What do we mean when we What do we mean when we use the term monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross?
- a monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
- a monohybrid cross produces a single progeny, whereas a dihybrid cross produces two progeny.
- a dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one.
- a monohybrid cross is performed for one generation, whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two generations.
- a monohybrid cross reseals in a 9:3:3:1 ratio whereas a dihybrid cross gives a 3:1 ratio.
c.
How many unique gametes could be produced through independent assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE ?
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 32
- 64
b.
Why did the F1 offspring of Mendel's classic pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties?
- no genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
- each allele affected phenotypic expression.
- the traits blended together during fertilization.
- one phenotype was completely dominant over another.
- different genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
d.
When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a single trait with a heterozygote, what is the chance of producing an offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype?
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
c.
Which of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance?
- pink flowers in snapdragons
- the ABO blood group in humans
- Huntington's disease in humans
- white and purple flower color in peas
- skin pigmentation in humans
e.
Which of the following is false, regarding the law of segregation?
- it states that each of two alleles for a given trait segregate into different gametes
- it can be explained by the segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
- it can account for the 3:1 ratio seen in the F2 generation of mender's crosses
- it can be used to predict the likelihood of transmission of certain genetic diseases within families
- it is a method that can be used to determine the number of chromosomes in a plant
e.
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a recessive human disorder in which an individual cannot appropriately metabolize a particular amino acid. The amino acid is not otherwise produced by humans. Therefore, the most efficient and effective treatment is which of the following?
- feed them the substrate that can be metabolized into this amino acid
- transfuse the patients with blood from unaffected donors
- regulate the diet of the affected persons to severely limit the uptake of the amino acid
- feed the patients the missing enzymes in a regular cycle, such as twice per week
- feed the patients an excess of the missing product
c.
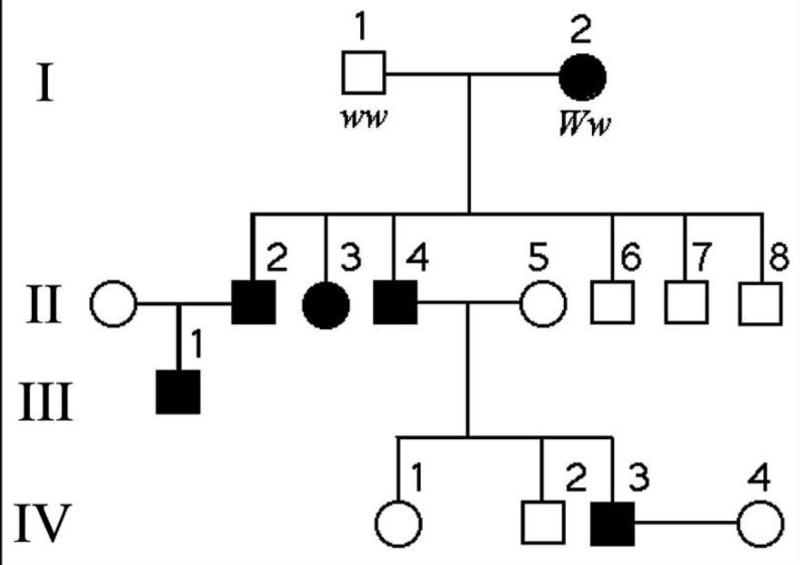
The following question refers to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 above for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle. What is the genotype of individual II-5?
- WW
- Ww
- ww
- WW or ww
- ww or Ww
c.
