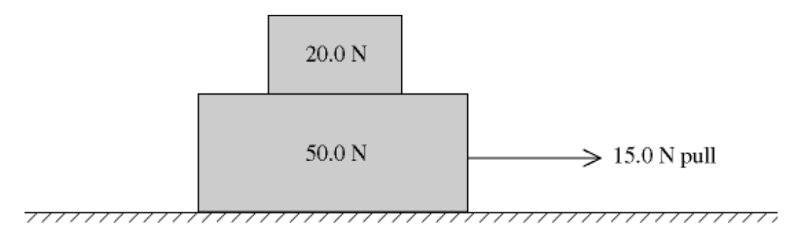
15) A 20.0-N box rests on a 50.0-N box on a perfectly smooth
horizontal floor. When a horizontal
15.0-N pull to the right is
exerted on the lower box (see figure), both boxes move together.
Find
the magnitude and direction of the net external force on the
upper box.
4.29 N to the right
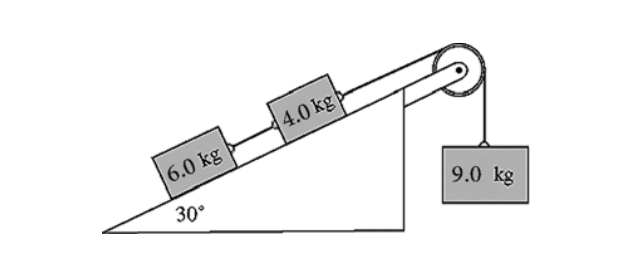
A system comprising blocks, a light frictionless pulley, a
frictionless incline, and connecting
ropes is shown in the
figure. The 9.0-kg block accelerates downward when the system
is
released from rest. The tension in the rope connecting the
6.0-kg block and the 4.0-kg block is
closest to
A) 30 N.
B) 33 N.
C) 36 N.
D) 39 N.
E) 42 N.
E
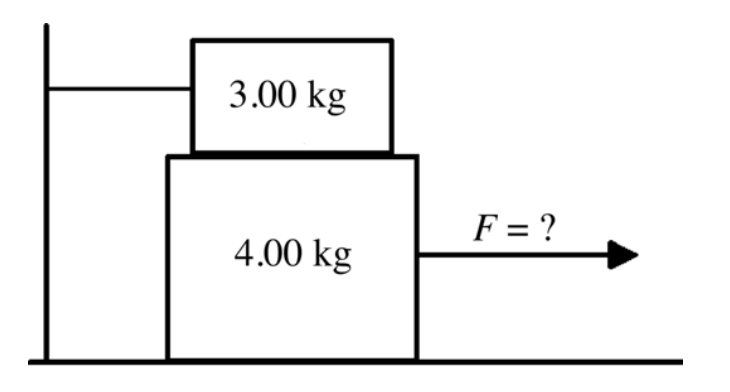
17) A 4.00-kg block rests between the floor and a 3.00-kg block as
shown in the figure. The
3.00-kg block is tied to a wall by a
horizontal rope. If the coefficient of static friction is
0.800
between each pair of surfaces in contact, what horizontal
force F must be applied to the
4.00-kg block to make it move?
A) 16.2 N
B) 54.9 N
C) 21.1 N
D) 23.5 N
E) 78.4 N
E
A 150-N box is being pulled horizontally in a wagon accelerating
uniformly at 3.00 m/s2. The
box does not move relative to the
wagon, the coefficient of static friction between the box and
the
wagonʹs surface is 0.600, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is
0.400. The friction force on
this box is closest to
A) 450
N.
B) 90.0 N.
C) 60.0 N.
D) 45.9 N.
D
A pickup truck is moving at 25 m/s with a toolbox of mass m resting
on the bed of the truck 2.5
m behind the cab. Suddenly the brakes
are applied, causing the toolbox to slide, and the truck
comes to
a stop in 4.7 s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the
toolbox and the bed of
the truck is 0.28. After the brakes are
applied, how much time elapses before the toolbox
strikes the cab?
