those one that lie around the body's center of gravity
Axial Skeleton
bones of the limbs or appendages
Appendicular Skeleton
which cover the one ends at movable joints
Articular cartilage
smooth and homogenous
compact bone
Spongy bone
composed of small trabeculae of one and lots of open space
are much longer than they are wide
Long bone
typically cube shaped, contain more spongy bone than compact bone
Short bone
generally thin, with two wafer/like layers of compact bone
Flat bone
ones that do not fall into one of the preceding categories
irregular bone
special types of short bones formed in tendons
sesamoid bones
shaft
Diaphysis
fibrous membrane covering
Periosteum
the end of the long bone
epiphysis
compact bone appears to be dense and homogenous
Trabeculae
Framework for support and movement
Skeletal System
Skeletal System Stores
minerals and lipids
Tissue that the skeletal system is made up of
connective tissue Bone & Cartilage
Main components Skeletal System are
Bone & Cartilage
INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL TEXTURES OF BONE
Compact & Spongy (cancellous)
composed of small trabeculae of one and lots of open space it is the inside layer of compact bone
spongy bone
runs parallel to the long axis of the bone and carries blood vessels, nerves and lymph vessels through the bony matrix
Central(haversian) canal
are living tissue
bones
a central canal and all the concentric lamellae surrounding it are referred to as
an osteon
cells living in bone
OSTEOCYTES cells
ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR BONE GROWTH AND CHANGES IN THE SHAPE OF BONES
OSTEOCYTES
Calcium from Microcrystallinen, non living matrix is very dense/hard calcium crystals called
Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite is just a
fancy name for bone
tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the first lamella and then from lamella to lamella.
Canaliculi
We look at bone based on how they
grow
when the body produces calcium in areas the a tendon irritates the area this is how you get
sesamoid bones
SHAFT OF A LONG BONE
diaphysis
the end of the long bone
epiphyis
WHEN DESCRIBING SECTIONS OF A LONG BONE WHEN TALKING ABOUT ENDS OF THE LONG BONE
proximal epiphysis distal epephysis
epiphsyatal line that separate spongy and compact bone
growth plate
hollow section in the diaphysis is called
the medullary cavity
is found in the medullary cavity
yellow bone marrow
pointed, pen-like
styloid
-Axial
-Protects vital organs; hematopoiesis
RIBS
1. Diaphysis
2. Epiphysis
3. Periosteum
4. Endosteum
5. Articular Cartilage
6. Epiphyseal Line
PARTS OF LONG BONES
supports the skull
-The atlas (1st vertebra)
support for trunk
-Bones in legs and pelvis provide
-Oval-shaped condyle fits with elliptical cavity of another bone
-Flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction
-ex: Fingers
Condyloid Joint
-Nearly flat/slight curved surface
-Sliding or twisting of bones
-ex: Wrist and Ankle
Gliding Joint
What is a movable joint?
A joint that allows the body to move forward...
A plate near the ends of long bones.
What is the epiphyseal plate?
The junction of two bones
articulation
a projection adjacent to a condyle
epicondyle
a narrow, slitlike opening through a bone
fissure
shaped like a shallow socket
glenoid
a club-shaped or hammer-shapped process
malleolus
Types of cartilage growth? (2 types)
1. appositional growth 2. interstitial growth
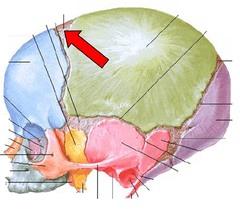
The skull is composed of two sets of bones. These are called?
1. The cranium 2. the facial bones
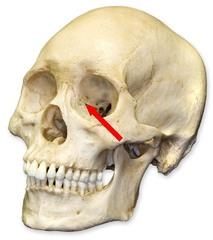
An opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass.
Supraorbital forameN
The smooth area between the eyes?
Glabella
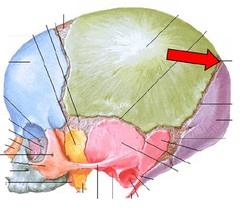
Posterolateral to the frontal bone, forming sides of cranium.
Parietal Bone
Midline articulation point of the two parietal bones.
Sagittal suture
Inferior to the parietal bones on lateral skull.
Temporal bone
A bridgelike projection joining the zygomatic bone anteriorly. Together these 2 bones form the zygomatic arch.
Zygomatic process
Rounded depression on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process, forms the socket for the mandibular condyle, the point where the mandible (lower jaw) joins the cranium.
Mandibular fossa
Point of articulation of parietals with frontal bone.
Coronal suture
a prominent, rounded epiphysis
HEAD
a narrow, prominent ridgelike projection
CREST
-Convex surface fits with concave surface of another bone
-Flexion or extension
-ex: Elbow and Knee
Hinge Joint
-Cylindrical surface of one bone fits in a ring formed by another bone/ligament
-Rotation
-ex: Neck
Pivot Joint
Both concave and convex bone surface
-Flexion, extension, adduction, abduction
SADDLE JOINT
Head of bone fits into socket of another
-Rotation
-ex: Shoulder and Hip
Ball and Socket Joint
Skeletal muscles attach to bones via
tendons
-Axial
-Protect spinal chord
Vertebrae
Are ribs axial or appendicular?
Axial
What is the primary inorganic component that makes up the skeletal system?
Calcium phosphate
the line of union in an immovable articulation
suture
an indentation of v-shaped depression
notch
found on joints
hyaline cartilage
What is the membrane surrounding individual bones? It's called
periosteum
peri means
around
THE SKULL IS THE BODY'S MOST COMPLEX BONEY STRUCTURE IT IS FORMED BY THE?
cranial bones and facial bones
cranial bones protect
the brain
facial bones protect the ??
