Sensory Portion (PNS)
Consist of nerve fibers the conduct impulses TOWARD the CNS.
Motor Arm (PNS)
Consists of nerve fibers that conduct impulses AWAY from the CNS.
Somatic Divison
Sometimes called the voluntary system.
Controls skeletal muscles.
Autonmic Nervous System
Efferent division of the peripheral nervous system that innervates cardiac and smooth muscles and glands; also called the involuntary or visceral motor system.
Sympathetic Nevous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for activity or to cope with some stressor (danger, excitement, etc.); the fight, fright, and flight subdivision.
Parasympethetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that oversees digestion, elimination, and glandular function; the resting and digesting subdivision.
Cerebral Hemisperes
The most superior portion of the brain.
Consist of gyri and sulci.
Divided into left and right hemispheres the into lobes.
Gyri
An outward fold of the surface of the cerebral cortex.
Sulci
A furrow on the brain, less deep than a fissure.
Fissures
The deepest depressions or inward folds on the brain.
Longitudinal Fissure
Divide brain into left and right hemisperes.
Transverse Fissure
Seperates the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe.
Central Sulcus
Divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
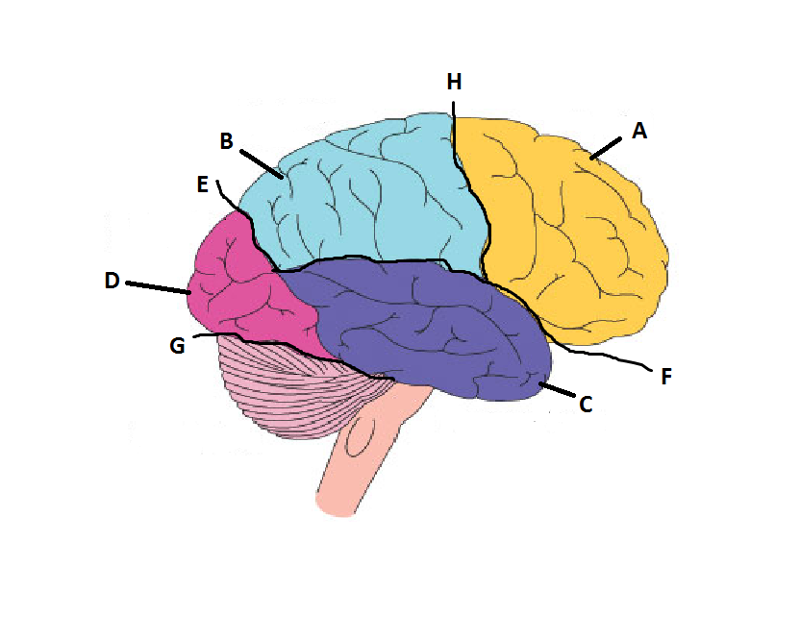
What is A?
Frontal Lobe
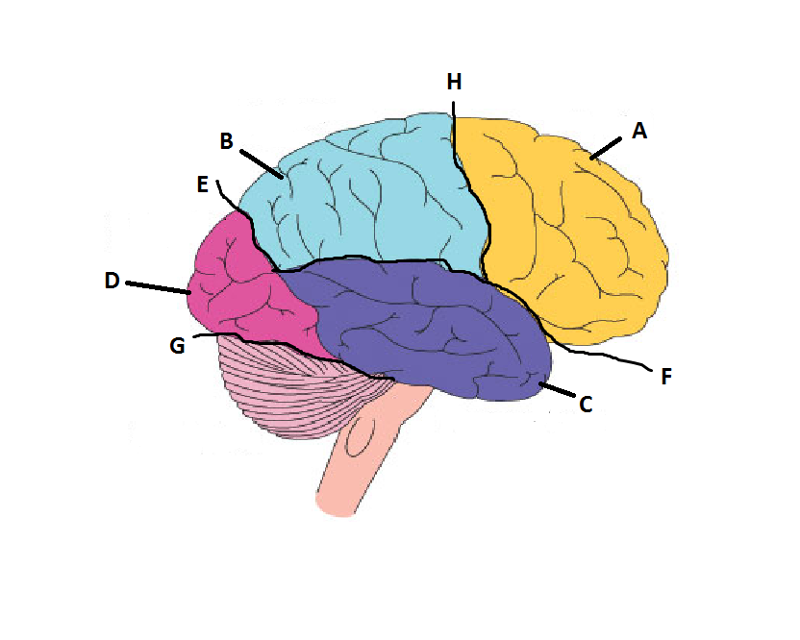
What is B?
