Muscular System
Muscular System
How do muscles produce movement?
By contracting in response to nervous stimulation
True/False
Muscle contraction results from the sliding together of ACTIN & MYOSIN FILAMENTS within the muscle cell or fiber.
~TRUE~
True/False
Each muscle cell is made up of MYOFIBRILS,which in turn are made up of still smaller units called SARCOMERES.
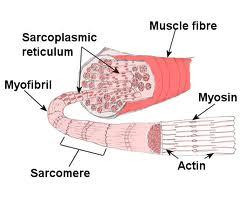
~TRUE~
What must be present in order for a muscle cell to contract?
Calcium & Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
What causes the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Nervous stimulation from the motor neuron.
__1_ ions attach to inhibitory _2__ on the _3__ _4__ within the cell, moving them aside so that _5__-__5_ can form between _6__ and _7__ _8__. Using energy supplied by _9__, the _10__ slide together to produce _11__.
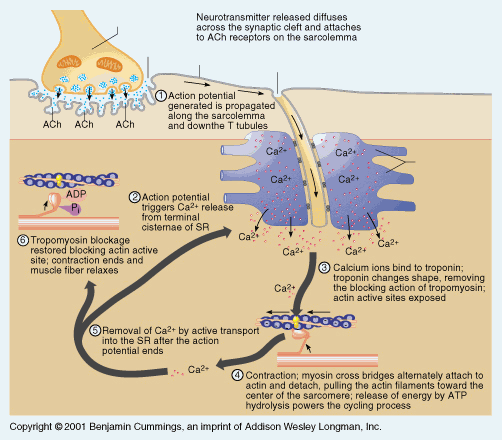
1. Calcium 9. ATP
2. Proteins 10. Filaments
3. Actin 11. Contraction
4. Filaments
5. Cross bridges
6. Actin
7. Myosin
8. Filaments
Skeletal muscle which make up the muscular system, are also called
Voluntary muscles- because they are under conscious control.
True/False
Skeletal muscles work in pairs
~TRUE~
The muscle that executes a given movement is the _1__, whereas the muscle that produces the opposite movement is the _2__. Other muscles known as _3__ may work in cooperation w/the prime mover.
1. Prime mover
2. Antagonist
3. Synergist
True/False
Muscles can be classified according to the movements they elicit.
~True~
There are flexors & extensors.
Flexors-
Extensors-
reduce the angle at the joint.
increase the angle.
Abductors
Draw a limb away from the midline (or body)
Adductors
Return the limb back toward the body (adding to the body).
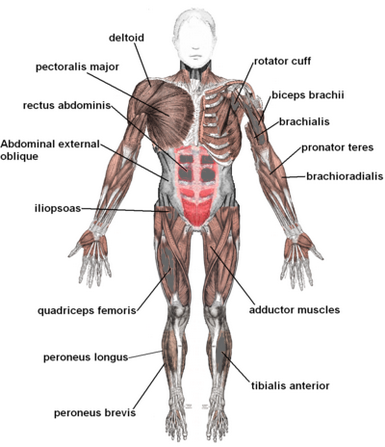
Diagram of the major contour muscles of the body. Study the names,notice their name is related to location & functions.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
NERVOUS SYSTEM
The Nervous system consists essentially of the
BRAIN, SPINAL CORD & THE NERVES
The Nervous system is broken into 2 categories the
CNS & the PNS
Central nervous system & Peripheral nervous system
CNS consists of
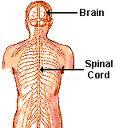
Brain & spinal cord
PNS consists of
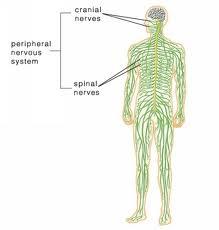
all the nerves & their branches that transmit information to & from the CNS.
The Nervous system enables us to
perceive many of the changes that take place in our external & internal environments & to respond to those changes (seeing, hearing, tasting, smelling & touching are examples of perception).
The Nervous system also enables us to
think, reason, remember & carry out other abstract activities.