1.4
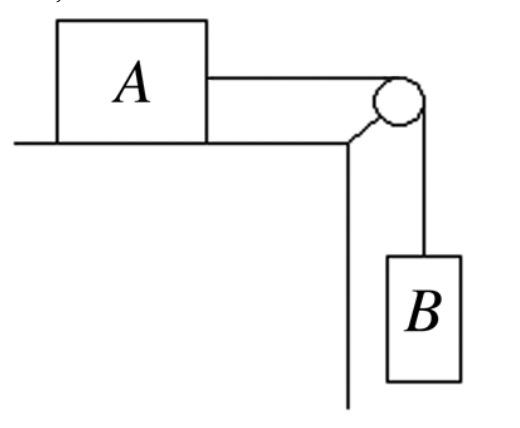
Two boxes are connected by a weightless cord running over a very
light frictionless pulley as
shown in the figure. Box A, of mass
8.0 kg, is initially at rest on the top of the table.
The
coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table
is 0.10. Box B has a mass of 15.0 kg,
and the system begins to
move just after it is released.
(a) Draw the free-body diagrams for each of the boxes, identifying
all of the forces acting on
each one.
(b) Calculate the
acceleration of each box.
(c) What is the tension in the cord?
Answer: (a) Box A is acted on by the downward force of gravity, the
upward normal force due to
the table top, the tension in the
string toward the right, and the force of friction due to
the
table top toward the left. Box B is acted on by the downward force of
gravity and
the upward tension of the string.
(b) 6.1
m/s2
(c) 56 N
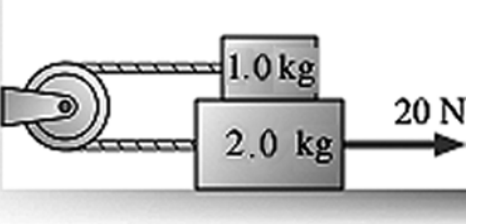
A rope pulls on the lower block in the figure with a tension force of
20 N. The coefficient of
kinetic friction between the lower block
and the surface is 0.16. The coefficient of kinetic
friction
between the lower block and the upper block is also 0.16. The pulley
has no
appreciable mass or friction. What is the acceleration of
the 2.0 kg block?
A) 4.1 m/s2
B) 5.1 m/s2
C) 8.4 m/s2
D) 9.2 m/s2
A
Three objects are connected as shown in the figure. The strings and
frictionless pulleys have
negligible masses, and the coefficient
of kinetic friction between the 2.0-kg block and the table
is
0.25. What is the acceleration of the 2.0-kg block?
A) 2.5 m/s2
B) 1.7 m/s2
C) 3.2 m/s2
D) 4.0 m/s2
A
A system comprised blocks, a light frictionless pulley, and
connecting ropes is shown in the
figure. The 9.0-kg block is on a
perfectly smooth horizontal table. The surfaces of the
12-kg
block are rough, with μk = 0.30 between the block and the
table. If the 5.0-kg block accelerates
downward when it is
released, find its acceleration.
A) 1.0 m/s2
B) 1.2 m/s2
C) 1.4 m/s2
D) 1.6
m/s2
E) 1.8 m/s2
A
24) Block A of mass 5.0 kg and block X are attached to a rope which
passes over a pulley, as
shown in the figure. An 80-N force P is
applied horizontally to block A, keeping it in contact
with a
rough vertical face. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction
between the wall and
block A are μs = 0.40 and μk = 0.30. The
pulley is light and frictionless. The mass of block X is
adjusted
until block A moves upward with an acceleration of 1.6 m/s2. What is
the mass of
block X?
A) 9.9 kg
B) 9.3 kg
C) 8.7 kg
D) 8.1 kg
E) 7.5 kg
a
In the figure, two wooden blocks each of 0.30 kg mass are connected
by a string that passes
over a very light frictionless pulley.
One block slides on a horizontal table, while the other
hangs
suspended by the string, as shown in the figure. At time t = 0, the
suspended block is
0.80 m over the floor, and the blocks are
released from rest. After 2.5 s, the suspended block
reaches the
floor. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the table
and the sliding
block?
