_____________ is the production of a new individual for the propagation of the species.
Reproduction
Reproduction slumbers until ___________
puberty
___________ ___________ organs, or Gonads (________) are called _______ in males and __________ in female.
- The primary sex organ
- seeds
- testis
- ovaries
Gonads are responsable for the production of _________, (or _________) and ___________.
- sex cells
- gametes
- sex hormones
Gonads have both __________ and ____________ functions
- Exocrines
- Endocrines
___________ function refers to ducts for production of and transport of gametes
Exocrine
Endocrine function refers to secretion of _________ __________
- sex hormones
Female sex hormones are
- Estrogens
- Progesterone
Male sex hormone is
Testosterone
The Haploid reproductive sex cells from :
- Male
- Female
- Sperm
- Ova
The Male Reproductive System role is to manufacture male gametes called ________ and deliver them to the ________ reproductive tract. where __________ can occur.
- Sperm
- female
- fertilization

The sperm-producing ______ or male _______ (seed), lie within the ___________.

- testis
- gonad
- scrotum
___________ , which means "pouch" is a sack of ______ and _______ ________ that hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis.
- Scrotum
- skin
- Superficial facia
Scrotum is covered with _______ and contains paired oval __________
- hair
- Testes
- Scrotum is affected by ________________.
- The superficial location of the scrotum, which provides a temperature about ____ ºC lower, is an essential adaptation for ________ production.
- Temperature
- 3ºC lower
- Sperm
Scrotum is formed of 3 main parts:
- Superficial fascia, which contain
- Dartos muscles
- Skin
- Scrotum is divided into ____ compartments, each one for each ______.
- This division starts with a loose Connective Tissue wall called ___________, which divides the scrotum into two compartments, at the superficial fascia
- Septum is supported by a median ridge (external) called ___________
- 2
- testes
- septum of scrotum
- Raphae
The changes of scrotal surface area help maintain a fairly constant intrascrotal temperature and reflect the activity of two sets of muscles called __________, which are subcutaneous muscle of the scrotum which are also a part of the ___________. This muscle causes the skin of the scrotum to wrinkle.
- dartos muscles
- septum
_____________ muscle surrounds each of the spermatic cords and testicles. It is a continuation of the internal oblique muscle.
_____________ muscle functions in controlling the temperature of the testes, which need to be kept at a temperature of 3 degrees ______
- Cremaster Muscle
- Cremaster
- lower
For maximum production of _________, Cremaster Muscle raises the testes during sexual arousal and upon exposure to the cold, and by lowering the testes away from the body when they get to warm.
Sperm
- The primary sex organ of the male is called__________
- these are plum size that weighs ____ to ___ grams, about _______ cm long, _____ wide, and is surrounded by ___ tunics.
- Testes
- 10 to 15 grams
- 1.5 cm
- 2.5 cm
- 2
Tunica _________ is an out-pocketing of the parietal peritoneum which becomes a serous covering of the testicle.
Vaginalis
Tunica ___________ is a white fibrous capsule which covers each testicle and invaginates to form ________ walls which divide the testes into many compartments called ___________ (about _____ to _____ of them).
- albuginea
- septa
- lobules
- 200 to 300 lobules
Lobules contain _________ tubules which produce ________ by spermatogenesis.
- seminiferous tubules
- sperm
- Seminiferous tubule are ______, highly ______ tubules which occupy the _________.
- These tubules are the ______ of sperm production.
- long
- coiled
- lobules
- site
- They contain Sustentacular (__________) or _______ cells, which secrete ________ to protect the developing ____________ from the male ________ system and nutrients.
- Sustentocytes
- Sertoli cells
- inhibin
- spermatozoa
- Immune
Excess sperm would cause an _________ from the immune system
attack
- Seminiferous tubules consist of a thick __________ epithelium surrounding a central fluid-containing _______.
- The epithelium consists of ________ ___________ (____ formation) cells embedded in substantially large columnar cells call _____________.
- squamous
- lumen
- spheroid spermatogenic cells
- sperm formation
- Sustentocytes
_________ cells form a smooth muscle-like layer (3 to 5) which contract. _______ cells may help to squeeze sperm and testicular fluids through the tubules and out of the testes
- Myoid Cells
Lying in the soft connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules are the ___________ _________ cells, also known (_______ cells). These cells produce androgens, also known as __________, which is the male sex hormone.