Facial Bones also allow us to present our feelings to the world using facial??
eyes, muscles
only bone that moves inside the skull is the
mandible
the irregular edges of the bones interlock and are united by very short connective tissue fibers
sutures
THE CORONAL, SAGITTAL SQUAMOUS AND LAMBDOID SUTURES CONNECT CRANIAL BONES ARE
THE MAJOR SKULL SUTURES
The cranium is divided into two major areas, what are these areas called?
cranial vault & cranial floor
FORMING THE SUPERIOR,LATERAL AND POSTERIOR WALLS OF THE SKULL
cranial vault
FORMING THE SKULL BOTTOM
cranial floor
internally the cranial floor has three distinct concavities
ANTERIOR MIDDLE AND POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSAE
FORMING SIDES OF THE CRANIUM
parietal bone
FORMS FOREHEAD
frontal bone
inferior to the parietal bone on the lateral skull
temporal bone
ARMS OF GLASSES
temples
FORMS THE LATERAL PORTIONS OF THE SKULL
TEMPORAL bone
POSTERIOR BONE OF THE CRANIAL FORMS FLOOR AND BACK WALL OF THE SKULL
occipital bone
cheek bone
zygomatic bone
FORMS THE UPPER JAW BONE AND PART OF THE ORBITS
maxilla
bone that flaps when you talk
mandible
means the butterfly
sphenoid bone
means crying
lacrimal bone
Provides sturdy support with some resilience or "give"
hyaline cartilage
MAXILLARY, SPHENOID ETHMOID AND FRONTAL AIR CAVITIES
PARANASAL sinuses
LOCATED IN THE THROAT SERVES AS A POINT OF ATTACHMENT FOR TONGUE AND NECK MUSCLES
hyloid
bone fractured from strangulation
hyloid bone
Four pairs, named for the bones they reside in.
Frontal sinus,Ethmoid sinus, Sphenoid sinus, Maxillary sinus
Paranasal bones
24 bones stacked in the
vertebral column
7 BONES C1-C7
cervical vertebrae
12 BONES IN MID BACK t1-t12
thoracic region
extending from the skull to the pelvis body's major axial support
vertebral column
in the vertebral column they're 24 single bones called? two fused bones called the ?? and the ??
vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
5 BONES LOWER BACK L1-L5 IS CALLED
THE LUMBAR REGION
ONCE HAD 5 BONES NOW FUSED TOGETHER MAKING ONLY 1 BONE
THE SACRUM
4 BONES FUSED TOGETHER TO MAKE ONE BONE
COXXYX
IN A VERTEBRA THE PART THAT BARES WEIGHT IS CALLED
THE BODY
IN A VERTEBRA THE HOLLOW PART IN THE CENTER WHERE THE SPINAL CORD GOES THROUGH IS CALLED
VERTEBRAL ARCH
is a part of the vertebra that connects to the spinous process.
THE LAMINA
From a lateral perspective, the posterior extensions directly off the vertebral body and are located on each side.
PEDICAL
a HOLE IN A BONE IS CALLED A
FORAMINA
cervical VERTEBRAE SMALL AND LIGHT AND THE VEREBRAL FORAMEN IS ?? IN SHAPE
TRIANGULAR
A FLAT JOINT
FACET
What is located within the intervertebral joints and are tightly bound to adjacent vertebral bodies for spinal stability but allow for flexibility and movement of the vertebral column?
intervertebral disks
The joints located along a portion of the vertebral column and articulates with the ribs to the thoracic vertebra.
costal joints
The joints found between the vertebral bodies.
intervertebral joints
Where was the term "atlas" for C1 derived from?
a Greek god who bore the world upon his shoulders
What is the distinquishing feature of C1?
t has no body but a thick arch of bone called the anterior arch which includes a small anterior tubercle
What is another term used to describe the second vertebra, C2?
axis
What is the most distinctive feature of C2?
dens; odontoid process
How many divisions are in the vertebral canal?
5; cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx
What is the vertebral column?
a complex succession of many bones called vertebrae
VISIBLE THROUGH THE SKIN
C-7
Where does the rotation of the head primarily occur?
between C1 and C2
C1 is the most bulky and solid part. What is it's purpose
support the weight of the head and assist in rotation of the head
What acts as a pivot for rotation of the head?
dens
What extends posteriorly from the vertebral body
RING OR ARCH
much more flexible than hyaline; tolerates repeated bending better; external ear and epiglottis
elastic cartilage
Where does the rotation of the head primarily occur?
between C1 and C2
The vertebral body is a thin ring of dense cortical bone
Vertebrae
compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae T-1- T-12
THORACIC VERTEBRAE
is derived from the Latin word “lumbus,” meaning lion, and arns its name. It is built for both power and flexibility L-1-L-5
LUMBAR VERTABRA
THE BONY THORAX IS COMPOSED OF THE STERNUM, RIBS,AND THORACIC VERTEBRAE
THORACIC CAGE
the largest and strongest in the movable part of the spinal column.
The regions of the spine consist of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral.
LUMBAR REGION
rib articulates with the vertebral column Costovertebral MEANS
RIB JOINTS
C-1 IS ALSO KNOWN AS THE
ATLAS
C-2 IS KNOWN AS THE
AXSIS
C1 SPINS ON THE
DENS
HOW MANY RIBS
24 12 ON EACH SIDE
HOW MANT PAIRS OF RIBS ARE THERE
12 PAIR
RIB PAIRS 1-7
TRUE RIBS
RIB PAIRS 8-12
FALSE RIBS`
RIB PAIRS 11-12
FLOATING RIBS
ATTACH TO THE VERTEBRA AND ATTACH TO THE BREAST BONE
TRUE RIBS
HOW MANY TRUE RIBS DO YOU HAVE
14
HOW MANY FALSE RIBS DO YOU HAVE
10
ATTACH TO THE VERTEBRA AND DO NOT ATTACH
FALSE RIBS
A TYPICAL FLAT BONE IS THE RESULT OF THE FUSION OF THREE BONES..