A) 0.35
B) 0.52
C) 0.84
D) 0.65
E) 0.95
E
26) A 4.00-kg box sits atop a 10.0-kg box on a horizontal table. The
coefficient of kinetic friction
between the two boxes and between
the lower box and the table is 0.600, while the coefficient
of
static friction between these same surfaces is 0.800. A horizontal
pull to the right is exerted
on the lower box, as shown in the
figure, and the boxes move together. What is the friction
force
on the UPPER box?
A) 19.3 N to the right
B) 19.3 N to the left
C) 23.5 N to
the right
D) 31.4 N to the right
E) 31.4 N to the left
a
27) Two blocks are connected by a string that goes over an ideal
pulley as shown in the figure.
Block A has a mass of 3.00 kg and
can slide over a rough plane inclined 30.0° to the
horizontal.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A
and the plane is 0.400. Block B has a mass of
2.77 kg. What is
the acceleration of the blocks?
A) 0.392 m/s2
B) 1.96 m/s2
C) 3.12 m/s2
D) 5.35
m/s2
E) 0.00 m/s2
a
28) The figure shows two packages that start sliding down a 20° ramp
from rest a distance
d = 6.6 m along the ramp from the bottom.
Package A has a mass of 5.0 kg and a coefficient of
kinetic
friction 0.20 between it and the ramp. Package B has a mass of 10 kg
and a coefficient of
kinetic friction 0.15 between it and the
ramp. How long does it take package A to reach the
bottom?
A) 2.7 s
B) 3.0 s
C) 3.2 s
D) 3.5 s
a
29) Two weights are connected by a massless wire and pulled upward
with a constant speed of
1.50 m/s by a vertical pull P. The
tension in the wire is T (see figure). P is closest to
A) 25 N.
B) 125 N.
C) 187.5 N.
D) 245 N.
E) 1225 N.
b
30) Two blocks are connected by a string that goes over an ideal
pulley as shown in the figure and
pulls on block A parallel to
the surface of the plane. Block A has a mass of 3.00 kg and can
slide
along a rough plane inclined 30.0° to the horizontal. The
coefficient of static friction between
block A and the plane is
0.400. What mass should block B have in order to start block A
sliding
up the plane?
2.54
The figure shows a 2000 kg cable car descending a high hill. A
counterweight of mass 1800 kg
on the other side of the hill aids
the brakes in controlling the cable carʹs speed. The
rolling
friction of both the cable car and the counterweight are
negligible. How much braking force
does the cable car need to
descend at constant speed?
A) 3800 N
B) 2900 N
C) 2000 N
D) 980 N
A
32) A system of blocks and a frictionless pulley is shown in the
figure. Block A has a mass of 2.0 kg
and is on a rough horizontal
surface for which μs = 0.40 between the surface and block A.
The
rope pulls horizontally on block A. Block C has a mass of 1.0
kg. An external force P = 23.0 N,
applied vertically to block A,
maintains the system at rest as shown in the figure. What is
the
friction force on block A?
A) 6.3 N
B) 6.9 N
C) 7.5 N
D) 5.7 N
E) 5.1 N
A
33) A 1520-N crate is to be held in place on a ramp that rises at
30.0° above the horizontal (see
figure). The massless rope
attached to the crate makes a 22.0° angle above the surface of
the
ramp. The coefficients of friction between the crate and the
surface of the ramp are μk = 0.450
and μs = 0.650. The pulley has
no appreciable mass or friction. What is the MAXIMUM weight
w
that can be used to hold this crate stationary on the ramp?
Answer: 1380 N
Var: 1
Copyright ©
34) Block A of mass 8.0 kg and block X are attached to a rope that
passes over a pulley. A 50-N
force P is applied horizontally to
block A, keeping it in contact with a rough vertical face.
The
coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the wall
and block A are μs = 0.40 and μk =
0.30. The pulley is light and
frictionless. In the figure, the mass of block X is adjusted
until
block A descends at constant velocity of 4.75 cm/s when it
is set into motion. What is the mass
of block X?
A) 6.5 kg
B) 7.2 kg
C) 8.0 kg
D) 8.8 kg
E) 9.5 kg
A