- Interstitial endocrine cells (Interstitial Endocrinocytes)
- leydig cells
- Testosterone
Undescended testes is a problem called _________ which could cause cancer.
cryptorchidism
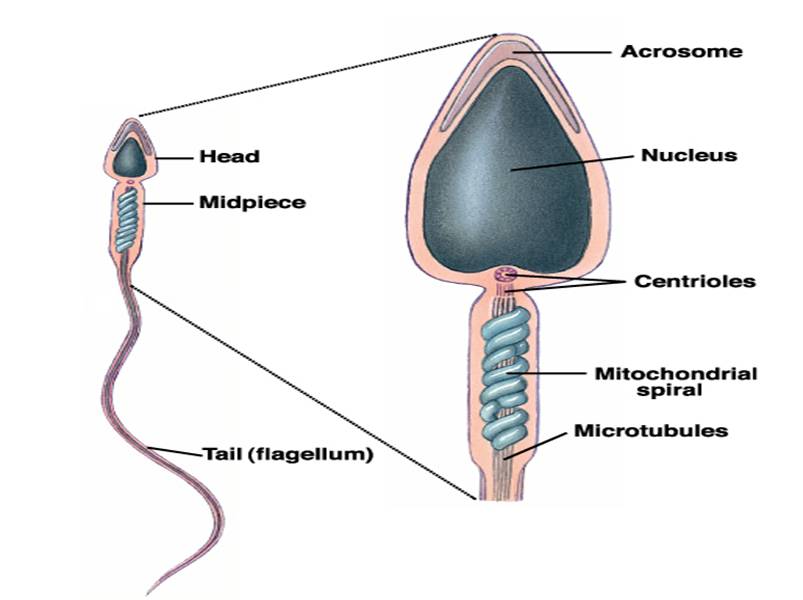
SPERM
All sperm are _________, which means they contain half the full chromosome number.
Sperm are produced by _________ sex cell division.
- haploid
- meiosis
Diploid cells account _______ chromosomes (also known as __________ chromosomes).
Haploid cells account ________ chromosomes (also known as __________ chromosomes).
- 46
- homologous
- 23
- ____________________ (Sperm formation) is the process that occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes that produces male gametes (______ or ___________).
- It begins at ___________
- Every day _______ million sperm are produced.
- Spermatogenesis
- sperm
- spermatozoa
- puberty
- 300 million
It takes ________ days to produce sperm from.
- It starts with ________ spermatocytes cells, forming
- _________ spermatocytes continue into meiosis II to
- _________ - small round cells with large spherical nuclei - compact DNA - and it is No Motile. turn into
- ________ or spermatozoon is formed
- 24 days
- Primary
- Secondary
- spermatids
- Sperm
Sperm consist of three main part which will subdivide:
- Head
- Midpiece
- Tail
- Head contain paternal _________.
- It has a ________ called the _________ which contains an enzyme called __________ which aids the sperm in penetrating into the _______.
- DNA
- cap
- Acrosome
- Hyaluonidase
- oocyte
Midpiece contains ___________ which use the ______ fructose to produce ______ for locomotion
- mitochondria
- sugar
- ATP
Tail is a __________ used to propel the ______ along its way.
- flagellum
- sperm
- Still in the testicle, next to the testis exists a "cup-like shaped" _____________ (means beside the testes) or _____________.
- This is a highly coiled tubule (____ft)
- It lies on the posterior border of the _________.
- Epididymis
- upon twin
- 20 ft
- testicle
- Epididymis is a section where sperm is _______ and under-go final ___________.
- This is a _______ from the testis which functions as a _______ area of sperm before __________ as well as an area of _____________
- stored
- maturation
- duct
- storage
- ejaculation
- maturation
The tails of ______ require to _____ to _____ days for the tail to mature for motility.
- sperm
- 10
- 14 days
Sperm are ejaculated from the _____________.
Once stimulated an ____________ is caused by the _______ muscles of the epididymis contracts, expelling sperm into the next segment.
- Epididymis
- ejaculation
- smooth muscle
To continue, the _________ _________, also known as Van Deferens, a tubule which carries sperm ______ from the epididymis toward the male _________.
Ductus Deferens means __________
- Ductus Deferens
- away
- urethra
- carrying away
- Ductus Deferens is lined with ______ _________ with _________.
- Contains _________ muscle for ___________, which delivers sperm toward the urethra.
- Columnar epithelium
- microvilli
- smooth
- peristalsis
Some men opt to take full responsability for birth control by having a ____________ which means "cut the vas". This procedure the physician makes a small incision into the scrotum and then cuts through and ligates or cauterizes each ____________.