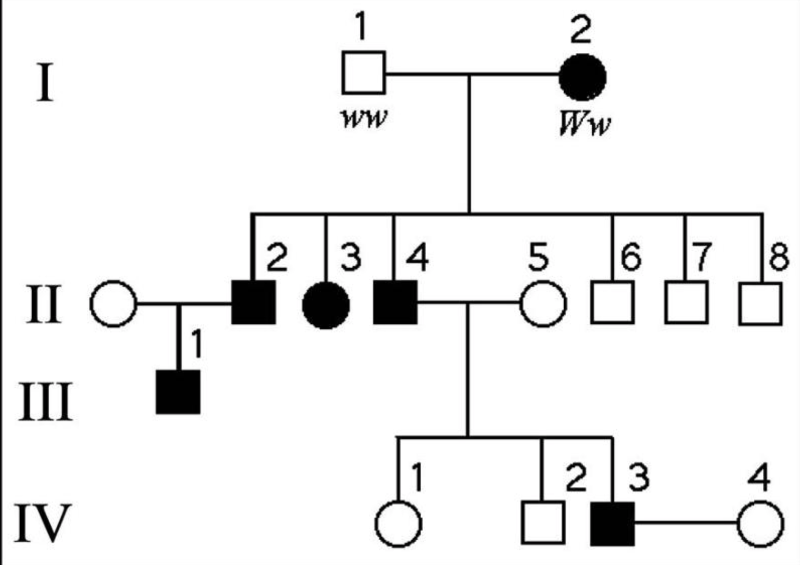
The following question refers to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 above for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle. What is the likelihood that the progeny of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait?
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
c.
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses with the dominant allele, S, have sharp pines, whereas homozygous recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all. The relationship between genes S and N is an example of
- incomplete dominance
- epistasis
- complete dominance
- pleiotropy
- codominance
b.
Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century?
- individuals inherit particular chromosomes attached to genes
- mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and in turn segregate during meiosis
- homologous chromosomes give rise to some genes and crossover chromosomes to other genes
- no more than a single pair of chromosomes can be found in a healthy normal cell
- natural selection acts on certain chromosome arrays rather than on genes
b.
When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result?
- the gene involved is on the Y chromosome
- the gene involved is on the X chromosome
- the gene involved is on an autosome, but only in males
- other male-specific factors influence eye color in flies
- other female-specific factors influence eye color in flies
b.
Which of the following statements is true of linkage?
- the closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them
- the observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a maximum value of 100%
- all of the traits that mendel studied-seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others-are due to genes linked on the same chromosome
- linked genes are found on different chromosomes
- crossing over occurs during prophase II of meiosis
a.
What does a frequency of recombination of 50% indicate?
- the two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes
- all of the offspring have combinations of traits that match one of the two parents
- the genes are located on sex chromosomes
- abnormal meiosis has occurred
- independent assortment is hindered
a.
What is the reason that linked genes are inherited together?
- they are located close together on the same chromosome
- the number of genes in a cell is greater than the number of chromosomes
- chromosomes are unbreakable
- alleles are paired together during meiosis
- genes align that way during metaphase I of meiosis
a.
One possible result of chromosomal breakage is for a fragment to join a non homologous chromosome. What is the alteration called?
- deletion
- transversion
- inversion
- translocation
- duplication
d.
Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions. Which of the following might then occur to make the cancer worse?
- an increase in nondisjunction
- expression of inappropriate gene products
- a decrease in mitotic frequency
- death of the cancer cells in the tumor
- sensitivity of the immune system
b.
What is the source of the extra chromosome 21 in an individual with Down syndrome?
- nondisjunction in the mother only
- nondisjunction in the father only
- duplication of the chromosome
- nondisjunction or translocation in either parent
- it is impossible to detect with current technology
d.
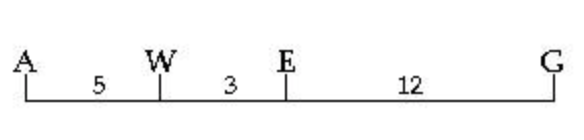
The following is a map of four genes on a chromosome: Figure 15.1. Between which two genes would you expect the highest frequency of recombination?
- A and W
- W and E
- E and G
- A and E
- A and G
e.