Parietal Lobe
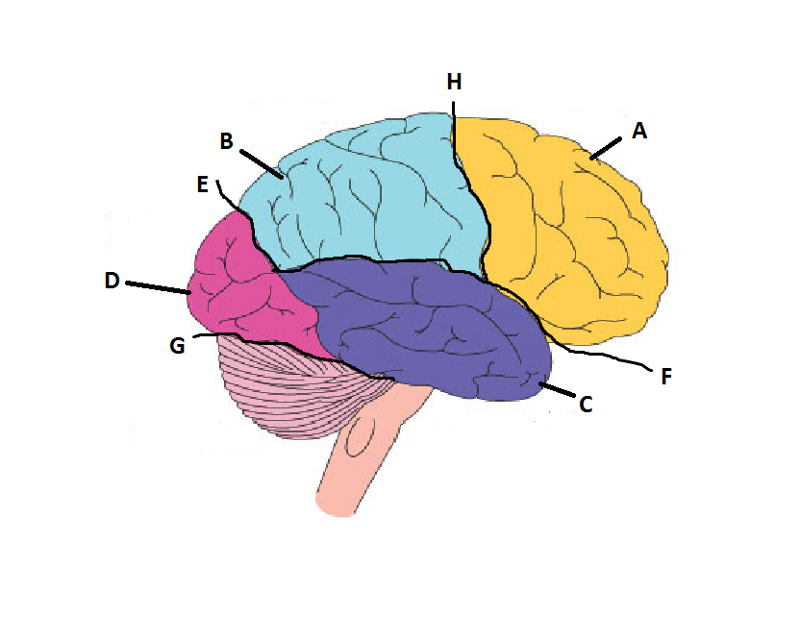
What is C?
Temporal Lobe
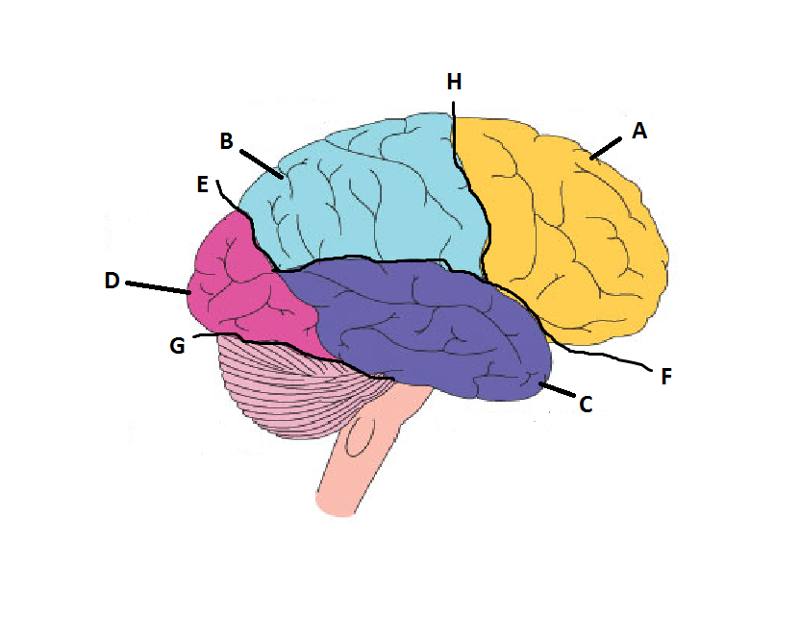
What is D?
Occipital Lobe
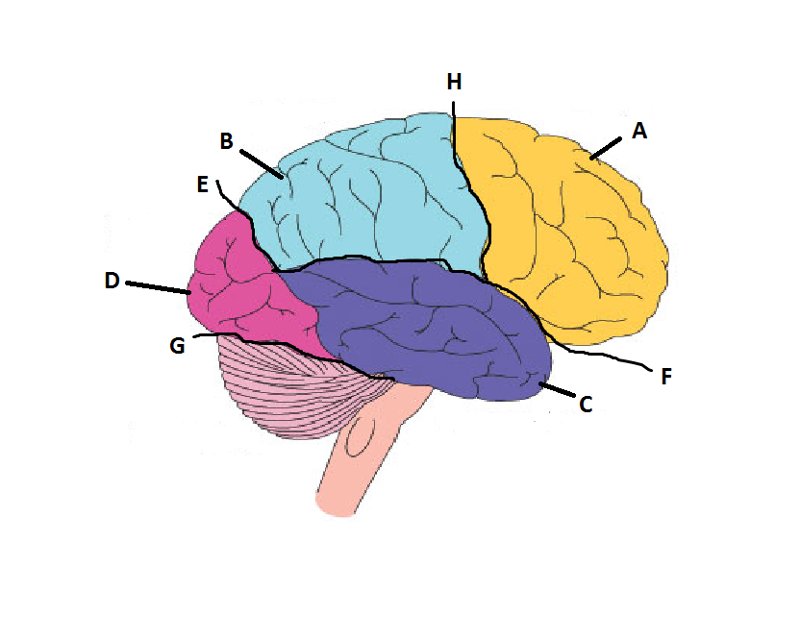
What is E?