THE STERNUM
FORMS THE BULK OF THE STERNUM
GLADIOLUS AKA BODY
which cover the one ends at movable joints
Articular cartilage
Provides sturdy support with some resilience or "give"
Hyaline Cartilage
THE POINT WHERE THE STERNAL BODY AND XIPHOID PROCESS FUSE LIES AT THE LEVEL OF THE NINTH THORACIC VERTEBRA
XIPHISTERNAL JOINT
tolerates repeated bending
ex. external ear and epiglottis
Elastic cartilage
Round or oval opening through a bone
Foramen
Shallow depression or groove such as that on the bony surface
Sulcus
Air-filled cavity
Sinus
Large, irregularly shaped projection
Trochanter
Raised area on or above a condyle
Epicondyle
Projection or prominence
Process
smooth, nearly flat articular surface
facet
great tensile strength and can withstand heavy compression
Fibrocartilage
a thin area of hyaline cartilage that provides for longitudinal growth of the bone during youth
epiphyseal plate
thin bone covering the epiphyseal plate after the growth stops
epiphyseal line
compact bone appears to be dense and homogenous
Trabeculae
lacunae arranged in concentric circles around the central canal
Circumferential lamellae
a central canal and all the concentric lamellae surrounding it
an osteon
tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the first lamella and then from lamella to lamella.
Canaliculi
canal that runs into the compact bone and marrow cavity form the periosteum at right angles of the shaft.
Perforating(Volkmann's) canal
immovable joints
synarthroses
slightly movable joints
amphiarthroses
freely movable joints
Diarthrases
bones joined by fibrous tissue
Fibrous joint
the irregular edges of the bones interlock and are united by very short connective tissue fibers
suture
the articulating bone ends are connected by a plate or pad of cartilage
cartilaginous joints
the bones are connected by a broad,flat disc of fibrocartilage
symphyses
the bony portions are united by hyaline cartilage
synchondroses
those in which the articulating bone ends are separated by a joint cavity containing synovial fluid
synovial joint
a HUMAN FETUS ABOUT TO BE BORN HAS HOW MANY BONES
275
are soft spots on a baby's head which, during birth, enable the bony plates of the skull to flex, allowing the child's head to pass through the birth
FONTANELS
ANTERIOR FONTANELLES ARE LOCATED BETWEEN THE
2 PARIETAL BONES AND THE FRONTAL BONE
THE SPHEROIDAL FONTANEL IS LOCATED BETWEEN THE
FRONTAL BONE, SPHEROIDAL BONE AND THE TEMPORAL PARIETAL BONE
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
Acromial (lateral) end
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
Medial (sternal) end
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
Acromion
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
Glenoid cavity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
Lateral Angle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # 4
Lateral border
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
Inferior angle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
Medial border
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
Infraspinous fossa
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
Spine of scapula
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