The Nervous system makes possible body movements by
skeletal muscles, by supplying them w/nerve impulses that cause contraction.
The Nervous system works closely with the
endocrine glands, correlating & intergrating body functions such as digestion & reproduction.
True/False
All actions of the nervous system depend on the transmission of nerve impulses over neurons, or nerve cells, the functional units of the nervous system.
~TRUE~
What is the functional unit of the Nervous system?
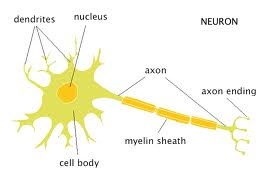
Neuron (nerve cell).
The main parts of a neuron are the
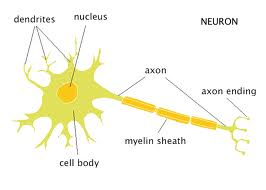
cell body, axon & dendrites.
Dendrites transmit the impulse ___ the cell body.
Towards
The word dendrites have the letter "T" in it, *think of "T for to" like to the cell body."
Axons transmit the impulse ___ from the cell body.
Away
*think of "A- A for Away from the cell body."
Sensory (afferent) neurons transmit nerve impulses ___ the CNS.
Toward
Motor (efferent) neurons transmit nerve impulses ___ from the CNS, toward the effector organs such as muscles, glands & digestive organs.
Away
Motor (efferent neurons) transmit nerve impulses AWAY from the CNs towards
effector organs such as the muscles, glands & digestive organs.
The major parts of the brain are the
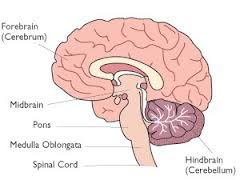
Cerebrum
* associated w/movement & sensory input
Cerebellum
* responsible for muscular coordination, including balance.
Medulla oblongata
* Controls many vital funcitons such as respiration & heart rate.
Cerebrum is associated with
movement & sensory input
Cerebellum is responsible for
muscular coordination, including balance.
Medulla oblongata
Controls many vital funcitons such as respiration & heart rate.
How long is the spinal cord?
Approximately 18 inches long.
True/False
The spinal cord extends from the base of the skull (foramen magnum) to the 1st or 2nd lumbar vertebrae (L1 or L2).
~True~
How many pairs of spinal nerves exit the spinal cord?
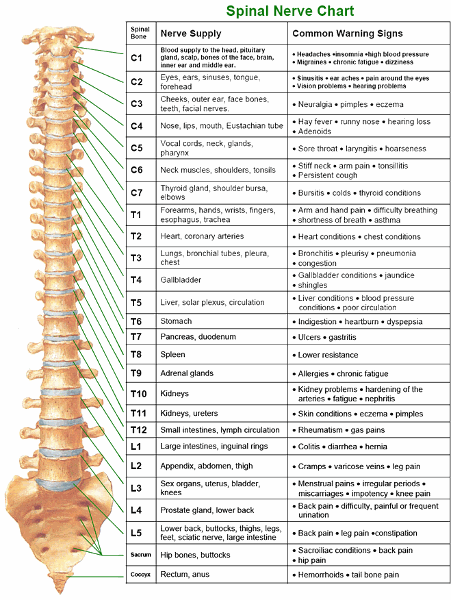
31
Simple (spinal) reflexes are those in which nerve impulses travel through the
spinal cord only and do not reach the brain.
Hesi Hint
Most reflex pathways involve impulses traveling
to & from the brain in ascending & descending tracts of the spinal cord.
Hesi Hint
Sensory impulses enter the _1__ of the spinal cord, & motor impulses leave through the _2__ of the spinal cord.
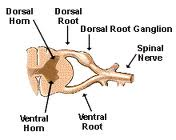
1. Dorsal horns
2. Ventral horns
Thank you for viewing my notecards, I hope you find them helpful. I've added more photos, diagrams & visual aids than the book (hesi study guide) has to offer, hope they help. :-)
~Post notecards of your own for others to benefit from as well~