The breaking down of food molecules for use by body cells is known as
Digestion
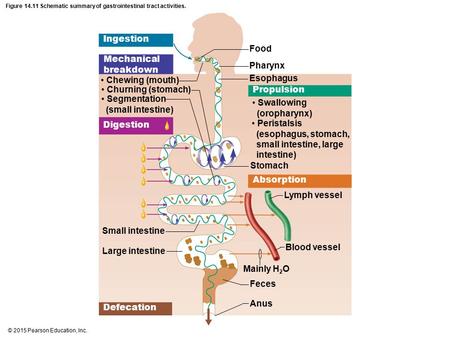
The Digestive Process includes:
- Ingestion
- Movement of food
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Defication
There are two types of digestions:
- Mechanical
- Chemical
The physical break down of food material with instruments, in this case teeth, tongue, etc. is known as
Mechanical Digestion
The break down of food via enzymes, acids, carbohydrates (to simple sugars), lipids (to glycerol and fatty acids), proteins (into shorter AA sequences), etc... is known as
Chemical Digestion
G.I. Tract stands for
Gastro Intestinal Tract (Digestive Tract)
_____________ is a continuous tube, about 30 ft. long, which includes:
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Large Intestine
- The Anus
G.I. Tract
G.I. tract uses ______________________ as the supportive structure peripheral to the digestive tract.
Accessory Organs
As accessory organs for the G.I. Tract we find:
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Salivary Glands
- Gastric and Intestinal Glands
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
- Appendix
Histiology of the GI Tract includes
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis Externa
- Serosa
The innermost lining of the GI tract, a continuous mucous membrane from the mouth to the anus.
Mucosa or Mucous membrane
1) Mucosa's main function is to:
- Secrete mucus, digestive enzymes and hormones
- Absorb the end products of digestion into the blood
- Protect against infectious disease.
Which GI may perform one or the three of them depending the particular region.
Mucosa consists of three sublayers:
- Lining Epithelial
- Lamina Propia
- Muscularis mucosa
a- Lining Epithelial in the GI Tract is found in TWO types:
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium located in:
- Mouth
- Esopagus
- Simple Columnar Epithelium
- From Stomach to Anus
Stratified Squamous Epithelium works for mouth and esophagus to (function)
- ___________________________
- __________________________
- Protect from abrasion
- Secretion of mucous and enzymes
Simple Columnar Epithelium works from the esophagus to the anus for...
- _____________________________
- _____________________________
- Secretion and
- Absorption

b- Lamina Propia is
- made of _______________,
- highly _________________,
- contain many ________ vessels and some _______
- Supports the _______________ and binds it to _________________
- Contains _____________ epithelium
- Loose C.T.
- Vascularized
- Lymph vessels and some Nodes
- Epithelium, and binds it to Muscularis Mucosa
- Glandular
c- Muscularis Mucosa is made of:
- _______________, which
- Pproduces __________________
- Contain ____________
- Form the ___________
- a scant layer of Smooth Muscle Cells
- local movements of the mucosa
- visceral muscle fibers
- form the Vili Folds
2) Submucosa is the layer below the ______________
It is made of ________________ which binds _________ and ____________ together. It is highly _____________.
- Mucosa
- Dense CT
- Muscularis and mucosa
- Vascularized
3) Muscularis Externa is the layer below the __________.
- Composed of ____ layers of __________:
- ______
- ______
- They are involved in _______________.
Submucosa
- 2 layers of muscle
- Circular Muscle
- Longitudinal Muscle
- Peristalsis
4) Serosa is the ____________ layer, also called _______
_________________.
outer-most
Viscerous Peritoneum
- Serosa layer is made (most of the time) of _____________ ____________ epithelium. However there are some structures Serosa uses to bind to the neighbor organs. P.e.
- Attached to Serosa, there is an extension of the peritoneum which binds the small intestine to the abdominal wall called ____________________.
- Another structure used to connect the Large Intestine to the abdominal wall is ___________.
- ______________ ___________ attaches liver to the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall.
- _________ ______________ suspends stomach and duodenum from the liver
- _________ _____________ a large "apron-like" fold of the serosa (stomach) an area of fat storage, conains lymph nodes.
- Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Mesentery
- Mesocolon
- Falciform Ligament
- Lesser Omentum
- Greater Omentum
GI Tract structures and accesory organs:
1) ________________ is formed by cheeks, hard and soft palates and tongue, stratified squamous epithelium
- Mouth or Buccal Cavity
2) _________________ moves food over the teeth, comprised of skeletal muscle. Also involved in speech, and contains taste buds.
Tongue
3) ______________ are made of fleshy folds of skin surrounding the opening of the mouth
LIPS
4) _____________________ The non-keratinized pigmented border between the skin and the mouth, this pigmented area occupies the transition zone.
Vermilion
What zone does Vermilion transition?
It is the transition zone between Dry and Wet Skin
5) _________ __________ is the mucous membrane connecting the gingiva to the lip.
Labial Frenulum
6) ________________ is the space between the cheeks, and the teeth and gingiva
Vestibule
7) _________________ is a membranous fold of tissue on the underside of the tongue which attaches the tongue to the floor of the mouth.
Lingual Frenulum
8) ___________________ are projections (on the surface of the tongue in the GI Tract), and we find different types:
- _________________
- _________________
- _________________
Papillae
- Filiform
- Fungiform
- Circumvallate
Papillae "mushroom-like", which covers the tip of the tongue
Funjiform Papillae
Papillae Doughnut-like, form an inverted "V" on the posterior surface of the tongue.
Circumvallate Papillae
Papillae conical, covers anterior 2/3's of the tongue
Filiform Papillae
9) _________ _________ secrete saliva to keep membranes moist and to soften and dissolve food materials.
Saliva also contains salivary enzyme called _________.
- Salivary Glands
- Enzyme amylase
The major Salivary Glands are:
- _______________
- _______________
- _______________
- Parotid Gland
- Submandibular Gland
- Sublingual Gland
This gland is located under and in front of the ears
Parotid Gland
This gland is located under the base of the tongue
Submandibular Gland
This gland is located under the tongue
Sublingual Gland
The secretions of the salivary glands are called ________.
- It has a pH of ____________
- It is ____% Water and the rest is salivary _______.
- Body produces ______ to ______ ml/day.
Saliva
- 6.35
- 95% and Salivary Amylase
- 1000 to 15000 ml/day
Salivary Amylase _______ _______ starches into simpler __________
- Breaks down
- Sugars
10) This accessory structure of GI tract is involved in mechanical digestion to destroy food in mouth.
Teeth
- Babies teeth are called _____________, and there are ______ of this kind.
- Adults teeth are called _____________, and there are ______ of this kind.
- Deciduous Teeth
- 20
- Permanent Teeth
- 32
Permanent and Deciduous Teeth are divided in 4 types:
- ____________ known as chisel-shaped
- ____________ known as cone-shaped of fangs
- ____________ known as Premolars
- ____________
- Incisors
- Cuspids of Canines
- Bicuspids
- Molars
Their main function is:
- Incisors
- Cuspids of Canines
- Bicuspids
- Molars
- Incisors - Cut food
- Cuspids of Canines - Pier/hole/tear food
- Bicuspids - grind food
- Molars - pulverized food
Dental formula
I2/2 : C1/1 : B2/2 : M3/3 = 16 teeth total of One Half of the Mouth
Oral Cavity involves different accessory organs like this one known as the "gums," this tissue surrounds the teeth, and its official name is ____________
Gingiva
The inflamation of gingivae is known as
Gingivitis
The exposed portion of the teeth is known as _________ ____________, and the ___________ __________ is the top portion covered with a hard white material called ____________.
- Clinical Crown
- Anatomical Crown
- Enamel (only covers the crown)
The constricted portion of the tooth where the crown and root meet is known as ___________
Neck
The portion of the tooth which is embedded in the alveolar portion of the maxillae or mandible is known as ________.
It is covered with a bone-like substance called _________.
- ROOT
- Cementum
_________ __________ anchor the root in the bony socket (alveolus) of the jaw.
This junction forms a fibrous joint called a _________
- Periodontal Ligaments
- Gomphosis
___________ is a protein-rich bonelike material, underlies the enamel cap and forms the bulk of the tooth.
- Dentin
_________ _________ is the unhardened central cavity of the tooth, contains arterial and venous capillaries and nerves.
Pulp Cavity
- ________ ________ is a canal that runs from the pulp cavity down through the central portion of the root.