Supraspinous fossa
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
Superior angle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME
MASTOID FONTANEL
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME
POSTERIOR FONTANEL
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME
SPHENOIDAL FONTANEL
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME
ANTERIOR FONTANEL
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME
LACRIMAL
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
SCAPULA
Acromion
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
SCAPULA
Glenoid cavity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
SCAPULA
Lateral angle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
SCAPULA
Lateral border
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
Inferior angle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
SCAPULA
Medial border
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11
Coracoid process
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
SCAPULA
Superior angle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12
SCAPULA
Subscapular fossa
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #13
SCAPULA
Suprascapular notch
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
humerus
Greater Tubercle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
humerus
Lesser Tubercle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
humerus
Deltoid Tuberosity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
humerus
Radial fossa
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
humerus
Capitulum
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
humerus
Trochlea
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
Medial epicondyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
humerus
Coronoid fossa
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
humerus
Anatomical neck
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
humerus
Head of Humerus
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
humerus
Greater Tubercle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
humerus
Deltoid Tuberosity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
Trochlea
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
humerus
Medial epicondyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
humerus
Anatomical neck
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
humerus
Head of Humerus
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11
humerus
Lateral epicondyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12
humerus
Olecranon fossa
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
FEMUR
Head
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
FEMUR
Lesser Trochanter
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
FEMUR
Medial epicondyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
FEMUR
Patellar surface
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
FEMUR
Lateral epicondyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
FEMUR
Greater Trochanter
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
Head
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
FEMUR
Lesser Trochanter