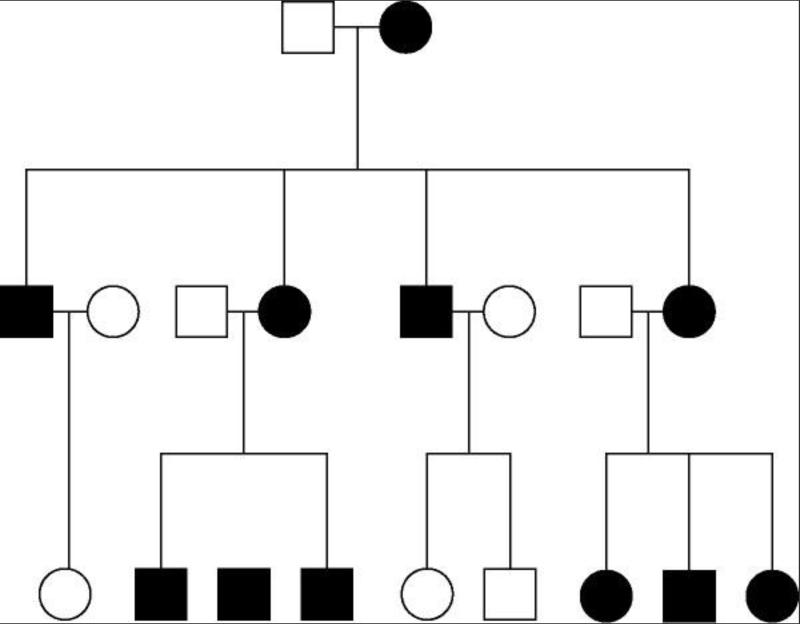
The pedigree in Figure 15.3 shows the transmission of a trait in a particular family. Assume that the individuals represented by unshaded symbols are not carriers. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is most likely
- mitochondrial
- autosomal recessive
- sex-linked dominant
- sex-linked recessive
- autosomal dominant
a.
In his transformation experiments, what did Griffith observe?
- Mutant mice were resistant to bacterial infections.
- Mixing a heat-killed pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living nonpathogenic strain can convert some of the living cells into the pathogenic form.
- Mixing a heat-killed nonpathogenic strain of bacteria with a living pathogenic strain makes the pathogenic strain nonpathogenic.
- Infecting mice with nonpathogenic strains of bacteria makes them resistant to pathogenic strains.
- Mice infected with a pathogenic strain of bacteria can spread the infection to other mice.
b.
In trying to determine whether DNA or protein is the genetic material, Hershey and Chase made use of which of the following facts?
- DNA does not contain sulfur, whereas protein does
- DNA contains phosphorus, but protein does not
- DNA contains nitrogen, whereas protein does not
- A and B only
- A, B, and C
d.
Cytosine makes up 42% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism. Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this sample will be thymine?
- 8%
- 16%
- 31%
- 42%
- it cannot be determined from the information provided
a.
What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding the strands that make up DNA?
- the twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands
- the 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand
- base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands
- one strand is positively charged and the other is negatively charged
- one strand contains only purines and the other contains only pyrimidines
b.
At a specific area of a chromosome, the sequence of nucleotides below is resent where the chain opens to form a replication fork: 3' C C T A G G C T G C A A T C C 5'. An RNA primer is formed starting at the underlined T (T) of the template. Which of the following represents the primer sequence?
- 5' G C C T A G G 3'
- 3' G C C T A G G 5'
- 5' A C G T Y A G G 3'
- 5' A C G U U A G G 3'
- 5' G C C U A G G 3'
d.
Refer to the following list of enzymes to answer the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- helicase
- nuclease
- ligase
- DNA polymerase I
- primase
Removes the RNA nucleotides from the primer and adds equivalent DNA nucleotides to the 3' end of Okazaki fragments
d.
Refer to the following list of enzymes to answer the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- helicase
- nuclease
- ligase
- DNA polymerase I
- primase
Separates the DNA strands during replication
a.
Refer to the following list of enzymes to answer the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- helicase
- nuclease
- ligase
- DNA polymerase I
- primase
Covalently connects segments of DNA
c.
Refer to the following list of enzymes to answer the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- helicase
- nuclease
- ligase
- DNA polymerase I
- primase
Synthesizes short segments of RNA
e.
Refer to the following list of enzymes to answer the following questions. The answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
- helicase
- nuclease
- ligase
- DNA polymerase I
- primase
DNA-cutting enzymes used in the repair of DNA damage
b.
The leading and the lagging strands differ in that
- the leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction
- the leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end
- the lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together
- the leading strand is synthesized at twice the rate of the lagging strand
a.
Which of the following helps to hold the DNA strands apart while they are being replicated?