- _________ _________ is the openingn at the end of this _______ canal.
- Root Canal
- Apical Foramen
- Root
Remember that The grinding up of the food stuff by the teeth is called
Mechanical Digestion
- The pulverization or physical breakdown of food and the mixing of the food with saliva is known as ____________, and...
- The act of swallowing a food stuff is called ___________
- Mastication
- Deglutination
_______ is a rounded mass of a substance, especially of chewed food at the moment of swallowing.
Bolus
11) _______________ is a muscular tube (A10 inches long) from the pharynx to the stomach.
- Lines with __________ ___________ ___________
- _________ is used to move bolus from the Pharynx to the stomach through this muscular contraction.
- Esophagus
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Peristalsis
12) ____________ is an enlarged section of the digestive tract which is formed of :
- Cardiac Region
- Fundus Region
- Body
- Pyloris
- Stomach
____________ The outside curvature of the stomach
Greater Curvature
___________ the inside curvature of the stomach
Lesser Curvature
____________ the large folds in the stomach that contain gastric pits with gastric glands
Rugea
The smooth lining is dotted with millions of Gastric ________, which are holes that lead into tubular gastric glands that produce the stomach secretion called ____________
- Gastric Pits
- Gastric Juice
Cells that line in the Gastric Pit are secretary gland cells, and are - Please tell what they do produce:
- _
- _
- _
- _
- Mocous Cells
- Parietal Cells
- G Cells
- Chief Cells
- Mocous Cells
Secrete Mucus
- Parietal Cells -
secrete HCL (which activates Pepsin from Pepsinogens)
- G Cells - Gastrin (hormone)
Secrete Gastrin (Hormone)
Chief Cells -
Produce Pepsinogen and Secrete Lipase.
The food that has been mixed with water and gastric juices, and has been in the GI Tract for more than 2-3 hours is calles
Chime
__________ is an:
- Active Enzyme that comes from Pepsinogens.
- Breaks down proteins into shorter AAs Sequences
Pepsin
____________ is an active enzyme that:
- splits butterfat molecules found in milk (only in babies).
Gastric Lipase
________ curds milk so it will stay in an infants stomach longer
Rennin
_____________ promotes secretion of gastric juices and increases motility of the stomach until the pH reaches 2.0. This is made by _____________
- Gastrin
- G Cells
_____________ decreases gastric secretions
- Secretín
_________________ inhibit stomach emtying
Cholecystokinin
13) ____________ is found in the duodenal loop formed as the duodenum leaves the stomach.
- Produces Enzymes that break down all categories of foodstuffs.
- Tadpole-shaped Gland that extends across the abdomen from its tail (next to the spleen) to its head, which is encircled by the C-shaped duodenum.
- It is Retroperitoneal and lies deep in the greater curvature of the stomach.
Pancreas
Pancreas contains exocrine and endocrine parts:
- The exocrine part of the pancreas produces:
________________ ____________, which consists of :
- Acini
- Ducts that transport Acinar cells
- _______of pancreatic cells (acinar cells) secrete Bicarbonate Ion and Pancreatic Enzymes
- Pancriatic Juice
- 99%
- The endocrine part of the pancreas represents 1% in ___________________, which are
- Alpha and __________ cells and secrete
- ____________ and ___________ hormones that play an important role in _____________ metabolism.
- Pancreatic islets
- Beta
- Insulin and glucagon
- Carbohydrate
- Pancreas secrete about _____ to _____ ml of pancreatic fluid each day.
- Also produces ______________ that breaks into Trypsin
- and produces chymotrypsinogen that breakes into ____________
- 1200 to 1500 ml
- Trypsinogen
- chymotrepsin
14) The second largest gland of the body.
- Its main function is to process the nutrient-rich blood delivered to it
- It has a falciform ligament which attaches it to the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall.
Liver
Liver functional cells are called __________ cells, they form ___________
- Hepatic cells or Hepatocytes
- Bile
Liver is composed of seasame seed-sized structural and functional units called_____________.
Consists of radial cords of ________ cells arranged around a _________ ______, capillaries enlarge to form vessels called ____________ which are lined with __________ reticuloendothelial cells (phagocytes). This remove ________ as ____________ and worn-out _______ cells from the blood as it flows past.