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
FEMUR
Medial epicondyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
FEMUR
Lateral epicondyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
FEMUR
Greater Trochanter
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
FEMUR
Lateral condyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
FEMUR
Medial condyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
FEMUR
Intercondylar notch
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
FEMUR
neck
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
TIBIA BONE ANTERIOR
Medial condyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
Medial malleolus
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
TIBIA
Anterior crest
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
TIBIA
Tibial tuberosity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
TIBIA
Lateral condyle
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
TIBIA
Intercondylar eminence
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
fibula
Head
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
fibula
Lateral Malleolus
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #A
Carpals
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #B
Metacarpals 1 through 5
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #C
Phalanges
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
Distal phalanx
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
Middle phalanx
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
Proximal phalanx
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #A
Phalanges
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #B
Metatarsal bones 1 through 5
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #C
Tarsal bones (7)
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
Talus (ankle)
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
Calcaneus (heel)
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
radius
Head
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
radius
Neck
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
radius
Styloid process of radius
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
radius
Radial tuberosity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
radius and ulna
Olecranon process
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
radius and ulna
Coronoid process
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
radius and ulna
Head of ulna
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
radius and ulna
Styloid process of ulna
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
radius and ulna
Trochlear notch
Medial view of left os coxa
Formed by the fusion of three bones:
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
Illium
Formed by the fusion of three bones:
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
Ischium
Formed by the fusion of three bones:
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
3) Pubis
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
Iliac crest
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
Anterior superior iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