Parieto-Occipital Sulcus
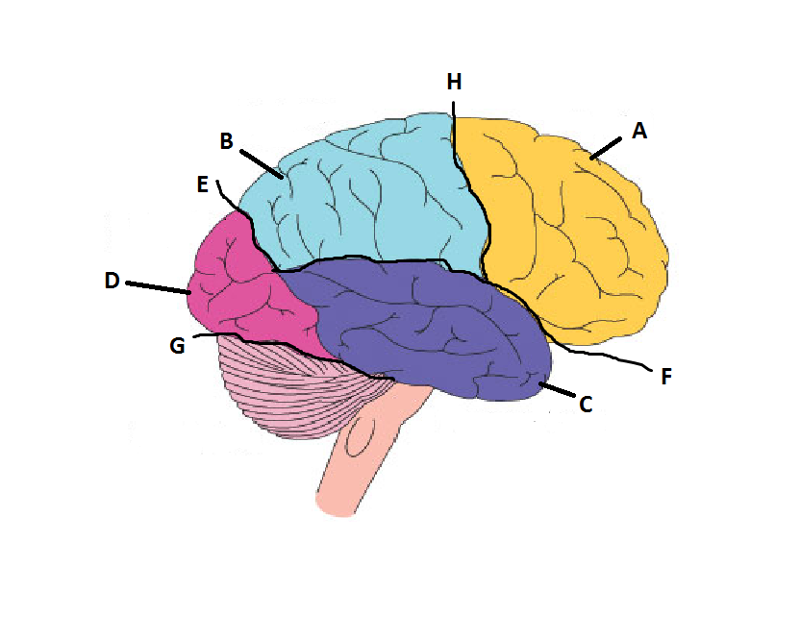
What is F?
Lateral Sulcus
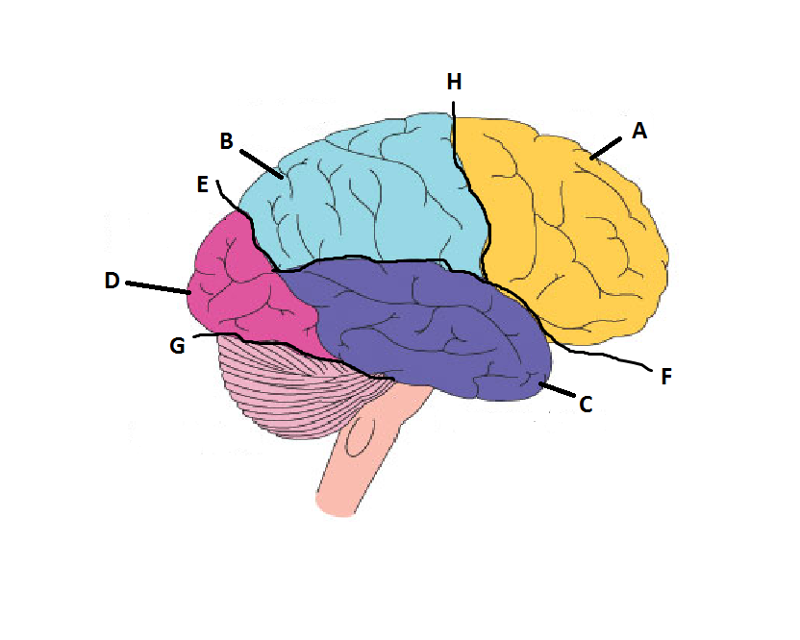
What is G?
