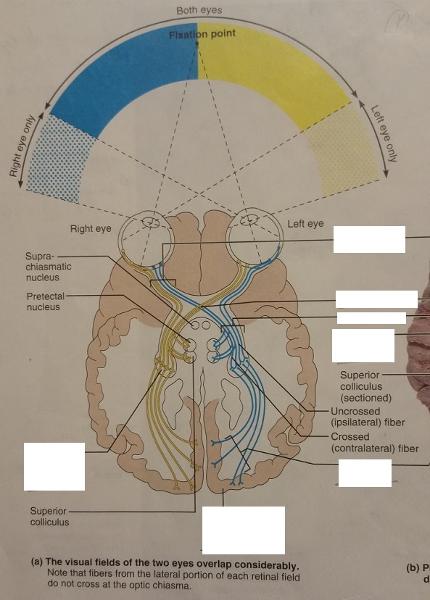
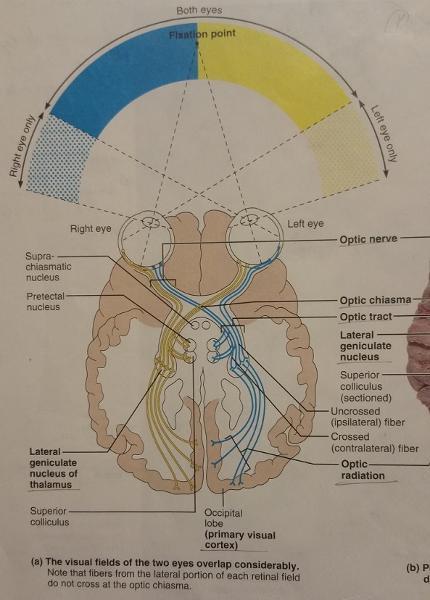
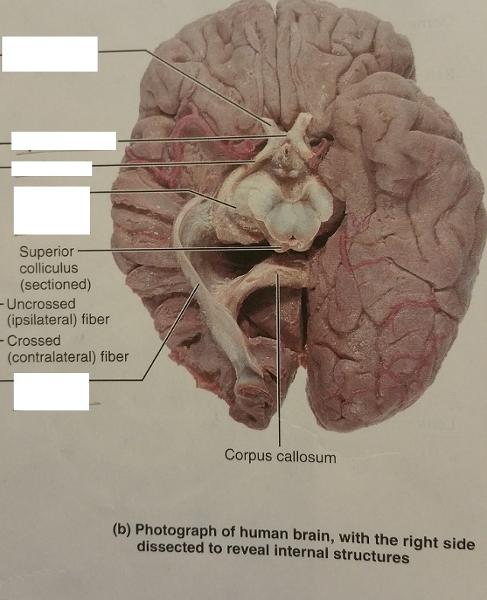
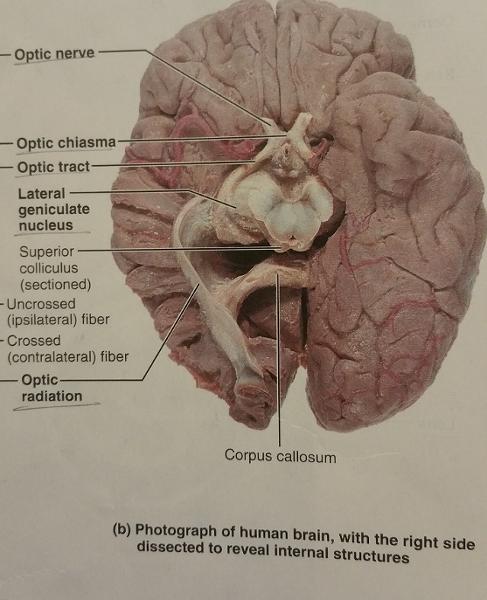
The axons of the ganglion cells of the retina converge at what aspect of the eyeball and exit from the eye at what nerve?
Converge at the posterior aspect of the eyball and exit the eye at the optic nerve.
The fibers from the medial side of each eye cross over to the opposite side at which eye feature?
Optic chiasma
The fiber tracts formed after the cross-over point of the optic chiasma are called what?
Optic tracts
Each optic optic tract contains fibers from the lateral side of the eye on the (same/opposite) side and from the medial side of the eye on the (same/opposite) side.
Same, opposite
The optic tract fibers synapse with neurons in which feature of the thalamus?
Lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
The neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus that synapse with the optic tract fibers form what radiation?
Optic radiation
The optic tract fibers after synapsing with neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, whose axons form the optic radiation, terminates in which cortex of which lobe?
Terminates in the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe.
1. The optic fiber tracts after terminating in the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe then synapse with what type of neurons?
2. Which type of interpretation then occurs?
1. Cortical neurons
2. Visual interpretation
Determine what effects lesions in the following areas would have on vision.
- In the right optic nerve:
- Through the optic chiasma:
- In the left optic tract:
- In the right cerebral cortex (primary visual cortex):
- In the right optic nerve: Right monocular vision loss (i.e. complete blindness for right eye)
- Through the optic chiasma: Bitemporal hemianopia (i.e. tunnel vision)
- In the left optic tract: Right homonymoas hemianopia (i.e. vision loss in right hemispheres for both eyes)
- In the right cerebral cortex (primary visual cortex): Left homonymoas hemianopia with macular sparing