Anterior inferior iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
Acetabulum
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
5) Pubis
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
Obturator foramen
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
Ishial ramus
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
Ishial Tuberosity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
Ishial spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
Greater sciatic notch
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11
Posterior inferior iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12
Posterior superior iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
Posterior Superior Iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
Posterior Inferior Iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
Greater sciatic notch
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
Ischial spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
Ischial tuberosity
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
Ischial ramus
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
Obturator foramen
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
Pubis
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
Anterior inferior iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
Anterior superior iliac spine
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11
Iliac crest
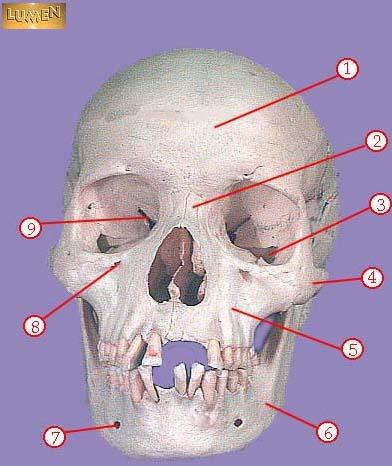
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
frontal bone
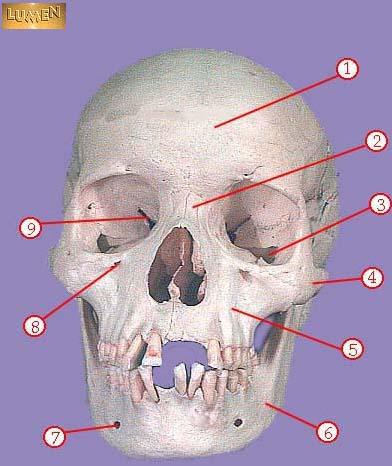
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
nasal bone
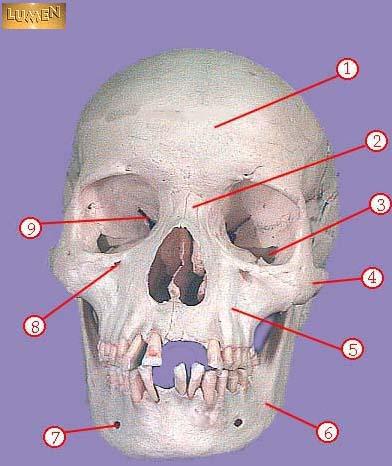
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
inferior orbital fissure
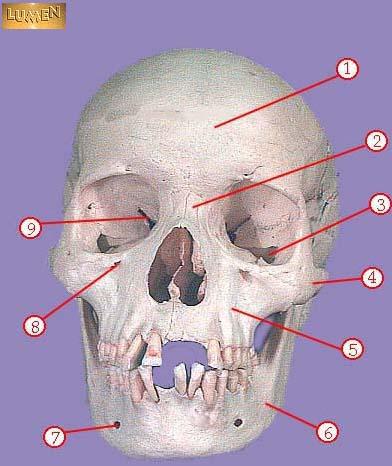
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
zygomatic
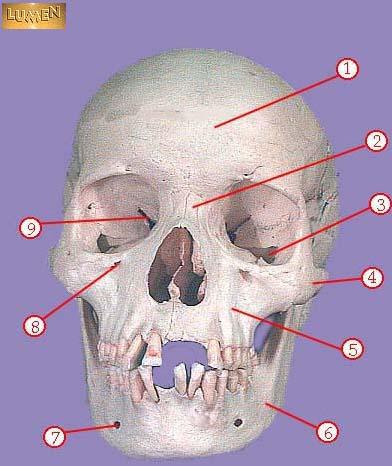
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
maxilla
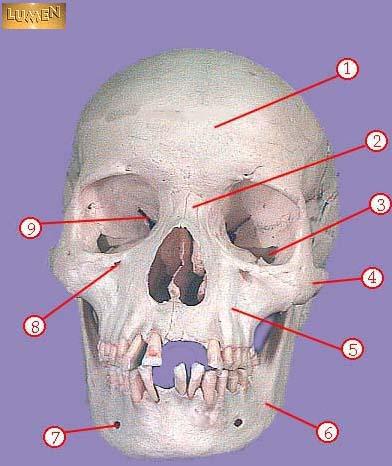
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
mandible
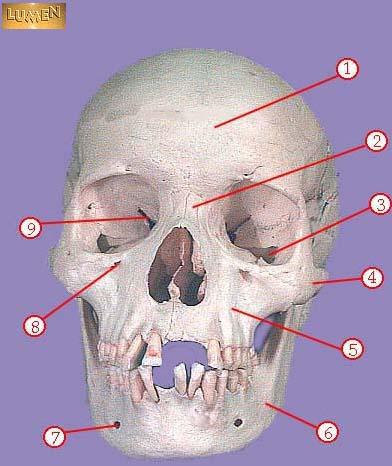
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
mental foramen
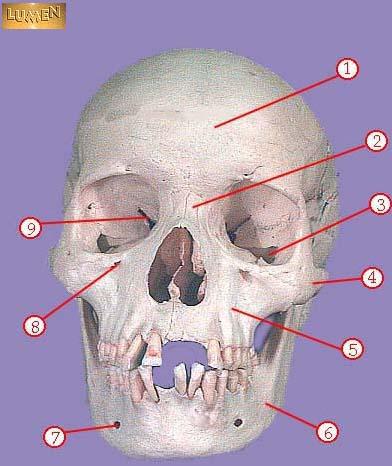
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
infraorbital foramen
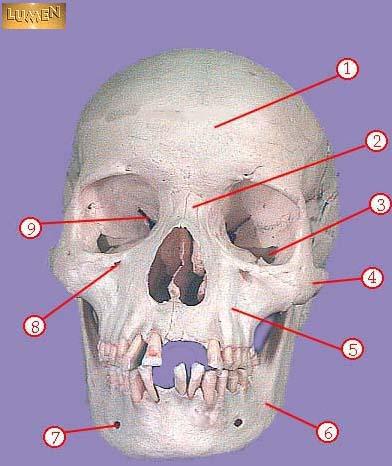
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
superior orbital fissure
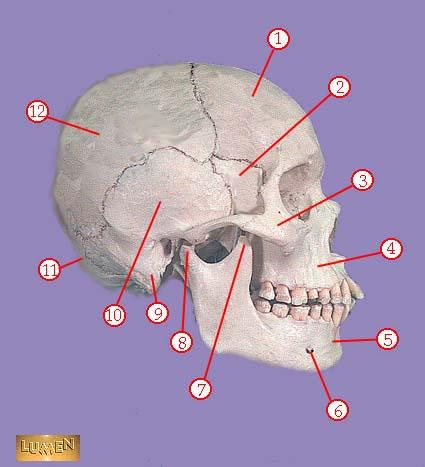
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
frontal bone
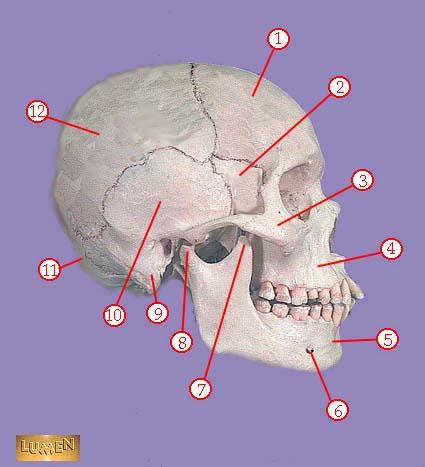
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
greater wing of sphenoid bone
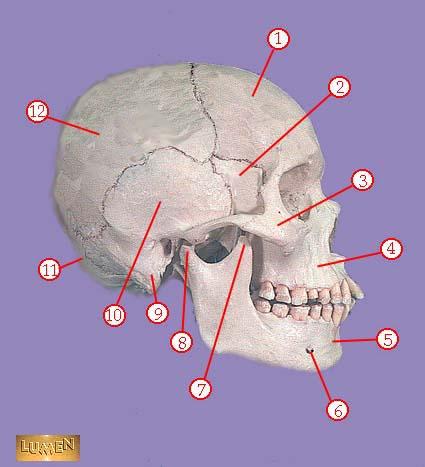
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
zygomatic bone
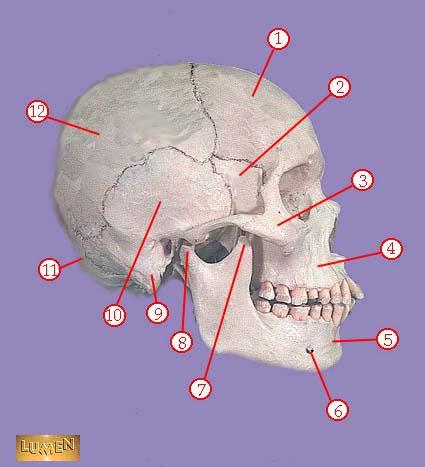
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
maxilla
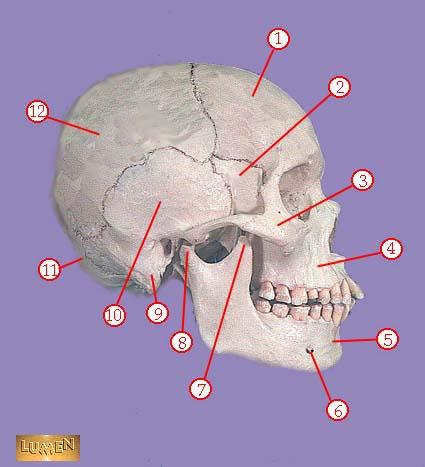
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
mandible
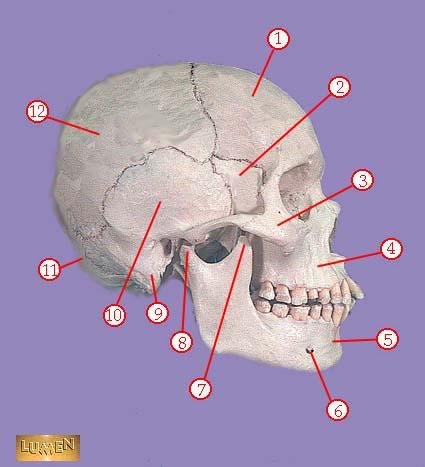
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
mental foramen
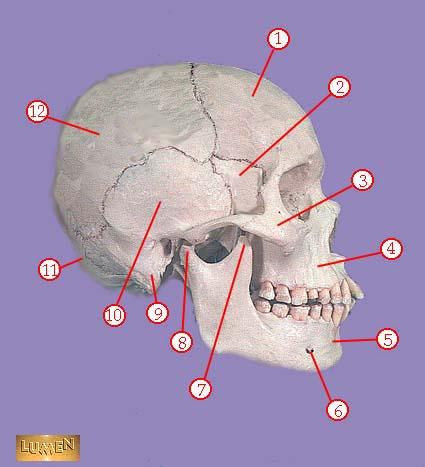
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
coronoid process of mandible