- vasectomy
- duct Diferens
Ductus Deferense goes upward through the ________ Cord, which is a connective tissue sheath enclosing :
- Spermatic Cord
- Duct Deferens
- Testicular Artery
- Testicular veins
- Autonomic Nerves
- Lymphatic vessels
- Cremaster muscle
Cremaster muscle is made of :
Skeletal muscle
Spermatic cord travels upward through the __________ _______, which is a hole in the abdominal wall through which the spermatic cord passes. It is a weak spot in the _______ of the __________ which can tear open causing an _____________________-
- Inguinal Canal
- floor
- abdomen
- inguinal hernia
The ductus deferens joins a duct from _________ vessicle and enters the prostate as the _____________
- Seminal vessicle
- Ejaculatory Duct
An approximate 8"inches duct in length which empties the urinary bladder is called:___________
It transports urine and semen (at different times), so it serves both _________ and ___________ systems in the next three regions
- Urethra
- Urinary
- Reproductive
- Prostatic Urethra
- Membranous Urethra
- Spongy Urethra
The portion of Urethra that passes through the prostate, and is about 1" in length, is called _________
Prostatic Urethra
___________ urethra is aprox. .5" in length as it passes through the urogenital diaphragm.
It is also known as
- Membranous urethra
- Intermediate part of the urethra
__________ urethra is approx. 6" in length, and passes through the corpus spongiosum
Spongy urethra
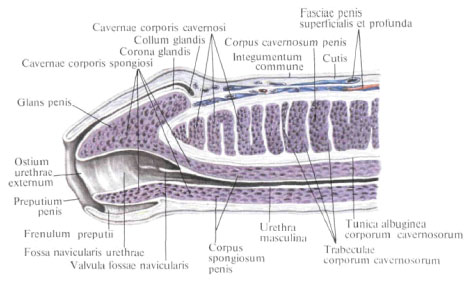
_______________ is an enlargement of the distal end of the urethra in the area of the glans penis.
Navicular Fossa
_____________ ____________ _________ is the distal opening of the urethra.
External Urethral Orifice
Accessory Sex Glands secrete most of the ________ portion of __________
- liquid
- semen
Accessory Sex Glands in males are:
- seminal vesicle,
- prostate,
- bulbo urethral
- urethral glands.
_________________ lie on the posterior surface of the urinary bladder; they secrete a viscous, ___________ (pH) fluid rich in fructose.
- Seminal Vesicle
- alkaline fluid.
The alkalinity helps to __________ the acidity of the _______ reproductive tract.
The fructose is used by the mitochondria of the sperm to produce ________ to power the ____________.
- neutralize
- female
- ATP
- flagellum
- The ___________ or Prostatic gland is a single ___________ -shaped gland about the size of a _______
- It is inferior to the __________ _________.
- Prostate
- doughnut-shaped
- chestnut
- urinary bladder
It secretes a ______, slightly ______ fluid containing citric acid, and several ________ enzymes to coagulate the ________ shortly after ejaculation.
It produces ____% of semen volume.
- milky
- alkaline
- clotting
- semen
- 30%
_____________________ Gland is about the size of a ____; they secrete an _____________ fluid to neutralize the acidity of the male ________, and mucus which ___________ the urethra as well as serving as a lubricant during __________ intercourse. Procudes ___% of semen vol.
- Bulbo urethral Gland
- pea
- alkaline
- urethra
- lubricate
- sex intercourse
- 5%
SEMEN Is a mixture of ________ and the secretions from the _________ _______.
It is a volume of about ____ to ___ ml, with _____ to _____ million sperm per ml
- sperm
- accessory glands
- 2.5 to 5 ml
- 50 to 150 million sperm
When the sperm count bring less than 20 million/ml sperm, it is considered _________
Steril
Sterility depend on:
- number of sperm
- size and shape of the sperm
- presence of hyaluronidase to dissolve the hyaluronic acid around the ovum
- motility
- Sperm is a transport medium to carry ________ and __________ acidity.
- nutrients
- neutralizes
________________ _________ is a natural antibiotic which destroys bacteria in the reproductive tract.
- Seminal plastin
PENIS is the mail _________ organ. Functions in ________ and ___________.
- copulatory
- urination
- copulation
Sex reproductive organs known as ___________ are not copulatory organs.
Gonads
_______ ___________ are two cylinders dorsolateral of tissue (at the top) of the penis.
Corpus cavernosa
_______ ___________ is one cylinder midventral of tissue, at the lower part of penis
Corpus Spongiosum
- During sexual arousal, _________ which convey blood to the two corporal _________ undergo __________ and engorge these two cylinders of tissue with blood.
- arteries
- cavernosa
- vasodilation
2- The __________ which drain blood from these two cylinders undergo _____________ and restrict blood from leaving the two cylinders
- veins
- vasoconstriction
The result of these two cylinders filling with blood is called an ______________
erection
The corpus ____________ does not undergo this process due to the fact that it would __________ the urethra and not allow passage of the __________.
- spongiosum
- close off
- sperm
The propulsion of the semen from the urethra to the exterior is called
ejaculation
_________ _________ or acorn, is the head of the penis.
Glans Penis
Foresink or __________ is a loose fitting flap of skin covering the glans
Prepuce
This flap of skin is remove during a process called
Circumcision