- Lobules
- Hepatic
- Central vein
- sinosoids
- Stellate
- debris
- bacteria
- blood cells
BILE Pathway
- ________ is secreted by the hepatic cells into ______ __________ which channel the bile into small ducts which eventually become the ______ and _______ ________ Ducts.
- Bile
- bile canaliculi
- Right
- Left Hepatic
2- These bile ducts join to form the _______________________________
- Common Hepatic Duct
3- The common hepatic duct and the ___________ duct (from __________) join to form the ________ _____________ Duct.
- Cyliac Duct
- Gallbladder
- Common Bile Duct
4- The common bile duct and the pancreatic duct join to form the _________________ __________ which empties into the duodenum via called __________ _________
- hepaticpancreatic Ampulla
- Duodenal Papilla
Hepatic Blood supply
1- The ___________ artery delivers oxygenated blood from the aorta to the liver.
- Hepatic Artery
2- The ___________ ________ vein carries deoxygenated blood containing nutrients from the digestive tract.
- Hepatic Portal Vein
3- The hepatic vein empties blood from the __________ to the IVC
Liver
4- Blood from the ___________________ vein and the _____________ artery enters into the sinusoids of the ______________ of the liver. This blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the ________ cells and ____________ _______________ cells also known as ___________ cells
- Hepatic Portal
- Hepatic
- lobules
- hepatic cells
- stellate reticuloendothelial cells
- Kepffer's cells
In liver, nutrients are stored or used to make new materials, poisons are stored or detoxified, and the blood is returned to the system.
Each lobule drains into its ______________ vein .
Many central veins join to form the _________ vein which drains into the IVC
- central vein
- hepatic vein
_______ is a salt produced b the hepatic cells, used to ____________ fats into smaller droplets to increase the surface area for __________ to act on fats by braking them down.
- Bile
- emulsify
- lipase
- _____ to ______ ml/day of Bile a day.
- pH of ____ to ____, which is __________
- 800 to 1000 ml
- 7.6 to 8.6
- Alkaline
____________ and _________ sumarize the hormonal and neural mechanism that control Bile secretion. HOWEVER, the major stimulus for enhance Bile secretion, is ___________
- Secretin
- CCK
- Secretin stimulates _________ and the flow of ___________
- CCK stimulates flow of ______________ and release _________ from the _____________
- hepatic cells
- Pancreatic Juice
- Pancreatic Juice
- Bile
- Gallbladder
Functions of the Liver are
- Carbohydrate metabolism - __________
- Lipid Metabolism - ________________
- Protein metabolism - _______________
- Removes _________ , _________ and ______
- Hepatic cells produce ________ for Fat ______
- Stores vitamines ___, ____, _____, _____ (fat soluble) and _______ (water soluble), _______ and _________
- Phagocytosis to remove ___________ and old _____ and _____
- Helps in the activation of vitamin ___
- Glycogen to glucose, etc.
- breaks down fats
- Deaminate proteins
- drogs, hormones and detox poison
- Bile for fat emulsification
- Stores vitamins A,D,E,K and B12. Iron and Copper
- Bacteria and old RBCs and WBCs
- D
15) _________________ is a pear-shaped sac which is used to store and concentrate bile salts.
Gallbladder
Gallbladder main function is to secrete __________ into the _____________ for fat _______________.
- Bile
- Duodenum
- Emulsification
16) ___________ is 1" Diameter.
- The major portion of absorption and digestion occurs in this intestine, about _____%
- It is divided into:
- __________
- __________
- __________
- Small Intestine
- 90%
- Duodenum
- Jujunum
- Ilium
- ________ - originates at the pyloric valve of the stomach - about 10" long.
- ________ - 90% of nutrients absorption. It is about 8 feet long.
- ________ - Joins to the large intestine, absorption of B12. It is about 12 Feet Long
- Duodenum
- Jujunum
- Ilium
- The mucosa of the small intestine contains _____ where intestinal glands are located
- Intestinal Glands called _________ of _________ - secrete digestive enzymes like ______, _________, and __________
- pits
- Crypts of Lieberkuhn
- peptase, lipase and amylase
- Duodenal glands known as __________ ________ - secrete mucus to protect _______
- _______ cells secrete mucus to protect _________ lining from acids.
- Brunner's Glands
- cells
- Goblet
- stomach