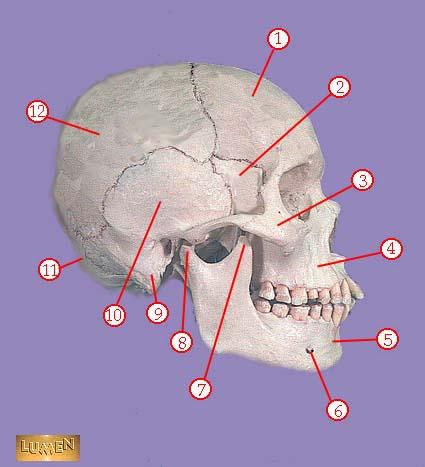
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
head of mandible
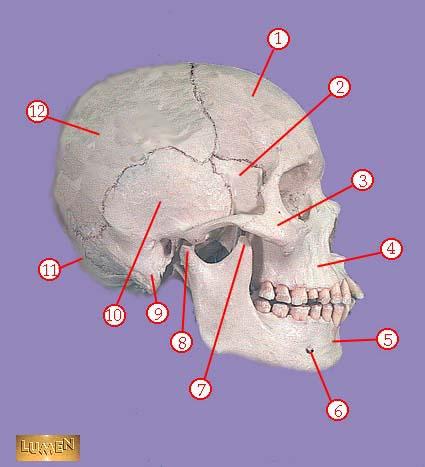
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
mastoid process
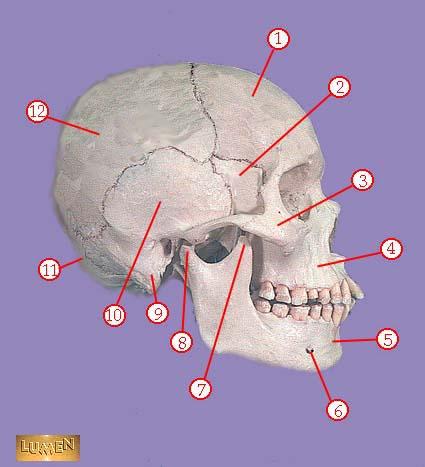
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
temporal bone
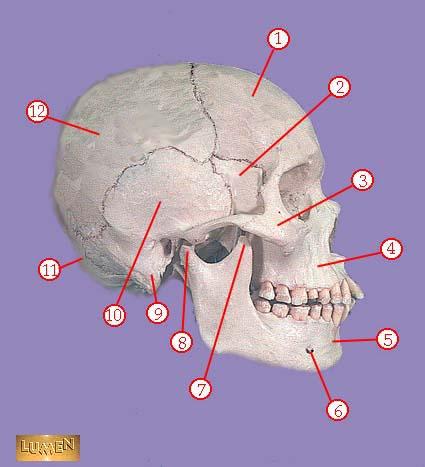
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11
occipital bone
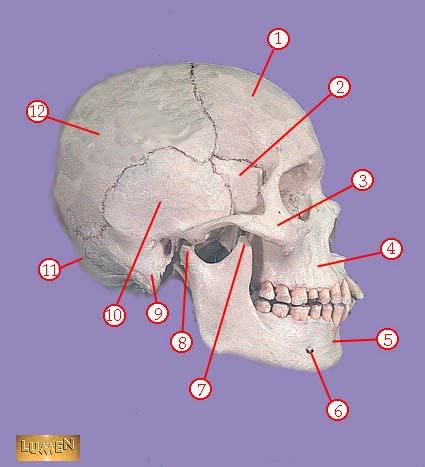
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12
parietal bone
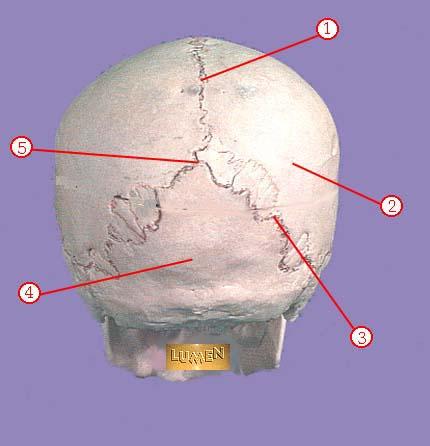
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
sagittal suture
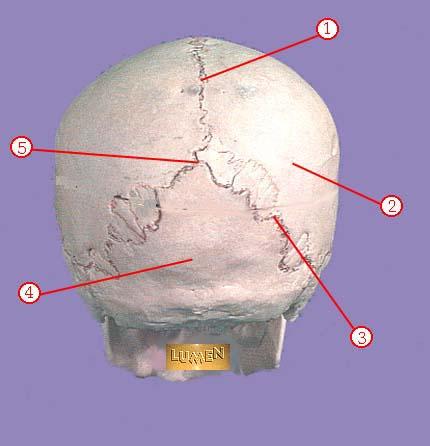
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
parietal bone
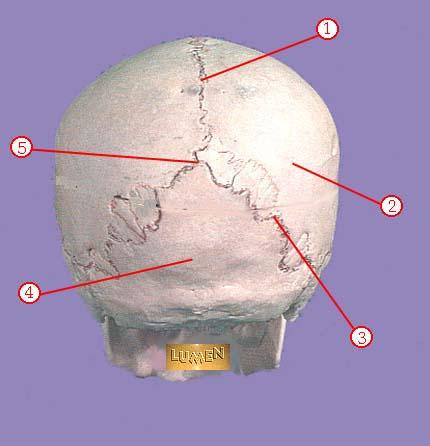
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
lambdoidal suture
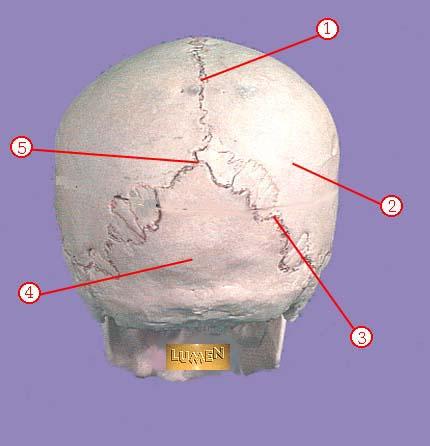
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
occipital bone
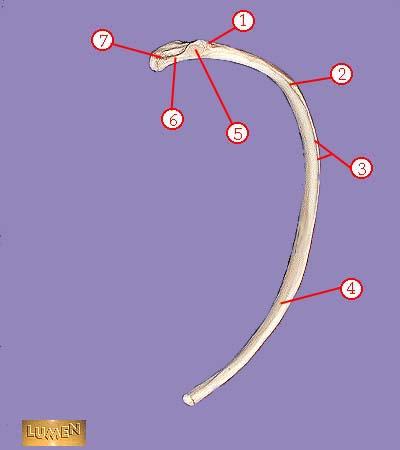
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
tuberosity
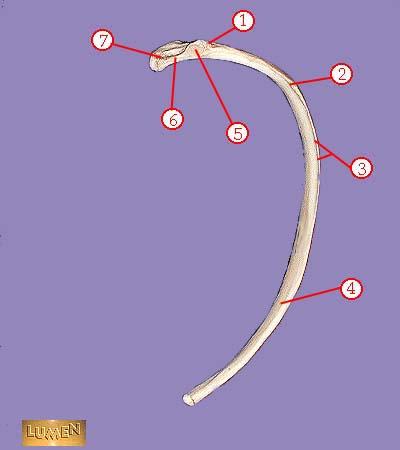
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
angle
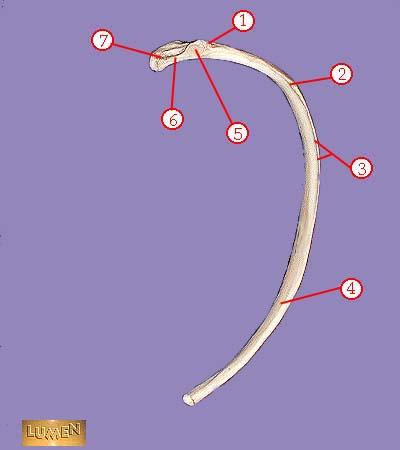
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
subcostal groove
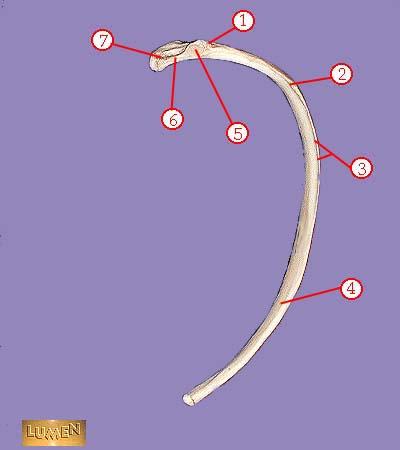
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
body or shaft
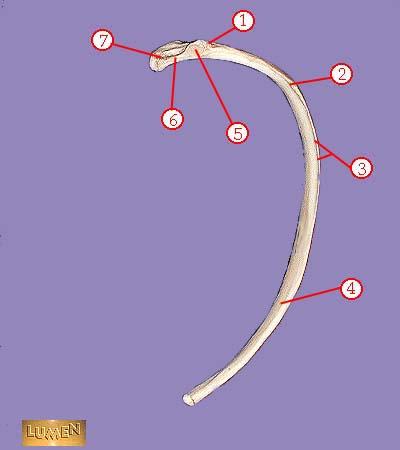
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
articular part of tuberosity
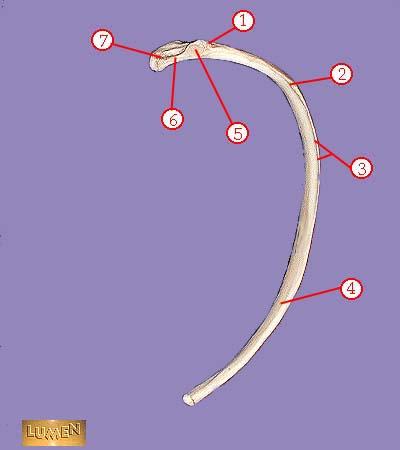
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
neck
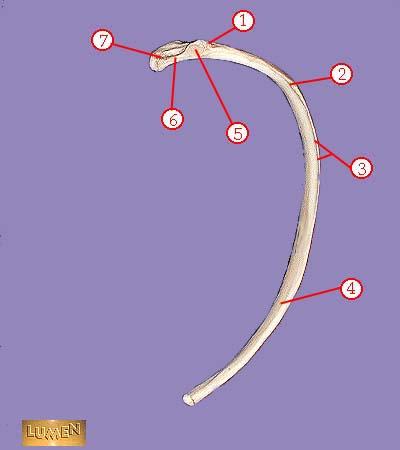
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
head
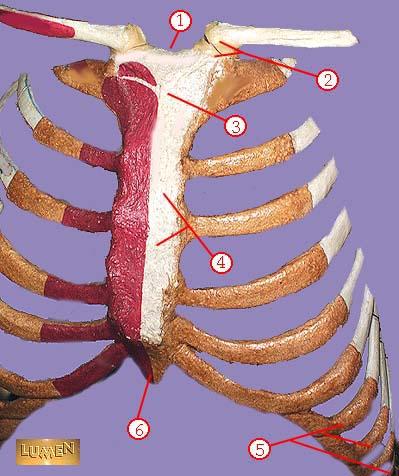
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
sternal notch
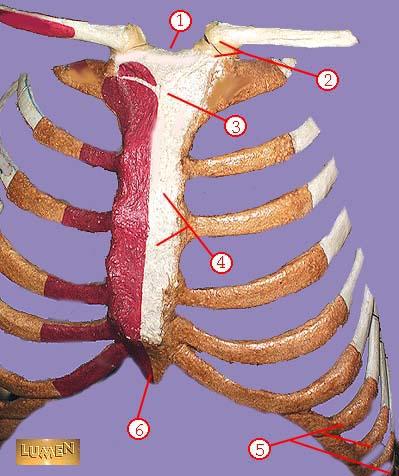
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
sternoclavicular joint
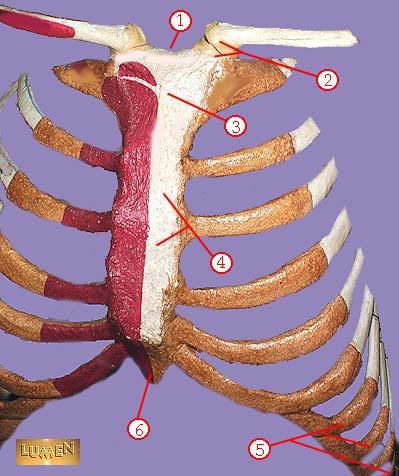
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
manubrium
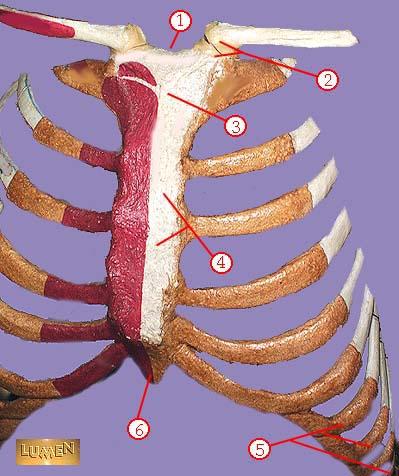
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
body of sternum GLADIOLUS
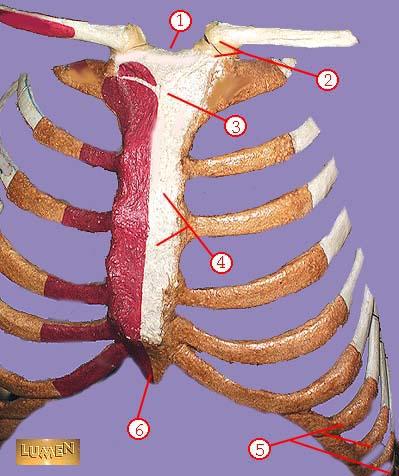
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
false ribs
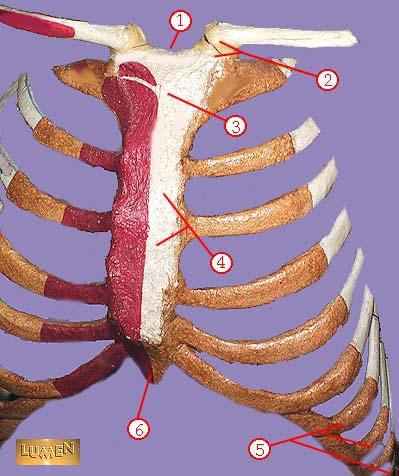
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
xiphoid process
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
...
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
...
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
...
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
...
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
...
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
...
The process when cartilage turns to bone
What is ossification?
The place where two bones meet.
What is a joint?
-composed of fibrous connective tissue
-permits tendons to slide easily and prevent them from slipping out of place
tendon sheaths?
Wraps entire muscle. Wrapped by Deep Fascia
Epimysium
Bundles of muscle fibers (myofiber)
Fascicles
Covers the fascicles (each BUNDLE of fibers)
Perimysium
Covers every individual muscle fiber