Transverse Sulcus
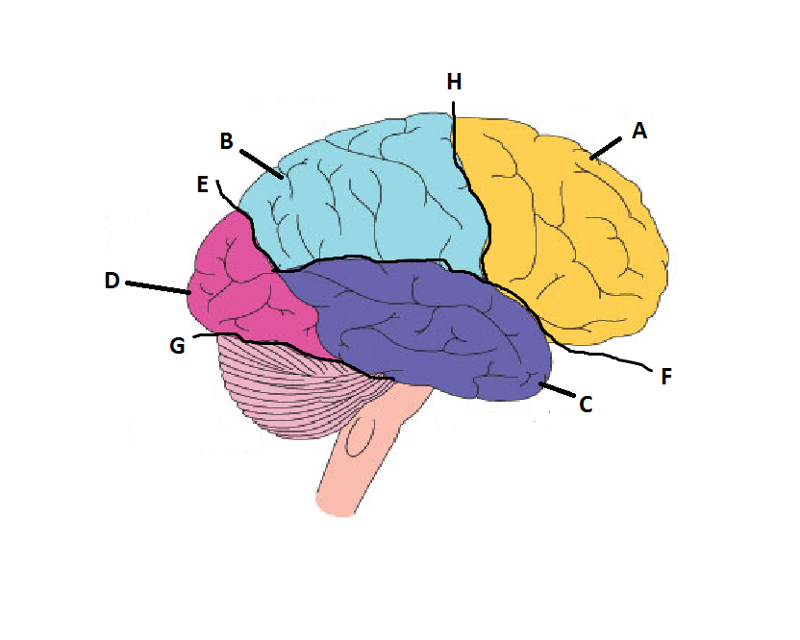
What is H?
Central Sulcuc
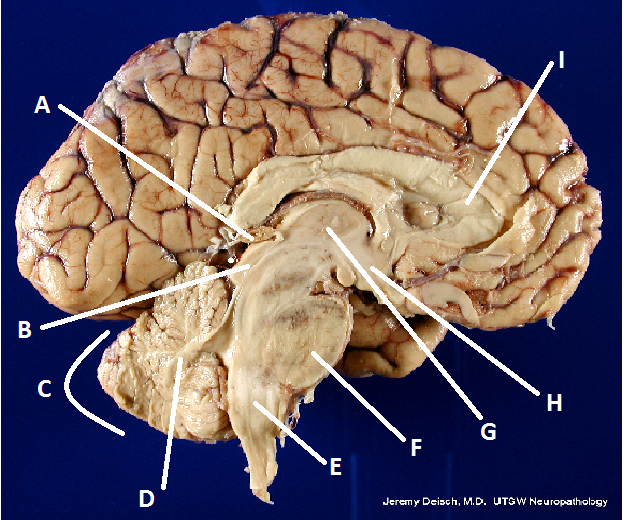
What is A?
Pineal body (gland)
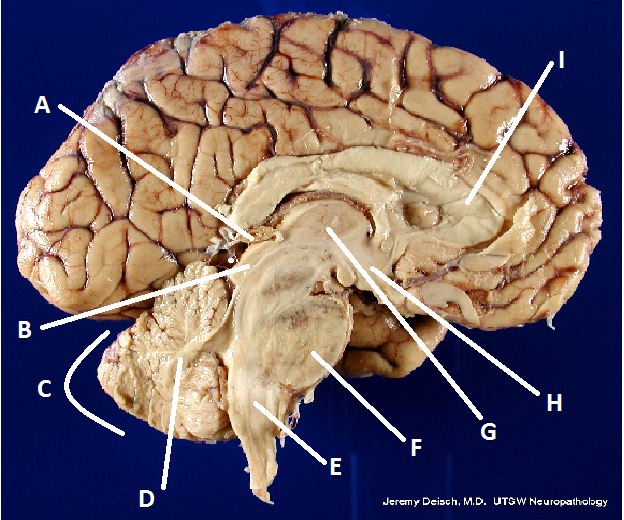
What is B?
Hypothalamus
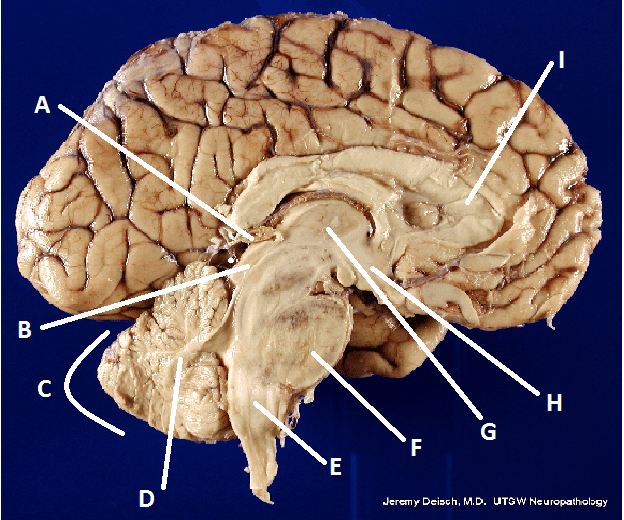
What is C?