- primase
- ligase
- DNA polymerase
- single-strand binding proteins
- exonuclease
d.
A particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is AAA. The anticodon on the tRNA that binds the mRNA codon is
- TTT
- UUA
- UUU
- AAA
- either UAA or TAA, depending on first base wobble
c.
What are polyribosomes?
- groups of ribosomes reading a single mRNA simultaneously
- ribosomes containing more than two subunits
- multiple copies of ribosomes associated with giant chromosomes
- aggregations of vesicles containing ribosomal RNA
- ribosomes associated with more than one tRNA
a.
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation in a gene?
- it changes an amino acid in the encoded protein
- it has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein
- it introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA
- it alters the reading frame of the mRNA
- it prevents introns from being excised
c.
A frameshift mutation could result from
- a base insertion only
- a base deletion only
- a base substitution only
- deletion of three consecutive bases
- either an insertion or a deletion of a base
e.
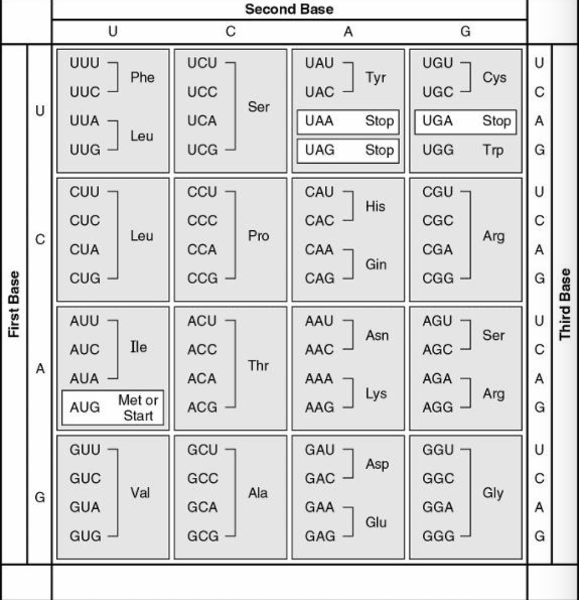
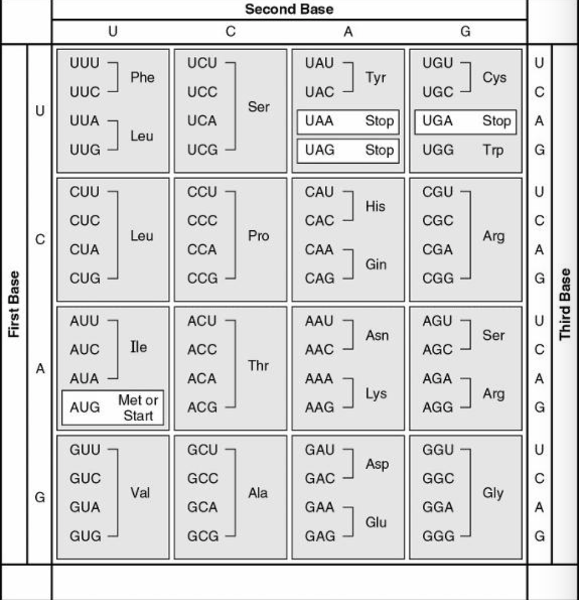
The following questions refers to this table of codons
What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
- met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
- met-glu-arg-arg-glu-leu
- met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
- met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
- met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
d.
The figure represents tRNA that recognizes and binds a particular amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine). Which codon on the mRNA strand codes for this amino acid?
- UGG
- GUG
- GUA
- UUC
- CAU
d.
Hershey and Chase set out to determine what molecule served as the unit of inheritance. They completed a series of experiments in which E. coli was infected by a T2 virus. Which molecular component of the T2 virus actually ended up inside the cell?
- protein
- RNA
- ribosome
- DNA
d.
Replication in prokaryotes differs from replication in eukaryotes for which of the following reasons?
- prokaryotic chromosomes have histones, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes do not
- prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes have many
- the rate of elongation during DNA replication is slower in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes
- prokaryotes produce Okazaki fragments during DNA replication, but eukaryotes do not
b.