Endomysium
1) Direction of muscle fibers
2) Relative size of muscle
3) Location of muscle
4) Number of origin
5) Location of origin
6) Shape of muscle
7) Action of muscle
Naming Muscles (7)
Origin vs Insertion
Origion: tendon attaching the muscle to the less movable bone is called the origin
Insertion: tendon attaching to muscle to the MORE movable bone is called the insertion
tendon attaching the muscle to the less movable bone is called the
Origion
tendon attaching to muscle to the MORE movable bone is called the
Insertion
Paris of muscles that act against each other are called what?
Antagonists
Muscles can't push, but they pull
True or False?
TRUE
Sarcolemma vs Sarcoplasm
Sarcolemma: Cell membrane
Sarcoplasm: Cytoplasm
Protein in muscle, stores oxygen. Unique oxygen binding protein...has a reddish pigment like blood.
Myoglobin
Thousands of protein fibers that run in the length of the cell. Accounting for as much as 80% of the volume of the sarcoplasm
---Myofribil are contractile elements of the cell
Myofibril
3 types of contractile proteins in Myofibril
1) Thinner filaments of actin
2) Thicker filaments of myosin
3) Elastic filaments
Location of mitochondria in the muscle
sarcoplasm
--darker
--lighter strip in midsection called H zone
--M line in the H zone (darker)
Dark A Bands
--lighter
--z disc in the middle (darker)
Light I bands
"muscle segment" is the region between two successive Z discs. The sarcomere is the smallest contractile unit of the muscle cell
(From I band to A band to I band)
Sarcomere
Factors that affect muscle action
Temperature
Age
Exercise
Biceps
Brachialis
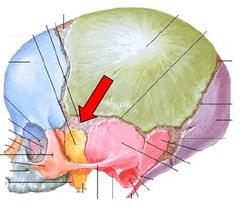
Canal leading ot eardrum and middle ear.
External auditory meatus
WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #
...
Needlelike projection inferior to external auditory meatus; attachment point for muscles and ligaments of the neck. This process os often broken off demonstrations.
Styloid process
Rough projection inferior and posterior to external auditory meatus, attatchment site for muscles.
Mastoid process
Tiny opening between the mastoid and styloid processes through which cranial nerve 7 leaves the cranium.
Stylomastoid foramen
Opening medial to the styloid process through which the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XIpass.
Jugular foramen
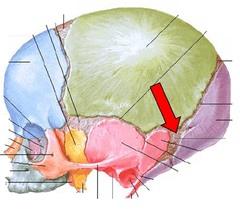
Most posterior bone of cranium, forms floor and back wall. Joins sphenoid bone anteriorly via its narrow basioccipital region.
Occipital Bone
Site of articulation of occipital bone and parietal bone.
Lamboid suture
Large opening in base of occipital, which allows the spinal cord to join with the brain.
Foramen magnum
Rounded projections lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas).
Occiptal condyles
Bat-shaped portions of the sphenoid anterior to the sella turcica.
Lesser wings
rregularly shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid. Forms the roof of the nasal cavity, upper nasal septum, and part of the medial orbit walls.
Ethmoid bone
Vertical projection providing a point of attachment for the dura mater, helping ot secure the brain within the skull.
Cristi galli