Cerebellum
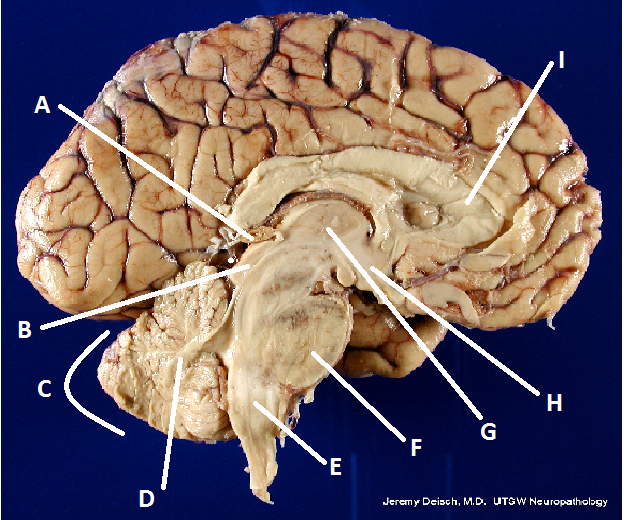
What is D?
Arbor Vita
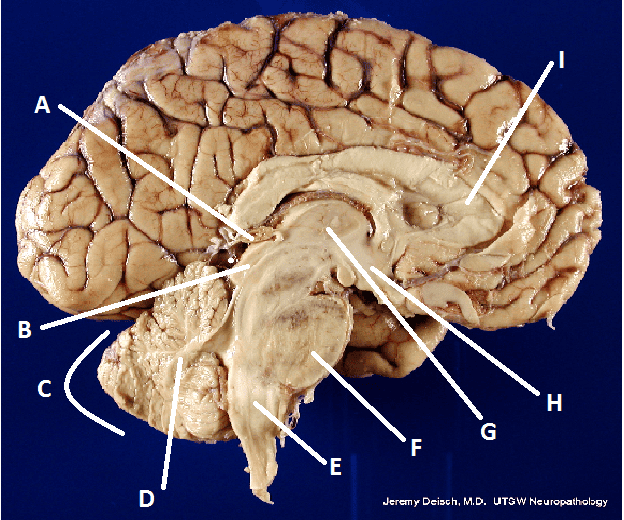
What is E?
Medulla Oblongata
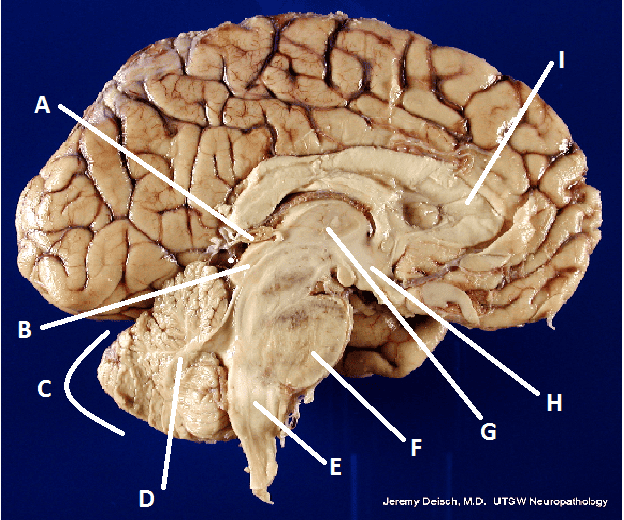
What is F?
Pons
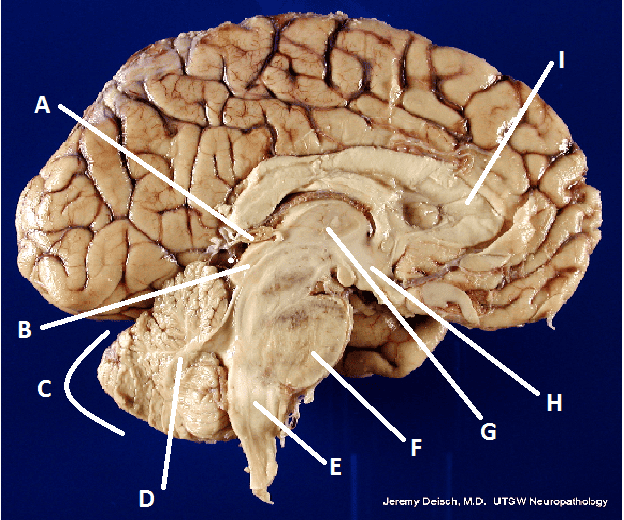
What is G?
Thalamus
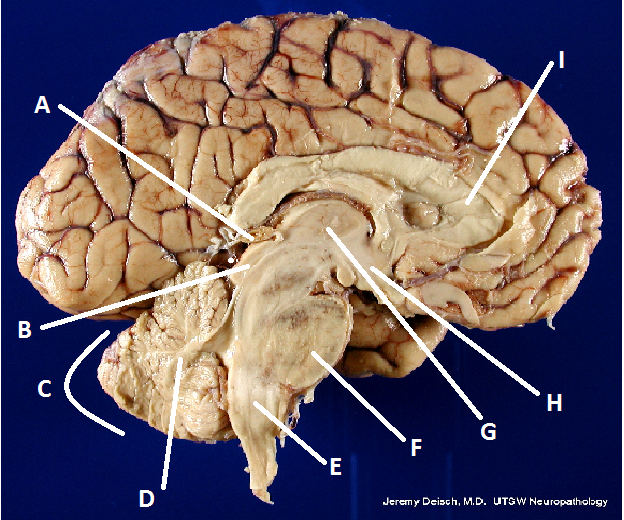
What is I?
Corpus Callosum
Diencephalon
That part of the forebrain between the cerebral hemispheres and the midbrain including the thalamus, the epithalamus, and the hypothalamus.
Olfactory Bulbs
Enlargements at the terminus of the olfactory nerve at the base of the brain just above the nasal cavities.
Octip Chiasma
The partial crossover of fibers of the optic nerves.
Thalamus
A mass of gray matter in the diencephalon of the brain.
Hypothalamas
Region of the diencephalon forming the floor of the third ventricle of the brain.
Pituitary Gland
Neuroendocrine gland located beneath the brain that serves a variety of functions including regulation of gonads, thyroid, adrenal cortex, lactation, and water balance.
Mammillary Gland
Along with the anterior and dorsomedial nuclei in the thalamus, are involved with the processing of recognition memory.
Epithalamus
Most dorsal portion of the diencephalon; forms the roof of the third ventricle with the pineal gland extending from its posterior border.
Pineal Body
A hormone-secreting part of the diencephalon of the brain thought to be involved in setting the biological clock and influencing reproductive function.
Choroid Plexus
A capillary knot that protrudes into a brain ventricle; involved in forming cerebrospinal fluid.
Corpus Callosum
A broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain.
Brain Stem
Collectively the midbrain, pons, and medulla of the brain.
Cerebral Peduncles
A bundle of myelinated neurons joining different parts of the brain.
Pons
the part of the brain stem connecting the medulla with the midbrain, providing linkage between upper and lower levels of the central nervous system.
Medulla Oblongota
Inferiormost part of the brain stem.
Superior Colliculi
Part of the copora quadrigemina
Inferior Colliculi
Part of the copora quadrigemina
Arbor Vitae
The arborescent appearance of the white matter in a vertical section of the cerebellum.
Meninges
Protective coverings of the central nervous system; from the most external to the most internal, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
Dura Mater
Outermost and toughest of the three membranes (meninges) covering the brain and spinal cord.
Arachnoid Mater
The middle layer of the three meninges.
Pia Mater
Innermost layer of the meninges.
Cranial Nerves
The 12 nerve pairs that arise from the brain.
Olfactory (I)
Function: Smell (purely sensory)
Optic (II)
Function: Sight (purely sensory)
Oculomotor (III)
Function: Visual Motor
Trochelear (IV)
Function: Visual Motor
Trigeminal (V)
Function: Major sensor of face
Adbucens (VI)
Function: Visual Motor
Facial (VII)
Function: Visual, lacrimal, salivary.
Vestibulochlear (VIII)
Function:Hearing (purely sensory)
Glassophyryngeal (IX)
Function: Throat and mouth
Vagus (X)
Function:Pharynx, larynx, and involuntary muslces
Accessory (XI)
Function: Motor
Hypoglossal (XII)
Function: Motor and tongue